 Understanding Academic Structure
Understanding Academic StructureSet up your academic structure before using the full functionality of the PeopleSoft Campus Solutions system. Make sure that you understand how the institution structures campuses, academic careers, academic organizations, academic departments or groups, and subject areas.
This chapter provides an overview of academic structure and discusses how to:
Define academic institutions.
Set up campuses.
Define academic careers.
Create career pointer exception rules.
Define academic level and load rules.
Define academic organizations.
Define academic groups.
Establish fields of study.
Modify Classification of Instructional Programs (CIP) and Higher Education General Information Survey (HEGIS) codes.
Define subject areas.
(NLD) Define Dutch academic structure.
 Understanding Academic Structure
Understanding Academic StructureThe academic structure and its elements are the building blocks for an academic institution. This diagram illustrates an institution's academic structure at a high level:
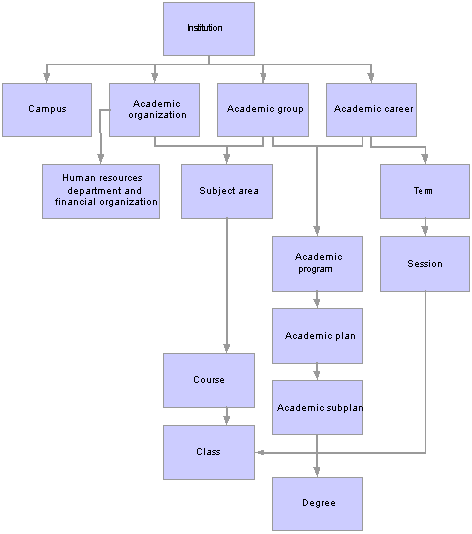
Viewing academic structure from an institutional perspective
An academic institution can have many campuses. Academic programs are part of academic careers and the academic institution. Subject areas are part of academic organizations and the academic institution. Academic plans and academic subplans are subdivisions of academic programs. Degree records are directly linked to academic plans. Courses and classes are subdivisions of subject areas and directly linked to terms and sessions.
 Defining Academic Institutions
Defining Academic InstitutionsTo set up academic institutions, use the Academic Institution Table component (INSTITUTION_TBL).
An academic institution is an entity, such as a university or college, that runs independently from other like entities and has its own set of rules and business processes. Typically, you define just one academic institution, but you can define as many as you need. Throughout Campus Solutions, you use academic institutions as a key value to group data into tables and to search those tables for data to extract.
This section lists prerequisites and discusses how to:
Define the name and location of academic institutions.
Set academic institution defaults and options.
Set additional institution defaults and options.
Activate instructor workload.
Set repeat checking controls.
(AUS, CAN, NZL, NLD) Activate other Student Administration features.
Identify self-service report types.

 Prerequisites
PrerequisitesYou must decide whether you want a single- or a multi-institution structure. Set up separate academic institutions only if the entities function as distinctly separate schools. Each academic institution must have these characteristics:
Separate schedule of classes.
Course catalogs are shared among institutions.
Independent statistics and transcripts.
Students who do not normally enroll in classes from one academic institution while attending another academic institution.
For example, although you might have a law school that is a separate entity in many ways, the law students might sometimes enroll in graduate courses as part of their law careers.
Also, before establishing academic institutions, define these items:
SetIDs
A setID is used throughout Campus Solutions as a substitute for an academic institution or a student financials business unit. Instead of keying a number of tables by academic institution or business unit, the tables are keyed by setID, which enables institutions to share common codes, structures, and facilities.
Grading schemes
Grading schemes are the rules that the academic institution uses for assigning and converting grades.
Country codes
Country codes enable you to define the address for the academic institution in the address format appropriate for the country in which the academic institution is located.
See Also

 Pages Used to Define Academic Institutions
Pages Used to Define Academic Institutions|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
INSTITUTION_TABLE |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Academic Institution Table, Academic Institution 1 |
Define the name and location of the academic institutions. |
|
|
INSTITUTION_TABLE1 |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Academic Institution Table, Academic Institution 2 |
Set academic institution defaults for transfer credit processing and for courses. |
|
|
INSTITUTION_TABLE3 |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Academic Institution Table, Academic Institution 3 |
Set additional academic institution defaults and options for attendance tracking, cohort reporting, National Student Clearinghouse (NSC) reporting, and interoperability for learning management systems (LMS). |
|
|
INSTITUTION_TABLE4 |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Academic Institution Table, Academic Institution 4 |
Activate the Instructor Workload feature and establish high-level limits, workload preferences, and default values for instructor workload at the institution. |
|
|
INSTITUTION_TABLE5 |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Academic Institution Table, Academic Institution 5 |
Set repeat checking controls for academic institutions. The academic institution level is the highest level of control for the automatic Repeat Rule Checking COBOL/SQL process (SRPCERPT). |
|
|
SSR_INST_FEATURES |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Academic Institution Table, Academic Institution 6 |
Set up student administrative functionality that can be selected or cleared, such as Canadian Reporting. |
|
|
SAA_INST_RPT_SETUP |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Academic Institution Table, Academic Institution 7 |
Identify the advisement report types to be used in self service. |

 Defining the Name and Location of Academic Institutions
Defining the Name and Location of Academic InstitutionsAccess the Academic Institution 1 page.
|
Residency Required |
Select to require residency data for students. Your selection appears in the Residency Required field on the Program 2 page for all academic programs within this academic institution. You can modify the selection for specific academic programs. When you attempt to activate a student into a term, the Term Activation SQR process (SRTRMAC) checks whether a student’s academic program requires that the student have residency data in the system. If it does and the student does not have residency data in the system, the Term Activation process does not activate the student into the term. This inactivation subsequently blocks the student from class enrollment and tuition calculation. |
|
Country |
Enter the country where this academic institution is located. Exit the field to populate the page with variable address fields. The address fields that appear depend on the country selected. Enter the primary location of this academic institution into the applicable fields. |
See Also

 Setting Academic Institution Defaults and Options
Setting Academic Institution Defaults and OptionsAccess the Academic Institution 2 page.
|
Transfer Grading Scheme |
Enter the default grading scheme that applies to courses that students transfer from external organizations to this academic institution. Your selection appears in the Grading Scheme field on the Organization Affiliation page, based on the academic institution that you enter on that page. |
|
Transfer Grading Basis |
Enter the default grading basis that applies to courses that students transfer from external organizations to this academic institution. Your selection appears in the Grading Basis field on the Organization Affiliation page, based on the academic institution that you enter on that page. |
|
School Grading Basis |
Currently not in use. |
|
Use SR Class Schedule Facility Conflict Checking |
Select to indicate that the system uses internal facility conflict checking functionality for all campuses at this academic institution. The system checks for facility conflicts whenever a facility is booked for a class on the Meetings page or the Exam page of the schedule of classes components. The check box value migrates from the Installation page to the Academic Institution 2 page to the Campus Table page. The system uses the value on the Campus Table page during processing. Clear this check box on the Campus Table page to use an external facility conflict checking process. Note. This check box has no relation to the Check for Facility Conflict check box on the Facility Table page, which controls whether you can schedule multiple events in the same facility. |
|
Print National ID on Enrl. Ver (print national ID on enrollment verification) |
Select to have the system display the student's national ID on the enrollment verification report. The system selects this check box by default. |
Use this group box to set default values for the course catalog and schedule of classes pages. These default values simplify data entry. You can override these default values for individual courses and classes.
|
Campus |
Enter the default campus for all courses within this academic institution. The campus value appears by default in the course catalog and the schedule of classes. Note. If this academic institution generally offers the same courses at more than one campus, you should not enter a value for a default campus because courses defined for a particular campus can be scheduled only for that same campus. |
|
Student Specific Permissions |
Select to have all classes scheduled at this academic institution require that you generate permissions for students to enroll in classes. This check box value migrates to the Basic Data page of the Schedule New Course component, where it can be overridden. Student-specific permissions require that you generate permissions for individual students. |
|
Auto Enroll from Wait List |
Select to have the system automatically enroll students from wait lists into classes whenever space becomes available in the classes and the wait list process is run. This check box value migrates to the Enrollment Control page of the Schedule New Course component, where it can be overridden. |
|
Enrollment Action Reason |
Enter the default enrollment action reason that the system posts to enrolled students’ records whenever a class is canceled. |
|
Drop Related Components When Canceling Enrollment Component Class |
This check box is selected by default. Clear this check box if you do not want to drop related components when you cancel the enrollment component of a multiple component class. |
|
Drop Related Components When Canceling Non-Enrollment Component Class |
This check box is selected by default. Clear this check box if you do not want to drop related components when canceling a non-enrollment component of a multiple component class. |
See Also

 Setting Additional Institution Defaults and Options
Setting Additional Institution Defaults and OptionsAccess the Academic Institution 3 page.
Attendance and Cohort Defaults
|
Class Meeting Attendance Type |
Enter the default attendance type that this academic institution uses for generating attendance rosters. The attendance type indicates the type of attendance roster, such as Class Meeting, Conference, Field Trip, Instructor Consultation, or Study Group. When you generate attendance rosters, the system uses this default attendance type, along with the fields that you have selected for this attendance type, to create the requested attendance rosters. After you generate the attendance rosters, you can change the attendance type for individual class meetings. When you define the possible attendance rosters and applicable fields for each course component (through the Components page of the Course Catalog component), define all possible scenarios. Defining all possible scenarios ensures proper attendance roster generation if you decide at a later date to modify the class meeting attendance type for this academic institution. This field is required for attendance roster batch generation. |
|
Student Attribute for Cohort |
Enter a default student attribute for cohort. Student attributes (such as cohort) are attached to a student’s program record on the Student Attributes page in the Student Program/Plan component. If a student has an attribute on the Student Attributes page equal to the one set here, the Consolidate Academic Statistics COBOL SQL process (SRPCCONP) writes this common student attribute to the student’s consolidated academic statistics record, which you can then prompt against for reporting purposes. The Consolidate Academic Statistics process searches for only the student attribute that you specify here. If the process does not find this student attribute on the student’s program record, then the process does not include a student attribute for cohort on the student’s consolidated statistics record. If the process finds multiple occurrences of this student attribute on the student’s program record, then it writes the one with the lowest primacy number to the student’s consolidated statistics record. |
Use the NSC Options group box to define how the NSC Extract SQR process (SRNSLCEX) calculates a student’s anticipated graduation date (AGD) and to define the default Federal Interagency Committee on Education (FICE) code that is in the NSC extract for this academic institution.
|
AGD Rule (anticipated graduation date rule) |
Indicate how you want the NSC Extract process to determine a student's AGD. By reporting a student’s AGD to the NSC, the NSC can provide this critical information to lending institutions so that they know when to begin collecting loans from students. Any modification to these translate values requires a substantial programming effort. Values are: Use Expected Grad Term: Select to have the NSC Extract process use the end date of the term that a student is expected to graduate as the basis for a student’s AGD. Define a student’s expected graduation term on the Student Program page. Use Term End Date: Select to have the NSC Extract process use the end date of the term that the institution is reporting to the NSC as the basis for a student’s AGD. |
|
Month Factor |
Enter the number of months that you want the NSC Extract process to add to the date determined by the AGD rule when the process calculates a student’s AGD. For example, use the term end date plus a month factor of 12 to report to the NSC that a student's anticipated graduation date is a year beyond the end date of the term that the institution reports to the NSC. |
|
FICE Code (Federal Interagency Committee on Education code) |
Enter the default FICE code that you want to appear in the NSC extract for this academic institution. This value appears on the NSC page, where you can override it for each branch code of an academic institution. |
Use the LMS Options group box to specify LMS file type default values and personal data extract parameters.
|
Provider for Authentication |
If all or most of the classes are LMS classes requiring self-service user authentication, select a provider for authentication. The provider serves as a high-level default. When this field is blank on the Components page of the Course Catalog component, the value entered on the Institution page is provided by default from the schedule of classes if a class is scheduled. Providers are defined on the LMS Provider Setup page. |
|
LMS Extract File Type (learning management systems extract file type) |
Select an LMS file type of Blackboard CourseInfo 4, WebCT API Input Format, or XML V1.01 that serves as a high-level default when all or most of the classes are LMS classes. When the field is blank on the Components page of the Course Catalog component, the value selected here appears on the schedule of classes if a class is scheduled. Any modification to these translate values requires a substantial programming effort. |
|
Phone Type and Address Usage |
Select a phone type and address usage to specify demographic information for the Person object. If you select the People option on the LMS Extract Output page, the values selected here determine which phone and address information is exported. Because phone numbers and addresses are stored as separate records in Campus Community, you may actually choose to retrieve an individual's work phone number and home address. Remember that if the phone type that you specify is not found for the individual, no phone number is extracted. This functionality is different from that of an address, where you can specify an address usage or preferred selection order that causes the first one found to be extracted. With a phone type, you can select only one choice; therefore, make it a target that is likely to be found for every person object in the extract process. You should select a voice line because the system automatically extracts fax lines in addition to whatever you select here. |
|
UserID Extract Option |
Identify whether the LMS extract should use the student or instructor's EmplID or UserID. |
See Also
Consolidating and Reporting Academic Statistics
Managing Biographical Information

 Activating Instructor Workload
Activating Instructor WorkloadAccess the Academic Institution 4 page.
See Also
Setting Up Instructor Workload

 Setting Repeat Checking Controls
Setting Repeat Checking ControlsAccess the Academic Institution 5 page.
Repeat Check
|
Process On Transfer Credit |
When you post online or batch transfer credit, use this check box to include or exclude the Repeat Rule Checking process. The check box is selected by default. |
|
Grade Match Option |
For multiple repeated classes, you can match a currently enrolled class with previous attempts by either the best grade or the worst grade. If multiple repeats are counted, the previous attempt selected is determined by the value that is entered in the Grade Match Option field. Best Grade: This process selects a class from previous attempts as follows:
Worst Grade: This process selects a class from previous attempts as follows:
|
Academic Program Options
|
Select Acad Prog During Enroll (select academic program during enrollment) |
Select to enable the Academic Program field on all enrollment pages that allow users to select an academic program to associate with each class. The field is only available within enrollment when a student is matriculated in more than one program. Clearing this check box hides the Academic Program field on all enrollment pages and associates the student's primary academic program with each class. |
See Also

 (AUS, CAN, NZL, NLD) Activating Other Student Administration Features
(AUS, CAN, NZL, NLD) Activating Other Student Administration FeaturesAccess the Academic Institution 6 page.
Important! To use country-specific functionality in the system, you must also activate the country's features on the Installation Student Administration setup page for setID-based functionality.
|
Australia |
Select to enable Australian DEST, HECS, Centrelink, and TAC functionality. |
|
Canada |
Select to enable Canadian government reporting. |
|
New Zealand |
Select to enable New Zealand Catalog, SDR, EFTS, StudyLink, and NZQA functionality. |
|
Netherlands |
Select to enable Netherlands Higher Education functionality. |
|
Studielink Participant |
Select to activate all online Studielink behavior. |
See Also
(CAN) Setting Up Government Reporting
(NLD) Managing Student Higher Education Information
(AUS) Setting Up Government Reporting
(NZL) Setting Up Government Reporting
Selecting Country-Specific Features

 Identifying Self-Service Report Types
Identifying Self-Service Report TypesAccess the Academic Institution 7 page.
Configure Self Service Report Types
|
Student academic requirement report |
Enter the type of report to be used in the My Academic Requirements feature. This field prompts on advisement report types that do not have the Include What-If Information or Include Planned Courses check boxes selected. |
|
Student plan & search by requirements |
Enter the type of report to be used on the My Planner and Search by My Requirements features. This field prompts on advisement report types that have the Include Planned Courses check box selected. |
|
Student What-If Report |
Enter the type of report to be used on the What-If Report. This field prompts on any advisement report type that has the Include What-If Information check box selected. |
 Setting Up Campuses
Setting Up CampusesTo set up campuses, use the Campus Table component (CAMPUS_TABLE).
A campus is an entity, usually associated with a separate physical administrative unit, that belongs to a single academic institution, uses the same course catalog, and produces a common transcript for students within the same academic career. The PeopleSoft Campus Solution system enables you to define as many campuses within an academic institution as necessary to meet your business needs.
This section lists prerequisites and discusses how to define campuses.

 Prerequisites
Prerequisites
Before you establish campuses, define these items:
Establishment IDs.
In Human Resources, you use the Location Table component to define work locations, but you also use the Location Table component to define general campus locations within Campus Solutions.
These campus locations are synonymous with central locations or addresses for the various campuses that comprise a college or university. If you have one main campus, you probably have a single location. However, if you offer classes at satellite locations or if you have geographically separate entities that make up the institution, you must define multiple locations.
To add locations in Campus Solutions, you must create at least one establishment value.
If you are implementing or have implemented Human Resources, these establishment values should already be defined by the human resources department.
Locations.
You define the physical locations of the campuses at the institution on the Location Table page. Each location requires an establishment ID.

 Page Used to Set Up Campuses
Page Used to Set Up Campuses|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
CAMPUS_TABLE |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Campus Table |
Define each campus that constitutes an academic institution and indicate which locations are valid for a particular campus. |

 Defining Campuses
Defining CampusesAccess the Campus Table page.
|
Use SR Class Schedule Facility Conflict Checking |
Select to enable the system to use internal facility conflict checking functionality for this campus. The system checks for facility conflicts whenever a facility is booked for a class on the Meetings page or the Exam page of the schedule of classes. The check box value migrates from the Installation page to the Academic Institution 2 page to the Campus Table page. The system uses the value on the Campus Table page during processing. Clear this check box on the Campus Table page to use an external facility conflict checking process. Note. This check box has no relation to the Check for Facility Conflict check box on the Facility Table page, which controls whether you can schedule multiple events at the same facility. |
Valid Campus Locations
|
Location Code (upper) |
Enter a location code for the primary location of the campus. Define locations on the Location Table page in Human Resources. |
|
Location Code (lower) |
Enter all valid location codes for this campus. When creating courses or scheduling classes at a particular campus, the system displays only the values that you list here. |
See Also
Setting Up Campus Community and PeopleSoft Enterprise HRMS Shared Elements
 Defining Academic Careers
Defining Academic CareersTo set up academic careers, use the Academic Career Table component (ACAD_CAREER_TBL).
This section provides an overview of academic careers and discusses how to:
Describe academic career parameters.
Set additional academic career parameters.
Set up academic career pointers.
Set repeat checking controls for academic careers.
Set up self-service options.

 Understanding Academic Careers
Understanding Academic CareersAcademic career is a concept used in Campus Solutions to designate all course work undertaken by a student at an academic institution; you group this course work in a single student record. For example, a university that has an undergraduate school, a graduate school, and several professional schools can define an undergraduate career, graduate career, and a separate career for each professional school (for example, law, medical or dental). You might also make extended education or continuing education its own academic career, or make separate academic careers for every school or college at the undergraduate level.
Academic careers have these common characteristics:
All credit is granted under a common unit type, such as semester hours or quarter hours.
A single repeat scheme is used.
Use the Academic Career component to create and define academic careers and all the parameters of each academic career. Academic career Values are: delivered with the system as translate values. If, when you are establishing academic careers, you find that you must define more academic career values, add the new values to the translate table for academic careers. The translate table for academic careers is in the ACAD_CAREER field in PeopleSoft Application Designer.
Warning! For online analytical processing (OLAP) purposes, it is important to carefully consider the code that you assign to each academic career in the translate table. When you design OLAP cubes for PowerPlay—a third-party application delivered with Campus Solutions—avoid having the same code for more than one dimension of the cube. For example, you do not want to use the same code, such as LAU (liberal arts undergraduate), for the academic career and the academic program.
See Also
Setting Up Academic Careers and Academic Programs for Reporting
Understanding Consolidating and Reporting Academic Statistics

 Pages Used to Define Academic Careers
Pages Used to Define Academic Careers|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
ACAD_CAREER_TBL |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Academic Career Table |
Describe academic careers and set parameters, such as grading scheme, for each academic career. |
|
|
ACAD_CAREER_TBL2 |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Academic Career Table, Academic Career Table 2 |
Set additional academic career parameters, such as default term unit types. |
|
|
ACAD_CAR_PTRS |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Academic Career Table, Academic Career Pointers |
Set up academic career pointers, which specify whether a student within an academic career can enroll in courses from another academic career at a particular academic institution. |
|
|
ACAD_CAR_RPT_CHK |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Academic Career Table, Repeat Checking |
Set repeat checking controls at the academic career level. Also, link repeat rules to academic careers. |
|
|
SSR_ACDCAR_SELFSRV |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Academic Career Table, Self Service Options |
Indicate if you want users to have the ability to select the students's academic program to be assigned to an enrollment record. Indicate how you want to enforce enrollment appointments for self-service enrollment within this academic career. |

 Describing Academic Career Parameters
Describing Academic Career ParametersAccess the Academic Career Table page.
|
Academic Plan Type |
Enter an academic plan type to indicate the highest level academic plan that is valid within this academic career—for example, Major, Minor, or Concentration. You can modify these translate values. No programming is associated with this field, but the institution can define restrictions based on this value. For example, if this value is set to Major for the undergraduate career, then students in that academic career could take academic plans involving majors, minors, and concentrations. But if this value is set to Concentration for the continuing education career, then the institution could create restrictions so that students in that academic career could not declare a major. |
|
Grading Scheme |
Enter the grading scheme for this academic career. This grading scheme defines the valid grading bases for this academic career. The system displays this grading scheme by default on the Program 1 page for academic programs within this academic career. You can override the default grading scheme for each academic program. Define grading scheme values on the Grading Scheme Table page. |
|
GB Default for Transfer Credit (grading basis default for transfer credit) |
Enter the default grading basis for credit transferred to this academic career. This grading basis appears by default on the Program 1 page, where you can override the value for academic programs within this academic career. |
|
Default Grade- Transfer Credit |
Enter the default grade for credit transferred to this academic career. This grade appears by default on the Program 1 page, where you can override the value for academic programs within this academic career. |
|
Default for Term Activation |
Enter either Term Begin Date or Term End Date. The value you Enter here determines the default value that appears on the Term Table page. The date specified determines the last date for which a student can be term activated. |
|
Last Term for Hist Enrl Data (last term for historical enrollment data) |
Enter the last term for historical enrollment data. The system uses this value in conjunction with the values entered for a student on the Historical Course Enrollment page to determine which historical enrollment information is printed on a student's transcript. This field restricts historical enrollment data to terms less than or equal to the value that you specify. Therefore, set this field value to the latest term possible for historical enrollment records. You can include historical enrollment on transcripts by Entering the corresponding option on the Enrollment/Statistics page of the Transcript Type component. Warning! The system populates the Last Term for Hist Enrl Data field with 0000. However, term 0000 does not allow historical enrollment data to appear on a transcript. If you want historical enrollment data to appear on a student's transcript, you must Enter another term value. |
See Also
Getting Started with PeopleSoft Enterprise Student Financials
Defining Dynamic Academic Calendars
Creating Historical Enrollment Records
Designating Enrollment and Statistics Data

 Setting Additional Academic Career Parameters
Setting Additional Academic Career ParametersAccess the Academic Career Table 2 page.
|
Term Unit Type |
Enter a term unit type to indicate what kind of units are calculated for this academic career. Values for this field are delivered with the system as translate values. These translate values can be modified. Note. When processing transfer credit between academic careers with different term unit types, use the Unit Conversion Table page first to set up unit conversion rules. |
|
Primacy Nbr (primacy number) |
Enter the primacy number for this academic career. The system uses this number to determine a student's primary academic career when you consolidate academic statistics. The system also uses this number to prioritize financial aid applications when students are enrolled in multiple academic careers at the same time. The lowest number takes precedence. Note. Coordinate the numbering with financial aid to avoid conflicts. |
|
Holiday Schedule |
Enter the holiday schedule for this academic career. The holiday schedule prevents scheduling classes for this academic career on designated holidays. Campus Solutions and Human Resources share the same holiday schedule. Each division of the institution probably has entries on the calendar because the information contained on the calendar is used for different purposes. Calendars are used to schedule classes and events. |
|
(NZL) Enroll Into Course Milestones |
Select to enable the tracking of NQF (national qualifications framework) Unit Standards for a specific career. |
|
Graduate Level Indicator |
Select to indicate that this academic career qualifies as graduate level for tax reporting purposes. You can then include this field in the NSC reporting process (by using the NSC Report page) to indicate on the NSC Extract report whether a student was enrolled at the graduate level during a reporting period or term. Otherwise, this field is informational only, and the institution can use it for various reporting purposes. Note. The NSC offers an optional service to institutions to assist them in fulfilling the reporting guidelines of the Taxpayer Relief Act of 1997. NSC member schools that choose to use this service are required to add a graduate level indicator to their reports and, therefore, should enter this option and enter the corresponding option on the NSC Report page. |
|
Use Dynamic Class Dates |
Select to make available the Dynamic Date page of the Academic Program Table component. You use the Dynamic Date page to set up reasons and penalties for canceling, withdrawing from, and dropping classes. These reasons and penalties relate to the corresponding landmark date deadlines on the dynamically calculated academic calendars, and they apply to students according to their academic program. |
|
Dynamic Class Date Rule |
Enter a dynamic date rule to have the system assign that rule to all course offerings that you tie to this academic career. You can override this default rule on an offering-by-offering basis through the Offerings page. This field prompts you with only the dynamic class date rules that have not been designated for open entry/exit (OEE) enrollment on the Dynamic Class Dates page. |
|
Allow OEE Enrollment (allow open entry/exit enrollment) |
Select to have all course offerings that you tie to this academic career permit, by default, the scheduling of OEE class sections. You can override this default on an offering-by-offering basis on the Offerings page of the Course Catalog component. If you select this check box, the OEE Dynamic Date Rule field becomes available. |
|
OEE Dynamic Date Rule (open entry/exit dynamic date rule) |
An OEE dynamic date rule is a dynamic class date rule that has been designated for OEE enrollment. The enrollment engine uses the OEE dynamic date rule to calculate significant class dates for a student whenever a student enrolls in an OEE class. This field is available for edit only if you select the Allow OEE Enrollment check box on the preceding page of this component. Select an OEE dynamic date rule to have the system assign that rule to all course offerings that you tie to this academic career. You can override this default rule on an offering-by-offering basis through the Offerings page of the Course Catalog component. This field prompts you with only the dynamic class date rules that have been designated for OEE enrollment on the Dynamic Class Dates page. |
|
AA Oprid Display Option (academic advisement operator identification display option) |
Select an available option to display or hide the operator ID, operator name, or Operator field on the advisement report. The default value is Display Operator. Display Name: If you select this option, the system displays the operator’s name on the advisement report. Display Operator: If you select this option, the system displays the operator’s ID on the advisement report. Do Not Display: If you select this option, the system does not display the Operator field on the advisement report. |
|
Edit Advisor Against |
Indicate which view the system should use when prompting you to assign an advisor for a student in this academic career. You assign advisors to students on the Student Advisor page. Your selection here appears on the Program 2 page. Select from these options: Personal Data: Prompts against all people with a PERSONAL_DATA record in the PeopleSoft system. Instructor Advisor: Prompts against all people defined as instructors and advisors on the Instructor/Advisor Table page, as defined for this academic career. Advisor Role: Prompts against all people defined as advisors on the Instructor/Advisor Table page, as defined for this academic career. |
See Also
Defining Dynamic Academic Calendars
Preparing for the Course Catalog and Schedule of Classes
Consolidating and Reporting Academic Statistics
PeopleSoft Enterprise Human Resources Management System documentation

 Setting Up Academic Career Pointers
Setting Up Academic Career PointersAccess the Academic Career Pointers page.
On the Career Pointer Exception page, you can set specific exceptions to the academic career pointers on the Academic Career Pointers page. For example, you might want to set the academic career pointers for the undergraduate career so that undergraduate students can, with permission, enroll in graduate, graduate business, and law courses; can always enroll in undergraduate and continuing education courses; and can never enroll in courses from any other academic career.
Note. Enter values for all possible academic careers, including the ones in which the student cannot enroll in courses. Although the system permits you to omit academic careers in which the student cannot enroll, this practice is not recommended.
|
Course Career |
Enter each academic career that you have defined for a particular academic institution. |
|
Allow Enrollment |
Enter whether a student can enroll in an academic career. Allow Enrollment Values are: translate values. Values are: Yes, No, and Permission. Selecting Permission requires the student to have a general permission or a student-specific permission at enrollment time. |

 Setting Repeat Checking Controls for Academic Careers
Setting Repeat Checking Controls for Academic CareersAccess the Repeat Checking page.
See Also

 Setting Up Self-Service Options
Setting Up Self-Service OptionsAccess the Self Service Options page.
|
Self Service Enrl Appt Edit (self-service enrollment appointment edit) |
Select one of the following options: Enrollment Engine Only: Select this option to have the enrollment engine enforce enrollment appointments in self-service enrollment only when a student submits an enrollment request with an action of enroll or swap for processing by the enrollment engine. Online and Engine: Select this option to have the system validate enrollment appointments in self-service enrollment when a student selects a term on the Select Enrollment Term Search page, and when the student enters or selects a class number on the Add Classes, Drop/Update Class, or Swap Classes pages. If the student does not have a valid enrollment appointment or if the open enrollment period for the session that the student is trying to enroll in has not yet begun, these edits prevent the student from submitting enrollment requests. When a qualifying student does submit an enrollment request with an action of enroll or swap, the enrollment engine still enforces enrollment appointments during processing. The system selects this option by default. Note. Modification of these translate values requires significant programming effort. |
 Creating Career Pointer Exception Rules
Creating Career Pointer Exception RulesTo set up career pointer exception rules, use the Career Pointer Exception Rule component (CAR_PTR_EXCEPTIONS).
This section provides an overview of career pointer exception rules and discusses how to define career pointer exception rules.

 Understanding Career Pointer Exception Rules
Understanding Career Pointer Exception RulesCareer pointer exception rules enable you to define exceptions to the regular academic career pointer guidelines from the Academic Career Pointers page. When students in academic programs with career pointer exception rules attempt to enroll in courses, the enrollment engine looks at the career pointer exception rule as defined on the Career Pointer Exception Rule page before proceeding to the academic career pointers as defined on the Academic Career Pointers page.
You can create career pointer exception rules to define the academic groups, subject areas, and catalog numbers into which a student can enroll. Then you can connect these career pointer exception rules to academic programs as necessary. Career pointer exception rules are connected to academic programs with the Career Pointer Exception Rule field on the Program 2 page. If that field is empty, the enrollment engine checks only the academic career pointer guidelines.
This list summarizes the system checks that occur during enrollment engine processing:
The enrollment engine checks the academic group, subject area, and catalog number of the requested course against the values entered on the Career Pointer Exception Rule page.
The enrollment engine verifies that the catalog number of the requested course is less than or equal to the maximum catalog number for that academic group and subject area combination. If the enrollment engine finds no match, the check proceeds to the next step.
The enrollment engine checks the academic group and subject area of the requested course plus a catalog number with a value of null against the values entered on the Career Pointer Exception Rule page.
The enrollment engine verifies that the catalog numbers for that entire academic group and subject area combination have not been restricted. If the enrollment engine finds no match, the check proceeds to the next step.
The enrollment engine checks the academic group of the requested course, a subject area with a value of null, and the catalog number of the requested course against the values entered on the Career Pointer Exception Rule page.
The enrollment engine verifies that the catalog number of the requested course is less than or equal to the maximum allowable catalog number of that academic group. If the enrollment engine finds no match, the check proceeds to the last step.
The enrollment engine checks the academic group of the requested course, subject area with a value of null, and a catalog number with a value of null against the values entered on the Career Pointer Exception Rule page.
The enrollment engine verifies that all subject areas and catalog numbers for the entire academic group have not been restricted. If the enrollment engine finds no match, it uses the enrollment request for the academic career pointers as defined on the Academic Career Pointers page.
This series of checks assures that the student, according to her or his academic career, is permitted to enroll in the requested course.

 Page Used to Create Career Pointer Exception Rules
Page Used to Create Career Pointer Exception Rules|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
CAR_PTR_EXCEPTIONS |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables Academic Structure, Career Pointer Exception Rule |
Define all possible career pointer exception rules—the exceptions to the academic career pointer guidelines established on the Academic Career Pointers page. After you define the career pointer exception rules, the institution can attach them to academic programs to ensure that students within an academic program can enroll only in permissible courses. |

 Defining Career Pointer Exception Rules
Defining Career Pointer Exception RulesAccess the Career Pointer Exception Rule page.
|
Academic Group |
Enter the academic group in which a student can request a course. |
|
Subject Area |
Enter the subject area within the academic group in which a student can request a course. To indicate all subject areas, leave this field blank. Otherwise, insert rows to specify each subject area within the academic group for which you want to create a rule. |
|
Catalog Nbr (catalog number) |
Enter the maximum catalog number within the subject area or academic group in which a student can request a course. To indicate all catalog numbers within a subject area or academic group, leave this field blank. |
|
Allow Enrollment |
Enter whether a student is permitted enrollment in courses that match the criteria specified in the previous fields. Allow Enrollment Values are: delivered with the system as translate values. Values are: Yes, No, and Permission. Entering Permission requires the student to have a general permission or a student-specific permission at enrollment time. |
|
Grading Basis Mapping Rule |
Enter the grading basis mapping rule for the requested courses. Define grading basis mapping rule values on the Grading Basis Exception Rule page. The system uses the grading basis mapping rule to translate grades earned in another academic group to valid grades within a student's academic career. |
See Also
Understanding Class Permissions
Defining Grading Basis Exception Rules
 Defining Academic Level and Load Rules
Defining Academic Level and Load RulesTo set up academic level and load rules, use the Level/Load Rules Table component (LVL_ST_RULE_TBL).
Use the Level/Load Rules component to define academic level and academic load rules for every academic career at your institution. Various system processes use these rules to determine a student’s academic level and academic load—processes such as class enrollment, financial aid reporting, and the consolidation of academic statistics.
This section discusses how to:
Define academic level and load determination values.
Define level rules.
(AUS) Define level dependent load rules.
Define load rules.
Define contiguous term load rules.
See Also
Consolidating and Reporting Academic Statistics

 Pages Used to Define Academic Level and Load Rules
Pages Used to Define Academic Level and Load Rules|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
LVL_ST_RULE_TBL |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure |
For each academic level rule, specify how the system processes must determine a student's academic level and academic load, and define how the Consolidate Academic Statistics process must map academic levels to Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System (IPEDS) academic levels. |
|
|
ACAD_LEVEL_TBL |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Level/Load Rules Table |
Associate academic levels with cumulative units or terms to link the academic levels to the corresponding National Student Loan Data System (NSLDS) loan years, and to link academic levels with federal direct lending years. |
|
|
SSR_LVL_LOAD_AUS |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Level/Load Rules Table |
Define values used for Australian EFTSL (equivalent full-time student load) and HECS (Higher Education Contribution Scheme) calculations. Page functionality is similar to the Academic Load Table page. |
|
|
ACAD_LOAD_TBL |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Level/Load Rules Table |
Define academic load rules, financial aid load rules, and NSC academic load rules. |
|
|
ACAD_LOAD2_TBL |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Level/Load Rules Table |
For contiguous terms, define the academic load rules, NSC academic load rules, and financial aid load rules. Contiguous terms are consecutive terms in which you combine academic load information. |

 Defining Academic Level and Load Determination Values
Defining Academic Level and Load Determination ValuesAccess the Level/Load Rules Table page.
(AUS) EFTSL Values and HECS Load Factor
Tuition Calculation for HECS currently calculates the HECS Load Factor, which is generally equal to the EFTSL value for a class. However, HECS is not calculated for all enrolled students. For example, HECS is not calculated for full-fee paying overseas students. In some cases, the HECS Load Factor may be different from the EFTSL value for a class. An example is a student who may complete a work experience class that contributes units to his progression, but for which there are no HECS charges (as the class may not consume institution resources). In this case, the billing units for the class should be made zero, but Academic Progress Units should be given. The HECS Load Factor is a calculation based on billing units, and the EFTSL calculation is based on Academic Progress Units. In this case, the HECS Load Factor is zero, but the EFTSL still has a value. Since EFTSL is required for every student, the system calculates EFTSL as a separate process.
You must ensure that the load/level rules are set up to reflect the full-time load for different programs. For example, the full-time load/level rules for one program may include a summer term as full-time compulsory attendance, while other programs may consider the summer term as an additional term for students to undertake study above the ordinary full-time load. When setting up the level/load rules, you can indicate whether or not the term should be included in the annual load calculation. For example, if the summer term is not considered part of the full-time load and the student takes summer classes, the student's annual EFTSL will be greater than if the student enrolled in a full-time load only for the other terms in the academic year.

 Defining Level Rules
Defining Level RulesAccess the Academic Level Table page.
|
Cum Units/Terms (cumulative units or terms) |
Enter the minimum number of cumulative units or terms that the system requires before it assigns a student to a corresponding academic level. The system uses only these values if you select Units or Terms on the Level/Load Rules Table page. |
|
Academic Level |
Enter an academic level for each increment of cumulative units or terms that you want to associate with this level and load rule. Values for this field are delivered with your system as translate values. You can modify these values. |
|
NSLDS Loan Year (National Student Loan Data System loan year) and Direct Lending Year |
Enter the NSLDS loan year and direct lending year values that correspond to each academic level that you define. The PeopleSoft Financial Aid application references these values during the FA Term Build (financial aid term year) process. |

 (AUS) Defining Level Dependent Load Rules
(AUS) Defining Level Dependent Load RulesAccess the Level Dependent Load Rules page.
|
Term Category |
Select every term category that is valid for the academic load rule. Values for this field are delivered with your system as translate values. You can modify these values. Note. Map every term category at your institution, regardless of your load determiner (units, default, or manual). |
|
Unit Term Total |
Enter the unit term total for each term category and session type. The unit term total represents the number of units that must be taken to qualify for the academic load level and financial aid level. |
|
Academic Load |
Select the academic load value that corresponds to the unit term total. Values for this field are delivered with your system as translate values. You can modify these values. |
|
Financial Aid Load |
Select the financial aid load value. The financial aid load represents the financial aid load level equivalent to the academic load value. Values for this field are delivered with your system as translate values. You can modify these values. |
|
Include in Annual Load Calc (include in annual load calculation) |
Select this check box to include this load value in Australian EFTSL and HECS calculations. Note. If you use this page to include load values, do not use the Academic Load Table page. |
See Also
(AUS) Generating Government Reports

 Defining Load Rules
Defining Load RulesAccess the Academic Load Table page.
The Consolidate Academic Statistics process uses these rules to determine a student’s academic load when it processes an Academic Statistics Period for which the academic load rule value = Term Load Rule applies.
Note. Multiple views of this page are available by clicking the tabs in the scroll area. We document fields that are common to all views first.
|
Term Category |
Select every term category that is valid for the academic load rule. Values for this field are delivered with your system as translate values. You can modify these values. Note. Map every term category at your institution, regardless of your load determiner (units, default, or manual). |
|
Session |
Enter the session type for the term category if you have more than one session in a term category and the sessions have different academic loads. For example, a summer session term type might have a 10-week session, a 12-week session, and two 6-week sessions. Your institution might not calculate the academic load for the 12-week session and the 6-week sessions in the same way. Note. At least one row must be included with a blank session code for each term category. The system uses the row or rows with a blank session code to calculate academic load for the term. The system also calculates the load for the regular session using the row or rows with cleared sessions, which is why the term load and the regular academic session load will always be the same. In addition, a field edit prevents you from entering 1 in the Session field, because the system assumes that the cleared Session field represents the regular academic session. You must have at least one row with a blank session code for each term category in order for the system to calculate academic load based on units. |
|
Unit Term Total |
Enter the unit term total for each term category and session type. The unit term total represents the number of units that must be taken to qualify for the academic load level and financial aid level. |
|
Academic Load |
Select the academic load value that corresponds to the unit term total. Values for this field are delivered with your system as translate values. You can modify these values. |
|
Res Terms Adj (residence terms adjust) |
Enter the residence terms adjust value for each term category and session type to determine what constitutes a full term based on a student’s academic load. In the exhibit, a part-time academic load is considered to be worth 50 percent of a full term, a three-quarter time academic load is considered to be worth 75 percent of a full term, and a full-time academic load is considered to be worth 100 percent of a full term. When a student is term activated, the student’s approved academic load is used to determine the value of the Terms of Residency field based on the residence terms adjust factor. In this example, a part-time student would have a current in residence terms setting of 0.50 and a full-time student would have a setting of 1.00. The system obtains the current in residence terms value from the Term Activation - Terms in Residence field. |
|
Financial Aid Load |
Select the financial aid load value. The financial aid load represents the financial aid load level equivalent to the academic load value. Values for this field are delivered with your system as translate values. You can modify these values. |
|
(AUS) Include in Annual Load Calc (include in annual load calculation) |
Select to include this load value in Australian EFTSL and HECS calculations. Note. If you use this page to include load values, do not use the Level Dependent Load Rules page. |
NSC Tab
Access the NSC tab.
|
NSC Academic Load (National Student Clearinghouse academic load) |
Select the academic load value that your institution reports to the NSC. Values for this field are delivered with your system as translate values. You can modify these values. |
|
Course Load Pct (course load percent) |
Enter the course percentage for the NSC academic load. For example, if you enteredHalf-Time for your NSC academic load, enter 50 (50 percent). |

 Defining Contiguous Term Load Rules
Defining Contiguous Term Load RulesAccess the Statistics Period Load page.
The Consolidate Academic Statistics process uses the rules on this page to determine a student’s academic load when it processes an Academic Statistics Period during which the academic load rule value = Contiguous Terms.
Note. For the Consolidate Academic Statistics process to effectively combine a student’s academic loads for contiguous terms, be sure that you define contiguous term academic load rules for every academic level rule at your institution.
|
Academic Load Rule |
Select Contiguous if you plan to use the Consolidated Academic Statistics process to combine a student’s academic load unit totals for consecutive terms. If you do not use the Consolidated Academic Statistics process, clear this field and the other fields on this page. |
|
Unit Total |
Enter the unit total for each contiguous term academic load rule. The unit term total represents the number of units that a student must take to qualify for the academic loads that you define on any given row of this page. |
|
Academic Load |
Select the academic load value that corresponds to the unit total for the row. Values for this field are delivered with your system as translate values. You can modify these values. |
|
NSC Academic Load (National Student Clearinghouse academic load) |
Select the NSC academic load value that corresponds to the unit total for the row. The NSC Extract process uses the NSC academic load for NSC reporting purposes. Values for this field are delivered with your system as translate values. You can modify these values. |
|
Financial Aid Load |
Select the financial aid load value corresponding to the unit total for the row. The financial aid load is the financial aid equivalent of the academic load for the row. Values for this field are delivered with your system as translate values. You can modify these values. |
 Defining Academic Organizations
Defining Academic OrganizationsTo set up academic organizations, use the Academic Organization Table component (ACADEMIC_ORG_TBL).
This section provides an overview of academic organizations and discusses how to:
Modify academic organizations.
Designate financial ownership for academic organizations.
Designate human resource ownership for academic organizations.

 Understanding Academic Organizations
Understanding Academic OrganizationsAcademic organization structure defines how an academic institution is organized from an administrative perspective. At the lowest level, an academic organization can be compared to an academic department. At the highest level, an academic organization can represent a division.
Before you begin using academic organizations, you must first use PeopleSoft Tree Manager, which you access through PeopleTools, to define the academic organizations themselves, the hierarchy and levels of each academic organization, and the relationship between academic organizations in the hierarchy. One of the primary uses of the tree is to partition an academic institution for security purposes, controlling such areas as a user’s access to course catalog data. The number and names of the levels in the academic organization tree can be revised by the institution by using PeopleTools.
Use the Academic Organization component to modify academic organization descriptions and to link each academic organization to one or more financial support or human resources departments on a percentage ownership basis. These relationships are used to report, analyze, and distribute revenue and workload credit.
See Also
Securing Academic Organizations
Enterprise PeopleTools PeopleBook: PeopleSoft Tree Manager

 Pages Used to Define Academic Organizations
Pages Used to Define Academic Organizations
 Modifying Academic Organizations
Modifying Academic OrganizationsAccess the Academic Organization Table page.
Warning! If you are adding new academic organizations directly to this page, the academic institution value on the academic organization
record must be the same as the academic institution that owns it in the academic organization tree. If these two values are not synchronized,
security and reporting are adversely affected. Therefore, you should add new academic organizations through PeopleSoft Tree
Manager.
The system populates the Effective Date, Status, Description, Short Description, Formal Description, Academic Institution, and Campus fields from the academic organization tree in PeopleSoft Tree Manager.
|
Academic Institution |
Enter the academic institution to which this academic organization belongs. This academic institution value must be the same as the academic institution on the academic organization tree. If these two Values are: not synchronized, security and reporting are adversely affected. |
|
(AUS) AOU Code (academic organization unit code) |
Enter a code to link an academic organization unit (AOU) code to an academic organization. |
|
Campus |
Enter the campus to which this academic organization belongs. |
|
Manager ID |
Enter the manager for the academic organization, such as the department chair. This value is informational only and is currently not used in any internal system processes. |
Edit Instructor Against
In this group box, select the view that the system should use when users search for an instructor to assign to classes while scheduling classes. Options are:
|
Personal Data |
This field is used for reporting purposes only. |
|
Instructor Advisor |
People defined as instructors and advisors in the Instructor/Advisor Table component. The Instructor/Advisor component enables you to link instructors to courses for which they are approved and available to teach for specified periods of time. When you are scheduling classes and entering an instructor, the system displays only these instructors, thus simplifying the assignment of instructors to classes. |
Assign Instructor By
If you select the Instructor Advisor option in the Edit Instructor Against group box, the Assign Instructor By group box becomes available. Select how the institution wants to assign instructors for this academic organization. You can select one, none, or any combination of these options: Campus, Subject, and Course. If you select none of these options, the instructor advisor edit applies to all courses within this academic organization.
Remember that for whichever options you select, you must define these same options for each instructor on the Approved Courses page of the Instructor/Advisor Table component. Only then does the instructor's name appear as a choice for the Instructor ID field on the Meetings page or Exam page when you schedule classes. For example, if you select the Subject and Campus options, you must enter values for both the Subject and Campus fields on the Approved Courses page to make the instructor approved and available for instruction.
Warning! Changing the saved selection for the Edit Instructor Against or Assign Instructor By group boxes removes an instructor's course rows on the Approved Courses page for the academic organization. The system, however, does maintain the rows for other academic organizations.
See Also
Designating Approved Instructors and Advisors

 Designating Financial Ownership for Academic Organizations
Designating Financial Ownership for Academic OrganizationsAccess the Acad Organization FS Owner page.
|
Business Unit |
Enter the business unit considered to be the financial support unit of this academic organization. |
|
Department |
Enter the department in which the business unit is housed. Enter department values on the Department Table page. |
|
Percent Owned |
Enter the percentage of the academic organization for which the business unit is responsible. You can have multiple business units with split ownership of the academic organization, but the total percent owned among all business units must equal 100. |

 Designating Human Resource Ownership for Academic Organizations
Designating Human Resource Ownership for Academic OrganizationsAccess the Acad Organization HR Owner page.
|
Department |
Enter the department responsible for human resources support for this academic organization. Enter department values on the Department Table page. |
|
Percent Owned |
Enter the percentage of the academic organization for which the human resources department is responsible. You can have multiple human resources departments with split ownership of the academic organization, but the total percent owned among all departments must equal 100. |
 Defining Academic Groups
Defining Academic GroupsTo set up academic groups, use the Academic Group Table component (ACADEMIC_GROUP_TBL).
This section provides an overview of academic groups and discusses how to:
Describe academic groups.
Link academic career catalog numbers to academic groups.
Define standard class meeting patterns.

 Understanding Academic Groups
Understanding Academic GroupsAcademic groups are the highest level breakdowns of the academic institution for academic structural purposes. Often each school or college within an academic institution is defined as an academic group. Sometimes units such as extended education are defined as an academic group if classes are offered separately from the standard colleges or schools. For example, PeopleSoft University comprises the College of Liberal Arts, the College of Engineering, the School of Law, the School of Education, and the Evening Extension Division. Each entity is defined as an academic group in the system. Academic groups can offer academic programs in more than one academic career, and academic careers can cross academic groups. In the previous example, the College of Liberal Arts and the College of Engineering contain both undergraduate and graduate academic careers, but the School of Law contains only one academic career, which is not shared with any other academic group.
To link an academic group to an academic institution and an academic organization, add the academic group through the Academic Group Table component and add the academic group as a child node to academic institutions and academic organizations in PeopleSoft Tree Manager—one aspect does not update the other aspect. In PeopleSoft Tree Manager, every node is defined by its relation to other nodes. In most cases, academic groups are defined as the next level of academic organization structure below academic institution. However, academic groups can occur at any level within the academic organization structure. It is not essential for academic groups to follow the same hierarchical structure as academic organizations. Although this is the case for most institutions, some might want to use academic groups and academic organizations to represent different dimensions of a matrix organization. In such a case, academic groups would not be child nodes in the academic organization tree but rather set apart as nodes at the same level as academic organizations.
Use the Academic Group Table component to define academic groups and link academic careers and standard class meeting patterns to them.

 Pages Used to Define Academic Groups
Pages Used to Define Academic Groups|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
ACADEMIC_GROUP_TBL |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Academic Group Table |
Describe academic groups. |
|
|
CATLG_CAREER_TBL |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Academic Group Table, Academic Career Level Table |
Link academic careers and ranges of catalog numbers to academic groups. These values serve as a data entry and tracking aid as you create the course catalog. When you enter a catalog number on the Offerings page of the Course Catalog component, the system displays the correct academic career value. |
|
|
STND_MTG_PAT_TBL |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Academic Group Table, Standard Meeting Patterns |
Define standard class meeting patterns for an academic group. All typical patterns must be defined here, including the to-be-announced class meeting pattern. These patterns are a data entry aid when scheduling classes. |

 Describing Academic Groups
Describing Academic GroupsAccess the Academic Group Table page.
Use the Course Defaults group box to set default values for the course catalog and schedule of classes pages. The fields in this group box simplify data entry. You can override these default values for individual courses and classes.
|
Student Specific Permissions |
Select to have all classes scheduled within this academic institution and academic group require that you generate permissions for students to enroll in classes. The check box value migrates to the Class Schedule Entry page, where it can be overridden. Student-specific permissions require that you generate permissions for individual students. |
|
Auto Enroll from Wait List |
Select to have all classes scheduled within this academic institution and academic group automatically enroll students from waiting lists into classes whenever spaces are available and the wait list process is run. The check box value migrates to the Enrollment Control page of the schedule of classes components, where it can be overridden. |

 Linking Academic Career Catalog Numbers to Academic Groups
Linking Academic Career Catalog Numbers to Academic GroupsAccess the Academic Career Level Table page.
|
Academic Career |
Enter the academic career that you want to link to this academic group. Insert additional rows to enter all academic careers that you want to link to this academic group. |
|
Catalog Nbr To (catalog number to) |
For each academic career that you link to this academic group, enter the course number immediately after the highest possible course catalog number for that academic career. For example, if the highest possible course catalog number within the College of Liberal Arts for the undergraduate academic career is 299, enter 300 in the field. Likewise, if the highest catalog number for the graduate academic career is 599, enter 600 into the field. The number that you enter defines the lowest possible catalog number for the subsequent academic career within this academic group. In this example, 300 would be the first catalog number of the graduate academic career within the College of Liberal Arts. When you create a new course offering on the Offerings page of the Course Catalog component, the system displays the academic career value based on the academic career and catalog number combinations from this page. In the preceding example, if you create a course within the College of Liberal Arts with a catalog number of 300, the system displays the academic career Graduate. If the catalog number is 299, the system displays the academic career Undergraduate. |

 Defining Standard Class Meeting Patterns
Defining Standard Class Meeting PatternsAccess the Standard Meeting Patterns page.
|
Standard Meeting Pattern |
Enter a code to represent the standard class meeting pattern for this academic group. Insert additional rows to add more standard meeting patterns for this academic group. |
|
Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, ThursdayFriday, Saturday, and Sunday |
Select the appropriate days of the week for this standard meeting pattern. |
|
Normal Class Duration |
Enter the number of minutes for each class in this standard meeting pattern. |
 Establishing Fields of Study
Establishing Fields of StudyTo set up fields of study, use the Field of Study Table component (STUDY_FIELD_TABLE).
This section lists the page used to establish fields of study.

 Page Used to Establish Fields of Study
Page Used to Establish Fields of Study|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
STUDY_FIELD_TABLE |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Reporting Codes, Field of Study Table |
Define fields of study. Link fields of study to academic subjects on the Subject Taxonomy page and to academic plans on the Academic Plan Taxonomy page. |
 Modifying CIP and HEGIS Codes
Modifying CIP and HEGIS CodesTo set up CIP and HEGIS codes, use the CIP Code Table component (CIP_CODE_TABLE) and the HEGIS Code Table component (HEGIS_CODE_TABLE). Use the SSR_CIP_CODE_TABLE and SSR_HEGIS_CODE_TABLE component interfaces to load the data into the tables for these component interfaces.
CIP and HEGIS codes are delivered with the system. You can modify descriptions of the codes and add new codes through the CIP Code Table page and the HEGIS Code Table page. This section discusses how to modify CIP and HEGIS codes.

 Pages Used to Modify CIP and HEGIS Codes
Pages Used to Modify CIP and HEGIS Codes|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
CIP_CODE_TABLE |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Reporting Codes, CIP Code Table |
Modify descriptions of the CIP codes shipped with Campus Solutions. |
|
|
HEGIS_CODE_TABLE |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Reporting Codes, HEGIS Code Table |
Modify descriptions of the HEGIS codes shipped with Campus Solutions. |

 Modifying CIP Codes
Modifying CIP CodesAccess the CIP Code Table page.
|
Alternative CIP Code (alternative classification of instructional programs code) |
Some states derive their own coding schemes from the CIP code. If applicable, enter the alternative CIP code of the state. |

 Modifying HEGIS Codes
Modifying HEGIS CodesAccess the HEGIS Code Table page.
|
Hegis Code Type |
Enter a code type. Two types of code are available, one for a training program and one for a training course. |
|
External Org ID (external organization ID) |
Enter an ID. This value is used for MBO codes. |
|
Education level |
Enter the level of education for which the code is offered. |
|
Lob Code (line of business) |
Enter the internal code of a national institution for the subqualification. |
|
Course Ref Code (course reference code) |
Enter the course to which the code is linked. |
|
Partial Qualification |
Select whenever the code is being used for a subqualification or a course. |
|
Final Qualification |
Select whenever the code is being used for a qualification or a training program. |
 Defining Subject Areas
Defining Subject AreasTo set up subject areas, use the Academic Subject Table component (SUBJECT_TABLE).
This section provides an overview of subject areas and discusses how to:
Describe subject areas.
Define subject area taxonomy.
Define subject and component multipliers.

 Understanding Subject Areas
Understanding Subject AreasSubject areas are the specific areas of instruction in which courses are offered within academic organizations. For example, when a course is identified as Math 101, math is the subject area. Subject areas are tied to the academic organization tree by the academic organization data for each subject area and by detail nodes for academic organizations in PeopleSoft Tree Manager. Subject areas are also tied to courses, which you link to later when developing the course catalogs.
Before using subject areas, use PeopleSoft Tree Manager, accessed through PeopleTools, to define the academic organizations and to create a hierarchical representation of subject areas by linking subject areas as detail nodes to the academic organizations. One of the primary uses of defining subject areas as detail nodes on the academic organization tree is to limit access to academic subjects.
See Also
Securing Your Academic Institution
Enterprise PeopleTools PeopleBook: PeopleSoft Tree Manager

 Pages Used to Define Subject Areas
Pages Used to Define Subject Areas|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
SUBJECT_TABLE |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Academic Subject Table |
Describe subject areas, modify existing subject area descriptions, link subject areas to academic organizations, and set other parameters, such as blind grading. |
|
|
SUBJECT_TAXONOMY |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Academic Subject Table, Subject Taxonomy |
Define subject area taxonomy by linking subject areas to CIP and HEGIS codes and to fields of study. |
|
|
SUBJ_WORKLD_TBL |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure, Academic Subject Table, Subject Workload |
Define subject and component multipliers by the weight of each component within each subject area at the academic institution. |

 Describing Subject Areas
Describing Subject AreasAccess the Academic Subject Table page.
|
External Subject Area |
Currently not in use. |
|
Academic Organization |
Enter the academic organization that offers courses in this subject area. Any academic organization entered here should also have a detail node associated with it for this subject area on the academic organization tree. |
|
Use Blind Grading |
Select to indicate that blind grading be used for every course within this subject area. This selection is the default value and can be changed on a course-by-course basis on the Offerings page of the Course Catalog component. Blind grading enables you to create a grade roster with randomly generated numbers rather than student IDs. |
|
Split Ownership |
Select to designate multiple academic organization owners for this subject area. If you select this check box, the Academic Organization field and the Percent Owned field become available for edit. |

 Defining Subject Area Taxonomy
Defining Subject Area TaxonomyAccess the Subject Taxonomy page.
|
CIP Code |
Enter the CIP code for this subject area. CIP code. Values are delivered with the system as translate values. You can modify CIP codes on the CIP Code Table page. |
|
HEGIS Code |
Enter the HEGIS code for this subject area. HEGIS codes are delivered with the system as translate values. You can modify HEGIS codes on the HEGIS Code Table page. |
|
Field of Study |
Enter a field of study for this subject area. |
|
(AUS) Field of Education Code |
Enter a code so that it is linked to the subject area. During DEST reporting, this value is used in compiling statistics. |
|
(AUS) HECS Band ID |
This ID is used in Student Financials, but is defined in Student Records. Band IDs determine how much a student pays for a class. Select an ID to link it to a course. You can select the ID for a subject, course offering, or field of education. The ID identifies the HECS band which is used to determine the HECS contribution for a class. |
|
(AUS) Discipline Group Code |
Enter a code to group students for DEST reporting. The code is assigned to the student by default during enrollment, but it can be overridden. |

 Defining Subject and Component Multipliers
Defining Subject and Component MultipliersAccess the Subject Workload page.
See Also
Setting Up Instructor Workload
 (NLD) Defining Dutch Academic Structure
(NLD) Defining Dutch Academic StructureTo set up Dutch academic structure, use these components: Cluster Code Table NLD (SSR_CLUST_CD_NLD), GBA Country Code Table (SSR_COUNTRY_NLD), MBO Code Table NLD (SSR_MBO_CD_NLD), BRINcode Table NLD (SCC_BRINCODE_NLD), GBA Nationality Code Table (SSR_NATIONAL_NLD), and Prior Education Table NLD (SSR_PRE_EDU_NLD).
This section lists the pages used to define values that set up academic structures in the Netherlands.

 Pages Used to Define Dutch Academic Structure
Pages Used to Define Dutch Academic Structure|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
SSR_CLUSTER_CD_NLD |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure Netherlands, Cluster Code Table NLD |
Define cluster codes, which can be registered for Prior Education table entries. These codes provide a higher level of aggregation that combines multiple forms of education into one educational cluster. During the admissions process, entering a cluster detail code for a specific student prior to education entry can refine this aggregation. |
|
|
SSR_COUNTRY_NLD |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure Netherlands, GBA Country Code Table |
Register GBA country codes, which are supplied by the Dutch Ministry of Internal Affairs. These codes are linked to the Country Code table. |
|
|
SSR_MBO_CD_NLD |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure Netherlands, MBO Code Table NLD |
Define MBO codes, which are used to register for specific forms of education on the Dutch Education table. |
|
|
SCC_BRINCODE_NLD |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure Netherlands, BRINcode Table NLD |
Register BRINcodes, which are defined by the Dutch Ministry of Higher Education and are used in CBAP. Use BRINcodes to communicate with the Ministry. You can register BRINcodes in combination with Academic Programs, Campuses, and Academic Organizations. |
|
|
SSR_NATIONAL_NLD |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure Netherlands, GBA Nationality Code Table |
Register GBA nationality codes, which are supplied by the Dutch Ministry of Internal Affairs. Registration of a student’s nationality is mandatory in the Netherlands. This official country code is necessary for use with CBAP functionality and BRON. |
|
|
SSR_PRE_EDU_NLD |
Set Up SACR, Foundation Tables, Academic Structure Netherlands, Prior Education Table NLD |
Define previous education codes, which are used to note a specific level of education attained by students. This information is relevant for the current admission to a specific academic program. |