
 PeopleCode Typographical Conventions
PeopleCode Typographical Conventions
This chapter provides a reference to PeopleCode built-in functions and language constructs and discusses:
PeopleCode typographical conventions
Functions by category
PeopleCode built-in functions and language constructs

 PeopleCode Typographical Conventions
PeopleCode Typographical Conventions
Throughout this book, we use typographical conventions to distinguish between different elements of the PeopleCode language, such as bold to indicate function names, italics for arguments, and so on.
Please take a moment to review the following typographical cues:
|
Font Type |
Description |
|
Indicates a PeopleCode program or other example |
|
Keyword |
In PeopleCode syntax, items in keyword font indicate function names, method names, language constructs, and PeopleCode reserved words that must be included literally in the function call. |
|
Variable |
In PeopleCode syntax, items in variable font are placeholders for arguments that your program must supply. |
|
... |
In PeopleCode syntax, ellipses indicate that the preceding item or series can be repeated any number of times. |
|
{Option1|Option2} |
In PeopleCode syntax, when there is a choice between two options, the options are enclosed in curly braces and separated by a pipe. |
|
[ ] |
In PeopleCode syntax optional items are enclosed in square brackets. |
|
&Parameter |
In PeopleCode syntax an ampersand before a parameter indicates that the parameter is an already instantiated object, or is a parameter variable that will receive a value during the execution of the function. |

 Functions by Category
Functions by Category
The following topics subdivide the PeopleCode built-in functions by functional category and provide links from within each category to the reference entries.

 Analytic Calculation Engine
Analytic Calculation Engine

 APIs
APIs

 Application Classes
Application Classes

 Application Engine
Application Engine

 Application Logging
Application Logging

 Arrays
Arrays

 Attachment
Attachment
See Also

 Bulk
Bulk

 Business Interlink
Business Interlink

 Character Processing
Character Processing

 Chart
Chart

 ChartField
ChartField

 Component Buffer
Component Buffer
See Also

 Component Interface
Component Interface

 Conversion
Conversion

 Currency and Financial
Currency and Financial

 Current Date and Time
Current Date and Time
See Also
Date and Time, SQL Date and Time.

 Custom Display Formats
Custom Display Formats

 Database and Platform
Database and Platform

 Data Buffer Access
Data Buffer Access
See Also

 Date and Time
Date and Time
See Also
Current Date and Time, SQL Date and Time.

 Debugging
Debugging

 Defaults, Setting
Defaults, Setting

 Effective Date and Effective Sequence
Effective Date and Effective Sequence

 Email
Email

 Environment
Environment

 Exceptions
Exceptions

 Executable Files, Running
Executable Files, Running
See Also

 Files
Files
See Also

 Financial
Financial

 Grids
Grids

 Images
Images
See Also

 Integration Broker
Integration Broker

 Internet
Internet
GenerateComponentContentRelURL

 Java
Java

 Language Constructs
Language Constructs

 Language Preference and Locale
Language Preference and Locale

 Logical (Tests for Blank Values)
Logical (Tests for Blank Values)

 Mail
Mail

 Math
Math

 Menu Appearance
Menu Appearance

 Message Catalog and Message Display
Message Catalog and Message Display

 Messages
Messages
See Also
XML.

 Mobile
Mobile

 Modal Transfers
Modal Transfers
See Also

 MultiChannel Framework
MultiChannel Framework

 Object
Object

 Object-Based
Object-Based

 Page
Page

 Page Control Appearance
Page Control Appearance

 Personalizations
Personalizations

 Process Scheduler
Process Scheduler

 Remote Call
Remote Call

 RowsetCache
RowsetCache

 Saving and Canceling
Saving and Canceling

 Scroll Select
Scroll Select

 Search Dialog
Search Dialog

 Secondary Pages
Secondary Pages
See Also

 SQL
SQL
See Also
Scroll Select, Data Buffer Access.

 SQL Date and Time
SQL Date and Time
See Also
Current Date and Time, Date and Time.

 SQL Shortcuts
SQL Shortcuts

 String
String

 Subrecords
Subrecords

 TimeZone
TimeZone

 Trace Control
Trace Control

 Transfers
Transfers
See Also
Modal Transfers, Secondary Pages.

 Type Checking
Type Checking

 User Information
User Information

 User Security
User Security

 Validation
Validation

 Workflow
Workflow

 XML
XML

 PeopleCode Built-in Functions and Language Constructs
PeopleCode Built-in Functions and Language Constructs
The following are the PeopleCode Built-In functions.

 Abs
AbsSyntax
Abs(x)
Description
Use the Abs function to return a decimal value equal to the absolute value of a number x.
Parameters
|
x |
Specify the number you want the decimal value for. |
Example
The example returns the absolute value of the difference between &NUM_1 and &NUM_2:
&RESULT = Abs(&NUM_1 - &NUM_2);
See Also

 AccruableDays
AccruableDaysSyntax
AccruableDays(StartDate, EndDate, Accrual_Conv)
Description
Use the AccruableDays function to return the number of days during which interest can accrue in a given range of time according to the Accrual_Conv parameter.
Parameters
|
StartDate |
The beginning of the time period for determining the accrual. This parameter takes a date value. |
|
EndDate |
The end of the time period for determining the accrual. This parameter takes a date value. |
|
Accrual_Conv |
The accrual convention. This parameter takes either a number or a constant value. Values for this parameter are: |
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
0 |
%Accrual_30DPM |
30/360: all months 30 days long according to NASD rules for date truncation |
|
1 |
%Accrual_30DPME |
30E/360: all months 30 days long according to European rules for date truncation |
|
2 |
N/A |
30N/360: all months but February are 30 days long according to SIA rules |
|
3 |
%Accrual_Fixed360 |
Act/360: months have variable number of days, but years have fixed 360 days |
|
4 |
%Accrual_Fixed365 |
Act/365: months have variable number of days, buy years have fixed 365 days |
|
5 |
%Accrual_ActualDPY |
Act/Act: months and years have a variable number of days |
Returns
An integer representing a number of days.
See Also

 AccrualFactor
AccrualFactorSyntax
AccrualFactor(StartDate, EndDate, Accrual_Conv)
Description
Use the AccrualFactor function to compute a factor that's equal to the number of years of interest accrued during a date range, according to Accrual_Conv parameter.
Parameters
|
StartDate |
The beginning of the time period for determining the accrual. This parameter takes a date value. |
|
EndDate |
The end of the time period for determining the accrual. This parameter takes a date value. |
|
Accrual_Conv |
The accrual convention. This parameter takes either a number or constant value. Values for this parameter are: |
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
0 |
%Accrual_30DPM |
30/360: all months 30 days long according to NASD rules for date truncation |
|
1 |
%Accrual_30DPME |
30E/360: all months 30 days long according to European rules for date truncation |
|
2 |
N/A |
30N/360: all months but February are 30 days long according to SIA rules |
|
3 |
%Accrual_Fixed360 |
Act/360: months have variable number of days, but years have fixed 360 days |
|
4 |
%Accrual_Fixed365 |
Act/365: months have variable number of days, buy years have fixed 365 days |
|
5 |
%Accrual_ActualDPY |
Act/Act: months and years have a variable number of days |
Returns
A floating point number representing a number of years.
See Also

 Acos
AcosSyntax
Acos(value)
Description
Use the Acos function to calculate the arccosine of the given value, that is, the size of the angle whose cosine is that value.
Parameters
|
value |
Any real number between -1.00 and 1.00 inclusive, the range of valid cosine values. If the input value is outside this range, an error message appears at runtime ("Decimal arithmetic error occurred. (2,110)"). Adjust your code to provide a valid input value. |
Returns
A value in radians between 0 and pi.
Example
The following example returns the size in radians of the angle whose cosine is 0.5:
&MY_ANGLE = Acos(0.5);
See Also
Asin, Atan, Cos, Cot, Degrees, Radians, Sin, Tan.

 ActiveRowCount
ActiveRowCountSyntax
ActiveRowCount(Scrollpath)
Where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ]] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Use the ActiveRowCount function to return the number of active (non-deleted) rows for a specified scroll area in the active page.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the ActiveRowCount Rowset class property instead.
ActiveRowCount is often used to get a limiting value for a For statement. This enables you to loop through the active rows of a scroll area, performing an operation on each active row. Rows that have been marked as deleted are not affected in a For loop delimited by ActiveRowCount. If you want to loop through all the rows of a scroll area, including deleted rows, use TotalRowCount.
Use ActiveRowCount with CurrentRowNumber to determine whether the user is on the last row of a record.
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
Returns
Returns a Number value equal to the total active (non-deleted) rows in the specified scroll area in the active page.
Example
In this example ActiveRowCount is used to delimit a For loop through a level-one scroll:
&CURRENT_L1 = CurrentRowNumber(1); &ACTIVE_L2 = ActiveRowCount(RECORD.ASSIGNMENT, &CURRENT_L1, RECORD.ASGN_HOME_HOST); &HOME_HOST = FetchValue(RECORD.ASSIGNMENT, &CURRENT_L1, ASGN_HOME_HOST.HOME_HOST, 1); If All(&HOME_HOST) Then For &I = 1 To &ACTIVE_L2 DeleteRow(RECORD.ASSIGNMENT, &CURRENT_L1, RECORD.ASGN_HOME_HOST, 1); End-For; End-If;
See Also
CurrentRowNumber, TotalRowCount, For.

 AddAttachment
AddAttachmentSyntax
AddAttachment(URLDestination, DirAndFilename, FileType, UserFile, MaxSize [, PreserveCase])
where URLDestination can have one of the following forms:
URL.URLname
Or a string URL, such as
ftp://user:[email protected]/
Note. You cannot specify a different port for an attachment when using an FTP server. You can only use the default port of 21.
Description
Use the AddAttachment function to transfer a file from one server to another. You could use this to associate a file with a row in a record, or with a page of data.
Note. If the specified subdirectories don't exist this function tries to create them.
File Name Considerations
When the file is transferred, the following characters are replaced with an underscore:
space
semicolon
plus sign
percent sign
ampersand
apostrophe
exclamation point
@ sign
pound sign
dollar sign
Restrictions on Use in PeopleCode Events
AddAttachment is a “think-time” function, which means that it should not be used in any of the following PeopleCode events:
SavePreChange
SavePostChange
Workflow
RowSelect
Any PeopleCode event that initiates as a result of a Select or SelectNew method, or any of the ScrollSelect functions.
If you want to transfer files in a "non-interactive" mode, with functions that aren't think-time, see the GetAttachment and PutAttachment functions.
Security Considerations
The FileType parameter is only a suggestion. Specifying it does not enforce specific file types. If you do not want specific file types (such as .exe or .bat) you must write PeopleCode to discern the name and file type of the attached file and delete it.
When the end user views attachments using the ViewAttachment function, some browsers treat documents as HTML regardless of file extension, and thus execute embedded Java script. You may want to write a PeopleCode program to only allow specific file extensions to be viewed.
See Also
Parameters
|
URLDestination |
A reference to a URL. This can be either a URL name, in the form URL.URLName, or a string. This is where the file is transferred to. |
|
DirAndFileName |
A directory and filename. This is appended to the URLDestination to make up the full URL where the file is transferred to.
Note. The URLDestination requires "/" (forward) slashes. Because the DirAndFileName parameter is appended to the URL, it also requires only "/" slashes. "\" (backward) slashes are not supported for either the URLDestination or the DirAndFileName parameter. |
|
FileType |
A string to use as a suggestion for the extension file type, such as ".doc", ".gif", ".properties" and so on. The user may still type in a filename of a different extension. The value given for this parameter is not enforced. Passing in a null string (that is, two double-quotes with no space ("")) invokes all files (*.*). |
|
UserFile |
The name of the file on the source system. |
|
MaxSize |
Specify, in kilobytes, the maximum size of the attachment. If you specify if 0, it indicates “no limit,” so any filesize can be added. This includes files with zero bytes. This is the default value. Note. MaxSize is not checked before the file is transferred to the web server. |
|
PreserveCase |
Specify a Boolean value to indicate whether the case of the directory and file name specified with DirAndFileName are preserved or not; true, preserve the case, false otherwise. The default value is false. |
Returns
You can check for either an integer or a constant value:
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
0 |
%Attachment_Success |
File was transferred successfully. |
|
1 |
%Attachment_Failed |
File was not successfully transferred. |
|
2 |
%Attachment_Cancelled |
File transfer didn't complete because the operation was canceled by the user. |
|
3 |
%Attachment_FileTransferFailed |
File transfer didn't succeed. |
|
4 |
%Attachment_NoDiskSpaceAppServ |
No disk space on the application server. |
|
5 |
%Attachment_NoDiskSpaceWebServ |
No disk space on the web server. |
|
6 |
%Attachment_FileExceedsMaxSize |
File exceeds maximum size. |
|
7 |
%Attachment_DestSystNotFound |
Cannot locate destination system for ftp. |
|
8 |
%Attachment_DestSystFailedLogin |
Unable to login to destination system for ftp. |
|
9 |
%Attachment_FileNotFound |
Cannot locate file. |
|
10 |
%Attachment_DeleteFailed |
Cannot delete file. |
Example
The following example is how to specify a URL for use with AddAttachment, with encryption, de-referencing the parameter for use with AddAttachment:
The following is for creating the password:
If All(&OPERPSWD) Then OPERPSWD = Encrypt("some value", RTrim(LTrim(&WRKOPERPSWD))); End-If;
The following code example shows how to access the password and enclose it in a URL:
SQLExec("select ftpid, operpswd, ftpaddress, ftpdirectory from PS_CDM_DIST_NODE where distnodename = 'HRFTP'", &FTPID, &OPERPSWD, &ftpaddress, &ftpdirectory); If All(&OPERPSWD) Then &OPERPSWD = Decrypt("some value", RTrim(LTrim(&OPERPSWD))); End-If;
Here is another example.
&uniquefilename = ""; &REC = GetRecord(); For &I = 1 To &REC.FieldCount &Fld = &REC.getfield(&I); If (&Fld.IsKey = True) Then If (&Fld.value = "" And &Fld.IsRequired = True) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "Please attach the file after filling out the required fields on this page."); Return; Else &uniquefilename = &uniquefilename | &Fld.value; End-If; End-If; End-For; &temp = Substitute(&uniquefilename, " ", ""); /* delete spaces */ ATTACHSYSFILENAME = Left(&uniquefilename, 64); /* make uniq part a max of 64 chars */ /* If you have created a subdirectory on the ftp server for this page, prepend it here: ATTACHSYSFILENAME = "HR/ABSENCEHIST/" | ATTACHSYSFILENAME; */ &retcode = AddAttachment(URL.MYFTP, ATTACHSYSFILENAME, "", ATTACHUSERFILE, 0); /* The actual name on the ftp file server is the following */ ATTACHSYSFILENAME = ATTACHSYSFILENAME | ATTACHUSERFILE; &temp = Substitute(ATTACHSYSFILENAME, " ", ""); /* delete spaces */ ATTACHSYSFILENAME = &temp; If (&retcode = %Attachment_Success) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "AddAttachment succeeded"); Hide(ATTACHADD); UnHide(ATTACHVIEW); UnHide(ATTACHDELETE); End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_Failed) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "AddAttachment failed"); ATTACHUSERFILE = ""; ATTACHSYSFILENAME = ""; End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_Cancelled) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "AddAttachment cancelled"); ATTACHUSERFILE = ""; ATTACHSYSFILENAME = ""; End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_FileTransferFailed) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "AddAttachment failed: File Transfer did not succeed"); ATTACHUSERFILE = ""; ATTACHSYSFILENAME = ""; End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_NoDiskSpaceAppServ) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "AddAttachment failed: No disk space on the app server"); ATTACHUSERFILE = ""; ATTACHSYSFILENAME = ""; End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_NoDiskSpaceWebServ) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "AddAttachment failed: No disk space on the web server"); ATTACHUSERFILE = ""; ATTACHSYSFILENAME = ""; End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_FileExceedsMaxSize) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "AddAttachment failed: File exceeds the max size"); ATTACHUSERFILE = ""; ATTACHSYSFILENAME = ""; End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_DestSystNotFound) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "AddAttachment failed: Cannot locate destination system for ftp"); ATTACHUSERFILE = ""; ATTACHSYSFILENAME = ""; End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_DestSysFailedLogin) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "AddAttachment failed: Unable to login into destination system for ftp"); ATTACHUSERFILE = ""; ATTACHSYSFILENAME = ""; End-If;
See Also
DeleteAttachment, GetAttachment, PutAttachment, ViewAttachment.
Using File Attachments in Applications

 AddEmailAddress
AddEmailAddressSyntax
AddEmailAddress(Type, Address [, Primary])
Description
Use the AddEmailAddress function to add an email address for the current user. You can only add one email address of a specific type for a user. If you try to add an email address for a type that is already associated with an email address, you receive an error.
Parameters
|
Type |
Specify the type of email address being added. This parameter takes a string value. The valid values are: |
|
Value |
Description |
|
BB |
Blackberry email address |
|
BUS |
Business email address |
|
HOME |
Home email address |
|
OTH |
Other email address |
|
WORK |
Work email address |
|
Address |
Specify the email address that you want to add as a string. |
|
Primary |
Specify whether this email address is the primary address for the user. This parameter takes a Boolean value: True, this email address is the primary email address, False otherwise. If not specified, the default is False. |
Returns
None.
See Also
ChangeEmailAddress, DeleteEmailAddress, MarkPrimaryEmailAddress.

 AddKeyListItem
AddKeyListItemSyntax
AddKeyListItem(field, value)
Description
Use the AddKeyListItem to add a new key field and its value to the current list of keys. It enables PeopleCode to help users navigate through related pages without being prompted for key values. A common use of AddKeyListItem is to add a field to a key list and then transfer to a page which uses that field as a key.
Parameters
|
field |
The field to add to the key list. |
|
value |
The value of the added key field used in the search. |
Returns
Returns a Boolean value indicating whether it completed successfully.
Example
The following example creates a key list using AddKeyListItem and transfers the user to a page named VOUCHER_INQUIRY_FS.
AddKeyListItem(VNDR_INQ_VW_FS.BUSINESS_UNIT, ASSET_ACQ_DET.BUSINESS_UNIT_AP); AddKeyListItem(VNDR_INQ_VW_FS.VOUCHER_ID, ASSET_ACQ_DET.VOUCHER_ID); TransferPage("VOUCHER_INQUIRY_FS");
See Also
ClearKeyList, TransferPage, Transfer.

 AddSystemPauseTimes
AddSystemPauseTimesSyntax
AddSystemPauseTimes(StartDay, StartTime, EndDay, EndTime)
Description
Use the AddSystemPauseTimes function to set when pause times occur on your system by adding a row to the system pause-times tables.
This function is used in the PeopleCode for the Message Monitor. Pause times are set up in the Message Monitor.
Parameters
|
StartDay |
Specify a number from 0-6. Values are: |
|
Value |
Description |
|
0 |
Sunday |
|
1 |
Monday |
|
2 |
Tuesday |
|
3 |
Wednesday |
|
4 |
Thursday |
|
5 |
Friday |
|
6 |
Saturday |
|
StartTime |
Specify a time, in seconds, since midnight. |
|
EndDay |
Specify a number from 0-6. Values are: |
|
Value |
Description |
|
0 |
Sunday |
|
1 |
Monday |
|
2 |
Tuesday |
|
3 |
Wednesday |
|
4 |
Thursday |
|
5 |
Friday |
|
6 |
Saturday |
|
EndTime |
Specify a time, in seconds, since midnight. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if the system pause time specified was added, False otherwise.
Example
Declare Function SetTime PeopleCode REFRESH_BTN FieldFormula; Component Boolean &spt_changed; Function GetSecond(&time) Returns number ; Return Hour(&time) * 3600 + Minute(&time) * 60 + Second(&time); End-Function; /* initialize; */ STARTDAY = "0"; AMM_STARTTIME = SetTime(0); ENDDAY = "0"; AMM_ENDTIME = SetTime(0); If DoModal(Panel.AMM_ADD_SPTIMES, MsgGetText(117, 13, ""), - 1, - 1) = 1 Then If AddSystemPauseTimes(Value(STARTDAY), GetSecond(AMM_STARTTIME), Value(ENDDAY), GetSecond(AMM_ENDTIME)) Then &spt_changed = True; DoSave(); Else MessageBox(16, MsgGetText(117, 13, ""), 117, 14, ""); End-If; End-If;
See Also
Using Integration Broker Monitor

 AddToDate
AddToDateSyntax
AddToDate(date, num_years, num_months, num_days)
Description
Use the AddToDate function to add the specified number of years, months, and days to the date provided.
Suppose, for example, that you want to find a date six years from now. You could not just multiply 6 times 365 and add the result to today’s date, because of leap years. And, depending on the current year, there may be one or two leap years in the next six years. AddToDate takes care of this for you.
You can subtract from dates by passing the function negative numbers.
Parameters
|
date |
The input date to be adjusted. |
|
num_years |
The number of years by which to adjust the specified date. num_years can be a negative number. |
|
num_months |
The number of months by which to adjust the specified date. This parameter can be a negative number. |
|
num_days |
The number of days by which to adjust the specified date. This parameter can be a negative number. |
Returns
Returns a Date value equal to the original date plus the number of years, months, and days passed to the function.
Example
The following example finds the date one year, three months, and 16 days after a field called BEGIN_DT:
AddToDate(BEGIN_DT, 1, 3, 16);
This example finds the date two months ago prior to BEGIN_DT:
AddToDate(BEGIN_DT, 0, -2, 0);
See Also
DateValue, Day, Days, Days360, Days365, Month, Weekday.

 AddToDateTime
AddToDateTimeSyntax
AddToDateTime(datetime, years, months, days, hours, minutes, seconds)
Description
Use the AddToDateTime function to add the specified number of years, months, days, hours, seconds, and minutes to the datetime provided. You can subtract from datetimes by passing the function negative numbers.
Parameters
|
datetime |
The Datetime value to which you want to add. |
|
years |
An integer representing the number of years. |
|
months |
An integer representing the number of months to add to datetime. |
|
days |
An integer representing the number of days to add to datetime. |
|
hours |
An integer representing the number of hours to add to datetime. |
|
minutes |
An integer representing the number of minutes to add to datetime. |
|
seconds |
An integer representing the number of seconds to add to datetime. |
Returns
Returns a Datetime value equal to the original date plus the number of years, months, days, hours, minutes, and seconds passed to the function.
Example
The following example postpones an interview scheduled in the INTRTime field by two days and two hours:
INTRTIME = AddToDateTime(INTRTIME, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0, 0);
See Also
AddToTime, DateValue, DateTimeValue, TimeValue.

 AddToTime
AddToTimeSyntax
AddToTime(time, hours, minutes, seconds)
Description
Use the AddToTime function to add hours, minutes, and seconds to time. This function returns the result as a Time value. To subtract from time, use negative numbers for hours, minutes, and seconds. The resulting value is always adjusted such that it represents an hour less than 24 (a valid time of day.)
Parameters
|
time |
A time value that you want to subtract from or add to. |
|
hours |
An integer representing the number of hours to add to time. |
|
minutes |
An integer representing the number of minutes to add to time. |
|
seconds |
An integer representing the number of seconds to add to time. |
Returns
A Time value equal to time increased by the number of hours, minutes, and seconds passed to the function.
Example
Assume that a time, &BREAKTime, is 0:15:00. The following moves the time &BREAKTime back by one hour, resulting in 23:15:00:
&BREAKTime = AddToTime(&BREAKTime, -1, 0, 0);
See Also
AddToDateTime, DateValue, DateTimeValue, TimeValue.

 All
AllSyntax
All(fieldlist)
Where fieldlist is an arbitrary-length list of field names in the form:
[recordname.]fieldname1 [, [recordname.]fieldname2] ...
Description
Use the All function to verify if a field contains a value, or if all the fields in a list of fields contain values. If any of the fields are Null, then All returns False.
A blank character field, or a zero (0) numeric value in a required numeric field is considered a null value.
Related Functions
|
None |
Checks that a field or list of fields have no value. |
|
AllOrNone |
Checks if either all the field parameters have values, or none of them have values. Use this in examples where if the user fills in one field, she must fill in all the other related values. |
|
OnlyOne |
Checks if exactly one field in the set has a value. Use this when the user must fill in only one of a set of mutually exclusive fields. |
|
OnlyOneOrNone |
Checks if no more than one field in the set has a value. Use this in examples when a set of fields is both optional and mutually exclusive; that is, if the user can put a value into one field in a set of fields, or leave them all empty. |
Returns
Returns a Boolean value based on the values in fieldlist. The All function returns True if all of the specified fields have a value; it returns False if any one of the fields does not contain a value.
Example
The All function is commonly used in SaveEdit PeopleCode to ensure that a group of related fields are all entered. For example:
If All(RETURN_DT, BEGIN_DT) and 8 * (RETURN_DT - BEGIN_DT) (DURATION_DAYS * 8 + DURATION_HOURS) Then Warning MsgGet(1000, 1, "Duration of absence exceeds standard hours for number of days absent."); End-if;
See Also
AllOrNone, None, OnlyOne, OnlyOneOrNone, SetDefault, SetDefaultAll.

 AllOrNone
AllOrNoneSyntax
AllOrNone(fieldlist)
Where fieldlist is an arbitrary-length list of field references in the form:
[recordname.]fieldname1 [, [recordname.]fieldname2] ...
Description
The AllOrNone function takes a list of fields and returns True if either of these conditions is true:
All of the fields have values (that is, are not Null).
None of the fields has a value.
For example, if field1 = 5, field2 = "Mary", and field3 = null, AllOrNone returns False.
This function is useful, for example, where you have a set of page fields, and if any one of the fields contains a value, then all of the other fields are required also.
A blank character field, or a zero (0) numeric value in a required numeric field is considered a null value.
Related Functions
|
All |
Checks to see if a field contains a value, or if all the fields in a list of fields contain values. If any of the fields is Null, then All returns False. |
|
None |
Checks that a field or list of fields have no value. None is the opposite of All. |
|
OnlyOne |
Checks if exactly one field in the set has a value. Use this when the user must fill in only one of a set of mutually exclusive fields. |
|
OnlyOneOrNone |
Checks if no more than one field in the set has a value. Use this in cases when a set of fields is both optional and mutually exclusive; that is, if the user can put a value into one field in a set of fields, or leave them all empty. |
Returns
Returns a Boolean value: True if all of the fields in fieldlist or none of the fields in fieldlist has a value, False otherwise.
Example
You could use AllOrNone as follows:
If Not AllOrNone(STREET1, CITY, STATE) Then WinMessage("Address should consist of at least Street (Line 1), City, State, and Country."); End-if;
See Also
All, None, OnlyOne, OnlyOneOrNone.

 AllowEmplIdChg
AllowEmplIdChgSyntax
AllowEmplIdChg(is_allowed)
Description
By default, the Component Processor does not allow an user to make any changes to a record if a record contains an EMPLID key field and its value matches the value of the user’s EMPLID. In some situations, though, such changes are warranted. For example, you would want employees to be able to change information about themselves when entering time sheet data.
The AllowEmplIdChg function enables the user to change records whose key matches the user’s own EMPLID, or prevents the user from changing these records. The function takes a single Boolean parameter that when set to True allows the employee to update their own data. When the parameter is set to False, the employee is prevented from updating this data.
After permission is granted, it stays through the life of the component, not the page. After a user switches to another component, the default value (not being able to make changes) is reapplied.
Parameters
|
is_allowed |
A Boolean value indicating whether the user is permitted to change the user's own data. |
Returns
Optionally returns a Boolean value: True if the function executed successfully, False otherwise.
Example
If Substring (%Page, 1, 9) = Substring(PAGE.TimeSHEET_PNL_A, 1, 9) Then AllowEmplIdChg(true); End-if;

 Amortize
AmortizeSyntax
Amortize(intr, pb, pmt, pmtnbr, payintr, payprin, balance)
Description
Use the Amortize function to compute the amount of a loan payment applied towards interest (payintr), the amount of the payment applied towards principal (payprin), and the remaining balance balance, based on the principal balance (pb) at the beginning of the loan term, the amount of one payment pmt, the interest rate charged during one payment period (intr), and the payment number pmtnbr.
Parameters
Note that payintr, payprin, and balance are “outvars”: you must pass variables in these parameters, which the Amortize function then fills with values. The remaining parameters are “invars” containing data the function needs to perform its calculation.
|
intr |
Number indicating the percent of interest charged per payment period. |
|
pb |
Principal balance at the beginning of the loan term (generally speaking, the amount of the loan). |
|
pmt |
The amount of one loan payment. |
|
pmtnbr |
The number of the payment. |
|
payintr |
The amount of the payment paid toward interest. |
|
payprin |
The amount of the payment paid toward principal. |
|
balance |
The remaining balance after the payment. |
Returns
None.
Example
Suppose you want to calculate the principal, interest, and remaining balance after the 24th payment on a loan of $15,000, at an interest rate of 1% per loan payment period, and a payment amount of $290.
&INTRST_RT=1; &LOAN_AMT=15000; &PYMNT_AMNT=290; &PYMNT_NBR=24; Amortize(&INTRST_RT, &LOAN_AMT, &PYMNT_AMNT, &PYMNT_NBR, &PYMNT_INTRST, &PYMNT_PRIN, &BAL); &RESULT = "Int=" | String(&PYMNT_INTRST) | " Prin=" | String(&PYMNT_PRIN) | " Bal=" | String(&BAL);
This example sets &RESULT equal to "Int=114 Prin=176 Bal=11223.72".

 Asin
AsinSyntax
Asin(value)
Description
Use the Asin function to calculate the arcsine of the given value, that is, the size of the angle whose sine is that value.
Parameters
|
value |
Any real number between -1.00 and 1.00 inclusive, the range of valid sine values. If the input value is outside this range, an error message appears at runtime ("Decimal arithmetic error occurred. (2,110)"). Adjust your code to provide a valid input value. |
Returns
A value in radians between -pi/2 and pi/2.
Example
The following example returns the size in radians of the angle whose sine is 0.5:
&MY_ANGLE = Asin(0.5);
See Also
Acos, Atan, Cos, Cot, Degrees, Radians, Sin, Tan.

 Atan
AtanSyntax
Atan(value)
Description
Use the Atan function to calculate the arctangent of the given value, that is, the size of the angle whose tangent is that value.
Parameters
|
value |
Any real number. |
Returns
A value in radians between -pi/2 and pi/2.
Example
The following example returns the size in radians of the angle whose tangent is 0.5:
&MY_ANGLE = Atan(0.5);
See Also
Acos, Asin, Cos, Cot, Degrees, Radians, Sin, Tan.

 BlackScholesCall
BlackScholesCallSyntax
BlackScholesCall(Asset_Price, Strike_Price, Interest_Rate, Years, Volatility)
Description
Use the BlackScholesCall function to return the value of a call against an equity underlying according to the Black-Scholes equations.
Parameters
|
Asset_Price |
The asset price. This parameter takes a decimal value. |
|
Strike_Price |
The strike price. This parameter takes a decimal value. |
|
Interest_Rate |
The risk-free interest rate. This parameter takes a decimal value. |
|
Years |
The number of years to option expiration. This parameter takes a number value (decimal). |
|
Volatility |
The volatility of underlying. This parameter takes a decimal value. |
Returns
A number representing the value of a call against an equity.
See Also

 BlackScholesPut
BlackScholesPutSyntax
BlackScholesPut(Asset_Price, Strike_Price, Interest_Rate, Years, Volatility)
Description
Use the BlackScholesPut function to return the value of a put against an equity underlying according to the Black-Scholes equations.
Parameters
|
Asset_Price |
The asset price. This parameter takes a decimal value. |
|
Strike_Price |
The strike price. This parameter takes a decimal value. |
|
Interest_Rate |
The risk-free interest rate. This parameter takes a decimal value. |
|
Years |
The number of years to option expiration. This parameter takes a number (decimal) value. |
|
Volatility |
The volatility of underlying. This parameter takes a decimal value. |
Returns
A number representing the value of a call against an equity.
See Also

 BootstrapYTMs
BootstrapYTMsSyntax
BootstrapYTMs(Date, MktInst, Accrual_Conv)
Description
Use the BootstrapYTMs function to create a zero-arbitrage implied zero-coupon curve from a yield-to-maturity curve using the integrated discount factor method, based on the Accrual_Conv.
Parameters
|
Date |
The trading date of the set of market issues. This parameter takes a date value. |
|
MktInst |
The market instrument properties. This parameter takes an array of array of number. The elements in the array specify the following: |
|
Elements |
Description |
|
1 |
tenor in days |
|
2 |
yield in percent |
|
3 |
price per 100 par |
|
4 |
coupon rate (zero for spot instruments) |
|
5 |
frequency of coupon payments |
|
6 |
unit of measure for coupon frequency, 0 for days, 1 for months, and 2 for years |
|
7 |
coefficient a of a curve interpolating the dataset |
|
8,9,10 |
coefficients b, c, and d of a curve interpolating the dataset |
Returns
An array of array of number. The elements in the array have the same type as the elements in the array for the MktInst parameter.
See Also

 Break
BreakSyntax
Break
Description
Use the Break statement to terminate execution of a loop or an Evaluate function. The program resumes execution immediately after the end of the statement. If the loop or Evaluate is nested in another statement, only the innermost statement is terminated.
Parameters
None.
Example
In the following example, Break is used to terminate the Evaluate statement, while staying within the outermost If statement:
If CURRENCY_CD = PriorEffdt(CURRENCY_CD) Then Evaluate ACTION When = "PAY" If ANNUAL_RT = PriorEffdt(ANNUAL_RT) Then Warning MsgGet(1000, 27, "Pay Rate Change action is chosen and Pay Rate has not been changed."); End-if; Break; When = "DEM" If ANNUAL_RT >= PriorEffdt(ANNUAL_RT) Then Warning MsgGet(1000, 29, "Demotion Action is chosen and Pay Rate has not been decreased."); End-if; Break; When-other End-evaluate; WinMessage("This message appears after executing either of the BREAK statements or after all WHEN statements are false"); End-if;
See Also

 BulkDeleteField
BulkDeleteFieldSyntax
BulkDeleteField(ProjectName, Field.FieldName [, ExclProj])
Description
Use the BulkDeleteField function to delete fields from records and pages, as well as the associated PeopleCode programs and modify the SQL either on the record, or, if the record is a subrecord, on the parent records.
Note. You must have the role Peoplesoft Administrator assigned to your UserId in order to use this function.
If you specify a project that contains objects such as fields which have an upgrade action of delete, those objects are ignored.
The field is removed from the page regardless of where the field exists on the page, whether on a grid or not.
If the field is in the SELECT clause of the SQL, the removal is straightforward. However, if the field is also used in a WHERE clause, or if the field is the only item in the SELECT clause, the record isn't modified and is instead inserted into a project called BLK_FieldName. The record should be examined and any additional changes made as necessary.
Deleting fields from records and pages does not remove the field definition itself and it does not remove the field from other areas, such as Projects, Crystal Reports, or message definitions.
In addition, this function does not delete the references to the field in the PeopleCode. You must manually remove the references to the deleted field. Use the Find In. . . tool to search for the field name you deleted.
Note. Because performing this operation changes records, you must subsequently rebuild the project (alter tables).
Using the Log File
Information about this operation is stored in a log field. The directory where the log file is placed depends on where the function is run from:
If the function is run in two-tier, the log file is located at PS_HOME/BulkOps.txt. This is also the default location if the system cannot find the other paths.
If the function is run from an application server, the log file is located at:
PS_HOME/APPSERV/Domain_Name/LOGS/BulkOps.txt
If the function is run from an Application Engine program, the log file is written to the process' output log directory, that is:
PS_HOME/APPSERV/prcs/Domain_Name/log_output/Process_Name_Instance/BulkOps.txt
Considerations Using this Function
This function is intended for use during configuration time only, before active runtime usage is initiated. Using this function during active runtime is not supported. Changes to data definitions are not recognized on a currently loaded component. In general, changes aren't recognized until the component is reloaded.
Bulk operations are time consuming, therefore, referencing the log file to see the progress of an operation is recommended. These operations accommodate errors and continue processing, logging the overall progress of the operation.
Warning! These operations take place in a separate transaction from the page's save status: the initiation of any of these operations immediately changes the definitions, even if the page is subsequently cancelled.
Considerations Using the Exclusion Project
If you specify ExclProj, the following items that are both in ProjectName and ExclProj are not changed, that is, the field specified is not removed from these items:
pages
records
associated SQL with records of type View
any PeopleCode associated with those items.
Individual SQL or PeopleCode items are not ignored by themselves, only as associated with records or pages.
Parameters
|
ProjectName |
The name of a project that is the source of records and pages to use. Note. When passing the project name as a parameter, if the project contains definitions with an upgrade action of delete, the system ignores those definitions. |
|
FieldName |
The name of the field to be deleted. This name must be prefixed with the reserved word Field. |
|
ExclProj |
The name of a project that has pages that should be ignored by this function. |
Returns
A constant value. The values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
%MDA_Success |
Bulk operation completed successfully. |
|
%MDA_Failure |
Bulk operation did not complete successfully. |
Example
&pjm = "MYPROJ"; &ret = BulkDeleteField(&pjm, Field.OrgId, "EXCLPROJ"); If (&ret = %MDA_Success) Then MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "BulkDeleteField succeeded"); Else MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "BulkDeleteField failed"); End-If;
See Also
BulkInsertField, BulkModifyPageFieldOrder.

 BulkInsertField
BulkInsertFieldSyntax
BulkInsertField(ProjectName, Field.FieldName, ModelName, ClonePCode [, ExclProj])
Description
Use the BulkInsertField function to insert a source field into records and pages in a project if and only if the model field specified by ModelName exists on those records and pages.
If you specify a project that contains objects such as fields which have an upgrade action of delete, those objects are ignored.
Note. You must have the role Peoplesoft Administrator assigned to your UserId in order to use this function.
Using the Log File
Information about this operation is stored in a log field. The directory where the log file is placed depends on where the function is run from:
If the function is run in two-tier, the log file is located at PS_HOME/BulkOps.txt. This is also the default location if the system cannot find the other paths.
If the function is run from an application server, the log file is located here:
PS_HOME/APPSERV/Domain_Name/LOGS/BulkOps.txt
If the function is run from an Application Engine program, the log file is written to the process' output log directory, that is:
PS_HOME/APPSERV/prcs/Domain_Name/log_output/Process_Name_Instance/BulkOps.txt
Considerations Inserting Fields into Records
In records, the source field is assigned the same record field properties as the model field on each record, and is inserted directly after the model field.
If the model field has a prompt table, a prompt table is created for the source field using the name of the source field with TBL appended to it.
If the record is either a SQL View or Dynamic View type, the associated SQL is modified by having the SELECT clause expanded to include the new field.
If the record is a subrecord, the parent records of type SQL View or Dynamic View that contain this subrecord are updated.
If the SQL contains the model field in the WHERE clause, or the SQL is complex, the associated record is inserted into a project called BLK_FieldName. You should examine this record and make any necessary changes.
If the model field has PeopleCode associated with it on the record or in a component, and ClonePCode has been set to True, this PeopleCode is cloned to the new field, with all references to the model field changed to refer to the new field.
Note. Because using this function changes records that are used to build application tables, you must rebuild (alter) the specified project before these changes can be used.
Considerations Inserting Fields into Pages
If the model field is in a grid, the system inserts the new field into the grid next to the model field and assigns it the same page field properties.
If the model field is not in a grid, the system inserts the new field onto the page to the right of the model field (in the first open space) and assigns it the same page field properties. If the system detects a questionable field position, it inserts the page into a project called BLK_FieldName. The page will work as-is, however, the GUI layout may not be optimal, so you should examine these pages by hand.
The page field name property isn't cloned if it exists on the model field. Instead, the field name of the new field is used, since the page field name should be a unique identifier for page elements.
Note. If the project you specified only contained pages and not records, you do not need to rebuild the project after using this function. The changes take affect when the component containing the page is reloaded.
Considerations Using this Function
This function is intended for use during configuration time only, before active runtime usage is initiated. Using this function during active runtime is not supported. Changes to data definitions are not recognized on currently loaded component. In general, changes aren't recognized until the component is reloaded.
Bulk operations are time consuming, therefore, referencing the log file to see the progress of an operation is recommended. These operations accommodate errors and continue processing, logging the overall progress of the operation.
Warning! These operations take place in a separate transaction from the page's save status: the initiation of any of these operations immediately changes the definitions, even if the page is subsequently cancelled.
Considerations Using the Exclusion Project
If you specify ExclProj, the following items that are both in ProjectName and ExclProj are not changed, that is, the field specified is not inserted to these items:
pages
records
associated SQL with records of type View
any PeopleCode associated with those items.
Individual SQL or PeopleCode items are not ignored by themselves, only as associated with records or pages.
Parameters
|
ProjectName |
The name of a project that is the source of records and pages to use. Note. When passing the project name as a parameter, if the project contains definitions with an upgrade action of delete, the system ignores those definitions. |
|
FieldName |
The name of the field to be inserted. This name must be prefixed with the reserved word Field. |
|
ModelName |
The name of a field on which to model the inserted field. Attributes are cloned from it for records and pages, PeopleCode is modified, and SQL inserted. |
|
ClonePCode |
Specify whether to clone the PeopleCode from the model to this field. This parameter takes a Boolean value: True, clone the PeopleCode programs, False, don't. |
|
ExclProj |
The name of a project that has pages that should be ignored by this function. |
Returns
A constant value. The values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
%MDA_Success |
Bulk operation completed successfully. |
|
%MDA_Failure |
Bulk operation did not complete successfully. |
Example
&pjm = "MYPROJ"; &ret = BulkInsertField(&pjm, Field.OrgId, Field.DeptId, TRUE, "EXCLPROJ"); If (&ret = %MDA_Success) Then MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "BulkInsertField succeeded"); Else MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "BulkInsertField failed"); End-If;
See Also
BulkModifyPageFieldOrder, BulkDeleteField.

 BulkModifyPageFieldOrder
BulkModifyPageFieldOrderSyntax
BulkModifyPageFieldOrder({ProjectName | PageList}, ColNames, RequireAll, [ColWidths])
Description
Use the BulkModifyPageFieldOrder function to reorder the grid columns as specified by ColNames. If ColWidths is specified, the columns are also resized. This can also be used to modify a single columns width.
Note. You must have the role Peoplesoft Administrator assigned to your UserId in order to use this function.
If you specify a project name as a parameter, and if that project contains objects such as fields which have an upgrade action of delete, those objects are ignored.
The reordering algorithm “bunches” these fields together at the first instance of any of these fields in a target page grid, and forces the remaining fields into the order specified.
This function only reorders fields inside a grid.
If the fields occur twice or more in a grid, from two or more records, such as work records, the fields are bunched together in record groupings before being sorted into the order specified. For example, the two records ABS_HIST and PERSONAL_HISTORY both contain the fields DURATION_DAYS and DURATION_HOURS. The following is an example of how the records are fields would be bunched together first:
ABS_HIST, DURATION_DAYS
ABS_HIST, DURATION_HOURS
PERSONAL_HISTORY, DURATION_DAYS
PERSONAL_HISTORY, DURATION_HOURS
Note. These changes take affect after components are reloaded.
Using the Log File
Information about this operation is stored in a log field. The directory where the log file is placed depends on where the function is run from:
If the function is run in two-tier, the log file is located at PS_HOME/BulkOps.txt. This is also the default location if the system cannot find the other paths.
If the function is run from an application server, the log file is located here:
PS_HOME/APPSERV/Domain_Name/LOGS/BulkOps.txt
If the function is run from an Application Engine program, the log file is written to the process' output log directory, that is:
PS_HOME/APPSERV/prcs/Domain_Name/log_output/Process_Name_Instance/BulkOps.txt
Considerations Using this Function
This function is intended for use during configuration time only, before active runtime usage is initiated. Using this function during active runtime is not supported. Changes to data definitions are not recognized on currently loaded component. In general, changes aren't recognized until the component is reloaded.
Bulk operations are time consuming, therefore, referencing the log file to see the progress of an operation is recommended. These operations accommodate errors and continue processing, logging the overall progress of the operation.
Warning! These operations take place in a separate transaction from the page's save status: the initiation of any of these operations immediately changes the definitions, even if the page is subsequently cancelled.
Parameters
|
ProjectName | PageList |
Specify either the name of a project that is the source of pages to use or an array of page names. Note. When passing the project name as a parameter, if the project contains definitions with an upgrade action of delete, the system ignores those definitions. |
|
ColNames |
Specify an array of string that indicate which fields and the desired order of those fields. |
|
RequireAll |
Specify whether all the fields in ColNames must be present before changes are made or not. This parameter takes a Boolean value: True, all fields must be present. |
|
ColWidths |
Specify an array of number that gives the pixel widths of the grid columns. Use a -1 to indicate that the width of a column shouldn't change. |
Returns
A constant value. The values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
%MDA_Success |
Bulk operation completed successfully. |
|
%MDA_Failure |
Bulk operation did not complete successfully. |
Example
Local Array of String &ColOrder; Local Array of Number &ColWidth; Local String &pjm, &ret; &pjm = "MYPROJ"; &ColWidth = CreateArray(50, 100, -1); &ColOrder = CreateArray("DEPTID", "ORGID", "PROJECT"); &ret = BulkModifyPageFieldOrder(&pjm, &ColOrder, TRUE, &ColWidth); If (&ret = %MDA_Success) Then MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "BulkModifyPageFieldOrder succeeded"); Else MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "BulkModifyPageFieldOrder failed"); End-If;
See Also
BulkInsertField, BulkDeleteField.

 BulkUpdateIndexes
BulkUpdateIndexesSyntax
BulkUpdateIndexes([StringFieldArray])
Description
Use BulkUpdateIndexes to update indexes (PSINDEXDEFN table) for records that contain a field whose NotUsed setting has changed.
A field whose NotUsed flag has been set to True does not show up in indexes. The only way to modify a field's NotUsed setting is through an API call such as in the following example:
SetDBFieldNotUsed(FIELD.OrgId, True);
The indexes of records that contain this field need to be updated to reflect the new settings.
Information about this operation can be logged by turning on PeopleCode tracing of internal functions (value 256.)
Considerations Using this Function
Do not invoke this function from runtime pages, as it modifies all records, including the records used to support the page it is invoked from. This function should be invoked from a PeopleSoft Application Engine program.
Note. If you do call this function from a page the operation completes successfully, but the page returns an error message. Switching to a new component clears up this error, however, any changes not saved to the database are lost.
This function is intended for use during configuration time only, before active runtime usage is initiated. Using this function during active runtime is not supported. Changes to data definitions are not recognized on currently loaded component. In general, changes aren't recognized until the component is reloaded.
Bulk operations are time consuming, therefore, referencing the log file to see the progress of an operation is recommended. These operations accommodate errors and continue processing, logging the overall progress of the operation.
Calling this function without any parameter rebuilds the indexes for all records, an operation that may take hours. By indicating a list of fields whose NotUsed flag has changed, only the affected records have their indexes updated, reducing the time required to run this function.
Warning! These operations take place in a separate transaction from the page's save status: the initiation of any of these operations immediately changes the definitions, even if the page is subsequently cancelled.
Parameters
|
StringFieldArray |
Specify an array of field names (as strings), such as DEPTID, representing the fields whose NotUsed flag has been modified. Only the records containing these fields are updated. If you don't specify a value for this parameter, the indexes for all records are rebuilt. |
Returns
A constant value. The values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
%MDA_Success |
Bulk operation completed successfully. |
|
%MDA_Failure |
Bulk operation did not complete successfully. |
Example
The following example uses the function without the optional array of field names:
&ret = BulkUpdateIndexes(); If (&ret = %MDA_Success) Then MessageBox(0, "MetaData Fn Status", 0, 0, "BulkUpdateIndexes succeeded"); Else MessageBox(0, "MetaData Fn Status", 0, 0, "BulkUpdateIndexes failed"); End-If;
The following example uses the function with an array of two field names passed to it:
&ret = BulkUpdateIndexes(CreateArray("DEPTID","PROJECT")); If (&ret = %MDA_success) Then MessageBox(0, "MetaData Fn Status", 0, 0, "BulkUpdateIndexes succeeded"); Else MessageBox(0, "MetaData Fn Status", 0, 0, "BulkUpdateIndexes failed"); End-If;
See Also
BulkDeleteField, BulkInsertField, BulkModifyPageFieldOrder.

 CallAppEngine
CallAppEngineSyntax
CallAppEngine(applid [, statereclist, processinstance ]);
Where statereclist is list of record objects in the form:
&staterecord1 [, &staterecord2] . . .
There can be only as many record objects in statereclist as there are state records for the Application Engine program. Additional record objects are ignored.
Description
Use the CallAppEngine function to start the PeopleSoft Application Engine program named applid. This is how to start your Application Engine programs synchronously from a page. (Prior to PeopleTools 8, you could do only this using the RemoteCall function.) Normally, you won’t run PeopleSoft Application Engine programs from PeopleCode in this manner. Rather, the bulk of your Application Engine execution will be run using the Process Scheduler, and the exception would be done using CallAppEngine.
The staterecord can be the hard-coded name of a record, but generally you use a record object to pass in values to seed particular state fields. The record name must match the state record name exactly.
The processinstance allows you to specify the process instance used by the Application Engine runtime. In your PeopleCode program this parameter must be declared of type integer since that is the only way the runtime can tell whether the last parameter is to be interpreted as a process instance. For more details see the Application Engine documentation.
Note. If you use this function, you shouldn't use the %TruncateTable or %Execute meta-SQL statement in any of your Application Engine steps. This is because on some platforms an implicit commit occurs after these statements, and all online processing should be done as a single logical unit of work.
After you use CallAppEngine, you may want to refresh your page. The Refresh method, on a rowset object, reloads the rowset (scroll) using the current page keys. This causes the page to be redrawn. GetLevel0().Refresh() refreshes the entire page. If you want only a particular scroll to be redrawn, you can refresh just that part.
See Using PeopleCode in Application Engine Programs.
Note. If you supply a non-zero process instance, all message logging is done under the process instance. You must build your own PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture page to access or delete the messages, since there is no Process Monitor entry for the process instance you used.
PeopleCode Event Considerations
You must include the CallAppEngine PeopleCode function within events that allow database updates because generally, if you’re calling Application Engine, you’re intending to perform database updates. This includes the following PeopleCode events:
SavePreChange (Page)
SavePostChange (Page)
Workflow
Message Subscription
FieldChange
If CallAppEngine results in a failure, all database updates is rolled back. All information the user entered into the component is lost, as if the user pressed ESC.
Application Engine Considerations
You can use the CallAppEngine function in a PeopleSoft Application Engine program, either directly (in a PeopleCode action) or indirectly (using a Component Interface). This functionality must be used carefully, and you should only do this once you have a clear understanding of the following rules and restrictions.
Dedicated cursors are not supported inside a "nested application engine instance" (meaning an application engine program invoked using CallAppEngine from within another application engine program). If a nested application engine instance has any SQL actions with ReUse set to Yes or Bulk Insert, those settings are ignored.
As in any other type of PeopleCode event, no commits are performed within the called application engine program. This is an important consideration. If a batch application engine program called another program using CallAppEngine, and that child program updated many rows of data, the unit-of-work might become too large, resulting in contention with other processes. A batch application engine program should invoke such child programs using a Call Section action, not CallAppEngine.
Temp tables are not shared between a batch application engine program and child program invoked using CallAppEngine. Instead, the child program is assigned an "online" temporary table instance, which is used for all temp tables in that program. In addition, if that child program invokes another program using CallAppEngine, that grandchild shares the online temp instance with the caller. In other words, only one online temp instance is allocated to a process at any one time, no matter how many nested CallAppEngine's there might be.
The lock on an online temp instance persists until the next commit. If the processing time of the called program is significant (greater than a few seconds), this would be unacceptable. As a general rule, application engine programs that make use of temp tables and have a significant processing time should be called from other application engine programs using a Call Section action, not CallAppEngine.
Save Events Considerations
To execute the Application Engine program based on an end user Save, use the CallAppEngine function within a Save event. When you use CallAppEngine, you should keep the following items in mind:
No commits occur during the entire program run.
During SavePreChange, any modified rows in the page have not been written to the database.
During SavePostChange, the modified rows have been written to the database. The Page Process issues one commit at the end of the Save cycle.
FieldChange Considerations
If you don’t want the CallAppEngine call to depend on a Save event, you can also initiate CallAppEngine from a FieldChange event. When having a FieldChange event initiate CallAppEngine, keep the following items in mind:
No commits occur within the program called by CallAppEngine. The called program remains a synchronous execution in the same unit of work.
The Component Processor commits all updates done in a FieldChange at the end of the event, which frees any locks that the Application Engine program might have acquired.
Do not include a DoSave function in the same FieldChange event. Not only is this not allowed, but it also indicates that you should be including the CallAppEngine within a Save event.
You can use the DoSaveNow function in the same FieldChange event, but it must be called prior to the first CallAppEngine function, but not afterward.
Parameters
|
applid |
Specify the name of the Application Engine program you want to start. |
|
statereclist |
Specify an optional record object that provides initial values for a state record. |
|
processinstance |
Specify the process instance used by the Application Engine runtime. |
Returns
None.
Example
The following calls the Application Engine program named MYAPPID, and passes initialization values.
&REC = CreateRecord(RECORD.INIT_VALUES); &REC.FIELD1.Value = "XYZ"; /* set the initial value for INIT_VALUES.FIELD1 */ CallAppEngine("MYAPPID", &REC);
See Also
Using PeopleCode in Application Engine Programs
Specifying Call Section Actions

 CancelPubHeaderXmlDoc
CancelPubHeaderXmlDocSyntax
CancelPubHeaderXmlDoc(PubID, PubNode, ChannelName, VersionName)
Description
Use the CancelPubXmlDoc function to programmatically cancel the message header of a publication contract, much the same as you can do in the message monitor. The message header, also known as the message instance, is the published message before the system performs any transformations.
The function is only available when the message has one of the following statuses:
Error
New
Retry
Timeout
Edited
Parameters
|
PubID |
Specify the PubID of the message. |
|
PubNode |
Specify the Pub Node Name of the message. |
|
ChannelName |
Specify the channel name of the message. |
|
VersionName |
Specify the version name of the message. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if the function completed successfully, False otherwise.
See Also

 CancelPubXmlDoc
CancelPubXmlDocSyntax
CancelPubXmlDoc(PubID, PubNode, ChannelName, VersionName, MessageName, SubNode[, Segment])
Description
Use the CancelPubXmlDoc function to programmatically cancel a message publication contract, much the same as you can do in the message monitor. This is the publication contract that exists after any transformations have been preformed.
The function is only available when the message has one of the following statuses:
Error
New
Retry
Timeout
Edited
Parameters
|
PubID |
Specify the PubID of the message. |
|
PubNode |
Specify the Pub Node Name of the message. |
|
ChannelName |
Specify the channel name of the message. |
|
VersionName |
Specify the version name of the message. |
|
MessageName |
Specify the name of the message. |
|
SubNode |
Specify the subnode of the message. |
|
Segment |
Specify an integer representing which segment you want to access. The default value is one, which means that if you do not specify a segment, the first segment is accessed. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if the function completed successfully, False otherwise.
See Also

 CancelSubXmlDoc
CancelSubXmlDocSyntax
CancelSubXmlDoc(PubID, PubNode, ChannelName, VersionName, MessageName, SubscriptionName[, Segment])
Description
Use the CancelSubXmlDoc function to programmatically cancel a message subscription contract, much the same as you can do in the message monitor.
The function is only available when the message has one of the following statuses:
Error
New
Retry
Timeout
Edited
Parameters
|
PubID |
Specify the PubID as a string. |
|
PubNode |
Specify the Pub Node name as a string. |
|
ChannelName |
Specify the Channel name as a string. |
|
VersionName |
Specify the version name as a string. |
|
MessageName |
Specify the message name as a string. |
|
SubscriptionName |
Specify the subscription name as a string. |
|
Segment |
Specify an integer representing which segment you want to access. The default value is one, which means that if you do not specify a segment, the first segment is accessed. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if function completed successfully, False otherwise.
See Also

 ChangeEmailAddress
ChangeEmailAddressSyntax
ChangeEmailAddress(Type, Address)
Description
Use the ChangeEmailAddress function to change the type of an email address that you've already added for the current user. You can only have one email address of a specific type for a user. If you try to use a type that already has an email address associated with it, you receive an error.
Parameters
|
Type |
Specify the type that you want to change the email address to. This parameter takes a string value. The valid values are: |
|
Value |
Description |
|
BB |
Blackberry email address |
|
BUS |
Business email address |
|
HOME |
Home email address |
|
OTH |
Other email address |
|
WORK |
Work email address |
|
Address |
Specify the email address that you want to add as a string. |
Returns
None.
See Also
AddEmailAddress, DeleteEmailAddress, MarkPrimaryEmailAddress.

 Char
CharSyntax
Char(n)
Description
Use the Char function to convert a decimal numeric value n to the corresponding Unicode character.
Parameters
|
n |
The numeric value to be converted expressed as a decimal Unicode UTF-16 value. |
Returns
Returns a String representing the Unicode character corresponding to the number n.
Example
This example sets &STRING1 to the Latin string “PS” (U+0050, U+0053), &STRING2 to the Unified Han (Japanese, Chinese and Korean) string “日本” (U+65E5, U+672C) and &STRING3 to the Unicode Plane 2 Han character “&#d842�” (surrogate pair U+D842, U+DD79 which is equivalent to the UTF-32 scalar value U+20797).
It should be noted that the single character in &STRING3 requires two calls to the Char function as it is a non-BMP Unicode character and therefore is represented by UTF-16 high and low surrogates.
&STRING1 = Char(80) | Char(83);&STRING2 = Char(26085) | Char(26412); &STRING3 = Char(55362) | Char(56697);
See Also

 CharType
CharTypeSyntax
CharType(source_str, char_code)
Description
Use the CharType function to determine whether the first character in source_str is of type char_code . The char_code parameter is a numeric value representing a character type (see the following Parameters section for details). Most character types supported by this function equate to specific Unicode character blocks or are based on Unicode character properties.
See Also
Selecting and Configuring Character Sets and Language Input and Output.
Parameters
|
source_str |
A String, the first character of which will be tested. |
|
char_code |
A Number representing the character type to be tested for. |
The following table shows valid values for char_code. You can specify either a Character Code or a Constant:
|
Numeric Value |
Constant |
Character Set |
|
0 |
%CharType_AlphaNumeric |
Basic Latin — Alphanumeric (printable range of 7-bit US-ASCII), Unicode characters in the range U+0020 — U+007E |
|
1 |
%CharType_ExtendedLatin1 |
Extended Latin-1 characters (ISO 8859-1 accents for Western European languages), Unicode characters in the range U+00BF — U+07E |
|
2 |
%CharType_HankakuKatakana |
Hankaku Katakana (half-width Japanese Katakana) |
|
3 |
%CharType_ZenkakuKatakana |
Zenkaku Katakana (full-width Japanese Katakana) |
|
4 |
%CharType_Hiragana |
Hiragana (Japanese) |
|
5 |
%CharType_Kanji |
Chinese, Japanese and Korean ideographic characters. Includes Japanese Kanji, Chinese Hanzi and Korean Hancha. |
|
6 |
%CharType_DBAlphaNumeric |
Full-width Latin Alphanumeric characters, primarily used for Japanese. Excludes |
|
7 |
None |
Korean Hangul syllables, excluding Hangul Jamo. |
|
8,9 |
None |
Reserved for future use. |
|
10 |
%CharType_JapanesePunctuation |
Full- and half-width punctuation, including space (U+0020) and Fullwidth / Ideographic Space (U+3000). |
|
11 |
None |
Greek |
|
12 |
None |
Cyrillic |
|
13 |
None |
Armenian |
|
14 |
None |
Hebrew |
|
15 |
None |
Arabic |
|
16 |
None |
Devanagari |
|
17 |
None |
Bengali |
|
18 |
None |
Gurmukhi |
|
19 |
None |
Gujarati |
|
20 |
None |
Oriya |
|
21 |
None |
Tamil |
|
22 |
None |
Telugu |
|
23 |
None |
Kannada |
|
24 |
None |
Malayalam |
|
25 |
None |
Thai |
|
26 |
None |
Lao |
|
27 |
None |
Tibetan |
|
28 |
None |
Georgian |
|
29 |
None |
Bopomofo |
Returns
CharType returns one of the following Number values. You can check for the constant values instead of the numeric values if you prefer:
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
1 |
%CharType_Matched |
Character is of type char_code. |
|
0 |
%CharType_NotMatched |
Character is not of type char_code. |
|
-1 |
%CharType_Unknown |
UNKNOWN: unable to determine whether character is of set char_code. This occurs if the character being checked is an unallocated Unicode codepoint, or was added in a version of Unicode greater than that supported by PeopleTools. |
Example
This example tests to see if a character is Hiragana:
&ISHIRAGANA = CharType(&STRTOTEST, %CharType_Hiragana); If &ISHIRAGANA = 1 Then WinMessage("Character type is Hiragana"); Else If &ISHIRAGANA = 0 Then WinMessage("Character type is not Hiragana"); Else WinMessage("Character type is UNKNOWN"); End-If; End-If;
See Also
ContainsCharType, ContainsOnlyCharType, ConvertChar.
Selecting and Configuring Character Sets and Language Input and Output

 ChDir
ChDirSyntax
ChDir(path)
Description
Use the ChDir function to change the current directory on a drive. This is similar to the DOS ChDir command. The drive and the directory are both specified in a path string.
Note. This function has been deprecated.

 ChDrive
ChDriveSyntax
ChDrive(str_dr)
Description
Use the ChDrive function to change the current disk drive to the drive specified by str_dr, which is a string consisting of a valid drive letter followed by a colon, for example "C:".
Note. This function has been deprecated.

 CheckMenuItem
CheckMenuItem
Syntax
CheckMenuItem(BARNAME.menubar_name, ITEMNAME.menuitem_name)
Description
Use the CheckMenuItem function to change the menu state by placing a check mark beside the menu item.
Note. This function has been deprecated.

 Clean
CleanSyntax
Clean(string)
Description
Use the Clean function to remove all non-printable characters, such as control codes, end of line marks, and unpaired Unicode combining marks, from a text string and returns the result as a String value. It is intended for use on text imported from other applications that contains characters that may not be printable. Frequently, low-level characters appear at the beginning and end of each line of imported data, and they cannot be printed.
Returns
Returns a String value purged of non-printable characters.
Example
Because Char(7) (U+0007) is a non-printable character, the following Clean function returns a null string:
&CLEANSTR = Clean(Char(7));
See Also

 ClearKeyList
ClearKeyListSyntax
ClearKeyList()
Description
Use the ClearKeyList function to clear the current key list. This function is useful for programmatically setting up keys before transferring to another component.
Returns
Optionally returns a Boolean value indicating whether the function succeeded.
Example
The following example sets up a key list and then transfers the user to a page named PAGE_2.
ClearKeyList( ); AddKeyListItem(OPRID, OPRID); AddKeyListItem(REQUEST_ID, REQUEST_ID); SetNextPage("PAGE_2"); TransferPage( );
See Also

 ClearSearchDefault
ClearSearchDefaultSyntax
ClearSearchDefault([recordname.]fieldname)
Description
Use the ClearSearchDefault function to disable default processing for the specified field, reversing the effects of a previous call to the SetSearchDefault function.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the SearchDefault Field class property instead.
If search default processing is cleared for a record field, the default value specified in the record field properties for that field will not be assigned when the field appears in a search dialog box. This function is effective only when used in SearchInit PeopleCode.
See Also
Parameters
|
[recordname .]fieldname |
The name of the target field, which is a search key or alternate search key that is about to appear in a search dialog box. The recordname prefix is required if the call to ClearSearchDefault is in a record definition other than recordname. |
Returns
Optionally returns a Boolean value indicating whether the function succeeded.
See Also
ClearSearchEdit, SetSearchDefault, SetSearchEdit, SetSearchDialogBehavior.
Search Processing in Update Modes

 ClearSearchEdit
ClearSearchEditSyntax
ClearSearchEdit([recordname.]fieldname)
Description
Use the ClearSearchEdit function to reverse the effects of a previous call to the SetSearchEdit function. If ClearSearchEdit is called for a specific field, the edits specified in the record field properties will not be applied to the field when it occurs in a search dialog.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the SearchEdit Field class property instead.
See Also
Parameters
|
[recordname .]fieldname |
The name of the target field, which is a search key or alternate search key about to appear in a search dialog box. The recordname prefix is required if the call to ClearSearchEdit is in a record definition other than recordname. |
Returns
Optionally returns a Boolean value indicating whether the function succeeded.
See Also
SetSearchEdit, SetSearchDefault, ClearSearchDefault, SetSearchDialogBehavior.
Search Processing in Update Modes

 Code
CodeSyntax
Code(str)
Description
Use the Code function to return the numerical Unicode UTF-16 value for the first character in the string str. (Normally you would pass this function a single character.) If the string starts with a non-BMP Unicode character, the value returned will be that of the Unicode high surrogate of the character (the first value of the surrogate pair).
Returns
Returns a Number value equal to the character code for the first character in str.
See Also

 Codeb
Codeb
Syntax
Codeb(str)
Description
Note. This function has been deprecated and is no longer supported.
See Also
Code.

 CollectGarbage
CollectGarbageSyntax
CollectGarbage()
Description
Use the CollectGarbage function to remove any unreachable application objects created by the Application Classes.
Sometimes there may be unrecoverable application objects that are can no longer be referenced from PeopleCode, but which have not been reclaimed and so are still taking up computer memory. Generally this situation arises only if you have application objects that form into loops of references.
This function is automatically invoked by the application server as part of its end-of-service processing, so generally you don't need to call it for online applications. However, in Application Engine (batch), it is possible that a long-running batch job could grow in memory usage over time as these unreferencable Application Objects accumulate. The solution to such a problem is to call CollectGarbage periodically to reclaim these objects.
Parameters
None.
Returns
None.
See Also

 CommitWork
CommitWorkSyntax
CommitWork()
Description
Use the CommitWork function to commit pending changes (inserts, updates, and deletes) to the database.
Considerations for Using CommitWork
The following are the considerations for using CommitWork.
This function is available in Application Engine PeopleCode, the FieldChange and SavePreChange events, and Message Subscription PeopleCode. If you use it anywhere else, you'll receive a runtime error.
When used with an Application Engine program, this function only applies to those Application Engine programs that run in batch (not online). If the program is invoked using the CallAppEngine function, the CommitWork call is ignored. The same is true for commit settings at the section or step level.
This function can only be used in an Application Engine program that has restart disabled. If you try to use this function in a program that doesn't have restart disabled, you'll receive a runtime error.
Component interfaces that rely on CommitWork to save data cannot be used in the Excel to Component Interface utility.
When CommitWork is called in the context of a component interface (such as, during a SavePreChange PeopleCode program that's associated with the component), if the caller of the component interface already has an open cursor (such as an active SQL object) the Commit does not take effect immediately, but only when the last cursor is closed.
See CallAppEngine.
FieldChange and SavePreChange Considerations
The following are the FieldChange and SavePreChange considerations:
All updates done in FieldChange (including those using CallAppEngine) should be considered a single database transaction. This is a fundamental change: previously, a single transaction was represented by a page or a component.
A consequence of this is that a message requiring a reply, or any other think-time action, causes a fatal error if located in FieldChange after a database update that has not been committed to the database using the CommitWork function. So it is possible for an application to update the database in FieldChange, then do a think-time action, by preceding the think-time action with a call to CommitWork.
CommitWork commits the updates and closes the database transaction (that is, the unit of work). The consequence of using CommitWork is that because it closes the database transaction, any subsequent rollback calls will not rollback the committed updates.
Just as any database updates in FieldChange required careful application design to ensure that the transaction model is appropriate, so too does the use of CommitWork.
When using CommitWork in the Component Processor environment (as opposed to using it in an Application Engine program) CommitWork produces an error if there are any open cursors, such as any open PeopleCode SQL objects.
See FieldChange Event.
Application Engine Considerations
The CommitWork function is useful only when you are doing row-at-a-time SQL processing in a single PeopleCode program, and you must commit without exiting the program. In a typical Application Engine program, SQL commands are split between multiple Application Engine actions that fetch, insert, update, or delete application data. Therefore, you would use the section or step level commit settings to manage the commits. This is the recommended approach.
However, with some types of Application Engine programs that are PeopleCode intensive, it can be difficult to exit the PeopleCode in order to perform a commit. This is the only time when the CommitWork function should be used.
See Restarting Application Engine Programs.
Restart Considerations
Disabling restart on a particular program means that the application itself is intrinsically self-restartable: it can be re-run from the start after an abend, and it performs any initialization, cleanup, and filtering of input data to ensure that everything gets processed once and only once, and that upon successful completion, the database is in the same state it would have been if no abend occurred.
Set-based applications should always use Application Engine's restart. Only row-by-row applications that have restart built into them can benefit from disabling Application Engine's restart.
Consider the following points to managing restarts in a self-restarting program:
Locking input transactions (optional).
If the input data can change, and if it's important not to pick up new data during a restart, there should be logic to lock transactions at the start of the initial run (such as updating rows with current Process Instance). The program should first check whether any rows have the current Process Instance (that is, is the process being restarted from the top after an abend?). If no rows found, do the update.
In some cases it is acceptable for a restarted process to pick up new rows, so that locking is not necessary. It depends on your application.
Also, if you don't lock transactions, you must provide some other way to manage concurrent processing of the same program. You don't want two simultaneous runs of the same program to use the same data, so you must have some strategy for dividing up the data such that there is no overlap.
Filtering input transactions (required).
After an input transaction is processed, the row should be updated accordingly (that is, setting a "processed" flag). The SELECT statement that drives the main processing loop should include a WHERE condition to filter out rows that have already been processed.
Messaging Considerations
You are responsible for coding any restart ability in messaging PeopleCode if you use the CommitWork function. Normally, the system rolls back the transaction in the event of a PeopleCode failure. This is not a problem, because the subscription can safely run again. However, if CommitWork has already been issued; data changes have already been saved and cannot be rolled back. It is important that a subsequent run of the subscription PeopleCode can work without error and not mishandle the previously saved data.
Returns
A Boolean value, True if data was successfully committed, False otherwise.
Example
The following example fetches rows and processes them one at a time, committing every 100 iterations. Because restart is disabled, you must have a marker indicating which rows have been processed, and use it in a conditional clause that filters out those rows.
Local SQL &SQL; Local Record &REC; Local Number &COUNT; &REC = CreateRecord(RECORD.TRANS_TBL); &SQL = CreateSQL("%SelectAll(:1) WHERE PROCESSED <> 'Y'"); &COUNT = 0; &SQL.Execute(&REC); While &SQL.Fetch(&REC) If (&COUNT > 99) Then &COUNT = 0; CommitWork(); /* commit work once per 100 iterations */ End-if; &COUNT = &COUNT + 1; /* do processing */ ... /* update transaction as "processed" */ &REC.PROCESSED.Value = 'Y'; &REC.Update(); End-While;
See Also
Using PeopleCode in Application Engine Programs.

 CompareLikeFields
CompareLikeFieldsSyntax
CompareLikeFields(from, to)
where from and to are constructions that reference rows of data on specific source and target records in the component buffer; each have the following syntax:
level, scrollpath, target_row
and where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ]] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Use the CompareLikeFields function to compare fields in a row on a specified source record to similarly named fields on a specified target record.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the CompareFields record class method instead.
If all of the like-named fields have the same data value, CompareLikeFields returns True; otherwise it returns False.
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
from |
A placeholder for a construction (level, scrollpath, target_row) that references the first row in the comparison. |
|
to |
A placeholder for a construction (level, scrollpath, target_row) that references the second row in the comparison. |
|
level |
Specifies the scroll level for the target level scroll. |
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
target_row |
Specifies the row number of each target row on its scroll level. |
Returns
Returns a Boolean value indicating whether all of the like-named fields in the two records have the same data value.
Example
The following example compares the like-named fields in two rows on levels 1 (&L1_ROW) and 2 (&L2_ROW) and returns True if all of the like-named fields in the two rows have the same value.
&L1_ROW = 1; &L2_ROW = 1; if CompareLikeFields(1, RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_PER, &L1_ROW, 2, RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_PER, 1, RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_DTL, &L2_ROW) then WinMessage("The fields match."); end-if;
See Also

 Component
ComponentSyntax
Component data_type &var_name
Description
Use the Component statement to declare PeopleCode component variables. A component variable, after being declared in any PeopleCode program, remains in scope throughout the life of the component.
The variable must be declared with the Component statement in every PeopleCode program in which it is used.
Declarations appear at the beginning of the program, intermixed with function declarations.
Note. Because a function can be called from anywhere, you cannot declare any variables within a function. You receive a design time error if you try.
The system automatically initializes temporary variables. Declared variables always have values appropriate to their declared type. Undeclared variables are initialized as null strings.
Not all PeopleCode data types can be declared as Component.
Parameters
|
data_type |
Specify a PeopleCode data type. |
|
&var_name |
A legal variable name. |
Example
Component string &PG_FIRST;
See Also

 ComponentChanged
ComponentChangedSyntax
ComponentChanged()
Description
Use the ComponentChanged function to determine whether a component has changed since the last save, whether by the user or by PeopleCode.
Returns
Returns a Boolean value: True if the component has changed.
Example
If ComponentChanged() Then /* do some stuff */ End-if;

 ConnectorRequest
ConnectorRequest
Syntax
ConnectorRequest(&Message)
Description
Use the ConnectorRequest function to send data to the connector using a message, when the connector properties are assigned in the message. In general, you would build a message, add the specific connector properties, then use ConnectorRequest.
You do not need to set up any transaction or relationship when you use this function. It is a direct call to the gateway.
The response to the message is returned as a nonrowset-based message. Use the GetXmlDoc message class method to retrieve the content data. The data is wrapped in the CDATA tag.
Parameters
|
&Message |
Specify an already instantiated message. |
Returns
A nonrowset-based message object.
See Also

 ConnectorRequestURL
ConnectorRequestURL
Syntax
ConnectorRequestURL(ConnectorStringURL)
Description
Use the ConnectorRequestURL function to go directly to the gateway for accessing information.
Parameters
|
ConnectorStringURL |
Specify the URL of the gateway as a string. This is a fully formed URL. |
Returns
A string containing the URL information returned from the message.
Example
The following is the type of URL that could be returned if you were trying to get a PSFT stock quote:
http://finance.yahoo.com/d/quotes.txt/?symbols=PSFT&format=l1c1d1t1
See Also

 ContainsCharType
ContainsCharTypeSyntax
ContainsCharType(source_str, char_code)
Description
Use the ContainsCharType function to determine if any of the characters in source_str are of type char_code. The char_code is a numerical value representing a character type (see the following Parameters section for details). Most character types supported by this function equate to specific Unicode character blocks or are based on Unicode character properties.
Parameters
|
source_str |
String to be examined. |
|
char_code |
A number value representing the character type to be tested for. The following table shows valid values. You can specify either a character code numeric value or a constant: |
|
Numeric Value |
Constant |
Character Set |
|
0 |
%CharType_AlphaNumeric |
Basic Latin — Alphanumeric (printable range of 7-bit US-ASCII), Unicode characters in the range U+0020 — U+007E |
|
1 |
%CharType_ExtendedLatin1 |
Extended Latin-1 characters (ISO 8859-1 accents for Western European languages), Unicode characters in the range U+00BF — U+07E |
|
2 |
%CharType_HankakuKatakana |
Hankaku Katakana (half-width Japanese Katakana) |
|
3 |
%CharType_ZenkakuKatakana |
Zenkaku Katakana (full-width Japanese Katakana) |
|
4 |
%CharType_Hiragana |
Hiragana (Japanese) |
|
5 |
%CharType_Kanji |
Chinese, Japanese and Korean ideographic characters. Includes Japanese Kanji, Chinese Hanzi and Korean Hancha. |
|
6 |
%CharType_DBAlphaNumeric |
Full-width Latin Alphanumeric characters, primarily used for Japanese. Excludes |
|
7 |
None |
Korean Hangul syllables, excluding Hangul Jamo. |
|
8,9 |
None |
Reserved for future use. |
|
10 |
%CharType_JapanesePunctuation |
Full- and half-width punctuation, including space (U+0020) and Fullwidth / Ideographic Space (U+3000). |
|
11 |
None |
Greek |
|
12 |
None |
Cyrillic |
|
13 |
None |
Armenian |
|
14 |
None |
Hebrew |
|
15 |
None |
Arabic |
|
16 |
None |
Devanagari |
|
17 |
None |
Bengali |
|
18 |
None |
Gurmukhi |
|
19 |
None |
Gujarati |
|
20 |
None |
Oriya |
|
21 |
None |
Tamil |
|
22 |
None |
Telugu |
|
23 |
None |
Kannada |
|
24 |
None |
Malayalam |
|
25 |
None |
Thai |
|
26 |
None |
Lao |
|
27 |
None |
Tibetan |
|
28 |
None |
Georgian |
|
29 |
None |
Bopomofo |
Returns
ContainsCharType returns one of the following Number values. You can check for the constant instead of the numeric value if you prefer:
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
1 |
%CharType_Matched |
String contains at least one character of set char_code. |
|
0 |
%CharType_NotMatched |
String contains no characters of set char_code. |
|
-1 |
%CharType_Unknown |
UNKNOWN: unable to determine whether character is of set char_code. This occurs if the character being checked is an unallocated Unicode codepoint, or was added in a version of Unicode greater than that supported by PeopleTools. |
Example
This example tests to see if the string contains any Hiragana:
&ANYHIRAGANA = ContainsCharType(&STRTOTEST, 4); If &ANYHIRAGANA = 1 Then WinMessage("There are Hiragana characters"); Else If &ANYHIRAGANA = 0 Then WinMessage("There are no Hiragana characters"); Else WinMessage("UNKNOWN"); End-If; End-If;
See Also
ContainsCharType, ContainsOnlyCharType, ConvertChar.
Selecting and Configuring Character Sets and Language Input and Output

 ContainsOnlyCharType
ContainsOnlyCharTypeSyntax
ContainsOnlyCharType(source_str, char_code_list)
Where char_code_list is a list of character set codes in the form:
char_code_1 [, char_code_2]. . .
Description
Use the ContainsOnlyCharType function to determine whether every character in source_str belongs to one or more of the character types in char_code_list. See the following Parameters section for a list of valid character code values. Most character types supported by this function equate to specific Unicode character blocks or are based on Unicode character properties.
Parameters
|
Source_str |
String to be examined. |
|
char_code_list |
A comma-separated list of character set codes. |
|
char_code_n |
Either a Number value identifying a character set, or a constant. The following table shows valid values. You can specify either a character code numeric value or a constant: |
|
Numeric Value |
Constant |
Character Set |
|
0 |
%CharType_AlphaNumeric |
Alphanumeric (7-bit ASCII codes; A-Z, a-z, 1-9, punctuation) |
|
1 |
%CharType_ExtendedLatin1 |
Extended Latin-1 characters (ISO8859-1 accents for Spanish, French, etc.) |
|
2 |
%CharType_HankakuKatakana |
Hankaku Katakana (single-byte Japanese Katakana) |
|
3 |
%CharType_ZenkakuKatakana |
Zenkaku Katakana (double-byte Japanese Katakana) |
|
4 |
%CharType_Hiragana |
Hiragana (Japanese) |
|
5 |
%CharType_Kanji |
Kanji (Japanese) |
|
6 |
%CharType_DBAlphaNumeric |
Double-byte Alphanumeric (Japanese) |
|
7,8,9 |
|
Reserved for future use |
|
10 |
%CharType_JapanesePunctuation |
Japanese punctuation |
Returns
ContainsOnlyCharType returns one of the following Number values. You can check for the constant instead of the numeric value, if you prefer:
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
1 |
%CharType_Matched |
String contains only characters belonging to the sets listed in char_code_list. |
|
0 |
%CharType_NotMatched |
String contains one or more characters that do not belong to sets listed in char_code_list. |
|
-1 |
%CharType_Unknown |
UNKNOWN: unable to determine whether character is of set char_code. This occurs if the character being checked is an unallocated Unicode codepoint, or was added in a version of Unicode greater than that supported by PeopleTools. |
Note. If any character in the string is determined to be UNKNOWN, the return value is UNKNOWN.
Example
This example tests to see is the string is only Hiragana or Punctuation:
&ONLYHIRAGANA = ContainsOnlyCharType(&STRTOTEST, 4, 10); If &ONLYHIRAGANA = 1 Then WinMessage("There are only Hiragana and Punctuation characters"); Else If &ONLYHIRAGANA = 0 Then WinMessage("Mixed characters"); Else WinMessage("UNKNOWN"); End-If End-If
See Also
CharType, ContainsCharType, ConvertChar.
Selecting and Configuring Character Sets and Language Input and Output

 Continue
ContinueSyntax
Continue
Description
Use the Continue statement to continue execution in a loop. How the statement performs depends on the type of loop:
In For loops, this statement continues to do the next step of the iteration
In While loops, this statement continues to the top of the loop and the test of the condition
In Repeat-Until loops, this statement continues to the Until check at the bottom of the loop.
Parameters
None.
Example
The following are tests of the continue statement in various types of loops:
SetTracePC(%TracePC_List); /* tests of continue statement */ &N = 0; For &I = 1 To 10; If &I > 5 Then Continue; End-If; &J = &I + 1; &K = 0; /* now a while loop in here */ While &J <= 10; &J = &J + 1; If &J = 7 Then Continue; End-If; For &A = 0 To 5; &K = &K + 2; End-For; /* no continue statement */ &Barf = 2; Repeat &Barf = &Barf; If &Barf = 1 Then Continue; End-If; Until &Barf = &Barf; &K = &K + 1; End-While; MessageBox(0, "", 0, 0, "K=" | &K); If &I < 2 Then Continue; End-If; &N = &N + 1; End-For; MessageBox(0, "", 0, 0, "N=" | &N);
See Also

 ConvertChar
ConvertCharSyntax
ConvertChar(source_str, source_str_category, output_str, target_char_code)
Description
Use the ConvertChar function to convert every character in source_str to type target_char_code, if possible, and place the converted string in output_str. ConvertChar supports the following conversions:
Conversion among Japanese Hankaku (half-width) Katakana, Zenkaku (full-width) Katakana, and Hiragana .
Conversion of Japanese Hankaku (half-width) Katakana, Zenkaku (full-width) Katakana, and Hiragana to Hepburn Romaji (Latin representation).
Conversion of full-width alphanumeric characters to their half-width equivalents.
Conversion of full-width punctuation characters to their half-width equivalents.
Other source_str and target_char_code combinations are either passed through without conversion, or not supported. Character types 0 and 1 (alphanumeric and extended Latin-1) are always passed through to output_str without conversion. See the Supported Conventions section later in this reference entry for details.
If ConvertChar is unable to determine whether the characters in source_str belong to the specified character set, the function returns a value of UNKNOWN (-1). If source_str can be partially converted, ConvertChar will partially convert string, echo the remaining characters to the output string as-is, and return a value of -2 (Completed with Issues).
Parameters
|
Source_str |
String to be converted. |
|
Source_str_category |
Language category of input string. You can specify either a number or a constant. |
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
0 |
%ConvertChar_AlphaNumeric |
Half-width AlphaNumeric |
|
1 |
%ConvertChar_ExtendedLatin1 |
Extended Latin-1 Characters (ISO8859-1 accents, Spanish, French etc.) |
|
2 |
%ConvertChar_Japanese |
Japanese (any) |
|
Output_str |
A String variable to receive the converted string. |
|
Target_char_code |
Either a Number or a constant representing the conversion target character type. You can specify either a character code numeric value or a constant: |
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
0 |
%CharType_AlphaNumeric |
Half-width AlphaNumeric — results in a Hepburn Romaji conversion when the input string contains Hiragana or Katakana |
|
2 |
%CharType_HankakuKatakana |
Hankaku Katakana (half—width Japanese Katakana) |
|
3 |
%CharType_ZenkakuKatakana |
Zenkaku Katakana (full-width Japanese Katakana) |
|
4 |
%CharType_Hiragana |
Hiragana (Japanese) |
|
6 |
%CharType_DBAlphaNumeric |
Full-width AlphaNumeric (Japanese) |
The following target values are not supported; if the source string is of the same type as any of these values, then the string is passed through without conversion.
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
1 |
%CharType_ExtendedLatin1 |
Extended Latin-1 characters (ISO8859-1 accents for Spanish, French, etc.) |
|
5 |
%CharType_Kanji |
Chinese, Japanese and Korean ideographic characters. |
|
10 |
%CharType_JapanesePunctuation |
Full- and half-width punctuation, including space (U+0020) and Fullwidth / Ideographic Space (U+3000). |
Supported Conversions
The following table shows which conversions are supported, which are passed through without conversion, and which are not supported:
|
Source |
Target |
Conversion |
|
0 (Alphanumeric US-ASCII) |
0-6 (All supported character types) |
Pass through without conversion |
|
1 (Extended Latin-1 characters) |
0-6 (All supported character sets) |
Pass through without conversion |
|
2 (Hankaku Katakana) |
0 (Alphanumeric — Hepburn romaji) |
Conversion supported |
|
1 (Extended Latin) |
Not supported |
|
|
2 (Hankaku Katakana) |
Pass through without conversion |
|
|
3 (Zenkaku Katakana) |
Conversion supported |
|
|
4 (Hiragana) |
Conversion supported |
|
|
5 (Kanji) |
Not supported |
|
|
6 (Full-width alphanumeric) |
Not supported |
|
|
3 (Zenkaku Katakana) |
0 (Alphanumeric) |
Conversion supported |
|
1 (Extended Latin) |
Not supported |
|
|
2 (Hankaku Katakana) |
Conversion supported |
|
|
3 (Zenkaku Katakana) |
Pass through without conversion |
|
|
4 (Hiragana) |
Conversion supported |
|
|
5 (Kanji) |
Not supported |
|
|
6 (Full-width alphanumeric) |
Not supported |
|
|
4 (Hiragana) |
0 (Alphanumeric- Hepburn Romaji) |
Conversion supported |
|
1 (Extended Latin) |
Not supported |
|
|
2 (Hankaku Katakana) |
Conversion supported |
|
|
3 (Zenkaku Katakana) |
Conversion supported |
|
|
4 (Hiragana) |
Pass through without conversion |
|
|
5 (Kanji) |
Not supported |
|
|
6 (Full-width alphanumeric) |
Not supported |
|
|
5 (Kanji) |
0-4, 6 |
Not supported |
|
5 (Kanji) |
Pass through without conversion |
|
|
6 (Full-width alphanumeric) |
0 (Alphanumeric) |
Conversion supported |
|
1-5 |
Not supported |
|
|
6 (Full-width alphanumeric) |
Pass through without conversion |
|
|
10 (Japanese punctuation) |
0 (Alphanumeric) |
Conversion supported |
|
1 (Extended Latin) |
Not supported |
|
|
3-6, 10 |
Pass through without conversion |
Returns
Returns either a Number or a constant with one of the following values, depending on what you’re checking for:
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
1 |
%ConvertChar_Success |
String successfully converted. |
|
0 |
%ConvertChar_NotConverted |
String not converted. |
|
-1 |
%ConvertChar_Unknown |
UNKNOWN: unable to determine whether character is of set char_code. This occurs if the character being checked is an unallocated Unicode codepoint, or was added in a version of Unicode greater than that supported by PeopleTools. |
|
-2 |
%ConvertChar_Issues |
Completed with issues. Conversion executed but there were one or more characters encountered that were either not recognized, or whose conversion is not supported. |
Note. If any character cannot be translated, it is echoed as-is to output_str. output_str could therefore be a mixture of converted and non-converted characters.
Example
This example attempts to convert a string to Hiragana:
&RETVALUE = ConvertChar(&INSTR, 2, &OUTSTR, 4); If &RETVALUE = 1 Then WinMessage("Conversion to Hiragana successful"); Else If &RETVALUE = 0 Then WinMessage("Conversion to Hiragana failed"); Else If &RETVALUE = - 1 Then WinMessage("Input string is UNKNOWN character type."); Else WinMessage("Some characters could not be converted."); End-If End-If End-If
See Also
CharType, ContainsCharType, ContainsOnlyCharType.
Selecting and Configuring Character Sets and Language Input and Output

 ConvertCurrency
ConvertCurrencySyntax
ConvertCurrency(amt, currency_cd, exchng_to_currency, exchng_rt_type, effdt, converted_amt [, error_process [, round] [, rt_index]])
Description
Use the ConvertCurrency function to convert between currencies. The result of the conversion is placed in a variable passed in converted_amt.
See Also
Controlling Currency Display Format.
Parameters
|
Amt |
The currency amount to be converted. |
|
Currency_cd |
The currency in which the amt is currently expressed. |
|
Exchng_to_currency |
The currency to which the amt should be converted. |
|
Exchng_rt_type |
The currency exchange rate to be used. This is the value of the RT_TYPE field in the RT_RATE table of RT_DFLT_VW. |
|
Effdt |
The effective date of the conversion to be used. |
|
Converted_amt |
The resulting converted amount. You must supply a variable for this parameter. If a conversion rate cannot be found, converted_amt is set equal to amt. |
|
Error_process |
An optional string that, if specified, contains one of the following values:
If error_process is not specified, it defaults to Fatal ("F"). |
|
Round |
Optional Boolean value indicating whether to round converted_amt to the smallest currency unit. If omitted, round defaults to False. |
|
rt_index |
An optional string to indicate which exchange rate index should be used to retrieve the exchange rate. If omitted, the Default Exchange Rate index (as specified on the Market Rate index definition) is used. |
Note. If the currency exchange rate is changed in a PeopleSoft table, this change will not be reflected in an already open page until the user closes the page, then opens it again.
Returns
ConvertCurrency returns a Boolean value where True means a conversion rate was found and converted_amt calculated, and False means a conversion rate was not found and a value of one (1) was used.
Example
rem **-----------------------------------------------**; rem * Convert the cost & accum_depr fields if books *; rem * use different currencies. *; rem **-----------------------------------------------**; rem; If &FROM_CUR <> &PROFILE_CUR_CD Then &CON_COST_FROM = &COST_COST; &CON_ACC_DEPR_FROM = &COST_ACCUM; ConvertCurrency(&CON_COST_FROM, &FROM_CUR, &PROFILE_CUR_CD, RT_TYPE,TRANS_DT, &CON_COST_TO, "F"); UpdateValue(COST_NON_CAP.COST, &COST_ROW_CUR, &CON_COST_TO); Else UpdateValue(COST_NON_CAP.COST, &COST_ROW_CUR, &COST_COST); End-If; UpdateValue(COST_NON_CAP.FROM_CUR, &COST_ROW_CUR, &PROFILE_CUR_CD); UpdateValue(COST_NON_CAP.OPRID, &COST_ROW_CUR, %UserIdId);

 ConvertDatetimeToBase
ConvertDatetimeToBaseSyntax
ConvertDatetimeToBase(textdatetime, {timezone | "Local" | "Base"});
Description
Use the ConvertDatetimeToBase function to convert the text value textdatetime to a datetime value, then further converts it to the base time. This function automatically calculates whether daylight savings time is in effect for the given textdatetime.
The system’s base time zone is specified on the PSOPTIONS table.
Parameters
|
textdatetime |
Specify a datetime value represented as text (for example, "01/01/1999 3:00 PM") |
|
timezone | Local | Base |
Specify a value for converting textdatetime. Values are:
|
Returns
Returns a datetime value in the base time zone.
Example
In the following example, &DATETIMEVAL would have a datetime value of "01-01-1999-07:00:00.000000", assuming the Base time (as defined in PSOPTIONS) was PST.
&DATETIMEVAL= ConvertDateTimeToBase("01/01/1999 10:00:00AM", "EST");
See Also
ConvertTimeToBase, FormatDateTime, IsDaylightSavings, DateTimeToTimeZone, TimeToTimeZone, TimeZoneOffset.

 ConvertRate
ConvertRateSyntax
ConvertRate(Rate, In_Frequency, Out_Frequency)
Description
Use the ConvertRate function to convert a rate between various compounding frequencies.
Parameters
|
Rate |
The rate to be converted. This parameter takes a number value. |
|
In_Frequency |
The frequency of the rate to be converted from. This parameter takes an array of number, with two elements. The first element is periodicity, (for example, if you chose daily compounding, 1 would represent daily while 7 would represent weekly.) The second element is the unit of measure of frequency. The values for the second element are: |
|
Value |
Description |
|
0 |
continuous compounding |
|
1 |
daily compounding |
|
2 |
monthly compounding |
|
3 |
yearly compounding |
|
Out_Frequency |
The frequency of the rate to be converted to. This parameter takes an array of number, with two elements. The first element is periodicity, (for example, if you chose daily compounding, 1 would represent daily while 7 would represent weekly.) The second element is the unit of measure of frequency. The values for the second element are: |
|
Value |
Description |
|
0 |
continuous compounding |
|
1 |
daily compounding |
|
2 |
monthly compounding |
|
3 |
yearly compounding |
Returns
A number representing the converted rate.
Example
The following example converts the specified values from days to years.
Local array of number &In, &Out; Local number &rate, &NewRate; &rate = 0.01891; &In = CreateArray(0, 0); &In[1] = 1; /* daily */ &In[2] = 1; /* compound_days */ &Out = CreateArray(0, 0); &Out[1] = 1; /* one year */ &Out[2] = 3; /* compound_years */ &NewRate = ConvertRate(&rate, &In, &Out);
See Also

 ConvertTimeToBase
ConvertTimeToBaseSyntax
ConvertTimeToBase(texttime,{timezone | "Local" | "Base"});
Description
Use the ConvertTimeToBase function to convert the text value texttime to a Time value and converts it to the base time. This function automatically calculates whether daylight savings time is in effect for the given texttime.
This function is useful for users to convert constant times in specific time zones into database time. For example, there is a deadline for completing Federal Funds transfers by 3:00 PM Eastern Time. ConvertTimeToBase does this conversion, taking into account daylight savings time. The date used to calculate whether daylight savings time is in effect is the current date.
The system’s base time zone is specified on the PSOPTIONS table.
Parameters
|
texttime |
Specify a time value represented as text (e.g., "3:00 PM") |
|
timezone | Local | Base |
Specify a value for converting textdatetime. Values are:
|
Returns
Returns a time value in the base time zone.
Example
In the following example, &TIMEVAL would have a time value of "07:00:00.000000", assuming the Base time (as defined in PSOPTIONS) was PST.
&TEXTTIME = ConvertTimeToBase("01/01/99 10:00:00AM", "EST");
See Also
ConvertDatetimeToBase, FormatDateTime, IsDaylightSavings, DateTimeToTimeZone, TimeToTimeZone, TimeZoneOffset.

 CopyAttachments
CopyAttachmentsSyntax
CopyAttachments(URLSource, URLDestination [, Record_Names [, PreserveCase]])
where URLSource and URLDestination can have one of the following forms:
URL.URLname
or a string URL, such as
ftp://user:[email protected]/
Note. You cannot specify a different port for an attachment when using an FTP server. You can only use the default port of 21.
Description
Use the CopyAttachments function to copy files from one system to another.
Note. If the specified subdirectories do not exist this function tries to create them.
Parameters
|
Source |
Specify the source location of the files to be moved. This parameter can either be a URL name in the form URL .URLName, or a string. |
|
Destination |
Specify the destination of the files being moved. This parameter can either be a URL name in the form URL .URLName, or a string. |
|
Record_Names |
Specify an array of record names that store valid references to files located on the system specified by Source. If you don't specify this parameter, all the records that contain the field ATTACHSYSFILENAME are used (that is, this function tries to get the attachments based on all those references from Source). |
|
PreserveCase |
Specify a Boolean value to indicate whether the case of the directory and file name specified with DirAndFileName are preserved or not; true, preserve the case, false otherwise. The default value is false. |
Returns
You can check for either a constant or a number value. The values are:
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
0 |
%Attachment_Success |
File was transferred successfully. |
|
1 |
%Attachment_Failed |
File was not successfully transferred. |
|
3 |
%Attachment_FileTransferFailed |
File transfer didn't succeed. |
|
7 |
%Attachment_DestSystNotFound |
Cannot locate destination system. |
|
8 |
%Attachment_DestSystFailedLogin |
Unable to login to destination system. |
|
9 |
%Attachment_FileNotFound |
Cannot locate file. |
|
10 |
%Attachment_DeleteFailed |
Cannot delete file. |
Example
&aRecs = CreateArray("HRATTS", "MFGATTS", "CRMATTS"); &ret = CopyAttachments("ftp://user:pass@system/HR/", "record://HRARCHIVE", &aRecs); If (&ret = %Attachment_Success) Then MessageBox(0, "Copy Archive Status", 0, 0, "CopyAttachmentArchive succeeded"); Else MessageBox(0, "Copy Archive Status", 0, 0, "CopyAttachmentArchivefailed"); End-If;
See Also
AddAttachment, DeleteAttachment, GetAttachment, PutAttachment, ViewAttachment.
Using File Attachments in Applications

 CopyFields
CopyFieldsSyntax
CopyFields(from, to)
where from and to are constructions that reference rows of data on specific source and target records in the component buffer; each have the following syntax:
level, scrollpath, target_row
and where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ]] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can also use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Use the CopyFields function to copy like-named fields from a row on the specific source record to a row on the specific target record.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the CopyFieldsTo or CopyChangedFieldsTo record class methods instead.
See Also
CopyFieldsTo, CopyChangedFieldsTo, CopyTo.
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
from |
A placeholder for a construction (level, scrollpath, target_row) that references the first row in the comparison. |
|
to |
A placeholder for a construction (level, scrollpath, target_row) that references the second row in the comparison. |
|
level |
Specifies the scroll level for the target level scroll. |
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
target_row |
Specifies the row number of each target row on its scroll level. |
Returns
Optionally returns a Boolean value indicating whether the function succeeded.
Example
The following example copies fields from PO_RECEIVED_INV (level 1 scroll) from row &ROW to PO_RECV_INV_VW (level 1 scroll), row &LOC_ROW:
CopyFields(1, RECORD.PO_RECEIVED_INV, &ROW, 1, RECORD.PO_RECV_INV_VW, &LOC_ROW);
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation

 CopyFromJavaArray
CopyFromJavaArraySyntax
CopyFromJavaArray(JavaArray, &PeopleCodeArray [, &RestrictionArray])
Description
Use the CopyFromJavaArray function to copy the array specified by JavaArray into one-dimensional PeopleCode array &PeopleCodeArray.
Note. The Java array must be at least the same size as the PeopleCode array.
The optional &RestrictionArray parameter is a PeopleCode array that contains the index elements of the elements to copy. For example if &RestrictionArray contains the indexes 3, 5 and 7, only elements 3, 5 and 7 in the PeopleCode array are copied to the Java array, and they are copied to the elements 3, 5 and 7. This allows you to minimize the copying when you have arrays that don’t require a full element by element copy. If &RestrictionArray is not specified, a complete array copy is done.
The array types between the PeopleCode array and the Java array must match the standard type mapping between Java and PeopleCode types. For example, trying to copy a PeopleCode array of Any into a Java array of int will fail because the Any PeopleCode type doesn't map onto the Java int type.
See Also
PeopleCode and Java Data Types Mapping
Parameters
|
JavaArray |
Specify the name of the Java array that you want to copy data from. |
|
&PeopleCodeArray |
Specify the name of an already instantiated PeopleCode array that you want to copy the data into. |
|
&RestrictionArray |
Specify an already instantiated and populated PeopleCode array that contains the set of elements the copy is restricted to. This array should be of type number. |
Returns
None.
Example
Local array of any &x = CreateArrayAny(); &x.Push("First bit"); &x.Push(1); &x.Push(%Datetime); &x.Push(%Date); &x.Push("Final bit"); Local array of number &selection = CreateArray(1, 3, 5); Local JavaObject &Jarray = CreateJavaArray("java.lang.Object[]", &x.Len); /* Full copy to a Java array */ CopyToJavaArray(&x, &Jarray); /* Full copy from Java array to PeopleCode array */ Local array of any &y = CreateArrayAny(); &y [5] = Null; /* make sure it's the right length */ CopyFromJavaArray(&Jarray, &y);
See Also
CopyToJavaArray, CreateJavaArray.

 CopyRow
CopyRowSyntax
CopyRow(destination_row, source_row)
Description
Use the CopyRow function to copy data from one row to another row.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the CopyTo row class method instead.
destination_row is the row number to which you want the source _row data values copied. The two rows, and the PeopleCode function call, must all be located on the same scroll level.
See Also
CopyTo, CopyFieldsTo, CopyChangedFieldsTo.
Parameters
|
destination_row |
Row number of row to which to copy data. |
|
source_row |
Row number of row from which to read data. |
Example
This example uses CopyRow to give an inserted row the same values as the previous row:
/* Get the row number of the inserted row and the previous row */ &NEW_ROW_NUM = CurrentRowNumber(); &LAST_ROW_NUM = &NEW_ROW_NUM - 1; /* Copy the data from the previous row into the inserted row */ CopyRow(&NEW_ROW_NUM, &LAST_ROW_NUM);

 CopyToJavaArray
CopyToJavaArraySyntax
CopyToJavaArray(&PeopleCodeArray, JavaArray [, &RestrictionArray])
Description
Use the CopyToJavaArray function to copy the one-dimensional array specified by &PeopleCodeArray into the Java array JavaArray. The Java array must be at least as large as the PeopleCode array.
The optional &RestrictionArray parameter is a PeopleCode array that contains the index elements of the elements to copy. For example if &RestrictionArray contains the indexes 3, 5 and 7, only elements 3, 5 and 7 in the PeopleCode array are copied to the Java array, and they are copied to the elements 3, 5 and 7. This allows you to minimize the copying when you have arrays that don’t require a full element by element copy. If &RestrictionArray is not specified, a complete array copy is done.
The array types between the PeopleCode array and the Java array must match the standard type mapping between Java and PeopleCode types. For example, trying to copy a PeopleCode array of Any into a Java array of int will fail because the Any PeopleCode type doesn't map onto the Java int type.
See Also
PeopleCode and Java Data Types Mapping
Parameters
|
&PeopleCodeArray |
Specify an already instantiated and populated one-dimentional PeopleCode array that contains the information you want to copy to a Java array. |
|
JavaArray |
Specify the Java array that you want to copy information into. |
|
&RestrictionArray |
Specify an already instantiated and populated PeopleCode array that contains the set of elements the copy is restricted to. This array should be of type number. |
Returns
None.
Example
The following example creates an array, then shows both copying the full array, as well as only copying elements of it.
Local array of any &x = CreateArrayAny(); &x.Push("First bit"); &x.Push(1); &x.Push(%Datetime); &x.Push(%Date); &x.Push("Final bit"); Local array of number &selection = CreateArray(1, 3, 5); Local JavaObject &Jarray = CreateJavaArray("java.lang.Object[]", &x.Len); /* Full copy to a Java array */ CopyToJavaArray(&x, &Jarray); /* Only copy elements 1, 3 and 5 */ CopyToJavaArray(&x, &Jarray, &selection);
See Also
CopyFromJavaArray, CreateJavaArray.

 Cos
CosSyntax
Cos(angle)
Description
Use the Cos function to calculate the cosine of the given angle (adjacent / hypotenuse).
Parameters
|
angle |
A value in radians. |
Returns
A real number between -1.00 and 1.00.
Example
The following example returns the cosine of an angle measuring 1.2 radians:
&MY_RESULT = Cos(1.2);
See Also
Acos, Asin, Atan, Cot, Degrees, Radians, Sin, Tan.

 Cot
CotSyntax
Cot(angle)
Description
Use the Cot function to calculate the cotangent of the given angle (adjacent / opposite, that is, the reciprocal of the tangent).
Parameters
|
angle |
A value in radians, excluding 0. If the input value is 0, you receive an error message at runtime (“Decimal arithmetic error occurred. (2,110)”). Adjust your code to provide a valid input value. |
Note. In theory, all values of angle such that mod(angle, pi) equals 0 are not valid for this function, because inputs approaching such values produce results that tend toward infinity. In practice, however, no computer system can represent such values exactly. Thus, for example, the statement Cot(Radians(180)) produces a number close to the largest value PeopleCode can represent, rather than an error.
Returns
A real number.
Example
The following example returns the cotangent of an angle measuring 1.2 radians:
&MY_RESULT = Cot(1.2);
See Also
Acos, Asin, Atan, Cos, Degrees, Radians, Sin, Tan.

 CreateAnalyticInstance
CreateAnalyticInstanceSyntax
CreateAnalyticInstance(AnalyticType, ID, Descr, &RecordRef, ForceDelete)
Description
Use the CreateAnalyticInstance function to create an analytic instance as identified by the analytic ID. If ID is an empty string, the system automatically generates a unique ID.
This function only creates the metadata for the ID. It doesn't load the instance into an analytic server.
If this analytic instance already exists in the system, and you specify ForceDelete as false, the analytic instance is not created. If you specify ForceDelete as true, the existing analytic instance is deleted and the new one is created.
Every analytic type definition is defined with an application package that contains three methods: Create, Delete, and Copy. The values in &RecordRef are passed to the Create method.
Parameters
|
AnalyticType |
Specify the name of the analytic type definition to be used. |
|
ID |
Specify the analytic instance identifier as a string. This parameter must be 20 characters or less. |
|
Descr |
Specify a description for this analytic instance as a string. |
|
&RecordRef |
Specify an already instantiated record object to pass values to the application package Create method that's associated with the analytic type definition. If you don't want to specify a record, you can specify NULL. |
|
ForceDelete |
Specify the behavior if the specified analytic ID already exists. This parameter takes a boolean value. If ForceDelete is set to false and the specified ID exists, this function terminates without creating a new analytic instance. If ForceDelete is set to true and the specified ID exists, the analytic instance is deleted and then recreated. |
Returns
An AnalyticInstance object if successful, null otherwise.
Example
Local AnalyticInstance π /* Create a brand new analytic instance */ &pi = CreateAnalyticInstance("BusinessPlanning", "Test", "PopulateTables", &argrec, True);
See Also
Understanding the Analytic Calculation Engine Classes
Creating Analytic Type Definitions

 CreateArray
CreateArraySyntax
CreateArray(paramlist)
Where paramlist is an arbitrary-length list of values in the form:
param1 [, param2] ...
Description
Use the CreateArray function to construct an array and returns a reference to it.
The type of the first parameter determines the type of array that is built. That is, if the first parameter is of type NUMBER, an array of number is built. If there is no first parameter an empty array of ANY is built.
The CreateArray function uses flattening and promotion as required to convert subsequent values into suitable elements of the array.
Parameters
|
paramlist |
Specify a list of values to be used as the elements of the array. |
Returns
Returns a reference to the array.
Example
Local Array of Array of Number &AAN; Local Array of Number &AN; &AAN = CreateArray(CreateArray(1, 2), CreateArray(3, 4), 5); &AN = CreateArray(6, &AAN[1]);
&AAN is a two dimensional array with three elements:
A one-dimensional array with 1 and 2 as elements.
A one-dimensional array with 3 and 4.
A one-dimensional array with only the element 5.
The last parameter to Array was promoted to a one-dimensional array. &AN is a one-dimensional array with 3 elements: 6, 1, and 2. The last parameter to Array in the last line was flattened into its two elements.
See Also
Using Flattening and Promotion

 CreateArrayAny
CreateArrayAnySyntax
CreateArrayAny([paramlist])
Where paramlist is an arbitrary-length list of values in the form:
param1 [, param2] ...
Description
Use the CreateArrayAny function to construct an array whose elements are of data type ANY and returns a reference to it.
The CreateArrayAny function uses flattening and promotion as required to convert subsequent values into suitable elements of the array.
If you don't specify any parameters with CreateArrayAny, it's the same as using the CreateArray function without any parameters.
If you don't know how many values are needed in a SQL statement until runtime, you can use an array of any to supply the values.
Parameters
|
paramlist |
Specify a list of values to be used as the elements of the array. |
Returns
Returns a reference to an array of ANY.
Example
local Array of Any &ArrayAny = CreateArrayAny(1, 2, "hi", "there"); local Array of Array of Any &AAAny = CreateArray(CreateArrayAny(1, 2), CreateArrayAny("hi"), "there");
&ArrayAny is a two dimensional array with four elements: 1, 2, "hi" and "there". All the elements have the data type Any.
&AAAny is a two-dimensional array with three elements: a one-dimensional array with 1 and 2 as elements, a one-dimensional array with "hi" as its element, and a one-dimensional array with only the element "there". The last parameter to the array was promoted to a one-dimensional array.
See Also
CreateArrayRept, CreateArray, Split.
Using Flattening and Promotion

 CreateArrayRept
CreateArrayReptSyntax
CreateArrayRept(val, count)
Description
Use the CreateArrayRept function to create an array that contains count copies of val. If val is itself an array, the created array has one higher dimension, and each element (sub-array) is the array reference val.
The type of the first parameter (val) determines the type of array that is built. That is, if the first parameter is of type NUMBER, an array of number is built. If count is zero, CreateArrayRept creates an empty array, using the val parameter for the type.
If you are making an array that is multi-dimensional, val will be the subarray used as the elements.
To make the subarrays distinct, use the Clone method. For example:
&A = CreateArrayRept(&AN, 4).Clone();
Parameters
|
val |
A value of any type. |
|
count |
The number of copies of val contained in the array. |
Returns
Returns a reference to the array.
Example
The following code sets &A to a new empty array of string:
&A = CreateArrayRept("", 0);
The following code sets &A to a new array of ten zeroes:
&A = CreateArrayRept(0, 10);
The following code sets &AAS to a new array of array of strings, with two subarrays:
&AAS = CreateArrayRept(CreateArray("one", "two"), 2);
Note that in this case, both elements (rows) of &AAS contain the same subarray, and changing the value of an element in one of them changes it in both of them. To get distinct subarrays, use the Clone method:
&AAS = CreateArrayRept(CreateArray("one", "two"), 2).Clone();
The following example shows how to create a two-dimension array using CreateArrayRept and Push. In addition, it shows how to randomly assigns values to the cells in a two-dimension array.
Local array of array of string &ValueArray; &Dim1 = 10; &Dim2 = 5; &ValueArray = CreateArrayRept(CreateArrayRept("", 0), 0); For &I = 1 To &Dim1 &ValueArray.Push(CreateArrayRept("", &Dim2)); End-For; &ValueArray[1][1] = "V11"; &ValueArray[2][1] = "V21"; WinMessage("&ValueArray[1][1] = " | &ValueArray[1][1] | " " | "&ValueArray[2][1] = " | &ValueArray[2][1], 0);
See Also

 CreateDirectory
CreateDirectorySyntax
CreateDirectory(path, [, pathtype])
Description
Use the CreateDirectory function to create the directory specified by path and any non-existent directories specified in path.
On UNIX systems, the directory has the mode 755, that is, read-write-execute permission for the owner, while group and other have only read and execute permission.
drwxr-xr-x
Working with Relative Paths
If you specify a relative path, that path is appended to the path specified by an environmental variable, if the variable exists, in a particular order. This means if the first environmental variable in order is found, that is the one that's used. If it isn't found, the next one is searched for, and if found, is used, and so on.
The environmental variables that get used are different, depending on whether the machine where the code is running is an application server or not. If the code is running on an application server, the following environmental variables are valid, and are searched for in the following order:
PS_FILEDIR[\relative_path]
PS_SERVDIR\Files[\relative_path]
If the code is not running on an application server, the following environmental variables are valid, and are searched for in the following order:
PS_FILEDIR[\relative_path]
PS_SERVDIR\Files[\relative_path]
TEMP[\relative_path]
The PS_FILEDIR environmental variable is not initialized and set to a path automatically. To use this environmental variable, you must set it yourself.
Note. Your system security should verify if a user has the correct permissions before allowing access to a drive (for example, if a user changes their TEMP environmental variable to a network drive they don’t normally have access to, your system security should detect this.)
Parameters
|
path |
Specify the path to be created. |
|
pathtype |
Specify whether the path is an absolute or relative path. The values for this parameter are:
If you don’t specify pathtype the default is %FilePath_Relative. If pathtype is an absolute path, whatever path you specify is used verbatim. You must specify a drive letter and the complete path. You can’t use any wildcards when specifying a path. The PeopleCode runtime automatically converts platform-specific separator characters to the appropriate form for where your PeopleCode program is executing. On a WIN32 system, UNIX "/" separators are converted to "\", and on a UNIX system, WIN32 "\" separators are converted to "/". |
Note. The syntax of the path only depends on the platform where your PeopleCode is executing.
Returns
None.
Example
CreateDirectory("D:\Resumes\New_Hires", %FilePath_Absolute);
See Also
FileExists, FindFiles, GetFile, GetAttachment, PutAttachment, RemoveDirectory.

 CreateException
CreateExceptionSyntax
CreateException(message_set, message_num, default_txt [, subslist])
where subslist is an arbitrary-length list of substitutions of undetermined (Any) data type to be substituted in the resulting text string, in the form:
substitution1 [, substitution2]. . .
Description
Use the CreateException function to create an exception object with the given properties. You can use this in your exception handling. Use this function either in conjunction with the Throw statement, or on its own to get more information of a message.
Parameters
|
message_set |
Specify the message set number of the message you want associated with this exception. |
|
message_num |
Specify the message number of the message you want associated with this exception. |
|
default_txt |
Specify the text you want associated with the exception if the message specified by message_set and message_num isn't found. |
|
subslist |
A comma-separated list of substitutions; the number of substitutions in the list is arbitrary. The substitutions are referenced in the message text using the % character followed by an integer corresponding to the position of the substitution in the subslist. The number of substitutions specified with this parameter are what get counted with the exception class SubsitutionCount property. |
Returns
A reference to an exception object if successful, NULL otherwise.
Example
Function t2 throw CreateException(2, 160, "'%1' doesn't support property or method '%2'", "SomeClass", "SomeMethod"); End-Function;
See Also

 CreateJavaArray
CreateJavaArraySyntax
CreateJavaArray(ElementClassName[], NumberOfElements)
Description
Use the CreateJavaArray function to create a Java array without knowing the number or value of the elements.
When you create an array in Java, you already know the number of elements in the array. If you don't know the number of elements in the array, but you want to use a Java array, use the CreateJavaArray function in PeopleCode. This creates a Java object that is a Java array, and you can pass in the number of elements that are to be in the array.
The first index in a Java array is 0. PeopleCode arrays start at 1.
Do the following to specify this type of array in Java:
new ElementClassName[NumberOfElements];
Parameters
|
ElementClassName[] |
Specify the array class name. This parameter takes a string value. |
|
NumberOfElements |
Specify the number of elements in the array. This parameter takes a number value. |
Returns
A Java object
See Also
CreateJavaObject, GetJavaClass.

 CreateJavaObject
CreateJavaObjectSyntax
CreateJavaObject(ClassName [ConstructorParams])
Where ConstructorParams has the form
Arguement1 [, arguement2] . . .
Description
Use the CreateJavaObject function to create a Java object that can be manipulated in PeopleCode.
Note. If you create a class that you want to call using CreateJavaObject, it must be located in a directory specified in the PS_CLASSPATH environment variable or in the <PS_HOME>/appserv/classes directory.
Use the CreateJavaObject function to create a Java array when you know how many values it should contain. If ClassName is the name of an array class (ending with [ ]), ConstructorParams are used to initialize the array.
In Java, do the following to initialize an array:
intArray = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13};
Do the following to initialize such a Java array from PeopleCode:
&IntArray = CreateJavaObject("int[]", 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13);
To initialize a Java array without knowing the number of parameters until runtime, use the CreateJavaArray function.
Parameters
|
ClassName |
Specify the name of an already existing class. |
|
ConstructorParams |
Specify any construction parameters required for the class. Constructors are matched by construction parameter type and placement. |
Returns
A Java object.
Example
The following is an example of using dot notation and CreateJavaObject.
&CHARACTER.Value = CreateJavaObject(&java_path).GetField(&java_newchar).Value; &NUMBER.Value = CreateJavaObject(&java_path).GetField(&java_newnum).Value; &DATE.Value = CreateJavaObject(&java_path).GetField(&java_newdate).Value;
See Also
CreateJavaArray, GetJavaClass.

 CreateMCFIMInfo
CreateMCFIMInfoSyntax
CreateMCFIMInfo(UserID, Network)
Description
Use the CreateMCFIMInfo function to create an instance of the MCFIMInfo class. This is used to initiate the instant messaging session.
Parameters
|
UserID |
Specify the PeopleSoft user as a string. This is the source user, or the user issuing the presence requests. |
|
NetworkID |
Specify which network to use for instant messaging. The values are:
|
Returns
An MCFIMInfo object if successful, a null value otherwise.

 CreateMessage
CreateMessageSyntax
CreateMessage(MESSAGE.messagename)
Description
Use the CreateMessage function to instantiate a message object that refers to a message definition created in PeopleSoft Application Designer. The CreateMessage function sets the following properties for the resulting message object, based on the values set for the message definition:
Name
ChannelName
Active
Other properties are set when the message is published or subscribed to (PubID, SubName, and so on,) or are dynamically generated at other times (Size, EditError, and so on.)
CreateMessage also sets the LANGUAGE_CD field in the level 0 PSCAMA record for a message based on the USERID default language group. If the message is being published from a component, the language code is set to the USERID language code for the component. If CreateMessage is called from an Application Engine program, the language code of the user who started the batch process is used.
Parameters
|
MESSAGE. messagename |
Specify the name of the message definition you want to create a message object for. |
Returns
Returns a reference to a message object.
Example
The following example creates a message &MSG based on the message definition PURCHASE_ORDER.
Local message &MSG; &MSG = CreateMessage(MESSAGE.PURCHASE_ORDER);
See Also
GetMessage, GetPubContractInstance, GetSubContractInstance.

 CreateObject
CreateObjectSyntax
CreateObject(str_class_name, create_par, . . .)
Where str_class_name either:
—identifies a class by class name
—identifies a class of OLE Automation object in the form:
app_name.object_name
Description
Use the CreateObject function to return an instance of a class. You can use this function to access an Application Class, a PeopleCode built-in object (like a chart), or an OLE Automation object.
If the class you are creating requires values to be passed, use the create_par parameters to supply them, or use the CreateObjectArray function.
Considerations Using Application Classes
You can use the CreateObject function to access an Application Class. You would want to do this when you were programming at a high-level, when you might not know the name of the class you wanted to access until runtime. You must specify a fully-qualified class name. In addition, the class name is case-sensitive.
The returned object has the type of class you specified.
Considerations Using PeopleCode Built-in Objects
For example, to generate a Peoplesoft chart object without using a chart control (that is, without using the GetChart function.) you could use:
&MyChart = CreateObject("Chart");
The returned object has the type of class you specified.
Note. The only way to instantiate a crypt object is using the CreateObject function.
Considerations Using OLE Automation Objects
CreateObject returns an instance of an OLE Automation object as a variable of type Object.
The str_class_name argument uses the syntax app_name.object_type, which consists of: app_name (the name of the application providing the object) and object_type (the class or type of the object to create), separated by a period (dot).
Any application that supports OLE Automation exposes at least one type of object. For example, a spreadsheet application may provide an application object, a worksheet object, and a toolbar object.
To create an OLE Automation object, you assign the object returned by CreateObject to a variable of type Object:
local object &WORKSHEET; &WORKSHEET = CreateObject("Excel.Sheet");
After an object is created, you can reference it using the object variable. In the previous example, you access properties and methods of the new object using the ObjectGetProperty, ObjectSetProperty, and ObjectDoMethod functions.
Note. If an object has registered itself as a single-instance object, only one instance of the object can be created, even if CreateObject is executed more than once. Note also that an object assigned to a global variable is not valid across processes: that is, the scope and lifetime of the global is the same as the scope and lifetime of the instance of PeopleTools in which the object was created.
Parameters
|
str_class_name |
Specify the name of the class that you want to instantiate an object from. |
|
create_par |
Specify the parameters required by the class for instantiating the object. |
Example
This example instantiates an Excel worksheet object, makes it visible, names it, saves it, and displays its name. Note the use of ObjectGetProperty in the example to return the Excel.Sheet.Application object.
&WORKAPP = CreateObject("COM", "Excel.Application"); &WORKBOOKS = ObjectGetProperty(&WORKAPP, "Workbooks"); ObjectDoMethod(&WORKBOOKS, "Add", "C:\TEMP\INVOICE.XLT"); /* This associates the INVOICE template w/the workbook */ ObjectDoMethod(&WORKAPP, "Save", "C:\TEMP\TEST1.XLS"); ObjectSetProperty(&WORKAPP, "Visible", True);
This following example illustrates the creation of an application class object. This code assumes that MyBaseClass is the superclass of both MySubclass1 and MySubclass2 classes.
local MyBaseClass &mbobj; local String &ClassName = "MySubclass1"; if &test then &ClassName = "MySubclass2"; end-if; &mbobj = CreateObject(&ClassName);
The following example creates a chart in an iScript, using the CreateObject function to generate a reference to a chart object.
Function IScript_GetChartURL() Local Chart &oChart; Local Rowset &oRowset; Local string &sMap; Local string &sURL; &oChart = CreateObject("Chart"); &oRowset = CreateRowset(Record.QE_CHART_RECORD); &oRowset.Fill("where QE_CHART_REGION= :1", "MIDWEST"); &oChart.SetData(&oRowset); &oChart.Width = 400; &oChart.Height = 300; &oChart.SetDataYAxis(QE_CHART_RECORD.QE_CHART_SALES); &oChart.SetDataXAxis(QE_CHART_RECORD.QE_CHART_PRODUCT); &oChart.SetDataSeries(QE_CHART_RECORD.QE_CHART_REGION); &oChart.HasLegend = True; &oChart.LegendPosition = %ChartLegend_Right; &sURL = %Response.GetChartURL(&oChart); &sMap = &oChart.ImageMap; %Response.Write("<HTML><IMG SRC="); %Response.Write(&sURL); %Response.Write(" USEMAP=#THEMAP></IMG><MAP NAME=THEMAP>"); %Response.Write(&sMap); %Response.Write("</MAP></HTML>"); End-Function;
See Also
ObjectDoMethod, ObjectGetProperty, ObjectSetProperty, CreateObjectArray, ObjectDoMethodArray.
Internet Script Classes (iScript)

 CreateObjectArray
CreateObjectArraySyntax
CreateObjectArray(Class_Name, Array_of_Args)
Description
Use the CreateObjectArray function to return an instance of a class.
Use this function when you must pass in parameters to create the object and you don’t know when you write the code how many parameters are required. If you can create the object without passing in additional values, or if you know how many parameters are required, use the CreateObject function instead.
The array of parameters is an array of Any. It must be a one-dimensional array, that is, you cannot pass in an array of array of Any. You cannot pass in field references, that is, you cannot pass in references of the form:
RECORD.FIELDNAME
If you do not want to supply any parameters, you can use an empty array, or a reference to a Null array.
Parameters
|
Class_Name |
Specify the name of the class you want to create an instance of, as a string. |
|
Array_Of_Args |
Specify an Array of Any containing all parameters for creating an instance of the class. |
Returns
A reference to newly created object.
Example
The following is an example of the creation of an Application Class object where the number of parameters used to create the object varies, depending on data in the database.
local String &ClassName, &RecName; local Record &Rec; /* Read class name and parameter record name from the database. */ SQLExec("SELECT CLASSNAME, RECNAME FROM %TABLE(RECORD.CLASSDATA)", &ClassName, &RecName); local Record &Rec = CreateRecord(@ ("RECORD." | &RecName)); /* Read the parameters from the database. */ local Array of Any &Params = CreateArrayAny(); SQLExec("%SelectAll(:1)", &Rec, &Params); /* Create the object. */ local MyPackage:BaseClass &Obj = CreateObjectArray(&ClassName, &Params);
See Also
CreateObject, ObjectDoMethod, ObjectGetProperty, ObjectSetProperty, ObjectDoMethodArray.

 CreateProcessRequest
CreateProcessRequestSyntax
CreateProcessRequest([ProcessType, ProcessName])
Description
Use the CreateProcessRequest function to create a ProcessRequest object. After you’ve created this object, you can assign values to its properties then use the Schedule method to submit the process request for scheduling.
If you specify PSJob for the process type, the ProcessRequest object contains all the items of the job.
Parameters
|
ProcessType |
Specify the process type as a string. Values depend on the process types defined for your system. |
|
ProcessName |
Specify the name of the process as a string. |
Returns
A reference to a ProcessRequest object.
Example
Local ProcessRequest &MYRQST; &MYRQST = CreateProcessRequest("PSJOB", &MyJobName);
See Also

 CreateRecord
CreateRecordSyntax
CreateRecord(RECORD.recname)
Description
Use the CreateRecord function to create a standalone record definition and its component set of field objects. The specified record must have been defined previously, that is, it must have a record definition. However, if you are calling this function from PeopleCode associated with a page, the record does not have to be included on the current page.
The record and field objects created by this function are accessible only within PeopleCode. They can be used with any of the record and field object methods and properties. The record and field objects are automatically deleted when there are no remaining references to them stored in any variables.
The fields created by this function are initialized to null values. Default processing is not performed. No data associated with the record definition’s SQL table is brought in: only the record definition.
You can select into a record object created this way using the SelectByKey record class method. You can also select into it using the SQLExec function.
Parameters
|
RECORD. recname |
Specify a record definition that already exists. |
Returns
This function returns a record object that references a new record buffer and set of fields.
Example
Local Record &REC2; &REC2 = CreateRecord(RECORD.OPC_METH);
In the following example, a free-standing record is created (&PSBATREPREQRES). Values are assigned to the fields associated with the record. Then a second record is created (&PUBHDR), and the values from the first record are used to populate the second record.
&PSBATREPREQRES = CreateRecord(RECORD.PSBATREPREQRES); &PSBATREPREQRES.BATREPID.Value = &BATREPID; &PSBATREPREQRES.PUBID.Value = &MSG.Pubid; &PSBATREPREQRES.CHNLNAME.Value = &MSG.ChannelName; &PSBATREPREQRES.PUBNODE.Value = &MSG.PubNodeName; &PSBATREPREQRES.MSGNAME.Value = &MSG.Name; &PUBHDR = CreateRecord(RECORD.PSAPMSGPUBHDR); &PSBATREPREQRES.CopyFieldsTo(&PUBHDR);
To create a PeopleCode record object for a record whose name is unknown when the PeopleCode is written, do the following.
Suppose a record name is in the PeopleCode variable &RECNAME. Use the @ operator to convert the string to a component name. The following code creates a corresponding record object:
&RECNAME = "RECORD." | Upper(&RECNAME); &REC = CreateRecord(@ &RECNAME);
The following example uses SQLExec to select into a record object, based on the effective date.
Local Record &DST; &DST = CreateRecord(RECORD.DST_CODE_TBL); &DST.SETID.Value = GetSetId(FIELD.BUSINESS_UNIT, DRAFT_BU, RECORD.DST_CODE_TYPE, ""); &DST.DST_ID.Value = DST_ID_AR; SQLExec("%SelectByKeyEffDt(:1,:2)", &DST, %Date, &DST); /* do further processing using record methods and properties */
See Also

 CreateRowset
CreateRowsetSyntax
CreateRowset({RECORD.recname | &Rowset} [, {FIELD.fieldname, RECORD.recname | &Rowset}] . . .)
Description
Use the CreateRowset function to create an unpopulated, standalone rowset.
A standalone rowset is a rowset that has the specified structure, but is not tied to any data (that is, to the component buffer or to a message.) In addition, a standalone rowset isn’t tied to the Component Processor. When you fill it with data, no PeopleCode runs (like RowInsert, FieldDefault, and so on.)
The first parameter determines the structure of the rowset to be created.
If you specify a record as the first parameter, it’s used as the primary level 0 record. If you don’t specify any other parameters, you create a rowset containing one row, with one unpopulated record. To populate this type of rowset with data, you should only use:
the Fill or FillAppend rowset class methods
a record method (SelectByKey)
the SQLExec function
If you specify a rowset object, you are creating a new rowset based on the structure of the specified rowset object, including any child rowsets. It will not contain any data. If you want to populate this type of rowset with data, use the CopyTo method or a SQL statement.
Note. You should not use the rowset Select or SelectNew methods for populating rowsets created using CreateRowset. Use Fill or FillAppend instead.
Restrictions on Using CreateRowset
The following methods and properties don’t work with a rowset created using CreateRowset:
Select
SelectNew
Any GUI methods (like HideAllRows)
Any effective date methods or properties (like EffDt, EffSeq, or GetCurrEffRow)
In addition, rowsets created using CreateRowset are not automatically tied to the database. This means if you insert or delete rows, the rows will not be inserted or deleted in the database when you save the page.
Parameters
|
RECORD.recname | &Rowset |
Specify either a record name or an existing rowset object. |
|
FIELD.fieldname, RECORD.recname | &Rowset |
Use FIELD.fieldname, RECORD.recname to specify a related display record. FIELD.fieldname refers to the controlling field, (not the related display field) while RECORD.recname refers to the related display record. If you specify &rowset, you are adding a child rowset object to the newly created rowset. This must be an existing rowset object. |
Returns
An unpopulated, standalone rowset object.
Example
The following creates a simple rowset of just a single record per row:
&RS = CreateRowset(RECORD.QA_MYRECORD);
The following creates a rowset with the same structure as the specified rowset:
&RS2 = CreateRowset(&RS);
The following code creates a rowset structure composed of four records in an hierarchical structure, that is,
QA_INVEST_HDR QA_INVEST_LN QA_INVEST_TRANS QA_INVEST_DTL
Note that you have to start at the bottom of the hierarchy, and add the upper levels, not the other way around.
Local Rowset &RS, &RS2, &RS_FINAL; &RS2 = CreateRowset(RECORD.QA_INVEST_DTL); &RS = CreateRowset(RECORD.QA_INVEST_TRANS, &RS2); &RS2 = CreateRowset(RECORD.QA_INVEST_LN, &RS); &RS_FINAL = CreateRowset(RECORD.QA_INVEST_HDR, &RS2);
The following example reads all of the QA_MYRECORD records into a rowset, and returns the number of rows read:
&RS = CreateRowset(RECORD.QA_MYRECORD); &NUM_READ = &RS.Fill();
To make a clone of an existing rowset, that is, to make two distinct copies, you can do the following:
&RS2 = CreateRowset(&RS); &RS.CopyTo(&RS2);
The following code example is used for creating multiple children in a standalone rowset:
Local Rowset &rsBOCMRole, &rsBOCMRel, &rsBOCMUse; &rsBOCMRole = CreateRowset(Record.BO_CM_ROLE); &rsBOCMRel = CreateRowset(Record.BO_CM_REL); &rsBOCMUse = CreateRowset(Record.BO_CM_USE); &rsBOCM = CreateRowset(Record.BO_CM, &rsBOCMUse, &rsBOCMRole, &rsBOCMRel);
See Also
GetRowset, GetLevel0, GetRecord, GetField.

 CreateRowsetCache
CreateRowsetCacheSyntax
CreateRowsetCache(&Rowset, [Rowset.]Name, Description)
Description
Use the CreateRowsetCache function to create a new RowsetCache object with the given name if it doesn't already exist.
Parameters
|
&Rowset |
Specify an already instantiated and populated rowset that you want to use for creating a RowsetCache object. The RowsetCache object will have the same format and data as &Rowset. |
|
Record.Name |
Specify the name of the created RowsetCache object. If you just specify name, you must enclose the name in quotation marks. |
|
Description |
Specify a description of the RowsetCache as a string. |
Returns
A reference to the new RowsetCache object if there is not already a RowsetCache object of the given name.
Example
Local RowsetCache &Cache; Local Rowset &RS; &RS = CreateRowset(Record.PSLANGUAGES); &NUM_READ = &RS.Fill(); &Cache = CreateRowsetCache(&RS, "AAROWSET1", "ROWSET_AAROWSET1");
See Also

 CreateSOAPDoc
CreateSOAPDocSyntax
CreateSOAPDoc()
Description
Use the CreateSOAPDoc function to create an empty SOAPDoc object. Then use the SOAPDoc class methods and properties, as well as the XmlDoc class methods and properties to populate the SOAPDoc object.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A reference to a SOAPDoc object.
Example
Local SOAPDoc &MyDoc; &MyDoc = CreateSOAPDoc();
See Also

 CreateSQL
CreateSQLSyntax
CreateSQL([{sqlstring | SQL.SqlName}[, paramlist]])
Where paramlist is an arbitrary-length list of values in the form:
inval1 [, inval2] ...
Description
Use the CreateSQL function to instantiate a SQL object from the SQL class and opens it on the given sqlstring and input values. sqlstring is a PeopleCode string value giving the SQL statement.
Any errors in the SQL processing cause the PeopleCode program to be terminated with an error message.
You can use CreateSQL with no parameters to create an empty SQL object that can be used to assign properties before being populated and executed.
Opening and Processing sqlstring
If sqlstring is a SELECT statement, it is immediately bound with the inval input values and executed. The SQL object should subsequently be the subject of a series of Fetch method calls to retrieve the selected rows. If you want to fetch only a single row, use the SQLExec function instead. If you want to fetch a single row into a PeopleCode record object, use the record Select method.
If sqlstring is not a SELECT statement, and either there are some inval parameters, or there are no bind placeholders in the SQL statement, the statement is immediately bound and executed. This means that there is nothing further to be done with the SQL statement and the IsOpen property of the returned SQL object will be False. In this case, using the SQLExec function would generally be better. If you want to delete, insert or update a record object, use the record Delete, Insert, or Update methods.
If sqlstring is not a SELECT statement, there are no inval parameters, and there are bind placeholders in the SQL statement, the statement is neither bound nor executed. The resulting SQL object should subsequently be the subject of a series of Execute method calls to affect the desired rows.
Using Arrays with paramlist
You can use a parameter of type "Array of Any" in place of a list of bind values or in place of a list of fetch result variables. This is particularly useful when fetching an unknown number of results.
&Sql1 = CreateSql("Select * from " | &TableName); &AAny = CreateArrayAny(); While &Sql1.Fetch(&AAny) /* Process the row in &AAny. */ ... End-While;
Because the Array of Any promotes to absorb any remaining select columns, it must be the last parameter for the SQL object Fetch method or (for results) SQLExec. For binding, it must be the only bind parameter, as it is expected to supply all the bind values needed.
Parameters
|
sqlstring| SQL.SqlName |
Specify either a SQL string containing the SQL command to be created or a reference to an existing SQL definition. This string can include bind variables, inline bind variables, and meta-SQL. |
|
paramlist |
Specify input values for the SQL string. |
Returns
None.
Example
This SQL object should be used in a series of Fetch method calls:
Local SQL &SQL; &SQL = CreateSQL("%SelectAll(:1) where EMPLID = :2", RECORD.ABSENCE_HIST, &EMPLID);
This SQL object has been opened, bound, and is already closed again:
&SQL = CreateSQL("Delete from %Table(:1) where EMPLID = :2", RECORD.ABSENCE_HIST, &EMPLID);
This SQL object should be used in a series of Execute method calls:
&SQL = CreateSQL("Delete from %Table(:1) where EMPLID = :2");
This SQL object is created as an empty object in order to set properties before being executed:
&Sql = CreateSQL(); &Sql.Tracename = "SQL1"; &Sql.ReuseCursor = True; &Sql.Open(......); /* do the deed */
See Also
DeleteSQL, FetchSQL, GetSQL, SQLExec, StoreSQL.

 CreateWSDLMessage
CreateWSDLMessage
Syntax
CreateWSDLMessage(MessageName, ChannelName)
Description
Use the CreateWSDLMessage function to create a nonrowset-based message. This function creates both the message as well as the channel.
To view the data for this message, you can either:
Use the GetMessageXmlDoc function
Use the GetMessage function, followed by the GetXmlDoc method (that is, &MSG.GetXmlDoc();)
You can then use the GetMessage function to return the shape of the nonrowset-based message.
Parameters
|
MessageName |
Specify the name of the message as a string. |
|
ChannelName |
Specify the name of the channel to be created for this message. |
Returns
A Boolean value: true if the channel is created successfully, false otherwise.
See Also
ConnectorRequest, ConnectorRequestURL.

 CreateXmlDoc
CreateXmlDocSyntax
CreateXmlDoc(XmlString, DTDValidation)
Description
Use the CreateXmlDoc function to create an XmlDoc object. If you specify a Null string for XmlString (""), you create an empty XmlDoc object.
Considerations Using CreateXmlDoc
The following coding is either ignored or removed from the XmlDoc object that is created with this function:
encoding attributes
PeopleSoft only supports UTF-8 encoding. Any specified encoding statement is removed, as all XmlDoc objects are considered UTF-8.
version attributes
Regardless of what version is specified in XmlString, the version attribute in the generated XmlDoc object is 1.0.
Parameters
|
XmlString |
Specify an XML string that you want to convert into an XmlDoc object that you can then manipulate using PeopleCode. You can also specify a Null string ("") to generate an empty XmlDoc object. |
|
DTDValidation |
Specify whether a DTD should be validated. This parameter takes a boolean value. If you specify true, the DTD validation occurs if a DTD is provided. If you specify false, and if a DTD is provided, it is ignored and the XML isn't validated against the DTD. False is the default value. In the case of application messaging, if a DTD is provided, it's always ignored and the XML isn't validated against the DTD. If the XML cannot be validated against a DTD, an error is thrown saying that there was an XML parse error. |
Returns
A reference to the newly created XmlDoc object.
Example
The following creates an empty XmlDoc object.
Local XmlDoc &MyDoc; &MyDoc = CreateXmlDoc("");
See Also

 CubicSpline
CubicSplineSyntax
CubicSpline(DataPoints, Control_Option, Left_Constraint, Right_Constraint)
Description
Use the CubicSpline function to compute a cubic spline interpolation through a set of at least four datapoints.
Parameters
|
DataPoints |
This parameter takes an array of array of number. The array’s contents are an array of six numbers. The first two of these six numbers are the x and y points to be fit. The last four are the four coefficients to be returned from the function: a, b, c and d. a is the coefficient of the x0 term, b is the coefficient of the x1 term, c is the coefficient of the x2 term, and d is the coefficient of the x3 term. |
|
Control_Option |
Specifies the control option. This parameter takes either a number or constant value. The values are: |
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
0 |
%SplineOpt_SlEstEst |
Generate an internal estimate of the beginning and ending slope of the cubic piecewise equations |
|
1 |
%SplineOpt_SlSetEst |
Use the user-specified value for the slope of the leftmost point, and generate an estimate for the rightmost point |
|
2 |
%SplineOpt_SlEstSet |
Use the user-specified value for the slope of the rightmost point, and generate an estimate for the leftmost point |
|
3 |
%SplineOpt_SlSetSet |
Use the user-specified values for the slopes of the leftmost and rightmost points |
|
4 |
%SplineOpt_CvEstEst |
Generate an internal estimate of the beginning and ending curvature of the cubic piecewise equations |
|
5 |
%SplineOpt_CvSetEst |
Use the user-specified value for the curvature of the leftmost point, and generate an estimate for the rightmost point |
|
6 |
%SplineOpt_CvEstSet |
Use the user-specified value for the curvature of the rightmost point, and generate an estimate for the leftmost point |
|
7 |
%SplineOpt_CvSetSet |
Use the user-specified values for the curvatures of the leftmost and rightmost points |
|
8 |
%SplineOpt_ClEstEst |
Generate an internal estimate of the beginning and ending curl of the cubic piecewise equations |
|
9 |
%SplineOpt_ClSetEst |
Use the user-specified value for the curl of the leftmost point, and generate an estimate for the rightmost point |
|
10 |
%SplineOpt_ClEstSet |
Use the user-specified value for the curl of the rightmost point, and generate an estimate for the leftmost point |
|
11 |
%SplineOpt_ClSetSet |
Use the user-specified values for the curls of the leftmost and rightmost points |
|
12 |
%SplineOpt_Natural |
Generate a “natural” spline |
|
13 |
%SplineOpt_ContCurl |
Generate a spline wherein the equation for the first segment is the exact same equation for the second segment, and where the equation for the penultimate segment is the same as the equation for the last segment. |
|
Left_Constraint |
A single number for the constraint for the left point. Specify a zero if this parameter isn’t needed. |
|
Right_Constraint |
A single number for the constraint for the right point. Specify a zero if this parameter isn’t needed. |
Returns
A modified array of array of numbers. The elements in the array correspond to the elements in the array used for DataPoints.
See Also

 CurrEffDt
CurrEffDtSyntax
CurrEffDt([level_num])
Description
Use the CurrEffDt function to return the effective date of the specified scroll level as a Date value.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the EffDt rowset class property instead.
If no level is specified, CurrEffDt returns the effective date of the current scroll level.
See Also
Returns
Returns a Date value equal to the current effective date of the specified scroll level.
Example
If INSTALLATION.POSITION_MGMT = "P" Then If All(POSITION_NBR) Then If (EFFDT = CurrEffDt(1) and EFFSEQ >= CurrEffSeq(1)) or (EFFDT > CurrEffDt(1) and EFFDT = %Date) Then Gray_employment( ); End-if; End-if; End-if;
See Also
CurrEffRowNum, CurrEffSeq, CurrentLevelNumber.

 CurrEffRowNum
CurrEffRowNumSyntax
CurrEffRowNum([level_num])
Description
Use the CurrEffRowNum function to return the effective row number of the selected scroll level.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the RowNumber row class property, in combination with the GetCurrEffRow rowset method, instead.
If no level is specified, it returns the effective row number of the current level.
See Also
Example
&ROW = CurrEffRowNum(1);
See Also
CurrEffSeq, CurrentLevelNumber, CurrEffRowNum.

 CurrEffSeq
CurrEffSeqSyntax
CurrEffSeq([level_num])
Description
Use the CurrEffSeq function to determine the effective sequence of a specific scroll area.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the EffSeq rowset class property instead.
If no level is specified, CurrEffSeq returns the effective sequence of the current scroll level.
See Also
EffSeq, GetCurrEffRow, DeleteEnabled.
Returns
Returns a Number representing the effective sequence of the specified scroll level.
Example
If INSTALLATION.POSITION_MGMT = "P" Then If All(POSITION_NBR) Then If (EFFDT = CurrEffDt(1) and EFFSEQ >= CurrEffSeq(1)) or (EFFDT > CurrEffDt(1) and EFFDT = %Date) Then Gray_employment( ); End-if; End-if; End-if;
See Also
CurrEffDt, CurrentLevelNumber, CurrEffRowNum.

 CurrentLevelNumber
CurrentLevelNumberSyntax
CurrentLevelNumber()
Description
Use the CurrentLevelNumber function to return the scroll level where the function call is located.
Returns
Returns a Number value equal to the scroll level where the function is being called. The function returns 0 if the field where the function is called is not in a scroll area.
Example
&LEVEL = CurrentLevelNumber();
See Also

 CurrentRowNumber
CurrentRowNumberSyntax
CurrentRowNumber([level])
Description
Use the CurrentRowNumber function to determine the row number of the row currently displayed in a specific scroll area.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the RowNumber row class property instead.
This function can determine the current row number on the level where the function call resides, or on a higher scroll level. It won’t work on a scroll level below the one where the PeopleCode program resides.
See Also
Parameters
|
level |
A Number specifying the scroll level from which the function returns the current row number. If the level parameter is omitted, it defaults to the scroll level where the function call resides. |
Returns
Returns a Number value equal to the current row number on the specified scroll level. The current number is the row where the PeopleCode program is being processed, or, if level specifies a higher level scroll, CurrentRowNumber returns the row number of the parent or grandparent row.
Example
CurrentRowNumber is typically used in component buffer functions to return the current row of the parent scroll of the target:
&VAL = FetchValue(RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_PER, CurrentRowNumber(), BUS_EXPENSE_DTL.CHARGE_DT, &COUNT);
The following example checks if the current row number is equal to the active row count (that is, whether the active row is the last record on the scroll):
If CurrentRowNumber() = ActiveRowCount(EMPLID) Then det_employment_dt(); End-if;
See Also
ActiveRowCount, CurrentLevelNumber, FetchValue.

 Date
DateSyntax
Date(date_num)
Description
The Date function takes a number in the form YYYYMMDD and returns a corresponding Date value. If the date is invalid, Date displays an error message.
Warning! Make sure that you pass a four-digit year in the year parameter of this function. Two-digit values are interpreted literally: 93, for example, represents the year 93 AD.
Returns
Returns a date equal to the date specified in date_num.
Example
Set the temporary variable &HIREDate to a date field containing the date July 1, 1997:
&HIREDate = Date(19970701);
See Also
Date3, DateValue, Day, Days360, Days365, Month, Weekday, Year.

 Date3
Date3Syntax
Date3(year, month, day)
Description
The Date3 function accepts a date expressed as three integers: year, month, and day. It returns a corresponding Date value. If the date is invalid, the Date3 displays an error message.
Warning! Make sure that you pass a four-digit year in the year parameter of this function. Two-digit values will be interpreted literally: 93, for example, represents the year 93 AD.
Parameters
|
year |
An integer for the year in the form YYYY. |
|
month |
An integer from 1 to 12 designating the month. |
|
day |
An integer from 1 to 31 designating the day of the month. |
Returns
Returns a Date value equal to the date specified in the function parameters.
Example
The following PeopleCode Date3 function returns the first day of the year in which the employee was hired:
Date3(HIRE_YEAR, 1, 1);
See Also
Date, DateValue, Day, Days360, Days365.

 DatePart
DatePartSyntax
DatePart(datetime_value)
Description
Use the DatePart function to determine a date based on a provided DateTime value.
Returns
Returns a Date value equal to the date part of a specified DateTime value.
Example
The following statement sets &D2 to a Date value for 11/12/1997:
&D1 = DateTimeValue("11/12/1997 10:23:15 AM"); &D2 = DatePart(&D1);

 DateTime6
DateTime6Syntax
DateTime6(year, month, day, hour, minute, second)
Description
The DateTime6 function returns a DateTime value based on integer values for the year, month, day, hour, minute, and second. If the result of this function is not an actual date, there is a runtime error.
Warning! Make sure that you pass a four-digit year in the year parameter of this function. Two-digit values will be interpreted literally: 93, for example, represents the year 93 AD.
Parameters
|
year |
A four-digit number representing the year. |
|
month |
A number between 1 and 12 representing the month. |
|
day |
A number representing the day of the month. |
|
hour |
A number from 0 to 23 representing the hour of the day. |
|
minute |
A number from 0 to 59 representing the minute of the hour. |
|
second |
A number from 0 to 59.999999 representing seconds. |
Returns
Returns a DateTime value based on the integers provided.
Example
The following example sets &DT to a DateTime value equal to 10:09:20 on March 15, 1997:
&DT = DateTime6(1997, 3, 15, 10, 9, 20);

 DateTimeToHTTP
DateTimeToHTTPSyntax
DateTimeToHTTP(datetime)
Description
Use the DateTimeToHTTP function to convert any datetime value to a datetime string in the format specified by HTTP 1.0 and 1.1 standards.
Note. Because the HTTP protocol is used to interchange information between diverse computing systems, the value returned from this function is always the ”US English” form of weekdays and months. If you want the value to use the localized form, use the DateTimeToLocalizeString function instead.
The standard HTTP datetime has the following fixed length format:
<dow><,><sp><dd><sp><mon><sp><year><sp><hh><:><mm><:><ss><sp><GMT>
where:
|
Value |
Description |
|
<dow> |
a 3-character day of week name, one of Sun, Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat. |
|
<,> |
a literal comma character |
|
<sp> |
a literal space character |
|
<dd> |
a 2-digit day of month, such as 02 or 22. |
|
<mon> |
is a 3-character month name, one of Jan, Feb, Mar, and so on. |
|
<year> |
a 4-digit year number |
|
<hh> |
a 24-hour hour number, such as 00 or 13 |
|
<mm> |
a 2-digit minute number, such as 01 or 56 |
|
<ss> |
a 2-digit second number, such as 03 or 59 |
|
<GMT> |
a literal 3-character GMT. |
As indicated by the trailing GMT, this datetime format is always expressed in GMT (or UTC, which is declared to be the same for the purposes of HTTP).
Parameters
|
datetime |
Specify the datetime value you want converted to HTTP format. This datetime is assumed to be in the base timezone of the installation. |
Returns
A string containing the converted datetime.
Example
&gmtdate = DateTimeToHTTP(AddToDateTime(%DateTime, 0,0,0,0,600,0)); %Response.setHeader("Last-Modified", &gmtdate);
See Also
AddToDateTime, DateTimeToLocalizedString, FormatDateTime.

 DateTimeToLocalizedString
DateTimeToLocalizedStringSyntax
DateTimeToLocalizedString({datetime | date}, [Pattern])
Description
Use the DateTimeToLocalizedString function to convert either datetime or date to a localized string. You can also specify a particular pattern to convert datetime or date to.
The Pattern is optional. Only specify Pattern if necessary.
If you need to change the pattern for each language, change the first message in Message Catalog set number 138. This is a format for each language.
Parameters
|
Datetime | Date |
Specify either the datetime or date that you want to convert. |
|
Pattern |
Specify the pattern you want to the localized datetime or date to be converted to. |
Using the Pattern Parameter
Pattern takes a string value, and indicates how you want the date or datetime converted.
The valid values for Pattern are as follows.
Note. The values for pattern are case-sensitive. For example, if you specify a lowercase m, you get minutes, while an uppercase M displays the month.
|
Symbol |
Definition |
Type |
Example |
|
G |
Era designator |
Text |
AD |
|
y |
Year |
Number |
1996 |
|
M |
Month in year |
Text&Number |
July&07 |
|
d |
Day in month |
Number |
10 |
|
h |
Hour in am/pm |
Number (1-12) |
12 |
|
H |
Hour in day |
Number (0-23) |
0 |
|
m |
Minute in hour |
Number |
30 |
|
s |
Second in minute |
Number |
55 |
|
S |
Millisecond |
Number |
978 |
|
E |
Day in week |
Text |
Tuesday |
|
a |
am/pm marker |
Text |
PM |
|
k |
Hour in day |
Number (1-24) |
24 |
|
K |
Hour in am/pm |
Number (0-11) |
0 |
|
' |
Escape for text |
Delimiter |
|
|
'' |
Single quote |
Literal |
' |
The number of pattern letters determine the format.
|
Type |
Pattern Format |
|
Text |
If 4 or more pattern letters are used, the full form is used. If less than 4 pattern letters are used, the short or abbreviated form is used if one exists. |
|
Number |
Use the minimum number of digits. Shorter numbers are zero-padded to this amount. The year is handled specially; that is, if the count of 'y' is 2, the year is truncated to 2 digits. |
|
Text&Number |
If 3 or more pattern letters are used, text is used, otherwise, a number is used. |
Any characters in Pattern are not in the ranges of ['a'..'z'] and ['A'..'Z'] are treated as quoted text. For instance, characters like ':', '.', ' ', '#' and '@' appear in the resulting string even they're not within single quotes.
A pattern containing any invalid pattern letter results in a runtime error.
Examples using a United States locale:
|
Pattern |
Result |
|
"yyyy.MM.dd G 'at' hh:mm:ss" |
1996.07.10 AD at 15:08:56 |
|
"EEE, MMM d, ''yy" |
Wed, July 10, '96 |
|
"h:mm a" |
12:08 PM |
|
"hh 'o''clock' a" |
12 o'clock PM |
|
"K:mm a" |
0:00 PM |
|
"yyyyy.MMMMM.dd GGG hh:mm aaa" |
1996.July.10 AD 12:08 PM |
Returns
A string.
Example
REM**************************************************************; Function ConvertDateToDTTM(&Date As date) Returns datetime ; REM ***********************************************************; &String = DateTimeToLocalizedString(&Date, "M/d/y"); &String = &String | " 00:00:00.000000"; &DateTime = DateTimeValue(&String); Return &DateTime; End-Function;
See Also
FormatDateTime, DateTimeToHTTP.

 DateTimeToTimeZone
DateTimeToTimeZoneSyntax
DateTimeToTimeZone(OldDateTime, SourceTimeZone, DestinationTimeZone)
Description
Use the DateTimeToTimeZone function to convert datetimes from the datetime specified by SourceTimeZone to the datetime specified by DestinationTimeZone.
Considerations Using this Function
Typically, this function is used in PeopleCode, not for displaying time. If you take a datetime value, convert it from base time to client time, then try to display this time, depending on the user settings, when the time is displayed the system might try to do a second conversion on an already converted datetime. This function could be used as follows: suppose a user wanted to check to make sure a time was in a range of times on a certain day, in a certain timezone. If the times were between 12 AM and 12 PM in EST, these resolve to 9 PM and 9 AM PST, respectively. The start value is after the end value, which makes it difficult to make a comparison. This function could be used to do the conversion for the comparison, in temporary fields, and not displayed at all.
Parameters
|
OldDateTime |
Specify the datetime value to be converted. |
|
SourceTimeZone |
Specify the time zone that OldDateTime is in. Valid values are:
|
|
DestinationTimeZone |
Specify the time zone that you want to convert OldDateTime to. Valid values are:
|
Returns
A converted datetime value.
Example
The following example. TESTDTTM, is a datetime field with a value 01/01/99 10:00:00. This example converts TESTDTTM from Pacific standard time (PST) to eastern standard time (EST).
&NEWDATETIME = DateTimeToTimeZone(TESTDTTM, "PST", "EST");
&NEWDATETIME will have the value 01/01/99 13:00:00 because EST is three hours ahead of PST on 01/01/99, so three hours are added to the datetime value.
See Also
ConvertDatetimeToBase, ConvertTimeToBase, FormatDateTime, IsDaylightSavings, TimeToTimeZone, TimeZoneOffset.

 DateTimeValue
DateTimeValueSyntax
DateTimeValue(string)
where string has the format:
MM/DD/YY[YY] hh:mm:ss.ssssss [{AM|PM}]
or
MM.DD.YY[YY] hh:mm:ss.ssssss [{AM|PM}]
Description
Use the DateTimeValue function to derive a DateTime value from a string representing a date and time.
Using this Function in Fields Without a Default Century Setting
This function may derive the wrong century setting if passed a 2-character year and DateTimeValue is executing in a PeopleCode event not associated with a field that has a default century setting.
For example, assume that TEST_DATE is a date field with a default century setting of 10. TEST_FIELD is a field with no default century setting. If the following PeopleCode program is executing in TEST_FIELD, the date will be calculated incorrectly:
TEST_DATE = DateTimeValue("10/13/11 15:34:25");
Though TEST_DATE has a century setting, it isn’t used because the PeopleCode fired in TEST_FIELD. Instead, DateTimeValue uses the 50/50 rule and calculates the year to be 2011 (instead of 1911).
Returns
Returns a DateTime value.
Example
Both of the following examples set &Date_TIME to a Datetime value equal to October 13, 1997 10:34:25 PM.
&Date_TIME = DateTimeValue("10/13/97 10:34:25 PM"); &Date_TIME = DateTimeValue("10/13/97 22:34:25");
See Also
Date, Date3, DateValue, Day, Days360, Days365, Month, Weekday, Year.

 DateValue
DateValueSyntax
DateValue(date_str)
Description
Use the DateValue function to convert a date string and returns the result as a Date type. date_str must be a string in the active date format user's current personalization date format.
If the user's Date Format personalization setting is set to DDMMYY (or it is defaulted to this from their browser locale or the system-wide personalization defaults) then the following code returns a Datetime value equal to September 10, 1997.
&DTM = DateValue("10/09/97");
If the user's Date Format personalization setting is set to MMDDYY (or it is defaulted to this from their browser locale or the system-wide personalization defaults) then the same function call returns a value equal to October 9, 1997.
Using this Function in Fields Without a Default Century Setting
This function may derive the wrong century setting if passed a 2-character year and DateValue is executing in a PeopleCode event not associated with a field that has a default century setting.
For example, assume that TEST_DATE is a date field with a default century setting of 10. TEST_FIELD is a field with no default century setting. If the following PeopleCode program is executing in TEST_FIELD, the date will be calculated incorrectly:
TEST_DATE = DateValue("10/13/11");
Though TEST_DATE has a century setting, it isn’t used because the PeopleCode fired in TEST_FIELD. Instead, DateValue uses the 50/50 rule and calculates the year to be 2011 (instead of 1911).
Returns
Returns a Date value.
See Also
Date, Date3, DateTimeValue, Day, Days360, Days365, Month, Weekday, Year.

 Day
DaySyntax
Day(dt_val)
Description
Use the Day function to determine an integer representing the day of the month based on a Date or DateTime value.
Returns
Returns a Number value equal to the day of the month for dt_val. The return value is an integer from 1 to 31.
Example
If HIRE_DATE is November, 1, 1997, the following Day function returns the integer 1:
&FIRST_DAY = Day(HIRE_DATE);
See Also
Date, Date3, DateValue, Days, Days360, Days365, Month, Weekday, Year.

 Days
DaysSyntax
Days(dt_val)
Description
Use the Days function to returns the Julian date for the dt_val specified. This function accepts a Date, DateTime, or Time value parameter.
Returns
Returns a Number value equal to the Julian date for dt_val.
Example
To find the number of days between two dates, use the Days function on both dates, and subtract one from the other:
&NUM_DAYS = Abs(Days(HIRE_Date) - Days(RELEASE_Date));
See Also
DateValue, Days360, Days365, Month, Weekday, Year.

 Days360
Days360Syntax
Days360(date_val1, date_val2)
Description
Use the Days360 function to return the number of days between the Date values date_val1 and date_val2 using a 360-day year (twelve 30-day months). Use this function to help compute payments if your accounting system is based on twelve 30-day months.
If date_val2 occurs before date_val1, Days360 returns a negative number.
Example
The following example sets &NUMDAYS to the number of days between TERM_START_DT and PMT_DT based on a 360-day calendar:
&NUMDAYS = Days360(TERM_START_DT, PMT_DT);
See Also
Date, Date3, DateValue, Day, Days, Days365, Month, Weekday, Year.

 Days365
Days365Syntax
Days365(date_val1, date_val2)
Description
Use the Days365 function to return the number of days between the Date values date_val1 and date_val2 using a 365-day year. Use this function to help compute payments if your accounting system is based on a 365-day year.
If date_val2 occurs before date_val1, Days365 returns a negative number.
Returns
Returns a Number value equal to the number of days between the two dates in a 365-day calendar.
Example
The following example sets &NUMDAYS to the number of days between and TERM_START_DT and PMT_DT, based on a 365-day calendar:
&NUMDAYS = Days360(TERM_START_DT, PMT_DT);
See Also
Date, Date3, DateValue, Day, Days360, Month, Weekday, Year.

 DBCSTrim
DBCSTrimSyntax
DBCSTrim(source_str)
Description
Note. This function has been deprecated.
Use the DBCSTrim function to remove a trailing DBCS lead byte at the end of the string.

 DBPatternMatch
DBPatternMatchSyntax
DBPatternMatch(Value, Pattern, CaseSensitive)
Description
Use the DBPatternMatch function to match the string in Value to the given pattern.
You can use wildcard characters % and _ when searching. % means find all characters, while _ means find a single character. For example, if you wanted to find if the string in Value started with the letter M, you'd use "M%" for Pattern. If you wanted to find either DATE or DATA, use "DAT_" for Pattern.
These characters can be escaped (that is, ignored) using a \. For example, if you want to search for a value that contains the character %, use \% in Pattern.
If Pattern is an empty string, this function retrieves the value just based on the specified case-sensitivity (that is, specifying "" for Pattern is the same as specifying "%").
Parameters
|
Value |
Specify the string to be searched. |
|
Pattern |
Specify the pattern to be used when searching. |
|
CaseSensitive |
Specify whether the search is case-sensitive. This parameter takes a Boolean value: True, the search is case-sensitive, False, it is not. |
Returns
Returns a Boolean value. True if the string matches the pattern, False otherwise.
See Also

 Declare Function
Declare FunctionSyntax
PeopleCode Function Syntax
Declare Function function_name PeopleCode record_name.field_name event_type
External Function Syntax
Declare Function function_name Library lib_name [ALIAS module_name ] [paramlist] [RETURNS ext_return_type [As pc_type]]
Where paramlist is:
([ext_param1 [, ext_param2] . . .)
and where ext_paramn is:
ext_datatype [{REF|VALUE}] [As pc_return_type]
Description
PeopleCode can call PeopleCode functions defined in any field on any record definition. You can create special record definitions whose sole purpose is to serve as function libraries. By convention, PeopleCode functions are stored in FieldFormula PeopleCode, in record definitions with names beginning in FUNCLIB_.
PeopleCode can also call external programs that reside in dynamic link libraries. You must declare either of these types of functions at the top of the calling program using the Declare Function statement.
To support processes running on an application server, you can declare and call functions compiled in dynamic link libraries on windows (*.DLL files) and shared libraries on UNIX (lib*.so files.) The PeopleCode declaration and function call syntax is the same regardless of platform, but UNIX libraries must be compiled with an interface function.
See Calling DLL Functions on the Application Server.
PeopleCode Functions
You can call a PeopleCode function defined on any record definition, provided you declare it at the top of the calling program. The declaration identifies the function name, as well as the record, field, and event type where the function definition resides. The function parameters and return type are not declared; they are determined from the function definition.
Note. You can define functions only in Record Field PeopleCode. You can’t define functions in Component PeopleCode, Component Record Field PeopleCode, and so on.
External Library Functions
Function declarations define routines in an external (C-callable) library. The function declaration provides the name of the library, an optional alias module_name, a list of parameters to pass to the function, an optional Returns clause specifying the type of any value returned by the external function, and the PeopleCode data type into which to convert the returned value. The library must be a DLL accessible by Windows or a shared library accessible by UNIX.
After you have declared an external library function, you can call it the same way as an external PeopleCode function. Like PeopleCode functions, you must pass the number of parameters the library function expects. Calls to external functions suspend processing: this means that you should exercise caution to avoid “think-time” errors when calling the function in the following PeopleCode events:
SavePreChange.
SavePostChange.
Workflow.
RowSelect.
Any PeopleCode event that fires as a result of a ScrollSelect (or one of its relatives) function calls, or a Select (or one of its relatives) Rowset class method.
See Think-Time Functions.
Parameters
The following are the parameters for the PeopleCode Function syntax:
|
function_name |
Name of the function. |
|
PeopleCode |
Reserved word that identifies the function as a PeopleCode function. |
|
recordname.fieldname |
Specifies the record and field where the function is located. |
|
event_type |
Component Processor event with which the function is associated. |
Note. event_type can be used to specify record field events only. You can’t specify a component record field event, a component record event, and so on.
The following are the parameters for the External Function syntax:
|
function_name |
Name of the function. |
|
Library |
Reserved word that identifies the function as an external library function. |
|
lib_name |
A string representing the name of the external library. The external routine must be located in a DLL named lib_name accessible by Windows, or an equivalent shared library in a UNIX system. |
|
Alias module_name |
Optionally specifies the name of the function’s entry point within the shared library. This is needed only if the C function name differs from function_name in the PeopleCode external function declaration. The external module is invoked using the __stdcall calling convention on Windows. |
|
Paramlist |
List of parameters expected by the function, each in the form: |
|
|
ext_datatype [{Ref|Value}] [As pc_type] |
|
ext_type |
The datatype of the parameter expected by the function. To specify the type you can use any of the following:
|
|
Ref | Value |
Optionally use one of these two reserved words to specify whether the parameter is passed by reference or by value. If Ref is specified, it is passed by pushing a reference (pointer) on the stack. If Value is specified the value is pushed on the stack (for integers, and so on.) If neither is specified, Ref is assumed. |
|
AS pc_type |
Specifies PeopleCode data type of the value passed to the function. You can choose between PeopleCode data types String, Number, Date, Boolean, and Any. |
|
Returns ext_return_type |
Specifies the data type of any value returned by the function. The Returns clause is omitted if the function is void (returns no value.) To specify the return type you can use any of the following:
|
|
|
The types String and LString are not allowed for the result type of a function. |
|
As pc_return_type |
Specifies the PeopleCode data type of the variable or field into which to read the returned value. You can choose between PeopleCode data types String, Number, Date, Boolean, and Any. If the As clause is omitted, PeopleTools selects an appropriate type based on the type of value returned by the external function (for example, all integer and floating point types are converted to Number). |
Example
Assume you have defined a PeopleCode function called VerifyZip. The function definition is located in the record definition FUNCLIB_MYUTILS, in the record field ZIP_EDITS, attached to the FieldFormula event. You would declare the function using the following statement:
declare function verifyzip PeopleCode FUNCLIB_MYUTILS.ZIP_EDITS FieldFormula;
Now assume you want to declare a function called PCTest, in PSUSER.DLL. It takes an integer and returns an integer. You would write this declare statement:
declare function pctest library "psuser.dll" (integer value as number) returns integer as number;
See Also

 Decrypt
DecryptSyntax
Decrypt(KeyString, EncryptedString)
Description
Use the Decrypt function to decrypt a string previously encrypted with the Encrypt function. This function is generally used with merchant passwords. For this function to decrypt a string successfully, you must use the same KeyString value used to encrypt the string.
Parameters
|
KeyString |
Specify the key used for encrypting the string. You can specify a NULL value for this parameter, that is, two quotation marks with no blank space between them (""). |
|
EncryptedString |
Specify the string you want decrypted. |
Returns
A clear text string.
Example
Encrypt and Decrypt support only strings.
&AUTHPARMS.WRKTOKEN.Value = Decrypt("", RTrim(LTrim(&MERCHANTID_REC.CMPAUTHNTCTNTOKEN.Value)));
See Also
Understanding PeopleSoft Security

 Degrees
DegreesSyntax
Degrees(angle)
Description
Use the Degrees function to convert the given angle from radian measurement to degree measurement.
Parameters
|
angle |
The size of an angle in radians. |
Returns
The size of the given angle in degrees.
Example
The following example returns the equivalent size in degrees of an angle measuring 1.2 radians:
&DEGREE_SIZE = Degrees(1.2);
See Also
Acos, Asin, Atan, Cos, Cot, Radians, Sin, Tan.

 DeleteAttachment
DeleteAttachmentSyntax
DeleteAttachment(URLSource, DirAndFileName[, PreserveCase])
where URLSource can have one of the following forms:
URL.URLname
Or a string URL, such as
ftp://user:[email protected]/
Note. You cannot specify a different port for an attachment when using an FTP server. You can only use the default port of 21.
Description
Use the DeleteAttachment function to delete a file on a specified system.
DeleteAttachment does not generate any type of “Are you sure” message. If you want the user to verify the deletion before it's performed, you must write your own checking code in your application.
File Name Considerations
When the file is transferred, the following characters are replaced with an underscore:
space
semicolon
plus sign
percent sign
ampersand
apostrophe
exclamation point
pound sign
dollar sign
Parameters
|
URLSource |
A reference to a URL. This can be either a URL name, in the form URL.URLName, or a string. This is where the file will end up. |
|
DirAndFileName |
A directory and filename. This is appended to the URLSource to make up the full URL of the file. |
|
PreserveCase |
Specify a Boolean value to indicate whether the case of the directory and file name specified with DirAndFileName are preserved or not; true, preserve the case, false otherwise. The default value is false. |
Note. The URLSource requires "/" slashes. Because the DirAndFileName parameter is appended to the URL, it also requires only "/" slashes. "\" are not supported in anyway for either the URLSource the DirAndFileName parameter.
Returns
An integer value. You can check for either the integer or the constant:
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
0 |
%Attachment_Success |
File was attached successfully. |
|
1 |
%Attachment_Failed |
File was not successfully attached. |
|
2 |
%Attachment_Cancelled |
File attachment didn't complete because the operation was canceled by the user. |
|
7 |
%Attachment_DestSystNotFound |
Cannot locate destination system for ftp. |
|
8 |
%Attachment_DestSystFailedLogin |
Unable to login to destination system for ftp. |
|
9 |
%Attachment_FileNotFound |
Cannot locate file. |
|
10 |
%Attachment_DeleteFailed |
Cannot delete file. |
Example
&retcode = DeleteAttachment(URL.BKFTP, ATTACHSYSFILENAME); If (&retcode = %Attachment_Success) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "DeleteAttachment succeeded"); UnHide(ATTACHADD); Hide(ATTACHVIEW); Hide(ATTACHDELETE); ATTACHUSERFILE = ""; ATTACHSYSFILENAME = ""; End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_Failed) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "DeleteAttachment failed"); End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_Cancelled) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "DeleteAttachment cancelled"); End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_FileTransferFailed) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "DeleteAttachment failed: File Transfer did not succeed"); End-If; /* following error message only in PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture */ If (&retcode = %Attachment_NoDiskSpaceAppServ) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "DeleteAttachment failed: No disk space on the app server"); End-If; /* following error message only in PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture */ If (&retcode = %Attachment_NoDiskSpaceWebServ) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "DeleteAttachment failed: No disk space on the web server"); End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_FileExceedsMaxSize) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "DeleteAttachment failed: File exceeds the max size"); End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_DestSystNotFound) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "DeleteAttachment failed: Cannot locate destination system for ftp"); End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_DestSysFailedLogin) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "DeleteAttachment failed: Unable to login into destination system for ftp"); End-If;
See Also
AddAttachment, GetAttachment, PutAttachment, ViewAttachment.
Using File Attachments in Applications

 DeleteEmailAddress
DeleteEmailAddressSyntax
DeleteEmailAddress(Type)
Description
Use the DeleteEmailAddress function to delete the email address associated with the specified type for the current user. You can only have one email address of a specific type for a user.
Note. You can only delete the Primary Email Address if it's the only address. If the email address you want to delete is marked as the primary email address, and it is not the only email address, you must mark another email address as primary before you can delete the email address you want to delete. Use the MarkPrimaryEmailAddress function to set the primary email address.
Parameters
|
Type |
Specify the type that you want to change the email address to. This parameter takes a string value. The valid values are: |
|
Value |
Description |
|
BB |
Blackberry email address |
|
BUS |
Business email address |
|
HOME |
Home email address |
|
OTH |
Other email address |
|
WORK |
Work email address |
Returns
None.
See Also
AddEmailAddress, ChangeEmailAddress, MarkPrimaryEmailAddress.

 DeleteImage
DeleteImageSyntax
DeleteImage(scrollpath, target_row, [recordname.]fieldname)
where scrollpath is:
[SCROLL.level1_recname, level1_row, [SCROLL.level2_recname, level2_row,]] SCROLL.target_recname
Description
Use the DeleteImage function to remove an image associated with a record field.
Note. To update an image field using this function, be sure that PSIMAGEVER field is also on the same record as the image field being updated.
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll area in the component buffer. |
|
target_row |
The row number of the target row. |
|
[recordname .]fieldname |
The name of the field associated with the image file. The field can be on scroll level one, two, or three of the active page. The recordname prefix is required if the function call is in a record definition other than recordname. |
Returns
Returns a Boolean value: True if image was successfully deleted, False otherwise.
Example
&Rslt = DeleteImage(EMPL_PHOTO.EMPLOYEE_PHOTO);
See Also

 DeleteRecord
DeleteRecordSyntax
DeleteRecord(level_zero_recfield)
Description
Use the DeleteRecord function to remove a high-level row of data and all dependent rows in other tables from the database.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the Delete record class method instead.
DeleteRecord deletes the component’s level-zero row from the database, deletes any dependent rows in other tables from the database, and exits the component.
This function, like DeleteRow, initially marks the record or row as needing to be deleted. At save time the row is actually deleted from the database and cleared from the buffer.
This function works only if the PeopleCode is on a level-zero field. It cannot be used from SavePostChange or WorkFlow PeopleCode.
See Also
Delete, Accessing the Data Buffer.
Parameters
|
level_zero_recfield |
A recordname.fieldname reference identifying any field on the level-zero area of the page. |
Returns
Optionally returns a Boolean value indicating whether the deletion was completed successfully.
Example
The following example, which is in SavePreChange PeopleCode on a level-zero field, deletes the high-level row and all dependent rows in other tables if the current page is EMPLOYEE_ID_DELETE.
if %Page = PAGE.EMPLOYEE_ID_DELETE then &success = DeleteRecord(EMPLID); end-if;
See Also

 DeleteRow
DeleteRowSyntax
DeleteRow(scrollpath, target_row)
Where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ]] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can also use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Use the DeleteRow function to delete rows programmatically.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the DeleteRow rowset class method instead.
See DeleteRow.
A call to this function causes the RowDelete event sequence to fire, as if an user had manually deleted a row.
DeleteRow cannot be executed from the same scroll level where the deletion will take place, or from a lower scroll level. Place the PeopleCode in a higher scroll level record.
When DeleteRow is used in a loop, you have to process rows from high to low to achieve the correct results, that is, you must delete from the bottom up rather than from the top down. This is necessary because the rows are renumbered after they are deleted (if you delete row one, row two becomes row one).
See Also
DeleteRow, Accessing the Data Buffer, Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation.
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
target_row |
The row number of the row to delete. |
Returns
Boolean (optional). DeleteRow returns a Boolean value indicating whether the deletion was completed successfully.
Example
In the following example DeleteRow is used in a For loop. The example checks values in each row, then conditionally deletes the row. Note the syntax of the For loop, including the use of the -1 in the Step clause to loop from the highest to lowest values. This ensures that the renumbering of the rows will not affect the loop.
For &L1 = &X1 To 1 Step - 1 &SECTION = FetchValue(AE_STMT_TBL.AE_SECTION, &L1); &STEP = FetchValue(AE_STMT_TBL.AE_STEP, &L1); If None(&SECTION, &STEP) Then DeleteRow(RECORD.AE_STMT_TBL, &L1); End-If; End-For;
See Also
InsertRow, Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation.

 DeleteSQL
DeleteSQLSyntax
DeleteSQL([SQL.]sqlname[, dbtype[, effdt]])
Description
Use the DeleteSQL function to programmatically delete a SQL definition. The SQL definition must have already been created and saved, either using the CreateSQL and StoreSQL functions, or by using Application Designer.
When you create a SQL definition, you must create a base statement before you can create other types of statements, that is, one that has a dbtype as GENERIC and effdt as the null date (or Date(19000101)). If you specify a base (generic) statement to be deleted, all statements as well as the generic statement are deleted.
If you specify a non-generic statement that ends up matching the generic statement, DeleteSQL does not delete anything, and returns False.
You must commit all database changes prior to using this function. This is to avoid locking critical Tools tables and hence freezing all other users. You receive a runtime error message if you try to use this function when there are pending database updates, and your PeopleCode program terminates. You need to commit any database updates prior to using this function. The CommitWork PeopleCode function has been enhanced to allow this.
Parameters
|
sqlname |
Specify the name of a SQL definition. This is either in the form SQL.sqlname or a string value giving the sqlname. |
|
dbtype |
Specify the database type associated with the SQL definition. This parameter takes a string value. If dbtype isn’t specified or is null (""), it set by default to the current database type (the value returned from the %DbName system variable.) Valid values for dbtype are as follows. These values are not case sensitive:
Note. Database platforms are subject to change. |
|
effdt |
Specify the effective date associated with the SQL definition. If effdt isn’t specified, it is set by default to the current as of date, that is, the value returned from the %AsOfDate system variable. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if the delete was successful, False if the specified SQL statement wasn’t found, and terminates with an error message if there was another problem (that is, date in incorrect format, and so on.)
Example
The following code deletes the ABCD_XY SQL definition for the current DBType and as of date:
&RSLT = DeleteSQL(SQL.ABC_XY); If NOT(&RSLT) Then /* SQL not found − do error processing */ End-if;
The following code deletes the ABCD_XY SQL Definition for the current DBType and November 3, 1998:
&RSLT = DeleteSQL(SQL.ABCD_XY, "",Date(19981103));
See Also
CreateSQL, FetchSQL, GetSQL, StoreSQL, CommitWork.

 DeleteSystemPauseTimes
DeleteSystemPauseTimesSyntax
DeleteSystemPauseTimes(StartDay, StartTime, EndDay, EndTime)
Description
Use the DeleteSystemPauseTimes function to delete pause times that occur on your system by adding a row to the system pause times table.
This function is used in the PeopleCode for the Message Monitor. Pause times are set up in the Message Monitor.
Parameters
|
StartDay |
Specify a number from 0-6. The values are: |
|
Value |
Description |
|
0 |
Sunday |
|
1 |
Monday |
|
2 |
Tuesday |
|
3 |
Wednesday |
|
4 |
Thursday |
|
5 |
Friday |
|
6 |
Saturday |
|
StartTime |
Specify a time, in seconds, since midnight. |
|
EndDay |
Specify a number from 0-6. The values are: |
|
Value |
Description |
|
0 |
Sunday |
|
1 |
Monday |
|
2 |
Tuesday |
|
3 |
Wednesday |
|
4 |
Thursday |
|
5 |
Friday |
|
6 |
Saturday |
|
EndTime |
Specify a time, in seconds, since midnight. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if the system pause time specified was deleted, False otherwise.
Example
Component Boolean &spt_changed; /* deleting a system pause time interval; */ If Not DeleteSystemPauseTimes(PSSPTIMES.STARTINGDAY, PSSPTIMES.STARTINGSECOND, PSSPTIMES.ENDINGDAY, PSSPTIMES.ENDINGSECOND) Then Error MsgGetText(117, 15, ""); Else &spt_changed = True; /* to force a save; */ PSSPTIMES.MSGSPTNAME = " "; DoSave(); End-If;
See Also
Using Integration Broker Monitor

 DeQueue
DeQueueSyntax
DeQueue(physical queue ID, task type, task number, agent ID)
Description
Once a task that has been placed in a queue by the EnQueue function and has been completed by the agent, use the DeQueue function to notify the queue server. The queue server removes the task from the queue and subtracts the cost of that task from the agent's workload.
Note. The queue server does not allow a task to be dequeued if the agent who owns that task is not logged on to that particular queue server. PeopleSoft recommends that you only use the DeQueue function in application pages that the MultiChannel Framework Console launches when agents accept or activate assigned tasks.
Parameters
|
physical queue ID |
The physical queue is the internal representation of the logical queue that the agent signs onto and to which the task currently belongs. This is a string value, such as “sales3” or “marketing2.” You retrieve the current physical queue from the query string in the URL of the page launched by the MultiChannel Framework console, using the GetParameter request class method with the value ps_qid. |
|
task type |
Specifies the type of task that an agent completed. It is a string value. The valid values are:
Note. This parameter is valid only for persistent tasks (email and generic). It is not valid for chat or voice tasks. |
|
task number |
Uniquely identifies a particular task. This is the task number returned by the Enqueue function when the system first inserted the task into a queue. This is a string value. You can retrieve the value from the query string in the URL of the application page launched by the MultiChannel Framework console. Use the GetParameter request class method with the value ps_tasknum. |
|
agent ID |
Identifies the agent who processed the task. This is a string value. You can retrieve the value from the query string in the URL of the application page launched by the MultiChannel Framework console. Use the GetParameter request class method with the value ps_agentid. |
Returns
Returns 0 for success. Otherwise, it returns a message number. The message set ID for MultiChannel Framework is 162.
For example, 1302 is returned when an invalid task type or no value is provided.
Example
PSMCFFUNCLIB.MCF_QUEUE.Value = %Request.GetParameter("ps_qid"); PSMCFFUNCLIB.MCF_TASKTYPE.Value = %Request.GetParameter("ps_tasktype"); PSMCFFUNCLIB.MCF_TASKNUM.Value = %Request.GetParameter("ps_tasknum"); PSMCFFUNCLIB.MCF_AGENTID.Value = %Request.GetParameter("ps_agentid"); &nret = DeQueue(PSMCFFUNCLIB.MCF_QUEUE, PSMCFFUNCLIB.MCF_TASKTYPE, PSMCFFUNCLIB.MCF_TASKNUM, PSMCFFUNCLIB.MCF_AGENTID); If &nret = 0 Then MessageBox(0, "", 0, 0, "Successfully dequeued."); End-If
See Also

 DetachAttachment
DetachAttachmentSyntax
DetachAttachment(URLSource, DirAndFileName, UserFile [,PreserveCase])
where URLSource can have one of the following forms:
URL.URLname
Or a string URL, such as
ftp://user:[email protected]/
Note. You cannot specify a different port for an attachment when using an FTP server. You can only use the default port of 21.
Description
Use the DetachAttachment function to enable a user to make a copy of an attached file on their local client system. The file is sent to the browser with appropriate HTTP headers to cause the browser to display a save dialog box to the user.
The detached file may have a different name than the name the user typed in.
Security Considerations
The FileType parameter used with the AddAttachment function is only a suggestion. Specifying it does not enforce specific file types. If you do not want specific file types detached (such as .exe or .bat) you must write PeopleCode to discern the name and file type of the attached file and delete it before detaching it.
Restrictions on Use in PeopleCode Events
DetachAttachment is a "think-time" function, which means that it shouldn’t be used in any of the following PeopleCode events:
SavePreChange
SavePostChange
Workflow
RowSelect
Any PeopleCode event that fires as a result of a ScrollSelect (or one of its relatives) function calls, or a Select (or one of its relatives) rowset class method.
See Think-Time Functions.
File Name Considerations
When the file is transferred, the following characters are replaced with an underscore:
space
semicolon
plus sign
percent sign
ampersand
apostrophe
exclamation point
pound sign
dollar sign
Parameters
|
URLSource |
A reference to a URL. This can be either a URL name, in the form URL.URLName, or a string. |
|
DirAndFileName |
A directory and filename. This is appended to the URLSource to make up the full URL of the file. |
|
PreserveCase |
Specify a Boolean value to indicate whether the case of the directory and file name specified with DirAndFileName are preserved or not; true, preserve the case, false otherwise. The default value is false. |
Note. The URLSource requires "/" slashes. Because the DirAndFileName parameter is appended to the URL, it also requires only "/" slashes. "\" are NOT supported in anyway for either the URLSource the DirAndFileName parameter.
Returns
An integer value. You can check for either the integer or the constant:
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
0 |
%Attachment_Success |
File was attached successfully. |
|
1 |
%Attachment_Failed |
File was not successfully attached. |
|
2 |
%Attachment_Cancelled |
File attachment didn't complete because the operation was canceled by the user. |
|
3 |
%Attachment_FileTransferFailed |
File transfer didn't succeed. |
|
5 |
%Attachment_NoDiskSpaceWebServ |
No disk space on the web server. |
|
7 |
%Attachment_DestSystNotFound |
Cannot locate destination system for ftp. |
|
8 |
%Attachment_DestSystFailedLogin |
Unable to login to destination system for ftp. |
|
9 |
%Attachment_FileNotFound |
Cannot locate file. |
|
10 |
%Attachment_DeleteFailed |
Cannot delete file. |
Example
&retcode = DetachAttachment(URL.MYFTP, ATTACHSYSFILENAME, ATTACHUSERFILE); If (&retcode = %Attachment_Failed) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "DetachAttachment failed"); End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_Cancelled) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "DetachAttachment cancelled"); End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_FileTransferFailed) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "DetachAttachment failed: File Transfer did not succeed"); End-If; /* following error message only in PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture */ If (&retcode = %Attachment_NoDiskSpaceAppServ) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "DetachAttachment failed: No disk space on the app server"); End-If; /* following error message only in PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture */ If (&retcode = %Attachment_NoDiskSpaceWebServ) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "DetachAttachment failed: No disk space on the web server"); End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_FileExceedsMaxSize) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "DetachAttachment failed: File exceeds the max size"); End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_DestSystNotFound) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "DetachAttachment failed: Cannot locate destination system for ftp"); End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_DestSysFailedLogin) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "DetachAttachment failed: Unable to login into destination system for ftp"); End-If;
In the following example, using the file object, a file is written on the application server. Because the absolute path isn't specified, the file is written to PS_SERVDIR/files directory.
The function PutAttachment takes the file from PS_SERVDIR/files directory and puts it on the ftp server specified in URL.GRADEBOOK.
The DetachAttachment function downloads the file into the user's machine.
/* Data buffer */ Component Rowset &Level0, &Students_Hdr, &Student_Grade; Component Row &Level0_Row; /* standalone rowset - populate from LAM_CLASS_ACTV */ Component Rowset &Class_Activity; Component number &Class_Act_No; Local File &Export_File; Local string &Export_Line; DoSaveNow(); &File_Name = %OperatorId | "_" | String(CLASS_SCTN_SCTY.STRM) | "_" | String(CLASS_SCTN_SCTY.CLASS_NBR) | ".txt"; &Export_File = GetFile(&File_Name, "W"); If &Export_File.IsOpen Then &Export_Line = "Last,First,Emplid,"; For &i = 1 To &Class_Activity.ActiveRowCount &Export_Line = &Export_Line | &Class_Activity(&i).LAM_CLASS_ACTV.DESCRSHORT.Value | ","; End-For; &Export_File.WriteLine(&Export_Line); For &i = 1 To &Students_Hdr.ActiveRowCount &Export_Line = &Students_Hdr(&i).GetRecord(Record.PERSONAL_DTA_VW).GetField(Field.NAME).Value | ","; &Export_Line = &Export_Line | &Students_Hdr(&i).STDNT_GRADE_HDR.EMPLID.Value | ","; &Student_Grade = &Level0_Row.GetRowset(Scroll.STDNT_GRADE_HDR)(&i).GetRowset(Scroll.STDNT_GRADE_DTL); For &j = 1 To &Student_Grade.ActiveRowCount &Export_Line = &Export_Line | String(&Student_Grade(&j).STDNT_GRADE_DTL.STUDENT_GRADE.Value) | ","; End-For; &Export_File.WriteLine(&Export_Line); End-For; &Export_File.Close(); End-If; &Put_File_Name = "files/" | &File_Name; &ret = PutAttachment(URL.GRADEBOOK, &File_Name, &Put_File_Name, "PS_SERVDIR"); &ret = DetachAttachment(GetURL(URL.GRADEBOOK), &File_Name, &File_Name);

 DisableMenuItem
DisableMenuItemSyntax
DisableMenuItem(BARNAME.menubar_name, ITEMNAME.menuitem_name)
Description
Use the DisableMenuItem function to disable (make unavailable) the specified menu item. To apply this function to a pop-up menu, use the PrePopup Event of the field with which the pop-up menu is associated.
If you’re using this function with a pop-up menu associated with a page (not a field), the earliest event you can use is the PrePopup event for the first "real" field on the page (that is, the first field listed in the Order view of the page in PeopleSoft Application Designer.)
Restrictions on Use With a Component Interface
This function is ignored (has no effect) when used by a PeopleCode program that’s been called by a Component Interface.
Parameters
|
menubar_name |
Name of the menu bar that owns the menu item, or, in the case of pop-up menus, the name of the pop-up menu that owns the menu item. |
|
menuitem_name |
Name of the menu item. |
Returns
None.
Example
DisableMenuItem(BARNAME.MYPOPUP1, ITEMNAME.DO_JOB_TRANSFER);
See Also

 DiscardRow
DiscardRowSyntax
DiscardRow()
Description
Use the DiscardRow function to prevent a row from being added to a page scroll during Row Select processing. This function is valid only in RowSelect PeopleCode. When DiscardRow is called during RowSelect processing, the current row is skipped (not added to the scroll). Processing then continues on the next row, unless the StopFetching function has also been called, in which case no more rows are added to the page.
If you try to discard a row and it's the only row in the scroll, the row is not discarded. You will still have one blank row in your scroll.
DiscardRow has the same functionality as the Warning function in the RowSelect event. The anomalous behavior of Warning is supported for compatibility with previous releases of PeopleTools.
Note. RowSelect processing is used infrequently, because it is more efficient to filter out rows of data using a search view or an effective-dated record before the rows are selected into the component buffer from the database server.
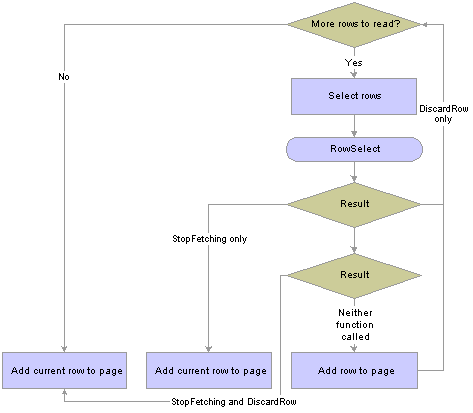
RowSelect Processing Logic
Parameters
None.
Returns
None.
See Also

 DoCancel
DoCancelSyntax
DoCancel( )
Description
Use the DoCancel function to cancel the current page.
In the Page Applet, the DoCancel function terminates the current component and returns the user to the search dialog box.
In the Menu Applet, the DoCancel function terminates the current component and returns the user to the current menu with no component active.
DoCancel terminates any PeopleCode programs executing prior to a save action. It does not stop processing of PeopleCode in SaveEdit, SavePreChange, and SavePostChange events.
Returns
None.
See Also
DoSave, DoSaveNow, DoModal, EndModal, WinEscape.

 DoModal
DoModalSyntax
DoModal(PAGE.pagename, title, xpos, ypos, [level, scrollpath, target_row])
where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ]] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can also use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Use the DoModal function to display a secondary page. Secondary pages are modal, meaning that the user must dismiss the secondary page before continuing work in the page from which the secondary page was called.
If you call DoModal without specifying a level number or any record parameters, the function uses the current context as the parent.
You can alternately specify a secondary page in a command push button definition without using PeopleCode. This may be preferable for performance reasons, especially with PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture.
DoModal can display on a single page. To display an entire component modally, use DoModalComponent.
Any variable declared as a Component variable will still be defined after using a DoModal function.
Restrictions on Use in PeopleCode Events
Control does not return to the line after DoModal until after the user has dismissed the secondary page. This interruption of processing makes DoModal a “think-time” function, which means that it shouldn’t be used in any of the following PeopleCode events:
SavePreChange.
SavePostChange.
Workflow.
RowSelect.
Any PeopleCode event that fires as a result of a ScrollSelect (or one of its relatives) function calls, or a Select (or one of its relatives) Rowset class method.
In addition, you can't use this function in the SearchInit event.
See Think-Time Functions.
Restrictions on Use With a Component Interface
This function is ignored (has no effect) when used by a PeopleCode program that’s been called by a Component Interface.
Considerations Using Exceptions and the DoModal Function
Using the DoModal function inside a try block not catch PeopleCode exceptions thrown in the new component. Starting a new component starts a brand new PeopleCode evaluation context. Catches are only caught for exceptions thrown within the current component.
In the following code example, the catch statement only catches exceptions thrown in the code prior to the DoModal, but not any exceptions that are thrown within the new component.
/* Set up transaction */ If %CompIntfcName = "" Then try &oTrans = &g_ERMS_TransactionCollection.GetTransactionByName(RB_EM_WRK.DESCR); &sSearchPage = &oTrans.SearchPage; &sSearchRecord = &oTrans.SearchRecord; &sSearchTitle = &oTrans.GetSearchPageTitle(); If Not All(&sSearchPage, &sSearchRecord, &sSearchTitle) Then Error (MsgGetText(17834, 8081, "Message Not Found")); End-If; &c_ERMS_SearchTransaction = &oTrans; /* Attempt to transfer to hidden search page with configurable filter */ &nModalReturn = DoModal(@("Page." | &sSearchPage), &sSearchTitle, - 1, - 1); catch Exception &e Error (MsgGetText(17834, 8082, "Message Not Found")); end-try;
Parameters
|
pagename |
The name of the secondary page. |
|
title |
The text that displays in the caption of the secondary page. |
|
xpos |
The pixel coordinates of the top left corner of the secondary page, offset from the top left corner of the parent page (the default of -1, -1 means centered). |
|
ypos |
The pixel coordinates of the top right corner of the secondary page, offset from the top right corner of the parent page (the default of -1, -1 means centered). |
|
level |
Specifies the level of the scroll level on the parent page that contains the row corresponding to level 0 on the secondary page. |
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
target_row |
The row number of the row in the parent page corresponding to the level 0 row in the secondary page. |
Returns
Returns a number that indicates how the secondary page was terminated. A secondary page can be terminated by the user clicking a built-in OK or Cancel button, or by a call to the EndModal function in a PeopleCode program. In either case, the return value of DoModal is one of the following:
1 if the user clicked OK in the secondary page, or if 1 was passed in the EndModal function call that terminated the secondary page.
0 if the user clicked Cancel in the secondary page, or if 0 was passed in the EndModal function call that terminated the secondary page.
Example
DoModal(PAGE.EDUCATION_DTL, MsgGetText(1000, 167, "Education Details - %1", EDUCATN.DEGREE), - 1, - 1, 1, RECORD.EDUCATN, CurrentRowNumber());
See Also
EndModal, IsModal, DoModalComponent.
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation

 DoModalComponent
DoModalComponentSyntax
DoModalComponent(MENUNAME.menuname, BARNAME.barname, ITEMNAME.menuitem_name, PAGE.component_item_name, action, RECORD.shared_record_name [, keylist])
where keylist is a list of field references in the form:
[recordname.]field1 [, [recordname.]field2]. . .
Or
&RecordObject1 [, &RecordObject2]. . .
Description
Use the DoModalComponent function to launch a modal component. The modal component launches from within an originating component. After the modal component displays, the user can’t proceed with changes to the originating component until either accepting or canceling the modal component.
Modal components can be displayed in any of the following action modes: Add, Update/Display, Update/Display All, Correction. A modal component can be launched from any component, including another modal component. You can use DoModalComponent from a secondary page.
The originating component and the modal component share data, including search keys, using a Shared Work Record or the values in the fieldlist parameter. If valid search keys are provided in the shared work record and populated with valid values before launching the modal component, the search is conducted using the provided search key values. If the fieldlist parameter isn't used and no search keys are provided, or if search key fields contain invalid values, the user accesses the modal component using a search dialog box.
Note. The user may see a different title for a search page if they enter the search page using this function versus from the regular navigation.
In the component_item_name parameter, make sure to pass the component item name for the page, not the page name. The component item name is specified in the Component Definition, in the Item Name column on the row corresponding to the specific page, as shown here:
Component Item Name parameter
Shared Work Records
The originating component and the modal component share fields in a Derived/Work record called a shared work record. Shared fields from this record must be placed at level zero of both the originating component and the modal component.
You can use the shared fields to:
Pass values that are assigned to the search keys in the modal component search record. If these fields are missing or not valid, the search dialog box appears, enabling the user to enter search keys.
Optionally pass other values from the originating component to the modal component.
Pass values back from the modal component to the originating component for processing.
To do this, you have to write PeopleCode that:
Assigns values to fields in the shared work record in the originating page at some point before the modal transfer takes place.
Accesses and changes the values, if necessary, in the modal component.
Accesses the values from the shared work record from the originating component after the modal component is dismissed.
Restrictions on Use With a Component Interface
This function is ignored (has no effect) when used by a PeopleCode program that’s been called by a Component Interface.
Restrictions on Use With SearchInit Event
You can't use this function in a SearchInit PeopleCode program.
Considerations Using Exceptions and the DoModalComponent Function
Using the DoModalComponent function inside a try block not catch PeopleCode exceptions thrown in the new component. Starting a new component starts a brand new PeopleCode evaluation context. Catches are only caught for exceptions thrown within the current component.
In the following code example, the catch statement only catches exceptions thrown in the code prior to using a DoModal function, but not any exceptions that are thrown within the new component.
/* Set up transaction */ If %CompIntfcName = "" Then try &oTrans = &g_ERMS_TransactionCollection.GetTransactionByName(RB_EM_WRK.DESCR); &sSearchPage = &oTrans.SearchPage; &sSearchRecord = &oTrans.SearchRecord; &sSearchTitle = &oTrans.GetSearchPageTitle(); If Not All(&sSearchPage, &sSearchRecord, &sSearchTitle) Then Error (MsgGetText(17834, 8081, "Message Not Found")); End-If; &c_ERMS_SearchTransaction = &oTrans; /* Attempt to transfer to hidden search page with configurable filter */ &nModalReturn = DoModal(@("Page." | &sSearchPage), &sSearchTitle, - 1, - 1); catch Exception &e Error (MsgGetText(17834, 8082, "Message Not Found")); end-try;
Parameters
|
menuname |
Name of the menu through which the modal component is accessed. |
|
barname |
Name of the menu bar through which the modal component is accessed. |
|
menuitem_name |
Name of the menu item through which the modal component is accessed. |
|
component_item_name |
The component item name of the page to be displayed on top of the modal component when it displays. The component item name is specified in the component definition. |
|
action |
String representing the action mode in which to start up the component. You can use either a character value (passed in as a string) or a constant: |
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
A |
%Action_Add |
Add |
|
U |
%Action_UpdateDisplay |
Update/Display |
|
L |
%Action_UpdateDisplayAll |
Update/Display All |
|
C |
%Action_Correction |
Correction |
|
E |
%Action_DataEntry |
Data Entry |
|
P |
%Action_Prompt |
Prompt |
|
|
If only one action mode is allowed for the component, that action mode is used. If more than one action mode is allowed, the user can select which mode to come up in. |
|
shared_record_name |
The record name of the shared work record (preceded by the reserved word Record). This record must include:
|
|
keylist |
An optional list of field specifications used to select a unique row at level zero in the page you are transferring to, by matching keys in the page you are transferring from. It can also be an already instantiated record object. If a record object is specified, any field of that record object that is also a field of the search record for the destination component is added to keylist. The keys in fieldlist must uniquely identify a row in the "to" page search record. If a unique row is not identified, the search dialog box appears. If the keylist parameter is not supplied then the destination components' search key must be found as part of the source component's level 0 record buffer. |
Returns
Returns a Boolean that indicates how the secondary page was terminated. A secondary page can be terminated by the user clicking a built-in OK or Cancel button, or by a call to the EndModalComponent function in a PeopleCode program. In either case, the return value of DoModalComponent is one of the following:
True if the user clicked OK in the secondary page, or if 1 was passed in the EndModal function call that terminated the secondary page.
False if the user clicked Cancel in the secondary page, or if 0 was passed in the EndModal function call that terminated the secondary page.
Example
The following example shows how to structure a DoModalComponent function call:
DoModalComponent(MENUNAME.MAINTAIN_ITEMS_FOR_INVENTORY, BARNAME.USE_A, ITEMNAME.ITEM_DEFINITION, COMPONENT.ESTABLISH_AN_ITEM, "C", RECORD.NEW7_WRK);
Supporting PeopleCode is required if you must assign values to fields in the shared work record or access those values, either from the originating component, or from the modal component.
See Also
IsModalComponent, Transfer, TransferPage, EndModalComponent.

 DoModalPanelGroup
DoModalPanelGroup
Syntax
DoModalPanelGroup(MENUNAME.menuname, BARNAME.barname, ITEMNAME.menuitem_name, PANEL.panel_group_item_name, action, RECORD.shared_record_name)
Description
Use the DoModalPanelGroup function to launch a modal component.
Note. The DoModalPanelGroup function is supported for compatibility with previous releases of PeopleTools. Future applications should use DoModalComponent instead.
See Also

 DoSave
DoSaveSyntax
DoSave()
Description
Use the DoSave function to save the current page. DoSave defers processing to the end of the current PeopleCode program event, as distinct from DoSaveNow, which causes save processing (including SaveEdit, SavePreChange, SavePostChange, and Workflow PeopleCode) to be executed immediately.
DoSave can be used only in FieldEdit, FieldChange, or MenuItemSelected PeopleCode.
Parameters
None.
Returns
None.
Example
The following example sets up a key list with AddKeyListItem, saves the current page, and then transfers the user to a page named PAGE_2.
ClearKeyListItem( ); AddKeyListItem(OPRID, OPRID); AddKeyListItem(REQUEST_ID, REQUEST_ID); SetNextPage("PAGE_2"); DoSave( ); TransferPage( );
See Also
DoCancel, DoSaveNow, TransferPage, AddKeyListItem.

 DoSaveNow
DoSaveNowSyntax
DoSaveNow()
Description
The DoSaveNow function is designed primarily for use with remote calls. It enables a PeopleCode program to save page data to the database before running a remote process (most frequently a COBOL process) that will access the database directly. It is generally necessary to call DoSaveNow before calling the RemoteCall function.
DoSaveNow causes the current page to be saved immediately. Save processing (including SaveEdit, SavePreChange, SavePostChange, and Workflow PeopleCode) is executed before continuing execution of the program where DoSaveNow is called. DoSaveNow differs from the DoSave function in that DoSave defers saving the component until after any running PeopleCode is completed.
DoSaveNow can only be called from a FieldEdit or FieldChange event.
If you call DoSaveNow and there are no changes to save, save processing is skipped entirely. You can call SetComponentChanged right before you call DoSaveNow. The SetComponentChanged function makes the Component Processor think there are changes and so will force full save processing.
See RemoteCall, DoSave.
Errors in DoSaveNow Save Processing
DoSaveNow initiates save processing. It handles errors that occur during save processing as follows:
If save processing encounters a SaveEdit error, it displays the appropriate message box. DoSaveNow immediately exits from the originating FieldChange or FieldEdit program. The user can correct the error and continue.
If save processing encounters a fatal error, it displays the appropriate fatal error. DoSaveNow handles the error by immediately exiting from the originating FieldChange or FieldEdit program. The user must then cancel the page.
If save processing completes with no errors, PeopleCode execution continues on the line after the DoSaveNow call in FieldChange or FieldEdit.
Restrictions on Use of DoSaveNow
The following restrictions apply:
DoSaveNow can be executed only from a FieldEdit or FieldChange event.
DoSaveNow is only allowed prior to the first CallAppEngine function in a FieldChange event, but not afterward.
Deferred operations should not be called before the DoSaveNow. Deferred operations include the DoSave, TransferPage, SetCursorPos, and EndModal functions.
Components that use DoSaveNow must not use the DoCancel, Transfer, TransferPage, or WinEscape functions in PeopleCode attached to save action events (SaveEdit, SavePreChange, and SavePostChange), because these functions terminate the component, which would cause the program from which DoSaveNow was called to terminate prematurely.
Note. You should be aware that DoSaveNow may result in unpredictable behavior if PeopleCode in save events deletes rows or inserts rows into scrolls. PeopleCode that runs after DoSaveNow must be designed around the possibility that rows were deleted or inserted (which causes row number assignments to change). Modifying data on a deleted row may cause it to become “undeleted.”
Parameters
None.
Returns
None.
Example
The following example calls DoSaveNow to save the component prior to running a remote process in the remote_depletion declared function:
Declare Function remote_depletion PeopleCode FUNCLIB_ININTFC.RUN_DEPLETION FieldFormula; /* Express Issue Page - run Depletion job through RemoteCall() */ If %Component = COMPONENT.EXPRESS_ISSUE_INV Then DoSaveNow(); &BUSINESS_UNIT = FetchValue(SHIP_HDR_INV.BUSINESS_UNIT, 1); &SHIP_OPTION = "S"; &SHIP_ID = FetchValue(SHIP_HDR_INV.SHIP_ID, 1); remote_depletion(&BUSINESS_UNIT, &SHIP_OPTION, &SHIP_ID, &PROGRAM_STATUS); End-If

 EnableMenuItem
EnableMenuItemSyntax
EnableMenuItem(BARNAME.menubar_name, ITEMNAME.menuitem_name)
Description
Use the EnableMenuItem function to enable (make available for selection) the specified menu item. To apply this function to a pop-up menu, use the PrePopup Event of the field with which the pop-up menu is associated.
If you’re using this function with a pop-up menu associated with a page (not a field), the earliest event you can use is the PrePopup event for the first "real" field on the page (that is, the first field listed in the Order view of the page in PeopleSoft Application Designer.)
Restrictions on Use With a Component Interface
This function is ignored (has no effect) when used by a PeopleCode program that’s been called by a Component Interface.
Parameters
|
menubar_name |
Name of the menu bar that owns the menu item, or, in the case of pop-up menus, the name of the pop-up menu that owns the menu item. |
|
menuitem_name |
Name of the menu item. |
Returns
None.
Example
EnableMenuItem(BARNAME.MYPOPUP1, ITEMNAME.DO_JOB_TRANSFER);
See Also
DisableMenuItem, HideMenuItem.

 EncodeURL
EncodeURLSyntax
EncodeURL(URLString)
Description
Use the EncodeURL function to apply URL encoding rules, including escape characters, to the string specified by URLString. The method used to encode the URLString is the standard defined by W3C. This function returns a string that contains the encoded URL. All characters outside the Unicode Basic Latin block (U+0020 — U+007F) are encoded, with the exception of the characters in the table below which are not encoded as they may represent valid components of URL or protocol syntax. If you need to encode such characters, use the EncodeURLForQueryString function.
The following table lists the punctuation characters in the Unicode Basic Latin block that are not encoded by the URLEncode function.
|
Punctuation Character |
Description |
|
Glyph |
Unicode Character Name |
|
! |
Exclamation mark |
|
# |
Number sign |
|
$ |
Dollar sign |
|
& |
Ampersand |
|
( |
Left parenthesis |
|
) |
Right parenthesis |
|
* |
Asterisk |
|
+ |
Plus sign |
|
, |
Coma |
|
- |
Hyphen, minus |
|
. |
Full stop, period |
|
/ |
Solidus, slash |
|
: |
Colon |
|
; |
Semi-colon |
|
= |
Equals sign |
|
? |
Question mark |
|
_ |
Underscore |
Parameters
|
URLString |
Specify the string you want encoded. This parameter takes a string value. |
Returns
An encoded string.
Example
The example below returns the following encoded URL:
http://corp.office.com/human%20resources/benefits/401kchange_home.htm?FirstName=Gunter&LastName=D%c3%9crst &MYSTRING = EncodeURL("http://corp.office.com/hr/benefits/401k/401k_home.htm");
See Also
EncodeURLForQueryString, Unencode.
Internet Script Classes (iScript)

 EncodeURLForQueryString
EncodeURLForQueryStringSyntax
EncodeURLForQueryString(URLString)
Description
Use the EncodeURLForQueryString function to encode URLString for use in a query string parameter in an URL. All characters outside the Unicode Basic Latin block (U+0020 — U+007F) are encoded, with the exception of the characters in the table below which are not encoded as they are typically valid in a query string.
If the link is constructed in a page, and the value is a link field, you should not call EncodeURL to encode the entire URL, as the PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture does this for you. You still need to unencode the parameter value when you retrieve it, however.
Always encode each field value being added directly to query strings using EncodeURLForQueryString.
The following table lists punctuation characters in the Unicode Basic Latin block that are not encoded by the URLEncodeForQueryString function.
|
Punctuation Character |
Description |
|
( |
Left parenthesis |
|
) |
Right parenthesis |
|
* |
Asterisk |
|
- |
Hyphen, minus |
|
. |
Full stop, period |
|
_ |
Underscore, low line |
Parameters
|
URLString |
Specify the string you want encoded. This parameter takes a string value. |
Returns
An encoded URL string.
Example
In an Internet Script, to construct an anchor with a URL in a query string parameter, do the following:
&url = "http://host/psp/ps/EMPLOYEE/HRMS/s/EMPL_INFO.FieldFormula.IScript_EMPL_INFO?emplid=1111&mkt=usa" &href = %Request.RequestURI | "?" | %Request.QueryString | "&myurl=" | EncodeURLForQueryString(&url); %Response.WriteLine("<a href= " | EncodeURL(&href) | ">My Link</a>");
The following uses a generic method to find, then encode, the URL, for the external link:
&StartPos = Find("?", &URL, 1); &CPColl = &Portal.ContentProviders; &strHREF = EncodeURLForQueryString(Substring(&URL, &StartPos + 1, Len(&URL) -&StartPos)); &LINK = &Portal.GetQualifiedURL("PortalServlet", "PortalOriginalURL=" | &CPColl.ItembyName(&CP_NAME).URI | "?" | &strHREF);
See Also
EncodeURL, Unencode, EscapeHTML, EscapeJavascriptString, EscapeWML.
Internet Script Classes (iScript)

 Encrypt
EncryptSyntax
Encrypt(KeyString, ClearTextString)
Description
Use the Encrypt function to encrypt a string. This function is generally used with merchant passwords.
The value you use for KeyString must be the same for Decrypt and Encrypt.
Size Considerations with Encrypt
The Encrypt function uses 56 bit DES. The size of the output string is grown to the nearest multiple of 8 bytes, encrypted (which doesn't modify the size), then encoded, which grows the resulting size to the next multiple of 3, then the system multiplies the size by 4/3.
For example, a 20 character field is 40 bytes long (unicode), which is an even multiple of 8. After it is encrypted, it is rounded up to 42 bytes (the next multiple of 3), then multiplied by 4/3 to get 56 bytes.
Parameters
|
KeyString |
Specify the key used for encrypting the string. You can specify a NULL value for this parameter, that is, two quotation marks with no blank space between them (""). |
|
ClearTextString |
Specify the string you want encrypted. |
Returns
An encrypted string.
Example
The following encrypts a field if it contains a value. It also removes any blanks either preceding or trailing the value.
If All(PSCNFMRCHTOKEN.WRKTOKEN) Then CMPAUTHTOKEN = Encrypt("", RTrim(LTrim(PSCNFMRCHTOKEN.WRKTOKEN))); End-If;
See Also
Understanding PeopleSoft Security

 EncryptNodePswd
EncryptNodePswdSyntax
EncryptNodePswd(Password)
Description
Use the EncryptNodePswd function to encrypt an Integration Broker node password.
Note. This function is generally used with Integration Broker node password encryption. This function should not be used casually, as once you encrypt your node password, there is no decrypt PeopleCode method.
Parameters
|
Password |
Specify the Integration Broker node password that you want encrypted, as a string. |
Returns
An encrypted password as a string.
Example
In the following example, the password is stored in the database in an encrypted form instead of as plain text:
PSMSGNODEDEFN.IBPASSWORD = EncryptNodePswd(RTrim(LTrim(PSNODE_WRK.WRKPASSWORD)));
See Also

 EndMessage
EndMessageSyntax
EndMessage(message, messagebox_title)
Description
Note. The EndMessage function is obsolete and is supported only for backward compatibility. The MessageBox function, which can now be used to display informational messages in any PeopleCode event, should be used instead.
Use the EndMessage function to display a message at the end of a transaction, at the time of the database COMMIT. This function can be used only in SavePostChange PeopleCode.
When an EndMessage function executes, PeopleTools:
Verifies that the function is in SavePostChange; if it is not, an error occurs and the function terminates.
Displays the message.
Terminates the SavePostChange PeopleCode program.
Because it terminates the SavePostChange program, EndMessage is always be the last statement executed in the program on the specific field and row where the EndMessage is called. For this reason, you must write the SavePostChange program so that all necessary processing takes place before the EndMessage statement. PeopleCode programs on other fields and rows execute as usual.
Parameters
|
message |
A string that must be enclosed in quotes containing the message text you want displayed. |
|
messagebox_title |
A string that must be enclosed in quotes containing the title of the message. It appears in the message box title bar. |
Returns
None.
Example
The following example is from SavePostChange event PeopleCode. It checks to see whether a condition is true, and if so, it displays a message and terminates the SavePostChange program. If the condition is false, then processing continues in the Else clause:
If BUSINESS_UNIT = BUS_UNIT_WRK.DEFAULT_SETID Then EndMessage(MsgGet(20000, 12, "Message not found in Message Catalog")," "); Else /* any other SavePostChange processing in Else clause */
See Also

 EndModal
EndModalSyntax
EndModal(returnvalue)
Description
Use the EndModal function to close a currently open secondary page. It is required only for secondary pages that do not have OK and Cancel buttons. If the secondary page has OK and Cancel buttons, then the function for exiting the page is built in and no PeopleCode is required.
Restrictions on Use With a Component Interface
This function is ignored (has no effect) when used by a PeopleCode program that’s been called by a Component Interface.
Parameters
|
returnvalue |
A Number value that determines whether the secondary page data is copied back to the parent page. A positive value runs SaveEdit PeopleCode and copies the data (this is the same as clicking the OK button). A value of zero skips SaveEdit and discards buffer changes made in the secondary page (this is the same as clicking the Cancel button). This value becomes the return value of the DoModal function that started the secondary page, and it can be tested after the secondary page is closed. |
Returns
None.
Example
The following statement acts as an OK button:
EndModal(1);
The following statement acts as a Cancel button:
EndModal(0);
See Also

 EndModalComponent
EndModalComponentSyntax
EndModalComponent(ReturnValue)
Description
Use the EndModalComponent function to close a currently open secondary component. You could use this for creating your own links to exit a modal component.
Restrictions on Use With a Component Interface
This function can’t be used by a PeopleCode program that’s been called by a Component Interface, and is ignored.
Parameters
|
ReturnValue |
A Number value that determines whether the modal component data is saved and copied back to the parent page. A positive value saves the data in the component to the database, including all save processing and PeopleCode (this is the same as pressing the OK button). It also copies the data in the shared work record, if any, back to the primary component. A value of zero skips save processing discards buffer changes made in the modal component (this is the same as pressing the Cancel button). |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if a non-zero value was used, False if zero was used.
Example
EndModalComponent(0); /* cancels the component without saving */ EndModalComponent(1); /* saves and closes the component */
See Also
DoModalComponent, EndModal, IsModal.

 EnQueue
EnQueueSyntax
EnQueue(logical queue, task type, Relative URL, Language_Code [,subject][, agent ID][, overflow timeout][, escalation timeout][, cost][, priority][, skill level])
Description
Use the EnQueue function to assign a task to one of the active, physical queues belonging to the specified logical queue. The physical queue to which the system assigns the task is chosen randomly to balance load across the queues.
Note. PeopleSoft recommends that you always follow the EnQueue function with the NotifyQ function.
See NotifyQ.
Parameters
|
logical queue ID |
Specifies the logical queue in which the task should be queued. It is a string value. The logical queue ID is a case-sensitive value. The case used in the EnQueue function must exactly match the case used when creating the logical queue ID with the MultiChannel Framework administration pages. |
|
task type |
Specifies the type of task to be inserted. It is a string value. The valid values are:
Note. This parameter does not apply to voice or chat. Chat tasks are enqueued using the InitChat function. Voice queueing is managed by PeopleSoft CTI. |
|
Relative URL |
The system uses this relative URL to generate the URL of the appropriate application page for the MultiChannel Framework console to launch when an agent accepts this task. The application page should contain the logic to enable the agent to resolve the task and either forward the task using the Forward function or dequeue the task using the DeQueue function. |
|
Language_Code |
This is the language code associated with the task to be enqueued. It is a string value that must exist in the PeopleSoft language table. The queue server only assigns this task to an agent whose list of languages contains this value. For example if an email to be enqueued is written in English, the language code would be “ENG”, and this email would only be assigned to agents whose language list contains English. |
|
subject |
This is an optional parameter. It is a string value describing the purpose of the request. This value appears on the agent's console when the system assigns the task. |
|
agent ID |
Specifies the assigned agent. This is an optional, string parameter. If specified, the system holds the task until the specified agent is available to take this task. If this parameter is left blank, the queue server assigns it to the first available agent. Note. For better performance, PeopleSoft recommends not specifying the target agent as this has a processing overhead for the queue servers and does not allow the system to balance workload across all available agents. |
|
overflow timeout |
This is an optional parameter. It is an integer value expressing the overflow timeout in minutes. The overflow timeout is the time period within which a queue server has to find an agent who accepts the task (clicks on the flashing icon on the MultiChannel console). If the task is not accepted within this time, the task is removed from the queue and placed in the MultiChannel overflow table. If you do not specify a value, the system uses the default value specified for that task type in the Task Configuration page. |
|
escalation timeout |
This is an optional parameter. It is an integer value expressing the escalation timeout in minutes. The escalation timeout is the time period within which a task must be completed by the agent and closed with DeQueue. If the task is not closed within this time, the task is removed from the queue and from the agent's accepted task list, which means the task becomes unassigned. Then the task is placed in the MultiChannel Framework escalation table. If no value is specified, the system uses the default specified for that task type in the Task Configuration pages. |
|
cost |
This is an optional parameter. It is an integer value measuring the workload each task places on an agent. The cost of a task is an estimate of the tasks's expected complexity and of the time required to resolve the task. The minimum value is 0, and there is no maximum value. The cost of a task is added to an agent's workload after accepting a task on the MultiChannel Framework console. A task can't be assigned to an agent if the difference between the current workload and the maximum workload defined for that agent on the Agent configuration page is less than the cost of this task. If you do not specify a value, the system uses the default value specified for that task in the Task Configuration pages. Note. If the required skill level or cost submitted exceeds the highest skill level or maximum workload of any of the agents on that queue, the task cannot be assigned. |
|
priority |
This is an optional parameter. It is an integer value expressing the priority level of the request. The minimum value is 0 and there is no maximum value. A higher value means a higher priority. Tasks are ordered on a physical queue based on their assigned priority. That is, the system assigns a task of a higher priority before it assigns a task of a lower priority. If no value is specified, the system uses the default value specified for that task type in the Task Configuration page. When tasks have the same priority, the system orders the tasks according to the time they were created. For example, suppose the following tasks exist: Priority 2 created at 11:15 AM and Priority 2 created at 11:16 AM. In this case, the system assigns the task created at 11:15 AM before the task created at 11:16 AM. |
|
skill level |
This is an optional parameter. It is an integer value expressing the minimum skill level required of the agent to whom the system routes the request. You set an agent's skill level in the Agent configuration page. The queue server assigns this task type to an available agent on that queue whose lowest skill level is greater than or equal to the skill level required by the task. If no value is specified, the system uses the default value specified for that task type in the Task Configuration page. Note. If the required skill level or cost submitted exceeds the highest skill level or maximum workload of any of the agents on that queue, the task cannot be assigned. |
Returns
If the insert was successful, the function returns a task number in the form of a string.
If unsuccessful, it returns a message number. The message set ID for MultiChannel Framework is 162.
For example, 1302 is returned when an invalid task type or no value is provided.
Example
&PortalValue = Portal.EMPLOYEE; &NodeValue = Node.QE_LOCAL; /*If running in Application Engine, this code assumes CONTENT URI has been set in node defn admin page*/ &MyCompURL = GenerateComponentContentRelURL(&PortalValue, &NodeValue, MenuName.PT_MCF, "GBL", Component.MCFEM_DEMOERMS_CMP, Page.MCFEM_ERMSMN, ""); &MyCompURL = &MyCompURL | "&ps_emailid=" | &emailid; /*Query string dependent on component. Our demo comonent just needs email id*/ rem The URL to be passed will look something like; rem "/psc/ps/EMPLOYEE/QE_LOCAL/c/PT_MCF.MCF_DEMOERMS_CMP.GBL?Page=MCFEM_ERMSMN"; &strtasknum = EnQueue(&queueID, "email", &MyCompURL, &langcode, &subject, "QEDMO", 15, 60, &cost, &priority, &minskill);
See Also

 Error
ErrorSyntax
Error str
Description
Use the Error function in FieldEdit or SaveEdit PeopleCode to stop processing and display an error message. It is distinct from Warning, which displays a warning message, but does not stop processing. Error is also used in RowDelete and RowSelect PeopleCode events.
Warning! The behavior of the Error function in the RowSelect event is very different from its normal behavior.
See the Error in RowSelect section for more details.
The text of the error message (the str parameter), should always be stored in the Message Catalog and retrieved using the MsgGet or MsgGetText functions. This makes it much easier for the text to be translated, and it also enables you to include more detailed Explain text about the error.
When Error executes in a PeopleCode program, the program terminates immediately and no statements after the Error are executed. In other respects behavior of Error differs, depending on which PeopleCode event the function occurs in.
Errors in FieldEdit and SaveEdit
The primary use of Error is in FieldEdit and SaveEdit PeopleCode:
In FieldEdit, Error stops processing, displays a message, and highlights the relevant field.
In SaveEdit, Error stops all save processing and displays a message, but does not highlight any field. You can move the cursor to a specific field using the SetCursorPos function, but be sure to call SetCursorPos before calling Error, otherwise Error stops processing before SetCursorPos is called. Note that an Error on any field in SaveEdit stops all save processing, and no page data is saved to the database.
Errors in RowDelete
When the user attempts to delete a row of data, the system first prompts for confirmation. If the user confirms, the RowDelete event fires. An Error in the RowDelete event displays a message and prevents the row from being deleted.
Error in RowSelect
The behavior of Error in RowSelect is totally anomalous, and is supported only for backward compatibility. It is used to filter rows that are being added to a page scroll after the rows have been selected and brought into the component buffer. No message is displayed. Error causes the Component Processor to add the current row (the one where the PeopleCode is executing) to the page scroll, then stops adding any additional rows to the page scroll.
The behavior of Error in the RowSelect event enables you to filter out rows that are above or below some limiting value. In practice this technique is rarely used, because it is more efficient to filter out rows of data before they are brought into the component buffer. This can be accomplished with search views or effective date processing.
Errors in Other Events
Do not use the Error function in any of the remaining events, which include:
FieldDefault
FieldFormula
RowInit
FieldChange
Prepopup
RowInsert
SavePreChange
SavePostChange
Parameters
|
Str |
A string containing the text of the error message. This string should always be stored in the Message Catalog and retrieved using the MsgGet or MsgGetText function. This makes translation much easier and also enables you to provide detailed Explain text about the error. |
Returns
None.
Example
The following example, from SaveEdit PeopleCode, displays an error message, stops all save processing, and places the cursor in the QTY_ADJUSTED field. Note that SetCursorPos must be called before Error.
If PAGES2_INV_WRK.PHYS_CYC_INV_FLG = "Y" Then SetCursorPos(%Page, PHYSICAL_INV.INV_LOT_ID, CurrentRowNumber(1), QTY_ADJUSTED, CurrentRowNumber()); Error MsgGet(11100, 180, "Message not found."); End-If;
See Also
MsgGet, MsgGetText, SetCursorPos, Warning, WinMessage.

 EscapeHTML
EscapeHTMLSyntax
EscapeHTML(TextString)
Description
Use the EscapeHTML function to replace all characters in TextString that would otherwise be interpreted as markup sequences.
The characters that are replaced are ones that would cause the browser to interpret them as HTML tags or other markup if they aren't encoded, and therefore pre-formatted HTML should not be passed to this function unless the output desired is a rendering of the HTML code itself as opposed to it's interpretation. This function is intended to make the text "browser safe".
This function is for use with strings that display in an HTML area.
Either HTML character entities (eg. <) or Numeric Character Representations (e.g. ') are output by the EscapeHTML function, depending on the character passed. The table below shows the escaping that is performed by EscapeHTML.
In addition to escaping characters that could be misinterpreted as HTML tags or other elements, EscapeHTML escapes the percentage sign (%) as this could interfere with meta HTML processing. As all PeopleTools HTML is generated in Unicode, it is not necessary to escape other Unicode characters — their value may be passed directly to the browser instead of a character entity or in Numeric Character Representation.
The following table lists the Unicode characters that are escaped by the EscapeHTML function.
For example, the less-than symbol (<) is replaced with <., a single quotation mark (') is replaced with '., and so on.
|
Unicode Character Name |
Glyph |
Escape Sequence |
|
Quotation mark |
” |
" |
|
Ampersand |
& |
& |
|
Less than sign |
< |
< |
|
Apostrophe, single quote |
' |
' |
|
Percentage sign |
% |
% |
|
New line |
Not applicable |
<BR> |
Parameters
|
TextString |
Specify a string of HTML that contains characters that must be replaced with HTML escape sequences. |
Returns
A string containing the original text plus HTML escape sequences.
See Also
EscapeJavascriptString, EscapeWML.

 EscapeJavascriptString
EscapeJavascriptStringSyntax
EscapeJavascriptString(String)
Description
Use the EscapeJavascriptString function to replace the characters in String that have special meaning in a JavaScript string as escape sequences.
For example, a single quotation markˋ ( ' ) is replaced by \', a new line character is replaced by \n, and so on.
This function is for use with text that becomes part of a JavaScript program.
The characters that are replaced are ones that cause the browser to misinterpret the JavaScript if they aren't encoded. This function is intended to make the text “browser safe.” The table below shows the strings that are replaced by this function, and their replacement character sequence.
|
Character Name |
Glyph |
Description |
|
Apostrophe, single quote |
' |
\' |
|
Quotation mark |
" |
\" |
|
New line |
Not applicable |
\n |
|
Carriage return |
Not applicable |
Deleted |
|
Double backslash |
\\ |
\\\\ |
Parameters
|
String |
Specify a string that contains character that need to be replaced with JavaScript escape sequences. |
Returns
A string containing the original text plus JavaScript escape sequences.
See Also

 EscapeWML
EscapeWMLSyntax
EscapeWML(String)
Description
Use the EscapeWML function to escape special characters that are significant to WML. This includes <, >, $ (escaped as $$), &, ' and ".
This function is for use with strings that display on an WML browser.
Parameters
|
String |
Specify a string that contains characters that need to be replaced with WML escape sequences. |
Returns
A string containing the original plus text plus WML escape sequences.
See Also
EscapeHTML, EscapeJavascriptString.

 Evaluate
EvaluateSyntax
Evaluate left_term When [relop_1] right_term_1 [statement_list] . . .
[When [relop_n] right_term_n [statement_list]] [When-other [statement_list]] End-evaluate
Description
Use the Evaluate statement to check multiple conditions. It takes an expression, left_term, and compares it to compatible expressions (right_term) using the relational operators (relop) in a sequence of When clauses. If relop is omitted, then = is assumed. If the result of the comparison is True, it executes the statements in the When clause, then moves on to evaluate the comparison in the following When clause. It executes the statements in all of the When clauses for which the comparison evaluates to True. If and only if none of the When comparisons evaluates to True, it executes the statement in the When-other clause (if one is provided).
To end the Evaluate after the execution of a When clause, you can add a Break statement at the end of the clause.
Considerations Using When Clause
Generally, you use the When clause without a semicolon at the end of the statement. However, in certain circumstances, this can cause an error. For example, the following PeopleCode produces an error because the PeopleCode compiler cannot separate the end of the Where clause with the beginning of the next statement:
When = COMPONENT.GARBAGE (create BO_SEARCH:Runtime:BusinessContact_Contact(&fBusObjDescr, Null, &fDerivedBOID, &fDerivedBORole, &fBusObjDescr1, Null, &fContactBOID, &fContactRoleID, &fCustBOID, &fCustRoleID, "")).SearchItemSelected(); End-Evaluate;
If you place a semicolon after the When clause, the two expressions are read separately by the compiler. For example:
When = COMPONENT.GARBAGE;
Example
The following is an example of a When statement taken evaluates ACTION and performs various statements based on its value:
&PRIOR_STATUS = PriorEffdt(EMPL_STATUS); Evaluate ACTION When "HIR" If %Mode = "A" Then Warning MsgGet(1000, 13, "You are hiring an employee and Action is not set to Hire."); End-if; Break; When = "REH" If All(&PRIOR_STATUS) and not (&PRIOR_STATUS = "T" or &PRIOR_STATUS = "R" ) Then Error MsgGet(1000, 14, "Hire or Rehire action is valid only if employee status is Terminated or Retired."); End-if; Break; When-Other /* default code */ End-evaluate;

 Exact
ExactSyntax
Exact(string1, string2)
Description
Use the Exact function to compare two text strings and returns True if they are the same, False otherwise. Exact is case-sensitive because it uses the internal character codes.
Returns
Returns a Boolean value: True if the two strings match in a case-sensitive comparison.
Example
The examples set &MATCH to True, then False:
&MATCH = Exact("PeopleSoft", "PeopleSoft"); &MATCH = Exact("PeopleSoft", "Peoplesoft");
See Also

 Exec
ExecSyntax
Exec(command_str [, parameter])
where parameter has one of the following formats:
Boolean constant
Exec_Constant + Path_Constant
Description
Exec is a cross-platform function that executes an external program on either UNIX or Windows.
This function has two parameter conventions in order to maintain upward compatibility with existing programs.
Note. All PeopleCode is executed on the application server. So if you're calling an interactive application, you receive an error. There shouldn't be any application interaction on the application server console.
The function can make either a synchronous or asynchronous call. Synchronous execution acts as a "modal" function, suspending the PeopleSoft application until the called executable completes. This is appropriate if you want to force the user (or the PeopleCode program) to wait for the function to complete its work before continuing processing. Asynchronous processing, which is the default, launches the executable and immediately returns control to the calling PeopleSoft application.
If Exec is unable to execute the external program, the PeopleCode program terminates with a fatal error. You may want to try to catch these exceptions by enclosing such statements in a try-catch statement (from the Exception Class).
Using an Absolute Path
If you don't specify anything for the second parameter, or if you specify a Boolean value, the path to PS_HOME is prefixed to the command_str.
If you specify constant values for the second parameter, PS_HOME may or may not be prefixed, depending on the values you select.
You can use the GetEnv function to determine the value of PS_HOME.
Restrictions on Use in PeopleCode Events
When Exec is used to execute a program synchronously (that is, if its synch_exec parameter is set to True) it behaves as a think-time function, which means that it can’t be used in any of the following PeopleCode events:
SavePreChange.
SavePostChange.
Workflow.
RowSelect.
Any PeopleCode event that fires as a result of a ScrollSelect (or one of its relatives) function calls, or a Select (or one of its relatives) Rowset class method.
See Also
Parameters
|
command_str |
Specify a string containing the path and name of the executable file. |
|
Boolean | Constants |
If you specify a Boolean value, it indicates whether to execute the external program synchronously or asynchronously. Values are:
If you don't specify a value, the program executes asynchronously. If you use this style, PS_HOME is always prefixed to command_str. If you specify constant values, you're specifying a numeric value composed of an exec_constant and a path_constant. The exec_constant specifies whether to execute the external program synchronously or not. The path_constant specifies how the path name is to be treated. The value specified is made up of the addition of these predefined constants. The function automatically converts the first token on command_str platform-specific separator characters to the appropriate form for where your PeopleCode program is executing, regardless of the path_constant. On a WIN32 system, a UNIX "/" separator is converted to "\", and on a UNIX system, a WIN32 "\" separator is converted to "/". This is only done for the first token on command_str assuming it to be some sort of file specification. This allows you to put file or program names in canonical form (such as, Unix style) as the first token on the exec command. For example:
Values are: |
|
Exec Constant |
Description |
|
%Exec_Asynchronous |
Program executes asynchronously (the default) |
|
%Exec_Synchronous |
Program executes synchronously. |
|
Path Constant |
Description |
|
%FilePath_Relative |
PS_HOME is prefixed to command_str. |
|
%FilePath_Absolute |
Nothing is prefixed to command_str. |
Returns
What is returned depends on what you specified for the second parameter.
If you specified a Boolean, a Number value equal to the process ID of the called process is returned.
If you specify constant values, the returned value contains the value of the exit code of the program executed using this function, unless you have executed the program asynchronously.
Example
&ExitCode = Exec("sh -c " | &scriptFile, %Exec_Synchronous + %FilePath_Absolute);
See Also
Declare Function, RemoteCall, WinExec, ScrollSelect, ScrollSelectNew, RowScrollSelect, RowScrollSelectNew, GetEnv.

 ExecuteRolePeopleCode
ExecuteRolePeopleCodeSyntax
ExecuteRolePeopleCode(RoleName)
Description
Use the ExecuteRolePeopleCode function to execute the PeopleCode Rule for the Role RoleName. This function returns an array of string containing dynamic members (UserIds).
Typically, this function is used by an Application Engine process that runs periodically and executes the role rules for different roles. It could then write the results of the rules (a list of users) into the security tables, effectively placing users in certain roles based on the rule.
Parameters
|
RoleName |
Specify the name of an existing role. |
Returns
An array of string containing the appropriate UserIds.
Example
The following saves valid users to a temporary table:
Local array of string &pcode_array_users; SQLExec("delete from ps_dynrole_tmp where ROLENAME=:1", &ROLENAME); If &pcode_rule_status = "Y" Then SQLExec("select RECNAME, FIELDNAME, PC_EVENT_TYPE, PC_FUNCTION_NAME from PSROLEDEFN where ROLENAME= :1", &ROLENAME, &rec, &fld, &pce, &pcf); If (&rec <> "" And &fld <> "" And &pce <> "" And &pcf <> "") Then &pcode_array_users = ExecuteRolePeopleCode(&ROLENAME); &pcode_results = True; Else &pcode_results = False; End-If; &comb_array_users = &pcode_array_users; End-If;
See Also
ExecuteRoleQuery, ExecuteRoleWorkflowQuery, IsUserInPermissionList, IsUserInRole.
Understanding PeopleSoft Security

 ExecuteRoleQuery
ExecuteRoleQuerySyntax
ExecuteRoleQuery(RoleName, BindVars)
where BindVars is an arbitrary-length list of bind variables that are stings in the form:
bindvar1 [, bindvar2]. . .
Description
Use the ExecuteRoleQuery function to execute the Query rule for the role rolename, passing in BindVars as the bind variables. This function returns an array object containing the appropriate user members (UserIds).
Parameters
|
RoleName |
Specify the name of an existing role. |
|
BindVars |
A list of bind variables to be substituted in the query. These bind variables must be strings. You can't use numbers, dates, and so on. |
Returns
An array object containing the appropriate UserIds.
See Also
ExecuteRolePeopleCode, ExecuteRoleWorkflowQuery, IsUserInPermissionList, IsUserInRole.
Understanding PeopleSoft Security

 ExecuteRoleWorkflowQuery
ExecuteRoleWorkflowQuerySyntax
ExecuteRoleWorkflowQuery(RoleName, BindVars)
where BindVars is an arbitrary-length list of bind variables in the form:
bindvar1 [, bindvar2]. . .
Description
Use the ExecuteRoleWorkflowQuery function to execute the Workflow Query rule for the role rolename, passing in BindVars as the bind variables. This function returns an array object containing the appropriate user members (UserIds).
Parameters
|
RoleName |
Specify the name of an existing role. |
|
BindVars |
A list of bind variables to be substituted in the query. |
Returns
An array object containing the appropriate UserIds.
See Also
ExecuteRolePeopleCode, ExecuteRoleQuery, IsUserInPermissionList, IsUserInRole.
Understanding PeopleSoft Security

 Exit
ExitSyntax
Exit([1])
Description
Use the Exit statement to immediately terminate a PeopleCode program. If the Exit statement is executed within a PeopleCode function, the main program terminates.
Note. Exit(1) does not rollback iScript transactions. To rollback in an iScript, you can use either the Error built-in function, or the MessageBox built-in function with a message error severity of error.
Parameters
|
1 |
Use this parameter to rollback database changes. Generally, this parameter is used in PeopleCode programs that affect messages. When used with a message, all database changes are rolled back, errors for the subscription contract are written to the subscription contract error table, and the status of the message is marked to Error. All errors that have occurred for this message are viewable in the message monitor: even those errors detected by the ExecuteEdits method. |
Note. This function takes only numeric values. It fails if you use a Boolean value, True or False.
Returns
None.
Example
The following example terminates the main program from a For loop:
For &I = 1 To ActiveRowCount(RECORD.SP_BUIN_NONVW) &ITEM_SELECTED = FetchValue(ITEM_SELECTED, &I); If &ITEM_SELECTED = "Y" Then &FOUND = "Y"; Exit; End-If; End-For;
See Also

 Exp
ExpSyntax
Exp(n)
Description
Exp returns the constant e raised to the power of n where n is a number. The constant e equals 2.71828182845904, the base of natural logarithms. The number n is the exponent applied to the base e.
Exp is the inverse of the Ln function, which is the natural logarithm of x.
Returns
Returns a Number value equal to the constant e raised to the power of n.
Example
The examples set &NUM to 2.71828182845904, then 7.389056099(e2):
&NUM = Exp(1); &NUM = Exp(2);
See Also

 ExpandBindVar
ExpandBindVarSyntax
ExpandBindVar(str)
Description
Inline bind variables can be included in any PeopleCode string. An inline bind variable is a field reference (in the form recordname.fieldname), preceded by a colon. The inline bind variable references the value in the field.
Use the ExpandBindVar function to expand any inline bind variables that it finds in str into strings (converting the data type of non-character fields) and returns the resulting string. This works with inline bind variables representing fields containing any data type except Object. It also expands bind variables specified using additional parameters.
See SQLExec.
Parameters
|
str |
A string containing one or more inline bind variables. |
Returns
Returns a String value equal to the input string with all bind variables expanded.
Example
A bind variable is included in the string &TESTSTR, which is then expanded into a new string containing the current value of BUS_EXPENSE_PER.EMPLID in place of the bind variable. If this program runs on the row for EMPLID 8001, the message displayed reads "This is a test using EmplID 8001".
&TESTSTR = "This is a test using EmplID :bus_expense_per.emplid"; &RESULT = ExpandBindVar(&TESTSTR); WinMessage(&RESULT);
See Also

 ExpandEnvVar
ExpandEnvVarSyntax
ExpandEnvVar(string)
Description
Use the ExpandEnvVar function to convert any environment variables that it finds within string into String values and returns the entire resulting string.
Parameters
|
string |
A string containing an environment variable. |
Returns
Returns a string equal to string with any enclosed environment variables expanded to their values.
Example
Assume that the environment variable %NETDRIVE% is equal to "N:". The following PeopleCode sets &newstring equal to "The network drive is equal to N:":
&newstring = ExpandEnvVar("The network drive is equal to %netdrive%.");
See Also
ExpandBindVar, GetEnv, GetCwd.

 ExpandSqlBinds
ExpandSqlBindsSyntax
ExpandSqlBinds(string)
Description
Prior to PeopleTools 8.0, the PeopleCode replaced runtime parameter markers in SQL strings with the associated literal values. For databases that offer SQL statement caching, a match was never found in the cache so the SQL had to be re-parsed and re-assigned a query path.
To process skipped parameter markers, each parameter marker is assigned a unique number. This doesn’t change the values associated with the parameter markers.
However, some SQL statements can’t contain parameter markers because of database compatibility.
To process these exceptions, use the ExpandSqlBinds function. This function does the bind variable reference expansion, and can be used within a SQLExec statement or on its own.
You should use ExpandSQLBinds only for those parts of the string that you want to put literal values into. For example, you wouldn't use ExpandSQLBinds with any meta-SQL statements. The following code shows how to use ExpandSQLBinds with %Table:
SQLExec(ExpandSqlBinds("Insert.... Select A.Field, :1, :2 from ", "01", "02") | "%table(:1)", Record.MASTER_ITEM_TBL);
Parameters
|
string |
Specify the string you want to do the bind variable reference expansion on. |
Returns
A string.
Example
The following example shows both the original string and what it expands to.
&NUM = 1; &STRING = "My String"; &STR2 = ExpandSqlBinds("This :2 is an expanded string(:1)", &STRING, &NUM);
The previous code produces the following value for &STR2:
This 1 is an expanded string(My String)
If you’re having problems with an old SQL statement binds, you can use ExpandSqlBinds with it. For example, if your SQLExec is this:
SQLExec("String with concatenated bindrefs ‘M’:2, ‘M’:1", &VAR1, &VAR2), &FETCHRESULT1, &FETCHRESULT2);
you can make it work by expanding it as follows:
SQLExec(ExpandSqlBinds("String with concatenated bindrefs ‘M’:2, ‘M’:1", &VAR1, &VAR2), &FETCHRESULT1, &FETCHRESULT2);
See Also

 Fact
FactSyntax
Fact(x)
Description
Use the Fact function to return the factorial of a positive integer x. The factorial of a number x is equal to 1*2*3*...*x. If x is not an integer, it is truncated to an integer.
Returns
Returns a Number equal to the factorial of x.
Example
The example sets &X to 1, 1, 2, then 24. Fact(2) is equal to 1*2; Fact(4) is equal to 1*2*3*4:
&X = Fact(0); &X = Fact(1); &X = Fact(2); &X = Fact(4);
See Also

 FetchSQL
FetchSQLSyntax
FetchSQL([SQL.]sqlname[, dbtype[, effdt]] )
Description
Use the FetchSQL function to return the SQL definition with the given sqlname as SQL.sqlname or a string value, matching the dbtype and effdt. If sqlname is a literal name, it must be in quotes.
Parameters
|
sqlname |
Specify the name of a SQL definition. This is either in the form SQL.sqlname or a string value giving the sqlname. |
|
dbtype |
Specify the database type associated with the SQL definition. This parameter takes a string value. If dbtype isn’t specified or is null (""), it is set by default to the current database type (the value returned from the %DbType system variable.) Values for dbtype are as follows. These values are not case-sensitive:
Note. Database platforms are subject to change. |
|
effdt |
Specify the effective date associated with the SQL definition. If effdt isn’t specified, it is set by default to the current as of date, that is, the value returned from the %AsOfDate system variable. |
Returns
The SQL statement associated with sqlname as a string.
Example
The following code gets the text associated with the ABCD_XY SQL Definition for the current DBType and as of date:
&SQLSTR = FetchSQL(SQL.ABC_XY);
The following code gets the text associated with the ABCD_XY SQL Definition for the current DBType and November 3, 1998:
&SQLSTR = FetchSQL(SQL.ABCD_XY, "", Date(19981103));
See Also
CreateSQL, DeleteSQL, SQLExec, GetSQL, StoreSQL.

 FetchValue
FetchValueSyntax
FetchValue(scrollpath, target_row, [recordname.]fieldname)
where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ]] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can also use SCROLL.scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Use the FetchValue function to return the value of a buffer field in a specific row of a scroll level.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the Value field class property instead.
This function is generally used to retrieve the values of buffer fields outside the current context; if a buffer field is in the current context, you can reference it directly using a [recordname.]fieldname expression.
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
target_row |
An integer specifying the row on the target scroll level where the referenced buffer field is located. |
|
[recordname.]fieldname |
The name of the field where the value to fetch is located. The field can be on scroll level one, two, or three of the active page. The recordname prefix is required if the call to FetchValue is in a record definition other than recordname. |
Returns
Returns the field value as an Any data type.
Example
The following example retrieves the value from field DEPEND_ID in record DEPEND on row &ROW_CNT from scroll level one:
&VAL = FetchValue(SCROLL.DEPEND, &ROW_CNT, DEPEND.DEPEND_ID);
See Also
ActiveRowCount, CopyRow, CurrentRowNumber, PriorValue, UpdateValue.
Referencing Data in the Component Buffer

 FieldChanged
FieldChangedSyntax
The syntax of the FieldChanged function varies depending on whether you want to use a scroll path reference or a contextual reference to specify the field.
If you want to use a scroll path reference, the syntax is:
FieldChanged(scrollpath, target_row, [recordname.]fieldname)
where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ]] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can also use SCROLL.scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
If you want to use a contextual reference, the syntax is:
FieldChanged([recordname.]fieldname)
In this construction the scroll level and row number are determined based on the current context.
Description
The FieldChanged function returns True if the referenced buffer field has been modified since being retrieved from the database either by a user or by a PeopleCode program.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the IsChanged field class property instead.
This is useful during SavePreChange or SavePostChange processing for checking whether to make related updates based on a change to a field.
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
[recordname.]fieldname |
The name of the field where the value to check is located. The field can be on scroll level one, two, or three of the active page. The recordname prefix is required if the call to FieldChanged is in a record definition other than recordname. |
|
target_row |
The row number of the target row. If this parameter is omitted, the function assumes the row on which the PeopleCode program is executing. |
Related Functions
Save PeopleCode programs (SaveEdit, SavePreChange, SavePostChange) normally process each row of data in the component. The following four functions enable you to control more precisely when the Component Processor should perform save PeopleCode:
FieldChanged
RecordChanged
RecordDeleted
RecordNew
These functions enable you to restrict save program processing to specific rows.
Example
The following example checks three fields and sets a flag if any of them has changed:
/* Set the net change flag to 'Yes' if the scheduled date, scheduled */ /* time or quantity requested is changed */ If FieldChanged(QTY_REQUESTED) Or FieldChanged(SCHED_DATE) Or FieldChanged(SCHED_TIME) Then NET_CHANGE_FLG = "Y"; End-If;
See Also
RecordChanged, RecordDeleted, RecordNew.

 FileExists
FileExistsSyntax
FileExists(filename [, pathtype])
Description
Use the FileExists function to determine whether a particular external file is present on your system, so you can decide which mode to use when you open the file for writing.
Note. If you want to open a file for reading, you should use the GetFile function or the Open File Class method with the "e" mode, which prevents another process from deleting or renaming the file between the time you tested for the file and when you open it.
Working With Relative Paths
If you specify a relative path, that path is appended to the path specified by an environmental variable, if the variable exists, in a particular order. This means if the first environmental variable in order is found, that is the one that's used. If it isn't found, the next one is searched for, and if found, is used, and so on.
The environmental variables that get used are different, depending on whether the machine where the code is running is an application server or not. If the code is running on an application server, the following environmental variables are valid, and are searched for in the following order:
PS_FILEDIR[\relative_path]
PS_SERVDIR\Files[\relative_path]
If the code is not running on an application server, the following environmental variables are valid, and are searched for in the following order:
PS_FILEDIR[\relative_path]
PS_SERVDIR\Files[\relative_path]
TEMP[\relative_path]
The PS_FILEDIR environmental variable is not initialized and set to a path automatically. If you want to use this environmental variable, you must set it yourself.
Note. Your system security should verify if a user has the correct permissions before allowing access to a drive (for example, if a user changes their TEMP environmental variable to a network drive they don’t normally have access to, your system security should detect this.)
Parameters
|
filespec |
Specify the name, and optionally, the path, of the file you want to test. |
|
pathtype |
If you have prepended a path to the file name, use this parameter to specify whether the path is an absolute or relative path. The valid values for this parameter are:
If you don’t specify pathtype the default is %FilePath_Relative. If the path is an absolute path, whatever path you specify is used verbatim. You must specify a drive letter as well as the complete path. You can’t use any wildcards when specifying a path. The function automatically converts platform-specific separator characters to the appropriate form for where your PeopleCode program is executing. On a WIN32 system, UNIX "/" separators are converted to "\", and on a UNIX system, WIN32 "\" separators are converted to "/". |
Note. The syntax of the file path does not depend on the file system of the platform where the file is actually stored; it depends only on the platform where the PeopleCode is executing.
Returns
A Boolean value: True if the file exists, False if it doesn’t.
Example
The following example opens a file for appending if it exists on the system:
If FileExists("c:\work\item.txt", %FilePath_Absolute) Then &MYFILE = GetFile("c:\work\item.txt", "A"); /* Process the file */ &MYFILE.Close(); End-If;
See Also

 Find
FindSyntax
Find(string, within_string [, number])
Description
Use the Find function to locate one string of text within another string of text and returns the character position of the string as an integer. Find is case-sensitive and does not allow wildcards.
If you need to do either case-sensitive search or pattern matching, just to find if a string matches a pattern, use the DBPatternMatch function.
If you need to find a quotation mark, you need to double it in a string.
&find = Find("""", PSOPRDEFN_SRCH.OPRID);
Parameters
|
string |
The text you are searching for. A tilde character (~) used in the string parameter stands for an arbitrary number of white spaces. |
|
within_string |
The text string you are searching within. |
|
number |
The position of within_string at which you want to start your search. If you omit number, Find starts at the first character of within_string. |
Returns
Returns a Number value indicating the starting position of string in within_string.
Find returns with 0 if string does not appear in within_string, if number is less than or equal to zero, or if number is greater than the length of within_string.
Example
In the following example, the first statement returns 1; the second statement returns 6.
&POS = Find("P", "PeopleSoft") &POS = Find("e", "PeopleSoft", 4)
See Also

 Findb
FindbSyntax
Findb(string, within_string [, number])
Description
Note. This function has been deprecated and is no longer supported.

 FindCodeSetValues
FindCodeSetValuesSyntax
FindCodeSetValues(CodesetName, &NameValuePairs, SourceNodeName, TargetNodeName)
Description
Use the FindCodeSetValues function to find a list of code set name-value pairs. Code sets are primarily used with data value translations as part of a transformation.
Parameters
|
CodeSetName |
Specify the name of the code set you want to find, as a string. |
|
&NameValuePairs |
Specify a 2 dimensional array containing the name value pairs in the specified code set that you want to use. |
|
SourceNodeName |
Specify the name of the source (initial) node used in the data transformation. |
|
TargetNodeName |
Specify the name of the target (result) node used in the data transformation. |
Returns
A two-dimensional array of any.
Example
This example checks the specified CodeSet values, with the name value pairs of "locale/en_us" and "uom/box". It takes the returned array and adds XML nodes to the document. The XML nodes names are the unique names of the CodeSet value, and the XML node value is the corresponding return value.
/* Get the data from the AE Runtime */ Local TransformData &incomingData = %TransformData; /* Set a temp object to contain the incoming document */ Local XmlDoc &tempDoc = &incomingData.XmlDoc; /* Declare the node */ Local XmlNode &tempNode; /* Create an array to hold the name value pairs */ Local array of array of string &inNameValuePairsAry; /* Clear out the doc and put in a root node */ If (&tempDoc.ParseXmlString("<?xml version=""1.0""?><xml/>")) Then /* Load the array with some values */ &inNameValuePairsAry = CreateArray(CreateArray("locale", "en_us"), CreateArray("uom", "box")); /* Find the codeset values */ &outAry = FindCodeSetValues("PS_SAP_PO_01", &inNameValuePairsAry, "SAP_SRC", "PSFT_TGT"); /* Local XmlNode &tempNode; */ /* Make sure something was returned */ If &outAry.Len > 0 Then /* Loop through the quantities and make sure they are all above 5 */ For &i = 1 To &outAry.Len /* Add the current system date to the working storage*/ &tempNode = &tempDoc.DocumentElement.AddElement(&outAry [&i][1]); &tempNode.NodeValue = &outAry [&i][2]; End-For; End-If; End-If;
See Also
Applying Filtering, Transformation and Translation

 FindFiles
FindFilesSyntax
FindFiles(filespec_pattern [, pathtype])
Description
Use the FindFiles function to return a list of the external filenames that match the filename pattern you provide, in the location you specify.
Working With Relative Paths
If you specify a relative path, that path is appended to the path specified by an environmental variable, if the variable exists, in a particular order. This means if the first environmental variable in order is found, that is the one that's used. If it isn't found, the next one is searched for, and if found, is used, and so on.
The environmental variables that are used are different, depending on whether the machine where the code is running is an application server. If the code is running on an application server, the following environmental variables are valid, and are searched for in the following order:
PS_FILEDIR[\relative_path]
PS_SERVDIR\Files[\relative_path]
If the code is not running on an application server, the following environmental variables are valid, and are searched for in the following order:
PS_FILEDIR[\relative_path]
PS_SERVDIR\Files[\relative_path]
TEMP[\relative_path]
The PS_FILEDIR environmental variable is not initialized and set to a path automatically. To use this environmental variable, you must set it yourself.
Note. Your system security should verify if a user has the correct permissions before allowing access to a drive (for example, if a user changes their TEMP environmental variable to a network drive they don’t normally have access to, your system security should detect this.)
Parameters
|
filespec_pattern |
Specify the path and filename pattern for the files you want to find. The path can be any string expression that represents a single relative or absolute directory location. The filename pattern, but not the path, can include two wildcards: * (Asterisk): matches zero or more characters at its position. ? (Question mark): matches exactly one character at its position. |
|
pathtype |
If you have prepended a path to the file name, use this parameter to specify whether the path is an absolute or relative path. The valid values for this parameter are:
If you don’t specify pathtype the default is %FilePath_Relative. If the path is an absolute path, whatever path you specify is used verbatim. You must specify a drive letter as well as the complete path. You can't use any wildcards when specifying a path. The function automatically converts platform-specific separator characters to the appropriate form for where your PeopleCode program is executing. On a WIN32 system, UNIX "/" separators are converted to "\", and on a UNIX system, WIN32 "\" separators are converted to "/". |
Note. The syntax of the file path does not depend on the file system of the platform where the file is actually stored; it depends only on the platform where the PeopleCode is executing.
Returns
A string array whose elements are filenames qualified with the same relative or absolute path you specified in the input parameter to the function.
Example
The following example finds all files in the system’s TEMP location whose names end with ".txt", then opens and processes each one in turn:
Local array of string &FNAMES; Local file &MYFILE; &FNAMES = FindFiles("\*.txt"); while &FNAMES.Len > 0 &MYFILE = GetFile(&FNAMES.Shift(), "R"); /* Open each file */ /* Process the file contents */ &MYFILE.Close(); end-while;
See Also

 FlushBulkInserts
FlushBulkInsertsSyntax
FlushBulkInserts()
Description
Use the FlushBulkInserts function to move the bulk inserted rows from the bulk insert buffers of the PeopleSoft process to the physical tables on the database. This flushes all open SQL objects that have pending bulk inserts, but performs no COMMITs. If the flush fails, the PeopleCode program terminates.
When executing a SQL insert using a SQL object with the BulkMode property set to True, the rows being inserted cannot be selected by this database connection until the bulk insert is flushed. For another connection to the database to be able to select those rows, both a flush and a COMMIT are required. To have your process see the bulk inserted rows without committing and without closing the SQL object or its cursor (that is, maintaining reuse for the SQL object), use FlushBulkInserts.
An example of using this function would be in preparation for a database commit where you do not want to close the SQL insert statement, but need to ensure that all the rows you have inserted up to this point are in fact in the database and not in the buffer.
Another example would be when another SQL statement in the same PeopleSoft process needs to select rows that have been inserted using bulk insert and you do not want to close the SQL insert statement. The SELECT cannot read rows in the bulk insert buffer, so you need to flush them to the table from which the SELECT is reading.
Parameters
None.
Returns
None. If the flush fails, the PeopleCode program terminates.
Example
&CM_DEPLETION_REC = CreateRecord(Record.CM_DEPFIFO_VW); &CM_DEPLETE_REC = CreateRecord(Record.CM_DEPLETE); &DEPLETE_FIFO_SEL = GetSQL(SQL.CM_DEPLETE_FIFO_SEL); &ONHAND_FIFO_SEL = GetSQL(SQL.CM_ONHAND_FIFO_SEL); DEPLETE_INS = GetSQL(SQL.CM_DEPLETE_INS); &DEPLETE_INS.BulkMode = True; &DEPLETE_FIFO_SEL.Execute(&CM_DEPLETION_REC, CM_COSTING_AET.BUSINESS_UNIT, CM_COSTING_AET.CM_BOOK); While &DEPLETE_FIFO_SEL.Fetch(&CM_DEPLETION_REC); /* Call functions that populate &CM_DEPLETE_REC.values */ . . . &DEPLETE_INS.Execute(&CM_DEPLETE_REC); . . . If &CM_DEPLETION_REC.CM_COST_PROC_GROUP.Value = "BINTOBIN" Then /* Bin to Bin transfers are both a deplete and receipt, call functions to create the receipt */ . . . /* Flush Bulk Insert to be able to see the current on hand quantities in CM_ONHAND_VW */ FlushBulkInserts(); End-if; End-While; . . .
See Also
Applying Filtering, Transformation and Translation.

 For
ForSyntax
For count = expression1 To expression2 [Step i]; statement_list End-for
Description
Use the For loop to cause the statements of the statement_list to be repeated until count is equal to expression2. Step specifies the value by which count will be incremented each iteration of the loop. If you do not include Step, count is incremented by 1 (or -1 if the start value is greater than the end value.) Any statement types are allowed in the loop, including other loops.
A Break statement inside the loop causes execution to continue with whatever follows the loop. If the Break occurs in a nested loop, the Break does not apply to the outside loop.
Example
The following example loops through all of the rows for the FIELDNAME scroll area:
&FIELD_CNT = ActiveRowCount(DBFIELD_VW.FIELDNAME); For &I = 1 to &FIELD_CNT; WinMessage(MsgGetText(21000, 1, "Present Row Number is: %1", &I)); End-for;

 FormatDateTime
FormatDateTimeSyntax
FormatDateTime(datetime, {timezone | "Local" | "Base"}, displayTZ)
Description
Use the FormatDateTime function to take a datetime value and convert it to text. If a specific time zone abbreviation, or a field reference, is passed in timezone, FormatDateTime adjusts the datetime to the user’s local time zone instead of the specified time zone. The system’s base time zone is specified on the PSOPTIONS table. The value datetime is assumed to be in base time.
See Using PeopleTools Utilities.
If Local is specified for time zone, FormatDateTime adjusts the datetime to the user’s local time zone instead of a specific time zone.
If True is specified for displayTZ, FormatDateTime appends the time zone abbreviation to the returned string.
Parameters
|
datetime |
Specify the datetime value to be formatted. |
|
timezone | Local | Base |
Specify a value for converting datetime. The values are:
|
|
displayTZ |
Specify whether the time zone abbreviation should be appended to the returned string. This parameter takes a Boolean: True if the abbreviation should be appended, False, otherwise. |
Returns
A formatted string value.
Example
The following example populates the &DISPDATE variable with a string containing the datetime value in the ORDER_DATE field adjusted to the user’s local time zone, and with the time zone abbreviation.
&DISPDATE=FormatDateTime(ORDER_DATE, "Local", True);
The following example populates the &DISPDATE variable with a string containing the datetime value in the SHIP_DATE field adjusted to the time zone stored in the SHIP_TZ field, and does not include the time zone abbreviation in the output.
&DISPDATE=FormatDateTime(SHIP_DATE, SHIP_TZ, False);
See Also
ConvertDatetimeToBase, ConvertTimeToBase, DateTimeToLocalizedString, IsDaylightSavings, DateTimeToTimeZone, TimeToTimeZone, TimeZoneOffset, DateTimeToHTTP.

 Forward
ForwardSyntax
Forward(from physical queue ID, from agent ID, task number, task type, to logical queue ID[, to agent ID])
Description
Use the Forward function to transfer a task from one agent to another agent or from one agent's logical queue to another logical queue. This enables agents to reroute tasks that are not appropriate for their skill level or functional expertise.
Keep the following in mind when using Forward:
The queue server subtracts the task's cost from the transferring agent's workload.
The system cannot forward tasks to logical queues that do not have active physical queues on the same MultiChannel Framework cluster as the physical queue to which the task currently belongs. That is, you can't forward tasks across MultiChannel Framework clusters.
A queue server does not allow a task to be transferred if the agent who owns that task is not logged on to that queue server. PeopleSoft recommends that you only use Forward for application pages that the MultiChannel Framework console launches when agents accept or activate assigned tasks.
Forward only applies to email and generic task types.
Parameters
|
from physical queue ID |
The physical queue is the internal representation of the logical queue that the agent signs onto and to which the task currently belongs. This is a string value, such as “sales3” or “marketing2.” You retrieve the current physical queue from the query string in the URL of the page launched by the MultiChannel Framework console. Use the GetParameter request class method with the value ps_qid |
|
from agent ID |
Specifies the current agent, as in the agent that “accepted” the task. This is a string value. You retrieve the current physical queue from the query string in the URL of the page launched by the MultiChannel Framework console. Use the GetParameter request class method with the value ps_agentid. |
|
task number |
Identifies the task to be forwarded. The EnQueue function returns this value. This is a string value. You retrieve the current physical queue from the query string in the URL of the page launched by the MultiChannel Framework console. Use the GetParameter request class method with the value ps_tasknum. |
|
task type |
Identifies the task type. This value is provided by the queue. This is a string value. Valid values are:
You retrieve the current physical queue from the query string in the URL of the page launched by the MultiChannel Framework console. Use the GetParameter request class method with the value ps_tasktype. |
|
to logical queue ID |
Specifies the logical queue to which the system forwards the task. This is a string value. The queue ID is case sensitive and must match the case used when you created the queue using the Queues page. |
|
to agent ID |
This is an optional parameter. It is a string value specifying a particular agent ID to receive the forwarded task. If this value is specified, the system holds the task until the specified agent is available on the new queue to take this task. This means that the specified agent must be able to log in to one of the physical queues belonging to the destination logical queue. The system determines which physical queue the specified agent has access to and assigns the task to that queue for that agent. If the agent ID is not specified, the physical queue is chosen at random from the active physical queues. Note. For better performance, PeopleSoft recommends not specifying the target agent as this has a processing overhead for the queue servers and does not allow the system to balance workload across all available agents. |
Returns
Returns 0 on success.
If unsuccessful, it returns a message number. The message set ID for MultiChannel Framework is 162.
For example, 1302 is returned when an invalid task type or no value is provided.
Example
Forward("SALES5", "TSAWYER", "email_2145", "email", "MARKETING", "GSALMON");
The following example shows how to retrieve parameters from the application page using the GetParameter request class method.
PSMCFFUNCLIB.MCF_QUEUE.Value = %Request.GetParameter("ps_qid"); PSMCFFUNCLIB.MCF_TASKTYPE.Value = %Request.GetParameter("ps_tasktype"); PSMCFFUNCLIB.MCF_TASKNUM.Value = %Request.GetParameter("ps_tasknum"); PSMCFFUNCLIB.MCF_AGENTID.Value = %Request.GetParameter("ps_agentid"); &nret = Forward(PSMCFFUNCLIB.MCF_QUEUE, PSMCFFUNCLIB.MCF_AGENTID, PSMCFFUNCLIB.MCF_TASKNUM, PSMCFFUNCLIB.MCF_TASKTYPE, &ToQueue); If &nret = 0 Then MessageBox(0, "", 0, 0, "Successfully forwarded."); End-If

 Function
FunctionSyntax
Function name [(paramlist)] [Returns data_type] [statements] End-function
Where paramlist is:
¶m1 [As data_type] [, ¶m2 [As data_type]]...
Where data_type is any valid data type, including Number, String, Date, Rowset, SQL, Record, and so on.
Where statements is a list of PeopleCode statements.
Description
PeopleCode functions can be defined in any PeopleCode program. Function definitions must be placed at the top of the program, along with any variable and external function declarations.
Functions can be called from the program in which they are defined, in which case they don’t need to be declared, and they can be called from another program, in which case they need to be declared at the top of the program where they are called.
Any variables declared within a function are valid for the scope of the function.
By convention, external PeopleCode functions are stored in records whose names begin in FUNCLIB_, and they are always placed in the FieldFormula event (which is convenient because this event should no longer be used for anything else).
Note. Functions can be stored in the FieldFormula event only for record fields, not for component record fields.
A function definition consists of:
The keyword Function followed by the name of the function and an optional list of parameters. The name of the function can be up to 100 characters in length.
An optional Returns clause specifying the data type of the value returned by the function.
The statements to be executed when the function is called.
The End-function keyword.
The parameter list, which must be enclosed in parentheses, is a comma-separated list of variable names, each prefixed with the & character. Each parameter is optionally followed by the keyword As and the name for one of the conventional PeopleCode data types (Number, String, Date, and so on) or any of the object data types (such as Rowset, SQL, and so on.) If you specify data types for parameters, then function calls are checked to ensure that values passed to the function are of the appropriate type. If data types are not specified, then the parameters, like other temporary variables in PeopleCode, take on the type of the value that is passed to them.
PeopleCode parameters are always passed by reference. This means that if you pass the function a variable from the calling routine and change the value of the variable within the function, the value of the variable is changed when the flow of execution returns to the calling routine.
If the function is to return a result to the caller, the optional Returns part must be included to specify the data type of the returned value. You have seven choices of value types: Number, String, Date, Time, DateTime, Boolean, or Any.
PeopleCode internal subroutines are part of the enclosing program and can access the same set of variables as the other statement-lists of the program, in addition to local variables created by the parameters and local variable declarations within the function.
Returning a Value
You can optionally return a value from a PeopleCode function. To do so, you must include a Return statement in the function definition, as described in the preceding section. For example, the following statement returns a Number value:
function calc_something(&parm1 as number, &parm2 as number) returns number
In the code section of your function, use the Return statement to return a value to the calling routine. When the Return statement executes, the function ends and the flow of execution goes back to the calling routine.
Example
This example returns a Boolean value based on the return value of a SQLExec:
function run_status_upd(&PROCESS_INSTANCE, &RUN_STATUS) returns Boolean; &UPDATEOK = SQLExec("update PS_PRCS_RQST set run_status = :1 where process_instance = :2", &RUN_STATUS, &PROCESS_INSTANCE); If &UPDATEOK Then Return True; Else Return False; End-if; End-function;
See Also

 GenerateActGuideContentUrl
GenerateActGuideContentUrlSyntax
GenerateActGuideContentlUrl(PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename, MENUNAME.menuname, Marketname, COMPONENT.componentname, ActivityGuide)
Description
Use the GenerateActGuideContentUrl function to create a URL string that represents an absolute reference to the specified activity guide (life event) for the content servlet. The ContentURI of the node that hosts the specified portal is used in the generated URL. The URL contains a reference to the content service (psc) servlet.
If you want to generate a URL for the portal service (psp) servlet, use the GenerateActGuidePortalURL function.
Parameters
|
portalname |
Specify the name of the portal used for this request, prefixed with the reserved word PORTAL. You can also use a string, such as %Portal, for this value. |
|
nodename |
Specify the name of the node that contains the activity guide, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. |
|
menuname |
Specify the name of the menu containing the activity guide, prefixed with the reserved word MENUNAME. You can also use a string, such as %Menu, for this value. |
|
Marketname |
Specify the name of the market of the component. You can also use a string, such as %Market, for this value. |
|
ComponentName |
Specify the name of the component, prefixed with the reserved word COMPONENT. You can also use a string, such as %Component, for this value. |
|
ActivityGuide |
Specify the name of the Activity Guide, as a string. |
Returns
A string with the following format:
http://Content URI of node/portal/node/l/ActivityGuide.component.market
This function returns a Null string if you specify an invalid portal or node.
Example
The following code:
&AGURL = GenerateActGuideContentUrl(%Portal, %Node, MENUNAME.MAINTAIN_SECURITY, "GBL", COMPONENT.CHANGE_PASSWORD, "QE_ACTIVITY_GUIDE_DEMO");
might produce the following URL string:
http://boynten8700/psc/ps/EMPLOYEE/QE_LOCAL/l/QE_ACTIVITY_GUIDE_DEMO.MAINTAIN_SECURITY.CHANGE_PASSWORD.GBL
See Also
GenerateActGuidePortalUrl, GenerateActGuideRelativeUrl.

 GenerateActGuidePortalUrl
GenerateActGuidePortalUrlSyntax
GenerateActGuidePortalUrl(PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename, MENUNAME.menuname, Marketname, COMPONENT.componentname, ActivityGuide)
Description
Use the GenerateActGuidePortalUrl function to create a URL string that represents an absolute reference to the specified activity guide (life event) for the portal servlet. The PortalURI of the node that hosts the specified portal is used in the generated URL. The URL contains a reference to the portal service (psp) servlet.
If you want to generate a URL for the portal content (psc) servlet, use the GenerateActGuideContentURL function.
Parameters
|
portalname |
Specify the name of the portal used for this request, prefixed with the reserved word PORTAL. You can also use a string, such as %Portal, for this value. |
|
nodename |
Specify the name of the node that contains the activity guide, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. |
|
menuname |
Specify the name of the menu containing the activity guide, prefixed with the reserved word MENUNAME. You can also use a string, such as %Menu, for this value. |
|
Marketname |
Specify the name of the market of the component. You can also use a string, such as %Market, for this value. |
|
ComponentName |
Specify the name of the component, prefixed with the reserved word COMPONENT. You can also use a string, such as %Component, for this value. |
|
ActivityGuide |
Specify the name of the Activity Guide, as a string. |
Returns
A string with the following format:
http://Portal URI of node/portal/node/l/ActivityGuide.component.market
This function returns a Null string if you specify an invalid portal or node.
Example
The following code:
&AGURL = GenerateActGuidePortalUrl(%Portal, %Node, MENUNAME.MAINTAIN_SECURITY, "GBL", COMPONENT.CHANGE_PASSWORD, "QE_ACTIVITY_GUIDE_DEMO");
might create the following URL string:
http://boynte700/psp/ps/EMPLOYEE/QE_LOCAL/l/QE_ACTIVITY_GUIDE_DEMO.MAINTAIN_SECURITY.CHANGE_PASSWORD.GBL
See Also
GenerateActGuideContentUrl, GenerateActGuideRelativeUrl.

 GenerateActGuideRelativeUrl
GenerateActGuideRelativeUrlSyntax
GenerateActGuideRelativeUrl(PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename, MENUNAME.menuname, Marketname, COMPONENT.componentname, ActivityGuide)
Description
Use the GenerateActGuideContentUrl function to create a URL string that represents an relative reference to the specified activity guide (life event). The relative reference is suitable for use on any page that itself has the simple URL format.
Parameters
|
portalname |
Specify the name of the portal used for this request, prefixed with the reserved word PORTAL. You can also use a string, such as %Portal, for this value. |
|
nodename |
Specify the name of the node that contains the activity guide, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. |
|
menuname |
Specify the name of the menu containing the activity guide, prefixed with the reserved word MENUNAME. You can also use a string, such as %Menu, for this value. |
|
Marketname |
Specify the name of the market of the component. You can also use a string, such as %Market, for this value. |
|
ComponentName |
Specify the name of the component, prefixed with the reserved word COMPONENT. You can also use a string, such as %Component, for this value. |
|
ActivityGuide |
Specify the name of the Activity Guide, as a string. |
Returns
A string with the following format:
../../../Portal/node/l/ActivityGuide.menu.component.market
This function returns a Null string if you specify an invalid portal or node.
Example
The following code:
&AGURL = GenerateActGuideRelativeUrl(%Portal, %Node, MENUNAME.MAINTAIN_SECURITY, "GBL", COMPONENT.CHANGE_PASSWORD, "QE_ACTIVITY_GUIDE_DEMO");
might produce the following URL string:
../../../EMPLOYEE/QE_LOCAL/l/QE_ACTIVITY_GUIDE_DEMO.MAINTAIN_SECURITY.CHANGE_PASSWORD.GBL
See Also
GenerateActGuideContentUrl, GenerateActGuidePortalUrl.

 GenerateComponentContentRelURL
GenerateComponentContentRelURLSyntax
GenerateComponentContentRelURL(PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename,MENUNAME.menuname, MARKET.marketname, COMPONENT.componentname, PAGE.pagename, action, [, keylist])
where keylist is a list of field references in the form:
[recordname.]field1 [, [recordname.]field2]. . .
OR
&RecordObject1 [, &RecordObject2]. . .
Description
Use the GenerateComponentContentRelURL function to create a URL string that represents a relative reference to the specified component for the content servlet. The relative reference is suitable for use on any page that itself has the simple URL format.
If you want to generate an absolute URL for a component, use the GenerateComponentContentURL function.
Note. PeopleSoft recommends using the Transfer function for opening new windows, not this function, as there may be problems maintaining state and window count.
Parameters
|
PortalName |
Specify the name of the portal used for this request, prefixed with the reserved word PORTAL. You can also use a string, such as %Portal, for this value. This parameter is ignored by the content service, but is a required part of the psc URL format. |
|
NodeName |
Specify the name of the node that contains the content, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. |
|
MenuName |
Specify the name of the menu containing the content, prefixed with the reserved word MENUNAME. You can also use a string, such as %Menu, for this value. |
|
Marketname |
Specify the name of the market of the component, prefixed with the reserved word MARKET. You can also use a string, such as %Market, for this value. |
|
ComponentName |
Specify the name of the component, prefixed with the reserved word COMPONENT. You can also use a string, such as %Component, for this value. |
|
Pagename |
Specify the name of the page that contains the content. If you specify a page name, it must be prefixed with the keyword PAGE. You can also specify an empty string ("") for this value. |
|
Action |
Specify a single-character code. Valid actions are:
You can also specify an empty string ("") for this value. |
|
Keylist |
An optional list of field specifications used to select a unique row at level zero in the page you are transferring to, by matching keys in the page you are transferring from. It can also be an already instantiated record object. If a record object is specified, any field of that record object that is also a field of the search record for the destination component is added to keylist. The keys in the fieldlist must uniquely identify a row in the "to" page search record. If a unique row is not identified, of if Force Search Processing has been selected, the search dialog appears. If the keylist parameter is not supplied the destination component's search key must be found as part of the source components level 0 record buffer. |
Returns
If the node has a Node Type of PIA, a string of the following format is returned:
../../../Portal/node/c/menu.component.market?parameters
If the node has a Node Type of ICType, a string of the following format is returned:
../../../portal/node/?ICType=Panel&Menu=menu&Market=market&PanelGroupName=component?parameters
The question mark and the text following the question mark may or may not be included, depending on whether or not you specified a page and action or not.
This function returns a Null string if you specify an invalid portal or node.
Example
The following code:
&MyCompURL = GenerateComponentContentRelURL("EMPLOYEEPORTAL", "CRM", MenuName.SFA, "GBL", Component.CUSTOMERINFO, Page.CUST_DATA1, "U", EMPLID);
Might create the following URL:
../../../psc/PS84/EMPLOYEEPORTAL/CRM/c/SFA.CUSTOMERINFO.GBL?page=CUST_DATA1&&Action=U&emplid=00001
Because this function terminates if the portal or node name is invalid, it's enclosed in a try-catch section so if an exception gets raised, it can be handled.
try &MyURL = GenerateComponentContentRelURL(%Portal, "HRMS", Menuname.ADMIN_WORKFORCE, "GBL", Component.ABSENCE_HISTORY, Page. ABSENCE_HISTORY, "U", EMPLID) catch ExceptionPortal &Ex1 /* error handling portal name not valid */ catch ExceptionNode &Ex2 /* error handling Node name not valid */ end-try;
See Also
GenerateComponentContentURL, GenerateComponentPortalRelURL, GenerateComponentPortalURL, GenerateComponentRelativeURL.
Internet Script Classes (iScript)

 GenerateComponentContentURL
GenerateComponentContentURLSyntax
GenerateComponentContentURL(PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename, MENUNAME.menuname, MARKET.marketname, COMPONENT.componentname, PAGE.pagename, action, [, keylist])
where keylist is a list of field references in the form:
[recordname.]field1 [, [recordname.]field2]. . .
OR
&RecordObject1 [, &RecordObject2]. . .
Description
Use the GenerateComponentContentURL function to create a URL string that represents an absolute reference to the specified component for the content servlet.
The ContentURI of the specified node is used in the generated URL. The URL contains a reference to the portal content (psc) servlet. If you want to generate a URL for the portal service (psp), use the GenerateComponentPortalURL function.
Parameters
|
PortalName |
Specify the name of the portal used for this request, prefixed with the reserved word PORTAL. You can also use a string, such as %Portal, for this value. This parameter is ignored by the content service, but is a required part of the psc URL format. |
|
NodeName |
Specify the name of the node that contains the content, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. |
|
MenuName |
Specify the name of the menu containing the content, prefixed with the reserved word MENUNAME. You can also use a string, such as %Menu, for this value. |
|
Marketname |
Specify the name of the market of the component, prefixed with the reserved word MARKET. You can also use a string, such as %Market, for this value. |
|
ComponentName |
Specify the name of the component, prefixed with the reserved word COMPONENT. You can also use a string, such as %Component, for this value. |
|
Pagename |
Specify the name of the page that contains the content. If you specify a page name, it must be prefixed with the keyword PAGE. You can also specify an empty string ("") for this value. |
|
Action |
Specify a single-character code. Valid actions are:
You can also specify an empty string ("") for this value. |
|
Keylist |
An optional list of field specifications used to select a unique row at level zero in the page you are transferring to, by matching keys in the page you are transferring from. It can also be an already instantiated record object. If a record object is specified, any field of that record object that is also a field of the search record for the destination component is added to keylist. The keys in the fieldlist must uniquely identify a row in the "to" page search record. If a unique row is not identified, of if Force Search Processing has been selected, the search dialog appears. If the keylist parameter is not supplied the destination component's search key must be found as part of the source components level 0 record buffer. |
Returns
If the node has a Node Type of PIA, a string of the following format is returned:
http://Content URI of host node/Portal/node/c/menu.component.market?parameters
If the node has a Node Type of ICType, a string of the following format is returned:
http://Content URI of host node/portal/node/?ICType=Panel&Menu=menu&Market=market&PanelGroupName=component?parameters
The question mark and the text following the question mark may or may not be included, depending on whether or not you specified a page and action or not.
This function returns a Null string if you specify an invalid portal or node.
Example
The following code:
&MyCompURL = GenerateComponentContentURL("EMPLOYEEPORTAL", "CRM", MenuName.SFA, "GBL", Component.CUSTOMERINFO, Page.CUST_DATA1, "U", EMPLID);
Might create the following URL:
http://serverx/servlets/psc/PS84/EMPLOYEEPORTAL/CRM/c/SFA.CUSTOMERINFO.GBL?page=CUST_DATA1&&Action=U&emplid=00001
Because this function terminates if the portal or node name is invalid, it's enclosed in a try-catch section so if an exception gets raised, it can be handled.
try &MyURL = GenerateComponentContentURL(%Portal, "HRMS", Menuname.ADMIN_WORKFORCE, "GBL", Component.ABSENCE_HISTORY, Page. ABSENCE_HISTORY, "U", EMPLID) catch ExceptionPortal &Ex1 /* error handling portal name not valid */ catch ExceptionNode &Ex2 /* error handling Node name not valid */ end-try;
See Also
GenerateComponentContentRelURL, GenerateComponentPortalRelURL, GenerateComponentPortalURL, GenerateComponentRelativeURL.
Internet Script Classes (iScript)

 GenerateComponentPortalRelURL
GenerateComponentPortalRelURLSyntax
GenerateComponentPortalRelURL(PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename, MENUNAME.menuname, MARKET.marketname, COMPONENT.componentname, PAGE.pagename, action, [, keylist])
where keylist is a list of field references in the form:
[recordname.]field1 [, [recordname.]field2]. . .
OR
&RecordObject1 [, &RecordObject2]. . .
Description
Use the GenerateComponentPortalRelURL function to create a URL string URL string that represents a relative reference the specified content (component). The relative reference is suitable for use on any page that itself has the simple URL format.
If you want to generate an absolute URL for a component, use the GenerateComponentPortalURL function.
Parameters
|
portalname |
Specify the name of the portal used for this request, prefixed with the reserved word PORTAL. You can also use a string, such as %Portal, for this value. |
|
nodename |
Specify the name of the node that contains the content, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. |
|
menuname |
Specify the name of the menu containing the content, prefixed with the reserved word MENUNAME. You can also use a string, such as %Menu, for this value. |
|
Marketname |
Specify the name of the market of the component, prefixed with the reserved word MARKET. You can also use a string, such as %Market, for this value. |
|
ComponentName |
Specify the name of the component, prefixed with the reserved word COMPONENT. You can also use a string, such as %Component, for this value. |
|
pagename |
Specify the name of the page that contains the content. If you specify a page name, it must be prefixed with the keyword PAGE. You can also specify a Null string ("") for this value. |
|
action |
Specify a single-character code. Valid actions are:
You can also specify a Null string ("") for this value. |
|
keylist |
An optional list of field specifications used to select a unique row at level zero in the page you are transferring to, by matching keys in the page you are transferring from. It can also be an already instantiated record object. If a record object is specified, any field of that record object that is also a field of the search record for the destination component is added to keylist. The keys in the fieldlist must uniquely identify a row in the "to" page search record. If a unique row is not identified, of if Force Search Processing has been selected, the search dialog appears. If the keylist parameter is not supplied the destination component's search key must be found as part of the source components level 0 record buffer. |
Returns
If the node has a Node Type of PIA, a string of the following format is returned:
../../../portal/node/c/menu.component.market?parameters
If the node has a Node Type of ICType, a string of the following format is returned:
../../../portal/node/?ICType=Panel&Menu=menu&Market=market&PanelGroupName=component?parameters
The question mark and the text following the question mark may or may not be included, depending on whether or not you specified a page and action or not.
This function returns a Null string if you specify an invalid portal or node.
Example
The following code:
&MyCompURL = GenerateComponentPortalRelURL("EMPLOYEEPORTAL", "CRM", MenuName.SFA, "GBL", Component.CUSTOMERINFO, , "", "");
Might create the following URL:
../../../EMPLOYEEPORTAL/CRM/c/sfa.customerinfo.gbl
See Also
GenerateComponentContentRelURL, GenerateComponentContentURL, GenerateComponentPortalURL, GenerateComponentRelativeURL, Internet Script Classes (iScript).

 GenerateComponentPortalURL
GenerateComponentPortalURLSyntax
GenerateComponentPortalURL(PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename, MENUNAME.menuname, MARKET.marketname, COMPONENT.componentname, PAGE.pagename, action, [, keylist])
where keylist is a list of field references in the form:
[recordname.]field1 [, [recordname.]field2]. . .
OR
&RecordObject1 [, &RecordObject2]. . .
Description
Use the GenerateComponentPortalURL function to create a URL string that represents an absolute reference to the specified component for the portal servlet. The PortalURI of the node that hosts the specified portal is used in the generated URL. The URL contains a reference to the portal service (psp) servlet.
If you want to generate a URL for the portal content (psc) servlet, use the GenerateComponentContentURL function.
Parameters
|
portalname |
Specify the name of the portal used for this request, prefixed with the reserved word PORTAL. You can also use a string, such as %Portal, for this value. |
|
nodename |
Specify the name of the node that contains the content, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. |
|
menuname |
Specify the name of the menu containing the content, prefixed with the reserved word MENUNAME. You can also use a string, such as %Menu, for this value. |
|
Marketname |
Specify the name of the market of the component, prefixed with the reserved word MARKET. You can also use a string, such as %Market, for this value. |
|
ComponentName |
Specify the name of the component, prefixed with the reserved word COMPONENT. You can also use a string, such as %Component, for this value. |
|
pagename |
Specify the name of the page that contains the content. If you specify a page name, it must be prefixed with the keyword PAGE. You can also specify a Null string ("") for this value. |
|
action |
Specify a single-character code. Valid actions are:
You can also specify a Null string ("") for this value. |
|
keylist |
An optional list of field specifications used to select a unique row at level zero in the page you are transferring to, by matching keys in the page you are transferring from. It can also be an already instantiated record object. If a record object is specified, any field of that record object that is also a field of the search record for the destination component is added to keylist. The keys in the fieldlist must uniquely identify a row in the "to" page search record. If a unique row is not identified, of if Force Search Processing has been selected, the search dialog appears. If the keylist parameter is not supplied the destination component's search key must be found as part of the source components level 0 record buffer. |
Returns
If the node has a Node Type of PIA, a string of the following format is returned:
http://Portal URI of host node/portal/node/c/menu.component.market?parameters
If the node has a Node Type of ICType, a string of the following format is returned:
http://Portal URI of host node/portal/node/?ICType=Panel&Menu=menu&Market=market&PanelGroupName=component?parameters
Note. If the host node is local, then Portal URI of host node will always be the one you're currently logged in as.
The question mark and the text following the question mark may or may not be included, depending on whether or not you specified a page and action or not.
This function returns a Null string if you specify an invalid portal or node.
Example
The following code:
&MyCompURL = GenerateComponentPortalURL("EMPLOYEEPORTAL", "CRM", MenuName.SFA, "GBL", Component.CUSTOMERINFO, , "", "");
Might create the following URL:
http://mike.com/servlets/psp/testsite/EMPLOYEEPORTAL/CRM/c/sfa.customerinfo.gbl
The following example uses a de-referenced name for the component.
&sComponent = "Component." | &sComponent; &sPage = "Page.EM_VCHR_PYMNT_CLN"; &rwCurrent = GetRow(); /*- The Search Record keys -*/ &sQueryString = &sQueryString | "&BUSINESS_UNIT=" | &rwCurrent.EM_VCHR_INQ_VW.EM_BUSINESS_UNIT.Value; &sQueryString = &sQueryString | "&VOUCHER_ID=" | &rwCurrent.EM_VCHR_INQ_VW.VOUCHER_ID.Value; &sQueryString = GenerateComponentPortalURL(%Portal, %Node, MenuName.EM_BILL_PRESENTMENT, %Market, @&sComponent, @&sPage, "U") | &sQueryString; %Response.RedirectURL(&sURL);
See Also
GenerateComponentContentRelURL, GenerateComponentContentURL, GenerateComponentPortalRelURL, GenerateComponentRelativeURL.
Internet Script Classes (iScript)

 GenerateComponentRelativeURL
GenerateComponentRelativeURLSyntax
GenerateComponentRelativeURL(PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename, MENUNAME.menuname, MARKET.marketname, COMPONENT.componentname, PAGE.pagename, action, [, keylist])
where keylist is a list of field references in the form:
[recordname.]field1 [, [recordname.]field2]. . .
OR
&RecordObject1 [, &RecordObject2]. . .
Description
Use the GenerateComponentRelativeURL function to create a URL string that represents a relative reference the specified content (component). The relative reference is suitable for use on any page that itself has the simple URL format.
If you want to generate an absolute URL for a component, use either the GenerateComponentContentURL or GenerateComponentPortalURL function.
Parameters
|
portalname |
Specify the name of the portal used for this request, prefixed with the reserved word PORTAL. You can also use a string, such as %Portal, for this value. |
|
nodename |
Specify the name of the node that contains the content, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. |
|
menuname |
Specify the name of the menu containing the content, prefixed with the reserved word MENUNAME. You can also use a string, such as %Menu, for this value. |
|
Marketname |
Specify the name of the market of the component, prefixed with the reserved word MARKET. You can also use a string, such as %Market, for this value. |
|
ComponentName |
Specify the name of the component, prefixed with the reserved word COMPONENT. You can also use a string, such as %Component, for this value. |
|
Pagename |
Specify the name of the page that contains the content. If you specify a page name, it must be prefixed with the keyword PAGE. You can also specify a Null string ("") for this value. |
|
Action |
Specify a single-character code. Valid actions are:
You can also specify a Null string ("") for this value. |
|
Keylist |
An optional list of field specifications used to select a unique row at level zero in the page you are transferring to, by matching keys in the page you are transferring from. It can also be an already instantiated record object. If a record object is specified, any field of that record object that is also a field of the search record for the destination component is added to keylist. The keys in the fieldlist must uniquely identify a row in the "to" page search record. If a unique row is not identified, of if Force Search Processing has been selected, the search dialog appears. If the keylist parameter is not supplied the destination component's search key must be found as part of the source components level 0 record buffer. |
Returns
If the node has a Node Type of PIA, a string of the following format is returned:
../../../portal/node/c/menu.component.market?parameters
If the node has a Node Type of ICType, a string of the following format is returned:
../../../portal/node/?ICType=Panel&Menu=menu&Market=market&PanelGroupName=component?parameters
The question mark and the text following the question mark may or may not be included, depending on whether or not you specified a page and action or not.
This function returns a Null string if you specify an invalid portal or node.
Example
The following code example:
&MyCompURL = GenerateComponentRelativeURL("EMPLOYEEPORTAL", "CRM", MenuName.SFA, "GBL", Component.CUSTOMERINFO, "", "");
Might yield the following:
../../../EMPLOYEEPORTAL/CRM/c/sfa.customerinfo.gbl
See Also
GenerateComponentContentRelURL, GenerateComponentContentURL, GenerateComponentPortalRelURL, GenerateComponentPortalURL.
Internet Script Classes (iScript)

 GenerateExternalPortalURL
GenerateExternalPortalURLSyntax
GenerateExternalPortalURL(PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename, URL)
Description
Use the GenerateExternalPortalURL function to create a URL string that represents an absolute reference the specified external content (URL) on the portal servlet.
The PortalURI of the node that hosts the specified portal is used in the generated URL. The generated URL contains a reference to the portal service (psp) servlet.
If you want to generate a relative URL, use the GenerateExternalRelativeURL function.
Parameters
|
portalname |
Specify the name of the portal used for this request, prefixed with the reserved word PORTAL. You can also use a string, such as %Portal, for this value. |
|
NodeName |
Specify the name of the node that contains the content, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. |
|
URL |
Specify the URL to be used for this content. |
Returns
A string of the following format is returned:
http://Portal URI of host node/Portal/node/e/encodedURL
When the portal servlet evaluates an external URL, the Node is ignored, so %Node can always be passed in for the Node parameter.
This function returns a Null string if you specify an invalid portal or node.
Example
The following code:
&url = GenerateExternalPortalURL("EMPLOYEEPORTAL", "CRM", "http://www.excite.com");
Might create the following URL:
http://myserver/psp/ps/EMPLOYEEPORTAL/CRM/e/http%3a%2f%2fwww.excite.com
See Also
Internet Script Classes (iScript)

 GenerateExternalRelativeURL
GenerateExternalRelativeURLSyntax
GenerateExternalRelativeURL(PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename, EncodedURL)
Description
Use the GenerateExternalRelativeURL function to create a URL string that represents a relative reference the specified external content (URL). The relative reference is suitable for use on any page that itself has the simple URL format and which is served by the portal servlet (psp).
If you want to generate an absolute URL, use the GenerateExternalPortalURL function.
Parameters
|
PortalName |
Specify the name of the portal used for this request, prefixed with the reserved word PORTAL. You can also use a string, such as %Portal, for this value. |
|
NodeName |
Specify the name of the node that contains the content, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. |
|
EncodedURL |
Specify the URL to be used for this content. |
Returns
A string of the following format is returned:
../../../Portal/node/e/encodedURL
This function returns a Null string if you specify an invalid portal or node.
Example
The following code:
&url = GenerateExternalRelativeURL("EMPLOYEEPORTAL", "CRM", "http://www.excite.com");
Might create the following URL:
../../../EMPLOYEEPORTAL/CRM/e/http%3a%2f%2fwww.excite.com
See Also
Internet Script Classes (iScript)

 GenerateHomepagePortalURL
GenerateHomepagePortalURLSyntax
GenerateHomepagePortalURL(PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename, Tabname)
Description
Use the GenerateHomepagePortalURL function to create a URL string that represents an absolute reference the specified homepage tab on the portal servlet.
The PortalURI of the node that hosts the specified portal is used in the generated URL. The generated URL contains a reference to the portal service (psp) servlet.
If you want to generate a relative URL, use the GenerateHomepageRelativeURL function.
Parameters
|
portalname |
Specify the name of the portal used for this request, prefixed with the reserved word PORTAL. You can also use a string, such as %Portal, for this value. Note. The value specified for this parameter is ignored. The node name that is used is automatically calculated. However, you must still specify a value for this parameter. |
|
nodename |
Specify the name of the node that contains the content, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. This should be the node that hosts the specified portal. |
|
Tabname |
Specify the name of the tab on the homepage that you want to generate a URL for. If you specify a null string (""), the default tab is used. |
Returns
If the node has a Node Type of PIA, a string of the following format is returned:
http://Portal URI of host node/Portal/node/h/?tab=tabname
This function returns a Null string if you specify an invalid portal or node.
Example
Specifying the following code:
&HomePage = GenerateHomepagePortalURL(%Portal, NODE.North_Asia, "");
Might generate the following string:
http://bejing/psp/psoft/crm/North_Asia/h/?tab=DEFAULT
See Also
Internet Script Classes (iScript)

 GenerateHomepageRelativeURL
GenerateHomepageRelativeURLSyntax
GenerateHomepageRelativeURL(PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename, Tabname)
Description
Use the GenerateHomepageRelativeURL function to create a URL string that represents a relative reference the specified homepage on the portal servlet. The relative reference is suitable for use on any page that itself has the simple URL format.
If you want to generate an absolute URL, use the GenerateHomepagePortalURL function.
Parameters
|
portalname |
Specify the name of the portal used for this request, prefixed with the reserved word PORTAL. You can also use a string, such as %Portal, for this value. |
|
nodename |
Specify the name of the node that contains the content, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. . This should be the node that hosts the specified portal. |
|
Tabname |
Specify the name of the tab on the homepage that you want to generate a URL for. If you specify a null string (""), the default tab is used. |
Returns
If the node has a Node Type of PIA, a string of the following format is returned:
../../../Portal/node/h/?tab=tabname
If the node has a Node Type of ICType, a string of the following format is returned:
./?cmd=start
This function returns a Null string if you specify an invalid portal or node.
Example
The following code:
&HomePage = GenerateHomepageRelativeURL(%Portal, NODE.North_Asia, "");
Might generate the following string:
../../../crm/North_Asia/h/?tab=DEFAULT
See Also
Internet Script Classes (iScript)

 GenerateMobileTree
GenerateMobileTreeSyntax
GenerateMobileTree(&CIObject [,CIObject_property])
Description
Use the GenerateMobileTree function to display data in a tree format, with nodes and leaves. The result of the GenerateMobileTree function is an HTML string, which can be displayed in an HTML area control.
Use this function in the OnInit event to display the mobile tree, and on the OnChange event for programs related to expanding, collapsing or selecting nodes.
Mobile HTML Tree
The positional links at the top of the page (First, Previous, Next, Last, Left, Right) enable the user to navigate around the tree. These links are automatically generated as part of the execution of GenerateTree.
The icon next to a node can have a + sign or a - sign in it, depending on whether the node is collapsed or expanded. When a node is collapsed, none of the nodes that report to the collapsed node are displayed, and the icon has a + sign. When a node is expanded, all the nodes that report to it are displayed, and the icon has a - sign. You can collapse and expand a node by clicking in the icon. This enables you to view the tree at different levels of detail. When the icon for a node has no + or − sign in it, it is a terminal node, and cannot be expanded or collapsed.
Using the GenerateMobileTree Function
The GenerateMobileTree function is similar to the GenerateTree function, however, there are several important differences.
The GenerateMobileTree function does not take a standalone rowset for data. Mobile does not support standalone rowsets, so you must populate your tree data one item at a time.
You cannot use the Tree Classes with the GenerateMobileTree function.
To use the GenerateMobileTree function:
Define the Component Interface.
You must use a Component Interface that is created from a component that contains the TREECTL_HDR and TREECTL_NODE records. When the Component Interface is synched to the device, these records do not have to contain any data, they can be populated using PeopleCode.
Add an HTML area to the mobile page.
This involves adding a long text field to the Component Interface, specifying how it displays on the mobile page, and so on. The value of the Component Interface long text field is what is displayed in the HTML area.
Determine what property on the Component Interface is going to contain the OnChange PeopleCode used to evaluate the end user action and call the appropriate PeopleCode programs.
The action an end user takes (selecting a row, or expanding or collapsing a node) is accessible to this property.
This property must be a character field that is at least 46 characters long. The field can be made invisible.
Specify this property as the value for the PAGE_FIELD_NAME field on the TREECTRL_HDR_SBR record.
Populate the tree, specify values for the nodes, leaves, images, and so on.
Parameters
|
&CIObject |
This is the mobile object that is to be viewed in a hierarchy tree view. This object is from a peer reference. |
|
CIObject_property |
This is a property on the mobile object that is to be viewed in a hierarchy tree view. |
Returns
None.
Example
In the OnInit event, generate the mobile tree.
Local ApiObject &ob; &ob = %ThisMobileObject; &MyCI = %Session.GetCompIntfc(ComIntfc.RDM_RELTREE); &MyCI.Key_01 = "2"; &MyCI.Create(); &MyCI.PAGE_FIELD_NAME = "TREELEVELNT"; &MyCI.RDM.RELTREE_NDE.InsertItem(1); &MyCI.RDM.RELTREE_NDE.Item(1).TREE_NODE = "NAME 1"; &MyCI.RDM.RELTREE_NDE.Item(1).DESCR = "Descr 1"; &MyCI.RDM.RELTREE_NDE.Item(1).PARENT_FLAG = "Y"; &MyCI.RDM.RELTREE_NDE.Item(1).TREE_LEVEL_NUM = 1; &MyCI.RDM.RELTREE_NDE.Item(1).LEAF_FLAG = "N"; &MyCI.RDM.RELTREE_NDE.InsertItem(2); &MyCI.RDM.RELTREE_NDE.Item(2).TREE_NODE = "NAME 3"; &MyCI.RDM.RELTREE_NDE.Item(2).DESCR = "Descr 2"; &MyCI.RDM.RELTREE_NDE.Item(2).PARENT_FLAG = "Y"; &MyCI.RDM.RELTREE_NDE.Item(2).TREE_LEVEL_NUM = 2; &MyCI.RDM.RELTREE_NDE.Item(2).LEAF_FLAG = "N"; &MyCI.RDM.RELTREE_NDE.InsertItem(3); &MyCI.RDM.RELTREE_NDE.Item(3).TREE_NODE = "NAME 1"; &MyCI.RDM.RELTREE_NDE.Item(3).DESCR = "Descr 3"; &MyCI.RDM.RELTREE_NDE.Item(3).PARENT_FLAG = "Y"; &MyCI.RDM.RELTREE_NDE.Item(3).TREE_LEVEL_NUM = 1; &MyCI.RDM.RELTREE_NDE.Item(3).LEAF_FLAG = "N"; &OB.QE_COMMENTS = GenerateMobileTree(&MyCI);
The following PeopleCode is used in the OnChange event (used for when a user selects a node, expands a node or closes a node):
Local ApiObject &ob; &ob = %ThisMobileObject; &MyCI = %Session.GetCompIntfc(ComIntfc.RDM_RELTREE); &MyCI.Key_01 = "2"; &MyCI.Get(); &MyCI.PAGE_FIELD_NAME = "TREECTLEVENT" If Left(%ThisMobileObject.TREELEVENT, 1) = "S" Then Warning ("This node has been selected"); End-If; &ob.QE_COMMENTS = GenerateMobileTree(&MyCI, %ThisMobileObject.TREELEVENT);
See Also

 GenerateQueryContentURL
GenerateQueryContentURLSyntax
GenerateQueryContentURL(PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename, QueryName, IsPublic [, IsNewWindow])
Description
Use the GenerateQueryContentURL function to create a URL string that represents an absolute reference the specified query (URL) on the content servlet.
The PortalURI of the node that hosts the specified portal is used in the generated URL. The generated URL contains a reference to the portal content (psc) servlet.
If you want to generate a relative URL, use the GenerateQueryRelativeURL function.
If you want to generate a URL for the portal service (psp) servlet, use the GenerateQueryPortalURL function.
Parameters
|
portalname |
Specify the name of the portal used for this request, prefixed with the reserved word PORTAL. You can also use a string, such as %Portal, for this value. |
|
nodename |
Specify the name of the node that contains the query, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. |
|
Queryname |
Specify the name of the query you want to generate a URL for. This parameter takes a string value. |
|
IsPublic |
Specify whether the query is public or private. This parameter takes a Boolean value: True, the query is public, False otherwise. |
|
IsNewWindow |
Specify whether the URL is for a new browser instance. This parameter takes a Boolean value: True, the URL is for a new browser instance, False otherwise. The default is False. If the value is True this function generates a new state block for use in a separate browser instance. This does not automatically open a new browser instance. It just supports it. |
Note. When Query is being run on a PeopleTools version prior to 8.16, the query URL does not include the ability to specify if a query is public or private. On PeopleTools versions 8.16 and higher, the generated URL contains either the keyword PUBLIC or PRIVATE prepended to the query name. If you are building a URL for a portal node that is on a PeopleTools release prior to 8.16, you must remove the public or private keyword before trying to use the URL.
Returns
If IsPublic is specified as True, and the node has a Node Type of PIA, a string of the following format is returned:
http://PortalURI/Portal/node/q/?ICAction=ICQryNameURL=PUBLIC.QueryName
If IsPublic is specified as False, and the node has a Node Type of PIA, a string of the following format is returned:
http://PortalURI/Portal/node/q/?ICAction=ICQryNameURL=PRIVATE.QueryName
This function returns a Null string if you specify an invalid portal or node.
Example
The following code example:
&url = GenerateQueryContentURL(%Portal, "RMTNODE", "QUERYNAME", True);
might produce a string as follows:
http://bsto091200/psc/ps/EMPLOYEE/RMTNODE/q/?ICAction=ICQryNameURL=PUBLIC.QUERYNAME
The following code example uses the optional parameter to produce a URL that supports a new browser instance:
&url = GenerateQueryContentURL(%Portal, "RMTNODE", "QUERYNAME", True, True);
might produce a string as follows:
http://bsto091200/psc/ps_newwin/EMPLOYEE/RMTNODE/q/?ICAction=ICQryNameURL=PUBLIC.QUERYNAME
See Also
GenerateQueryPortalURL, GenerateQueryRelativeURL.
Internet Script Classes (iScript)
Getting Started with PeopleSoft Query

 GenerateQueryPortalURL
GenerateQueryPortalURLSyntax
GenerateQueryPortalURL(PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename, QueryName, IsPublic [, IsNewWindow])
Description
Use the GenerateQueryPortalURL function to create a URL string that represents an absolute reference the specified query (URL) on the portal servlet.
The PortalURI of the node that hosts the specified portal is used in the generated URL. The generated URL contains a reference to the portal service (psp) servlet.
If you want to generate a relative URL, use the GenerateQueryRelativeURL function.
If you want to generate a URL for the portal content (psc) servlet, use the GenerateQueryContentURL function.
Parameters
|
portalname |
Specify the name of the portal used for this request, prefixed with the reserved word PORTAL. You can also use a string, such as %Portal, for this value. |
|
nodename |
Specify the name of the node that contains the query, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. |
|
Queryname |
Specify the name of the query you want to generate a URL for. This parameter takes a string value. |
|
IsPublic |
Specify whether the query is public or private. This parameter takes a Boolean value: True, the query is public, False otherwise. |
|
IsNewWindow |
Specify whether the URL is for a new browser instance. This parameter takes a Boolean value: True, the URL is for a new browser instance, False otherwise. The default is False. If the value is True this function generates a new state block for use in a separate browser instance. This does not automatically open a new browser instance. It just supports it. |
Note. When Query is being run on a PeopleTools version prior to 8.16, the query URL does not include the ability to specify if a query is public or private. On PeopleTools versions 8.16 and higher, the generated URL contains either the keyword PUBLIC or PRIVATE prepended to the query name. If you are building a URL for a portal node that is on a PeopleTools release prior to 8.16, you must remove the public or private keyword before trying to use the URL.
Returns
If IsPublic is specified as True, and the node has a Node Type of PIA, a string of the following format is returned:
http://PortalURI/Portal/node/q/?ICAction=ICQryNameURL=PUBLIC.QueryName
If IsPublic is specified as False, and the node has a Node Type of PIA, a string of the following format is returned:
http://PortalURI/Portal/node/q/?ICAction=ICQryNameURL=PRIVATE.QueryName
This function returns a Null string if you specify an invalid portal or node.
Example
The following code example:
&url = GenerateQueryPortalURL(%Portal, "RMTNODE", "QUERYNAME", True);
might produce a string as follows:
http://bsto091200/psp/ps/EMPLOYEE/RMTNODE/q/?ICAction=ICQryNameURL=PUBLIC.QUERYNAME
The following code example uses the optional parameter to produce a URL that supports a new browser instance:
&url = GenerateQueryPortalURL(%Portal, "RMTNODE", "QUERYNAME", True, True);
might produce a string as follows:
http://bsto091200/psp/ps_newwin/EMPLOYEE/RMTNODE/q/?ICAction=ICQryNameURL=PUBLIC.QUERYNAME
See Also
GenerateQueryContentURL, GenerateQueryRelativeURL.
Internet Script Classes (iScript)
Getting Started with PeopleSoft Query

 GenerateQueryRelativeURL
GenerateQueryRelativeURLSyntax
GenerateQueryRelativeURL(PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename, QueryName, IsPublic [, IsNewWindow])
Description
Use the GenerateQueryRelativeURL function to creates a URL string that represents a relative reference to the specified query on the portal servlet. The relative reference is suitable for use on any page that itself has the simple URL format.
If you want to generate an absolute URL, use either the GenerateQueryPortalURL or GenerateQueryContentURL function.
Parameters
|
portalname |
Specify the name of the portal used for this request, prefixed with the reserved word PORTAL. You can also use a string, such as %Portal, for this value. |
|
nodename |
Specify the name of the node that contains the query, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. |
|
Queryname |
Specify the name of the query you want to generate a URL for. This parameter takes a string value. |
|
IsPublic |
Specify whether the query is public or private. This parameter takes a Boolean value: True, the query is public, False otherwise. |
|
IsNewWindow |
Specify whether the URL is for a new browser instance. This parameter takes a Boolean value: True, the URL is for a new browser instance, False otherwise. The default is False. If the value is True this function generates a new state block for use in a separate browser instance. This does not automatically open a new browser instance. It just supports it. |
Note. When Query is being run on a PeopleTools version prior to 8.16, the query URL does not include the ability to specify if a query is public or private. On PeopleTools versions 8.16 and higher, the generated URL contains either the keyword PUBLIC or PRIVATE prepended to the query name. If you are building a URL for a portal node that is on a PeopleTools release prior to 8.16, you must remove the public or private keyword before trying to use the URL.
Returns
If IsPublic is specified as True, and the node has a Node Type of PIA, a string of the following format is returned:
../../../portal/node/q/?ICAction=ICQryNameURL=PUBLIC.QueryName
If IsPublic is specified as False, and the node has a Node Type of PIA, a string of the following format is returned:
../../../portal/node/q/q/?ICAction=ICQryNameURL=PRIVATE.QueryName
This function returns a Null string if you specify an invalid portal or node.
Example
The following code example:
&url = GenerateQueryRelativeURL(%Portal, "RMTNODE", "QUERYNAME", True);
might produce a string as follows:
../../../EMPLOYEE/RMTNODE/q/?ICAction=ICQryNameURL=PUBLIC.QUERYNAME
See Also
GenerateQueryContentURL, GenerateQueryPortalURL.
Internet Script Classes (iScript)
Getting Started with PeopleSoft Query

 GenerateScriptContentRelURL
GenerateScriptContentRelURLSyntax
GenerateScriptContentRelURL(PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename, RECORD.recordname, FIELD.fieldname, event_name, function_name, [, keylist])
where keylist is a list of field references in the form:
[recordname.]field1 [, [recordname.]field2]. . .
OR
&RecordObject1 [, &RecordObject2]. . .
Description
Use the GenerateScriptContentRelURL function to create a URL string that represents a relative reference to the specified iScript. The generated URL contains a reference to the portal content (psc) servlet.
If you want to generate an absolute URL for an iScript for the portal content servlet, use the GenerateScriptContentURL function.
Parameters
|
portalname |
Specify the name of the portal used for this request, prefixed with the reserved word PORTAL. You can also use a string, such as %Portal, for this value. |
|
nodename |
Specify the name of the node that contains the iScript, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. |
|
recordname |
Specify the name of the record containing the iScript, prefixed with the reserved word RECORD. |
|
fieldname |
Specify the name of the field containing the iScript, prefixed with the reserved word FIELD. |
|
event_name |
Specify the name of the event containing the iScript. This is generally the FieldFormula event. |
|
function_name |
Specify the name of the iScript function. |
|
keylist |
An optional list of parameters used with the function. It can also be an already instantiated record object. |
Returns
If the node has a Node Type of PIA, a string of the following format is returned:
/psc/s/recname.fieldname.event_name.function_name?parameters
If the node has a Node Type of ICType, a string of the following format is returned:
/portal/node/?ICType=Script&ICScriptProgramName=recname.fieldname.event_name.function_name?parameters
The question mark and the text following the question mark may or may not be included, depending on whether or not you specified a page and action or not.
This function returns a Null string if you specify an invalid portal or node.
Example
The following code:
&MyScriptURL = GenerateScriptContentRelURL("EMPLOYEEPORTAL", "CRM", Record.WEBLIB_CRM, Field.SFASCRIPTS, "FieldFormula", "Iscript_SFAHOME ");
Might yield the following URL:
/psc/s/WEBLIB_CRM.SFASCRIPTS.FieldFormula.IScript_SFAHOME
See Also
GenerateScriptContentURL, GenerateScriptPortalRelURL, GenerateScriptPortalURL, GenerateScriptRelativeURL.
Internet Script Classes (iScript)

 GenerateScriptContentURL
GenerateScriptContentURLSyntax
GenerateScriptContentURL(PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename, RECORD.recordname, FIELD.fieldname, event_name, function_name, [, keylist])
where keylist is a list of field references in the form:
[recordname.]field1 [, [recordname.]field2]. . .
OR
&RecordObject1 [, &RecordObject2]. . .
Description
Use the GenerateScriptContentURL function to create a URL string that represents an absolute reference to the specified iScript for the content servlet.
The ContentURI of the specified node is used in the generated URL. The URL contains a reference to the portal content (psc) servlet.
If you want to generate a URL for an iScript for the portal servlet, use the GenerateScriptPortalURL function.
Parameters
|
portalname |
Specify the name of the portal used for this request, prefixed with the reserved word PORTAL. You can also use a string, such as %Portal, for this value. |
|
nodename |
Specify the name of the node that contains the iScript, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. |
|
recordname |
Specify the name of the record containing the iScript, prefixed with the reserved word RECORD. |
|
fieldname |
Specify the name of the field containing the iScript, prefixed with the reserved word FIELD. |
|
event_name |
Specify the name of the event containing the iScript. This is generally the FieldFormula event. |
|
function_name |
Specify the name of the iScript function. |
|
keylist |
An optional list of parameters used with the function. It can also be an already instantiated record object. |
Returns
If the node has a Node Type of PIA, a string of the following format is returned:
http://Content URI of host node/portal/node/s/recname.fieldname.event_name.function_name?parameters
If the node has a Node Type of ICType, a string of the following format is returned:
http://Content URI of host node/portal/node/?ICType=Script&ICScriptProgramName=recname.fieldname.event_name.function_name?parameters
The question mark and the text following the question mark may or may not be included, depending on whether or not you specified a page and action or not.
This function returns a Null string if you specify an invalid portal or node.
Example
The following code:
&MyScriptURL = GenerateScriptContentURL("EMPLOYEEPORTAL", "CRM", Record.WEBLIB_CRM, Field.SFASCRIPTS, "FieldFormula", "Iscript_SFAHOME ");
Might yield the following URL:
http://mike.com/servlets/psc/testsite/EMPLOYEEPORTAL/CRM/s/WEBLIB_CRM.SFASCRIPTS.FieldFormula.IScript_SFAHOME
See Also
GenerateScriptContentRelURL, GenerateScriptPortalRelURL, GenerateScriptPortalURL, GenerateScriptRelativeURL.
Internet Script Classes (iScript)

 GenerateScriptPortalRelURL
GenerateScriptPortalRelURLSyntax
GenerateScriptPortalRelURL(PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename, RECORD.recordname, FIELD.fieldname, event_name, function_name, [, keylist])
where keylist is a list of field references in the form:
[recordname.]field1 [, [recordname.]field2]. . .
OR
&RecordObject1 [, &RecordObject2]. . .
Description
Use the GenerateScriptPortalRelURL function to create a URL string that represents a relative reference to the specified iScript. The generated URL contains a reference to the portal service (psp) servlet.
If you want to generate an absolute URL for an iScript for the portal service servlet, use the GenerateScriptPortalURL function.
Parameters
|
portalname |
Specify the name of the portal used for this request, prefixed with the reserved word PORTAL. You can also use a string, such as %Portal, for this value. |
|
nodename |
Specify the name of the node that contains the iScript, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. |
|
recordname |
Specify the name of the record containing the iScript, prefixed with the reserved word RECORD. |
|
fieldname |
Specify the name of the field containing the iScript, prefixed with the reserved word FIELD. |
|
event_name |
Specify the name of the event containing the iScript. This is generally the FieldFormula event. |
|
function_name |
Specify the name of the iScript function. |
|
keylist |
An optional list of parameters used with the function. It can also be an already instantiated record object. |
Returns
If the node has a Node Type of PIA, a string of the following format is returned:
/psp/s/recname.fieldname.event_name.function_name?parameters
If the node has a Node Type of ICType, a string of the following format is returned:
/portal/node/?ICType=Script&ICScriptProgramName=recname.fieldname.event_name.function_name?parameters
The question mark and the text following the question mark may or may not be included, depending on whether or not you specified a page and action or not.
This function returns a Null string if you specify an invalid portal or node.
Example
The following code:
&MyScriptURL = GenerateScriptPortalRelURL("EMPLOYEEPORTAL", "CRM", Record.WEBLIB_CRM, Field.SFASCRIPTS, "FieldFormula", "IScript_SFAHOME");
Might yield the following:
/psp/s/WEBLIB_CRM.SFASCRIPTS.FieldFormula.IScript_SFAHOME
See Also
GenerateScriptContentRelURL, GenerateScriptContentURL, GenerateScriptPortalURL, GenerateScriptRelativeURL.
Internet Script Classes (iScript)

 GenerateScriptPortalURL
GenerateScriptPortalURLSyntax
GenerateScriptPortalURL(PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename, RECORD.recordname, FIELD.fieldname, event_name, function_name, [, keylist])
where keylist is a list of field references in the form:
[recordname.]field1 [, [recordname.]field2]. . .
OR
&RecordObject1 [, &RecordObject2]. . .
Description
Use the GenerateScriptPortalURL function to create a URL string that represents an absolute reference to the specified iScript for the portal servlet. The PortalURI of the node that hosts the specified portal is used in the generated URL. The URL contains a reference to the portal service (psp) servlet.
If you want to generate a URL for an iScript for the portal content (psc) servlet, use the GenerateScriptContentURL function.
Parameters
|
portalname |
Specify the name of the portal used for this request, prefixed with the reserved word PORTAL. You can also use a string, such as %Portal, for this value. |
|
nodename |
Specify the name of the node that contains the iScript, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. |
|
recordname |
Specify the name of the record containing the iScript, prefixed with the reserved word RECORD. |
|
fieldname |
Specify the name of the field containing the iScript, prefixed with the reserved word FIELD. |
|
event_name |
Specify the name of the event containing the iScript. This is generally the FieldFormula event. |
|
function_name |
Specify the name of the iScript function. |
|
keylist |
An optional list of parameters used with the function. It can also be an already instantiated record object. |
Returns
If a node has a Node Type of PIA, a string of the following format is returned:
http://Portal URI of host portal/portal/node/s/recname.fieldname.event_name.function_name?parameters
If the node has a Node Type of ICType, a string of the following format is returned:
http://Portal URI of host node/portal/node/?ICType=Script&ICScriptProgramName=recname.fieldname.event_name.function_name?parameters
The question mark and the text following the question mark may or may not be included, depending on whether or not you specified a page and action or not.
This function returns a Null string if you specify an invalid portal or node.
Example
The following code:
&MyScriptURL = GenerateScriptPortalURL("EMPLOYEEPORTAL", "CRM", Record.WEBLIB_CRM, Field.SFASCRIPTS, "FieldFormula", "IScript_SFAHOME");
Might yield the following:
http://mike.com/servlets/psp/testsite/EMPLOYEEPORTAL/CRM/s/WEBLIB_CRM.SFASCRIPTS.FieldFormula.IScript_SFAHOME
See Also
GenerateScriptContentRelURL, GenerateScriptContentURL, GenerateScriptPortalRelURL, GenerateScriptRelativeURL.
Internet Script Classes (iScript)

 GenerateScriptRelativeURL
GenerateScriptRelativeURLSyntax
GenerateScriptRelativeURL(PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename, RECORD.recordname, FIELD.fieldname, event_name, function_name, [, keylist])
where keylist is a list of field references in the form:
[recordname.]field1 [, [recordname.]field2]. . .
OR
&RecordObject1 [, &RecordObject2]. . .
Description
Use the GenerateScriptRelativeURL function to create a relative URL string that represents a relative reference to the specified iScript. The relative reference is suitable for use on any page that has the simple URL format.
If you want to generate an absolute URL for an iScript, use either the GenerateScriptContentURL or GenerateScriptPortalURL function.
Parameters
|
portalname |
Specify the name of the portal used for this request, prefixed with the reserved word PORTAL. You can also use a string, such as %Portal, for this value. |
|
nodename |
Specify the name of the node that contains the iScript, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. |
|
recordname |
Specify the name of the record containing the iScript, prefixed with the reserved word RECORD. |
|
fieldname |
Specify the name of the field containing the iScript, prefixed with the reserved word FIELD. |
|
event_name |
Specify the name of the event containing the iScript. This is generally the FieldFormula event. |
|
function_name |
Specify the name of the iScript function. |
|
keylist |
An optional list of parameters used with the function. It can also be an already instantiated record object. |
Returns
If the node has a Node Type of PIA, a string of the following format is returned:
portal/node/s/recname.fieldname.event_name.function_name?parameters
If the node has a Node Type of ICType, a string of the following format is returned:
portal/node/?ICType=Script&ICScriptProgramName=recname.fieldname.event_name.function_name?parameters
The question mark and the text following the question mark may or may not be included, depending on whether or not you specified a page and action or not.
This function returns a Null string if you specify an invalid portal or node.
Example
The following code:
&MyScriptURL = GenerateScriptRelativeURL("EMPLOYEEPORTAL", "CRM", Record.WEBLIB_CRM, Field.SFASCRIPTS, "FieldFormula", "IScript_SFAHOME");
Might yield the following:
../../../EMPLOYEEPORTAL/CRM//s/WEBLIB_CRM.SFASCRIPTS.FieldFormula.IScript_SFAHOME
See Also
GenerateScriptContentRelURL, GenerateScriptContentURL, GenerateScriptPortalRelURL, GenerateScriptPortalURL.
Internet Script Classes (iScript)

 GenerateTree
GenerateTreeSyntax
GenerateTree(&rowset [, TreeEventField])
Description
Use the GenerateTree function to display data in a tree format, with nodes and leaves. The result of the GenerateTree function is an HTML string, which can be displayed in an HTML area control. The tree generated by GenerateTree is called an HTML tree.
The GenerateTree function can be used in conjunction with the Tree Classes to display data from trees created using Tree Manager.
The GenerateTree function works with both an HTML area control and a hidden field. The TreeEventField parameter contains the contents of the invisible character field used to process the HTML tree events.
When an end-user selects a node, expands a node, collapses a node, or uses one of the navigation links, that event (end-user action) is passed to the invisible field, and the invisible field's FieldChange PeopleCode is executed.
See Also
Using HTML Tree Actions (Events).
Parameters
|
&rowset |
Specify the name of the rowset you've populated with tree data. |
|
TreeEventField |
Specify the contents of the invisible character field used to process the HTML tree events. The first time the GenerateTree function is used, that is, to generate the initial tree, you don't need to include this parameter. Subsequent calls require this parameter. |
Returns
A string that contains HTML code that can be used with the HTML control to display a tree.
Example
In the following example, TREECTLEVENT is the name of the invisible control field that contains the event string that was passed from the browser.
HTMLAREA = GenerateTree(&TREECTL, TREECTLEVENT);
See Also
Using the GenerateTree Function.

 GenerateWorklistPortalURL
GenerateWorklistPortalURLSyntax
GenerateWorklistPortalURL(PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename, BusProc, Activity, Event, Worklist, Instance)
Description
Use the GenerateWorklistPortalURL function to create a URL string that represents an absolute reference the specified Worklist (URL) on the portal servlet.
The PortalURI of the node that hosts the specified portal is used in the generated URL. The generated URL contains a reference to the portal service (psp) servlet.
If you want to generate a relative URL, use the GenerateWorklistRelativeURL function.
Parameters
|
portalname |
Specify the name of the portal used for this request, prefixed with the reserved word PORTAL. You can also use a string, such as %Portal, for this value. |
|
nodename |
Specify the name of the node that contains the content, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. |
|
BusProc |
Specify the business process of the Worklist. |
|
Activity |
Specify the activity of the Worklist. |
|
Event |
Specify the event of the Worklist. |
|
Instance |
Specify the instance of the Worklist. |
Returns
A string of the following format:
http://PortalURI/Portal/node/w/BusProc.Activity.Event.Worklist.Instance
This function returns a Null string if you specify an invalid portal or node.
See Also
Internet Script Classes (iScript)
Understanding PeopleSoft Workflow

 GenerateWorklistRelativeURL
GenerateWorklistRelativeURLSyntax
GenerateWorklistRelativeURL(PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename, BusProc, Activity, Event, Worklist, Instance)
Description
Use the GenerateWorklistRelativeURL function to create a URL string that represents a relative reference to the specified Worklist on the portal servlet. The relative reference is suitable for use on any page that itself has the simple URL format.
If you want to generate an absolute URL, use the GenerateWorklistPortalURL function.
Parameters
|
portalname |
Specify the name of the portal used for this request, prefixed with the reserved word PORTAL. You can also use a string, such as %Portal, for this value. |
|
nodename |
Specify the name of the node that contains the content, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. |
|
BusProc |
Specify the business process of the Worklist. |
|
Activity |
Specify the activity of the Worklist. |
|
Event |
Specify the event of the Worklist. |
|
Instance |
Specify the instance of the Worklist. |
Returns
A string of the following format:
../../../Portal/Node/w/BusProc.Activity.Event.Worklist.Instance
This function returns a Null string if you specify an invalid portal or node.
Example
Given the following activity:
Example activity
The following is an example PeopleCode statement used to access this activity:
GenerateWorklistRelativeURL(%Portal, %Node, "Administer Workflow", "Find Timeout Worklists", "Worklist Current Operator", "Timeout Notification", 1);
See Also
Internet Script Classes (iScript)
Understanding PeopleSoft Workflow

 GetAESection
GetAESectionSyntax
GetAESection(ae_applid, ae_section [, effdt])
Description
Use the GetAESection function to open and associate an AESection PeopleCode object with the base section, as specified. If no base section by the specified name is found, one is created. This enables you to create base sections as needed.
Warning! When you open or get an AESection object, (that is, the base section) any existing steps in the section are deleted.
After you’ve instantiated the AESection object, set the template section using the SetTemplate AESection class method. You can copy steps from the template section to the base section before you start the PeopleSoft Application Engine program. This is useful for applications that let users input their "rules" into a user-friendly page, then convert these rules, at save time, into Application Engine constructs.
When an AESection is opened (or accessed), the system first looks to see if it exists with the given input parameters. If such a section doesn’t exist, the system looks for a similar section based on market, database platform, and effective date.
The AESection Object is designed for use within an online program. Typically, dynamic sections should be constructed in response to an end user action.
Note. Do not call an AESection object from an Application Engine PeopleCode Action. If you need to access another section, use the CallSection action instead.
Parameters
|
ae_applid |
Specifies the application ID of the section you want to modify. |
|
ae_section |
Specifies the section name of the base section you want to modify. If no base section by the specified name is found, one is created. |
|
effdt |
Specifies the effective date of the section you want to modify (optional). |
Returns
An AESection object is returned.
See Also

 GetAnalyticGrid
GetAnalyticGridSyntax
GetAnalyticGrid(PAGE.pagename, gridname)
Description
Use the GetAnalyticGrid function to instantiate an analytic grid object from the AnalyticGrid class, and populates it with the grid specified by gridname, which is the Page Field Name on the General tab of that analytic grid’s page field properties.
Specify a grid name consisting of any combination of uppercase letters, digits and "#", "$", "@", and "_".
Note. PeopleSoft builds a page grid one row at a time. Because the AnalyticGrid class applies to a complete grid, you can’t attach PeopleCode that uses the AnalyticGrid class to events that occur before the grid is built; the earliest event you can use is the page Activate event.
See Activate Event.
When you place an analytic grid on a page, the grid is automatically named the same as the name of the primary record of the scroll for the grid (in the Page Field Name.)
Note. If the name of the record changes, the Page Field Name is not automatically updated. You must change this name if you want the name of the grid to reflect the name of the record.
This is the name you use with the GetAnalyticGrid function. You can change this name on the General tab of the Analytic Grid control properties.
To change a grid name:
Open the page in PeopleSoft Application Designer, select the analytic grid and access the Analytic Grid control properties.
On the General tab, type the new grid name in Page Field Name.
Note. Every grid on a page must have a unique name.
Parameters
|
PAGE. pagename |
Specify the name of the page definition containing the grid you want to access. |
|
gridname |
Specify the Page Field Name on the General tab of the grid’s page field properties. |
Returns
A reference to an AnalyticGrid object.
See Also

 GetAnalyticInstance
GetAnalyticInstanceSyntax
GetAnalyticInstance(ID)
Description
Use the GetAnalyticInstance function to return a reference to the AnalyticInstance object as specified by the ID.
The analytic instance specified by ID must already be created before using this function.
Parameters
|
ID |
Specify the analytic instance identifier that you want to access. |
Returns
An AnalyticInstance object if successful, null otherwise.
See Also

 GetArchPubHeaderXmlDoc
GetArchPubHeaderXmlDocSyntax
GetArchPubHeaderXmlDoc(PubID, PubNode, ChannelName, VersionName[, Segment])
Description
Use the GetArchPubHeaderXmlDoc function to retrieve an archived message header from the message queue. The message header, also known as the message instance, is the published message before any transformations were performed.
Note. This function should not be used in standard message processing. It should only be used when accessing archived messages.
Parameters
|
PubID |
Specify the PubID of the message. |
|
PubNode |
Specify the Pub Node Name of the message. |
|
ChannelName |
Specify the channel name of the message. |
|
VersionName |
Specify the version name of the message. |
|
Segment |
Specify an integer representing which segment you want to access. The default value is one, which means that if you do not specify a segment, the first segment is accessed. |
Returns
A reference to an XmlDoc object if successful, a null value if not successful.
See Also
GetPubHeaderXmlDoc, GetArchPubXmlDoc.

 GetArchPubXmlDoc
GetArchPubXmlDocSyntax
GetArchPubXmlDoc(PubID, PubNode, ChannelName, VersionName, MessageName, SubNode[, Segment])
Description
Use the GetArchPubXmlDoc function to retrieve an archived message from the message queue. This is the message after any transformations have been preformed.
This function creates and loads a data tree for the specified message version, and returns a null value if not successful.
This function is used for publication contract error correction when the error correction process needs to fetch a particular message instance for the publication contract in error. SQL on the Publication Contract table is used to retrieve the key fields.
Note. This function should not be used in standard message processing. It should only be used when accessing archived messages.
Parameters
|
PubID |
Specify the PubID of the message. |
|
PubNode |
Specify the Pub Node Name of the message. |
|
ChannelName |
Specify the channel name of the message. |
|
VersionName |
Specify the version name of the message. |
|
MessageName |
Specify the name of the message. |
|
SubNode |
Specify the subnode of the message. |
|
Segment |
Specify an integer representing which segment you want to access. The default value is one, which means that if you do not specify a segment, the first segment is accessed. |
Returns
A reference to an XmlDoc object if successful, NULL if not successful.
See Also
GetArchPubHeaderXmlDoc, GetPubHeaderXmlDoc.

 GetArchSubXmlDoc
GetArchSubXmlDocSyntax
GetArchSubXmlDoc(PubID, PubNode, ChannelName, VersionName, MessageName[, Segment])
Description
Use the GetArchSubXmlDoc function to retrieve an archived message from the message queue.
This function creates and loads a data tree for the specified message version, and returns a null value if not successful.
This function is used for subscription contract error correction, when the error correction process needs to fetch a particular message instance for the subscription contract in error. SQL on the Subscription Contract table is used to retrieve the key fields.
Note. This function should not be used in standard message processing. It should only be used when accessing archived messages.
Parameters
|
PubID |
Specify the PubID of the message. |
|
PubNode |
Specify the Pub Node Name of the message. |
|
ChannelName |
Specify the channel name of the message. |
|
VersionName |
Specify the version name of the message. |
|
MessageName |
Specify the name of the message. |
|
Segment |
Specify an integer representing which segment you want to access. The default value is one, which means that if you do not specify a segment, the first segment is accessed. |
Returns
A reference to an XmlDoc object if successful, NULL if not successful.
See Also

 GetAttachment
GetAttachmentSyntax
GetAttachment(URLSource, SysFileName, LocalFile [, LocalDirEnvVar[, PreserveCase]])
where URLSource can have one of the following forms:
URL.URLname
OR a string URL, such as
ftp://user:[email protected]/
Note. You cannot specify a different port for an attachment when using an FTP server. You can only use the default port of 21.
Description
Use the GetAttachment function to transfer a file from the file server to the application sever.
File Name Considerations
When the file is transferred, the following characters are replaced with an underscore:
space
semicolon
plus sign
percent sign
ampersand
apostrophe
exclamation point
pound sign
dollar sign
Note. The @ sign is not changed to an underscore on files transferred with this function.
Considerations Using DB2 UDB for OS/390 and z/OS Databases
When you use the GetAttachment function on either the DB3 UDB for OS/390 or z/OS databases, you may need to convert the file for the transfer to complete correctly.
For example, you can use the following conversion, and place it in a shell script named convert.sh:
dd if=$1 of=$1.temp conv=ebcdic tr -d '\045' < $1.temp > $1.temp2 tr '\015' '\n' < $1.temp2 > $1.temp3
At this point $1.temp3 contains the file that GetFile can use.
Parameters
|
URLSource |
A reference to a URL. This can be either a URL name, in the form URL.URLName, or a string. This is where the file is transferred to. |
|
SysFileName |
The relative path and filename of the file on the file server. This is appended to URLSource to make up the full URL where the file is transferred from. This parameter takes a string value.
Note. The URLSource requires "/" slashes. Because SysFileName is appended to the URL, it also requires only "/" slashes. "\" are NOT supported in anyway for either the URLSource or the SysFileName parameter. |
|
LocalFile |
The name, and possible full path, to the destination file on the application server. This parameter takes a string value. If you specify only a file name, the file is assumed to be in the directory specified by the TMP environment variable or the directory specified by LocalDirEnvVar. If the file is not in the TMP directory and you don't specify LocalDirEnvVar you must use the full path name as appropriate to the operating system (that is, on Unix use "\"). |
|
LocalDirEnvVar |
The name of the environment variable containing path information. If specified, the path value in the environment variable is prepended to LocalFile. Use this if you don't want to hard code path names in the LocalFile parameter. This parameter takes a string value.
Note. Only operating system environment variables are recognized with this parameter, rather than variables defined in configuration files. |
|
PreserveCase |
Specify a Boolean value to indicate whether the case of the directory and file name specified with DirAndFileName are preserved or not; true, preserve the case, false otherwise. The default value is false. |
Returns
An integer value. You can check for either the integer or the constant:
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
0 |
%Attachment_Success |
File was transferred successfully. |
|
1 |
%Attachment_Failed |
File was not successfully transferred. |
Example
The following transfers the file "resume.txt" from the file server to the application server using ftp.
GetAttachment("ftp://anonymous:[email protected]/HRarchive/", "NewHire/11042000resume.txt", "c:/NewHires/resume.txt";
In this example, all resumes are in the directory NewHires, which is pointed to by the environment variable RESUMES.
&SysFileName = %DATE | &LASTNAME; GetAttachment(URL.MYFTP, &SysFileName, "resume.txt", "RESUMES");
The following example gets employee photos from an ftp archive, and writes them to a record.
Local File &FILE; Local Record &REC; Local SQL &SQL; &REC = CreateRecord(Record.EMPL_PHOTO); &SQL = CreateSQL("%SelectAll(:1)", Record.EMPL_PHOTO); While &SQL1.Fetch(&REC) /* photos are stored in FTP archive by EmplID */ &EmplId = &REC.EmplId.Value; &SysFileName = &EmplId | "_PHOTO.GIF"; /* Store files with same name on local system */ GetAttachment(URL.FTPARCHIVE, &SysFileName, &SysFileName, "PHOTOS"); /* get the file */ &FileName = "C:\HRArchive\Photos" | &SysFileName; &FILE = GetFile(&FileName, "w", "a", %FilePath_Absolute); /* Write file to record */ &FILE.WriteRaw(&REC.EMPLOYEE_PHOTO.Value); End-While; &FILE.Close();
See Also
AddAttachment, DeleteAttachment, PutAttachment, ViewAttachment.
Using File Attachments in Applications

 GetBiDoc
GetBiDocSyntax
GetBiDoc(XMLstring)
Description
Use the GetBiDoc function to create a BiDocs structure. You can populate the structure with data from XMLstring. This is part of the incoming Business Interlink functionality, which enables PeopleCode to receive an XML request and return an XML response.
Parameters
|
XMLstring |
A string containing XML. You can specify a NULL string for this parameter, that is, two quotation marks ("") without a space between them. |
Return Value
A BiDocs object.
Example
The following example gets an XML request, puts it into a text string, and puts that into a BiDoc. After this is done, the GetDoc method and the GetValue method can get the value of the skills XML element, which is contained within the postreq XML element in the XML request.
Local BIDocs &rootInDoc, &postreqDoc; Local string &blob; Local number &ret; &blob = %Request.GetContentBody(); /* process the incoming xml(request)- Create a BiDoc and fill with the request*/ &rootInDoc = GetBiDoc(&blob); &postreqDoc = &rootInDoc.GetDoc("postreq"); &ret = &postreqDoc.GetValue("skills", &skills);
You can also create an empty BiDoc with GetBiDoc, as in the following example.
Local BIDocs &rootInDoc, &postreqDoc; Local string &blob; Local number &ret; &blob = %Request.GetContentBody(); /* process the incoming xml(request)- Create a BiDoc and fill with the request*/ &rootInDoc = GetBiDoc(""); &ret = &rootInDoc.ParseXMLString(&blob); &postreqDoc = &rootInDoc.GetDoc("postreq"); &ret = &postreqDoc.GetValue("skills", &skills);
See Also
PeopleSoft Business Interlinks

 GetCalendarDate
GetCalendarDateSyntax
GetCalendarDate(comparedate, periods, periodadjustment, outfieldname, company, paygroup)
Description
Use the GetCalendarDate function to return the value of a Date field from the PS_PAY_CALENDAR table. If a table entry is not found, GetCalendarDate returns 1899-01-01.
Processing Rules
The following are the processing rules for GetCalendarDate:
The function SELECTs all the values for outfieldname, PAY_BEGIN_DT and PAY_END_DT from PS_PAY_CALENDAR. The result set is sorted in increasing PAY_END_DT order.
A SQL SELECT statement is generated in the following form:
SELECT outfieldname, PAY_BEGIN_DT, PAY_END_DT FROM PS_PAY_CALENDAR WHERE COMPAny=:1 AND PAYGROUP=:2 ORDER BY PAY_END_DT;
Rows are fetched from the result set until the value of comparedate falls between PAY_BEGIN_DT and PAY_END_DT. The value of outfieldname is stored in a storage stack.
A work variable equal to the value in periods is set.
If the value of outfieldname in the located result row is equal to comparedate, then the value in periodadjustment is added to the work variable. Because periodadjustment may be negative, the result may be negative.
If the work variable is negative then the saved value of outfieldname is returned from the storage stack at the level specified by the work variable. If the work variable is positive then fetch forward the number of times specified by the work variable. The value of outfieldname is returned from the most recently fetched (current) row.
Parameters
|
comparedate |
A date field set by the caller as the date of interest, for example, "1997-02-17." |
|
periods |
A numeric variable set by the caller specifying the number of periods forward or backward to be returned. |
|
periodadjustment |
A numeric variable that adjusts the periods if the comparedate equals the period end date. This is typically used to adjust for period end dates. Usually the periodadjustment is either -1, 0, or 1. |
|
outfieldname |
The name of a date field in the PS_PAY_CALENDAR table. For example PAY_BEGIN_DT. The value of this field is not referenced or modified by the routine, but the name of the field is used to build a SQL SELECT statement and to indicate which value from the table to return in the return date. |
|
company |
A field set by the caller to be equal to the company code of interest, for example, "CCB". |
|
paygroup |
A variable set by the caller to be equal to the PayGroup code of interest, for example, "M01". |
Returns
Returns a Date value from the PS_PAY_CALENDAR table.
Example
The following examples use the sample PS_PAY_CALENDAR entries in the following table. In the example, comparedate and the result date are Date type fields defined in some record.
|
COMPANY |
PAYGROUP |
PAY_END_DT |
PAY_BEGIN_DT |
CHECK_DT |
|
CCB |
MO1 |
1997-01-31 |
1997-01-01 |
1997-01-31 |
|
CCB |
MO1 |
1997-02-28 |
1997-02-01 |
1997-02-28 |
|
CCB |
MO1 |
1997-03-31 |
1997-03-01 |
1997-03-29 |
|
CCB |
MO1 |
1997-04-30 |
1997-04-01 |
1997-04-30 |
|
CCB |
MO1 |
1997-05-31 |
1997-05-01 |
1997-05-31 |
|
CCB |
MO1 |
1997-06-30 |
1997-06-01 |
1997-06-28 |
|
CCB |
MO1 |
1997-07-31 |
1997-07-01 |
1997-07-31 |
|
CCB |
MO1 |
1997-08-31 |
1997-08-01 |
1997-08-30 |
|
CCB |
MO1 |
1997-09-30 |
1997-09-01 |
1997-09-30 |
|
CCB |
MO1 |
1997-10-31 |
1997-10-01 |
1997-10-31 |
|
CCB |
MO1 |
1997-11-30 |
1997-11-01 |
1997-11-27 |
|
CCB |
MO1 |
1997-12-31 |
1997-12-01 |
1997-12-31 |
|
CCB |
SM1 |
1997-01-15 |
1997-01-01 |
1997-01-15 |
Find the begin date of the pay period containing the date 1997-05-11 (the value of &COMPAREDate). The result date returned would be 1997-05-01.
&RESULT_Date = GetCalendarDate(&COMPAREDate, 0, 0, PAY_BEGIN_DT, COMPAny, PAYGROUP);
Or:
&RESULT_Date = GetCalendarDate(&COMPAREDate, 1, -1, PAY_BEGIN_DT, COMPAny, PAYGROUP);

 GetChart
GetChartSyntax
GetChart(RecordName.FieldName)
Description
Use the GetChart function to get a reference to a chart object. You associate a record and field name with a chart definition in PeopleSoft Application Designer.
Parameters
|
RecordName.FieldName |
Specify the record and field name associated with the chart. |
Returns
A reference to a chart object.
Example
&MyChart = GetChart(Chart_Record.Chart_Field);
See Also

 GetChartURL
GetChartURLSyntax
GetChartURL(&Chart)
Description
Use the GetChartURL function to generate the URL of a chart object. This URL can then be used in your application for displaying a chart.
Parameters
|
&Chart |
Specify an already instantiated chart object. |
Returns
A URL as a string.
Example
Function IScript_GetChartURL() local object &MyChart; local string &MyURL; &MyChart = CreateObject("Chart"); &MyChart .SetData = xx; /* xx will be a data row set */ &MyURL = %Response.GetChartURL(&MyChart); &sMap = &oChart.ImageMap; %Response.Write("<HTML><IMG SRC="); %Response.Write(&MyURL); %Response.Write(" USEMAP=#THEMAP></IMG><MAP NAME=THEMAP>"); %Response.Write(&sMap); %Response.Write("</MAP></HTML>"); End-Function;
See Also

 GetCwd
GetCwdSyntax
GetCwd()
Description
Use the GetCwd function to determine the current working directory of the process that executes it. This means that in PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture it returns the current working directory on the server, in an Application Engine program it returns the current working directory of the Application Engine process, and so on.
Returns
Returns a string containing the path of the current working directory.
Example
The example stores a string specifying the current working directory in &CWD.
&CWD = GetCwd();
See Also

 GetEnv
GetEnvSyntax
GetEnv(env_var_str)
Description
Use the GetEnv function to return the value of an environment variable specified by env_var_str as a string. If the environment variable does not exist, it returns a null string.
You can use the GetEnv function to determine the actual path of PS_HOME. You could use this with the Exec function, which automatically prepends the command string with the path of PS_HOME.
Parameters
|
env_var_str |
A string containing an environment variable. |
Returns
Returns a string equal to env_var_str with any enclosed environment variables expanded to their values.
Example
Assume that the environment string NETDRIVE is equal to "N:". The following statement returns "N:" in &NETDRIVE:
&NETDRIVE = GetEnv("netdrive");
Note that on UNIX systems, the environment variable names are case-sensitive. That is, "netdrive" is a different variable from "NetDrive".
See Also

 GetField
GetFieldSyntax
GetField([recname.fieldname])
Description
Use the GetField function to create a reference to a field object for the current context; that is, from the row containing the currently executing program.
If you don't specify recname.fieldname, the current field executing the PeopleCode is returned.
Note. For PeopleCode programs located in events that are not associated with a specific row, record, and field at the point of execution this function is invalid. That is, you cannot use this function in PeopleCode programs on events associated with high-level objects like pages or components. For events associated with record level programs (like component record), this function is valid, but it must be specified with a field name, as there is an assumed record, but no assumed field name.
When GetField is used with an associated record and field name on component buffer data, the following is assumed:
&FIELD = GetRow().recname.fieldname;
Parameters
|
recname.fieldname |
If you don't want to refer to the field executing the PeopleCode, specify a record name and field name. |
Returns
This function returns a field object that references the field from the specified record.
Example
Local Field &CHARACTER; &CHARID = GetField(FIELD.CHAR_ID);
See Also

 GetFile
GetFileSyntax
GetFile(filename, mode [, charset] [, pathtype])
Description
Use the GetFile function to instantiate a new file object from the File class, associate it with an external file, and open the file so you can use File class methods to read from or write to it.
GetFile is similar to the Open file class method, but Open associates an existing file object with an external file. If you plan to access only one file at a time, you need only one file object. Use GetFile to instantiate a file object for the first external file you access, then use Open to associate the same file object with as many different external files as you want. You need to instantiate multiple file objects with GetFile only if you expect to have multiple files open at the same time.
Working With Relative Paths
If you specify a relative path, that path is appended to the path specified by an environmental variable, if the variable exists, in a particular order. This means if the first environmental variable in order is found, that is the one that's used. If it isn't found, the next one is searched for, and if found, is used, and so on.
If GetFile is called from Application Engine when running standalone that is, when not within an application server domain), the following environmental variables are valid, and are searched for in the following order:
PS_FILEDIR[\relative_path]
PS_SERVDIR\Files[\relative_path]
If the code is not running on an application server, the following environmental variables are valid, and are searched for in the following order:
PS_FILEDIR[\relative_path]
PS_SERVDIR\Files[\relative_path]
TEMP[\relative_path]
The PS_FILEDIR environmental variable is not initialized and set to a path automatically. If you want to use this environmental variable, you must set it yourself.
Note. Your system security should verify if a user has the correct permissions before allowing access to a drive (for example, if a user changes their TEMP environmental variable to a network drive they don’t normally have access to, your system security should detect this.)
Parameters
|
filespec |
Specify the name, and optionally, the path, of the file you want to open. |
|
mode |
A string indicating how you want to access the file. The mode can be one of the following: "R" (Read mode): opens the file for reading, starting at the beginning. "W" (Write mode): opens the file for writing. Warning! When you specify Write mode, any existing content in the file is discarded. "U" (Update mode): opens the file for reading or writing, starting at the end. Any existing content is retained. Use this mode and the GetPosition and SetPosition methods to maintain checkpoints of the current read/write position in the file. In Update mode, any write operation clears the file of all data that follows the position you set. Note. Currently, the effect of the Update mode and the GetPosition and SetPosition methods is not well defined for Unicode files. Use the Update mode only on files stored with a non-Unicode character set. "E" (Conditional "exist" read mode): opens the file for reading only if it exists, starting at the beginning. If it doesn’t exist, the Open method has no effect. Before attempting to read from the file, use the IsOpen property to confirm that it’s open. "N" (Conditional "new" write mode): opens the file for writing, only if it doesn’t already exist. If a file by the same name already exists, the Open method has no effect. Before attempting to write to the file, use the IsOpen property to confirm that it’s open. You can insert an asterisk (*) in the filename to ensure that a new file is created. The system replaces the asterisk with numbers starting at 1 and incrementing by 1, and checks for the existence of a file by each resulting name in turn. It uses the first name for which a file doesn’t exist. In this way you can generate a set of automatically numbered files. If you insert more than one asterisk, all but the first one are discarded. |
|
charset |
A string indicating the character set you expect when you read the file, or the character set you want to use when you write to the file. You can abbreviate Unicode UTF-16 to "U" and the host operating system's default non-Unicode (sometimes referred to as the ANSI character set) to “A”. All other character sets must be spelled out in full, for example, ASCII, THAI, or UTF8. If non-Unicode (“A”) is specified, or you don't specify a character set, the character set used is dependent on the application server configuration. On a Windows application server, the default non-Unicode character set is dependent on the Windows ANSI Codepage (ACP) which can be checked using the DOS command chcp. On a Unix application server, the default non-Unicode character set is specified in the application server configuration file, psappsrv.cfg, and can be modified using PSADMIN. You can also use a record field value to specify the character set (for example, RECORD.CHARSET.) A list of supported character set names valid for this argument can be found in PeopleTools 8.45 PeopleBook: Global Technology. See Character Sets in the PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture. Note. If you attempt to read data from a file using a different character set than was used to write that data to the file, the methods used generate a runtime error or the data returned is unusable. When a file is opened for reading using the “U” charset argument, GetFile expects the file to begin with a Unicode Byte Order Mark (BOM), otherwise known as a sentinal. This mark indicates whether the file is written in big endian order or little endian order. A BOM consisting of the hex value 0xFEFF indicates a big endian file, a BOM consisting of the hex value 0xFFEF indicates a little endian file. If the Unicode UTF-16 file being opened does not start with a BOM, an error is returned. The BOM is automatically stripped from the file when it is read into the buffers by GetFile. When a file is opened for writing using the “U” charset argument, the Unicode BOM is automatically written to the start of the file, dependent on whether the application server hardware platform operates in little endian or big endian mode. Byte Order Marks are not expected or supported for files in other character sets, including UTF8. Note. When working with XML documents, specify UTF8 for charset. |
|
pathtype |
If you have prepended a path to the file name, use this parameter to specify whether the path is an absolute or relative path. The valid values for this parameter are:
If you don’t specify pathtype the default is %FilePath_Relative. If the path is an absolute path, whatever path you specify is used verbatim. You must specify a drive letter as well as the complete path. You can’t use any wildcards when specifying a path. The function automatically converts platform-specific separator characters to the appropriate form for where your PeopleCode program is executing. On a WIN32 system, UNIX "/" separators are converted to "\", and on a UNIX system, WIN32 "\" separators are converted to "/". |
Note. The syntax of the file path does not depend on the file system of the platform where the file is actually stored; it depends only on the platform where your PeopleCode is executing.
Returns
A file object.
Example
The following example opens an existing Unicode file for reading:
&MYFILE = GetFile(&SOMENAME, "E", "U"); If &MYFILE.IsOpen Then while &MYFILE.ReadLine(&SOMESTRING); /* Process the contents of each &SOMESTRING */ End-While; &MYFILE.Close(); End-If;
The following example opens a numbered file for writing in a non-Unicode format, without overwriting any existing files:
&MYFILE = GetFile("c:\temp\item*.txt", "N", %FilePath_Absolute); If &MYFILE.IsOpen Then &MYFILE.WriteLine("Some text."); &MYFILE.Close(); End-If;
The following example uses the CHARSET field to indicate the character set to be used:
&MYFILE = GetFile("INPUT.DAT", "R", RECORD.CHARSET);
See Also
FileExists, FindFiles, GetFile.
File Access Interruption Recovery

 GetGanttChart
GetGanttChart
Syntax
GetGanttChart([RecordName.FieldName])
Description
Use the GetGanttChart function to get a reference to a Gantt chart object. You associate a record and field name with a chart definition in PeopleSoft Application Designer.
Parameters
|
RecordName.FieldName |
Specify the record and field associated with the chart you want to get. |
Returns
A reference to a chart object.
Example
&oGantt = GetGanttChart(QE_CHART_DUMREC.QE_CHART_FIELD);
See Also

 GetGrid
GetGridSyntax
GetGrid(PAGE.pagename, gridname [, occursnumber])
Description
Use the GetGrid function to instantiate a grid object from the Grid class, and populates it with the grid specified by gridname, which is the Page Field Name on the General tab of that grid’s page field properties.
Use the GetGrid function to return a reference to a grid object. If you want to access an AnalyticGrid, use the GetAnalyticGrid function instead.
Specify a grid name consisting of any combination of uppercase letters, digits and "#", "$", "@", and "_".
Note. PeopleSoft builds a page grid one row at a time. Because the Grid class applies to a complete grid, you can’t attach PeopleCode that uses the Grid class to events that occur before the grid is built; the earliest event you can use is the page Activate Event.
See Activate Event.
Using the Occurs Count
The occurs number (occursnumber) parameter that you specify with the GetGrid function does not refer to the row number of the grid. Rather, it’s the occurrence of the grid within a scroll. If your grid is contained within a scroll, and the occurs number of the scroll is greater than 1, then to specify the correct grid within the scroll you must use the occursnumber parameter.
Using the Grid Name
When you place a grid on a page, the gird is automatically named the same as the name of the primary record of the scroll for the grid (in the Page Field Name.)
Note. If the name of the record changes, the Page Field Name is not automatically updated. You must change this name if you want the name of the grid to reflect the name of the record.
This is the name you use with the GetGrid function. You can change this name on the Record tab of the Grid properties.
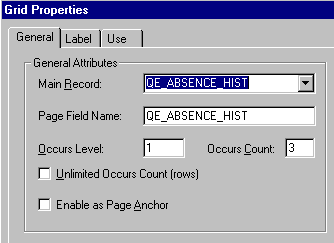
Changing a grid name
Open the page in PeopleSoft Application Designer, select the grid and access the page field properties.
On the General tab, type the new grid name in Page Field Name.
Note. Every grid on a page must have a unique name.
Parameters
|
PAGE. pagename |
Specify the name of the page definition containing the grid you want. |
|
gridname |
Specify the Page Field Name on the General tab of the grid’s page field properties. |
|
occursnumber |
Optionally, specify the occurs number to identify the grid. Because you can use occurs count to generate multiple instances of a grid within a scroll just as you can with other page fields, occursnumber enables you to identify which one of those grids you want. The default value is 1. |
Returns
A Grid object populated with the requested grid.
Example
This example retrieves the second grid named "EMPL_GRID" within a scroll:
local Grid &MYGRID; &MYGRID = GetGrid(PAGE.EMPLOYEE_CHECKLIST, "EMPL_GRID", 2);
See Also

 GetHTMLText
GetHTMLTextSyntax
GetHTMLText(HTML.textname [, paramlist])
Where paramlist is an arbitrary-length list of values of undetermined (Any) data type in the form:
inval1 [, inval2] ...
Description
Use the GetHTMLText function to retrieve a predefined HTML text from an HTML definition in the user's current language, or the base language if no entry exists in the user's current language. If any values are included in paramlist, they are substituted into the HTML text based on positional reference (for example, %BIND(:1) is the first parameter, %BIND(:2) is the second, and so on.)
Note. Use the GetHTMLText function only to retrieve HTML, or HTML that contains a JavaScript program, from an HTML definition. If you have an HTML definition that contains only JavaScript, use the GetJavaScriptURL response class method to access it.
See GetJavaScriptURL.
Restrictions on Use
Use this function with the PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture. If run from a 2 tier environment, the parameter substitution does not take place.
Parameters
|
HTML. textname |
Specify the name of an existing HTML text from an HTML definition. |
Returns
The resulting HTML text is returned as a string.
Example
The following is the text in the HTML definition TEST_HTML:
This is a %BIND(:1) and %BIND(:2) test.
The following is the PeopleCode program:
Local Field &HTMLfield; &string = GetHTMLText(HTML.TEST_HTML, "good", "simple"); &HTMLfield = GetRecord(Record.CHART_DATA).HTMLAREA; &HTMLfield.Value = &string;
The output from &string (displayed in an HTML area control) is:
This is a good and simple test.
See Also
Internet Script Classes (iScript).
Using HTML Definitions and the GetHTMLText Function

 GetImageExtents
GetImageExtentsSyntax
GetImageExtents(IMAGE.ImageName)
Description
Use the GetImageExtents function to return the width and height of the image specified by ImageName.
Parameters
|
ImageName |
Specify the name of the image on the page. This image must exist on the page. |
Returns
An array of data type number, where element 1 is the image height and element 2 is the image width.
Example
Local array of number &ImageExtents; &ImageExtents = GetImageExtents(Image.PT_TREE_EXPANDED); WinMessage("Height is " | &ImageExtents[1] | " and width is " | &ImageExtents[2]);
See Also
Specifying Image Field Attributes.

 GetInterlink
GetInterlinkSyntax
GetInterlink(Interlink.name)
Description
Use the GetInterlink function to instantiate a Business Interlink definition object based on a Business Interlink definition created in PeopleSoft Application Designer. The Business Interlink object can provide a gateway for PeopleSoft applications to the services of any external system.
After you use this function, you may want to refresh your page. The Refresh rowset class reloads the rowset (scroll) using the current page keys. This causes the page to be redrawn. GetLevel0().Refresh() refreshes the entire page. If you only want a particular scroll to be redrawn, you can refresh just that part.
Generally, do not use the GetInterlink function in a program you create from scratch. If you drag a Business Interlink definition from the project workspace (in PeopleSoft Application Designer) to an open PeopleCode editor window, a "template" is created, with values filled in based on the Business Interlink definition you dragged in.
The following is the template created from dragging the Business Interlink definition LDAP_SEARCHBIND to an open PeopleCode editor window.
/* ===> This is a dynamically generated PeopleCode template to be used only as a helper to the application developer. You need to replace all references to '<*>' OR default values with references to PeopleCode variables and/or a Rec.Fields.*/ /* ===> Declare and instantiate: */ Local Interlink &LDAP_SEARCHBI_1; Local BIDocs &inDoc; Local BIDocs &outDoc; Local Boolean &RSLT; Local number &EXECRSLT; &LDAP_SEARCHBI_1 = GetInterlink(INTERLINK.LDAP_SEARCHBIND); /* ===> You can use the following assignments to set the configuration parameters. */ &LDAP_SEARCHBI_1.Server = "jtsay111198.peoplesoft.com"; &LDAP_SEARCHBI_1.Port = 389; &LDAP_SEARCHBI_1.User_DN = "cn=Admin,o=PeopleSoft"; &LDAP_SEARCHBI_1.Password = &password; &LDAP_SEARCHBI_1.UserID_Attribute_Name = "uid"; &LDAP_SEARCHBI_1.URL = "file://psio_dir.dll"; &LDAP_SEARCHBI_1.BIDocValidating = "Off"; /* ===> You might want to call the following statement in a loop if there is more than one row of data to be added. */ /* ===> Add inputs: */ &inDoc = &LDAP_SEARCHBI_1.GetInputDocs(""); &ret = &inDoc.AddValue("User_ID", <*>); &ret = &inDoc.AddValue("User_Password", <*>); &ret = &inDoc.AddValue("Connect_DN", <*>); &ret = &inDoc.AddValue("Connect_Password", <*>); &Directory_Search_ParmsDoc = &inDoc.AddDoc("Directory_Search_Parms"); &ret = &Directory_Search_ParmsDoc.AddValue("Host", <*>); &ret = &Directory_Search_ParmsDoc.AddValue("Port", <*>); &ret = &Directory_Search_ParmsDoc.AddValue("Base", <*>); &ret = &Directory_Search_ParmsDoc.AddValue("Scope", <*>); &ret = &Directory_Search_ParmsDoc.AddValue("Filter", <*>); /* ===> The following statement executes this instance: */ &EXECRSLT = &LDAP_SEARCHBI_1.Execute(); If ( &EXECRSLT <> 1 ) Then /* The instance failed to execute */ Else &outDoc = &LDAP_SEARCHBI_1.GetOutputDocs(""); &ret = &outDoc.GetValue("Distinguished_Name", <*>); &ret = &outDoc.GetValue("return_status", <*>); &ret = &outDoc.GetValue("return_status_msg", <*>); End-If; /* If NOT &RSLT ... */
See Also
Generating PeopleCode for a Business Interlink.
Parameters
|
Interlink. name |
Specify the name of the Business Interlink definition from which to instantiate a Business Interlink object. |
Returns
A Business Interlink object.
Example
The following example instantiates a Business Interlink object based on the Business Interlink definition QE_RP_SRAALL.
Local Interlink &SRA_ALL_1; &SRA_ALL_1 = GetInterlink(Interlink.QE_RP_SRAALL);
See Also
PeopleSoft Business Interlinks

 GetJavaClass
GetJavaClassSyntax
GetJavaClass(ClassName)
Description
Use the GetJavaClass function to access a Java class so that you can manipulate it in PeopleCode. This is used for those classes that have static members, where it isn't appropriate to instantiate an object of the class. You can call only static methods, that is, class methods, with the object created with this function.
In Java, you access such static members of a class by using the class name:
result = java.class.name.SomeStaticMethod();
To do this in PeopleCode, do the following:
&Result = GetJavaClass("java.class.name").SomeStaticMethod();
Note. If you create a class that you want to call using GetJavaClass, it must be located in a directory specified in the PS_CLASSPATH environment variable.
Parameters
|
ClassName |
Specify the name of an already existing class. This parameter takes a string value. |
Returns
A JavaObject that refers to the named Java class.
Example
The Java class java.lang.reflect.Array has no public constructors and has only static methods. The methods are used to manipulate Java array objects. One of these static methods is GetInt:
public static int getInt(Object array, int index)
To use this method, get the class by using GetJavaClass. This code illustrates accessing the value of the fifth element of an integer array.
Local JavaObject &RefArray, &MyArray; . . . &RefArray = GetJavaClass("java.lang.reflect.Array"); . . . &MyArray = CreateJavaArray(“int[]”, 24); . . . &FifthElement = &RefArray.getInt(&MyArray, 4);
See Also
CreateJavaObject, CreateJavaArray.

 GetLevel0
GetLevel0Syntax
GetLevel0()
Description
Use the GetLevel0 function to create a rowset object that corresponds to level 0 of the component buffer. If used from PeopleCode that isn’t associated with a page, it returns the base rowset from the current context.
Parameters
GetLevel0 has no parameters. However, it does have a default method, GetRow, and a shortcut. Specifying GetLevel0()(1) is the equivalent of specifying GetLevel0().GetRow(1).
Returns
This function returns a rowset object that references the base rowset. For a component, this is the level 0 of the page. For a PeopleSoft Application Engine program, this is the state record rowset. For a message, this is the base rowset.
Note. You can also get the base rowset for a message using the GetRowset message class method, that is, &MSG.GetRowset().
Example
The following code sample returns the level one rowset.
Local Rowset &ROWSET; &ROWSET = GetLevel0().GetRow(1).GetRowset(SCROLL.LEVEL1_REC);
The following is equivalent to the previous example.
Local Rowset &ROWSET; &ROWSET = GetLevel0()(1).GetRowset(SCROLL.LEVEL1_REC);
To reference a level 2 rowset you would have code similar to this:
Local Rowset &ROWSET_LEVEL2, &ROWSET_LEVEL0, &ROWSET_LEVEL1; &ROWSET_LEVEL2 = GetLevel0().GetRow(1).GetRowset(SCROLL.LEVEL1_REC).GetRow(5). GetRowset(SCROLL.LEVEL2_REC); /* or */ &ROWSET_LEVEL0 = GetLevel0(); &ROWSET_LEVEL1 = &ROWSET_LEVEL0.GetRow(1).GetRowset(SCROLL.LEVEL1_REC); &ROWSET_LEVEL2 = &ROWSET_LEVEL1.GetRow(5).GetRowset(SCROLL.LEVEL2_REC); /* or */ &ROWSET_LEVEL2 = GetLevel0()(1).LEVEL1_REC(5).GetRowset(SCROLL.LEVEL2_REC);
See Also

 GetMethodNames
GetMethodNamesSyntax
GetMethodNames(Type, Name)
Description
Use the GetMethodNames function to return either the method names for a Component Interface, or the function names of a WEBLIB record.
Parameters
|
Type |
Specify the type of methods or functions you want returned. This parameter takes a string value. The values are:
|
|
Name |
Specify the name of the Component Interface or WEBLIB record that you want to know the methods or functions for. |
Returns
An array of string containing the method or function names.
Example
Local array of string &Array; &Array = GetMethodNames("CompIntfc", CompIntfc.USER_PROFILE); &Array = GetMethodNames("WebLib", Record.WEBLIB_PORTAL);
See Also

 GetMessage
GetMessageSyntax
GetMessage()
Description
Use the GetMessage function in any of the messaging PeopleCode events. It retrieves a message from the message queue for the current message being processed.
Note. The GetMessage function does not load the message with data. It always creates a new instance of a message object. You must use another method, such as GetRowset, to populate the message object.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A reference to an empty message object if successful, NULL if not successful.
Example
Local message &MSG; &MSG = GetMessage();
See Also

 GetMessageInstance
GetMessageInstanceSyntax
GetMessageInstance(pub_id, pub_nodename, channelname)
Description
Use the GetMessageInstance function to get a message from the message queue.
Note. This function has been deprecated and is no longer supported.

 GetMessageXmlDoc
GetMessageXmlDocSyntax
GetMessageXmlDoc()
Description
Use the GetMessageXmlDoc function in any of the messaging PeopleCode events. It retrieves an XML message, either from the message queue for asynchronous messages, or in memory for synchronous messages, for the current message being processed. An XML message is a message that is unstructured, that is, isn't based on a record hierarchy. It creates and loads a data tree for the default message version, and returns NULL if not successful.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A reference to an XmlDoc object if successful, NULL if not successful.
Example
The following example uses the GetMessageXmlDoc built-in function.
Local XmlDoc &BIGMAN; Local XmlNode &node, &root; Local string &outstring; Local Rowset &LEVEL0; Local Record &SALES_ORDER_INFO, &REC; &CRLF = Char(13) | Char(10); &BIGMAN = GetMessageXmlDoc(); &root = &BIGMAN.DocumentElement; &child_count = &root.ChildNodeCount; /* Get values out of XMLDoc */ &node_array = &root.GetElementsByTagName("QE_ACCT_ID"); &acct_id_node = &node_array.Get(2); &account_id_value = &acct_id_node.NodeValue; &node_array = &root.GetElementsByTagName("QE_ACCOUNT_NAME"); &acct_name_node = &node_array.Get(2); &account_name_value = &acct_name_node.NodeValue; &node_array = &root.GetElementsByTagName("QE_ADDRESS"); &address_node = &node_array.Get(2); &address_value = &address_node.NodeValue; &node_array = &root.GetElementsByTagName("QE_PHONE"); &phone_node = &node_array.Get(2); &phone_value = &phone_node.NodeValue; &outstring = "GetMessageXMLDoc Test"; &outstring = &outstring | &CRLF | &account_id_value | &CRLF | &account_name_value | &CRLF | &address_value | &CRLF | &phone_value; &SALES_ORDER_INFO = CreateRecord(Record.QE_SALES_ORDER); &SALES_ORDER_INFO.GetField(Field.QE_ACCT_ID).Value = &account_id_value; &SALES_ORDER_INFO.GetField(Field.DESCRLONG).Value = &outstring; &SALES_ORDER_INFO.Update();
See Also
PublishXmlDoc, SyncRequestXmlDoc.

 GetNextNumber
GetNextNumberSyntax
GetNextNumber ({record.field | record_name, field_name}, max_number)
Description
Use the GetNextNumber function to increment the value in a record for the field you specify by one and returns that value. You might use this function to increment an employee ID field by one when you are adding a new employee. If the new value generated exceeds max_number, a negative value is returned and the field value isn't incremented.
The maximum value possible for max_number is 2147483647.
PeopleCode Event Considerations
Because this function results in a database update (specifically, UPDATE, INSERT, and DELETE) it should only be issued in the following events:
SavePreChange
WorkFlow
SavePostChange
If you use this function in an event other than these, you need to ensure that the dataflow is correct and that you don't receive unexpected results.
GetNextNumber and GetNextNumberWithGapsCommit
The following is some of the differences between the two functions, to enable you to better chose which one is better for your application.
|
GetNextNumber |
GetNextNumberWithGapsCommit |
|
No AutoCommit (which can be a problem, as the table is locked until all Save events are finished.) |
AutoCommit (this can be a performance enhancement as table is not locked as long). |
|
Ability to use WHERE criteria for maintaining multiple sequence numbers in a single record. |
|
|
Ability to increment by more than 1. |
|
|
Allowed in SavePostChange |
Can be used in any PeopleCode event. |
Parameters
|
record.field |
Specify the record and field identifiers for the field for which you want the new number. This is the recommended way to identify the field. |
|
record_name |
Specify as a string the name of the record containing the field for which you want the new number. This parameter with field_name was used prior to PeopleTools 8. |
|
field_name |
Specify as a string the name of the field for which you want the new number. This parameter with record_name was used prior to PeopleTools 8.
Note. If you use the older syntax (record_name, field_name), you have to manually update these two parameters in your programs whenever that record or field is renamed. The new syntax (record.field) is automatically updated, so you won't have to maintain it. |
|
max_number |
Specify the highest allowed value for the field you're incrementing. The maximum value possible for max_number is 2147483647. |
Returns
A Number value equal to the highest value of the field specified plus one.
GetNextNumber returns an error if the value to be returned would be greater than max_number. The function returns one of the following:
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
Number |
N/A |
The new number |
|
-1 |
%GetNextNumber_SQLFailure |
SQL failure |
|
-2 |
%GetNextNumber_TooBig |
Number too large, beyond max_number |
|
-3 |
%GetNextNumber_NotFound |
No number found, invalid data format |
Example
If %Component = "RUN_AR33000" Then DUN_ID_NUM = GetNextNumber(INSTALLATION_AR.DUN_ID_NUM, 99999999); End-if;
The following uses the constant to check for the value returned:
&VALUE = GetNextNumber(INSTALLATION_AR.DUN_ID_NUM, 999); Evaluate &VALUE When = %GetNextNumber_SQLFailure /* do processing */ When = %GetNextNumber_TooBig /* do processing */ When = %GetNextNumber_NotFound /* Do processing */ When-other /* do other processing */ End-Evaluate;
See Also

 GetNextNumberWithGaps
GetNextNumberWithGapsSyntax
GetNextNumberWithGaps(record.field, max_number, increment [, WHERE_Clause, paramlist])
Where paramlist is an arbitrary-length list of values in the form:
var1 [, var2] ...
Description
Use the GetNextNumberWithGaps function to determine the highest value in a table for the field you specify, and return that value plus increment.
Note. This function has been deprecated and remains for backward compatibility only. Use the GetNextNumberWithGapsCommit function instead.
This function also enables you to specify a SQL WHERE clause as part of the function for maintaining multiple sequence numbers in a single record.
Note. GetNextNumberWithGaps also issues a COMMIT after incrementing the sequence number if no other database updates have occurred since the last COMMIT. This limits the time a database lock is held on the row and so may improve performance.
PeopleCode Event Considerations
Because this function results in a database update (specifically, UPDATE, INSERT, and DELETE) it should only be issued in the following events:
SavePreChange
WorkFlow
If you use this function in an event other than these, you need to ensure that the dataflow is correct and that you don't receive unexpected results.
Parameters
|
record.field |
Specify the record and field identifiers for the field for which you want the new number. This is the recommended way to identify the field. |
|
max_number |
Specify the highest allowed value for the field you're incrementing. You can specify up to 31 digits for this value. |
|
increment |
Specify the value you want the numbers incremented by. You can specify up to 31 digits for this value. |
|
WHERE_Clause |
Specify a WHERE clause for maintaining multiple sequence numbers. |
|
paramlist |
Parameters for the WHERE clause. |
Returns
A Number value equal to the highest value of the field specified plus one.
GetNextNumberWithGaps returns an error if the value to be returned would be greater than max_number. The function returns one of the following:
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
Number |
N/A |
The new number |
|
-1 |
%GetNextNumber_SQLFailure |
SQL failure |
|
-2 |
%GetNextNumber_TooBig |
Number too large, beyond max_number |
|
-3 |
%GetNextNumber_NotFound |
No number found, invalid data format |
Example
The following PeopleCode:
&greg = GetNextNumberWithGaps(GREG.DURATION_DAYS, 999999, 50, "where emplid = :1", 8001);
results in the following:
2-942 21.53.09 0.000 Cur#4.PTTST81B RC=0 Dur=0.000 Connect=PTTST81B/sa/ 2-943 21.53.09 0.000 Cur#4.PTTST81B RC=0 Dur=0.000 COM Stmt=UPDATE PS_GREG SET DURATION_DAYS = DURATION_DAYS + 50 where emplid = 8001 2-944 21.53.09 0.000 Cur#4.PTTST81B RC=0 Dur=0.000 EXE 2-945 21.53.09 0.000 Cur#4.PTTST81B RC=0 Dur=0.000 COM Stmt=SELECT DURATION_DAYS FROM PS_GREG where emplid = 8001 2-946 21.53.09 0.000 Cur#4.PTTST81B RC=0 Dur=0.000 EXE 2-947 21.53.09 0.000 Cur#4.PTTST81B RC=0 Dur=0.000 Fetch 2-948 21.53.09 0.010 Cur#4.PTTST81B RC=0 Dur=0.010 Commit 2-949 21.53.09 0.010 Cur#4.PTTST81B RC=0 Dur=0.010 Disconnect
See Also

 GetNextNumberWithGapsCommit
GetNextNumberWithGapsCommitSyntax
GetNextNumberWithGapsCommit(record.field, max_number, increment [, WHERE_Clause, paramlist])
Where paramlist is an arbitrary-length list of values in the form:
var1 [, var2] ...
Description
Use the GetNextNumberWithGapsCommit function to return the sequence number value plus increment for the given field residing in the given record. This function also enables you to specify a SQL Where clause as part of the function for maintaining multiple sequence numbers in a single record.
This function is typically used for obtaining a new sequence number for the application, for example, getting a new Purchase Order number to be used in the application transaction.
Use this function instead of the GetNextNumberWithGaps function. The GetNextNumberWithGaps function is very restrictive in its usage. The GetNextNumberWithGapsCommit function can be used in any event. The sequence number (record.field ) is incremented right away and it doesn't hold any database internal row lock beyond the execution of this function.
Note. A secondary database connection is used to increment and retrieve record.field. The default behavior is to keep the secondary database connection persistent in order to improve performance for the next GetNextNumberWithGapsCommit usage. If the database administrator find the persistent connection too high an overhead for the production environment (which should not be the case since PeopleSoft uses application server to mulitplex the database connection), the database administrator can change the default behavior to use an on-demand connection method. The persistent second connection is disabled using DbFlags bit eight in the application server and process scheduler configuration files. The second connection can be completely disabled using DbFlags bit four in the application server and process scheduler configuration files
Considerations Using GetNextNumberWithGapsCommit
The following restrictions apply to the GetNextNumberWithGapsCommit function:
This function does not work on the Informix database with the PeopleSoft Application Engine server on Unix systems; it is disabled internally. This function does work with a PeopleSoft Application Engine program on these databases.
This function does not work with PeopleSoft Application Engine programs on the Unix System Services (USS) on z/OS.
Using this function with a secondary database connection may create a deadlock. For example, if you use GetNextNumberWithGapsCommit as well as GetNextNumber in the same application, on the same database table, in the same unit of work, with a different counter on the same row in different columns, you will create a deadlock because the system uses row level locking.
For a DB2 UDB for OS/390 and z/OS database, the database table that holds the sequence number need to be placed in a row-level locking tablespace, or else the GetNextNumberWithGapsCommit function may be blocked by other sequence numbers which happens to be in the same page.
See Also
Parameters
|
record.field |
Specify the record and field names for the field for which you want the new number. This is the recommended way to identify the field. |
|
max_number |
Specify the highest allowed value for the field you're incrementing. You can specify up to 31 digits for this value. |
|
increment |
Specify the value you want the numbers incremented by. You can specify up to 31 digits for this value. |
|
WHERE_Clause |
Specify a SQL Where clause for maintaining multiple sequence numbers. |
|
paramlist |
Specify the parameters for the SQL Where clause. |
Returns
A number value equal to the highest value of the field specified plus one increment.
The GetNextNumberWithGapsCommit function returns an error if the value to be returned would be greater than max_number. The function returns one of the following:
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
Number |
None |
The new number |
|
-1 |
%GetNextNumber_SQLFailure |
SQL failure |
|
-2 |
%GetNextNumber_TooBig |
Number returned is too large, beyond max_number. |
|
-3 |
%GetNextNumber_NotFound |
No number found, invalid data format. |
Example
The following PeopleCode increments the MCF_EMAIL_ID field by one and returns the new value, committing immediately.
&LAST_AUTO_NBR = GetNextNumberWithGapsCommit(MCF_INSTALL.MCF_EMAIL_ID, 2147483647, 1);
The above code produces output similar to the following:
1-192 10.39.54 0.320 Cur#2.1980.DB844901 RC=0 Dur=0.320 Connect=Secondry/DB844901/testdb2/ 1-193 10.39.54 0.000 GNNWGC ---- Successful obtain Second DB connection 1-194 10.39.54 0.010 Cur#2.1980.DB844901 RC=0 Dur=0.010 COM Stmt=UPDATE PS_MCF_INSTALL SET MCF_EMAIL_ID = MCF_EMAIL_ID + 1 1-195 10.39.54 0.000 Cur#2.1980.DB844901 RC=0 Dur=0.000 COM Stmt=SELECT MCF_EMAIL_ID FROM PS_MCF_INSTALL 1-196 10.39.54 0.000 Cur#2.1980.DB844901 RC=0 Dur=0.000 Commit 1-197 10.39.54 0.000 Cur#2.1980.DB844901 RC=0 Dur=0.000 Disconnect
See Also

 GetNextProcessInstance
GetNextProcessInstanceSyntax
GetNextProcessInstance([Commit])
Description
Use the GetNextProcessInstance function to retrieve the next available process instance from the Process Scheduler System table. When determining to find the next process instance in the sequence, the function ensures the next available process instance does not exist in both the Process Request and Message Log tables.
By default, the function commits the changes to the Process Scheduler System table to set it to the next available process instance for the next available request. If this function is called within a PeopleCode function where issuing a COMMIT to the database destroys a unit of work, specify "0" for Commit.
Parameters
|
Commit |
Specify whether the current data instance should be committed to the database. This parameter takes a string value: "1", commit the data, "0", do not commit the data. "1" is the default value. |
Returns
Return a number: 0 if successful, 1 if the system detected an error retrieving the next available process instance.
See Also

 GetNRXmlDoc
GetNRXmlDocSyntax
GetNRXmlDoc(NRID, EntityName)
Description
Use the GetNRXmlDoc function in any of the messaging PeopleCode events. It retrieves an XML message, categorized as non-repudiation, from the message queue for the specified non-repudiation ID. An XML message is a message that is unstructured, that is, isn't based on a record hierarchy. It creates and loads a data tree for the default message version, and returns Null if not successful.
Parameters
|
NRID |
Specify the non-repudiation ID for the XML message that you want to retrieve. This parameter takes a numeric value. |
|
EntityName |
Specify the name of the entity that signed the data, as a string. For Peoplesoft, this is the node name. |
Returns
A reference to an XmlDoc object if successful, Null if not successful.
See Also

 GetPage
GetPageSyntax
GetPage(PAGE.pagename)
Description
Use the GetPage function to return a reference to a page object. Generally, page objects are used to hide or unhide pages in a component.
Generally, the PeopleCode used to manipulate a page object would be associated with PeopleCode in the Activate event.
Note. The page object shouldn’t be used until after the Component Processor has loaded the page: that is, don’t instantiate this object in RowInit PeopleCode, use it in PostBuild or Activate instead.
Note
An expression of the form
PAGE.name.property
is equivalent to GetPage(name).property.
Parameters
|
PAGE. pagename |
The name of the page for which you want to create an object reference. Must be a page in the current context. |
Returns
A page object that references the page.
Example
In the following example, a page is hidden based on the value of the current field.
If PAYROLE_TYPE = "Global" Then GetPage(PAGE.JOB_EARNINGS).Visible = False; End-If;
See Also

 GetPubContractInstance
GetPubContractInstanceSyntax
GetPubContractInstance(pub_id, pub_nodename, channelname, sub_nodename)
Description
Note. This function is no longer available. It has been replaced with the GetPubXmlDoc function.
See GetPubXmlDoc.

 GetPubHeaderXmlDoc
GetPubHeaderXmlDocSyntax
GetPubHeaderXmlDoc(PubID, PubNode, ChannelName, VersionName[, Segment])
Description
Use the GetPubHeaderXmlDoc function to retrieve the message header from the message queue. The message header, also known as the message instance, is the published message before any transformations were performed.
Note. This function should not be used in standard message processing. It should only be used when correcting or debugging a publication contract that is in error.
Parameters
|
PubID |
Specify the PubID of the message. |
|
PubNode |
Specify the Pub Node Name of the message. |
|
ChannelName |
Specify the channel name of the message. |
|
VersionName |
Specify the version name of the message. |
|
Segment |
Specify an integer representing which segment you want to access. The default value is one, which means that if you do not specify a segment, the first segment is accessed. |
Returns
A reference to an XmlDoc object if successful, NULL if not successful.
See Also
ReSubmitPubHeaderXmlDoc, GetPubXmlDoc.

 GetPubXmlDoc
GetPubXmlDocSyntax
GetPubXmlDoc(PubID, PubNode, ChannelName, VersionName, MessageName, SubNode [, Segment])
Description
Use the GetPubXmlDoc function to retrieve a message from the message queue. This is the message after any transformations have been preformed. It creates and loads a data tree for the specified message version, and returns NULL if not successful. This function is used for publication contract error correction when the error correction process needs to fetch a particular message instance for the publication contract in error. SQL on the Publication Contract table is used to retrieve the key fields.
Note. This function should not be used in standard message processing. It should only be used when correcting or debugging a publication contract that is in error.
Parameters
|
PubID |
Specify the PubID of the message. |
|
PubNode |
Specify the Pub Node Name of the message. |
|
ChannelName |
Specify the channel name of the message. |
|
VersionName |
Specify the version name of the message. |
|
MessageName |
Specify the name of the message. |
|
SubNode |
Specify the subnode of the message. |
|
Segment |
Specify an integer representing which segment you want to access. The default value is one, which means that if you do not specify a segment, the first segment is accessed. |
Returns
A reference to an XmlDoc object if successful, NULL if not successful.
See Also
ReSubmitPubXmlDoc, ReSubmitPubHeaderXmlDoc.

 GetRecord
GetRecordSyntax
GetRecord([RECORD.recname])
Description
Use the GetRecord function to create a reference to a record object for the current context, that is, from the row containing the currently executing program.
The following code:
&REC = GetRecord();
is equivalent to:
&REC = GetRow().GetRecord(Record.recname);
or
&REC = GetRow().recname;
Note. This function is invalid for PeopleCode programs located in events that aren't associated with a specific row and record at the point of execution. That is, you cannot use this function in PeopleCode programs on events associated with high-level objects like pages (the Activate event) or components (component events).
Parameters
With no parameters, this function returns a record object for the current context (the record containing the program that is running).
If a parameter is given, RECORD. recname must specify a record in the current row.
Returns
GetRecord returns a record object.
Example
In the following example, the level 2 rowset (scroll) has two records: EMPL_CHKLST_ITM, (the primary record) and CHKLST_ITM_TBL. If the code is running from a field on the EMPL_CHKLST_ITM record, the following returns a reference to that record:
&REC = GetRecord(); /*returns primary record */
The following returns the other record in the current row.
&REC2 = GetRecord(RECORD.CHKLST_ITM_TBL);
The following event uses the @ symbol to convert a record name that’s been passed in as a string to a component name.
Function set_sub_event_info(&REC As Record, &NAME As string) &FLAGS = CreateRecord(RECORD.DR_LINE_FLG_SBR); &REC.CopyFieldsTo(&FLAGS); &INFO = GetRecord(@("RECORD." | &NAME)); If All(&INFO) Then &FLAGS.CopyFieldsTo(&INFO); End-If; End-Function;
See Also

 GetRelField
GetRelFieldSyntax
GetRelField(ctrl_field, related_field)
Description
Use the GetRelField function to retrieve the value of a related display field and returns it as an unspecified (Any) data type.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the GetRelated field class method instead.
The field ctrl_field specifies the display control field, and related_field specifies the name of the related display field whose value is to be retrieved. In most cases, you could get the value of the field by referencing it directly. However, there are two instances where GetRelField can be useful:
If there are two related display fields bound to the same record field, but controlled by different display control fields, use this function to specify which of the two related display fields you want.
If all of a page’s level-zero fields are search keys, the Component Processor does not load the entire row of level-zero data into the component buffer; it only loads the search keys. Adding a non-search-key level-zero field to the page would cause the Component Processor to load the entire row into the component buffer. To prevent a large row of data from being loaded into the buffer, you may occasionally want to make a level-zero display-only field a related display, even though the field is in the primary level-zero record. You won’t be able to reference this related display field directly, but you can using GetRelField.
See GetRelated.
Using GetRelField With a Control Field
PeopleCode events on the Control Field can be triggered by the Related Edit field. When this happens, there can be different behavior than with other types of fields:
If the events are called from FieldEdit of the Control Field, and that FieldEdit is triggered by a change in the Related Edit field, the functions return the previous value.
If the events are called from FieldChange of the Control Field, and that FieldChange is triggered by a change in the Related Edit field, the functions return the value entered into the Related Edit. This may be a partial value that will subsequently be expanded to a complete value when the processing is complete.
Example
In the following example, there are two related display fields in the page bound to PERSONAL_DATA.NAME. One is controlled by the EMPLID field of the high-level key, the other controlled by an editable DERIVED/WORK field in which the user can enter a new value. Use GetRelField to get the value of the related display controlled by EMPLID.
/* Use a related display of a required non-default field to verify * that the new Employee Id is not already in use */ If GetRelField(EMPLID, PERSONAL_DATA.NAME) <> "" Then Error MsgGet(1000, 65, "New Employee ID is already in use. Please reenter."); End-If;
See Also

 GetRow
GetRowSyntax
GetRow()
Description
Use the GetRow function to obtain a row object for the current context, that is the row containing the currently executing program.
Using the GetRow function is equivalent to:
&ROW = GetRowset().GetRow(CurrentRowNumber());
Note. For PeopleCode programs located in events that are not associated with a specific row at the point of execution, this function is invalid. That is, you cannot use this function in PeopleCode programs on events associated with high-level objects like pages or components.
Parameters
None.
Returns
GetRow returns a row object that references the current row in the component buffers. If the program is not being run from a page (such as from PeopleSoft Application Engine, or as part of a Message program) it references that data.
Example
Local Row &ROW; &ROW = GetRow();
See Also

 GetRowset
GetRowsetSyntax
GetRowset([SCROLL.scrollname])
Description
Use the GetRowset function to get a rowset object based on the current context. That is, the rowset is determined from the row containing the program that is running.
Syntax Format Considerations
An expression of the form
RECORD.scrollname.property
or
RECORD.scrollname.method(. . .)
is converted to an object expression by using GetRowset(SCROLL. scrollname).
Parameters
If a parameter is specified, it must be the name of the primary record for the scroll that is a child of the current context.
Returns
With no parameters, GetRowset returns a rowset object for the rowset containing the currently running program. If a parameter is specified, it returns a rowset for that child scroll. scrollname must be the name of the primary record for the scroll.
Example
In the following example, RS1 is a level 1 rowset, and RS2 is a child rowset of RS1.
Local Rowset &RS1, &RS2; &RS1 = GetRowset(); &RS2 = GetRowset(SCROLL.EMPL_CHKLST_ITM);
See Also

 GetRowsetCache
GetRowsetCacheSyntax
GetRowsetCache([Rowset.]name)
Description
Use GetRowsetCache to return the existing rowset cache with the given name.
Note. This function returns a RowsetCache object, not a rowset object. You must use the Get RowsetCache method in order to convert a RowsetCache object into a rowset object.
Every time you use the GetRowsetCache function, you should verify that the function executed successfully by testing for a null object. For example:
Local RowsetCache &RSC; &RSC = GetRowsetCache(Rowset.MyRowset); If All(&RSC) Then /* do processing */ Else /* call to populate rowset cache */ End-if;
Parameters
|
Record.name |
Specify the name of a RowsetCache. If you just specify name, you must enclose the name in quotation marks. |
Returns
A RowsetCache object populated with the rowset cache instance specified.
Example
&Cache1 = GetRowsetCache("AAROWSET1");
See Also

 GetSelectedTreeNode
GetSelectedTreeNode
Syntax
GetSelectedTreeNode(RECORD.recordname)
Description
Use the GetSelectedTreeNode function to determine what node the user has selected in a dynamic tree control.
Note. Dynamic tree controls have been deprecated. Use the GenerateTree function or Tree Viewer.
See Also
Viewing Trees From Application Pages

 GetSession
GetSessionSyntax
GetSession()
Description
Use the GetSession function to retrieve a PeopleSoft session object.
After you use GetSession, you can instantiate many other types of objects, like Component Interfaces, data trees, and so on.
After you use GetSession you must connect to the system using the Connect property.
If you are connecting to the existing session and not doing additional error checking, you may want to use the %Session system variable instead of GetSession. %Session returns a connection to the existing session.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A PeopleSoft session object.
Example
Local ApiObject &MYSESSION; &MYSESSION = GetSession();
See Also

 GetSetId
GetSetIdSyntax
GetSetId({FIELD.fieldname | text_fieldname}, set_ctrl_fieldvalue, {RECORD.recname | text_recname}, treename)
Description
Use the GetSetId function to return a string containing a setID based on a set control field (usually BUSINESS_UNIT), a set control value, and one of the following:
The name of a control table (or view) belonging to a record group in the TableSet Control controlled by the set control value.
The name of a tree in the TableSet Control controlled by the set control value.
If you want to pass a control record name to the function, you must pass an empty string in the treename parameter. Conversely, if you want to pass a tree name, you must pass an empty string in the text_recname parameter. In practice, tree names are rarely used in this function.
Note. This function does not validate the parameters passed to it. It is up to your application to ensure that only valid data is used. If an invalid value is used, the defined default value is used.
Parameters
|
fieldname |
Specify the set control field name as a FIELD reference. Use this parameter (recommended) or the text_fieldname parameter. |
|
text_fieldname |
Specify the name of the set control field as a string. Use this parameter or the fieldname parameter. |
|
set_ctrl_fieldvalue |
Specify the value of the set control field as a string. |
|
recname |
Specify as a RECORD reference the name of the control record belonging to the record group for which you want to obtain the setID corresponding to the set control value. Use this parameter (recommended) or the text_recname parameter. |
|
text_recname |
Specify as a string the name of the control record belonging to the record group for which you want to obtain the setID corresponding to the set control field value. Use this parameter or the recname parameter. |
|
treename |
Specify as a string the name of the tree for which you want to obtain the setID corresponding to the set control field value. |
Returns
GetSetId returns a five-character setID string.
Example
In this example, BUSINESS_UNIT is the Set Control Field, and PAY_TRMS_TBL is a control table belonging to a record group controlled by the current value of BUSINESS_UNIT. The function returns the setID for the record group.
&SETID = GetSetId(FIELD.BUSINESS_UNIT, &SET_CTRL_VAL, RECORD.PAY_TRMS_TBL, "");
See Also

 GetSQL
GetSQLSyntax
GetSQL(SQL.sqlname [, paramlist])
Where paramlist is an arbitrary-length list of values in the form:
inval1 [, inval2] ...
Description
Use the GetSQL function to instantiate a SQL object and associates it with the SQL definition specified by sqlname. The SQL definition must already exist, either created using PeopleSoft Application Designer or the StoreSQL function.
Processing of the SQL definition is the same as for a SQL statement created by the CreateSQL function.
Setting Data Fields to Null
This function does not set Component Processor data buffer fields to NULL after a row not found fetching error. However, it does set fields that aren’t part of the Component Processor data buffers to NULL.
Using Arrays With paramlist
You can use a parameter of type "Array of Any" in place of a list of bind values. This is primarily used when you don't know the number of values being supplied until the code runs.
For example, suppose you had a SQL definition INSERT_TEST, that had PeopleCode that dynamically (that is, at runtime) generated the following SQL statement:
"INSERT INTO PS_TESTREC (TESTF1, TESTF2, TESTF3, TESTF4, . . .TESTN) VALUES (:1, :2, %DateTimeIn(:3), %TextIn(:4). . .N)";
Suppose you have placed the values to be inserted into an Array of Any, say &AAny:
&AAny = CreateArrayAny("a", 1, %DateTime, "abcdefg", . . .N);
You can execute the insert by:
GetSQL(SQL.INSERT_TEST, &AAny);
Because the Array of Any promotes to absorb any remaining select columns, it must be the last parameter for the SQL object Fetch method or (for results) SQLExec. For binding, it must be the only bind parameter, as it is expected to supply all the bind values needed.
Parameters
|
SQL.sqlname |
Specify the name of a SQL definition. |
|
paramlist |
Specify input values for the SQL string. |
Returns
A SQL object.
Example
The following code creates and opens an SQL object on the SQL definition stored as ABCD_XY (for the current market, database type and as of date). It binds the given input values, and executes the statement. If the SQL.ABCD is a SELECT, this should be followed by a series of Fetch method calls.
&SQL = GetSQL(SQL.ABCD_XY, ABSENCE_HIST, &EMPLID);
The following is a generic function that can be called from multiple places to retrieve a specific record using the SQL Objects.
Local SQL &SQL; Local string &SETID, &TEMPLATE; Local date &EFFDT; Function FTP_GET_TEMPLATE(&REC As Record) Returns Boolean ; &TEMPLATE = FTP_RULE_TEMPLATE; &EFFDT = EFFDT; &SETID = SETID; &SQL = GetSQL(SQL.FTP_TEMPLATE_SELECT, &SETID, &TEMPLATE, &EFFDT); If &SQL.Status = 0 Then If &SQL.Fetch(&REC) Then &SQL.Close(); Return True; End-If; Else &TITLE = MsgGet(10640, 24, "SQL Error"); MessageBox(64, &TITLE, 10640, 23, "SQL Object Not Found in SQL", SQL.FTP_TEMPLATE_SELECT); End-If; &SQL.Close(); Return False; End-Function;
The SQL definition FTP_TEMPLATE_SELECT has the following code. Note that it uses the %List and %EFFDTCHECK meta-SQL statements. This makes the code easier to maintain: if there are any changes to the underlying record structure, this SQL definition won’t have to change:
SELECT %List(FIELD_LIST,FTP_DEFAULT_TBL A) FROM PS_FTP_TEMPLATE_TBL A WHERE A.SETID = :1 AND A.FTP_RULE_TEMPLATE = :2 AND %EFFDTCHECK(FTP_DEFAULT_TBL A1,A,:3) AND A.EFF_STATUS = 'A'
See Also
CreateSQL, DeleteSQL, FetchSQL, SQLExec.

 GetStoredFormat
GetStoredFormatSyntax
GetStoredFormat(scrollpath, target_row, [recordname.]fieldname)
where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ]] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can also use SCROLL.scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Use the GetStoredFormat function to return the name of a field’s custom stored format.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the StoredFormat field class property instead.
To return the format for a field on level zero of the page, pass 1 in target_row.
See Also
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
target_row |
An integer specifying the row of the target field. If you are testing a field on level zero, pass 1 in this parameter. |
|
[recordname .]fieldname |
The name of the field from which to get the stored format name. The field can be on any level of the active page. The recordname prefix is required if the call to GetStoredFormat is in a record definition other than recordname. |
Returns
Returns a String equal to the name of the stored custom format for the field.
Example
This example returns a string containing the custom format for postal codes on level zero of the page or on the current row of scroll level one. This function is called in the RowInit event, so no looping is necessary.
Function get_postal_format() Returns string &CURR_LEVEL = CurrentLevelNumber(); Evaluate &CURR_LEVEL When = 0 &FORMAT = GetStoredFormat(POSTAL, 1); When = 1 &FORMAT = GetStoredFormat(POSTAL, CurrentRowNumber(1)); End-Evaluate; Return (&FORMAT); End-Function;
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation

 GetSubContractInstance
GetSubContractInstanceSyntax
GetSubContractInstance(pub_id, pub_nodename, channelname, messagename, sub_name)
Description
Note. This function is no longer available. It has been replaced with the GetSubXmlDoc function.
See GetSubXmlDoc.

 GetSubXmlDoc
GetSubXmlDocSyntax
GetSubXmlDoc(PubID, PubNode, ChannelName, VersionName, MessageName[, Segment])
Description
Use the GetSubXmlDoc function to retrieve a message from the message queue. It creates and loads a data tree for the specified message version, and returns NULL if not successful. This function is used for subscription contract error correction, when the error correction process needs to fetch a particular message instance for the subscription contract in error. SQL on the Subscription Contract table is used to retrieve the key fields.
Note. This function should not be used in standard message processing. It should only be used when correcting or debugging a subscription contract that is in error.
Parameters
|
PubID |
Specify the PubID of the message. |
|
PubNode |
Specify the Pub Node Name of the message. |
|
ChannelName |
Specify the channel name of the message. |
|
VersionName |
Specify the version name of the message. |
|
MessageName |
Specify the name of the message. |
|
Segment |
Specify an integer representing which segment you want to access. The default value is one, which means that if you do not specify a segment, the first segment is accessed. |
Returns
A reference to an XmlDoc object if successful, NULL if not successful.
See Also

 GetSyncLogData
GetSyncLogDataSyntax
GetSyncLogData(GUID, pubnode, chnlname, msg_name, logtype [, message_version])
Description
Use the GetSyncLogData to return a log containing information about the specified synchronous message. You can use this information for debugging. Using this function, you can obtain the request and response data in a synchronous request, both pre- and post-transformation.
This function is used in the PeopleCode for the Message Monitor.
Parameters
|
GUID |
Specify the GUID for the published synchronous message as a string. This property is populated after the message is sent. |
|
pubnode |
Specify the name of the node that the synchronous message was published from as a string. |
|
chnlname |
Specify the name of the channel the synchronous message was published to as a string. |
|
msg_name |
Specify the message definition name that you want to retrieve log data from as a string. |
|
Log_type |
Specify the type of log data you want to obtain, as a number. Values are: 1: the original request 2: the transformed request 3: the original response 4: the transformed response |
|
message_version |
Specify the message version name as a string. |
Returns
An XML string containing the log data.
Example
Local String &guid, &pubnode, &channel, &msg_name; Local Number &log_type; .. .. &descrlong = GetSyncLogData(&guid, &pubnode, &channel, &msg_name, &log_type);
See Also
Using Integration Broker Monitor.

 GetTreeNodeParent
GetTreeNodeParent
Syntax
GetTreeNodeParent(node)
Description
Use the GetTreeNodeParent function to access data from dynamic tree controls.
Note. Dynamic tree controls have been deprecated. Use the GenerateTree function or Tree Viewer.
See Also
Viewing Trees From Application Pages

 GetTreeNodeRecordName
GetTreeNodeRecordName
Syntax
GetTreeNodeRecordName(node)
Description
Use the GetTreeNodeRecordName function in accessing data from dynamic tree controls.
Note. Dynamic tree controls have been deprecated. Use the GenerateTree function or Tree Viewer.
See Also
Viewing Trees From Application Pages

 GetTreeNodeValue
GetTreeNodeValue
Syntax
GetTreeNodeValue(node, [recordname.]fieldname)
Description
Use the GetTreeNodeValue function in accessing data from dynamic tree controls.
Note. Dynamic tree controls have been deprecated. Use the GenerateTree function or Tree Viewer.
See Also
Viewing Trees From Application Pages

 GetURL
GetURLSyntax
GetURL(URL.URLIdentifier)
Description
Use the GetURL function to return the URL, as a string, for the specified URLIdentifier. The URLIdentifier must exist and been created using URL Maintenance. If a language-specific URL exists for the user's current session language, it is returned. Otherwise, the base language version of the URL is returned.
Note. If the URL identifier contains spaces, you must use quotation marks around URLIdentifier. For example, GetURL(URL."My URL");
Parameters
|
URLIdentifier |
Specify a URL Identifier for a URL that already exists and was created using the URL Maintenance page. |
Returns
A string containing the URL value for that URL Identifier, using the user's language preference.
Example
Suppose you have a URL with the identifier PEOPLESOFT, and the following URL:
http://www.peoplesoft.com
From the following code example
&PS_URL = GetURL(URL.PEOPLESOFT);
&PS_URL has the following value:
http://www.peoplesoft.com
Suppose you have the following URL stored in the URL Maintenance, with the name QE_CALL:
/S/WEBLIB_QE_MCD.QE_MCD_MAIN.FieldFormula.iScript_Call
You could combine this in the following code to produce an HTML string used as part of a response:
&output = GetHTMLText(HTML.QE_PHONELIST, %Request.RequestURI | "?" | GetURL(URL.QE_CALL));
See Also

 GetUserOption
GetUserOptionSyntax
GetUserOption(Level, OPTN)
Description
Use the GetUserOption function to return the default value for the specified option.
Parameters
|
Level |
Specify the option category level as a string. |
|
OPTN |
Specify the option as a string. |
Returns
The default value for the specified option.
Example
Local Any &MyValue; &MyValue = GetUserOption("PPLT", "TZONE");
See Also
Managing PeopleSoft Personalizations

 GetWLFieldValue
GetWLFieldValueSyntax
GetWLFieldValue(fieldname)
Description
When the user has opened a page from a Worklist (by selecting one of the work items) use the GetWLFieldValue function to retrieve the value of a field from the current row of the application Worklist record. You can use the %WLName system variable to check whether the page was accessed from a Worklist.
Returns
Returns the value of a specified field in the Worklist record as an Any data type.
Example
This example, from RowInit PeopleCode, populates page fields with values from the Worklist record. The %WLName system variable is used to determine whether there is a currently active Worklist (that is, whether the user accessed the page using a Worklist).
&WL = %WLName; If &WL > " " Then &TEMP_NAME = "ORDER_NO"; ORDER_NO = GetWLFieldValue(&TEMP_NAME); &TEMP_NAME = "BUSINESS_UNIT"; BUSINESS_UNIT = GetWLFieldValue(&TEMP_NAME); &TEMP_NAME = "SCHED_Date"; &SCHED_Date = GetWLFieldValue(&TEMP_NAME); SCHED_Date = &SCHED_Date; &TEMP_NAME = "DEMAND_STATUS"; DEMAND_STATUS = GetWLFieldValue(&TEMP_NAME); End-If;
See Also
MarkWLItemWorked, TriggerBusinessEvent.

 Global
GlobalSyntax
Global data_type &var_name
Description
Use the Global statement to declare PeopleCode global variables. A global variable, once declared in any PeopleCode program, remains in scope throughout the PeopleSoft session. The variable must be declared with the Global statement in any PeopleCode program in which it is used.
Declarations tend to appear at the beginning of the program, intermixed with function declarations.
Not all PeopleCode data types can be declared as Global. For example, ApiObject data types can only be declared as Local.
Parameters
|
data_type |
Specify a PeopleCode data type. |
|
&var_name |
A legal variable name. |
Example
The following example declares a global variable and then assigns it the value of a field:
global string &AE_APPL_ID; &AE_APPL_ID = AE_APPL_ID;
See Also

 Gray
GraySyntax
Gray(scrollpath, target_row, [recordname.]fieldname)
where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ]] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can also use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
If you put the function on the same scroll level as the field being changed, you can use the following syntax:
Gray(Fieldname)
The more complex syntax can be used to loop through a scroll on a lower level than the PeopleCode program.
Description
Use the Gray function to make a field unavailable for entry a page field, preventing the user from making changes to the field.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the Enabled field class property instead.
Gray makes a field display-only, while Hide makes it invisible. You can undo these effects using the built-in functions Ungray and Unhide.
Note. If you specify a field as Display Only in PeopleSoft Application Designer, using the PeopleCode functions Gray, followed by Ungray, will not make it editable. This function shouldn't be used in any event prior to RowInit.
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
target_row |
An integer specifying the row on the target scroll level where the referenced buffer field is located. |
|
[recordname .]fieldname |
The name of the field to gray. The field can be on scroll level one, two, or three of the active page. The recordname prefix is required if the call to Gray is in a record definition other than recordname. |
Returns
Optionally returns a Boolean value indicating whether the function succeeded.
Example
This example, which would typically be found in the RowInit event, disables the page’s address fields if the value of the SAME_ADDRESS_EMPL field is "Y".
If SAME_ADDRESS_EMPL = "Y" Then Gray(STREET1); Gray(STREET2); Gray(CITY); Gray(STATE); Gray(ZIP); Gray(COUNTRY); Gray(HOME_PHONE); End-if;
See Also

 GrayMenuItem
GrayMenuItem
Syntax
GrayMenuItem(BARNAME.menubar_name, ITEMNAME.menuitem_name)
Description
Note. The GrayMenuItem function is supported for compatibility with previous releases of PeopleTools. New applications should use DisableMenuItem instead.
See Also

 Hash
HashSyntax
Hash(ClearTextString)
Description
The Hash function returns a fixed length value, based on the input. The output is always 28 characters. The input is variable length, with no maximum size.
Regardless of the operating system platform, underlying character encoding or hardware byte order, identical character strings always generate identical hash values regardless of the platform on which the hash generation is run. Because of this, hash output should not be used as a unique key to a table of data. Given the output of hash, it is impossible to determine the input.
Some of the original data is deliberately lost during the conversion process. This way, even if you know the algorithm, you can't “un-hash” the data.
Generally the Hash function is used like a checksum, to compare hashed values to ensure they match.
Parameters
|
ClearTextString |
Specify the string you want converted. |
Returns
A hash string.
Example
MessageBox("Please confirm password"); &HASHPW = Hash(&PASSWD); &OPERPSWD = USERDEFN.OPERPSWD.Value; If not (&HASHPW = &OPERPSWD) Then /* do error handling */ End-if;
See Also

 HermiteCubic
HermiteCubicSyntax
HermiteCubic(DataPoints)
Description
Use the HermiteCubic function to compute a set of interpolating equations for a set of at least three datapoints. This particular Hermitian cubic is designed to mimic a hand-drawn curve.
Parameters
|
DataPoints |
This parameter takes an array of array of number. The array’s contents are an array of six numbers. The first two of these six numbers are the x and y points to be fit. The last four are the four coefficients to be returned from the function: a, b, c and d. a is the coefficient of the x0 term, b is the coefficient of the x1 term, c is the coefficient of the x2 term, and d is the coefficient of the x3 term. |
Returns
A modified array of array of numbers. The elements in the array correspond to the elements in the array used for DataPoints.
See Also

 Hide
HideSyntax
Hide(scrollpath, target_row, [recordname.]fieldname)
where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ]] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can also use SCROLL.scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Use the Hide function to make a page field invisible.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the Visible field class property instead.
You can display the field again using Unhide, but Unhide has no effect on a field that has been made display-only in the page definition.
Gray, Hide, Ungray, and Unhide usually appear in RowInit programs that set up the initial display of data, and in FieldChange programs that change field display based on changes the user makes to a field. Generally, you put the functions on the same scroll level as the field that is being changed. This reduces the complexity of the function’s syntax to:
Hide(fieldname)
The more complex syntax can be used to loop through a scroll on a lower level than the PeopleCode program.
Note. This function shouldn't be used in any event prior to RowInit.
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
target_row |
An integer specifying the row on the target scroll level where the referenced buffer field is located. |
|
[recordname .]fieldname |
The name of the field to hide. The field can be on scroll level one, two, or three of the active page. The recordname prefix is required if the call to Hide is in a record definition other than recordname. |
Returns
Boolean (optional). Hide returns a Boolean value indicating whether it executed successfully.
Example
This example hides the page’s address fields if SAME_ADDRESS_EMPL is equal to "Y":
If SAME_ADDRESS_EMPL = "Y" Then Hide(STREET1); Hide(STREET2); Hide(CITY); Hide(STATE); Hide(COUNTRY); Hide(HOME_PHONE); End-if;
See Also

 HideMenuItem
HideMenuItemSyntax
HideMenuItem(BARNAME.menubar_name, ITEMNAME.menuitem_name)
Description
Use the HideMenuItem function to hide a specified menu item. To apply this function to a pop-up menu, use the PrePopup Event of the field with which the pop-up menu is associated.
If you’re using this function with a pop-up menu associated with a page (not a field), the earliest event you can use is the PrePopup event for the first “real” field on the page (that is, the first field listed in the Order view of the page in PeopleSoft Application Designer.)
When a menu is first displayed, all menus are visible by default, so there is no need for a function to re-display a menuitem that has been hidden.
Restrictions on Use With a Component Interface
This function is ignored (has no effect) when used by a PeopleCode program that’s been called by a Component Interface.
Parameters
|
menubar_name |
Name of the menu bar that owns the menuitem, or, in the case of pop-up menus, the name of the pop-up menu that owns the menuitem. |
|
menuitem_name |
Name of the menu item. |
Returns
None.
Example
HideMenuItem(BARNAME.MYPOPUP1, ITEMNAME.DO_JOB_TRANSFER);
See Also
DisableMenuItem, EnableMenuItem.

 HideRow
HideRowSyntax
HideRow(scrollpath) [, target_row])
Where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ]] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can also use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Use the HideRow function to hide a row occurrence programmatically.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the Visible row class property instead.
It hides the specified row and any associated rows at lower scroll levels.
Hiding a row just makes the row invisible, it does not affect database processing such as inserting new rows, updating changed values, or deleting rows.
When you hide a row, it becomes the last row in the scroll or grid, and the other rows are renumbered accordingly. If you later use UnHideRow to make the row visible again, it is not moved back to its original position, but remains in its new position. When HideRow is used in a loop, you have to process rows from the highest number to the lowest to achieve the correct results.
Note. HideRow cannot be executed from the same scroll level as the row that is being hidden, or from a lower scroll level. Place the PeopleCode in a higher scroll level record.
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
target_row |
An integer specifying which row in the scroll to hide. If this parameter is omitted, the row on which the PeopleCode program is executing is assumed. |
Returns
Boolean (optional). HideRow returns a Boolean value indicating whether the function executed successfully.
Example
This example hides all rows in scroll level 1 where the EXPORT_SW field is equal to "Y". Note that the loop has to count backwards from ActiveRowCount to 1.
For &ROW = ActiveRowCount(RECORD.EXPORT_OBJECT) to 1 step - 1 &EXPORT_SW = FetchValue(EXPORT_OBJECT.EXPORT_SW, &ROW); If &EXPORT_SW "Y" Then HideRow(RECORD.EXPORT_OBJECT, &ROW); Else /* WinMessage("not hiding row " | &ROW);*/ End-if; End-for;
See Also

 HideScroll
HideScrollSyntax
HideScroll(scrollpath)
Where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ]] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can also use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Use the HideScroll function to programmatically hide a scroll bar and all data items within the scroll.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the HideAllRows rowset class method instead.
Typically this function is used in RowInit and FieldChange PeopleCode to modify the page based on user action.
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
Returns
HideScroll returns a Boolean value indicating whether the function executed successfully.
Example
This example, from RowInit PeopleCode, initializes the visibility of the scroll based on a field setting:
If %Component = COMPONENT.APPR_RULE Then If APPR_AMT_SW = "N" Then HideScroll(RECORD.APPR_RULE_LN, CurrentRowNumber(1), RECORD.APPR_RULE_DETL, CurrentRowNumber(2), RECORD.APPR_RULE_AMT); Else UnhideScroll(RECORD.APPR_RULE_LN, CurrentRowNumber(1), RECORD.APPR_RULE_DETL, CurrentRowNumber(2), RECORD.APPR_RULE_AMT); End-If; End-If;
The corresponding FieldChange PeopleCode dynamically changes the appearance of the page based on user changes to the APPR_AMT_SW field:
If APPR_AMT_SW = "N" Then HideScroll(RECORD.APPR_RULEs_LN, CurrentRowNumber(1), RECORD.APPR_RULE_DETL, CurrentRowNumber(2), RECORD.APPR_RULE_AMT); &AMT_ROWS = ActiveRowCount(RECORD.APPR_RULE_LN, CurrentRowNumber(1), RECORD.APPR_RULE_DETL, CurrentRowNumber(2), RECORD.APPR_RULE_AMT); For &AMT_LOOP = &AMT_ROWS To 1 Step - 1 DeleteRow(RECORD.APPR_RULE_LN, CurrentRowNumber(1), RECORD.APPR_RULE_DETL, CurrentRowNumber(2), RECORD.APPR_RULE_AMT, &AMT_LOOP); End-For; Else UnhideScroll(RECORD.APPR_RULE_LN, CurrentRowNumber(1), RECORD.APPR_RULE_DETL, CurrentRowNumber(2), RECORD.APPR_RULE_AMT); End-If;
See Also
UnhideRow, HideRow, UnhideScroll.

 HistVolatility
HistVolatilitySyntax
HistVolatility(Closing_Prices, Trading_Days)
Description
Use the HistVolatility function to compute the historical volatility of a market-traded instrument.
Parameters
|
Closing_Prices |
An array of number. The elements in this array contain a vector of closing prices for the instrument. |
|
Trading_Days |
The number of trading days in a year. |
Returns
A number.
See Also

 Hour
HourSyntax
Hour(time_value)
Description
Use the Hour function to extract a Number value for the hour of the day based on a Time or Datetime value. The value returned is a whole integer and is not rounded to the nearest hour.
Parameters
|
time_value |
A Datetime or Time value. |
Returns
Returns a Number equal to a whole integer value from 0 to 23 representing the hour of the day.
Example
If &TIMEOUT contains a Time value equal to 04:59:59 PM, the following example sets &TIMEOUT_HOUR to 16:
&TIMEOUT_HOUR = Hour(&TIMEOUT);
See Also

 Idiv
IdivSyntax
Idiv(x, divisor)
Description
The Idiv function is an explicit integer division operation. It divides one number (x) by another (divisor).
Parameters
|
X |
Specify an integer to be divided. |
|
divisor |
Specify the integer used to divide the first parameter. |
Returns
An integer value.
Example
The following example sets &I1 to 1 and &I2 to -1:
&I1 = Idiv(3, 2); &I2 = Idiv(17, 10);
See Also
Mod, Int, Integer, Round, Truncate, Value.

 If
IfSyntax
If condition Then [statement_list_1] [Else [statement_list_2]] End-If
Description
Use the If statement to execute statements conditionally, depending on the evaluation of a conditional expression. The Then and Else clauses of an If consist of arbitrary lists of statements. The Else clause may be omitted. If condition evaluates to True, all statements in the Then clause are executed; otherwise, all statements in the Else clause are executed.
Example
The following example’s first If statement checks for BEGIN_DT and RETURN_DT, and makes sure that RETURN_DT is greater (later) than BEGIN_DT. If this is True, the execution continues at the following line, otherwise execution continues at the line beginning with WinMessage:
If All(BEGIN_DT, RETURN_DT) and BEGIN_DT = RETURN_DT Then &DURATION_DAYS = RETURN_DT - BEGIN_DT; If &DURATION_DAYS 999 Then DURATION_DAYS = 999; Else DURATION_DAYS = &DURATION_DAYS; End-if; Else WinMessage("The beginning date is later then the return date!"); End-if;

 InboundPublishXmlDoc
InboundPublishXmlDocSyntax
InboundPublishXmlDoc(&XmlDoc, Message.MessageName, Node.PubNodeName [, Enqueue])
Description
Use the InboundPublishXmlDoc function to send an asynchronous message that simulates an inbound request from an external node. The content data is based on an XmlDoc object.
This function is used to test inbound message processing. Though you are sending a message to yourself, it goes through all the inbound message processing on PubNodeName.
The &XmlDoc object must already be instantiated and populated. The message included in the function call should be a nonrowset-based message, that is, one that isn't based on a hierarchical record structure.
Parameters
|
&XmlDoc |
Specify an already instantiated and populated XmlDoc object that you want to test. |
|
MessageName |
Specify an already existing nonrowset-based message, prefaced with the reserved word Message. |
|
PubNodeName |
Specify a node. This is for Sender Specified Routing (SSR), prefixed with the reserved word Node. The node defines the target for the published message. |
|
Enqueue |
Specify if the message is enqueued. This parameter takes a Boolean value. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if the message was successfully published, False otherwise.
Example
The following code example re-publishes the XmlDoc and simulates that it is coming from the node EXTERNAL.
Local XMLDOC &xmldoc = GetMessageXmlDoc(); InBoundPublishXmlDoc(&xmldoc, NODE.EXTERNAL);
See Also
GetMessageXmlDoc, SyncRequestXmlDoc.

 InitChat
InitChatSyntax
InitChat(logical queue ID, application data URL, customer username, [chat_subject][, chat_question][, wizard_URL][, priority][, skill_level][, cost])
Description
Use the InitChat function to engage a customer and an agent in a chat session. It places a chat request on a MultiChannel Framework queue and immediately launches a customer chat window. When an agent accepts this task from the queue, the system launches an agent chat window.
Note. Chats are implicitly queued with the current language setting of the initiator (%Language_user). Chats are only assigned to agents who have this language in their language list as specified on the Languages page of the Agents component.
Parameters
|
logical queue ID |
Specifies the logical queue in which the task should be queued. It is a string value. The logical queue ID is a case-sensitive value. The case used in the InitChat function must exactly match the case used when creating the logical queue ID on the Queues page. |
|
application data relative URL |
This is the relative URL of the application page you want the agent to see on the left side of the agent-to-customer chat window when the agent accepts the chat. This value needs to be provided by your program. Note. This URL parameter must not point to content that includes JavaScript that breaks surrounding frames or that references the "top" window. In addition, the application page should not contain URL links to such content. This is because the Agent Chat Console is framed by the RenServer API which sends and receives the chat text. |
|
customer username |
This reflects the name of the customer or end user initiating the chat request. This value can be derived from the signon mechanism (%UserID) or by prompting the user. This is the name used to identify the chat requestor in the MultiChannel Framework chat console. For example, in the chat history window, all text sent by the customer is prefixed with this name. |
|
chat_subject |
This is an optional string parameter. The application can indicate a subject of the chat request. This could be prompted from the user or inferred from the page from which the chat is initiated. The system displays the subject on the agent's chat console when it assigns the chat to an agent. |
|
chat_question |
This is an optional string parameter. The application can indicate a specific question to be addressed in the chat. This could be prompted from the user or inferred from the page from which the chat is initiated. The value appears in the agent's chat window history box immediately after accepting the chat. This enables the agent to know the customer's question without having to ask. |
|
wizard_URL |
This feature leads the agent to an application page from which the agent can select a URL to push to the customer. This is an optional string parameter. This is the relative URL of the application page you wish the agent to launch when the agent clicks the Grab button on the Agent Chat console. If you do not provide this value, a default wizard is launched with no application-specific functionality. If you do provide this value, the application page must provide a wizard for pushing a URL to the customer. The wizard page provided by the application must be able to write the URL generated by the wizard to the URL field. The URL field is defined by PeopleSoft. In addition, you need to embed the HTML definition, MCF_GRABURL, which provides the Push and Push and Close buttons that push the URL in the URL field to the customer. See the Example section for examples showing the PeopleCode that would be used to generate the relative URL that is passed in to InitChat and the PeopleCode that would be used to embed the provided MCF_GRABURL definition into your application page. |
|
priority |
This is an optional parameter. It is an integer value expressing the priority level of the request. The minimum value is 0 and there is no maximum value. Specify the priority of this chat task. A higher value means a higher priority. MultiChannel Framework tasks are ordered on a physical queue based on their assigned priority, which means the system assigns a task of a higher priority before it assigns a task of a lower priority. If no value is specified, the system uses the default value specified for that task type on the Task Configuration page. When tasks have the same priority, the system orders the tasks according to time they were created. For example, suppose the following tasks exist: Priority 2 created at 11:15 AM and Priority 2 created at 11:16 AM. In this case, the system places the task created at 11:15 AM before the task created at 11:16 AM. |
|
skill level |
This is an optional parameter. It is an integer value expressing the minimum skill level required of the agent to whom the system routes the request. You set an agent's skill level in the Agent page. The minimum value is 0 and there is no maximum value. The queue server assigns this task type to an available agent on that queue with the lowest skill level greater than or equal to the skill level required by the task. If no value is specified, the system uses the default value specified for that task type in the Task Configuration page. |
|
cost |
This is an optional parameter. It is an integer value measuring the workload each task places on an agent. The cost of a task is an estimate of the tasks's expected complexity and of the time required to resolve the task. The minimum value is 0, and there is no maximum value. The cost of a task is added to an agent's workload after accepting a task on the MultiChannel Framework console. A task can't be assigned to an agent if the difference between the current workload and the maximum workload defined for that agent on the Agent configuration page is less than the cost of this task. If you do not specify a value, the system uses the default value specified for that task in the Task Configuration pages. Note. If the required skill level or cost submitted exceeds the highest skill level or maximum workload of any of the agents on that queue, the task cannot be assigned. |
Returns
Returns a unique Chat ID in the form of an integer. You can use this ID to reference the chat in the chat log.
If unsuccessful, it returns a message number. The message set ID for MultiChannel Framework is 162.
For example, 1302 is returned when an invalid task type or no value is provided.
Example
For example, the following PeopleCode could be used to generate the relative URL that is passed in to InitChat.
&WizURL = GenerateComponentContentRelURL(%Portal, %Node, MenuName.PT_MCF, "GBL", Component.MCF_DEMO_CMP, Page.MCF_URLWIZARD, "U");
The following is an example of embedding the provided MCF_GRABURL definition into your application page, using the GetHTMLText function.
Function IScript_GrabURL() &cssPTMCFDEF = %Response.GetStyleSheetURL(StyleSheet.PTMCFDEF); &cssPTSTYLEDEF = %Response.GetStyleSheetURL(StyleSheet.PTSTYLEDEF); &titleGrabURL = MsgGetText(162, 1170, "URL Wizard"); &psDomain = SetDocDomainForPortal(); If (&psDomain = "") Then &psDomain = SetDocDomainToAuthTokenDomain(); End-If; &labelBtPush = MsgGetText(162, 1181, "Push"); &labelBtPushClose = MsgGetText(162, 1186, "Push and Close"); &HTML = GetHTMLText(HTML.MCF_GRABURL, &titleGrabURL, &cssPTSTYLEDEF, &cssPTMCFDEF, &psDomain, &labelBtPush, &labelBtPushClose); %Response.Write(&HTML); End-Function;
The following is an example of the usage of InitChat.
&ret = InitChat("SALES", "http://www.support.company.com/products.html", "John Smith", "Widgets", "How to order widgets", "", 2, 2);
The following example illustrates how to pass a PeopleCode-generated URL using the GenerateComponentContentRelURL function for Application Data URL and wizards.
&urlTestComponent = GenerateComponentContentRelURL(%Portal, %Node, MenuName.UTILITIES, "GBL", Component.MESSAGE_CATALOG1, Page.MESSAGE_CATALOG, "U"); &WizURL = GenerateComponentContentRelURL(%Portal, %Node, MenuName.PT_MCF, "GBL", Component.MCF_DEMO_CMP, Page.MCF_URLWIZARD, "U"); try &ret = InitChat(&QUEUEID, &urlTestComponent, &Username, &subject, &question, &wizurl, &priority, &minskill); catch Exception &E MessageBox(0, "", 0, 0, "Caught exception: " | &E.ToString()); end-try;

 InsertImage
InsertImageSyntax
InsertImage(scrollpath, target_row, [recordname.]fieldname)
where scrollpath is:
[SCROLL.level1_recname, level1_row, [SCROLL.level2_recname, level2_row,]] SCROLL.target_recname
Description
Use the InsertImage function to associate an image file with a record field on a page. After the image file is associated with the record field, it can be saved to the database when the component is saved.
The following are the valid types of image files that can be associated with a record field:
JPEG
BMP
DIB
InsertImage uses a search page to enable the end-user to select the image file to be used. This is the same search page used to add an attachment.
Note. To update an image field using this function, be sure that PSIMAGEVER field is also on the same record as the image field being updated.
Restrictions on Use in PeopleCode Events
InsertImage is a “think-time” function, which means it shouldn’t be used in any of the following PeopleCode events:
SavePreChange
SavePostChange
Workflow
RowSelect
Any PeopleCode event that fires as a result of a ScrollSelect (or one of its relatives) function calls, or a Select (or one of its relatives) Rowset class method.
See Think-Time Functions.
Image Size Considerations
The size of the image that can be saved to the database depends on the database platform.
|
Database Platform |
Size limitation |
|
DB2/400 |
30 KB |
|
DB2/MVS |
31 KB |
|
DB2/Unix |
31 KB |
Platforms other than those listed here are effectively without a size limit, that is, they allow for images equal to or greater than 2 GB.
Platform size limitations are subject to change.
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll area in the component buffer. |
|
target_row |
The row number of the target row. |
|
[recordname .]fieldname |
The name of the field to be associated with the image file. The field can be on scroll level one, two, or three of the active page. The recordname prefix is required if the function call is in a record definition other than recordname. |
Returns
The InsertImage function returns either a constant or a number:
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
0 |
%InsertImage_Success |
Image was successfully associated with the record field. |
|
1 |
%InsertImage_Failed |
Image was not successfully associated with the record field. When the component is saved the image file will not be saved to the database. |
|
2 |
%InsertImage_Canceled |
User canceled the transaction so image file isn't associated with record field. |
|
3 |
%InsertImage_ExceedsMaxSize |
Image exceeds the maximum allowed size. |
Example
&RC = InsertImage(EMPL_PHOTO.EMPLOYEE_PHOTO);
See Also

 InsertRow
InsertRowSyntax
InsertRow(scrollpath, target_row [, turbo])
where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can also use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Use the InsertRow function to programmatically perform the ALT+7 and ENTER (RowInsert) function.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the InsertRow rowset class method instead.
InsertRow inserts a new row in the scroll buffer and causes a RowInsert PeopleCode event to fire, followed by the events that normally follow a RowInsert, as if the user had manually pressed ALT+7 and ENTER.
InsertRow can be executed in turbo or non-turbo mode. To execute the function in turbo mode, pass a value of True in the optional turbo parameter. Non-turbo mode is the default. In turbo mode, default processing is performed only for the row being inserted.
In scrolls that are not effective-dated, the new row is inserted after the target row specified in the function call. However, if the scroll is effective-dated, then the new row is inserted before the target row, and all the values from the previous current row are copied into the new row, except for EffDt, with is set to the current date.
Note. InsertRow cannot be executed from the same scroll level where the insertion will take place, or from a lower scroll level. Place the PeopleCode in a higher scroll level record.
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
target_row |
The row number indicating the position where the new row will be inserted. |
|
turbo |
Specifies whether default processing is performed on the entire table or just the row being inserted. Pass a value of True to execute this parameter. Non-turbo mode is the default. |
Returns
Optionally returns a Boolean value indicating whether the function executed successfully.
Example
The example inserts a row on the level-two page scroll. The PeopleCode has to be in the scroll-level-one record:
InsertRow(RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_PER, &L1_ROW, RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_DTL, &L2_ROW);
See Also
DeleteRow, HideRow, UnhideRow.

 Int
IntSyntax
Int(decimal)
Description
Use the Int function to truncate a decimal number x to an integer and returns the result as a Number value.
Note. PeopleSoft only supports 32 bit integers. The largest integer value we support is 4294967295.
Parameters
|
decimal |
A decimal number to be truncated. |
Returns
Returns a Number equal to decimal truncated to a whole integer.
Example
The following example sets &I1 to 1 and &I2 to -4:
&I1 = Int(1.975); &I2 = Int(-4.0001);
See Also

 Integer
IntegerSyntax
Integer(decimal)
Description
Use the Integer function to convert decimal to an integer (32 bit signed twos complement number) by truncating any fraction part towards zero and returns the result as an Integer value.
Differences between Int and Integer
There is one primary difference between the Int function and the Integer function.
The Int function rounds to a number in floating-decimal-point representation with a range of -9,999,999,999,999,999,999,999,999,999,999 to 9,999,999,999,999,999,999,999,999,999,999.
The Integer function truncates to a number in 32 bit binary twos-complement representation with a range of -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647.
Parameters
|
decimal |
A decimal number to be truncated to an integer. |
Returns
Returns an Integer equal to decimal truncated to a whole integer. If decimal is outside the range that can be represented by an integer type, the result isn't defined.
See Also
Mod, Int, Round, Truncate, Value.

 IsAlpha
IsAlphaSyntax
IsAlpha(String)
Description
Use the IsAlpha function to determine if String contains only textual characters, including alphabetic characters from several scripts including Latin, Greek, Cyrillic and Thai, ideographic characters from Chinese, Japanese and Korean and Japanese kana. It excludes all punctuation, numerics, spaces and control codes
Parameters
|
String |
Specify the string you want to search for alphabetic and other textual characters. |
Returns
A Boolean value: true if the string contains only alphabetic and textual characters, false if it contains any numbers, punctuation or spaces.
Example
&Value = Get Field().Value; If IsAlpha(&Value) Then /* do textual processing */ Else /* do non-textual processing */ End-if;
See Also
IsAlphaNumeric, IsDigits, IsDate, IsDateTime, IsNumber, IsTime.

 IsAlphaNumeric
IsAlphaNumericSyntax
IsAlphaNumeric(String)
Description
Use the IsAlphaNumeric function to determine if String contains only textual and numeric characters.
Textual characters include all characters valid for the IsAlpha function. Alphanumeric characters do not include sign indicators and comma and period decimal points. If you want to check for numbers as well as sign indicators, use the IsNumber function.
Parameters
|
String |
Specify the string you want to search for alphanumeric characters. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if the string contains only alphanumeric characters, False otherwise.
Example
&Value = Get Field().Value; If IsAlphaNumeric(&Value) Then /* do alphanumeric processing */ Else /* do non-alphanumeric processing */ End-if;
See Also

 IsDate
IsDateSyntax
IsDate(Value)
Description
Use the IsDate function to determine if Value contains a valid date.
You can use this function when you want to determine if a value is compatible with the Date built-in function.
Parameters
|
Value |
Specify either a string or number you want to search for a valid date. Value is a number of the format YYYYMMDD or string of the format YYYY-MM-DD. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if the string contains a valid date, False otherwise.
Example
If IsDate(&Num) Then &Datevalue = Date(&Num); End-if;
See Also
IsAlphaNumeric, IsDigits, IsDateTime, IsNumber, IsTime.

 IsDateTime
IsDateTimeSyntax
IsDateTime(String)
Description
Use the IsDateTime function to determine if String contains a datetime string in the standard PeopleSoft format, that is, in the following format:
yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss.mmmmmm
Parameters
|
String |
Specify the string you want to search for a valid datetime. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if the string contains a valid datetime, False otherwise.
Example
The following example uses the short form of dot notation, by combining the getting the field value with getting the value of IsDateTime and making it a conditional statement:
If IsDateTime(GetField().Value) Then /* do date processing */ Else /* do non-date processing */ End-if;
See Also
IsAlphaNumeric, IsDigits, IsDate, IsNumber, IsTime.

 IsDaylightSavings
IsDaylightSavingsSyntax
IsDaylightSavings(datetime, {timezone | "Local" | "Base"});
Description
Use the IsDaylightSavings function to determine if daylight savings is active in the specified time zone at the specified datetime. For time zones that don’t observe daylight savings time, this function always returns False.
The system’s base time zone is specified on the PSOPTIONS table.
Parameters
|
datetime |
The datetime value you want to check. |
|
timezone | Local | Base |
Specify a value for converting datetime. The values are:
|
Returns
A Boolean value: True if daylight savings is active in the specified time zone at the specified datetime. Returns False otherwise.
Example
In the first example, TESTDTTM has value of 01/01/99 10:00:00AM. &OUTPUT is False.
&OUTPUT = IsDaylightSavings(TESTDTTM, "EST")
In this example, TESTDTTM has value of 04/05/99 12:00:00AM. &OUTPUT has a value of True: 12:00am PST = 3:00am EST, so Daylight Savings Time has switched on.
&OUTPUT = IsDaylightSavings(TESTDTTM, "EST")
In this example, TESTDTTM has value of 04/05/99 12:00:00AM. &OUTPUT returns False: 12:00am PST = 1:00am MST, so Daylight Savings Time hasn't started yet.
&OUTPUT = IsDaylightSavings(TESTDTTM, "MST")
In this example, TESTDTTM has value of 07/07/99 10:00:00. &OUTPUT returns False: ESTA is Indiana time, where they do not observe Daily Savings Time.
&OUTPUT = IsDaylightSavings(TESTDTTM, "ESTA")
See Also
ConvertDatetimeToBase, ConvertTimeToBase, DateTimeToTimeZone, TimeToTimeZone, TimeZoneOffset.

 IsDigits
IsDigitsSyntax
IsDigits(String)
Description
Use the IsDigits function to determine if String contains only digit (numeric) characters. Numeric characters do not include sign indicators and comma and period decimal points. If you want to check for numbers as well as sign indicators, use the IsNumber function.
Parameters
|
String |
Specify the string you want to search. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if the string contains digits, False otherwise.
Example
If IsDigits(&MyValue) Then /* do processing */ Else /* do error processing */ End-if;
See Also
IsAlpha, IsAlphaNumeric, IsDate, IsDateTime, IsNumber, IsTime.

 IsDisconnectedClient
IsDisconnectedClientSyntax
IsDisconnectedClient()
Description
Use the IsDisconnectedClient function to determine whether the current environment that is being accessed is the Disconnected Client. This function enables you to provide alternate code paths when running in a Disconnected Client environment.
Note. This feature only returns true when running on a PeopleSoft Mobile Synchronization Client. This functionality is not available in all product lines.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A boolean value: true if the current environment is the Disconnected Client, false otherwise.
Example
if (IsDisconnectedClient()) then WinMessage("DisconnectedClient = true"); else WinMessage("DisconnectedClient = false"); end-if;
See Also
Understanding PeopleSoft Mobile Agent

 IsHidden
IsHiddenSyntax
IsHidden(scrollpath, target_row)
Where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can also use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Use the IsHidden function to verify whether a row is hidden or not.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the Visible row class property instead.
It returns True if the row is hidden, otherwise it returns False. IsHidden must be called in a PeopleCode program on a higher scroll level than one you are checking.
See Also
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
target_row |
The row number indicating the position of the row. |
Example
The following example tests whether a specific row on scroll level one is hidden:
&ROW_CNT = ActiveRowCount(RECORD.LD_SHP_INV_VW); &FOUND = True; If &ROW_CNT = 1 Then &ORDER = FetchValue(LD_SHP_INV_VW.ORDER_NO, 1); If None(&ORDER) Then &FOUND = False; End-If; End-If; If &FOUND Then For &I = 1 To &ROW_CNT If Not IsHidden(RECORD.LD_SHP_INV_VW, &I) Then UpdateValue(ITEM_SELECTED, &I, "N"); End-If; End-For; End-If;
See Also
GenerateScriptContentURL, UnhideRow.

 IsMenuItemAuthorized
IsMenuItemAuthorizedSyntax
IsMenuItemAuthorized(MENUNAME.menuname, BARNAME.barname, ITEMNAME.menuitem_name, PAGE.component_item_name[, action])
Description
The IsMenuItemAuthorized function returns True if the current user is allowed to access the specified menu item.
Note. You don't need to use this function to gray internal link pushbuttons/hyperlinks. This function is generally used for transfers that are part of some PeopleCode processing.
Parameters
|
menuname |
The name of the menu where the page is located, prefixed with the reserved word MENUNAME. |
|
barname |
The name of the menu bar where the page is located, prefixed with the reserved word BARNAME. |
|
menu_itemname |
The name of the menu item where the page is located, prefixed with the reserved word ITEMNAME. |
|
component_item_name |
Specify the component item name of the page to be displayed on top of the component when it displays. The component item name is specified in the component definition. If you specify a page, it must be prefixed with the keyword PAGE. You can also specify a null ("") for this parameter. |
|
action |
String representing the action mode in which to start up the page. If action is omitted, the current action is used. Values are: |
|
Constant |
Description |
|
%Action_Add |
Add |
|
%Action_UpdateDisplay |
Update/Display |
|
%Action_UpdateDisplayAll |
Update/Display All |
|
%Action_Correction |
Correction |
|
%Action_DataEntry |
Data Entry |
|
%Action_Prompt |
Prompt |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if the user is authorized to access the specified page, False otherwise.
See Also
DoModal, DoModalComponent, Transfer, TransferPage.

 IsMessageActive
IsMessageActiveSyntax
IsMessageActive(Message.Message_Name)
Description
Use the IsMessageActive built-in function to determine whether the specified message definition has been set to inactive in PeopleSoft Application Designer.
Note. This function is used only with XmlDoc messages, that is, after you get an XmlDoc message (using GetMessageXmlDoc) use this function to determine if the message is active. Use the IsActive message class property to determine if a rowset-based message definition is active.
This function returns True if the message definition for the XmlDoc message is active, False if it’s been inactivated from PeopleSoft Application Designer. If you have a lot of PeopleCode associated with publishing an XmlDoc message, you might use this function to check if the message is active before you publish it.
Parameters
|
Message_Name |
Specify the name of the message you want to inquire about. The message name must be prefixed with the reserved work Message. This function is used only with XmlDoc message definitions. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if the message is active, False otherwise.
Example
&Active = IsMessageActive(Message.MyMessage); If &Active Then /* code for getting message, populating it and publishing it */ End-if;
See Also

 IsModal
IsModalSyntax
IsModal()
Description
The IsModal function returns True if executed from PeopleCode running in a modal secondary page and False if executed elsewhere. This function is useful in separating secondary page-specific logic from general PeopleCode logic.
Restrictions on Use With a Component Interface
This function is ignored (has no effect) when used by a PeopleCode program that’s been called by a Component Interface.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A Boolean value.
Example
The following example executes logic specific to a secondary page:
If Not IsModal() Or Not (%Page = PAGE.PAY_OL_REV_RUNCTL Or %Page = PAGE.PAY_OL_RE_ASSGN_C Or %Page = PAGE.PAY_OL_RE_ASSGN_S) Then Evaluate COUNTRY When = "USA" When = "CAN" If Not AllOrNone(ADDRESS1, CITY, STATE) Then Warning MsgGet(1000, 5, "Address should consist of at least Street (Line 1), City, State, and Country.") End-If; Break; When-Other; If Not AllOrNone(ADDRESS1, CITY, COUNTRY) Then Warning MsgGet(1000, 6, "Address should consist of at least Street (Line 1), City, and Country.") End-If; End-Evaluate; End-If;
See Also

 IsModalComponent
IsModalComponentSyntax
IsModalComponent()
Description
Use the IsModalComponent function to test whether a modal component is currently executing, enabling you to write PeopleCode that only executes when a component has been called with DoModalComponent.
Restrictions on Use With a Component Interface
This function is ignored (has no effect) when used by a PeopleCode program that’s been called by a Component Interface.
Parameters
None.
Returns
Returns a Boolean value: True if the current program is executing from a modal component, False otherwise.
Example
If IsModalComponent() then /* Logic that executes only if component is executing modally. */ end-if;
See Also

 IsModalPanelGroup
IsModalPanelGroup
Syntax
IsModalPanelGroup()
Description
Use the IsModalPanelGroup function to test whether a modal component is currently executing.
Note. The IsModalPanelGroup function is supported for compatibility with previous releases of PeopleTools. New applications should use the IsModalComponent function instead.
See Also

 IsNumber
IsNumberSyntax
IsNumber(Value)
Description
Use the IsNumber function to determine if Value contains a valid numeric value. Numeric characters include sign indicators and comma and period decimal points.
To determine if a value is a number and if it's in the user's local format, use the IsUserNumber function.
Parameters
|
Value |
Specify a string you want to search to determine if it is a valid number. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if Value contains a valid numeric value, False otherwise.
Example
&Value = Get Field().Value; If IsNumber(&Value) Then /* do numeric processing */ Else /* do non-numeric processing */ End-if;
See Also
IsAlpha, IsAlphaNumeric, IsDigits, IsDate, IsDateTime, IsTime.

 IsOperatorInClass
IsOperatorInClass
Syntax
IsOperatorInClass(operclass1 [, operclass2]. . .)
Description
The IsInOperatorClass takes an arbitrary-length list of strings representing the names of operator classes and determines whether the current operator belongs to any class in a list of classes.
Note. The IsOperatorInClass function is supported for compatibility with previous releases of PeopleTools. New applications should use the IsUserInPermissionList function instead.
See Also

 IsSearchDialog
IsSearchDialogSyntax
IsSearchDialog()
Description
Use the IsSearchDialog function to determine whether a search dialog, add dialog, or data entry dialog box is currently executing. Use it to make processes conditional on whether a search dialog box is running.
Returns
Returns a Boolean value: True if a search dialog box is executing, False otherwise.
Example
If Not (IsSearchDialog()) Then If %Component = COMPONENT.SALARY_GRADE_TBL Then If All(SALARY_MATRIX_CD) Then Gray(RATING_SCALE) End-If; calc_range_spread(); End-If; End-If;
See Also

 IsTime
IsTimeSyntax
IsTime(Value)
Description
Use the IsTime function to determine if Value contains a valid Time.
You can use this function when you want to determine if a value is compatible with the Time function.
Parameters
|
Value |
Specify either a string or number you want to search for to determine if it's a valid Time. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if the string contains a valid Time value, False otherwise.
Example
If IsTime(&Num) Then &Timevalue = Time(&Num); End-if;
See Also
IsAlpha, IsAlphaNumeric, IsDigits, IsDate, IsDateTime, IsNumber, IsTime.

 IsUserInPermissionList
IsUserInPermissionListSyntax
IsUserInPermissionList(PermissionList1 [, PermissionList2]. . .)
Description
Use the IsUserInPermissionList function to take an arbitrary-length list of strings representing the names of Permission Lists and determine whether the current user belongs to any of the Permission Lists.
Parameters
|
PermissionList |
An arbitrary-length list of string, each of which represents a Permission List. |
Returns
Returns a Boolean value: True if the current user has access to one or more of the Permission Lists, False otherwise.
See Also
ExecuteRolePeopleCode, ExecuteRoleQuery, ExecuteRoleWorkflowQuery, IsUserInRole.

 IsUserInRole
IsUserInRoleSyntax
IsUserInRole(rolename1 [, rolename2]. . .)
Description
Use the IsUserInRole function to take an arbitrary-length list of strings representing the names of roles and determine whether the current user belongs to any role in an array of roles.
Parameters
|
rolename |
An arbitrary-length list of strings, each of which represents a role. |
Returns
Returns a Boolean value: True if the current user belongs to one or more of the roles in the user role array, False otherwise.
See Also

 IsUserNumber
IsUserNumberSyntax
IsUserNumber(Value)
Description
Use the IsUserNumber function to determine if Value contains a valid numeric value that uses the locale-specific form of the number for the current user. Numeric characters include sign indicators and comma and period decimal points.
For example, if your regional settings specified periods for the thousands separator, and the number uses commas, this function returns false.
To determine if a value is a number regardless if it's in the user's local format, use the IsNumber function.
Parameters
|
Value |
Specify a string you want to search to determine if it is a valid number in the correct format. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if Value contains a valid numeric value in the correct format, False otherwise.
Example
&Value = Get Field().Value; If IsUserNumber(&Value) Then /* display number */ Else /* do other processing */ End-if;
See Also
IsAlpha, IsAlphaNumeric, IsDigits, IsDate, IsDateTime, IsTime.

 Left
LeftSyntax
Left(source_str, num_chars)
Description
Use the Left function to return a substring containing the leftmost number of characters in source_str. num_chars specifies how many characters to extract. If the string contains Unicode non-BMP characters, each code unit of the surrogate pair is counted as a separate character and care should be taken not to split the surrogate pair.
Parameters
|
source_str |
A String from which to derive the substring. |
|
num_chars |
A Number specifying how many characters to take from the left of source_str. The value of num_chars must be greater than or equal to zero. If num_chars is greater than the length of source_str, Left returns the entire string. If num_chars is omitted, it is assumed to be one. |
Returns
Returns a String value derived from source_str.
Example
The following example sets &SHORT_ZIP to "90210":
&SHORT_ZIP = Left("90210-4455", 5);
See Also

 Len
LenSyntax
Len(str)
Description
Use the Len function to determine the number of characters in a string. If the string contains Unicode non-BMP characters, each code unit of the surrogate pair is counted as a separate character.
Returns
Returns a Number value equal to the number of characters, including spaces, in str.
Example
The following example sets &STRLEN to 10, then to 0:
&STRLEN = Len("PeopleSoft"); &STRLEN = Len("");
See Also
Lenb.

 Lenb
Lenb
Syntax
Lenb(str)
Description
Note. This function has been deprecated and is no longer supported.

 LinearInterp
LinearInterpSyntax
LinearInterp(DataPoints)
Description
Use the LinearInterp function to compute a set of lines through a sequence of at least two points.
Parameters
|
DataPoints |
This parameter takes an array of array of number. The array’s contents are an array of six numbers. The first two of these six numbers are the x and y points to be fit. The last four are the four coefficients to be returned from the function: a, b, c and d. a is the coefficient of the x0 term, b is the coefficient of the x1 term, c is the coefficient of the x2 term, and d is the coefficient of the x3 term. |
Returns
A modified array of array of numbers. The elements in the array correspond to the elements in the array used for DataPoints. The c and d elements contain zeros.
See Also

 Ln
LnSyntax
Ln(i)
Description
Use the Ln function to determine the natural logarithm of a number. Natural logarithms are based on the constant e, which equals 2.71828182845904. The number i must be a positive real number. Ln is the inverse of the Exp function.
Returns
A Number equal to the natural logarithm of i.
Example
The following examples set &I to 2.302585 and &J to 1:
&I = Ln(10); &J = Ln(2.7182818);
See Also

 Local
LocalSyntax
Local data_type &var_name [= expression]
Description
Use the Local statement to explicitly define local variables in PeopleCode.
Variable declarations can appear at the start of the program, intermixed with function declarations. Local variable declarations can also appear in the body of a program, including inside functions.
The scope of local variables declared outside of a function is the PeopleCode program. The scope of local variables declared inside a function is to the end of the function. Also, these function local variables are different variables for each call of the function (even for recursive calls,) in the same manner as parameters.
Local variable declarations intermixed with the body of the program or inside functions can include initialization, that is, the variable can be set to a value at the same time it is declared.
In the absence of an initialization, the system automatically initializes temporary variables. Declared variables always have values appropriate to their declared type. Undeclared local variables are initialized as null strings.
Parameters
|
data_type |
Any PeopleCode data type. |
|
&var_name |
A legal variable name. |
|
expression |
Specify the value of the variable. This parameter is optional. |
Example
local string &LOC_FIRST;
The following example scopes the local variable &Constant as a local variable, as well as initializing it.
Local Number &Constant = 42;
See Also

 LogObjectUse
LogObjectUse
Syntax
LogObjectUse([annotation])
Description
Use the LogObjectUse function to write to the system log a list of all the current PeopleCode objects with the current count, the object class name, and the maximum count of objects of this type.
While this function is mainly used to determine memory usage, the output is also an informative display of the object use in your system at a particular point in time.
Parameters
|
annotations |
Specify a string to become the first line in the log file. This enables you to easily identify output corresponding to your use of this built-in. |
Returns
None.
Example
The following is an example of output that can be generated in the system log.
PeopleCode side - after Java 1902 JavaPeerReference 0 Field 14 0 ContentRefCollection 4 0 PortalCollection 3 83 String 116459 0 PT_NAV:NavEndNode 6 0 PT_NAV:NavFolderNode 35 0 PT_NAV:NavTheme 1 0 PT_NAV:NavNodeCollection 4 0 PortalRegistry 7 0 PT_BRANDING:HeaderLinkBase 1 0 PT_NAV:NavNode 45 0 PT_BRANDING:HeaderLinkHP 1 0 BIDocs 4 0 Interlink 1 0 PT_NAV:NavPortal 1 1 SyncServer 1 0 TabDefinition 1 951 Rowset 220001 0 FolderCollection 4 0 SQL 5 0 Folder 69 1 Response 14 1 Foxtest 3 0 Record 1 23 Array 264 1 Request 15 0 AttributeCollection 40 0 UserHomepage 2 0 Portal 3 0 NodeCollection 3 0 UserTabCollection 1 0 ObjPropRef 3 951 FOXTEST:Test 110001 0 PT_BRANDING:BrandingBase 3 0 ContentRef 13 0 PT_NAV:NavPagelet 1 0 TabDefinitionCollection 1 0 Session 10 0 NetworkNode 3
See Also

 Log10
Log10Syntax
Log10(x)
Description
Use the Log10 function to return the base-10 logarithm of a number x as a number value. The number x must be a positive real number.
Returns
Returns a Number equal to the base-10 logarithm of x.
Example
The following example sets &X to 1 and &Y to 1.39794:
&X = Log10(10); &Y = Log10(25);
See Also

 Lower
LowerSyntax
Lower(string)
Description
Use the Lower function to convert all uppercase characters in a text string to lowercase characters and returns the result as a String value. Lower does not change characters that are not letters or characters do not have case sensitivity.
Returns
A String value equal to string, but in all lowercase format.
Example
The example sets &GOODKD to "k d lang":
&GOODKD = Lower("K D Lang");
See Also

 LTrim
LTrimSyntax
LTrim(string1 [,string2])
Description
Use the LTrim function to return a string formed by deleting from the beginning of string1, all occurrences of each character in string2. If string2 is omitted, " " is assumed; that is, leading blanks are trimmed.
Example
The following removes leading blanks from &NAME:
&TRIMMED = LTrim(&NAME);
The following removes leading punctuation marks from REC.INP:
&TRIMMED = LTrim(REC.INP, ".,;:!?");
See Also

 MarkPrimaryEmailAddress
MarkPrimaryEmailAddressSyntax
MarkPrimaryEmailAddress(Type)
Description
Use the MarkPrimaryEmailAddress function to specify which email address is the primary email address for the current user. You can only have one primary email address per user.
Parameters
|
Type |
Specify the type that you want to change the email address to. This parameter takes a string value. The valid values are: |
|
Value |
Description |
|
BB |
Blackberry email address |
|
BUS |
Business email address |
|
HOME |
Home email address |
|
OTH |
Other email address |
|
WORK |
Work email address |
Returns
None.
See Also
AddEmailAddress, ChangeEmailAddress, DeleteEmailAddress.

 MarkWLItemWorked
MarkWLItemWorkedSyntax
MarkWLItemWorked()
Description
Use the MarkWLItemWorked function to mark the current Worklist entry as worked using this function. This function works only if you’ve invoked a page from the Worklist. This function should be called only in Workflow PeopleCode. You can use the %WLName system variable to check whether the page has been accessed using a Worklist.
Returns
Returns a Boolean value indicating whether it executed successfully. The return value is not optional.
Example
This example, which would be in the WorkFlow event, checks to see whether a page check box MARK_WORKED_SW is selected, and if so, it marks the item in the worklist as complete:
If MARK_WORKED_SW = "Y" Then If MarkWLItemWorked() Then End-If; End-If;
See Also

 Max
MaxSyntax
Max(param_list)
Where param_list has the form
parameter1, parameter2 [, parameter3, . . . parameterN]
Description
Use the Max function to determine the maximum value in the parameter list. The type of every item in the parameter list must be compatible with the first parameter in the list.
For example, if the first parameter is a string and the second parameter is a number with value 123.456, the second parameter is converted to the string "123.456" before the comparison is performed.
If all the values in the parameter list are alpha characters, "Z" is greater than "A" so Max("Z", "A") returns "Z".
Parameters
|
param_list |
Specify a list of items to be compared. All items in the parameter list must be of the same type. If a value isn't defined, the system assumes it's of the same type as the first parameter. |
Returns
The item in the list that has the maximum value.
Example
&RSULT = Max("A", "B", "C", "D", "E");
See Also
Min.

 MessageBox
MessageBoxSyntax
MessageBox(style, title, message_set, message_num, default_txt [, paramlist])
where paramlist is an arbitrary-length list of parameters of undetermined (Any) data type to be substituted in the resulting text string, in the form:
param1 [, param2]. . .
Description
Use the MessageBox function to display a message box window. This function combines dialog-display ability with the text-selection functionality of MsgGet, MsgGetText, or MsgGetExplainText. The style parameter selects the buttons to be included. title determines the title of message.
Note. title isn't available for messages displayed in the PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture. Also, style is ignored if the message has any severity other than Message.
The remaining parameters are used to retrieve and process a text message selected from the Message Catalog.
MessageBox can be used for simple informational display, where the user reads the message, then clicks an OK button to dismiss the message box. Use MessageBox as a way of branching based on user choice, in which case the message box contains two or more buttons (such as OK and Cancel or Yes, No, and Cancel). The value returned by the function tells you which button the user clicked, and your code can branch based on that value.
In the MessageBox dialogs, both the Text and the Explanation, that is, more detailed information stored in the Message Catalog, are included.
If MessageBox displays buttons other than OK, it causes processing to stop while it waits for user response. This makes it a "user think-time" function, restricting its use to certain PeopleCode events.
See MsgGet, MsgGetText, MsgGetExplainText.
Message Retrieval
MessageBox retrieves a message from the Message Catalog and substitutes the values of the parameters into the text message and explanation.
You can access and update the Message Catalog through PeopleTools Utilities, using the Message Catalog page located under the Use menu. You can enter message text in multiple languages. The message_set and message_num parameters specify the message to retrieve from the catalog. If the message is not found in the Message Catalog, the default message provided in default_txt is used. Message sets 1 through 19,999 are reserved for use by PeopleSoft applications. Message sets 20,000 through 32,767 can be used by PeopleSoft users.
The optional paramlist is a comma-separated list of parameters; the number of parameters in the list is arbitrary. The parameters are referenced in the message text using the % character followed by an integer corresponding to the position of the parameter in the paramlist. For example, if the first and second parameters in paramlist were &FIELDNAME and &USERNAME, they would be inserted into the message string as %1 and %2. To include a literal percent sign in the string, use %%; %\ is used to indicate an end-of-string and terminates the string at that point. This is generally used to specify fixed-length strings with trailing blanks.
Message Severity
MessageBox specifies processing for error handling functions based on the Message Severity of the message, which you can set in the Message Catalog. This enables you to change the severity of an error without changing the underlying PeopleCode, by setting the severity level for the message in the Message Catalog. The Message Severity settings and processing options are:
|
Severity |
Processing |
|
Message |
The message is displayed and processing continues. |
|
Warning |
The message is displayed and treated as a warning. |
|
Error |
The message is displayed and treated as an error. |
|
Cancel |
The message is displayed and forces a Cancel. |
In addition, in the PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture the Message Severity dictates how the message displays:
If the message has a severity of Warning, Error or Cancel, the message is displayed in a pop-up dialog box with a single OK button regardless of the value of the style parameter.
If the message has a severity of Message and style is %MsgStyle_OK (0), the message displays in a pop-up dialog box with the single OK button.
If the message has a severity of Message and style is not %MsgStyle_OK (0), the message displays in a separate window.
Restrictions on Use in PeopleCode Events
If MessageBox displays any buttons other than OK, it returns a value based on the end-user response and interrupts processing until the end-user has clicked one of the buttons. This makes it a "user think-time" function, subject to the same restrictions as other think-time functions which means that it cannot be used in any of the following PeopleCode events:
SavePreChange.
Workflow.
RowSelect.
SavePostChange.
Any PeopleCode event that fires as a result of a ScrollSelect (or one of its relatives) function calls, or a Select (or one of its relatives) Rowset class method.
If the style parameter specifies a single button (that is, the OK button), the function can be called in any PeopleCode event.
See Think-Time Functions.
Restrictions on Use With PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture
In the PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture, you can’t change the icon of a message box. You can change the number and type of buttons, and the default button, but the message always displays with the warning icon (a triangle with an exclamation mark in it.)
In addition, you can't change the message box title.
If the message has a severity of Warning and the MessageBox PeopleCode is in a SaveEdit event, the message is displayed in a new window with the OK and Cancel buttons.
Restrictions on Use With PeopleSoft Application Engine
If you call MessageBox from a PeopleCode action in an Application Engine program, the syntax is the same. However, all GUI-related parameters like style and title are ignored. You should use 0 and "".
Note. If you have an existing MessageBox in code called from a page, it should work as is.
The actual message data is routed to PS_MESSAGE_LOG at runtime, and you can view it from the Process Monitor by drilling down to the process details.
Parameters
|
Style |
Either a numerical value or a constant specifying the contents and behavior of the dialog box. This parameter is calculated by cumulatively adding either a value or a constant from each of the following list of categories: |
Note. In PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture style is ignored if the message has any severity other than Message. If the message has a severity of Warning and the MessageBox PeopleCode is in a SaveEdit event, the message is displayed in a new window with the OK and Cancel buttons.
|
Category |
Value |
Constant |
Meaning |
|
Buttons |
0 |
%MsgStyle_OK |
The message box contains one pushbutton: OK. |
|
1 |
%MsgStyle_OKCancel |
The message box contains two pushbuttons: OK and Cancel. |
|
|
2 |
%MsgStyle_AbortRetryIgnore |
The message box contains three pushbuttons: Abort, Retry, and Ignore. |
|
|
3 |
%MsgStyle_YesNoCancel |
The message box contains three pushbuttons: Yes, No, and Cancel. |
|
|
4 |
%MsgStyle_YesNo |
The message box contains two push buttons: Yes and No. |
|
|
5 |
%MsgStyle_RetryCancel |
The message box contains two push buttons: Retry and Cancel. |
|
title |
Title of message box. If a null string is specified, then PeopleTools provides an appropriate value. |
Note. title isn't available for messages displayed in the PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture.
|
message_set |
The message set number of the message to be displayed. When message set and number are provided, it overrides the specified text. A value less than one indicates that the message comes from the provided text and not the Message Catalog. |
|
message_num |
The message number of the message to be displayed. |
|
default_txt |
Default text to be displayed in the message box. |
|
paramlist |
A comma-separated list of parameters; the number of parameters in the list is arbitrary. The parameters are referenced in the message text using the % character followed by an integer corresponding to the position of the parameter in the paramlist. |
Returns
Returns either a Number value or a constant. The return value is zero if there is not enough memory to create the message box. In other cases the following menu values are returned:
|
Value |
Constant |
Meaning |
|
-1 |
%MsgResult_Warning |
Warning was generated. |
|
1 |
%MsgResult_OK |
OK button was selected. |
|
2 |
%MsgResult_Cancel |
Cancel button was selected. |
|
3 |
%MsgResult_Abort |
Abort button was selected. |
|
4 |
%MsgResult_Retry |
Retry button was selected. |
|
5 |
%MsgResult_Ignore |
Ignore button was selected. |
|
6 |
%MsgResult_Yes |
Yes button was selected. |
|
7 |
%MsgResult_No |
No button was selected. |
Note. In PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture, pressing the ESC key has no effect.
Example
Suppose the following string literal is stored in the Message Catalog as the message text:
Expenses of employee %1 during period beginning %2 exceed allowance.
The following is stored in the Explanation:
You don't have the authority to approve this expense. Only a director can approve this.
Here %1 is a placeholder for the employee ID and %2 a placeholder for the expense period date. The following MessageBox call provides bind variables corresponding to these placeholders at the end of its parameter list:
MessageBox(0, "", 30000, 1, "Message not found.", BUS_EXPENSE_PER.EMPLID, BUS_EXPENSE_PER.EXPENSE_PERIOD_DT);
The call would display a message box similar to this, if the message severity was Error or Warning.
Example of message box
Suppose the following is stored in the Message Catalog as the message text:
File not found.
The following is stored in the Explanation:
The file you specified wasn't found. Either select retry, and specify a new file, or cancel.
Suppose this message had a Severity of message, and you used the %MsgStyle_RetryCancel, in the following code:
MessageBox(%MsgStyle_RetryCancel, "", 30000, 2, "Message not found.");
This is how the message displays:

Example message with Retry and Cancel buttons
If the message severity is of type Cancel, the message displayed looks like this:
Critical type error message
See Also
MsgGet, MsgGetText, MsgGetExplainText.

 Min
MinSyntax
Min(param_list)
Where param_list has the form
parameter1, parameter2 [, parameter3, . . . parameterN]
Description
Use the Min function to determine the minimum value in the parameter list. The type of every item in the parameter list must be compatible with the first parameter in the list.
For example, if the first parameter is a string and the second parameter is a number with value 123.456, the second parameter is converted to the string "123.456" before the comparison is performed.
If all the values in the parameter list are alpha characters, "a" is less than "m", so Min("a", "m") returns "a".
Parameters
|
param_list |
Specify a list of items to be compared. All items in the parameter list must be of the same type. If a value isn't defined, the system assumes it's of the same type as the first parameter. |
Returns
The item in the list that has the minimum value.
Example
&RES = Min(&A, Max(&B, &C, &D), "-20");
See Also
Max.

 Minute
MinuteSyntax
Minute(timevalue)
Description
Use the Minute function to extract the minute component of a Time value.
Returns
Returns the minute part of timevalue as a Number data type.
Example
If &TIMEOUT contains "16:48:01" then the example sets &TIMEOUT_MINUTES to 48:
&TIMEOUT_MINUTES = Minute(&TIMEOUT);
See Also

 Mod
ModSyntax
Mod(x, divisor)
Description
The Mod function is the modulus math function, which divides one number (x) by another (divisor) and returns the remainder.
Returns
Returns a Number equal to the remainder of the division of the number x by divisor.
Example
The example sets &NUM1 to one and &NUM2 to zero:
&NUM1 = Mod(10,3); &NUM2 = Mod(10,2);
See Also

 Month
MonthSyntax
Month(datevalue)
Description
Use the Month function to return the month of the year as an integer from 1 to 12 for the specified datevalue. The Month function accepts a Date or DateTime value as a parameter.
Parameters
|
datevalue |
A Date or DateTime value on the basis of which to determine the month. |
Returns
Returns a Number value from 1 to 12 specifying the month of the year.
Example
This example sets &HIRE_MONTH to 3:
&HIREDATE = DateTime6(1997, 3, 15, 10, 9, 20); &HIRE_MONTH = Month(&HIRE_DATE);
See Also
Date, Date3, DateValue, Day, Days360, Days365, Weekday, Year.

 MSFGetNextNumber
MSFGetNextNumberSyntax
MSFGetNextNumber(Key1, Key2, Key3)
Description
Use the MSFGetNextNumber function to return the next number from the mobile system that is specified by the key fields that are passed in.
You might use this function to increment an employee ID field by one when you are adding a new employee.
Note. This feature is only applicable when running on a PeopleSoft Mobile Synchronization Client. This functionality is not available in all product lines.
Parameters
|
Key1 |
Specify the first key field value used to identify the mobile object that contains the numeric field values. |
|
Key2 |
Specify the second key field value used to identify the mobile object that contains the numeric field values. |
|
Key3 |
Specify the third key field value used to identify the mobile object that contains the numeric field values. |
Returns
A number.
Example
&nextNumber = MSFGetNextNumber(&ds1, &ds2, &ds3);
See Also
Understanding PeopleSoft Mobile Agent

 MsgGet
MsgGetSyntax
MsgGet(message_set, message_num, default_msg_txt [, paramlist])
where paramlist is an arbitrary-length list of parameters of undetermined (Any) data type to be substituted in the resulting text string, in the form:
param1 [, param2]. . .
Description
Use the MsgGet function to retrieve a message from the PeopleCode Message Catalog and substitutes in the values of the parameters into the text message.
You can access and update the Message Catalog through the PeopleTools Utilities, using the Message Catalog page located under the Use menu. You can enter message text in multiple languages. The Message Catalog also enables you to enter more detailed "Explain" text about the message. The message_set and message_num parameters specify the message to retrieve from the catalog. If the message is not found in the Message Catalog, the default message provided in default_msg_txt is used. Message sets 1 through 19,999 are reserved for use by PeopleSoft applications. Message sets 20,000 through 32,767 can be used by PeopleSoft users.
The optional paramlist is a comma-separated list of parameters; the number of parameters in the list is arbitrary. The parameters are referenced in the message text using the % character followed by an integer corresponding to the position of the parameter in the paramlist. For example, if the first and second parameters in paramlist were &FIELDNAME and &USERNAME, they would be inserted into the message string as %1 and %2. To include a literal percent sign in the string, use %%; %\ is used to indicate an end-of-string and terminates the string at that point. This is generally used to specify fixed-length strings with trailing blanks.
MsgGet suffixes the message with "[Message Set# and Message Error#]", so it can be processed by a user not conversant in the translated language.
Example
&MsgText = MsgGet(30000, 2, "Message not found");
See Also
MsgGetText, MsgGetExplainText, MessageBox.

 MsgGetExplainText
MsgGetExplainTextSyntax
MsgGetExplainText(message_set, message_num, default_msg_txt [, paramlist])
where paramlist is an arbitrary-length list of parameters of undetermined (Any) data type to be substituted in the resulting text string, in the form:
param1 [, param2]. . .
Description
Use the MsgGetExplainText function to retrieve the Explain text of a message from the PeopleCode Message Catalog and substitutes the values of the parameters in paramlist into the explain text. It returns the resulting message explain text as a String data type.
You can access and update the Message Catalog through the PeopleTools Utilities, using the Message Catalog. You can enter messages in multiple languages.
Message sets 1 through 19,999 are reserved for use by PeopleSoft applications. Message sets 20,000 through 32,767 can be used by PeopleSoft users.
Unlike the MsgGet function, MsgGetExplainText returns the message without a message set and message number appended to the message.
Parameters
|
message_set |
Specify the message set to be retrieved from the catalog. This parameter takes a number value. |
|
message_num |
Specify the message number to be retrieved from the catalog. This parameter takes a number value. |
|
default_msg_txt |
Specify the text to be displayed if the message isn't found. This parameter takes a string value. |
|
paramlist |
Specify values to be substituted into the message explain text. The parameters listed in the optional paramlist are referenced in the message explain text using the % character followed by an integer referencing the position of the parameter in the function call. For example, if the first and second parameters in paramlist were &FIELDNAME and &USERNAME, they would be inserted into the message string as %1 and %2.
Note. This substitution only takes place in message explain text when the MsgGetExplainText function is used. If you use a message box, the parameter substitution will not occur in the explain text. To include a literal percent sign in the string, use %%; %\ is used to indicate an end-of-string and terminates the string at that point. This is generally used to specify fixed-length strings with trailing blanks. |
Example
Suppose the following explain text is stored in the Message Catalog:
A reference was made to a record.field (%1.%2) that is not defined within Application Designer. Check for typographical errors in the specification of the record.field or use Application Designer to add the new field or record.
Here %1 is a placeholder for the record name and %2 a placeholder for the field name. If the record.field in error was MyRecord.Field5, the above would resolve as follows:
A reference was made to a record.field (MyRecord.Field5) that is not defined within Application Designer. Check for typographical errors in the specification of the record.field or use Application Designer to add the new field or record.
See Also
MsgGetText, MsgGet, MessageBox.

 MsgGetText
MsgGetTextSyntax
MsgGetText(message_set, message_num, default_msg_txt [, paramlist])
where paramlist is an arbitrary-length list of parameters of undetermined (Any) data type to be substituted in the resulting text string, in the form:
param1 [, param2]. . .
Description
Use the MsgGetText function to retrieve a message from the PeopleCode Message Catalog and substitutes the values of the parameters in paramlist into the text message. It returns the resulting message text as a String data type.
You can access and update the Message Catalog through the PeopleTools Utilities window, using the Message Catalog page located under the Use menu. You can enter message text in multiple languages. The message_set and message_num parameters specify the message to retrieve from the catalog. If the message is not found in the Message Catalog, the default message provided in default_msg_txt is used. Message sets 1 through 19,999 are reserved for use by PeopleSoft applications. Message sets 20,000 through 32,767 can be used by PeopleSoft users.
The parameters listed in the optional paramlist are referenced in the message text using the % character followed by an integer referencing the position of the parameter in the function call. For example, if the first and second parameters in paramlist were &FIELDNAME and &USERNAME, they would be inserted into the message string as %1 and %2. To include a literal percent sign in the string, use %%; %\ is used to indicate an end-of-string and terminates the string at that point. This is generally used to specify fixed-length strings with trailing blanks.
Unlike the MsgGet function, MsgGetText returns the message without a message set and message number appended to the message.
Example
&MsgText = MsgGetText(30000, 2, "Message not found");
See Also
MsgGet, MsgGetExplainText, MessageBox.

 NextEffDt
NextEffDtSyntax
NextEffDt(field)
Description
Use the NextEffDt function to return the value of the specified field from the record with the next effective date (and effective sequence number if specified). The return value is an Any data type. This function is valid only for effective-dated records.
If the next record doesn't exist, the statement is skipped. If the NextEffDt function isn't a top-level statement, that is, if it's contained within a compound statement or a loop, the statement is skipped and execution restarts with the next top-level statement.
In the following example, execution skips to the top If statement:
If ACTION <> "REH" Then /* skip to here if NextEffDt fails to find next record */ If STD_HOURS <> NextEffDt(STD_HOURS) And Day(EFFDT) <> 1 Then Error MsgGet(30000, 8, "Meldung nicht vorhanden - WAZ bzw. Beschäftigungsgradänderungen sind nur zum ersten eines Monats zulässig.") End-If; End-If; /* if NextEffDt fails, run to here directly */
See Also
NextRelEffDt, PriorRelEffDt, PriorEffDt.

 NextRelEffDt
NextRelEffDtSyntax
NextRelEffDt(search_field, fetch_field)
where fieldlist is an arbitrary-length list of fields in the form:
field1 [,field2]. . .
Description
Use the NextRelEffDt function to locate the next occurrence of the search_field with the next effective date (and effective sequence number if the record contains an effective sequence number). It then returns the value of the specified fetch_field corresponding to the search_field. The return value is an Any data type. Typically, this function is used to retrieve values for related display fields.
This function is valid only for effective-dated records.
If a next record doesn't exist, the statement is skipped. If the NextRelEffDt function isn't a top-level statement, that is, if it's contained within a compound statement or a loop, the statement is skipped and execution restarts with the next top-level statement.
See Also
GetRelField, NextEffDt, PriorRelEffDt, PriorEffDt.

 NodeDelete
NodeDeleteSyntax
NodeDelete(nodeName)
Description
Use the NodeDelete function to delete the specified node and all subordinate objects (transactions, node properties, certificates, and so on.)
Warning! Once this function has completed, you cannot recover the node.
Event Considerations
PeopleSoft recommends only using this function in the SavePostChange event. In addition, you should put a warning in the SaveEdit event, so the user has a chance to change their mind about deleting the node.
If you use a pushbutton on a page to delete a node, PeopleSoft recommends the following code in the FieldChange event:
If %Page = Page.YourDeletePage Then /* changes the record in the buffer so that the DoSaveNow fires */ PSMSGNODEDEFN.DESCR = PSMSGNODEDEFN.DESCR | " "; DoSaveNow(); ClearKeyList(); /* Transfer to another component or display information message; */ End-If;
Parameters
|
nodeName |
Specify the name of the node you want to delete, as a string. All node names are uppercase. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True, the function completed successfully deleted, False otherwise.
Example
&Rslt = NodeDelete("QEM_TEST_NODE"); If Not &Rslt Then /* Do error processing */ End-if;
See Also
Configuring Nodes and Transactions

 NodeRename
NodeRenameSyntax
NodeRename(oldNodeName, newNodeName)
Description
Use the NodeRename function to rename a node. All node names are uppercase.
Event Considerations
PeopleSoft recommends using this function only in the SavePreChange event. This gives the user a chance to edit any other page fields before executing, which may be important because this function affects several tables.
Parameters
|
oldNodeName |
Specify the name of the node that you want to change, as a string. |
|
newNodeName |
Specify the new name for the node, as a string. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True, the function completed successfully deleted, False otherwise.
Example
&Rslt = NodeRename("QEM_TEST_NODE", "QE_TEST_NODE"); If Not &Rslt Then /* Do error processing */ End-if;
See Also
Configuring Nodes and Transactions

 NodeSaveAs
NodeSaveAsSyntax
NodeSaveAs(oldNodeName, newNodeName)
Description
Use the NodeSaveAs function to create a copy of the node specified by oldNodeName, and save it to the database as newNodeName. All node names are uppercase.
Event Considerations
PeopleSoft recommends using this function only in the SavePreChange event. This gives the user a chance to edit any other page fields before executing, which may be important because this function affects several tables.
Parameters
|
oldNodeName |
Specify the name of the node that you want to copy, as a string. |
|
newNodeName |
Specify the name for the new node, as a string. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True, the function completed successfully deleted, False otherwise.
Example
&Rslt = NodeSaveAs("PRODUCTION_NODE", "MY_TEST_NODE"); If Not &Rslt Then /* Do error processing */ End-if;
See Also
Configuring Nodes and Transactions

 NodeTranDelete
NodeTranDeleteSyntax
NodeTranDelete(MsgNodeName, EffDt, TrxType, RqstMsgName, RqstMsgVer);
Description
Use the NodeTranDelete function to delete a node transaction.
Warning! If you delete a node transaction, any transaction modifier using that transaction is also deleted.
Parameters
|
MsgNodeName |
Specify the message node name as a string. |
|
EffDt |
Specify the effective date as a string. |
|
TrxType |
Specify the transaction type as a string. |
|
RqstMsgName |
Specify the request message name as a string. |
|
RqstMsgVer |
Specify the request message version as a string. |
Returns
A Boolean value, True if the function completed successfully, False otherwise.
Example
&ret = NodeTranDelete("QE_LOCAL", "1900-01-01", "IA", "ROLESYNCH_MSG", "VERSION_1");
See Also

 None
NoneSyntax
None(fieldlist)
where fieldlist is an arbitrary-length list of fields in the form:
[recordname.]fieldname1 [, [recordname.]fieldname2] ...
Description
The None function takes an arbitrary number of field names as parameters and tests for values. None returns True if none of the specified fields contain a value. It returns False if any one of the fields contains a value.
A blank character field, or a zero (0) numeric value in a required numeric field is considered a null value.
Related Functions
|
All |
Checks to see if a field contains a value, or if all the fields in a list of fields contain values. If any of the fields is Null, then All returns False. |
|
AllOrNone |
Checks if either all the field parameters have values, or none of them have values. Use this in cases where if an end-user fills in one field, she must all fill in the other related values. |
|
OnlyOne |
Checks if exactly one field in the set has a value. Use this when the end-user must fill in only one of a set of mutually exclusive fields. |
|
OnlyOneOrNone |
Checks if no more than one field in the set has a value. Use this in cases when a set of fields is both optional and mutually exclusive; that is, if the end-user puts can put a value into one field in a set of fields, or leave them all empty. |
Example
The following example uses None to check whether REFERRAL_SOURCE has a value:
If None(REFERRAL_SOURCE) or REFERRAL_SOURCE = "EE" Then Gray(EMP_REFERRAL_ID); End-if;
The following example uses None with a variable:
&ONETIME = FetchValue(POSN_INCUMB_WS.EMPLID, 1); If None(&ONETIME) Then /* do processing */ End-if;
See Also
All, AllOrNone, OnlyOne, OnlyOneOrNone.

 NotifyQ
NotifyQSyntax
NotifyQ(logical queue ID, task type)
Description
Use the NotifyQ function to notify the queue server of an incoming task. NotifyQ should always follow the use of the EnQueue function. EnQueue inserts the task into the PeopleSoft database, and NotifyQ notifies the queue server about a task's existence and location.
When you process a batch of tasks to be enqueued, PeopleSoft recommends calling NotifyQ just once (after the last task is processed). NotifyQ forces the queue server to reorder its internal lists and save its state to the database, and therefore affects performance.
NotifyQ is not required for chat or voice tasks, and should not be used for these tasks.
Note. If tasks of different types or tasks that are assigned to different logical queues are enqueued, at least one NotifyQ is required for each logical queue and for each task type. This ensures that the system is notified of tasks waiting to be assigned.
Parameters
|
logical queue ID |
Specifies the logical queue in which the task should be queued. It is a string value. The logical queue ID is a case-sensitive value. The case used in the NotifyQ function must exactly match the case used when creating the logical queue ID on the Queues page. |
|
task type |
Specifies the type of task to be inserted. It is a string value. The valid values are:
|
Returns
Returns 0 if the function was successful.
If unsuccessful, it returns a message number. The message set ID for MultiChannel Framework is 162.
For example, 1302 is returned when an invalid task type or no value is provided.
Example
&strtasknum = EnQueue(&queueID, "email", &MyCompURL, &langcode, &subject, "QEDMO", 15, 60, &cost, &priority, &minskill); &nret = NotifyQ(&queueID, "email"); If &nret = 0 Then MessageBox(0, "", 162, 1547, "Queue Successfully notified."); End-If

 NumberToDisplayString
NumberToDisplayStringSyntax
NumberToDisplayString(Format, Number [, Width] [, Precision])
Description
Use the NumberToDisplayString function to format Number according to the pattern specified in Format. The decimal and thousand's separator are formatted with what is with the current user's personalizations.
Specify the Width and Precision parameters when you want to dynamically specify the width or precision. Both width and precision can be set based on Format. For example, the following statically specifies the width to be 6, and the precision to be 2:
&MyValue = NumberToDisplayString("%6.2", &Num);
The following example show the width taken dynamically from the &Width variable:
&MyValue = NumberToDisplayString("%*.2", &Num, &Width);
The following example shows how both the width and the precision values are taken dynamically from the &Width and &Precision variables, respectively.
&MyValue = NumberToDisplayString("%*.*", &Num, &Width, &Precision);
Parameters
|
Format |
Specify the pattern for how Number is supposed to be formatted. See Using the Format parameter, below. |
|
Number |
Specify the number to be formatted. |
|
Width |
Specify the width of the string to be formatted. |
|
Precision |
Specify the precision of the string to be formatted. |
Using the Format Parameter
The Format parameter has the following format:
%[flags][width][.precision][R | T] [type]
Flags have the following format:
|
Flag |
Description |
|
- |
Left align the number. |
|
$ |
Fill out field on left hand side with international currency symbol. |
|
# |
Force the number to have a decimal point. |
|
blank |
Pad left hand side with blanks only indicating a negative number with a '-' sign. |
|
+ |
Prefix output with plus sign. |
|
M |
Append " (cr)" on right for negative numbers and " (dr)" for positive numbers. |
|
m |
Opposite of M: " (dr)" for negative and " (cr)" for positive. |
|
A |
Bracket negative numbers with "[" and "]". |
|
a |
Bracket negative numbers with "(" and ")". |
|
q |
Display zeros as blanks. |
|
Q |
Display zeros as "None". |
|
0 |
Pad left hand side with zeroes. This must be the last flag before any other pattern indicators. |
Width must be specified as a non-negative integer. Specifying an asterisks ("*") allows for dynamic field width specification. The maximum width is 50.
Precision specifies how many digits follow the ".". It must be specified as a non-negative integer. Specifying an asterisks ("*") allows for a dynamic precision specification. The maximum precision is 50.
R specifies rounding in conversion from the internal PeopleCode representation, that is, specifying 12.345 with precision of 2 (%n.2Rt) prints 12.35. In the absence of the R control rounding is the default.
T specifies truncation in conversion from the internal PeopleCode representation, that is, specifying 2.345 with precision of 2 (%n.2Tt) prints 12.34.
Type has the following format:
|
Type |
Description |
|
t |
Type has format like printf %f. For example, the form dddd.dddd. This is the default value. |
|
v |
1000ths separator delimited output. For example, if the separator is a comma, the format is 1,000,000.02. |
|
w |
Scientific format like printf %e. For example, the form d.ddddeddd where "e" indicates exponent. d specifies 1 decimal digit and dddd specifies an arbitrary number. |
|
W |
Scientific format (like above, for "w") except "e" is "E". |
|
z |
Scientific Engineering format like printf %e where the exponent is always a multiple of 3 and the mantissa is between 1 and a 1000. |
|
Z |
Scientific Engineering format (like above, for "z") except "e" is "E". |
Returns
A string value.
Example
In the following example, &Str1 would be "0001234,56".
&Num = 1234.56; &Str1 = NumberToDisplayString("%#010.2t", &Num);
In the following example, &Str2 would be "$$$1234.56".
&Num = 1234.56; &Str2 = NumberToDisplayString("%$10.2", &Num);
In the following example, &Str3 would be " 1,234.56".
&Num = 1234.56; &Str3 = NumberToDisplayString("%10.2v", &Num);
In the following example, &Str4 would be "1.23456e+003".
&Num = 1234.56; &Str4 = NumberToDisplayString("%w", &Num);
See Also

 NumberToString
NumberToStringSyntax
NumberToString(Format, Number [, Width] [, Precision])
Description
Use the NumberToString function to format Number according to the pattern specified in Format.
Specify the Width and Precision parameters when you want to dynamically specify the width or precision. Both width and precision can be set based on Format. For example, the following statically specifies the width to be 6, and the precision to be 2:
&MyValue = NumberToString("%6.2", &Num);
The following example show the width taken dynamically from the &Width variable:
&MyValue = NumberToString("%*.2", &Num, &Width);
The following example shows how both the width and the precision values are taken dynamically from the &Width and &Precision variables, respectively.
&MyValue = NumberToString("%*.*", &Num, &Width, &Precision);
Parameters
|
Format |
Specify the pattern for of how Number is supposed to be formatted. |
|
Number |
Specify the Number to be formatted. |
|
Width |
Specify the width of the string to be formatted. |
|
Precision |
Specify the precision of the string to be formatted. |
Using the Format Parameter
The Format parameter has the following format:
%[flags][width][.precision][R | T] [type]
Flags have the following format:
|
Flag |
Description |
|
- |
Left align the number. |
|
$ |
Fill out field on left hand side with international currency symbol. |
|
# |
Force the number to have a decimal point. |
|
blank |
Pad left hand side with blanks only indicating a negative number with a '-' sign. |
|
+ |
Prefix output with plus sign. |
|
M |
Append " (cr)" on right for negative numbers and " (dr)" for positive numbers. |
|
m |
Opposite of M: " (dr)" for negative and " (cr)" for positive. |
|
A |
Bracket negative numbers with "[" and "]". |
|
a |
Bracket negative numbers with "(" and ")". |
|
q |
Display zeros as blanks. |
|
Q |
Display zeros as "None". |
|
0 |
Pad left hand side with zeroes. This must be the last flag before any other pattern indicators. |
Width must be specified as a non-negative integer. Specifying an asterisks ("*") allows for dynamic field width specification. The maximum width is 50.
Precision specifies how many digits follow the ".". It must be specified as a non-negative integer. Specifying an asterisks ("*") allows for a dynamic precision specification. The maximum precision is 50.
R specifies rounding in conversion from the internal PeopleCode representation, that is, specifying 12.345 with precision of 2 (%n.2Rt) prints 12.35. In the absence of the R control rounding is the default.
T specifies truncation in conversion from the internal PeopleCode representation, that is, specifying 2.345 with precision of 2 (%n.2Tt) prints 12.34.
Type has the following format:
|
Type |
Description |
|
t |
Type has format like printf %f. For example, the form dddd.dddd. This is the default value. |
|
v |
1000ths separator delimited output. For example, if the separator is a comma, the format is 1,000,000.02. |
|
w |
Scientific format like printf %e. For example, the form d.ddddeddd where "e" indicates exponent. d specifies 1 decimal digit and dddd specifies an arbitrary number. |
|
W |
Scientific format (like above, for "w") except "e" is "E". |
|
z |
Scientific Engineering format like printf %e where the exponent is always a multiple of 3 and the mantissa is between 1 and a 1000. |
|
Z |
Scientific Engineering format (like above, for "z") except "e" is "E". |
Returns
A string value.
Example
In the following example, &Str1 would be "0001234.56".
&Num = 1234.56; &Str1 = NumberToString("%#010.2t", &Num);
In the following example, &Str2 would be "$$$1234.56".
&Num = 1234.56; &Str2 = NumberToString("%$10.2", &Num);
In the following example, &Str3 would be " 1,234.56".
&Num = 1234.56; &Str3 = NumberToString("%10.2v", &Num);
In the following example, &Str4 would be "1.23456e+003".
&Num = 1234.56; &Str4 = NumberToString("%w", &Num);
See Also
NumberToDisplayString, String, Value.

 ObjectDoMethod
ObjectDoMethodSyntax
ObjectDoMethod(obj_this, str_method_name [, paramlist])
Where paramlist is a list of parameters of arbitrary length:
param1 [, param2]. . .
Description
Use the ObjectDoMethod function to invoke the method specified by str_method_name for the object object_this, passing in any required parameters using paramlist.
You can use ObjectDoMethod with Component Interfaces, Application Classes, OLE Automation objects, and so on.
This method can be useful if you know the number of parameters you need to pass for a method. If you don't know how many parameters you may need to pass when you write your PeopleCode, use the ObjectDoMethodArray function.
Parameters
|
obj_this |
Specify an already instantiated object. This variable must have been instantiated either with CreateObject, or another function or method that creates objects. |
|
str_method_name |
A string containing the name of an exposed method of obj_this. |
|
paramlist |
The parameter list to pass to the str_method_name method. |
Returns
None.
Example
This simple example instantiates an Excel worksheet object, makes it visible, names it, saves it, and displays its name.
&WORKAPP = CreateObject("Excel.Application"); &WORKBOOKS = ObjectGetProperty(&WORKAPP, "Workbooks"); ObjectDoMethod(&WORKBOOKS, "Add", "C:\TEMP\INVOICE.XLT"); /* This associates the INVOICE template w/the workbook */ ObjectDoMethod(&WORKAPP, "Save", "C:\TEMP\TEST1.XLS"); ObjectSetProperty(&WORKAPP, "Visible", True);
This simple example invokes a user-defined method associated with the current component interface object:
ObjectDoMethod(%CompIntfcName, &inMethodName);
See Also
CreateObject, ObjectGetProperty, ObjectSetProperty, CreateObjectArray, ObjectDoMethodArray.

 ObjectDoMethodArray
ObjectDoMethodArraySyntax
ObjectDoMethodArray(Object_Name, Method_Name, Array_of_Args)
Description
Use the ObjectDoMethodArray function to invoke the method specified by method_name for the object object_name, passing in any required parameters using the array.
Use this function when you're not certain, at the time you're writing your PeopleCode program, how many parameters a method is going to require. If you know the number of parameters, use the ObjectDoMethod function instead.
The array of parameters is an array of Any. It can only be one-dimensional. You cannot pass in field references, that is, you can't pass in references of the form RECORD.FIELDNAME.
If you don't want to supply any parameters, you can use an empty array, or a reference to a Null array.
Parameters
|
Object_Name |
Specify an already instantiated object on which the method is to be evaluated. |
|
Method_Name |
Specify the name of an exposed method for the object. |
|
Array_Of_Args |
Specify an Array of Any containing the parameters for the method. |
Returns
Depends on the specified object and method if a result is returned or not.
Example
&MyRslt = ObjectDoMethodArray(&MyObject, "My-Method", &MyArray);
See Also
CreateObject, ObjectGetProperty, ObjectSetProperty, CreateObjectArray, ObjectDoMethod.

 ObjectGetProperty
ObjectGetPropertySyntax
ObjectGetProperty(obj_this, str_property_name [, index_param_list])
Description
Use the ObjectGetProperty function to return the value of a property str_property_name of the object obj_this.
Note. The object must have already been instantiated, either using CreateObject or another function or method that returns an object. Default" OLE Automation object properties are not supported. You must specify the object property that you want to retrieve explicitly.
Parameters
|
obj_this |
Specify an already instantiated object. This variable must have been instantiated either with CreateObject or another function or method that creates objects. |
|
str_property_name |
A string containing the name of an exposed property of obj_this. |
|
index_param_list |
A comma-separated list for accessing an OLE automation object indexed property. (These parameters are only used with OLE/COM objects.) |
Returns
Returns an Any value equal to the value of the str_property_name property of the obj_this object.
Example
This simple example instantiates an Excel worksheet object, makes it visible, names it, saves it, and displays its name.
&WORKAPP = CreateObject("Excel.Application"); &WORKBOOKS = ObjectGetProperty(&WORKAPP, "Workbooks"); ObjectDoMethod(&WORKBOOKS, "Add", "C:\TEMP\INVOICE.XLT"); /* This associates the INVOICE template w/the workbook */ ObjectDoMethod(&WORKAPP, "Save", "C:\TEMP\TEST1.XLS"); ObjectSetProperty(&WORKAPP, "Visible", True);
Excel Worksheets had an index property called Range that has the following signature:
Property Range (Cell1 [, Cell2]) as Range
In the following example, the range is A1:
&CELL = ObjectGetProperty(&SHEET, "Range", "A1");
See Also
CreateObject, ObjectDoMethod, ObjectSetProperty, CreateObjectArray, ObjectDoMethodArray.

 ObjectSetProperty
ObjectSetPropertySyntax
ObjectSetProperty(obj_this, str_property_name, val [, index_param_list])
Description
Use the ObjectSetProperty function to set the value of a property str_property_name of the object obj_this to val.
The object must have already been instantiated, either using CreateObject or another function or method that returns an object.
Note. Default OLE Automation object properties are not supported. You must specify the object property that you want to set explicitly.
Parameters
|
obj_this |
Specify an already instantiated object. This variable must have been instantiated either with CreateObject or another function or method that creates objects. |
|
str_property_name |
A string containing the name of an exposed property of obj_this. |
|
val |
str_property_name is set to this value. |
|
index_param_list |
A comma-separated list of parameters for accessing an OLE automation object indexed property. (This is only used with COM/OLE objects.) |
Returns
None.
Example
This simple example instantiates an Excel worksheet object, makes it visible, names it, saves it, and displays its name.
&WORKAPP = CreateObject("Excel.Application"); &WORKBOOKS = ObjectGetProperty(&WORKAPP, "Workbooks"); ObjectDoMethod(&WORKBOOKS, "Add", "C:\TEMP\INVOICE.XLT"); /* This associates the INVOICE template w/the workbook */ ObjectDoMethod(&WORKAPP, "Save", "C:\TEMP\TEST1.XLS"); ObjectSetProperty(&WORKAPP, "Visible", True);
See Also
CreateObject, ObjectDoMethod, ObjectGetProperty, CreateObjectArray, ObjectDoMethodArray.

 OnlyOne
OnlyOneSyntax
OnlyOne(fieldlist)
where fieldlist is an arbitrary-length list of fields in the form:
[recordname.]fieldname1 [, [recordname.]fieldname2] ...
Description
Use the OnlyOne function to check a list of fields and return True if one and only one of the fields has a value. If all of the fields are empty, or if more than one of the fields has a value, OnlyOne returns False. This function is used to validate that only one of a set of mutually exclusive fields has been given a value.
A blank character field, or a zero numeric value in a required numeric field is considered a Null value.
Related Functions
|
All |
Checks to see if a field contains a value, or if all the fields in a list of fields contain values. If any of the fields is Null, then All returns False. |
|
None |
Checks that a field or list of fields have no value. None is the opposite of All. |
|
AllOrNone |
Checks if either all the field parameters have values, or none of them have values. Use this in cases where if an end-user fills in one field, she must all fill in the other related values. |
|
OnlyOneOrNone |
Checks if no more than one field in the set has a value. Use this in cases when a set of fields is both optional and mutually exclusive; that is, if the end-user puts can put a value into one field in a set of fields, or leave them all empty. |
Example
You typically use OnlyOne as follows:
If OnlyOne(param_one, param_two) Then value_a = "y"; End-if;
See Also
All, AllOrNone, None, OnlyOneOrNone.

 OnlyOneOrNone
OnlyOneOrNoneSyntax
OnlyOneOrNone(fieldlist)
where fieldlist is an arbitrary-length list of fields in the form:
[recordname.]fieldname1 [, [recordname.]fieldname2] ...
Description
Use the OnlyOneOrNone function to check a list of fields and return True if either of these conditions is true:
Only one of the fields has a value.
None of the fields has a value.
This function is useful when you have a set of mutually exclusive fields in a page and the entire set of fields is optional. The end-user can leave all the fields blank or enter a value in one of the fields only.
A blank character field, or a zero numeric value in a required numeric field is considered a null value.
Related Functions
|
All |
Checks to see if a field contains a value, or if all the fields in a list of fields contain values. If any of the fields is Null, then All returns False. |
|
None |
Checks that a field or list of fields have no value. None is the opposite of All. |
|
AllOrNone |
Checks if either all the field parameters have values, or none of them have values. Use this in cases where if an end-user fills in one field, she must fill in all the other related values. |
|
OnlyOne |
Checks if exactly one field in the set has a value. Use this when the end-user must fill in only one of a set of mutually exclusive fields. |
Example
You typically use OnlyOneOrNone as follows:
If OnlyOneOrNone(param_one, param_two) Then value_a = "y"; End-if;
See Also
All, AllOrNone, None, OnlyOne.

 PanelGroupChanged
PanelGroupChanged
Syntax
PanelGroupChanged()
Description
Use the PanelGroupChanged function to determine whether a component has changed since the last save, whether by the user or by PeopleCode.
Note. The PanelGroupChanged function is supported for compatibility with previous releases of PeopleTools. New applications should use the ComponentChanged function instead.
See Also

 PingNode
PingNodeSyntax
PingNode(MsgNodeName)
Description
Use the PingNode function to ping the specified node. It returns an XmlDoc object that you must go through to find the status of the node.
Parameters
|
MsgNodeName |
Specify the name of the message node you want to ping, as a string. |
Returns
An XmlDoc object. The node in the XmlDoc object with the name of status contains information about the node you pinged.
Example
Local XmlDoc &ErrorInfo; &ErrorInfo = PingNode("TESTNODENAME"); &Root = &ErrorInfo.DocumentElement; &MsgNodeArray = &Root.GetElementsByTagName("msgnode"); For &M = 1 To &MsgNodeArray.Len &MsgNode = &MsgNodeArray [&M]; &MsgText = &MsgNode.FindNode("status").NodeValue; If &MsgText <> "Success (117,73)" Then Error ("Web Server not available for web service"); End-If; End-For;
See Also
Defining Message Channels and Messages

 PriorEffDt
PriorEffDtSyntax
PriorEffDt(field)
Description
Use the PriorEffDt function to return the value of the specified field from the record with the prior effective date. This function is valid only for effective-dated records.
If the record contains an effective sequence number field, the value of this field is compared along with the effective-date field when the prior effective date/effective record sequence is determined. Therefore, if there is an effective-sequence number, it's possible that the effective-date field will be the same as the current record, but the sequence number would be earlier.
If a prior record does not exist, the statement is skipped. If the PriorEffDt function is not a top-level statement, that is, if it's contained with a compound statement or a loop, the statement is skipped and execution begins with the next top-level statement.
In the following example, execution skips to the top If statement:
If ACTION <> "REH" Then /* skip to here if PriorEffdt fails to find prior record */ If STD_HOURS <> PriorEffdt(STD_HOURS) And Day(EFFDT) <> 1 Then Error MsgGet(30000, 8, "Meldung nicht vorhanden - WAZ bzw. Beschäftigungsgradänderungen sind nur zum ersten eines Monats zulässig.") End-If; End-If; /* if PriorEffdt fails, run to here directly */
Example
If CURRENCY_CD = PriorEffdt(CURRENCY_CD) Then Evaluate ACTION When = "PAY" If ANNUAL_RT = PriorEffdt(ANNUAL_RT) Then Warning MsgGet(1000, 27, "Pay Rate Change action is chosen and Pay Rate has not been changed."); End-if; Break; When = "DEM" If ANNUAL_RT >= PriorEffdt(ANNUAL_RT) Then Warning MsgGet(1000, 29, "Demotion Action is chosen and Pay Rate has not been decreased."); end-if; When-other End-evaluate; WinMessage("This message appears after executing either of the BREAK statements or after all WHEN statements are false"); End-if;
See Also
NextEffDt, NextRelEffDt, PriorRelEffDt.

 PriorRelEffDt
PriorRelEffDtSyntax
PriorRelEffDt(search_field, fetch_field)
Description
Use the PriorRelEffDt function to locate the prior occurrence of the search_field with the prior effective date (and effective-sequence number if specified), then return the value of the specified fetch_field corresponding to the search_field. The return value is an Any data type. Typically, this function is used to retrieve values for related display fields.
This function is valid only for effective-dated records.
If a prior record does not exist, then the statement is skipped. If the PriorRelEffDt function isn't a top-level statement, that is, if it's contained within a compound statement or a loop, the statement is skipped and execution restarts with the next top-level statement.
See Also
NextEffDt, NextRelEffDt, PriorEffDt.

 PriorValue
PriorValueSyntax
PriorValue(fieldname)
Description
Use the PriorValue function in FieldEdit and FieldChange PeopleCode to obtain the prior value of a buffer field that the user just changed. It returns the value that was in the buffer field before the user changed it, not the value of the field the last time the component was saved.
PriorValue gives correct results only in FieldEdit and FieldChange PeopleCode, and only for the buffer field where the function is executing. If you pass another field name to the function, it returns the current value of the buffer field, not the prior value.
Parameters
|
fieldname |
The name of the record field. For correct results, this must be the name of the field where the call to PriorValue executes. |
Returns
Returns an Any value equal to the value that was in the current buffer field immediately prior to the last edit.
Example
The following example from FieldChange PeopleCode gets the prior value of a field:
&PRIOR = PriorValue(QUANTITY); DERIVED_TEST.TOTAL_AMT = (DERIVED_TEST.TOTAL_AMT - &PRIOR) + QUANTITY;
See Also

 Product
ProductSyntax
Product(numlist)
where numlist is an arbitrary-length list of numbers in the form
n1 [, n2]. . .
Description
Use the Product function to multiply all the numbers in numlist and returns the product as a Number data type. The numbers in the list can be any number expressed as a number, variable, or expression.
Returns
Returns a Number value equal to the product of the numbers in numlist.
Example
The example sets &N2 to 96:
&N2 = Product(4,80,0.3);
See Also
Fact.

 Prompt
PromptSyntax
Prompt(title, heading, {fieldlist | &Record})
where fieldlist is an arbitrary-length list of fields in the form:
field1 [, label1 [, tempvar1]] [, field2 [, label2 [, tempvar2]]]...
Note that the label parameter is required before the temporary variable.
Description
Use the Prompt function to display a page prompting the user to insert values into one or more text boxes. If the user cancels the page, any entered values are discarded and the function returns False. When the prompt page is displayed, the text boxes are initially filled with default values from the fields in fieldlist. The user can change the values in the text boxes, then if the user clicks OK, the values are placed either into the buffer for the appropriate field, or into a temporary variable, if a tempvar for that field is provided in the function call.
Prompt can also take a record object. This is primarily used with the Query classes, when running a query, to prompt the end-user for the prompt values of a query.
Prompt is a think-time function, and as such cannot be used during the PeopleCode attached to the following events:
SavePreChange
Workflow
RowSelect
SavePostChange
Any PeopleCode event that fires as a result of a ScrollSelect (or one of its relatives) function calls, or a Select (or one of its relatives) Rowset class method.
Prompt should also not be called in any PeopleCode event that fires as a result of a ScrollSelect or its relatives, or a Select Rowset class method or its relatives.
See Also
Parameters
|
title |
Used as the title for the page. |
|
heading |
Displayed in the page above the fields. If a zero-length string ("") is passed, the heading line is omitted in the page. |
|
fieldlist | &Record |
A list of one or more fields; each field in the list consists of a [recordname.]fieldname followed by an optional label and an optional temporary variable for storing the input value. The label parameter is required if you supply the temporary variable parameter. Instead of a list of fields, you can also specify an already instantiated and populated record object. |
|
field |
The name of the field being prompted for, the form [recordname.]fieldname. |
|
label |
Optional label for the prompted field. If this parameter is omitted, the field RFT Long value is used. This parameter is required before the tempvar parameter. |
|
tempvar |
Optional temporary variable to receive the user-entered value. If this parameter is omitted, the value is placed into the buffer for the field specified. Using a temp variable enables the PeopleCode program to inspect and process the entered value without affecting the buffer contents. |
Returns
Optionally returns a Boolean value:
False if the user clicks the Cancel button.
True if the user clicks the OK button.
Example
The following example prompts for a single field, using calls to the MsgGetText function to retrieve values for the window title and prompt, and places the result into FISCAL_YEAR field:
Prompt(MsgGetText(5000, 182, " "), MsgGetText(5000, 184, " "), FISCAL_YEAR);
To following example places the results of the prompt into a temporary variable:
Prompt("Change Voucher", "", VOUCHER_ID, "Change Voucher ID to", &NEW_VOUCHER_ID);
The following code is in the USA push button FieldChange PeopleCode, and calls for the single field as shown in the page.
When = PAGE.PERSONAL_DATA1 /* Administer Global Personnel - USA Flag Btn on PERSONAL_DATA1 Page */ Prompt("US Social Security Number", "", PERSONAL_DATA.SSN); Break;

 Proper
ProperSyntax
Proper(string)
Description
Use the Proper function to capitalize the first letter in a text string and any other letters in a text string that follow any character other than another letter. It also converts all other letters in a text string to lowercase. Punctuation and other characters that have no case sensitivity are not changed.
Returns
Returns a String value with the first character of each word capitalized.
Example
The example sets the value of &BADKD to "K. D. Lang".
&BADKD = Proper("k. d. LANG")
See Also

 PublishXmlDoc
PublishXmlDocSyntax
PublishXmlDoc(&XmlDoc, Message.MessageName [, Node.NodeName])
Description
Use the PublishXmlDoc function to send an asynchronous message that is based on an XmlDoc object. The XmlDoc object must already be instantiated and populated. The message included in the function call should be an unstructured message, that is, one that isn't based on a hierarchical record structure.
If you want to retrieve an XmlDoc message that was sent asynchronously, use the GetMessageXmlDoc built-in function.
If you want to handle an XmlDoc as a Message object, you need to define a Message object with a hierarchical structure and migrate the data in the XmlDoc object into the Message object.
Parameters
|
&XmlDoc |
Specify an already instantiated and populated XmlDoc object that you want to send as an asynchronous message. |
|
MessageName |
Specify an already existing nonrowset-based message, prefaced with the reserved word Message. |
|
NodeName |
Specify a node. This is for Sender Specified Routing (SSR), prefixed with the reserved word Node. The node defines the target for the published message. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if the message was successfully published, False otherwise.
Example
Local XmlDoc &MyDoc; . . . PublishXmlDoc(&MyDoc, Message.MyXmlMessage, Node.MyNode);
See Also
GetMessageXmlDoc, SyncRequestXmlDoc.

 PutAttachment
PutAttachmentSyntax
PutAttachment(URLDestination, SysFileName, LocalFile [, LocalDirEnvVar [, PreserveCase]])
where URLDestination can have one of the following forms:
URL.URLname
OR a string URL, such as
ftp://user:[email protected]/
Note. You cannot specify a different port for an attachment when using an FTP server. You can only use the default port of 21.
Description
Use the PutAttachment function to transfer a file from the application sever to the file server.
Note. If the specified subdirectories don't exist this function tries to create them.
File Name Considerations
When the file is transferred, the following characters are replaced with an underscore:
space
semicolon
plus sign
percent sign
ampersand
apostrophe
exclamation point
pound sign
dollar sign
Note. The @ sign is not changed to an underscore on files transferred with this function.
User Filenames for PutAttachment
If a user attaches a file through the browser dialog box generated by AddAttachment, the filename is converted before that filename is returned to the AddAttachment call for storage.
For example, "My Resume.doc" is returned through the AddAttachment parameter as "My_Resume.doc", with the space changed to an underscore.
No comparable mapping occurs for user filenames with PutAttachment, which requires the user filename as an input parameter, rather than an output parameter that is returned to the user.
Instead, before storing the ATTACHUSERFILE value, code similar to this should be invoked:
&ATTACHUSERFILE = Substitute(&ATTACHUSERFILE, " ", "_"); &ATTACHUSERFILE = Substitute(&ATTACHUSERFILE, ";", "_"); &ATTACHUSERFILE = Substitute(&ATTACHUSERFILE, "+", "_"); &ATTACHUSERFILE = Substitute(&ATTACHUSERFILE, "%", "_"); &ATTACHUSERFILE = Substitute(&ATTACHUSERFILE, "&", "_"); &ATTACHUSERFILE = Substitute(&ATTACHUSERFILE, "'", "_"); &ATTACHUSERFILE = Substitute(&ATTACHUSERFILE, "!", "_"); &ATTACHUSERFILE = Substitute(&ATTACHUSERFILE, "@", "_"); &ATTACHUSERFILE = Substitute(&ATTACHUSERFILE, "#", "_"); &ATTACHUSERFILE = Substitute(&ATTACHUSERFILE, "$", "_");
File System Considerations
If you are uncertain which type of file system the file is going to transferred to, either a Unix or Windows system, you should use the last parameter (LocalDirEnvVar) and not specify a path to the file.
The following code example works for Windows systems, but not Unix systems:
PutAttachment(FTPINFO, TARGETFILENAME, "c:\temp\resume.doc");
The following code example works for Unix systems, but not Windows systems:
PutAttachment(FTPINFO, TARGETFILENAME, "/tmp/resume.doc");
The following two examples work for both Windows and Unix systems:
PutAttachment(FTPINFO, TARGETFILENAME, "resume.doc", "TMP"); PutAttachment(FTPINFO, TARGETFILENAME, "resume.doc", "PS_HOME");
Parameters
|
URLDestination |
A reference to a URL. This can be either a URL name, in the form URL.URLName, or a string. This is where the file is transferred to. |
|
SysFileName |
The relative path and filename of the file on the file server. This is appended to URLDestination to make up the full URL where the file is transferred to. This parameter takes a string value. Note. The URLDestination requires "/" slashes. Because SysFileName is appended to the URL, it also requires only "/" slashes. "\" are not supported for either the URLDestination or the SysFileName parameter. |
|
LocalFile |
The name, and possible full path, to the destination file on the application server. This is where the file is transferred from. This parameter takes a string value. If you only specify a file name, the file is assumed to be in the directory specified by the TMP environment variable or the directory specified by LocalDirEnvVar. If the file is not in the TMP directory and you don't specify LocalDirEnvVar you must use the full path name as appropriate to the operating system (that is, on Unix use "\"). |
|
LocalDirEnvVar |
The name of an environment variable containing path information. If specified, the path value in the environment variable is prepended to LocalFile. Use this if you don't want to hardcode path names in the LocalFile parameter. This parameter takes a string value. Note. Only operating system environment variables are recognized with this parameter, rather than variables defined in configuration files. |
|
PreserveCase |
Specify a Boolean value to indicate whether the case of the directory and file name specified with DirAndFileName are preserved or not; true, preserve the case, false otherwise. The default value is false. |
Returns
An integer value or a constant:
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
0 |
%Attachment_Success |
File was transferred successfully. |
|
1 |
%Attachment_Failed |
File was not successfully transferred. |
|
3 |
%Attachment_FileTransferFailed |
File was not successfully transferred. |
|
4 |
%Attachment_NoDiskSpaceAppServ |
Transfer failed because no space was available on the application server. |
|
5 |
%Attachment_NoDiskSpaceWebServ |
Transfer failed because no space was available on the web server. |
|
6 |
%Attachment_FileExceedsMaxSize |
Transfer failed because the file was too large for the database platform. Check your database platform specifications. |
|
7 |
%Attachment_DestSystNotFound |
Transfer failed because the destination system wasn't found. Check the URLDestination parameter. |
|
8 |
%Attachment_DestSysFailedLogin |
Transfer failed because the system couldn't connect to the destination system specified with URLDestination. |
|
9 |
%Attachment_FileNotFound |
Transfer failed because the LocalFile couldn't be found. |
|
10 |
%Attachment_DeleteFailed |
Transfer failed because the file couldn't be deleted from application server. |
Example
The following transfers the file "resume.txt" from the application server to the file server.
PutAttachment("ftp://anonymous:[email protected]/HRarchive/", "NewHire/11042000resume.txt", " "C:\NewHires\resume.txt".");
See Also
AddAttachment, DeleteAttachment, GetAttachment, ViewAttachment.
Using File Attachments in Applications

 Quote
QuoteSyntax
Quote(String)
Description
Use the Quote function to enclose a string in single quotation marks. This function also can be used to put quotation marks around SQL statements.
Parameters
|
String |
Specify the string you want to enclose in single quotation marks. |
Returns
The string specified by String enclosed in single quotation marks.
Example
The following code returns 'Bob':
&QuotedString = Quote("Bob");
The following code returns 'Bob''s' (two single quotes to represent the apostrophe)
&QuotedString = Quote("Bob's");
The following code returns '%'' OR USER ID LIKE ''%':
&QuotedString = Quote("%' OR USERID LIKE '%");

 Radians
RadiansSyntax
Radians(angle)
Description
Use the Radians function to convert the given angle from degree measurement to radian measurement.
Parameters
|
angle |
The size of an angle in degrees. |
Returns
The size of the given angle in radians.
Example
The following example returns the equivalent size in radians of an angle measuring 65.5 degrees:
&RADIAN_SIZE = Radians(65.5);
The following example returns the value of pi, that is, 180 degrees expressed as radians:
&PI = Radians(180);
Note. This example represents pi with a high degree of accuracy, but no computer system can represent irrational numbers exactly. Thus, the results of extended calculations based on pi have the potential for a cumulative reduction in precision.
See Also
Acos, Asin, Atan, Cos, Cot, Degrees, Sin, Tan.

 Rand
RandSyntax
Rand( )
Description
Use the Rand function to generate a random number greater than or equal to 0 and less than 1. To generate a random integer that is greater than or equal to 0 but less than x, use Int(Rand()*x).
Returns
Returns a random Number value greater than or equal to 0 and less than 1.
Example
The example sets &RANDOM_NUM to a random value less than 100.
&RANDOM_NUM = Int(Rand( )*100)
See Also
Int.

 RecordChanged
RecordChangedSyntax
The syntax of the RecordChanged function varies, depending on whether you use a scroll path reference or a contextual reference to designate the row being tested.
Using a scroll path reference, the syntax is:
RecordChanged(scrollpath, target_row)
where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row,]] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can also use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Using a contextual reference the syntax is:
RecordChanged(RECORD.target_recname)
A contextual reference specifies the current row on the scroll level designated by RECORD. target_recname.
An older construction, in which a record field expression is passed, is also supported. The record field is any field in the row where the PeopleCode program is executing (typically the one on which the program is executing).
RecordChanged(recordname.fieldname)
Description
Use the RecordChanged function to determine whether the data in a specific row has been modified since it was retrieved from the database either by the user or by a PeopleCode program.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the IsChanged record class property instead.
This is useful during save processing for making updates conditional on whether rows have changed.
Note. The word "record" is used in this function name in a misleading way. Remember that this function (like the related functions RecordDeleted and RecordNew) checks the state of a row, not a record.
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
RECORD .target_recname |
The primary scroll record of the scroll level where the row being referenced is located. As an alternative, you can use SCROLL. scrollname. |
Returns
Returns a Boolean value:
True if any data in the target row has been changed.
False if no data in the target row has been changed.
Example
This example shows a RecordChanged call using a contextual reference:
If RecordChanged(RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_DTL) Then WinMessage("Changed row msg from current row.", 64); End-If;
The following example, which would execute on level one, checks rows on level two to determine which have been changed:
For &I = 1 To ActiveRowCount(RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_PER, CurrentRowNumber(1), RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_DTL); If RecordChanged(RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_PER, CurrentRowNumber(1), RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_DTL, &I) Then WinMessage("Changed row message from level one.", 64); End-If; End-For;
See Also
FieldChanged, RecordDeleted, RecordNew.

 RecordDeleted
RecordDeletedSyntax
The syntax of the RecordDeleted function varies, depending on whether you use a scroll path reference or a contextual reference to designate the row being tested.
Using a scroll path reference, the syntax is:
RecordDeleted(scrollpath, target_row)
where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row,]] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can also use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Using a contextual reference the syntax is:
RecordDeleted(RECORD.target_recname)
A contextual reference specifies the current row on the scroll level designated by RECORD. target_recname.
An older construction, in which a record field expression is passed, is also supported. The record field is any field in the row where the PeopleCode program is executing (typically the one on which the program is executing).
RecordDeleted(recordname.fieldname)
Description
Use the RecordDeleted function to verify if a row of data has been marked as deleted, either by an end-user row delete (F8) or by a call to DeleteRow.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the IsDeleted record class property instead.
RecordDeleted is useful during save processing to make processes conditional on whether a row has been deleted.
Deleted rows are not actually removed from the buffer until after the component has been successfully saved, so you can check for deleted rows all the way through SavePostChange PeopleCode.
RecordDeleted is not typically used in a loop, because it is easier to put it on the same scroll level as the rows being checked in SavePreChange or SavePostChange PeopleCode: these events execute PeopleCode on every row in the scroll, so no looping is necessary.
Note. To avoid confusion, note that this function (like the related functions RecordChanged and RecordNew) checks the state of a row, not a record.
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
RECORD. target_recname |
The primary scroll record of the scroll level where the row being referenced is located. As an alternative, you can use SCROLL. scrollname. |
Returns
Returns a Boolean value:
True if the target row has been deleted.
False if the target row has not been deleted.
Example
This example shows a RecordDeleted call using a contextual reference
If RecordDeleted(RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_DTL) Then WinMessage("Deleted row msg from current row.", 64); End-If;
The following example, which would execute on level zero, checks rows on level one to determine which have been deleted:
For &I = 1 To TotalRowCount(RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_PER, CurrentRowNumber(1), RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_DTL); If RecordDeleted(RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_PER, CurrentRowNumber(1), RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_DTL, &I) Then WinMessage("Deleted row message from level one.", 64); End-If; End-For;
Note that the loop is delimited by TotalRowCount. For loops delimited by ActiveRowCount don’t process deleted rows.
See Also
FieldChanged, RecordChanged, RecordNew, TotalRowCount, ActiveRowCount.

 RecordNew
RecordNewSyntax
The syntax of the RecordNew function varies, depending on whether you use a scroll path reference or a contextual reference to designate the row being tested.
Using a scroll path reference, the syntax is:
RecordNew(scrollpath, target_row)
where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row,]] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can also use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Using a contextual reference the syntax is:
RecordNew(RECORD.target_recname)
A contextual reference specifies the current row on the scroll level designated by RECORD. target_recname.
An older construction, in which a record field expression is passed, is also supported. The record field is any field in the row where the PeopleCode program is executing (typically the one on which the program is executing).
RecordNew(recordname.fieldname)
Description
Use the RecordNew function to check a specific row to determine whether it was added to the component buffer since the component was last saved.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the IsNew row class property instead.
This function is useful during save processing to make processes conditional on whether or not a row is new.
Note. To avoid confusion, remember that this function (like the related functions RecordChanged and RecordDeleted) checks the state of a row, not a record. In normal PeopleSoft usage, the word "record" denotes a table-level object (such as a table, view, or Derived/Work record).
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
RECORD. target_recname |
The primary scroll record of the scroll level where the row being referenced is located. As an alternative, you can use SCROLL. scrollname. |
Returns
Returns a Boolean value:
True if the target row is new.
False if the target row is not new.
Example
This example shows a RecordNew call using a contextual reference:
If RecordNew(RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_DTL) Then WinMessage("New row msg from current row.", 64); End-If;
The following example, which would execute on level one, checks rows on level two to determine which have been added:
For &I = 1 To ActiveRowCount(RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_PER, CurrentRowNumber(1), RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_DTL); If RecordNew(RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_PER, CurrentRowNumber(1), RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_DTL, &I) Then WinMessage("New row message from level one.", 64); End-If; End-For;
See Also
FieldChanged, RecordChanged, RecordDeleted.

 RefreshTree
RefreshTree
Syntax
RefreshTree(Record.bound_recname)
Description
Use the RefreshTree function to update a dynamic tree.
Note. Dynamic tree controls have been deprecated. Use the GenerateTree function or Tree Viewer.
See Also
Viewing Trees From Application Pages

 RelNodeTranDelete
RelNodeTranDeleteSyntax
RelNodeTranDelete(RelationshipId , SrcTrxType, SrcNode, SrcRqstMsgName, SrcRqstMsgVer, TgtNode, TgtRqstMsgName, TgtRqstMsgName, TgtRqstMsgVer);
Description
Use theRelNodeTranDelete function to delete a transaction modifier.
Parameters
|
RelationshipId |
Specify the relationship ID as a string. |
|
ScrTrxType |
Specify the source transaction type as a string. |
|
SrcNode |
Specify the source node as a string. |
|
ScrRqstMsgName |
Specify the source request message name as a string. |
|
ScrRqstMsgVer |
Specify the source request message version as a string. |
|
TgtNode |
Specify the target node as a string. |
|
TgtRqstMsgName |
Specify the target request message name as a string. |
|
TgtRqstMsgName |
Specify the target message name as a string. |
|
TgtRqstMsgVer |
Specify the target request message version as a string. |
Returns
A Boolean value, True if the function completed successfully, False otherwise.
Example
&ret = RelNodeTranDelete("QE_TEST", "CMS_TEST", "CMS_TEST_LOCAL", "OA", "ROLESYNCH_MSG", "VERSION_1", "CMS_TEST_LOCAL2", "ROLESYNCH_MSG2", "VERSION_1",);
See Also
Editing Transaction Message Details

 RemoteCall
RemoteCallSyntax
RemoteCall(dispatcher_name [, service_paramlist] [, user_paramlist])
where service_paramlist and user_paramlist are arbitrary-length lists of parameters in the form:
var1, val1 [, var2, val2]. . .
Description
Use the RemoteCall function to call a Tuxedo service from a PeopleSoft application. A typical use of Remote Call is to run data-intensive, performance-sensitive programs near or on the database server.
Note. After PeopleTools 8 you can no longer use RemoteCall to start an Application Engine program. You must use CallAppEngine instead.
Because complex PeopleCode processes can now be run on the application server in three-tier mode, the RemoteCall PeopleCode function has more limited utility. However, RemoteCall can still be very useful, because it provides a way to take advantage of existing COBOL processes.
In three-tier mode, RemoteCall always runs on the application server.
In two-tier mode, RemoteCall always runs on the client.
This means that it is no longer necessary to set a location for the remote call in PeopleSoft Configuration Manager.
Each RemoteCall service can have zero or more standard parameters and any number of user parameters. The standard parameters are determined by the RemoteCall dispatcher, the user parameters by the COBOL program being run.
There is only one RemoteCall dispatcher delivered with PeopleTools 7, PSRCCBL, which executes a COBOL program using the connect information of the current end-user.
In the application server configuration file, you can specify where RemoteCall can find the COBOL executables
RemoteCall can be used from any type of PeopleCode except SavePostChange, SavePreChange, Workflow, and RowSelect. However, remote programs that change data should not be run as part of the SaveEdit process, because the remote program may complete successfully even though an error occurs in a later part of the save process. For remote programs that change data, the normal place for them would be in the FieldChange PeopleCode behind a command push button, or in a pop-up menu item.
After you use RemoteCall, you may want to refresh your page. The Refresh method, on a rowset object, reloads the rowset (scroll) using the current page keys. This causes the page to be redrawn. The following code refreshes the entire page:
GetLevel0().Refresh()
If you only want a particular scroll to be redrawn, you can refresh just that part.
See Also
Parameters
The parameters passed to RemoteCall can be broken into three parts: the RemoteCall Dispatcher Name, the standard Parameter Lists for the service, and the User Parameter Lists for the program being called on the service.
Dispatcher Name
The dispatcher_name parameter is a string value that specifies the type of RemoteCall performed. For PeopleTools 7 there is only one RemoteCall dispatcher delivered, PSRCCBL, which executes a COBOL program using the connect information of the current end-user, so the value you pass to this parameter should always be "PSRCCBL". Future versions of PeopleTools may provide support for Red Pepper, SQR, or customer supplied remote calls.
Parameter Lists
Both the standard parameter list and user parameter list have the same form. Think of the parameters passed to the service as being passed as pairs of variable names and values of input and output parameters:
variable_name, value
Where:
variable_name is a string literal or string variable that contains the name of the input or output variable as referenced in the remote program. For example, if the remote program expects a variable named "USERNAME", then the PeopleCode should use "USERNAME" or &VARIABLE (which had been assigned the value "USERNAME").
For input variables, value is the value to be passed to the remote program with the variable name. It can be either a variable or literal with a data type that corresponds to the variable_name variable. For output variables, value is the value returned to the PeopleCode program from the remote program. It must be a variable in this case, representing the buffer into which the value is returned.
An arbitrary number of parameters can be passed to the service. There is, however, a limitation on the number of variables that can be passed in PeopleCode, which is limited by the size of the PeopleCode parameter stack, currently 128.
In the case of the PSRCCBL dispatcher, there are three standard parameters, listed in the following table:
|
Dispatcher |
Parameter |
Required |
Description |
|
PSRCCBL |
PSCOBOLPROG |
Y |
Name of the COBOL program to run. |
|
PSRCCBL |
PSRUNCTL |
N |
Run-control parameter to pass to the COBOL program. |
|
PSRCCBL |
INSTANCE |
N |
Process instance parameter to pass to the COBOL program. |
User Parameter List
For PSRCCBL, the remote COBOL program must match the user parameters to the usage of its application. The names of the parameters are sent to the server and can be used by the COBOL program. The COBOL program returns any modified (output) parameters by name. Parameters which are not returned are not modified, and any extra returned parameters (that is, parameters beyond the number passed or of different names) are discarded with no effect.
Returns
None.
Example
You could use the following PeopleCode to execute the program "CBLPROG1":
Rem Set the return code so we are sure it is sent back. &Returncode = -1; Rem Set the parameters that will be sent across. ¶m1 = "John"; ¶m2 = "Smith"; Rem Set the standard parameters that indicate program name and run-control. &RemoteCobolPgm = "CBLPROG1"; /* call the remote function */ RemoteCall ("PSRCCBL", "PSCOBOLPROG", &RemoteCobolPgm, "PSRUNCTL", workrec.runctl, "FirstName", ¶m1, "LastName", ¶m2, "Returncode", &Returncode, "MessageSet", &msgset, "MessageID", &msgid, "MessageText1", &msgtext1, "MessageText2", &msgtext2); if &Returncode <> 0 WinMessage(MsgGet(&msgset, &msgid, "default message", &msgtext1, &msgtext2)); end-if;
See Also

 RemoveDirectory
RemoveDirectorySyntax
RemoveDirectory(path [, remove_parameters])
where remove_parameters can be in the form:
path_type [+ directory_type]
Description
Use the RemoveDirectory function to remove the directory specified by path. You can also specify whether to remove just the directory, or to delete the directory and all subdirectories, including any files, that is, to remove the entire directory tree.
Working With Relative Paths
If you specify a relative path, that path is appended to the path specified by an environmental variable, if the variable exists, in a particular order. This means if the first environmental variable in order is found, that is the one that's used. If it isn't found, the next one is searched for, and if found, is used, and so on.
The environmental variables that are used are different, depending on whether the machine where the code is running is an application server. If the code is running on an application server, the following environmental variables are valid, and are searched for in the following order:
PS_FILEDIR[\relative_path]
PS_SERVDIR\Files[\relative_path]
If the code is not running on an application server, the following environmental variables are valid, and are searched for in the following order:
PS_FILEDIR[\relative_path]
PS_SERVDIR\Files[\relative_path]
TEMP[\relative_path]
The PS_FILEDIR environmental variable is not initialized and set to a path automatically. If you want to use this environmental variable, you must set it yourself.
Note. Your system security should verify if a user has the correct permissions before allowing access to a drive (for example, if a user changes their TEMP environmental variable to a network drive they don’t normally have access to, your system security should detect this.)
Parameters
|
path |
Specify the directory to be removed. |
|
remove_parameters |
Specify additional considerations about the directory to be removed. Specify whether the path is an absolute or relative path. Values are:
If you don’t specify pathtype the default is %FilePath_Relative. If the path is an absolute path, whatever path you specify is used verbatim. You must specify a drive letter as well as the complete path. You can’t use any wildcards when specifying a path. The Component Processor automatically converts platform-specific separator characters to the appropriate form for where your PeopleCode program is executing. On a WIN32 system, UNIX "/" separators are converted to "\", and on a UNIX system, WIN32 "\" separators are converted to "/". Specify whether to remove only the specified directory or to remove the directory and all its subdirectories. The default is to just remove the specified directory. The valid values are:
|
Returns
None.
Example
The following example is for an NT operating system:
RemoveDirectory("C:\temp\mydir\temp", %filepath_absolute + %remove_subtree);
The following example is for a UNIX operating system:
RemoveDirectory("/temp/mydir/temp", %filepath_absolute + %remove_subtree);
See Also
CreateDirectory, DeleteAttachment, FileExists, FindFiles.

 RenameDBField
RenameDBFieldSyntax
RenameDBField(Field.NewFieldName, Field.OldFieldName [, FixRefsOnly])
Description
Use the RenameDBField function to modify a field definition to have a new name. This function also cleans up most references, such as in PeopleCode programs and on records so they now use the new name.
Note. Because using this function changes records that are used to build application tables, you must rebuild (alter) the specified project before these changes can be used.
Considerations Using this Function
In SQL associated with records of type view, the field name is not changed. You must fix those by hand.
This function is intended for use during configuration time only, before active runtime usage is initiated. Using this function during active runtime is not supported. Changes to data definitions are not recognized on currently loaded component. In general, changes aren't recognized until the component is reloaded.
This operation is time consuming.
Warning! These operations take place in a separate transaction from the page's save status: the initiation of any of these operations immediately changes the definitions, even if the page is subsequently cancelled.
Parameters
|
NewFieldName |
Specify the new field name to be used. This name must be prefixed by the reserved word Field. |
|
OldFieldName |
Specify the name of the field to be changed. This name must be prefixed by the reserved word Field. |
|
FixRefsOnly |
Specify to rename all references of OldFieldName to NewFieldName whether or not NewFieldName exists or not. This paramter takes a Boolean value. The default value is False. For example, suppose a company renames a field PROJECT to MYPROJECT. Then they receive a patch which has records, pages, code, and so on that references Field.PROJECT. In this case you could set this parameter to True, rename MYPROJECT to PROJECT, and have all the references to the field PROJECT redirect to the field MYPROJECT even if neither field exists in the database, nor if only one exists. Note. Using this parameter is a completely freeform path to renaming references. Be aware that the system won't work if pages and records are not eventually pointing to a valid field. |
Returns
A constant value. The values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
%MDA_Success |
Bulk operation completed successfully. |
|
%MDA_Failure |
Bulk operation did not complete successfully. |
|
%MDA_FieldNotFound |
The field specified by OldFieldName wasn't found in the specified project or page list. |
|
%MDA_Duplicate |
The field specified by NewFieldName already exists. |
Example
&ret = RenameDBField(Field.OrgId, Field.DeptId, True); If (&ret = %MDA_Success) Then MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "RenameDBField succeeded"); Else MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "RenameDBField failed"); End-If;
The following example de-references the field name for the function.
&oldcf = "CF1"; &newcf = "XYZ_STORE_ID"; &new = "FIELD." | &newcf; &old = "FIELD." | &oldcf; &ret = RenameDBField(@(&new), @(&old)); If (&ret = 0) Then MessageBox(0, "RenameDBField", 0, 0, "Succeeded"); Else MessageBox(0, "RenameDBField", 0, 0, "Failed"); End-If;
See Also

 RenamePage
RenamePageSyntax
RenamePage(Page.NewPageName, Page.OldPageName)
Description
Use the RenamePage function to modify a page definition to have a new name. This function also cleans up most references so they now use the new name.
Considerations Using this Function
This function is intended for use during configuration time only, before active runtime usage is initiated. Using this function during active runtime is not supported. Changes to data definitions are not recognized on currently loaded component. In general, changes aren't recognized until the component is reloaded.
This operation is time consuming
Warning! These operations take place in a separate transaction from the page's save status: the initiation of any of these operations immediately changes the definitions, even if the page is subsequently cancelled.
Parameters
|
NewPageName |
Specify the new page name to be used. This name must be prefixed by the reserved word Page. |
|
OldPageName |
Specify the name of the page to be changed. This name must be prefixed by the reserved word Page. |
Returns
A constant value. The values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
%MDA_Success |
Bulk operation completed successfully. |
|
%MDA_Failure |
Bulk operation did not complete successfully. |
|
%MDA_PageNotFound |
The page specified with OldPageName wasn't found. |
Example
&ret = RenamePage(PAGE.OrgIdTbl, PAGE.DeptIdTbl); If (&ret = %MDA_Success) Then MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "RenamePage succeeded"); Else MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "RenamePage failed"); End-If;
See Also

 RenameRecord
RenameRecordSyntax
RenameRecord(Record.NewRecordName, Record.OldRecordName)
Description
Use the RenameRecord function to modify a record definition to have a name. This function also cleans up most references so they now use the new name.
Note. Because using this function changes records that are used to build application tables, you must rebuild (alter) the specified project before these changes can be used.
Considerations Using this Function
This function is intended for use during configuration time only, before active runtime usage is initiated. Using this function during active runtime is not supported. Changes to data definitions are not recognized on currently loaded component. In general, changes aren't recognized until the component is reloaded.
This operation is time consuming.
Warning! These operations take place in a separate transaction from the page's save status: the initiation of any of these operations immediately changes the definitions, even if the page is subsequently cancelled.
Parameters
|
NewRecordName |
Specify the new record name to be used. This name must be prefixed by the reserved word Record. |
|
OldRecordName |
Specify the name of the record to be changed. This name must be prefixed by the reserved word Record. |
Returns
A constant value. The values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
%MDA_Success |
Bulk operation completed successfully. |
|
%MDA_Failure |
Bulk operation did not complete successfully. |
|
%MDA_RecordNotFound |
The record specified with OldRecordName wasn't found. |
Example
&ret = RenameRecord(RECORD.OrgIdTbl, RECORD.DeptIdTbl); If (&ret = %MDA_Success) Then MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "RenameRecord succeeded"); Else MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "RenameRecord failed"); End-If;
See Also

 Repeat
RepeatSyntax
Repeat statement_list Until logical_expression
Description
Use the Repeat loop to cause the statements in statement_list to be repeated until logical_expression is True. Any kind of statements are allowed in the loop, including other loops. A Break statement inside the loop causes execution to continue with whatever follows the end of the loop. If the Break is in a nested loop, the Break does not apply to the outside loop.
Example
The following example repeats a sequence of statements until a complex Boolean condition is True:
Repeat &J = &J + 1; &ITEM = FetchValue(LOT_CONTROL_INV.INV_ITEM_ID, &J); &LOT = FetchValue(LOT_CONTROL_INV.INV_LOT_ID, &J); Until (&ITEM = &INV_ITEM_ID And &LOT = &INV_LOT_ID) Or &J = &NUM_LOT_ROWS;

 Replace
ReplaceSyntax
Replace(oldtext, start, num_chars, newtext)
Description
Use the Replace function to replace a specified number of characters in a string.
Parameters
|
oldtext |
A String value, part of which is to be replaced. |
|
start |
A Number designating the position in oldtext from which to start replacing characters. |
|
num_chars |
A Number, specifying how many characters to replace in oldtext. |
|
newtext |
A String value that replaces num_chars characters. |
Returns
Returns a String value in which specific characters in oldtext are replaced with newtext.
Example
After the following statement &NEWDATESTR equals "1997":
&NEWDATESTR = Replace("1996",3,2,"97");
If this example, where the number of characters in newtext is less than num_chars, &SHORTER equals "txtx":
&SHORTER = Replace("txt123",4,3,"x");
In this example, where the number of characters in newtext is greater than num_chars, &LONGER equals "txtxxxx":
&LONGER = Replace("txt123",4,3,"xxxx");
See Also

 Rept
ReptSyntax
Rept(str, reps)
Description
Use the Rept function to replicate a text string a specified number of times and combine the result into a single string.
Parameters
|
str |
A String value to be replicated. |
|
reps |
A Number value specifying how many times to replicate str. If reps is 0, Rept returns an empty string. If reps is not a whole integer, it is truncated. |
Returns
Returns a String value equal to str repeated reps times.
Example
This example sets &SOMESTARS to "**********".
&SOMESTARS = Rept("*",10);

 ReSubmitPubHeaderXmlDoc
ReSubmitPubHeaderXmlDocSyntax
ReSubmitPubHeaderXmlDoc(PubID, PubNode, ChannelName, VersionName)
Description
Use the ReSubmitPubHeaderXmlDoc function to programmatically resubmit a message instance, as the message instance existed before any transformations were performed, much the same as you can do in the message monitor. This function resubmits the corresponding publication contract header.
You may want to use this method after an end-user has finished fixing any errors in the message data, and you want to resubmit the message, rerunning the PeopleCode.
The function is only available when the XML message has one of the following statuses:
Error
Timeout
Edited
Canceled
Parameters
|
PubID |
Specify the PubID as a number. |
|
PubNode |
Specify the Pub node as a string. |
|
ChannelName |
Specify the channel name as a string. |
|
VersionName |
Specify the version name as a string. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if function completed successfully, False otherwise.
See Also

 ReSubmitPubXmlDoc
ReSubmitPubXmlDocSyntax
ReSubmitPubXmlDoc(PubID, PubNode, ChannelName, VersionName, MessageName, SubNode[, Segment])
Description
Use the ReSubmitPubXmlDoc function to programmatically resubmit a message, much the same as you can do in the message monitor. This is the message publication as it exists after any transformations have been preformed. This function resubmits the corresponding publication contract.
You may want to use this method after an end-user has finished fixing any errors in the message data, and you want to resubmit the message, rerunning the PeopleCode.
The function is only available when the message has one of the following statuses:
Error
Timeout
Edited
Canceled
Parameters
|
PubID |
Specify the PubID as a number. |
|
PubNode |
Specify the Pub node as a string. |
|
ChannelName |
Specify the channel name as a string. |
|
VersionName |
Specify the version name as a string. |
|
MessageName |
Specify the name of the message as a string. |
|
SubNode |
Specify the name of the sub node as a string. |
|
Segment |
Specify an integer representing which segment you want to access. The default value is one, which means that if you do not specify a segment, the first segment is accessed. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if function completed successfully, False otherwise.
See Also
ReSubmitSubXmlDoc, ReSubmitPubHeaderXmlDoc.

 ReSubmitSubXmlDoc
ReSubmitSubXmlDocSyntax
ReSubmitSubXmlDoc(PubID, PubNode, ChannelName, VersionName, MessageName, SubscriptionName[, Segment])
Description
Use the ReSubmitSubXmlDoc function to programmatically resubmit a message, much the same as you can do in the message monitor. This function resubmits the corresponding subscription contract.
You may want to use this method after an end-user has finished fixing any errors in the message data, and you want to resubmit the message, rerunning the subscription PeopleCode.
The function is only available when the message has one of the following statuses:
Error
Timeout
Edited
Canceled
Parameters
|
PubID |
Specify the PubID as a number. |
|
PubNode |
Specify the Pub node as a string. |
|
ChannelName |
Specify the channel name as a string. |
|
VersionName |
Specify the version name as a string. |
|
MessageName |
Specify the name of the message as a string. |
|
SubscriptionName |
Specify the name of the subscription as a string. |
|
Segment |
Specify an integer representing which segment you want to access. The default value is one, which means that if you do not specify a segment, the first segment is accessed. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if function completed successfully, False otherwise.
See Also
ReSubmitPubHeaderXmlDoc, ReSubmitPubXmlDoc.

 Return
ReturnSyntax
Return [expression]
Description
Use the Return function to return from the currently active function; the flow of execution continues from the point where the function was called. If the function returns a result, that is, if a return value is specified in the Returns clause of the function definition, expression specifies the value to pass back to the caller and must be included. If the function does not return a result, the expression is not allowed. If Return appears in a main program, it acts the same as the Exit function.
Example
In the example a Boolean return value is specified in the Returns clause of the Function statement. The Return statement returns a True or False value to the calling routine, based on the contents of &UPDATEOK.
function run_status_upd(&PROCESS_INSTANCE, &RUN_STATUS) returns Boolean; &UPDATEOK = SQLExec( )("update PS_PRCS_RQST set run_status = :1 where process_instance = :2", &RUN_STATUS, &PROCESS_INSTANCE); If &UPDATEOK Then Return True; Else Return False; End-if; End-function;
See Also

 ReturnToServer
ReturnToServerSyntax
ReturnToServer({TRUE | FALSE | &NODE_ARRAY, | &Message})
Description
Use the ReturnToServer function to return a value from a PeopleCode messaging program to the publication or subscription server. You would use this in either your publication or subscription routing code, to either return an array of nodes that the message should be published to, or to do error processing (return False if entire message wasn’t received.)
What is returned depends on where the PeopleCode program is called from.
From OnRoute Publication:
TRUE: All nodes the message was published to are returned.
FALSE: No nodes are returned (generally used with error checking).
&NODE_ARRAY: The nodes specified in the array are returned.
&Message: Return a response message. This must be an already instantiated message object.
Note. You can return XmlDoc objects as responses. Only homogeneous type transactions are supported, that is, you can only return an XmlDoc object as a response if and only if an XmlDoc object was used in the request. Similarly, you can only return a Message object if and only if a Message object was used in the request.
From OnRoute Subscription:
TRUE: The subscription node is returned.
FALSE: No node is returned. This is generally used with error checking.
Parameters
|
TRUE | FALSE |&NODE_ARRAY | &Message |
Specify TRUE if you want publication nodes or the subscription node returned. Specify FALSE if you don't want any nodes returned, and nothing written to the database. This is generally used with error checking. Specify an object reference to an array of node names if you want to return a list of nodes to be published to. Specify a reference to a response message if you want to return a message. |
Returns
None.
Example
The following is an example of a publication routing rule, which would be in the OnRoutePublication. It is used to create publication contracts.
local message &MSG; local array &NODE_ARRAY; &MSG = GetMessage(); &EMPLID = &MSG.GetRowset()(1).QA_INVEST_HDR.EMPLID.Value; &SELECT_SQL = CreateSQL("select PUBNODE from PS_EMPLID_NODE where EMPLID = :1", &EMPLID); &NODE_ARRAY = CreateArray(); While &SELECT_SQL.Fetch(&PUBNODE) &NODE_ARRAY.Push(&PUBNODE); End-While; ReturnToServer(&NODE_ARRAY);
The following is an example of a subscription routing rule, which would be placed in the OnRouteSubscribe event:
local message &MSG; &MSG = GetMessage(); &BUSINESS_UNIT = &MSG.GetRowset()(1).PO_HDR.BUSINESS_UNIT.Value; SQLExec("Select BUSINESS_UNIT From PS_BUSINESS_UNIT where BUSINESS_UNIT = :1",&BUSINESS_UNIT,&FOUND); If all(&FOUND) Then ReturnToServer(True); Else ReturnToServer(False); End-if;
The following is a basic example of using an XmlDoc object:
Local XmlDoc &xmldoc; . . . /* build xmldoc */ . . . ReturnToServer(&xmldoc);
See Also
Defining Message Channels and Messages

 ReValidateNRXmlDoc
ReValidateNRXmlDocSyntax
ReValidateNRXmlDoc(NRID, EntityName)
Description
Use the ReValidateNRXmlDoc function to revalidate a non-repudiation XML message. After a document has been signed and validated, you can use this function to verify it was delivered or received by the system calling the function. This function is primarily used by the Message Monitor.
Parameters
|
NRID |
Specify the non-repudiation ID for the XML message that you want to revalidate. This parameter takes a numeric value. |
|
EntityName |
Specify the name of the entity that signed the data, as a string. For Peoplesoft, this is the node name. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if message is revalidated, False otherwise.
See Also

 RevalidatePassword
RevalidatePasswordSyntax
RevalidatePassword()
Description
Use the Revalidate function to validate the current end-user password.
This function displays a window prompting the user for the same password that the user signed onto the database with.
Revalidate password
Restrictions on Use in PeopleCode Events
Control does not return to the line after RevalidatePassword until after the user has filled in a value or pressed ENTER. This interruption of processing makes RevalidatePassword a “think-time” function which means that it shouldn’t be used in any of the following PeopleCode events:
SavePreChange.
Workflow.
RowSelect.
SavePostChange.
Any PeopleCode event that fires as a result of a ScrollSelect (or one of its relatives) function calls, or a Select (or one of its relatives) Rowset class method.
See Think-Time Functions.
Restrictions on Use in Signon PeopleCode
RevalidatePassword does not work in Signon PeopleCode. If you use this function in Signon PeopleCode, you create an infinite loop.
Returns
Returns a numeric value or a constant: you can check for either.
|
Value |
Constant |
Meaning |
|
0 |
%RevalPW_Valid |
Password Validated |
|
1 |
%RevalPW_Failed |
Password Validation Check Failed |
|
2 |
%RevalPW_Cancelled |
Password Validation Cancelled |
Example
RevalidatePassword is commonly used in the SaveEdit PeopleCode to verify that the user entering the data is the same as the one who signed onto the database.
&TESTOP = RevalidatePassword(); Evaluate &TESTOP /* Password does not match the current value */ When 1 Error MsgGet(48, 18, "Message Not Found"); Break; End-Evaluate;

 Right
RightSyntax
Right(str [, num_chars])
Description
Use the Right function to return a specified number of characters from the right side of a string. The function is useful if, for example, you want to get the last set of characters in a zip code or other fixed-length identification string. If the string contains Unicode non-BMP characters, each code unit of the surrogate pair is counted as a separate character and care should be taken not to split the surrogate pair.
Parameters
|
str |
A String value from which you want to get the rightmost characters. |
|
num_chars |
A Number value, greater than or equal to zero. If num_chars is omitted it is assumed to be equal to 1. |
Returns
Returns a String value equal to the rightmost num_chars character(s) in str.
Example
If &ZIP is equal to "90210-4455", the following example sets &SUFFIX to "4455":
&SUFFIX = Right(&ZIP, 4)
See Also
Left.

 Round
RoundSyntax
Round(dec, precision)
Description
Use the Round function to round a decimal number to a specified precision.
Parameters
|
dec |
A Number value to be rounded. |
|
precision |
A number value specifying the decimal precision to which to round dec. |
Returns
Returns a Number value equal to dec rounded up to precision decimal places.
Example
The following examples set the value of &TMP to 2.2, 9, then 24.09:
&TMP = Round(2.15,1); &TMP = Round(8.789,0); &TMP = Round(24.09372,2);
See Also

 RoundCurrency
RoundCurrencySyntax
RoundCurrency(amt, currency_cd, effdt)
Description
Different currencies are represented at different decimal precessions. The RoundCurrency function is a rounding function that takes currency precision into account, using a value stored in the CURRENCY_CD_TBL PeopleTools table.
Parameters
|
amt |
The amount to be rounded. |
|
currency_cd |
The currency code. |
|
effdt |
The effective date of currency rounding. |
Returns
Returns a Number value equal to amt rounded to the currency precision for currency_cd.
Example
The following example rounds 12.567 to 12.57, using the appropriate currency precision for US Dollars ("USD"):
&RESULT = RoundCurrency(12.567, "USD", EFFDT);
See Also
Controlling Currency Display Format.

 RowFlush
RowFlushSyntax
RowFlush(scrollpath, target_row)
Where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Use the RowFlush function to remove a specific row from a page scroll and from the component buffer.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the FlushRow rowset method instead.
Rows that are flushed are not deleted from the database.
RowFlush is a specialized and rarely used function. In most situations, you will want to use DeleteRow to remove a row from the component buffer and remove it from the database as well when the component is saved.
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
target_row |
The row number of the row to flush. |
Returns
None.
Example
The following example flushes a row in a view from the component buffer:
RowFlush(RECORD.BNK_RCN_DTL_VW, &ROW1);
See Also

 RowScrollSelect
RowScrollSelectSyntax
RowScrollSelect(levelnum, scrollpath, RECORD.sel_recname [, sqlstr [, bindvars]] [, turbo])
Where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ] RECORD.target_recname
and where bindvars is an arbitrary-length list of bind variables in the form:
bindvar1 [, bindvar2]. . .
To prevent ambiguous references, you can use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
The RowScrollSelect is similar to ScrollSelect except that it reads data from the select record into a scroll under a specific parent row, rather than automatically distributing the selected rows under the correct parent rows throughout the buffer.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the Select rowset method instead.
You must use the WHERE clause in the SQL string to ensure that only rows that match the parent row are read into the scroll from the select record. Otherwise, all rows are read in under the specified parent row.
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
levelnum |
Specifies the scroll level of the scroll area into which selected rows will be read. It can be 1, 2, or 3. |
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
RECORD. sel_recname |
Specifies the select record. The selname record must be defined in PeopleSoft Application Designer and SQL created as a table or a view, unless sel_recname and target_recname are the same. The sel_recname record can contain fewer fields than target_recname, although it must contain any key fields to maintain dependencies page records. This enables you to limit the amount of data read into the component buffers. |
|
sqlstr |
Contains a WHERE clause to restrict the rows selected from sel_recname and/or an ORDER BY clause to sort the rows. The WHERE clause may contain the PeopleSoft SQL platform functions that are used for SQLExec processing, such as %DateIn or %Substring. |
|
bindvars |
A list of bind variables to be substituted in the WHERE clause. |
|
turbo |
Setting this Boolean parameter to True turns on Turbo ScrollSelect. |
Returns
The number of rows read (optional.) This counts only lines read into the specified scroll. It does not include any additional rows read into autoselect child scrolls of the scroll.
Example
Here is an example of RowScrollSelect using bind variables:
If All(QTY_PICKED) Then &LEVEL1ROW = CurrentRowNumber(1); &LEVEL2ROW = CurrentRowNumber(2); &ORDER_INT_LINE_NO = FetchValue(RECORD.SHIP_SUM_INV_VW, &LEVEL1ROW, ORDER_INT_LINE_NO, &LEVEL2ROW); &INV_ITEM_ID = FetchValue(RECORD.SHIP_SUM_INV_VW, &LEVEL1ROW, INV_ITEM_ID, &LEVEL2ROW); &QTY = RowScrollSelect(3, RECORD.SHIP_SUM_INV_VW, CurrentRowNumber(1), RECORD.SHIP_DTL_INV_VW, CurrentRowNumber(2), RECORD.DEMAND_LOC_INV, RECORD.DEMAND_LOC_INV, "WHERE BUSINESS_UNIT = :1 AND ORDER_NO = :2 AND DEMAND_SOURCE = :3 AND SOURCE_BUS_UNIT = :4 AND ORDER_INT_LINE_NO = :5 AND SCHED_LINE_NO = :6 AND INV_ITEM_ID = :7 AND DEMAND_LINE_NO = :8", SHIP_HDR_INV.BUSINESS_UNIT, ORDER_NO, DEMAND_SOURCE, SOURCE_BUS_UNIT, ORDER_INT_LINE_NO, SCHED_LINE_NO, INV_ITEM_ID, DEMAND_LINE_NO, True); End-If;
See Also
RowScrollSelectNew, ScrollSelect, ScrollSelectNew, ScrollFlush, SQLExec.

 RowScrollSelectNew
RowScrollSelectNewSyntax
RowScrollSelectNew(levelnum, scrollpath, RECORD.sel_recname, [sqlstr [, bindvars]] [, turbo])
Where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ] RECORD.target_recname
where bindvars is an arbitrary-length list of bind variables in the form:
binvar1 [, bindvar2]. . .
To prevent ambiguous references, you can use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
The RowScrollSelectNew function is similar to RowScrollSelect, except that all rows read into the work scroll are marked new so they are automatically inserted into the database at Save time.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the SelectNew rowset method instead.
This capability can be used, for example, to insert new rows into the database by selecting data using a view of columns from another database tables.
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
level |
Specifies the scroll level of the scroll area into which selected rows are read. It can be 1, 2, or 3. |
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
RECORD. sel_recname |
Specifies the select record. The selname record must be defined in the record definition and SQL created as a table or a view, unless sel_recname and target_recname are the same. The sel_recname record can contain fewer fields than target_recname, although it must contain any key fields to maintain dependencies with other page records. This enables you to limit the amount of data read into the data buffers. |
|
sqlstr |
Contains a WHERE clause to restrict the rows selected from sel_recname and/or an ORDER BY clause to sort the rows. The WHERE clause may contain the PeopleSoft SQL platform functions that are used for SQLExec processing, such as %DateIn or %Substring. |
|
bindvars |
A list of bind variables to be substituted in the WHERE clause. The same restrictions that exist for SQLExec exist for these variables. |
|
turbo |
Setting this Boolean parameter to True turns on Turbo ScrollSelect. This will improve the performance of ScrollSelect verbs by as much as 300%, but should be implemented with caution on existing applications. |
Returns
The number of rows read (optional.) This counts only lines read into the specified scroll. It does not include any additional rows read into autoselect child scrolls of the scroll.
Example
The following example reads rows into the level 2 scroll and marks the rows as new:
&QTY = RowScrollSelectNew(2, RECORD.BI_LINE_VW, &ROW1, RECORD.BI_LINE_DST, RECORD.BI_LINE_DST, "where business_unit = :1 and invoice = :2 and line_seq_num = :3", BI_HDR.BUSINESS_UNIT, BI_HDR.INVOICE, &CURR_LINE_SEQ);
See Also
RowScrollSelect, ScrollSelect, ScrollSelectNew, ScrollFlush, SQLExec.

 RTrim
RTrimSyntax
RTrim(source_str [, trim_str])
Description
Use the RTrim function to remove characters, usually trailing blanks, from the right of a string.
Parameters
|
source_str |
A String from which you want to remove trailing characters. |
|
trim_str |
A String consisting of a list of characters, all occurrences of which are removed from the right of source_str. Characters in trim_str that occur in source_str to the left of any character not in trim_str are be removed. If this parameter is not specified, " " is assumed. |
Returns
Returns a String formed by deleting, from the end of source_str, all occurrences of each character specified in trim_str.
Example
The following example removes trailing blanks from &NAME and places the results in &TRIMMED:
&TRIMMED = RTrim(&NAME);
The following example removes trailing punctuation marks from REC.INP and places the results in &TRIMMED:
&TRIMMED = RTrim(REC.INP, ".,;:!?");
See Also

 ScheduleProcess
ScheduleProcess
Syntax
ScheduleProcess(process_type, process_name [, run_location] [, run_cntl_id] [, process_instance] [, run_dttm] [, recurrence_name] [, server_name])
Description
Use the ScheduleProcess function to schedule a process or job, writing a row of data to the Process Request table (PSPRCSRQST).
Note. This function is no longer supported. Use the CreateProcessRequest function instead.
See Also

 ScrollFlush
ScrollFlushSyntax
ScrollFlush(scrollpath)
Where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Use the ScrollFlush function to remove all rows inside the target scroll area and frees its associated buffer.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the Flush rowset method instead.
Rows that are flushed are not deleted from the database. This function is often used to clear a work scroll before a call to ScrollSelect.
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
Returns
None.
Example
The following example clears the level-one scroll then fills the level-one and level-two scrolls.
/* Throw away all rows */ ScrollFlush(RECORD.DBFIELD_VW); /* Fill in new values */ &FIELDSEL = "where FIELDNAME like '" | FIELDNAME | "%'"; &ORDERBY = " order by FIELDNAME"; ScrollSelect(1, RECORD.DBFIELD_VW, RECORD.DBFIELD_VW, &FIELDSEL | &ORDERBY); ScrollSelect(2, RECORD.DBFIELD_VW, RECORD.DBFIELD_LANG_VW, RECORD.DBFIELD_LANG_VW, &FIELDSEL | " and LANGUAGE_CD = :1" | &ORDERBY, DBFIELD_SRCH.LANGUAGE_CD);
See Also
RowFlush, RowScrollSelect, RowScrollSelectNew, ScrollSelect, ScrollSelectNew.

 ScrollSelect
ScrollSelectSyntax
ScrollSelect(levelnum, [RECORD.level1_recname, [RECORD.level2_recname,]] RECORD.target_recname, RECORD.sel_recname [, sqlstr [, bindvars]] [, turbo])
where bindvars is an arbitrary-length list of bind variables in the form:
bindvar1 [, bindvar2]. . .
Description
The ScrollSelect function, like the related ScrollSelect functions (ScrollSelectNew, RowScrollSelect, and RowScrollSelectNew) reads data from database tables or views into a scroll area on the active page.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the Select rowset class method instead.
See Select.
Using ScrollSelect
ScrollSelect automatically places child rows in the target scroll area under the correct parent row in the next highest scroll area. If it cannot match a child row to a parent row an error occurs.
ScrollSelect selects rows from a table or view and adds the rows to a scroll area of a page. Let’s call the record definition of the table or view that it selects from the select record; and let’s call the record definition normally referenced by the scroll area (as specified in the page definition) the default scroll record. The select record can be the same as the default scroll record, or it can be a different record definition that has compatible fields with the default scroll record. If you define a select record that differs from the default scroll record, you can restrict the number of fields that are loaded into the component buffers by including only the fields that you actually need.
ScrollSelect accepts an SQL string that can contain a WHERE clause restricting the number of rows selected into the scroll area. The SQL string can also contain an ORDER BY clause to sort the rows.
ScrollSelect functions generate a SQL SELECT statement at runtime, based on the fields in the select record and WHERE clause passed to them in the function call. This gives ScrollSelect functions a significant advantage over SQLExec: they enable you to change the structure of the select record without affecting the PeopleCode, unless the field affected is referred to in the WHERE clause string. This can make the application easier to maintain.
Often, ScrollSelect is used to select rows into a work scroll, which is sometimes hidden using HideScroll. A work scroll is a scroll in which the No Auto Select option is selected on the record definition in PeopleSoft Application Designer so that PeopleTools does not automatically populate the scroll at page startup. You can right-click on the scroll or grid then select the scroll’s No Auto Select attribute check box in the record property dialog box.
Depending on how you intend the scroll to be used by the end-user, you may also want to select No Auto Update to prevent database updates, and prevent row insertions or deletions in the scroll area by selecting No Row Insert or No Row Update.
To call ScrollSelect at page startup, place the function call in the RowInit event of a key field on the parent scroll record. For example, if you want to fill scroll level one, place the call to ScrollSelect in the RowInit event of a field on level zero.
Parameters
|
levelnum |
Specifies the level of the scroll level to be filled (the target scroll area. The value can be 1, 2, or 3. |
|
target_recname |
Specifies a record identifying the target scroll, into which the selected rows are read. If target_recname is on scroll level 2, it must be proceeded by a RECORD. level1_recname. If it is on level 3, you must specify both RECORD. level1_recname and RECORD. level2_recname. |
|
RECORD. sel_recname |
Specifies the select record. The selname record must be defined in PeopleSoft Application Designer and SQL created (using Build, Project) as a table or a view, unless sel_recname and target_recname are the same. The sel_recname record can contain fewer fields target_recname, although it must contain any key fields to maintain dependencies with other page records. This enables you to limit the amount of data read into the component buffers. |
|
sqlstr |
Contains a WHERE clause to restrict the rows selected from sel_recname and/or an ORDER BY clause to sort the rows. The WHERE clause can contain the PeopleSoft meta-SQL functions such as %Datein or %CurrentDateIn. It can also contain inline bind variables. |
|
bindvars |
A list of bind variables to be substituted in the WHERE clause. The same restrictions that exist for SQLExec exist for these variables. |
|
turbo |
Setting this Boolean parameter to True turns on Turbo ScrollSelect. This improves the performance of ScrollSelect verbs by as much as 300%, but should be implemented with caution on existing applications, which may depend on the behavior of ScrollSelect without Turbo. |
Returns
The number of rows read (optional.) This counts only lines read into the specified scroll. It does not include any additional rows read into autoselect child scrolls of the scroll.
Example
This example uses WHERE clauses to reset the rows in two scroll areas:
&FIELD_CNT = ActiveRowCount(DBFIELD_VW.FIELDNAME); For &I = 1 to &FIELD_CNT; If RecordChanged(DBFIELD_VW.FIELDNAME, &I, DBFIELD_LANG_VW.FIELDNAME, 1) Then &FIELDNAME = FetchValue(DBFIELD_VW.FIELDNAME, &I); &RET = WinMessage("Descriptions for " | &FIELDNAME | " have been changed. Discard changes?", 289, "DBField Changed!"); If &RET = 2 Then /* Cancel selected */ Exit; End-if; End-if; End-for; /* Now throw away all rows */ ScrollFlush(RECORD.DBFIELD_VW); /* Fill in new values */ &FIELDSEL = "where FIELDNAME like '" | FIELDNAME | "%'"; &ORDERBY = " order by FIELDNAME"; &QTY1 = ScrollSelect(1, RECORD.DBFIELD_VW, RECORD.DBFIELD_VW, &FIELDSEL | &ORDERBY); &QTY2 = ScrollSelect(2, RECORD.DBFIELD_VW, RECORD.DBFIELD_LANG_VW, RECORD.DBFIELD_LANG_VW, &FIELDSEL | " and LANGUAGE_CD = :1" | &ORDERBY, DBFIELD_SRCH.LANGUAGE_CD);
See Also
RowScrollSelect, RowScrollSelectNew, ScrollFlush, ScrollSelectNew, SQLExec.

 ScrollSelectNew
ScrollSelectNewSyntax
ScrollSelectNew(levelnum, [RECORD.level1_recname, [RECORD.level2_recname, ]] RECORD.target_recname, RECORD.sel_recname [, sqlstr [, bindvars]] [, turbo])
and where bindvars is an arbitrary-length list of bind variables in the form:
bindvar1 [, bindvar2]. . .
Description
The ScrollSelectNew function is similar to ScrollSelect, except that all rows read into the work scroll are marked new so they are automatically inserted into the database at Save time.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the SelectNew rowset class method instead.
This capability can be used, for example, to insert new rows into the database by selecting data using a view of columns from other database tables.
See Also
Parameters
|
levelnum |
Specifies the level of the scroll level to be filled (the target scroll area. The value can be 1, 2, or 3. |
|
target_recname |
Specifies a record identifying the target scroll, into which the selected rows are read. If target_recname is on scroll level 2, it must be proceeded by a RECORD. level1_recname. If it is on level 3, you must specify both RECORD. level1_recname and RECORD. level2_recname. |
|
RECORD. sel_recname |
Specifies the select record. The selname record must be defined in PeopleSoft Application Designer and SQL created as a table or a view (using Build, Project), unless sel_recname and target_recname are the same. The sel_recname record can contain fewer fields target_recname, although it must contain any key fields to maintain dependencies with other records on the page. This enables you to limit the amount of data read into the component buffers. |
|
sqlstr |
Contains a WHERE clause to restrict the rows selected from sel_recname and/or an ORDER BY clause to sort the rows. The WHERE clause may contain the PeopleSoft SQL platform functions that are used for SQLExec processing, such as %Datein or %Substring. |
|
bindvars |
A list of bind variables to be substituted in the WHERE clause. The same restrictions that exist for SQLExec exist for these variables. |
|
turbo |
Setting this Boolean parameter to True turns on Turbo ScrollSelect. This improves the performance of ScrollSelect verbs by as much as 300%, but should be implemented with caution on existing applications. |
Returns
The number of rows read (optional.) This counts only lines read into the specified scroll. It does not include any additional rows read into autoselect child scrolls of the scroll.
Example
The following statement selects rows from DATA2 and reads them into scroll level one on the page. If the end-user saves the page, these rows will be inserted into DATA1:
&QTY = ScrollSelectNew(1, RECORD.DATA1, RECORD.DATA2, "Where SETID = :1 and CUST_ID = :2", CUSTOMER.SETID, CUSTOMER.CUST_ID);
See Also
RowScrollSelect, RowScrollSelectNew, ScrollSelect, ScrollFlush, SQLExec.

 Second
SecondSyntax
Second(timevalue)
Description
Use the Second function to extract the seconds component of a Time value.
Parameters
|
timevalue |
A Time value from which to extract seconds. |
Returns
Returns a Number equal to the seconds part of timevalue.
Example
Assume that &TIMEOUT contains Time value of 16:48:21. The following would set &SECS to 21:
&SECS = Second(&TIMEOUT);
See Also

 SendMail
SendMailSyntax
SendMail(flags, recipients, CCs, BCCs, subject, text, [, attachment_filenames][, attachment_titles] [, Mail_From] [,mail_sep] [, Content_Type] [,Reply_To] [,Sender])
Description
Use the SendMail function to send an email message from a PeopleSoft page. The APIs that support these subsystems must be present on the system for the function to work.
Note. The code that actually calls SendMail determines the run location, not the originating code.
The function sends a message using standard mail options, including recipient, CC, BCC, subject, and the text of the note. The message can include attached files, for which you supply fully qualified file names (that is, file names with paths) and titles (which appear in place of the fully qualified filename in the message). In addition, you can specify a Mail_From , which identifies the source email address. You can also use the Reply_To parameter to specify the email address to be used by the recipient for replying, which should be different than the Mail_From address.
The flags parameter of this function and its return codes are platform dependent: the SMTP mail API ignores any additional flags. For this reason, SendMail should be used only in customizations that run on a known platform, if it is used at all. The preferred, platform-independent method for sending email from PeopleCode is to define an email routing as part of a business event, then trigger the business event using the TriggerBusinessEvent function.
For workflow, in the activity email routing, you can specify the field map for Reply_To and Sender.
See Also
Parameters
|
flags |
An integer value passed directly to the mail system API to control mail system options. The value passed in this parameter is platform-dependent. The SMTP mail API ignores this parameter. |
|
recipients |
A string consisting of a semicolon-separated list of email addresses containing the names of the message’s primary recipients. |
|
CCs |
A string consisting of a semicolon-separated list of email addresses that are sent copies of the message. |
|
BCCs |
A string consisting of a semicolon-separated list of email addresses that are sent copies of the message. These recipients won’t appear on the message list. |
|
subject |
A string containing the text that appears in the message’s Subject field. |
|
text |
The text of the message. |
|
attachment_filenames |
A string consisting of a semicolon-separated list of fully qualified filenames, containing the complete path to the file and the filename itself. |
|
attachment_titles |
Another semicolon-separated list containing titles for each of the files provided in the attachment_filenames parameter. The titles appear near the attachment icons in place of the fully qualified filename. |
|
Mail_From |
A string used to populate the 'reply-to' field. If this parameter isn't specified, the sender address from application server configuration file is used. |
|
Mail_Sep |
Specify the delimiter to be used to separate one email address from another. The default value is a semicolon (;). |
|
Content_Type |
Specify the content type of the email as a string. The default value is plain text. If you want to specify HTML, you should use the following:
|
|
Reply_To |
Specify the email address that the receiver should use when replying to this email instead of the Mail_From value. |
|
Sender |
Specifies who the email is from, as a string. This may be different than the values specified for Mail_From or Reply_To parameters. |
Returns
Returns a Number value, which, if not one of the following general return codes, is platform-dependent.
General Return Codes
|
Return Code |
Description |
|
0 |
No Error |
|
-1 |
No mail interface installed. |
Example
The following example sets up several variables that are then used to construct an email message that includes two attachments:
&MAIL_FLAGS = 0; &MAIL_TO = "[email protected];[email protected]"; &MAIL_CC = ""; &MAIL_BCC = "[email protected]"; &MAIL_SUBJECT = "Live long and prosper!"; &MAIL_TEXT = "Please read my attached CV. You will be amazed and hire me forthwith."; &MAIL_FILES = "c:\mydocs\resume.doc;c:\mydocs\coverlet.doc"; &MAIL_TITLES = "My CV;READ ME"; &MAIL_SENDER = "[email protected]"; &RET = SendMail(&MAIL_FLAGS, &MAIL_TO, &MAIL_CC, &MAIL_BCC, &MAIL_SUBJECT, &MAIL_TEXT, &MAIL_FILES, &MAIL_TITLES, &MAIL_SENDER); if not (&RET = 0) then WinMessage("Return status from mail = " | &RET); end-if;

 SetAuthenticationResult
SetAuthenticationResultSyntax
SetAuthenticationResult(AuthResult [, UserId] [,ResultDocument] [,PasswordExpired] [DaysLeftBeforeExpire])
Description
Use the SetAuthenticationResult function in signon PeopleCode to customize the authentication process. It enables the developer using Signon PeopleCode to implement additional authentication mechanisms beyond the basic PeopleSoft ID and Password authentication.
When PasswordExpired is True, it indicates the password is expired, the passwordexpired.html page is displayed during login when signon PeopleCode is enabled.
When DaysLeftBeforeExpire is greater than 0, and PasswordExpired is False, indicating that the password will expire in x days, the passwordwarning.html page is displayed during login when signon PeopleCode is enabled.
Note. If you set AuthResult to False, ResultDocument must be the text of an error message. This text is displayed on the signon screen.
Parameters
|
AuthResult |
Specify whether the authentication is successful. This parameter takes a Boolean value. If True is used, the end-user of the UserId specified on the Signon page is allowed access to the system. When AuthResult is True, the customer is responsible for providing a logout to the end user. They will remain logged in until a logout command is issued from the user, or the session expires. |
|
UserId |
Specify the UserId of the user signing on. The default value is the UserId entered on the signon page. This parameter takes a string value. This is the value returned by %SignonUserId |
|
ResultDocument |
When ResultDocument is blank (""), this parameter value is ignored. Otherwise, specify a message to be displayed in the signonresultdoc.html file when AuthResult is True. If AuthResult is False, the ResultDocument text value is displayed on the signon screen. If ResultDocument has a value, any values in PasswordExpired and DaysLeftBeforeExpire are ignored. |
|
PasswordExpired |
Specify if the user’s password has expired. The values are:
If this value is specified as True, the user is allowed to log in, but is able to access only a limited portion of the system: just enough to change their expired password. |
|
DaysLeftBeforeExpire |
A numeric value indicating the number of days left before the password expires. If the value is greater than 0, a warning is displayed when Authorized is True and Expired is False. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if function completed successfully, False otherwise.
Example
If updateUserProfile(%SignonUserId, %SignonUserPswd, &array_attribs) Then SetAuthenticationResult(True, &SignonUserID, "", False); End-If;
The following example is within a function used for logging onto a system:
If (AddToDateTime(&fmc_wsl_exp_date, 0, 0, 0, 0, 10, 0) >= %Datetime) Then /* WSL logon was within last x minutes, so accept WSL for PS logon */ SetAuthenticationResult( True, Upper(&userID), "", False); Else /* WSL logonn was too long ago, so request a more recent WSL logon */ SetAuthenticationResult( False, "getmorerecentcookie", "", False,7); /*displays the customized passwordwarning.html. */ End-If;
In the following example, AuthResult is True and ResultDocument is set as text to be displayed in an HTML tag.
SetAuthenticationResult( True, &USERID, "Result Doc Text", False, 0);
As part of this example, specify the following in the configuration properties:
singonresultdoc_page=signonresultdoctext.html
In signonresultdoctext.html, add a meta field as follows:
<%=resultDoc%>: <html> .... <tr><td class="PSSRCHACTION" no wrap=true><%=resultDoc%></td></tr> ..... </html>
This produces a screen shot similar to the following:
Example with Result Doc Text
See Also

 SetChannelStatus
SetChannelStatusSyntax
SetChannelStatus(ChannelName, Status)
Description
Use the SetChannelStatus to set the status of the specified channel. You could use this function to restart a channel that had been paused, or pause a running channel.
Parameters
|
ChannelName |
Specify the channel name. |
|
Status |
Specify the status you want to set the channel to. The values are:
|
Returns
A Boolean value: True if the channel status was changed successfully. False otherwise.
Example
/* User has clicked on a channel to change its status */ If CHNL_STATUS = "1" Then rem running, so pause; &status = 2; Else rem paused. So run; &status = 1; End-If; If SetChannelStatus(AMM_CHNL_SECVW.CHNLNAME, &status) Then CHNL_STATUS = String(&status); Else MessageBox(0, MsgGetText(117, 1, ""), 117, 22, ""); End-If;
See Also
Understanding PeopleSoft Integration Broker

 SetComponentChanged
SetComponentChanged
Syntax
SetComponentChanged()
Description
Use the SetComponentChanged function to set the changed flag for the component. This flag is used to determine if save processing is needed or not, when the user clicks Save, or save is triggered through DoSave PeopleCode. This flag is also used to determine if a save warning needs to be issued to the user when they leave the component.
Using SetComponentChanged causes full save processing to occur the next time a save is triggered. This includes the SaveEdit, SavePreChange, Workflow, and SavePostChange events. This function can be used to replace a workaround of changing a field to a different value then back to force save processing.
Using SetComponentChanged does not cause unchanged data to be saved. The Component Processor only saves changed data to the database. If nothing in the component has been changed, nothing is saved to the database.
After save processing has completed successfully, the flag is cleared.
Most components do not need to use this function. The changed flag is automatically set when the user changes any value in the component, as well as when PeopleCode changes a database field buffer value. This function is for certain pages that have a requirement to have save processing execute even if the user has not changed a value.
Note. Using this function causes a save warning to be issued to the user when they try to leave the component, assuming the save warning feature is enables, and the end user has not saved the component since the function was called.
Using SetComponentChanged before DoSave forces save processing to occur.
Parameters
None.
Returns
None.
See Also

 SetControlValue
SetControlValueSyntax
SetControlValue(Value, PageName, PageFieldName [, RowNumber] [, &Field])
Description
Use the SetControlValue function to set an override string on the current field so that it simulates an end-user entering data.
When a page is refreshed after a PeopleCode program completes, each field value gets set from the buffer. However, if you use this function to specify an override string for a field, the value you specify is used instead of the value in the buffer. This value is inserted directly into the control on the page, as if the end-user typed it in. The field buffer remains unchanged. All validations, FieldEdit and FieldChange PeopleCode run immediately.
This function can be used in the following scenario: Suppose you have a text field that has a menu pop-up associated with it. The end-user can use a secondary page to select an item to be used for the value. From the menu PeopleCode, you can verify that the value is valid, but the field doesn’t turn red and the end-user can leave the field. This could potential mean saving the page with bad data. You can use this function after the secondary page is dismissed. This causes the same edits to be run as if the end-user had typed in the value.
This function doesn't work for radio button or check box controls.
Considerations With Field Verification
SetControlValue only sets the value of the field. If you specify an incorrect value, SetControlValue has an error at runtime.
For example, suppose you are setting a value like "1900-01-01" into a date field that is expecting the format 01/01/1900. If the end-user entered 1900-01-01 they would get an error, so SetControlValue causes an error with this value also. You may want to use a value in the format the end-user might enter. You can get this value by using the FormattedValue method on a field. For example:
&DATE_IN_EFFECT = SF_PRDN_AREA_IT.DATE_IN_EFFECT.FormattedValue; ... SetControlValue(&DATE_IN_EFFECT, %Page, "DATE_IN_EFFECT", &OCCURSNUM);
The FormattedValue function converts the field value from the PeopleSoft representation to the representation the end-user would see and enter.
Restrictions on Use With a Component Interface
This function is ignored (has no effect) when used by a PeopleCode program that’s been called by a Component Interface.
Parameters
|
Value |
Specify an override value on the current field. This parameter takes a string value. |
|
pagename |
Specify the name of page where the field exists. |
|
pagefieldname |
Specify the page field name. This is not the name of the field. This is the name that is assigned to the field in PeopleSoft Application Designer, on the page field properties. |
|
RowNumber |
Specify the row number of the field. The default value is 1 if this parameter isn't set. |
|
&Field |
Specify an already instantiated field object referencing the field you want to override. |
Note. If you want to set an override string for a field on the level 1 scroll for a page, you don't need to specify either a row number or a field object. However, if you want to set the override string for a field on either the second or third level scroll for a page, you must specify both a row number and a field object for SetControlValue to work.
Returns
None.
Example
Declare Function item_seach PeopleCode FUNCLIB_ITEM.INV_ITEM_ID FieldFormula; &SEARCHREC = "PS_" | RECORD.MG_ITEM_OWN1_VW; item_seach("", SF_PRDN_AREA.BUSINESS_UNIT, "ITEM", &SEARCHREC, "", &INV_ITEM_ID, ""); SetControlValue(&INV_ITEM_ID);
The following example is used in the PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture:
Declare Function item_search PeopleCode FUNCLIB_ITEM.INV_ITEM_ID FieldFormula; Component string &ITEM_ID_SEARCH; &ITEMRECNAME = "PS_" | Record.MG_ITEM_PDO_VW; item_serach("", EN_PDO_WRK.BUSINESS_UNIT, "ITEM", &ITEMRECNAME, "", &INV_ITEM_ID, ""); If All(&INV_ITEM_ID) Then Evaluate &ITEM_ID_SEARCH When "F" SetControlValue(&INV_ITEM_ID, Page.EN_PDO_COPY, "FROM_ITEMID") When "T" SetControlValue(&INV_ITEM_ID, Page.EN_PDO_COPY, "TO_ITEMID") End-Evaluate; End-If;

 SetCursorPos
SetCursorPosSyntax
SetCursorPos(Page.pagename, scrollpath, target_row, [recordname.]fieldname)
where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ]] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Use the SetCursorPos to place the focus in a specific field anywhere in the current component. To transfer to a page outside the current component, use Transfer.
You can use the SetCursorPos function in combination with an Error or Warning function in SaveEdit to place the focus on the field that caused the error or warning condition. You must call SetCursorPos before an Error statement, because Error in SaveEdit terminates all save processing, including the program from which it was called.
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
Pagename |
The name of the page specified in the page definition, preceded by the keyword Page. The pagename page must be in the current component. You can also pass the %page system variable in this parameter (without the Page reserved word). |
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
[recordname .]fieldname |
Specify a field designating the record and field in the scroll where you want to place the cursor. |
|
target_row |
The row number of the row in which you want to place the cursor. |
Returns
None.
Example
The following example places the cursor in the appropriate field if a SaveEdit validation fails. Note the use of the %page system variable to get the page name. Note also that SetCursorPos is called before Error.
If None(&ITEM_FOUND) Then SetCursorPos(%Page, INV_ITEM_ID, CurrentRowNumber()); Error (MsgGet(11100, 162, "Item is not valid in the order business unit.", INV_ITEM_ID, CART_ATTRIB_INV.ORDER_BU)); End-If;
The following example is similar, but uses the Page reserved word and page name:
If %Component = COMPONENT.BUS_UNIT_TBL_GL Then SetCursorPos(PAGE.BUS_UNIT_TBL_GL1, DEFAULT_SETID, CurrentRowNumber()); End-If; Error MsgGet(9000, 165, "Default TableSet ID is a required field.");
See Also

 SetDBFieldAuxFlag
SetDBFieldAuxFlagSyntax
SetDBFieldAuxFlag(Field.FieldName, FlagNumber, Setting)
Description
Use the SetDBFieldAuxFlag function to set the auxiliary flag mask (AuxFlagMask) property for the specified field. This field indicates properties about the field.
Currently, only one flag comes preset from PeopleSoft: a 1 indicates a ChartField. If you want to associate a property with a field, you must coordinate with other developers to make certain that no one else is setting a property using the same flag number.
Use the GetAuxFlag Field method to read the current setting of the property.
If you use this function, the change is made to the database field, but it doesn't require a rebuild of the database. However, the change is not reflected in the component buffer. You must reload the component for the new setting to take place.
Considerations Using this Function
This function is intended for use during configuration time only, before active runtime usage is initiated. Using this function during active runtime is not supported. Changes to data definitions are not recognized on currently loaded component. In general, changes aren't recognized until the component is reloaded.
Warning! These operations take place in a separate transaction from the page's save status: the initiation of any of these operations immediately changes the definitions, even if the page is subsequently cancelled.
Parameters
|
Fieldname |
Specify the name of the field that you want the AuxMaskFlag property changed. This name must be prefixed by the reserved word Field. |
|
FlagNumber |
Specify the flag value, a number between 1 and 32. A 1 is a ChartField. |
|
Setting |
Specify whether this flag should be on (True) or off (False). |
Returns
A constant value. The values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
%MDA_Success |
Bulk operation completed successfully. |
|
%MDA_Failure |
Bulk operation did not complete successfully. |
|
%MDA_FieldNotFound |
The specified field was not found in the database. |
Example
&ret = SetDBFieldAuxFlag(Field.OrgId, 1, True); If (&ret = %MDA_Success) Then MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "SetDBFieldAuxFlag succeeded"); Else MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "SetDBFieldAuxFlag failed"); End-If;
See Also

 SetDBFieldCharDefn
SetDBFieldCharDefnSyntax
SetDBFieldCharDefn(Field.FieldName, Length [, FormatFamily])
Description
Use the SetDBFieldCharDefn function to create a field definition of type character, with the indicated name, length, and format family.
Note. After using this function, you should use the SetDBFieldLabel function to define the label for the new field.
Considerations Using this Function
This function is intended for use during configuration time only, before active runtime usage is initiated. Using this function during active runtime is not supported. Changes to data definitions are not recognized on currently loaded component. In general, changes aren't recognized until the component is reloaded.
Warning! These operations take place in a separate transaction from the page's save status: the initiation of any of these operations immediately changes the definitions, even if the page is subsequently cancelled.
Parameters
|
Fieldname |
Specify the name of the new field that you want to create. This name must be prefixed by the reserved word Field. |
|
Length |
Specify the length of the new field as a number. |
|
FormatFamily |
Specify the format family of the new field. This parameter is optional: the default value is upper case. The valid values are:
|
Returns
A constant value. The values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
%MDA_Success |
Bulk operation completed successfully. |
|
%MDA_Failure |
Bulk operation did not complete successfully. |
|
%MDA_Duplicate |
The field specified by FieldName already exists. |
|
%MDA_FieldFmtLength |
The specified length conflicts with the specified format family and was overwritten when the field was created. |
Example
&ret = SetDBFieldCharDefn(Field.OrgId, 10, %FormatFamilyType_MixedCase); If (&ret = %MDA_Success) Then MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "SetDBFieldCharDefn succeeded"); Else MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "SetDBFieldCharDefn failed"); End-If;
You can also use this function with de-referenced parameters, as follows:
&ret = SetDBFieldCharDefn(@("FIELD." | FS_CF_UPD_AET.FIELDNAME), FS_CF_UPD_AET.NEW_CF_LENGTH, %FormatFamilyType_MixedCase);
The following example adds a new character field:
&cf = "CF1"; &len = 10; &frmt = %FormatFamilyType_Upper; &fld = "FIELD." | &cf; &ret = SetDBFieldCharDefn(@(&fld), &len, &frmt); If (&ret = 0) Then MessageBox(0, "SetDBFieldCharDefn", 0, 0, "Succeeded"); Else MessageBox(0, "SetDBFieldCharDefn", 0, 0, "Failed"); End-If;
See Also

 SetDBFieldFormat
SetDBFieldFormatSyntax
SetDBFieldFormat(Field.FieldName, FormatFamily [, FamilyName, DisplayName])
Description
Use the SetDBFieldFormat function to change the format family for a field.
Use the StoredFormat Field property to determine the existing format family for a field.
If you only want to change the display format of a single field at runtime, and not change the database field, use the DisplayFormat Field property.
Note. This function only works with character fields.
Considerations Using this Function
This function is intended for use during configuration time only, before active runtime usage is initiated. Using this function during active runtime is not supported. Changes to data definitions are not recognized on currently loaded component. In general, changes aren't recognized until the component is reloaded.
Warning! These operations take place in a separate transaction from the page's save status: the initiation of any of these operations immediately changes the definitions, even if the page is subsequently cancelled.
Parameters
|
FieldName |
Specify the name of the field that you want to modify. This name must be prefixed by the reserved word Field. |
|
FormatFamily |
Specify the new format family of the field. The valid values are:
|
|
FamilyName |
Specify a new family name. This parameter is optional, and only valid if FormatFamily is specified as custom (%FormatFamilyType_Custom). |
|
DisplayName |
Specify a new display name. This parameter is optional, and only valid if FormatFamily is specified as custom (%FormatFamilyType_Custom). |
Returns
A constant value. The values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
%MDA_Success |
Function completed successfully. |
|
%MDA_Failure |
Function didn't complete successfully. |
Example
&ret = SetDBFieldFormat(Field.OrgId, %FormatFamilyType_Custom, "Postal_Code", "Normal"); If (&ret = %MDA_Success) Then MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "SetDBFieldFormat succeeded"); Else MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "SetDBFieldFormat failed"); End-If;
See Also
SetDBFieldFormatLength, StoredFormat, DisplayFormat.

 SetDBFieldFormatLength
SetDBFieldFormatLengthSyntax
SetDBFieldFormatLength(FieldName, Length)
Description
Use the SetDBFieldFormatLength function to change the format length for a field. This length controls the maximum number of characters an end-user can type into an edit box for this character field. This can be used to limit the user without having to rebuild or alter the table.
Note. This function only works with character fields.
Considerations Using this Function
This function is intended for use during configuration time only, before active runtime usage is initiated. Using this function during active runtime is not supported. Changes to data definitions are not recognized on currently loaded component. In general, changes aren't recognized until the component is reloaded.
Warning! These operations take place in a separate transaction from the page's save status: the initiation of any of these operations immediately changes the definitions, even if the page is subsequently cancelled.
Parameters
|
FieldName |
Specify the name of the field that you want to modify. This name must be prefixed by the reserved word Field. |
|
Length |
Specify the new format length as a number. Valid values are between 1 and 254. |
Returns
A constant value. The values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
%MDA_Success |
Function completed successfully. |
|
%MDA_Failure |
Function didn't complete successfully. |
|
%MDA_FieldNotFound |
The specified field wasn't found in the database. |
|
%MDA_Unsupported |
You tried to use this function on a non character field. This function is only supported on character fields. |
Example
&ret = SetDBFieldFormatLength(FIELD.OrgId, 10); If (&ret = %MDA_success) Then MessageBox(0, "MetaData Fn Status", 0, 0, "SetDBFieldFormatLength succeeded"); Else MessageBox(0, "MetaData Fn Status", 0, 0, "SetDBFieldFormatLength failed"); End-If;
See Also
SetDBFieldFormat, FormatLength.

 SetDBFieldLabel
SetDBFieldLabelSyntax
SetDBFieldLabel(Field.FieldName, LabelID, Long, Short, Default [, LanguageID])
Description
Use the SetDBFieldLabel function to either modify an existing label, or add a new label to a field definition.
Considerations Using this Function
This function is intended for use during configuration time only, before active runtime usage is initiated. Using this function during active runtime is not supported. Changes to data definitions are not recognized on currently loaded component. In general, changes aren't recognized until the component is reloaded.
Warning! These operations take place in a separate transaction from the page's save status: the initiation of any of these operations immediately changes the definitions, even if the page is subsequently cancelled.
Parameters
|
FieldName |
Specify the name of the field that you want to modify. This name must be prefixed by the reserved word Field. |
|
LabelID |
Specify the label ID of the field label that you want to modify as a string. If the specified label ID isn't found, a new label, with the specified label ID, is created for the field. |
|
Long |
Specify the new long label for the field as a string. |
|
Short |
Specify the new short label for the field as a string. |
|
Default |
Specify whether the new label is the default label for the field. This parameter takes a Boolean value: True, set the label as the default, False, don't. |
|
LanguageID |
Specify the three character language code to use with this field. This parameter is optional. If you don't specify a language code, the language of the current user is used. |
Returns
A constant value. The values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
%MDA_Success |
Function completed successfully. |
|
%MDA_Failure |
Function didn't complete successfully. |
|
%MDA_FieldNotFound |
The specified field wasn't found. |
Example
&ret = SetDBFieldLabel(Field.OrgId, "ORGID", "Organization ID", "OrgId", TRUE); If (&ret = %MDA_Success) Then MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "SetDBFieldLabel succeeded"); Else MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "SetDBFieldLabel failed"); End-If;
See Also

 SetDBFieldLength
SetDBFieldLengthSyntax
SetDBFieldLength(Field.FieldName, Length)
Description
Use the SetDBFieldLength function to modify an existing character field to have a new length.
Note. Because using this function changes records that are used to build application tables, you must rebuild (alter) the specified project before these changes can be used.
Use the Length Field class property to find the existing length of a field.
Note. This function only works with character fields.
Considerations Using this Function
This function is intended for use during configuration time only, before active runtime usage is initiated. Using this function during active runtime is not supported. Changes to data definitions are not recognized on currently loaded component. In general, changes aren't recognized until the component is reloaded.
Warning! These operations take place in a separate transaction from the page's save status: the initiation of any of these operations immediately changes the definitions, even if the page is subsequently cancelled.
Parameters
|
FieldName |
Specify the name of the field that you want to modify. This name must be prefixed by the reserved word Field. |
|
Length |
Specify the new field length as a number between 1 and 254. |
Note. If a default has been specified for this field in any record, and the size of the default is greater than the new size, you must modify the record field separately.
Returns
A constant value. The values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
%MDA_Success |
Function completed successfully. |
|
%MDA_Failure |
Function didn't complete successfully. |
|
%MDA_Unsupported |
The specified field isn't a character field. This function is only supported for character fields. |
|
%MDA_FieldNotFound |
The specified field wasn't found. |
|
%MDA_FieldFmtLength |
The specified length isn't compatible with the current format family, or there are record field defaults greater than the specified size. |
Note. If a default has been specified for this field in any record, and the size of the default is greater than the new size, you must modify the record field separately.
Example
&ret = SetDBFieldLength(Field.OrgId, 10); If (&ret = %MDA_Success) Then MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "SetDBFieldLength succeeded"); Else MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "SetDBFieldLength failed"); End-If;
You can also use this function with de-referenced parameters, as follows:
&ret = SetDBFieldLength(@("FIELD." | FS_CF_UPD_AET.FIELDNAME), FS_CF_UPD_AET.NEW_CF_LENGTH);
See Also

 SetDBFieldNotUsed
SetDBFieldNotUsedSyntax
SetDBFieldNotUsed(Field.FieldName, NotUsed)
Description
Use the SetDBFieldNotUsed function to specify whether a database field is used as a chart field or not.
SetDBFieldNotUsed does the following for a field:
Specifies whether the field is included in the index when indexes are built for records that contain this field. The column always remains in the table associated with the record.
Specifies that the field is ignored in Query.
Specifies that the field is ignored in nVision.
In addition, fields marked as Search Keys or List Box Items in the PeopleSoft Application Designer that are set as not used do not display in search dialogs and list boxes.
Considerations Using this Function
This function is primarily intended for use during configuration time only, before active runtime usage is initiated. Using this function during active runtime is not, in general, supported. Changes to data definitions are not recognized on currently loaded component. In general, changes aren't recognized until the component is reloaded. Using this function to modify records in components that have not been loaded, and then loading those components will, while not changing indices, prevent Query and nVision from using the field, and may be used to key display of the field in pages.
Warning! These operations take place in a separate transaction from the page's save status: the initiation of any of these operations immediately changes the definitions, even if the page is subsequently cancelled.
Parameters
|
FieldName |
Specify the name of the field that you want to modify. This name must be prefixed by the reserved word Field. |
|
NotUsed |
Specify whether this field is to be used as a chart field. This parameter takes a Boolean value: True, this field is not used, False, this field is used. |
Returns
A constant value. The values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
%MDA_Success |
Function completed successfully. |
|
%MDA_Failure |
Function didn't complete successfully. |
|
%MDA_FieldNotFound |
The specified field wasn't found. |
Example
&ret = SetDBFieldNotUsed(Field.OrgId, True); If (&ret = %MDA_Success) Then MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "SetDBFieldNotUsed succeeded"); Else MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "SetDBFieldNotUsed failed"); End-If;
See Also

 SetDefault
SetDefaultSyntax
SetDefault([recordname.]fieldname)
Description
Use the SetDefault function to set a field to a null value, so that the next time default processing occurs, it is set to its default value: either a default specified in its record field definition or one set programmatically by PeopleCode located in a FieldDefault event. If neither of these defaults exist, the Component Processor leaves the field blank.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the SetDefault field class property instead.
Blank numbers correspond to zero on the database. Blank characters correspond to a space on the database. Blank dates and long characters correspond to NULL on the database. SetDefault gives each field data type its proper value.
See SetDefault.
Where to Use SetDefault
If a PeopleCode program or function executes the SetDefault built-in on a field that does not exist in the component buffer, the remainder of the program or function is skipped. In the case of a function, execution of the calling program continues with the next statement after the call to the function. However, if the program containing the SetDefault call is at the "top level", meaning that it was called directly from the component processor or application engine runtime, it exits.
Therefore, if you want to control the behavior of SetDefault, you should encapsulate any calls to this built-in function inside your own functions. This enables your overall programs to continue, whether or not the SetDefault succeeds.
Parameters
|
[recordname.]fieldname |
Specify a field designating the fields that you want to set to its default value. |
Returns
Optionally returns a Boolean value indicating whether the function executed successfully.
Example
This example resets the PROVIDER to its null value. This field is reset to its default value when default processing is next performed:
If COVERAGE_ELECT = "W" Then SetDefault(PROVIDER); End-if;
See Also
SetDefaultAll, SetDefaultNext, SetDefaultPrior.

 SetDefaultAll
SetDefaultAllSyntax
SetDefaultAll([recordname.]fieldname)
Description
Use the SetDefaultAll function to set all occurrences of the specified recordname.fieldname within a scroll to a blank value, so that the next time default processing is run these fields are set to their default value, as specified by the record definition, or one set programmatically by PeopleCode located in a FieldDefault event. If neither of these defaults exist, the Component Processor leaves the field blank.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the SetDefault rowset method instead.
See Also
Example
The following example sets the fields TO_CUR and CUR_EXCHNG_RT to their default values on every row of the scroll area where the PeopleCode is run:
SetDefaultAll(TO_CUR); SetDefaultAll(CUR_EXCHNG_RT);
See Also
SetDefault, SetDefaultNext, SetDefaultNextRel, SetDefaultPrior, SetDefaultPriorRel.

 SetDefaultNext
SetDefaultNextSyntax
SetDefaultNext([recordname.]fieldname)
Description
Use the SetDefaultNext function to locate the next occurrence of the recordname.fieldname with the next effective date (and effective-sequence number if specified) and set the field to a blank value, so that the next time default processing is run this field will be set to its default value, as specified by the record definition, or one set programmatically by PeopleCode located in a FieldDefault event. If neither of these defaults exist, the Component Processor leaves the field blank.
SetDefaultNext is typically used to reset values within a scroll which are calculated within default PeopleCode based on a next value.
This function is valid only for effective-dated records. If a next record does not exist, then the statement is skipped.
See Also
SetDefaultAll, SetDefaultNextRel, SetDefaultPrior, SetDefaultPriorRel.

 SetDefaultNextRel
SetDefaultNextRelSyntax
SetDefaultNextRel(search_field, default_field)
Description
Use the SetDefaultNextRel function to locate the next occurrence of the search_fieldwith the next effective date (and effective-sequence number if the record contains an effective-sequence number), then set the value of the specified default_fieldcorresponding to the search_field to a blank value, so that the next time default processing is run this field will be set to its default value, as specified by the record definition, or one set programmatically by PeopleCode located in a FieldDefault event. If neither of these defaults exist, the Component Processor leaves the field blank.
This function is valid only for effective-dated records. If a next record does not exist, then the statement is skipped.
See Also
SetDefault, SetDefaultAll, SetDefaultPrior, SetDefaultPriorRel.

 SetDefaultPrior
SetDefaultPriorSyntax
SetDefaultPrior([recordname.]fieldname)
Description
Use the SetDefaultPrior function to locate the prior occurrence of the recordname.fieldname with the prior effective date (and effective-sequence number if specified), then set the field to a blank value, so that the next time default processing is run this field will be set to its default value, as specified by the record definition, or one set programmatically by PeopleCode located in a FieldDefault event. If neither of these defaults exist, the Component Processor leaves the field blank.
SetDefaultPrior is typically used to reset values within a scroll which are calculated within FieldDefault PeopleCode based on a next value.
This function is valid only for effective-dated records. If a prior record does not exist, then the statement is skipped.
See Also
SetDefault, SetDefaultAll, SetDefaultNext, SetDefaultNextRel, SetDefaultPriorRel.

 SetDefaultPriorRel
SetDefaultPriorRelSyntax
SetDefaultPriorRel(search_field, default_field)
Description
Use the SetDefaultPriorRel function to locate the prior occurrence of the search_field with the prior effective date (and effective sequence-number if the record contains an effective-equence number) and then sets the specified default_field to a blank value, so that the next time default processing is run this field will be set to its default value, as specified by the record definition, or one set programmatically by PeopleCode located in a FieldDefault event. If neither of these defaults exist, the Component Processor leaves the field blank.
This function is valid only for effective-dated records. If a next record does not exist, then the statement is skipped.
See Also
SetDefault, SetDefaultAll, SetDefaultNext, SetDefaultNextRel, SetDefaultPrior.

 SetDisplayFormat
SetDisplayFormatSyntax
SetDisplayFormat(scrollpath, target_row, [recordname.]fieldname, display_format_name)
where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ]] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Usethe SetDisplayFormat function to change the display format of Custom Defined Fields at runtime. For instance, you may want to update a custom numeric display to reveal more decimal points.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the DisplayFormat field property instead.
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
target_row |
The row number of the target row. |
|
[recordname .]fieldname |
The name of the field to change. The field can be on scroll level one, two, or three of the active page. The recordname prefix is required if the call to SetDisplayFormat is in a record definition other than recordname. |
|
display_format_name |
The name of the custom display format specified in the field definition. |
Returns
Returns a Boolean value indicating whether the function executed successfully. The return value is not optional.
See Also

 SetLabel
SetLabelSyntax
SetLabel(scrollpath, target_row, [recordname.]fieldname, new_label_text)
Where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ]] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Use the SetLabel function to change the label text of a page field or grid column heading.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the Label field property instead.
You can't use this function to set labels longer than 100 characters. If you try to set a label of more than 100 characters, the label is truncated to 100 characters.
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
target_row |
The row number of the target row. |
|
[recordname .]fieldname |
The name of the field with the associated label text. The field can be on scroll level one, two, or three of the active page. The recordname prefix is required if the function call is in a record definition other than recordname. |
|
new_label_text |
A String value specifying the new value for the field or grid column label. |
Returns
Optionally returns a Boolean value indicating whether the function completed successfully.
Example
If training_loc = "HAW" then SetLabel(voucher_tbl.training_loc, "Hawaii Training Center"); End-if;

 SetLanguage
SetLanguageSyntax
SetLanguage(language_code)
Description
Use the SetLanguage function to set the end-user's current language preference to the specified language_code. language_code must be a valid translate value for the field LANGUAGE_CD. SetLanguage returns True if it is successful, and it returns False if it fails or an invalid value was passed. The new language preference is temporary, remaining in effect only until the user logs off, or until another call is made to SetLanguage.
Note. SetLanguage does not work in Signon PeopleCode, or with asynchronous messages.
Considerations Using SetLanguage With %Language
The value of %Language depends on the type of application:
For online applications, %Language is the language code that the current component is using.
For non-online applications (such as in an application engine program), %Language is the language code of the user based on their language preference in their User Profile.
SetLanguage changes the default language for the current session only. The language change does not take effect until the component buffer is flushed and repopulated. For example, transferring to a new component causes the buffer to be flushed.
%Language reflects the value using SetLanguage after the function is executed.
SetLanguage changes the current user interface and data language simultaneously. If the Multi Language Entry personalization option is enabled, users can change the data language independently from the user interface language. There is no way to change the data language from PeopleCode without also changing the user interface language using SetLanguage.
Parameters
|
language_code |
A valid language code, stored in the Translate table for the LANGUAGE_CD field. |
Returns
Optionally returns a Boolean value indicating whether the function executed successfully. Returns False if an invalid language code is passed.
Example
The following example switches the language code and displays a message informing the end-user of the change:
If SetLanguage(LANGUAGE_CD) Then WinMessage(MsgGet(102, 5, "Language preference changed to ", LANGUAGE_CD)); Else WinMessage(MsgGet(102, 6, "Error in setting language. Language is currently %1", %Language)); End-if;
See Also

 SetMessageStatus
SetMessageStatus
Syntax
SetMessageStatus(Message.MessageName, Status)
Description
Use the SetMessageStatus function to specify whether a message is active or inactive.
Parameters
|
MessageName |
Specify the name of the message definition that you want to change the status for. Prefix this name with the reserved word Message. |
|
Status |
Specify the status for the message. Valid values are:
|
Returns
A Boolean value: true if the status is set correctly, false otherwise.
See Also
Configuring Message Definition Properties

 SetNextPanel
SetNextPanel
Syntax
SetNextPanel(panelname)
Description
Use the SetNextPanel to specify the panel name to which the user will be transferred when selecting the NextPanel (F6) function or specifying it with the PeopleCode TransferPage function.
Note. The SetNextPanel function is supported for compatibility with previous releases of PeopleTools. New applications should use the SetNextPage function instead.
See Also

 SetNextPage
SetNextPageSyntax
SetNextPage(pagename)
Description
Use the SetNextPage function to specify the page name to which the user is transferred when selecting the NextPage (ALT+6 and ENTER) function or specifying it with the PeopleCode TransferPage function.
SetNextPage validates that pagename is listed on current menu. This selection is cleared when the user transfers to a new page.
Parameters
|
pagename |
A String equal to the name of the page as specified in the page definition. |
Returns
Optionally returns a Boolean value indicating whether the function executed successfully.
Example
See AddKeyListItem.
ClearKeyListItem( ); AddKeyListItem(OPRID, OPRID); AddKeyListItem(REQUEST_ID, REQUEST_ID); SetNextPage("PAGE_2"); DoSave( ); TransferPage( );
The following example sets up and transfers the user to page JOB_DATA.
If SetNextPage(PAGE.JOB_DATA) Then TransferPage( ); End-if;
See Also

 SetPageFieldPageFieldName
SetPageFieldPageFieldNameSyntax
SetPageFieldPageFieldName(Page.PageName, Record.RecordName, Field.FieldName, PageFieldName)
Description
Use the SetPageFieldPageFieldName function to add or change a page field name for a field. The page field name is set on the General tab of the page field properties. Changing a name to itself is not supported.
The first field on the page with the specified record name and field name is the field that's changed.
Considerations Using this Function
This function is intended for use during configuration time only, before active runtime usage is initiated. Using this function during active runtime is not supported. Changes to data definitions are not recognized on currently loaded component. In general, changes aren't recognized until the component is reloaded.
Warning! These operations take place in a separate transaction from the page's save status: the initiation of any of these operations immediately changes the definitions, even if the page is subsequently cancelled.
Parameters
|
PageName |
Specify the page containing the field you want to change. This name must be prefixed by the reserved word Page. |
|
RecordName |
Specify the record containing the field you want to change. This name must be prefixed by the reserved word Record. |
|
FieldName |
Specify the name of the field that you want to modify. This name must be prefixed by the reserved word Field. |
|
PageFieldName |
Specify the page field name that you want associated with the page field as a string. |
Returns
A constant value. The values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
%MDA_Success |
Function completed successfully. |
|
%MDA_Failure |
Function didn't complete successfully. |
|
%MDA_PageNotFound |
The specified page wasn't found. |
|
%MDA_PageFieldNotFound |
The specified field wasn't found on the specified page. |
|
%MDA_Duplicate |
A second field by the same name was found on the page. Only the first page field name was changed. |
Example
The following example adds a page field name to a page field.
&ret = SetPageFieldPageFieldName(Page.ABSENCE_HIST, Record.ABSENCE_HIST, Field.EMPLID, "EMPLID")
The following example adds a page field name to a page field using dereferenced parameters.
&Pnl = "Page." | "ABSENCE_HIST"; &Rec = "Record." | "ABSENCE_HIST"; &Field = "Field." | "EMPLID"; &Name = "EMPLID" &ret = SetPageFieldPageFieldName(@(&Pnl), @(&Rec), @(&Field), &Name);
See Also

 SetPasswordExpired
SetPasswordExpiredSyntax
SetPasswordExpired(NewValue)
Description
Use the SetPasswordExpired function to set the password expired status for the current user. When the user's password expired flag is set to True, they can only access the page that allows them to change their password. The function returns the old value, that is, the value that represented the status of the flag before it was set to NewValue.
Parameters
|
NewValue |
Specify a new value for the user's password expired flag. This parameter takes a Boolean value |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if you've set the password expire flag to False, False if you've set the password expire flag to True.
Example
If %PasswordExpired Then &NewValue = SetPasswordExpired(True); End-If;
See Also
Understanding PeopleSoft Security

 SetPostReport
SetPostReportSyntax
SetPostReport()
Description
Use the SetPostReport function to create a reference to a PostReport object. After you’ve created this object, you can assign values to its properties, then use the Put method to initiate the posting of the files to the Report Repository.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A reference to a PostReport object.
See Also

 SetRecFieldEditTable
SetRecFieldEditTableSyntax
SetRecFieldEditTable(Record.RecordName, Field.FieldName, EditTable [, TableEditType])
Description
Use the SetRecFieldEditTable function to set the edit table value for a record field. This overwrites the value for the edit table for the record field. Use the SetEditTable Record method to just set the edit table value at runtime.
If you specify a null value for EditTable, and no value is specified for TableEditType, the table edit flag is turned off, that is, no prompt table is set for the record field.
Considerations Using this Function
This function is intended for use during configuration time only, before active runtime usage is initiated. Using this function during active runtime is not supported. Changes to data definitions are not recognized on currently loaded component. In general, changes aren't recognized until the component is reloaded.
Warning! These operations take place in a separate transaction from the page's save status: the initiation of any of these operations immediately changes the definitions, even if the page is subsequently cancelled.
Parameters
|
RecordName |
Specify the record containing the field you want to change. This name must be prefixed by the reserved word Record. |
|
FieldName |
Specify the name of the field that you want to modify. This name must be prefixed by the reserved word Field. |
|
EditTable |
Specify the name of the edit table record. This name must be prefixed by the reserved word Record. If you don't want to specify a record name, specify Record."". |
|
TableEditType |
Specify the type of edit table record to be associated with the record field. If you specify a value for EditTable (and not a null value) this parameter is required. You can specify either a constant or numeric value for this parameter. Valid values are: |
|
Constant Value |
Numeric Value |
Used for which types of fields |
|
%EditTableType_NoEdit |
0 |
char, num, date, time, datetime |
|
%EditTableType_Prompt |
1 |
char, num, date, time datetime |
|
%EditTableType_YesNo |
2 |
char |
|
%EditTableType_Translate |
3 |
char fields with length 4 or less only |
|
%EditTableType_OneZero |
4 |
number fields only |
Returns
A constant value. The values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
%MDA_Success |
Function completed successfully. |
|
%MDA_Failure |
Function didn't complete successfully. |
|
%MDA_RecordNotFound |
The specified record wasn't found. |
|
%MDA_RecFieldNotFound |
The specified field wasn't found on the record. |
Example
&ret = SetRecFieldEditTable(RECORD.AbsHist, Field.OrgId, RECORD.EmplId_Tbl, %EditTableType_Prompt); If (&ret = %MDA_Success) Then MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "SetRecFieldEditTable succeeded"); Else MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "SetRecFieldEditTable failed"); End-If;

 SetRecFieldKey
SetRecFieldKeySyntax
SetRecFieldKey(Record.RecordName, Field.FieldName, Key)
Description
Use the SetRecFieldKey function to specify whether a field on a record is a key field or not.
Use the IsKey field class property to determine whether or not the field is already a key.
Note. Because performing this operation changes records, you must subsequently rebuild the project (alter tables).
Considerations Using this Function
This function is intended for use during configuration time only, before active runtime usage is initiated. Using this function during active runtime is not supported. Changes to data definitions are not recognized on currently loaded component. In general, changes aren't recognized until the component is reloaded.
Warning! These operations take place in a separate transaction from the page's save status: the initiation of any of these operations immediately changes the definitions, even if the page is subsequently cancelled.
Parameters
|
RecordName |
Specify the record containing the field you want to change. This name must be prefixed by the reserved word Record. |
|
FieldName |
Specify the name of the field that you want to modify. This name must be prefixed by the reserved word Field. |
|
Key |
Specify whether the field is a key or not. This parameter takes a Boolean value: True, the field is a key field, False, it isn't. |
Returns
A constant value. The values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
%MDA_Success |
Function completed successfully. |
|
%MDA_Failure |
Function didn't complete successfully. |
|
%MDA_RecordNotFound |
The specified record wasn't found. |
|
%MDA_RecFieldNotFound |
The specified field wasn't found on the record. |
Example
&ret = SetRecFieldKey(RECORD.AbsHist, Field.OrgId, True); If (&ret = %MDA_Success) Then MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "SetRecFieldKey succeeded"); Else MessageBox(0, "Metadata Fn Status", 0, 0, "SetRecFieldKey failed"); End-If;
See Also

 SetReEdit
SetReEditSyntax
SetReEdit(reedit_on)
Description
Use the SetReEdit to switch re-edit mode on and off. When re-edit mode is on, definitional edits (such as translate table and prompt table edits), as well as FieldEdit PeopleCode, are run on each editable field in the component when the component is saved. If an error is found, the component data is not saved. SetReEdit can be called at any time during the life of the component before the SaveEdit event fires, and would typically be called in RowInit when other page settings are being initialized. When a component is started, re-edit mode is off by default.
SetReEdit is used primarily in financial applications, where transactions are sometimes brought into the database by non-online processes. When re-edit mode is on, the values read in during these transactions can be validated by simply bringing them up in the page and saving. Any errors are then reported, as if the end-user had entered all of the data online.
Parameters
|
reedit_on |
A Boolean value specifying whether to switch re-edit mode on or off. True turns re-edit mode on, False turns re-edit mode off. |
Example
This example is used in RowInit PeopleCode to initialize component settings. After re-edit mode is on, field-level edits are re-applied when the component is saved.
SetReEdit(True);

 SetSearchDefault
SetSearchDefaultSyntax
SetSearchDefault([recordname.]fieldname)
Description
Use the SetSearchDefault function to set system defaults (default values set in record field definitions) for the specified field on search dialog boxes. It does not cause the FieldDefault event to fire.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the SearchDefault field property instead.
The system default occurs only once, when the search dialog box first starts, immediately after SearchInit PeopleCode. If the end-user subsequently blanks out a field, the field is not reset to the default value. The related function ClearSearchDefault disables default processing for the specified field. SetSearchDefault is effective only when used in SearchInit PeopleCode programs.
See Also
Parameters
|
[recordname .]fieldname |
The name of the target field, a search or alternate search key that is about to appear in the search dialog box. The recordname prefix is required if the call to SetSearchDefault is in a record definition other than recordname. |
Example
This example, from SearchInit PeopleCode turns on edits and defaults for the SETID field in the search dialog box:
SetSearchEdit(SETID); SetSearchDefault(SETID);
See Also
ClearSearchDefault, ClearSearchEdit, SetSearchDialogBehavior, SetSearchEdit.
Search Processing in Update Modes

 SetSearchDialogBehavior
SetSearchDialogBehaviorSyntax
SetSearchDialogBehavior(force_or_skip)
Description
Use the SetSearchDialogBehavior function in SearchInit PeopleCode to set the behavior of search and add dialog boxes before a page is displayed, overriding the default behavior. There are two dialog behavior settings: skip if possible (0) and force display (1).
Skip if possible means that the dialog box is skipped if all of the following are true:
All required keys have been provided (either by system defaults or by PeopleCode).
If this an Add dialog box, then no duplicate key error results from the provided keys; if this error occurs, the processing resets to the default behavior.
If this is a Search dialog box, then at least one row is returned based on the provided keys.
Force display means that the dialog box displays even if all required keys have been provided.
The default behavior of the search and add dialog boxes is force display.
Note. SetSearchDialogBehavior can only be used in SearchInit PeopleCode.
Parameters
|
force_or_skip |
A Number equal to one of the following values:
|
Returns
None.
Example
The following function call, which must occur in SearchInit PeopleCode, sets the dialog behavior to skip if possible.
SetSearchDialogBehavior(0);
See Also
SetSearchDefault, SetSearchEdit, ClearSearchEdit, ClearSearchDefault, IsUserInRole.
Search Processing in Update Modes

 SetSearchEdit
SetSearchEditSyntax
SetSearchEdit([recordname.]fieldname)
Description
Use the SetSearchEdit function to enable system edits (edits specified in the record field definition) for the specified [recordname.]fieldname, for the life of the search dialog box, or until the ClearSearchEdit function is called with that same field.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the SearchEdit field property instead.
See SearchEdit.
Using SetSearchEdit
In the Add mode search dialog, the following edits are performed when the end-user clicks the Add button. In any other mode, the following edits are performed when the end-user clicks the Search button:
Formatting
Required Field
Yes/No Table
Translate Table
Prompt Table
SetSearchEdit does not cause the FieldEdit, FieldChange, or SaveEdit PeopleCode events to fire during the search dialog.
You might use SetSearchEdit to control access to the system. For example, you can apply this function to the SETID field of a dialog box and require the end-user to enter a valid SETID.
If you use this function in the SearchInit event, the search page options are limited to the "=" and "IN" operators.
Parameters
|
fieldname |
The name of the search dialog field on which to enable field edits. |
Returns
Returns a Boolean value indicating whether the function executed successfully.
Example
This example turns on edits and system defaults for the SETID field in the search dialog box:
SetSearchEdit(SETID); SetSearchDefault(SETID);
See Also
ClearSearchEdit, ClearSearchDefault, SetSearchDefault, SetSearchDialogBehavior.
Search Processing in Update Modes

 SetTempTableInstance
SetTempTableInstanceSyntax
SetTempTableInstance(instance_number)
Description
Use the SetTempTableInstance function to set the default temp table instance to the specified number for the processing of temporary tables. This default is used by all %Table meta-SQL references to temporary tables, and by all SQL operations. Generally, you use this function only when you’re trying to use any of the ScrollSelect functions, the Rowset class Select or SelectAll methods, the record class SQL methods (SelectByKey, Insert, and so on.), or any of the meta-SQL statements that use %Table (%InsertSelect, %SelectAll, %Delete, and so on.) Generally, %Table should be used to override the default.
If you use this built-in within an Application Engine program, and the program uses a process-level instance on the request, the old instance value must be saved, then restored after you’re finished using the new instance.
If you pass a zero for instance_number, the Fill method uses the physical table instance with no table append, for example, if the temporary table record is FI_INSTR_T, the physical table used is PS_FI_INSTR_T.
Parameters
|
instance_number |
Specify the instance number for the temporary tables. |
Returns
Existing (or previous) instance number.
Example
To avoid interfering with other uses of temporary tables, you should only set the temporary table instance for your process, then set it back to the default. For example:
/* Set temp table instance */ &PrevInstNum = SetTempTableInstance(&NewInstNum); /* use the temporary table */ . . . /* Restore the temp table instance */ SetTempTableInstance(&PrevInstNum);
See Also

 SetTracePC
SetTracePCSyntax
SetTracePC(n)
Description
Use the SetTracePC function to control Trace PeopleCode settings programmatically. This is useful if you want to isolate and debug a single program or part of a program.
Note. If you’re using an API with the Session class, use the Trace Setting class properties instead of this function.
You can set options prior to starting a PeopleTools session using the Trace tab of PeopleSoft Configuration Manager.
Trace PeopleCode creates and writes data to a trace file that it shares with Trace SQL; Trace SQL and Trace PeopleCode information are both output to the file in the order of execution. The trace file uses a file name and location specified in the Trace page of PeopleSoft Configuration Manager. If no trace file is specified in PeopleSoft Configuration Manager, the file is set by default to DBG1.TMP in your Windows Temp directory. If you specify only a file name, and no directory is specified, the file is written to the directory you’re running Tools from. This file is cleared each time you log on and can be opened in a text editor while you are in a PeopleTools session, so if you want to save it, you must print it or copy it from your text editor.
Trace timings are given in the elapsed time in seconds, but reported in microseconds and include CPU time and "cycles". The CPU time measurement, depending on platform, may not be very precise. The "cycles" is a measure of how much PeopleCode the program is executing. It counts loops around the PeopleCode interpreter. This cycle count is only updated when some tracing or debugging is going on. So, for example, turning the trace off then back on again will skip some cycles.
Note. PeopleSoft recommends using a value of %TracePC_EachStmt (2048) instead of %TracePC_Functions (1) and %TracePC_List (2).
See Also
Trace Setting Class Properties.
Understanding PeopleSoft Configuration Manager
Parameters
|
options |
Either a number or a constant value that sets trace options. Calculate options by either totaling the numbers associated with any of the following options or by adding constants together: |
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
0 |
%TracePC_None |
Set trace off. |
|
1 |
%TracePC_Functions |
Provide a trace of the program as it is executed. This implies options 64, 128, and 256 described in the following rows. |
|
2 |
%TracePC_List |
Provide a listing of the entire program. |
|
4 |
%TracePC_Assigns |
Show the results of all assignments made to variables. |
|
8 |
%TracePC_Fetches |
Show the values fetched for all variables. |
|
16 |
%TracePC_Stack |
Show the contents of the internal machine stack. This option is normally used for debugging the PeopleCode language and not PeopleCode programs. |
|
64 |
%TracePC_Starts |
Provide a trace showing when each program starts. |
|
128 |
%TracePC_ExtFuncs |
Provide a trace showing the calls made to each external PeopleCode routine. |
|
256 |
%TracePC_IntFuncs |
Provide a trace showing the calls made to each internal PeopleCode routine. |
|
512 |
%TracePC_ParamsIn |
Show the values of the parameters to a function. |
|
1024 |
%TracePC_ParamsOut |
Show the values of the parameters as they exist at the return from a function. |
|
2048 |
%TracePC_EachStmt |
Show each statement as it's executed (and don't show statements on branches not taken.) |
|
32768 |
%TracePC_Evaluations |
Start the timing tracing of the start and end of top-level program evaluations. This is similar to the Trace Start of Programs, but only traced when the call isn't directly from PeopleCode. It traces recursive evaluations, like what happens when a ScrollSelect in a RowInit event causes another recursive RowInit to fire during the outer RowInit. If both Trace Evaluations (32768) and Trace Start of Programs (64) are on (32768+64 = 32832) then all routine calls (functions, methods, get, set for both internal and external PeopleCode to PeopleCode calls) are traced. The resulting trace file can be processed by a program to add up the timings for each routine and separate the in-routine timings from those for called routines. |
Returns
None.
Example
The following example is part of a SavePreChange PeopleCode program that sets PeopleCode trace based on page field settings:
DEBUG_CODE = 0; If DEBUG_TRACE_ALL = "Y" Then DEBUG_CODE = DEBUG_CODE + 1 End-if; If DEBUG_LIST = "Y" Then DEBUG_CODE = DEBUG_CODE + 2 End-if; If DEBUG_SHOW_ASSIGN = "Y" Then DEBUG_CODE = DEBUG_CODE + 4 End-if; If DEBUG_SHOW_FETCH = "Y" Then DEBUG_CODE = DEBUG_CODE + 8 End-if; If DEBUG_SHOW_STACK = "Y" Then DEBUG_CODE = DEBUG_CODE + 16 End-if; If DEBUG_TRACE_START = "Y" Then DEBUG_CODE = DEBUG_CODE + 64 End-if; If DEBUG_TRACE_EXT = "Y" Then DEBUG_CODE = DEBUG_CODE + 128 End-if; If DEBUG_TRACE_INT = "Y" Then DEBUG_CODE = DEBUG_CODE + 256 End-if; If DEBUG_SHOW_PARMS = "Y" Then DEBUG_CODE = DEBUG_CODE + 512 End-if; If DEBUG_SHOW_PARMSRT = "Y" Then DEBUG_CODE = DEBUG_CODE + 1024 End-if; SetTracePC(DEBUG_CODE);
The following example sets Trace PC to show a listing of all the calls made to external routines as well as calls made to internal routines:
SetTracePC(384);
The following is identical to the previous example:
SetTracePC(%TracePC_ExtFuncs + %TracePC_IntFuncs);
If you need a thorough trace, you can use a value of 3596. That combines the following:
|
Value |
Description |
|
2048 |
Show each statement as it's executed |
|
1024 |
Show the values of the parameters as they return |
|
512 |
Show the values of the parameters to a function |
|
8 |
Show the values fetched for all variables |
|
4 |
Show the results of all assignments |
See Also
Employing Database Level Auditing

 SetTraceSQL
SetTraceSQLSyntax
SetTraceSQL(options)
Description
Use the SetTraceSQL function to programmatically control the Trace SQL utility, enabling you to control TraceSQL options during the course of program execution.
Note. If you’re using an API with the Session class, use the Trace Setting class properties instead of this function.
When you interact with PeopleTools, SQL statements transparently perform actions such as page construction. The Trace SQL utility creates and updates a file showing the SQL statements generated by PeopleTools.
You can set options prior to starting a PeopleTools session using the Trace tab of PeopleSoft Configuration Manager.
Trace SQL creates and writes data to a trace file that it shares with Trace PeopleCode; Trace SQL and Trace PeopleCode information are both output to the file in the order of execution. The trace file uses a file name and location specified in the Trace page of PeopleSoft Configuration Manager. If no trace file is specified in PeopleSoft Configuration Manager, the file is set by default to DBG1.TMP in your Temp directory. If you specify only a file name, and no directory is specified, the file is written to the directory you’re running Tools from. This file is cleared each time you log on and can be opened in a text editor while you are in a PeopleTools session, so if you want to save it, you must print it or copy it from your text editor.
See Also
Trace Setting Class Properties.
Understanding PeopleSoft Configuration Manager
Parameters
|
options |
Either a Number value or a constant that sets trace options. Calculate options by either totaling the numbers associated with any of the following options, or adding constants together: |
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
0 |
%TraceSQL_None |
No output |
|
1 |
%TraceSQL_Statements |
SQL statements |
|
2 |
%TraceSQL_Variables |
SQL statement variables (binds) |
|
4 |
%TraceSQL_Connect |
SQL connect, disconnect, commit and rollback |
|
8 |
%TraceSQL_Fetch |
Row Fetch (indicates that it occurred and the return code - not the data fetched.) |
|
16 |
%TraceSQL_MostOthers |
All other API calls except Set Select Buffers |
|
32 |
%TraceSQL_SSB |
Set Select Buffers(identifies the attributes of the columns to be selected) |
|
64 |
%TraceSQL_DBSpecific |
Database API-specific calls |
|
128 |
%TraceSQL_Cobol |
COBOL Statement Timings |
|
256 |
%TraceSQL_SybBind |
Sybase Bind Information |
|
512 |
%TraceSQL_SybFetch |
Sybase Fetch Information |
|
1024 |
%TraceSQL_DB2400Server |
Manager information for DB2/400 only |
|
4096 |
%TraceSQL_ManagerInfo |
All manager information. |
|
8192 |
%TraceSQL_AppEngineInfo |
Trace Application Engine information. |
Note. PeopleSoft recommends setting options to 3 to provide most essential information without performance degradation. Options 8 and 32 greatly increase the volume of the trace and will noticeably degrade performance.
Returns
None.
Example
The following example switches off Trace SQL:
SetTraceSQL(0);
The following is identical to the previous example:
SetTraceSQL(%TraceSQL_None);
The following example sets Trace SQL to typical settings that won’t degrade performance:
SetTraceSQL(3);
The following is identical to the previous example:
SetTraceSQL(%TraceSQL_Statements + %TraceSQL_Variables);
See Also
Employing Database Level Auditing

 SetupScheduleDefnItem
SetupScheduleDefnItemSyntax
SetupScheduleDefnItem(ScheduleName, JobName)
Description
Use the SetupScheduleDefnItem function to create a ProcessRequest object. After you’ve created this object, you can assign values to its properties then specific methods created to either schedule or print info for a Scheduled Jobset.
Parameters
|
ScheduleName |
Specify the process type as a string. Values depend on the Scheduled Jobset defined for your system. |
|
JobsName |
Specify the name of the job name as a string. |
Returns
A reference to a ProcessRequest object.
Example
Local ProcessRequest &MYRQST; &MYRQST = SetupScheduleDefnItem("SampleSchedule", &MyJobName);
See Also

 SetUserOption
SetUserOptionSyntax
SetUserOption(Level, OPTN, Value)
Description
Use the SetUserOption to set the default value for the specified option.
Parameters
|
Level |
Specify the option category level as a string. |
|
OPTN |
Specify the option as a string. |
|
Value |
Specify the value of the option. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True, if the function completed successfully, False otherwise.
See Also
Managing PeopleSoft Personalizations

 Sign
SignSyntax
Sign(n)
Description
Use the Sign function to determine the sign of a number.
Parameters
|
n |
A number value of which to determine the sign. |
Returns
Returns a number value equal to:
1 if n is positive
0 if n is 0
-1 if n is negative
Example
The example sets &NUMSIGN to 1:
&NUMSIGN = Sign(25);
See Also
Abs.

 Sin
SinSyntax
Sin(angle)
Description
Use the Sin function to calculate the sine of the given angle (opposite / hypotenuse).
Parameters
|
angle |
A value in radians. |
Returns
A real number between -1.00 and 1.00.
Example
The following example returns the sine of an angle measuring 1.2 radians:
&MY_RESULT = Sin(1.2);
See Also
Acos, Asin, Atan, Cos, Cot, Degrees, Radians, Tan.

 SinglePaymentPV
SinglePaymentPVSyntax
SinglePaymentPV(int_rate, n_per)
Description
Use the SinglePaymentPV function to calculate the future value of a single monetary unit after a specified number of periods at a specified interest rate.
Parameters
|
int_rate |
A number representing the interest rate at which value is accrued per period. |
|
n_per |
A number specifying the number of periods on which to base the calculated value. |
Returns
Returns a number value equal to the value of the unit after n_per periods at an interest rate of int_rate per period.
Example
The example calculates &PMT as .857338820301783265:
&PMT = SinglePaymentPV(8, 2);
See Also

 SortScroll
SortScrollSyntax
SortScroll(level, scrollpath, sort_fields)
Where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, [RECORD.level2_recname,] RECORD.target_recname
and where sort_fields is a list of field specifiers in the form:
[recordname.]field_1, order_1 [, [recordname.]field_2, order_2]. . .
Description
The SortScroll function programmatically sorts the rows in a scroll area on the active page. The rows can be sorted on one or more fields.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the Sort rowset method instead.
The type of sort done by this function, that is, whether it is a linguistic or binary sort, is determined by the Sort Order Option on the PeopleTools Options page.
See Also
Sort.
Parameters
|
level |
Integer specifying the level of the scroll to sort. It can be 1, 2, or 3. |
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll area in the component buffer. |
|
sort_fields |
A list of field and order specifiers which act as sort keys. The rows in the scroll area are sorted by the first field in either ascending or descending order, then by the second field in either ascending or descending order, and so on. |
|
[recordname.]field_n |
Specifies a sort key field in target_recname. The recordname prefix is required if the call to SortScroll is in a record other than target_recname. |
|
order_n |
A single-character string. "A" specifies ascending order; "D" specifies descending order. |
Returns
Optionally returns a Boolean value indicating whether the function executed successfully.
Example
The first example repopulates a scroll in a page programmatically by first flushing its contents, selecting new contents using ScrollSelect, then sorting the rows in ascending order by EXPORT_OBJECT_NAME:
Function populate_scrolls; ScrollFlush(RECORD.EXPORT_OBJECT); ScrollSelect(1, RECORD.EXPORT_OBJECT, RECORD.EXPORT_OBJECT, "where export_type = :EXPORT_TYPE_VW.EXPORT_TYPE"); SortScroll(1, RECORD.EXPORT_OBJECT, EXPORT_OBJECT.EXPORT_OBJECT_NAME, "A"); End-function;
The second example sorts the rows on scroll level one by primary and secondary key fields:
SortScroll(1,RECORD.EN_BOM_COMPS,EN_BOM_COMPS.SETID,"A", EN_BOM_CMOPS.INV_ITEM_ID,"A");
See Also
HideScroll, RowScrollSelect, RowScrollSelectNew, ScrollSelect, ScrollSelectNew, UnhideScroll.

 Split
SplitSyntax
Split(string, separator)
Description
Use the Split function to convert a string into an array of strings by looking for the string separator in the given string.
Note. Split does not split an array.
If separator is omitted, a blank is used.
If separator is a null string (""), the string is split into single characters.
If separator is the last character in the string, you will not get an empty string. For example, in the following code, &array only has a value of 2:
&test = "value1:value2:"; &array = Split(&test, ":");
Parameters
|
string |
The string to be converted into an array |
|
separator |
The character used for dividing the string. |
Returns
Returns a reference to the array.
Example
The following code produces in &AS the array ("This", "is", "a", "simple", "example.").
&STR = "This is a simple example."; &AS = Split(&STR);
See Also

 SQLExec
SQLExecSyntax
SQLExec({sqlcmd | SQL.sqlname}, bindexprs, outputvars)
where bindexprs is a list of expressions, one for each :n reference within sqlcmd or the text found in the SQL defintion sqlname, in the form:
inexpr_1 [, inexpr_2]. . .
and where outputvars is a list of variables, record fields, or record object references, one for each column selected by the SQL command, in the form:
out_1 [, out_2]. . .
Description
Use the SQLExec function to execute a SQL command from within a PeopleCode program by passing a SQL command string. The SQL command bypasses the Component Processor and interacts with the database server directly. If you want to delete, insert, or update a single record, use the corresponding PeopleCode record object method.
If you want to delete, insert, or update a series of records, all of the same type, use the CreateSQL or GetSQL functions, then the Execute SQL class method.
Limitation of SQLExec SELECT Statement
SQLExec can only Select a single row of data. If your SQL statement (or your SQL.sqlname statement) retrieves more than one row of data, SQLExec sends only the first row to its output variables. Any subsequent rows are discarded. This means if you want to fetch only a single row, SQLExec can perform better than the other SQL functions, because only a single row is fetched. If you need to SELECT multiple rows of data, use the CreateSQL or GetSQL functions and the Fetch SQL class method. You can also use ScrollSelect or one of the Select methods on a rowset object to read rows into a (usually hidden) work scroll.
Note. The PeopleSoft record name specified in the SQL SELECT statement must be in uppercase.
Limitations of SQLExec UPDATE, DELETE, and INSERT Statements
SQLExec statements that result in a database update (specifically, UPDATE, INSERT, and DELETE) can only be issued in the following events:
SavePreChange
WorkFlow
SavePostChange
FieldChange
Remember that SQLExec UPDATEs, INSERTs, and DELETEs go directly to the database server, not to the Component Processor (although SQLExec can look at data in the buffer using bind variables included in the SQL string). If a SQLExec assumes that the database has been updated based on changes made in the component, that SQLExec can be issued only in the SavePostChange event, because before SavePostChange none of the changes made to page data has actually been written back to the database.
Setting Data Fields to Null
SQLExec does not set Component Processor data buffer fields to NULL after a row not found fetching error. However, it does set fields that aren’t part of the Component Processor data buffers to NULL. Work record fields are also reset to NULL.
Using Meta-SQL in SQLExec
Different DBMS platforms have slightly different formats for dates, times, and datetimes; and PeopleSoft has its own format for these data types as well. Normally the Component Processor performs any necessary conversions when platform-specific data types are read from the database into the buffer or written from the buffer back to the database.
When an SQLExec statement is executed, these automatic conversions don't take place. Instead, you need to use meta-SQL functions inside the SQL command string to perform the conversions. The basic types of meta-SQL functions are:
General functions that expand at runtime to give you lists of fields, key fields, record fields, and so on. %InsertSelect or %KeyEqual are typical examples.
In functions that expand at runtime into platform-specific SQL within the WHERE clause of a SELECT or UPDATE statement or in an INSERT statement. %DateIn is a typical example.
Out functions that expand at runtime into platform-specific SQL in the main clause of SELECT statement. %DateOut is a typical example.
Following is an example of an SQL SELECT using both and "in" and "out" metastring:
select emplid, %dateout(effdt) from PS_CAR_ALLOC a where car_id = '" | ®ISTRATION_NO | "' and plan_type = '" | &PLAN_TYPE | "' and a.effdt = (select max (b.effdt) from PS_CAR_ALLOC b where a.emplid=b.emplid and b.effdt <= %currentdatein) and start_dt <= %currentdatein and (end_dt is null or end_dt >= %currentdatein)";
See Meta-SQL.
Bind Variables in SQLExec
Bind variables are references within the sqlcmd string to record fields listed in bindvars. Within the string, the bind variables are integers preceded by colons:
:1, :2,. . .
The integers need not in numerical order. Each of these :n integers represents a field specifier in the bindvars list, so that :1 refers to the first field reference in bindvars, :2 refers to the second field reference, and so on.
For example, in the following statement:
SQLExec("Select sum(posted_total_amt) from PS_LEDGER where deptid between :1 and :2", DEPTID_FROM, DEPTID_TO, &SUM);
:1 is replaced by the value contained in the record field DEPTID_FROM; :2 is replaced by the value contained in the record field DEPTID_TO.
Note the following points:
Bind variables can be used to refer to long character (longchar) fields. Long character fields are represented in PeopleCode as strings. You should use %TextIn() Meta-SQL to ensure these fields are represented correctly on all database platforms.
Bind variables can be passed as parameters to meta-SQL functions, for example:
SQLExec(". . .%datein(:1). . .", START_DT, &RESULT)
If a bind variable :n is a Date field that contains a null value, SQLExec replaces all occurrences of ":n" located before the first WHERE clause with "NULL" and all occurrences of "= :n" located after the first WHERE to "IS NULL".
Inline Bind Variables in SQLExec
Inline bind variables are included directly in the SQL string in the form:
:recordname.fieldname
The following example shows the same SQLExec statement with standard bind variables, then with inline bind variables:
Rem without Inline Bind Variables; SQLExec("Select sum(posted_total_amt) from PS_LEDGER where deptid between :1 and :2", deptid_from, deptid_to, &sum); Rem with Inline Bind Variables; SQLExec("Select sum(posted_total_amt) from PS_LEDGER where deptid between :LEDGER.DEPTID_FROM and :LEDGER.DEPTID_TO", &sum);
Inline bind variables, like all field and record references enclosed in strings, are considered by PeopleTools as a "black box". If you rename records and fields, PeopleTools does not update record and field names that are enclosed in strings as inline bind variables. For this reason, you should use standard bind variable in preference to inline bind variables wherever standard bind variables are available (as they are in SQLExec).
Prior to PeopleTools 8.0, PeopleCode replaced runtime parameter markers in SQL strings with the associated literal values. For databases that offer SQL statement caching, a match was never found in the cache so the SQL had to be re-parsed and re-assigned a query path. However, with PeopleTools 8.0, PeopleCode passes in bind variable parameter markers. For databases with SQL caching, this can offer significant performance improvements.
If you use inline bind variables, they will still be passed as literals to the database. However, if you convert them to bind variables, you may see significant performance improvements.
Output Variables in SQLExec
If you use SQLExec to Select a row of data, you must place the data into variables or record fields so that it can be processed. You list these variables or fields, separated by commas in the output part of the statement following the bindvars list. Supply one variable or field for each column in the row of data retrieved by SQLExec. They must be listed in the same order in which the columns will be selected.
The number of output variables cannot exceed 64.
Using Arrays for Bind Variables
You can now use a parameter of type Array of Any in place of a list of bind values or in place of a list of fetch result variables. This is generally used when you don't know how many values are needed until the code runs.
For example, suppose that you had some PeopleCode that dynamically (that is, at runtime) generated the following SQL statement:
&Stmt = "INSERT INTO PS_TESTREC (TESTF1, TESTF2, TESTF3, TESTF4, . . . N) VALUES (:1, :2, %DateTimeIn(:3), %TextIn(:4), . . .N)";
Suppose you have placed the values to be inserted into an Array of Any, say &AAny:
&AAny = CreateArrayAny("a", 1, %DateTime, "abcdefg", . . .N);
You can execute the insert by:
SQLExec(&Stmt, &AAny);
Because the Array of Any promotes to absorb any remaining select columns, it must be the last parameter for the SQL object Fetch method or (for results) SQLExec. For binding, it must be the only bind parameter, as it is expected to supply all the bind values needed.
SQLExec Maintenance Issues
SQLExec statements are powerful, but they can be difficult to upgrade and maintain. If you use a SQL string passed in the command, it’s considered a "black box" by PeopleCode. If field names or table names change during an upgrade, table and field references within the SQL string are not updated automatically. For these reasons, you should use a SQL definition and the meta-SQL statements provided in PeopleTools 8.0, instead of typing in a SQL string.
Generally, you should use SQLExec only when you must interact directly with the database server and none of the ScrollSelect functions, or record class methods (which are somewhat easier to maintain) will serve your purpose effectively.
Be Careful How You Use It
SQLExec performs any SQL statement the current Access ID has database privileges to perform. This normally includes SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements against application data tables. However, you can set up users to use Access IDs with more privileges (typically, AccessIDs have full database administrator authority). In such cases, the user could alter the structure of tables using SQLExec, or even drop the database.
Warning! The PeopleSoft application will not stop the end-user from doing anything that the Access ID has privileges to do on the database server, so be very careful what you write in an SQLExec statement.
Parameters
|
sqlcmd | SQL.sqlname |
Specify either a String containing the SQL command to be executed or a reference to an existing SQL definition. This string can include bind variables, inline bind variables, and meta-SQL. |
|
bindexprs |
A list of expressions, each of which corresponds to a numeric (:n) bind variable reference in the SQL command string. It can also be a reference to a record object or an array of Any containing all the bind values. See Bind Variables in SQLEXEC for more details. |
|
outputvars |
A list of PeopleCode variables or record fields to hold the results of a SQL SELECT. There must be one variable for each column specified in the SELECT statement. It can also be a reference to a record object or an Array of Any that contains all the selected values. |
Returns
Optionally returns a Boolean value indicating whether the function executed successfully.
Note. Not returning a row is not considered an error. If this is a concern, consider using the %SqlRows system variable after your call to SQLExec.
Example
The following example, illustrates a SELECT statement in a SQLExec:
SQLExec("SELECT COUNT(*) FROM PS_AE_STMT_TBL WHERE AE_PRODUCT = :1 AND AE_APPL_ID = :2 AND AE_ADJUST_STATUS = 'A' ", AE_APPL_TBL.AE_PRODUCT, AE_APPL_TBL.AE_APPL_ID, AE_ADJ_AUTO_CNT);
Note the use of bind variables, where :1 and :2 correspond to AE_APPL_TBL.AE_PRODUCT and AE_APPL_TBL.AE_APPL_ID. AE_ADJ_AUTO_CNT is an output field to hold the result returned by the SELECT.
The next example is also a straightforward SELECT statement, but one which uses the %datein meta-SQL function, which expands to appropriate platform-specific SQL for the :5 bind variable:
SQLExec("SELECT 'X', AE_STMT_SEG FROM PS_AE_STMT_B_TBL where AE_PRODUCT = :1 AND AE_APPL_ID = :2 AND AE_SECTION = :3 AND DB_PLATFORM = :4 AND EFFDT = %datein(:5) AND AE_STEP = :6 AND AE_STMT_TYPE = :7 AND AE_SEQ_NUM = :8", AE_STMT_TBL.AE_PRODUCT, AE_STMT_TBL.AE_APPL_ID, AE_STMT_TBL.AE_SECTION, AE_STMT_TBL.DB_PLATFORM, AE_STMT_TBL.EFFDT, AE_STMT_TBL.AE_STEP, AE_STMT_TBL.AE_STMT_TYPE, &SEG, &EXIST, &STMT_SEG);
This last example (in SavePreChange PeopleCode) passes an INSERT INTO statement in the SQL command string. Note the use of a date string this time in the %datein meta-SQL, instead of a bind variable:
SQLExec("INSERT INTO PS_AE_SECTION_TBL ( AE_PRODUCT, AE_APPL_ID, AE_SECTION, DB_PLATFORM, EFFDT, EFF_STATUS, DESCR, AE_STMT_CHUNK_SIZE, AE_AUTO_COMMIT, AE_SECTION_TYPE ) VALUES ( :1, :2, :3, :4, %DATEIN('1900-01-01'), 'A', ' ', 200, 'N', 'P' )", AE_APPL_TBL.AE_PRODUCT, AE_APPL_TBL.AE_APPL_ID, AE_SECTION, DB_PLATFORM);
In the following example, a SQLExec statement is used to select into a record object.
Local Record &DST; &DST = CreateRecord(RECORD.DST_CODE_TBL); &DST.SETID.Value = GetSetId(FIELD.BUSINESS_UNIT, DRAFT_BU, RECORD.DST_CODE_TYPE, ""); &DST.DST_ID.Value = DST_ID_AR; SQLExec("%SelectByKeyEffDt(:1,:2)", &DST, %Date, &DST); /* do further processing using record methods and properties */
See Also
CreateSQL, FetchSQL, GetSQL, StoreSQL, ScrollSelect.

 Sqrt
SqrtSyntax
SQRT(n)
Description
Use the Sqrt function to calculate the square root of a number.
Parameters
|
n |
A number of which you want to find the square root. |
Returns
Returns a number equal to the positive square root of n. If n is a negative number, Sqrt displays an error.
Example
The examples return 15, 4, and 8.42615, respectively:
&NUM = Sqrt(225); &NUM = Sqrt(16); &NUM = Sqrt(71);

 StartWork
StartWorkSyntax
StartWork()
Description
Use the StartWork function to mark the start of a unit of work.
Once this function is executed, no updates to the database are allowed until a unit of work is completed. A unit of work is completed by an event completing (such as a FieldChange event) in which case all the Updates are saved.
A unit of work can also be completed using the CommitWork built-in function.
If a SQL failure occurs anytime during the unit of work, after the StartWork function has been called and before the unit of work completes, all updates are rolled back, up to when the StartWork function was executed.
This function can be used for nested component interface calls, such that if the lower level component interface fails, any database changes made by the calling component interface can be rolled back.
Parameters
None.
Returns
None.
Example
&oCI = &SESSION.GetCompIntfc(CompIntfc.CUSTOMER); If &oCI <> Null Then . . . For &i = 1 To &rsCustomer.RowCount &recCust = &rsCustomer(&Transaction).GetRecord(Record.CUSTOMER); StartWork(); If &oCI.Create() Then rem ***** Set CI Properties *****; . . . If Not &oCI.Save() Then rem ***** Error Handling *****; ..... End-If; End-If; rem ***** CommmitWork ensures that all transactions between *****; rem ***** StartWork and CommitWork get committed to the database *****; CommitWork(); &oCI.Cancel(); . . . End-For; End-If
See Also

 StopFetching
StopFetchingSyntax
StopFetching()
Description
The StopFetching function is called during Row Select processing, during which rows of data that have been selected down from the database can be filtered as they are added to the component. This function is valid only in RowSelect PeopleCode. If StopFetching is called without DiscardRow, it adds the current row to the component, then stops adding any more rows. If StopFetching is called with DiscardRow, the system skips the current row and stops adding rows to the component.
StopFetching has the same functionality as the Error function in the RowSelect event. The anomalous behavior of Error is supported for compatibility with previous releases of PeopleTools.
Note. Row Select processing is used infrequently, because it is more efficient to filter out rows of data using a search view or an effective-dated record before the rows are selected down to the client from the database server.

RowSelect Processing Logic
Returns
None.
See Also

 StoreSQL
StoreSQLSyntax
StoreSQL(sqlstring, [SQL.]sqlname[, dbtype[, effdt [, ownerid [, description]]]])
Description
Use the StoreSQL function to write the given sqlstring value to a SQL definition, storing it under the name sqlname, with the database type dbtype and the effective date effdt. If sqlname is a literal name, it must be in the form SQL.sqlname or in quotes ("sqlname").
To specify a generic statement, that is, one that is overridden by any other matching statement, specify dbtype as Default and effdt as the null date (or Date(19000101).
You must commit all database changes prior to using this function. This is to avoid locking critical Tools tables and hence freezing all other users. You receive a runtime error message if you try to use this function when there are pending database updates, and your PeopleCode program terminates. You need to commit any database updates prior to using this function. The CommitWork PeopleCode function has been enhanced to allow this.
Parameters
|
sqlstring |
Specify the SQL string to be saved as the SQL definition. This parameter takes a string value. |
|
sqlname |
Specify the name of the SQL definition to be created. This is either in the form SQL.sqlname or a string value giving the sqlname. |
|
dbtype |
Specify the database type to be associated with the SQL definition. This parameter takes a string value. If dbtype isn’t specified or is null (""), it is set by default to the current database type (the value returned from the %DbName system variable.) Values for dbtype are as follows. These values are not case-sensitive:
Note. Database platforms are subject to change. |
|
effdt |
Specify the effective date to be associated with the SQL definition. If effdt isn’t specified, it is set by default to the current as of date, that is, the value returned from the %AsOfDate system variable. |
|
ownerid |
Specify the four character ownerId associated with this SQL statement. If not specified, no ownerId is associated. |
|
description |
Specify the description text associated with this SQL statement. |
Returns
None.
Example
The following code stores the select statement as a SQL definition under the name SELECT_BY_EMPLID, for the current database type and effective as of the current as of date:
StoreSQL("%Select(:1) where EMPLID = :2", SQL.SELECT_BY_EMPLID);
See Also
CreateSQL, DeleteSQL, FetchSQL, GetSQL, SQLExec, CommitWork.

 String
StringSyntax
String(value)
Description
Use the String to convert any non-string data type (except Object) to a string.
Normally the Component Processor automatically handles data type conversions. However, for some operations, such as comparisons, you want to specify the data type explicitly. Assume, for example, that you have two fields FIELD_I and FIELD_J containing number values 5000 and 10000. As character fields, 10000 is less than 5000 (because the first character in 10000 is less than the first character in 5000). As numbers, however, 10000 is of course greater than 5000.
Note. Due to the internal representation of numbers, sometimes String represents numbers differently. If you want to control exactly how a number is represented, use the NumberToString function.
Parameters
|
value |
A value of any type other than object, to be converted to its String representation. |
Returns
Returns a String value representing value.
Example
To force the comparison of the two fields as strings, you could use:
if string(FIELD_1) > string(FIELD_2). . .
You can use the String function with a field object as follows:
&DATE = GetRecord(RECORD.DERIVED_HR).GetField(FIELD.EFFDT); &STR = String(&DATE.Value);
See Also
Char, Exact, Find, Left, Substring, Value, NumberToString.

 Substitute
SubstituteSyntax
Substitute(source_text, old_text, new_text)
Description
Use the Substitute function to replace every occurrence of a substring found in a string with a new substring. To replace text that occurs in a specific location in a text string use the Replace function.
Parameters
|
source_text |
A String in which you want to replace substrings. |
|
old_text |
A String equal to the substring of source_text you want to replace. A tilde character (~) used in the old_text parameter stands for an arbitrary number of white spaces. For example, the following substitution: Substitute("2003* 0723* * * * ~", "* ~", "~") produces the result 2003~0723~~~~~, not the result 2003* 0723* * * ~. |
|
new_text |
A String with which to replace occurrences of old_text in source_text. |
Returns
Returns a String resulting from replacing every occurrence of old_text found in source_text with new_text.
Example
The following example changes "Second Annual Conference" to "Third Annual Conference":
&newstr = Substitute("Second Annual Conference","Second","Third");
The next example sets &newstr to "cdcdcd":
&newstr = Substitute("ababab", "ab", "cd");
See Also

 Substring
SubstringSyntax
Substring(source_str, start_pos, length)
Description
Use the Substring function to extract a substring of a specified number of characters beginning at a specified location in a source string. If the string contains Unicode non-BMP characters, each code unit of the surrogate pair is counted as a separate character, care should be taken not to split a surrogate pair using Substring.
If you know the exact length of source_str, and that it is null terminated, you can set length to 1 plus the exact length of source_str to get everything from start_pos to the end.
Parameters
|
source_str |
A String from which to extract a substring. |
|
start_pos |
A number representing the character position in source_str where the substring starts, starting at 1. |
|
length |
A number specifying the number of characters in the substring. |
Returns
Returns a String equal to a substring length characters long beginning at character start of source_str.
Example
This example sets &PAGE_NAME to the first eight characters of the name of the current page:
&PAGE_NAME = Substring(%page,1,8);
See Also
Char, Exact, Find, Left, Right, String, Substringb.

 Substringb
Substringb
Syntax
Substringb(source_str, start_pos, length)
Description
Note. This function has been deprecated and is no longer supported.

 SwitchUser
SwitchUserSyntax
SwitchUser(UserID, Password, AuthToken , ExtAuthInfo)
Note. Password is not encrypted: it is passed as a string.
Description
Use the SwitchUser function to change the user ID of the current user logged onto the PeopleSoft system.
Note. SwitchUser changes the Portal user rather than the content specific user. This means it changes the user ID in all databases to which the user is connected.
The SwitchUser function might be used as follows. Suppose there is a special user ID in the system called REGIST. REGIST only has access to the self-registration component. The self-registration component has logic that asks the user a list of questions and information based on data in the database. Are you a customer, vendor, or employee? Enter your customer name. Enter other information related to this customer account (such as information only this customer knows or information this customer just received from a workflow email). After the program verifies the information, create a User ID for this customer. After the user ID is created, the program should take the user directly into their transaction without having to logoff, by using SwitchUser.
Considerations Using SwitchUser
You must never call SwitchUser from Signon PeopleCode. SwitchUser calls Signon PeopleCode, therefore creating an infinite loop.
Do not use SwitchUser in PeopleSoft Application Engine or in asynchronous subscription PeopleCode.
Do not use SwitchUser in a Component Interface. The user is only switched for the duration of the service call. During the next call, the user reverts to the original user.
Parameters
|
UserID |
Specify the User ID to be started. This parameter takes a string value. |
|
Password |
Specify the Password for this User ID. This parameter takes a string value. Note. Password is not encrypted: it is passed as a string. |
|
AuthToken |
Specify a single signon authentication token used to authenticate the user. If you are authenticating the user by Userid and password, specify a NULL value for this parameter, that is, two quotation marks with no blank space between them (""). If you specify a token, and the token is valid, SwitchUser switches to the User ID embedded in the token. All other parameters are ignored if a token is used. This parameter takes a string value. |
|
ExtAuthInfo |
Specify binary data (encoded as a base64 string) used as additional input to authenticate the user. If your application doesn't use external authentication information, specify a NULL value for this parameter, that is, two quotation marks with no blank space between them (""). |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if user ID is switched successfully, False otherwise.
Example
The most common use of SwitchUser specifies only a Userid and Password. If the SwitchUser function executes successfully, you should check to see if the password for the new user id has expired.
If Not SwitchUser("MYUSERID", "MYPASSWORD", "", "") Then /* switch failed, do error processing */ Else If %PasswordExpired Then /* application specific processing for expired passwords */ End-If; End-If;
See Also
Understanding PeopleSoft Security

 SyncRequestXmlDoc
SyncRequestXmlDocSyntax
SyncRequestXmlDoc(&XmlDoc, Message.MessageName [, Node.NodeName])
Description
Use the SyncRequestXmlDoc function to send a synchronous message that is based on an XmlDoc object. The XmlDoc object must already be instantiated and populated. The message included in the function call should be an unstructured message, that is, one that isn't based on a hierarchical record structure.
If you want to handle an XmlDoc as a Message object, you need to define a Message object with a hierarchical structure and migrate the data in the XmlDoc object into the Message object.
Parameters
|
&XmlDoc |
Specify an already instantiated and populated XmlDoc object that you want to send as a synchronous message. |
|
MessageName |
Specify an already existing nonrowset-based message, prefixed with the reserved word Message. |
|
NodeName |
Specify a node. This is for Sender Specified Routing (SSR) prefixed with the reserved word Node. The node defines the target for the published message. |
Returns
A reference to an XmlDoc object that is the response.
Example
Local XmlDoc &reqdoc, &respdoc; . . . &respdoc = SyncRequestXmlDoc(&reqdoc, Message.MY_MESSAGE, Node.MY_NODE);
See Also
Defining Message Channels and Messages

 Tan
TanSyntax
Tan(angle)
Description
Use the Tan function to calculate the tangent of the given angle (opposite / adjacent).
Parameters
|
angle |
A value in radians. |
Note. In theory, values of angle such that angle mod pi = pi/2 are not valid for this function, because inputs approaching such values produce results that tend toward infinity. In practice, however, no computer system can represent such values exactly. Thus, for example, the statement Tan(Radians(90)) produces a number close to the largest value PeopleCode can represent, rather than an error.
Returns
A real number.
Example
The following example returns the tangent of an angle measuring 1.2 radians:
&MY_RESULT = Tan(1.2);
See Also
Acos, Asin, Atan, Cos, Cot, Degrees, Radians, Sin.

 Throw
ThrowSyntax
Throw Expression
Description
Use the Throw statement to throw an exception. This can be used to create your own exceptions, instead of using one generated by the system.
Parameters
|
Expression |
Specify the exception object that you want to throw. This can either be an already defined and created exception object, or one that you create with the Throw statement. |
Returns
None.
Example
Local Exception &ex; Function t1(&i As integer) Returns number Local number &res = &i / 0; End-Function; Function t2 throw CreateException(2, 160, "'%1' doesn't support property or method '%2'", "SomeClass", "SomeMethod"); End-Function; try /* This will cause a divide by 0 leading to an exception */ /* This code will never be caught since t1(2) will resume execution in the catch block below. It is here to show how an exception can be thrown directly bythe PeopleCode itself. */ t2(); Local number &res = t1(2); catch Exception &caught MessageBox(0, "", 0, 0, "Caught exception: " | &caught.ToString()); end-try;
See Also
Defining Message Channels and Messages

 Time
TimeSyntax
Time(n)
Description
Use the Time function to derive a Time value from a Number value. Use it to assign values to Time fields and variables, since Time values cannot be directly represented as constants.
Parameters
|
n |
A Number in the form HHMMSS[.SSSSSS], representing a time to a precision of up to .000001 second, based on a 24-hour clock. |
Returns
Returns a Time value based on the number n.
Example
The example sets &START_TIME to 12:34:56.123456:
&START_TIME = Time(123456.123456);
See Also
Date, DateTimeValue, Time3, TimeValue.

 Time3
Time3Syntax
Time3(hours, mins, secs)
Description
Use the Time3 function to derive a Time value from three supplied numbers. It can be used to assign values to Time fields and variables, since Time values cannot be directly represented as constants.
Parameters
|
hours |
A Number in the form HH between 00 and 23, representing hours on a 24-hour clock. |
|
mins |
A Number in the form MM between 00 and 59, representing minutes of the hour. |
|
secs |
A Number in the form SS[.SSSSSS], between 00 and 59.999999, representing seconds. |
Returns
Returns a Time value based equal to the sum of the three input values representing hours, minutes, and seconds, to a precision of .000001 second.
Example
The example sets &START_TIME to 11.14.09.300000:
&START_TIME = Time3(11,14,9.3);
See Also
Date3, DateTime6, Time, TimeValue.

 TimePart
TimePartSyntax
TimePart(datetime_val)
Description
Use the TimePart function to derive the Time component of a DateTime value.
Parameters
|
datetime_val |
A DateTime value from which to extract the Time component. |
Returns
Returns a Time value.
Example
The example set &T to 15.34.35.000000:
&DT = DateTimeValue("12/13/1993 3:34:35 PM"); &T = TimePart(&DT);
See Also
DatePart, Hour, Minute, Second.

 TimeToTimeZone
TimeToTimeZoneSyntax
TimeToTimeZone(OldTime, SourceTimeZone, DestinationTimeZone);
Description
Use the TimeToTimeZone function to convert a time field from the time specified by SourceTimeZone to the time specified by DestinationTimeZone.
Considerations Using this Function
This function should generally be used in PeopleCode, not for displaying time. If you take a time value, convert it from base time to client time, then try to display this time, depending on the user settings, when the time is displayed the system might try to do a second conversion on an already converted time. This function could be used as follows: suppose a user wanted to check to make sure a time was in a range of times on a certain day, in a certain timezone. If the times were between 12 AM and 12PM in EST, these resolve to 9 PM and 9AM PST, respectively. The start value is after the end value, which makes it difficult to make a comparison. This function could be used to do the conversion for the comparison, in temporary fields, and not displayed at all.
Parameters
|
OldTime |
Specify the time value to be converted. |
|
SourceTimeZone |
Specify the time zone that OldTime is in. Values are: timezone - a time zone abbreviation or a field reference to be used for converting OldTime. Local - use the local time zone for converting OldTime. Base - use the base time zone for converting OldTime. |
|
DestinationTimeZone |
Specify the time zone that you want to convert OldTime to. Values are: timezone - a time zone abbreviation or a field reference to be used for converting OldTime. Local - use the local time zone for converting OldTime. Base - use the base time zone for converting OldTime. |
Returns
A converted time value.
Example
The following example TESTTM is a time field with a value 01/01/99 10:00:00. This example converts TESTTM from Eastern Standard Time (EST) to Pacific Standard Time (PST).
&NEWTIME = TimeToTimeZone(TESTTM, "EST", "PST");
&NEWTIME is a time variable with a value of 7:00:00AM.
See Also
ConvertDatetimeToBase, ConvertTimeToBase, FormatDateTime, IsDaylightSavings, DateTimeToTimeZone, TimeZoneOffset.

 TimeValue
TimeValueSyntax
TimeValue(time_str)
Description
Use the TimeValue function to calculate a Time value based on an input string. This function can be used to assign a value to a Time variable or field using a string constant, since a Time value cannot be represented with a constant.
Parameters
|
time_str |
A String representing a time in the form HH:MM:SS.SSSSSS, based on a 24-hour clock. |
Returns
Returns a Time value based on time_str.
Example
The example sets &START_TIME to 12.13.00.000000:
&START_TIME = TimeValue("12:13:00 PM");
See Also

 TimeZoneOffset
TimeZoneOffsetSyntax
TimeZoneOffset(DateTime {[, timezone | "Base" | "Local"]})
Description
Use the TimeZoneOffset function to generate a time offset for datetime. The offset represents the relative time difference to GMT. If no other parameters are specified with datetime, the server's base time zone is used.
Parameters
|
datetime |
Specify the datetime value to be used for generating the offset. |
|
timezone | Local | Base |
Specify a value to be used with datetime. The values are: timezone - a time zone abbreviation or a field reference to be used with datetime. Local - use the local time zone with datetime. Base - use the base time zone with datetime. |
Returns
An offset string of the following format:
Shh:mm
where
|
S |
is + or -, with + meaning East of Greenwich |
|
hh |
is the hours of offset |
|
mm |
is the minutes of offset |
See Also
ConvertDatetimeToBase, ConvertTimeToBase, FormatDateTime, IsDaylightSavings, DateTimeToTimeZone, TimeToTimeZone.

 TotalRowCount
TotalRowCountSyntax
TotalRowCount(scrollpath)
Where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Use the TotalRowCount function to calculate the number of rows (including rows marked as deleted) in a specified scroll area of a page.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the RowCount rowset property instead.
Rows that have been marked as deleted remain accessible to PeopleCode until the database has been updated; that is, all the way through SavePostChange.
TotalRowCount is used to calculate the upper limit of a For loop if you want the loop to go through rows in the scroll that have been marked as deleted. If the logic of the loop does not need to execute on deleted rows, use ActiveRowCount instead.
See Also
ActiveRowCount, For, RowCount.
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
Returns
Returns a Number equal to the total rows (including rows marked as deleted) in the target scroll.
Example
The example uses TotalRowCount to calculate the limiting value on a For loop, which loops through all the rows in the scroll area:
&ROW_COUNT = TotalRowCount(RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_PER, CurrentRowNumber(1), RECORD.BUS_EXPENSE_DTL); for &I = 1 to &ROW_COUNT /* do something with row &I that has to be done to deleted as well as active rows */ end-for;
See Also
ActiveRowCount, CopyRow, CurrentRowNumber, FetchValue, For.

 Transfer
TransferSyntax
Transfer(new_instance, MENUNAME.menuname, BARNAME.barname, ITEMNAME.menu_itemname, PAGE.component_item_name, action [, keylist] [, AutoSearch]);
where keylist is a list of field references in the form:
[recordname.]field1 [, [recordname.]field2]. . .
OR
&RecordObject1 [, &RecordObject2]. . .
Description
Use the Transfer function to close the current page and transfers the end-user to another page, either within the current component or in another component. Transfer can either start a new instance of the application and transfer to the new page there, or close the old page and transfer to the new one in the same instance of PeopleTools.
Note. The Transfer function cannot be used with an internet script or an application engine program.
Transfer is more powerful than the simpler TransferPage, which permits a transfer only within the current component in the current instance of PeopleTools. However, any variables declared as Component do not remain defined after using the Transfer function, whether you’re transferring within the same component or not.
You can use Transfer from a secondary page (either with or without using a pop-up menu) only if you’re transferring to a separate instance of a component. You cannot use Transfer from a secondary page if you’re not transferring to a separate instance of a component.
If you provide a valid search key for the new page in the optional keylist, the new page opens directly, using the values provided from keylist as search key values. A valid key means that enough information is provided to uniquely identify a row: not all of the key values need to be provided. If no key is provided, or if the key is invalid, or if not enough information is provided to identify a unique row, the search dialog box displays, enabling the end user to search for a row.
Note. If Force Search Processing is specified in PeopleSoft Application Designer for the component, the search dialog box always displays, whether the keylist is provided or not.
If barname+itemname+component_item_name is an invalid combination, an error message displays explaining that there were invalid transfer parameters.
In the component_item_name parameter, make sure to pass the component item name for the page, not the page name. The component item name is specified in the component definition, in the Item Name column on the row corresponding to the specific page, as shown here:
Component Item Name
Differences Between Transfer and TransferExact
When you do a transfer, the first thing the system checks is whether all the key field values for the target component are provided.
If all the keys aren't provided, the search page is displayed. In this scenerio, TransferExact and Transfer are the same.
If all the keys are provided, a Select is done against the search record for that component using those keys.
If you use the Transfer function, a LIKE operator is used in the Where clause of that Select for each key.
If you use the TransferExact fuction, the equals operator is used in the Where clause for each key. Using equals allows the database to take full advantage of key indexes for maximum performance.
See TransferExact.
Restrictions on Use With a Component Interface
This function is ignored (has no effect) when used by a PeopleCode program that’s been called by a Component Interface.
Restrictions on Use With SearchInit Event
You can't use this function in a SearchInit PeopleCode program.
Considerations Using Exceptions and the Transfer Function
Using the Transfer function, inside a try block, to transfer a user to a page in another component, does not catch PeopleCode exceptions thrown in the new component. Starting a new component starts a brand new PeopleCode evaluation context. Catches are only caught for exceptions thrown within the current component.
In the following code example, the catch statement only catches exceptions thrown in the code prior to using the DoModal function, but not any exceptions that are thrown within the new component.
/* Set up transaction */ If %CompIntfcName = "" Then try &oTrans = &g_ERMS_TransactionCollection.GetTransactionByName(RB_EM_WRK.DESCR); &sSearchPage = &oTrans.SearchPage; &sSearchRecord = &oTrans.SearchRecord; &sSearchTitle = &oTrans.GetSearchPageTitle(); If Not All(&sSearchPage, &sSearchRecord, &sSearchTitle) Then Error (MsgGetText(17834, 8081, "Message Not Found")); End-If; &c_ERMS_SearchTransaction = &oTrans; /* Attempt to transfer to hidden search page with configurable filter */ &nModalReturn = DoModal(@("Page." | &sSearchPage), &sSearchTitle, - 1, - 1); catch Exception &e Error (MsgGetText(17834, 8082, "Message Not Found")); end-try;
See Also
Creating Component Definitions
Parameters
|
new_instance |
Set this parameter to True to start a new application instance, or to False to use the current window and replace the page already displayed. |
|
Menuname |
The name of the menu where the page is located prefixed with the reserved word MENUNAME. |
|
Barname |
The name of the menu bar where the page is located, prefixed with the reserved word BARNAME. |
|
menu_itemname |
The name of the menu item where the page is located, prefixed with the reserved word ITEMNAME. |
|
component_item_name |
The component item name of the page to be displayed on top of the component when it displays. The component item name is specified in the component definition. This parameter must be prefixed with the keyword PAGE. |
|
Action |
Uses a single-character code as in %Action. Valid actions are "A" ( add), "U" (update), "L" (update/display all), "C" (correction), and "E" (data entry). |
|
Keylist |
An optional list of field specifications used to select a unique row at level zero in the page you are transferring to, by matching keys in the page you are transferring from. It can also be an already instantiated record object. If a record object is specified, any field of that record object that is also a field of the search record for the destination component is added to keylist. The keys in the fieldlist must uniquely identify a row in the "to" page search record. If a unique row is not identified, or if Force Search Processing is selected for the component, the search dialog box appears. If the keylist parameter is not supplied then the destination component's search key must be found as part of the source components level 0 record buffer. |
|
AutoSearch |
Specify whether an automatic search on the target search page is executed after the transfer. This means the search results are already shown without the end-user having to click the Search button. This parameter takes a Boolean value: True, do an automatic search. The default value is False (that is, the user has to click the Search button). |
Returns
None.
Example
The example starts a new instance of PeopleTools and transfers to a new page in Update mode. The data in the new page is selected by matching the EMPLID field from the old page.
Transfer(true, MENUNAME.ADMINISTER_PERSONNEL, BARNAME.USE, ITEMNAME. PERSONAL_DATA, PAGE.PERSONAL_DATA_1, "U");
The following example is used with workflow.
Local Record &WF_WL_DEFN_VW, &MYREC, &PSSTEPDEFN; If All(WF_WORKLIST_VW.BUSPROCNAME) Then &BPNAME = FetchValue(WF_WORKLIST_VW.BUSPROCNAME, CurrentRowNumber()); &WLNAME = FetchValue(WF_WORKLIST_VW.WORKLISTNAME, CurrentRowNumber()); &INSTANCEID = FetchValue(WF_WORKLIST_VW.INSTANCEID, CurrentRowNumber()); &WF_WL_DEFN_VW = CreateRecord(RECORD.WF_WL_DEFN_VW); &PSSTEPDEFN = CreateRecord(RECORD.PSSTEPDEFN); SQLExec("select %List(SELECT_LIST, :1) from %Table(:1) where Busprocname = :2 and Worklistname = :3", &WF_WL_DEFN_VW, &BPNAME, &WLNAME, &WF_WL_DEFN_VW); SQLExec("select %List(SELECT_LIST, :1) from %Table(:1) where Activityname = :2 and Stepno = 1 and Pathno = 1", &PSSTEPDEFN, &WF_WL_DEFN_VW.ACTIVITYNAME.Value, &PSSTEPDEFN); Evaluate &PSSTEPDEFN.DFLTACTION.Value When = 0 &ACTION = "A"; When = 1 &ACTION = "U"; When-Other &ACTION = "U"; End-Evaluate; &MYREC = CreateRecord(@("RECORD." | &WF_WL_DEFN_VW.WLRECNAME.Value)); SQLExec("Select %List(SELECT_LIST, :1) from %Table(:1) where Busprocname = :2 and Worklistname = :3 and Instanceid = :4", &MYREC, &BPNAME, &WLNAME, &INSTANCEID, &MYREC); Transfer( True, @("MENUNAME." | &PSSTEPDEFN.MENUNAME.Value), @("BARNAME." | &PSSTEPDEFN.BARNAME.Value), @("ITEMNAME." | &PSSTEPDEFN.ITEMNAME.Value), @("PAGE." | &PSSTEPDEFN.PAGEITEMNAME.Value), &ACTION, &MYREC); End-if;
See Also
TransferPage, DoModalComponent, TransferExact.

 TransferExact
TransferExactSyntax
TransferExact(new_instance, MENUNAME.menuname, BARNAME.barname, ITEMNAME.menu_itemname, PAGE.component_item_name, action [, keylist] [, AutoSearch]);
where keylist is a list of field references in the form:
[recordname.]field1 [, [recordname.]field2]. . .
OR
&RecordObject1 [, &RecordObject2]. . .
Description
Use the TransferExact function to close the current page and transfers the user to another page, either within the current component or in another component. TransferExact can either start a new instance of the application and transfer to the new page there, or close the old page and transfer to the new one in the same instance of PeopleTools.
Note. The TransferExact function cannot be used with an internet script or an application engine program.
TransferExact is more powerful than the simpler TransferPage, which permits a transfer only within the current component in the current instance of PeopleTools. However, any variables declared as Component do not remain defined after using the TransferExact function, whether you’re transferring within the same component or not.
You can use TransferExact from a secondary page (either with or without using a pop-up menu) only if you’re transferring to a separate instance of a component. You cannot use TransferExact from a secondary page if you’re not transferring to a separate instance of a component.
If you provide a valid search key for the new page in the optional keylist, the new page opens directly, using the values provided from keylist as search key values. A valid key means that enough information is provided to uniquely identify a row: not all of the key values need to be provided. If no key is provided, or if the key is invalid, or if not enough information is provided to identify a unique row, the search dialog box displays, enabling the end user to search for a row.
Note. If Force Search Processing is specified in PeopleSoft Application Designer for the component, the search dialog box always displays, whether the keylist is provided or not.
If barname+itemname+component_item_name is an invalid combination, an error message displays explaining that there were invalid transfer parameters.
In the component_item_name parameter, make sure to pass the component item name for the page, not the page name. The component item name is specified in the component definition, in the Item Name column on the row corresponding to the specific page, as shown here:

Component Item Name
Differences Between Transfer and TransferExact
When you do a transfer, the first thing the system checks is whether all the key field values for the target component are provided.
If all the keys aren't provided, the search page is displayed. In this scenario, TransferExact and Transfer are the same.
If all the keys are provided, a Select is done against the search record for that component using those keys.
If you use the Transfer function, a LIKE operator is used in the Where clause of that Select for each key.
If you use the TransferExact fuction, the equals operator is used in the Where clause for each key. Using equals allows the database to take full advantage of key indexes for maximum performance.
See Transfer.
Restrictions on Use With a Component Interface
This function is ignored (has no effect) when used by a PeopleCode program that’s been called by a Component Interface.
Restrictions on Use With SearchInit Event
You can't use this function in a SearchInit PeopleCode program.
Considerations Using Exceptions and the TransferExact Function
Using the TransferExact function inside a try block to transfer a user to a page in another component does not catch PeopleCode exceptions thrown in the new component. Starting a new component starts a brand new PeopleCode evaluation context. Catches are only caught for exceptions thrown within the current component.
In the following code example, the catch statement only catches exceptions thrown in the code prior to using the DoModal function, but not any exceptions that are thrown within the new component.
/* Set up transaction */ If %CompIntfcName = "" Then try &oTrans = &g_ERMS_TransactionCollection.GetTransactionByName(RB_EM_WRK.DESCR); &sSearchPage = &oTrans.SearchPage; &sSearchRecord = &oTrans.SearchRecord; &sSearchTitle = &oTrans.GetSearchPageTitle(); If Not All(&sSearchPage, &sSearchRecord, &sSearchTitle) Then Error (MsgGetText(17834, 8081, "Message Not Found")); End-If; &c_ERMS_SearchTransaction = &oTrans; /* Attempt to transfer to hidden search page with configurable filter */ &nModalReturn = DoModal(@("Page." | &sSearchPage), &sSearchTitle, - 1, - 1); catch Exception &e Error (MsgGetText(17834, 8082, "Message Not Found")); end-try;
See Also
Creating Component Definitions
Parameters
|
new_instance |
Set this parameter to True to start a new application instance, or to False to use the current window and replace the page already displayed. |
|
Menuname |
The name of the menu where the page is located prefixed with the reserved word MENUNAME. |
|
Barname |
The name of the menu bar where the page is located, prefixed with the reserved word BARNAME. |
|
menu_itemname |
The name of the menu item where the page is located, prefixed with the reserved word ITEMNAME. |
|
component_item_name |
The component item name of the page to be displayed on top of the component when it displays. The component item name is specified in the component definition. This parameter must be prefixed with the keyword PAGE. |
|
Action |
Uses a single-character code as in %Action. Valid actions are "A" ( add), "U" (update), "L" (update/display all), "C" (correction), and "E" (data entry). |
|
Keylist |
An optional list of field specifications used to select a unique row at level zero in the page you are transferring to, by matching keys in the page you are transferring from. It can also be an already instantiated record object. If a record object is specified, any field of that record object that is also a field of the search record for the destination component is added to keylist. The keys in the fieldlist must uniquely identify a row in the "to" page search record. If a unique row is not identified, or if Force Search Processing is selected for the component, the search dialog box appears. If the keylist parameter is not supplied then the destination component's search key must be found as part of the source components level 0 record buffer. |
|
AutoSearch |
Specify whether an automatic search on the target search page is executed after the transfer. This means the search results are already shown without the end-user having to click the Search button. This parameter takes a Boolean value: True, do an automatic search. The default value is False (that is, the user has to click the Search button). |
Returns
None.
Example
The example starts a new instance of PeopleTools and transfers to a new page in Update mode. The data in the new page is selected by matching the EMPLID field from the old page.
TransferExact(true, MENUNAME.ADMINISTER_PERSONNEL, BARNAME.USE, ITEMNAME.PERSONAL_DATA, PAGE.PERSONAL_DATA_1, "U");
Using the following PeopleCode program:
&MYREC = CreateRecord(RECORD.QEOPC_9A2FIELDS); &MYREC.QE_TITLE.Value = "KEY"; Transfer(False, MenuName.QE_PEOPLECODE_PAGES, BarName.USE, ItemName.QEPC9PROPSTESTS, Page.QEOPC_9A2FIELDS, "U", &MYREC);
The following SQL is produced:
SELECT DISTINCT TOP 301 QE_TITLE, QEPC_ALTSRCH FROM PS_QEOPC_9A2FIELDS WHERE QE_TITLE LIKE 'KEY%' ORDER BY QE_TITLE
If you change the Transfer to TransferExact:
&MYREC = CreateRecord(RECORD.QEOPC_9A2FIELDS); &MYREC.QE_TITLE.Value = "KEY"; TransferExact(False, MenuName.QE_PEOPLECODE_PAGES, BarName.USE, ItemName.QEPC9PROPSTESTS, Page.QEOPC_9A2FIELDS, "U", &MYREC);
The following SQL is produced:
SELECT DISTINCT TOP 301 QE_TITLE, QEPC_ALTSRCH FROM PS_QEOPC_9A2FIELDS WHERE QE_TITLE=:1 ORDER BY QE_TITLE
See Also
TransferPage, DoModalComponent, Transfer.

 TransferMobilePage
TransferMobilePageSyntax
TransferMobilePage([MOBILEPAGE.]PageName, Tab, &CIObject);
Description
Use the TransferMobilePage function to close the current Mobile Page Detail View and transfer the end user to another Mobile Page Detail View. This function is only supported in the OnChange event or on the OnInit event for level 0 objects.
A new working set is not started when transferring between objects in the same component.
The Tab parameter takes the definitional number, not the number of the tab that is displaying. For example, if there are three tabs defined, but only tabs one and three are showing (you've hidden tab number two) you would specify a 3 for the Tab parameter to transfer to tab number three, even though it is displaying as tab number two.
Note. When a user is transferred using TransferMobilePage, the Return To list hyperlink is not displayed on the Mobile Page.
Parameters
|
PageName |
Specify the mobile page definition used to display the page. This parameter takes a string value. It is good programming practice to preface this parameter with the keyword MOBILEPAGE, since it provides automatic rename support, however, it is not necessary to use it. |
|
Tab |
Specify an integer (1 to n) that determines what tab to make active. This parameter takes a number value. |
|
&CIObject |
Specify an already instantiated mobile object. |
Returns
None.
Example
&MyCI = %Session.GetCompIntfc(COMPINTFC.myci); &MyCI.Key1 = "x"; &MyCI.Ket2 = "y"; If Not(&MyCI.Get()) Then; errorstuff(); End-if; Transfer(MOBILEPAGE.MyCIPageName, 1, &MyCI);

 TransferNode
TransferNodeSyntax
TransferNode(new_instance, NODE.nodename, MENUNAME.menuname, MARKET.marketname, COMPONENT.componentname, PAGE.component_item_name, action [, keylist]);
where keylist is a list of field references in the form:
[recordname.]field1 [, [recordname.]field2]. . .
OR
&RecordObject1 [, &RecordObject2]. . .
Description
Use the TransferNode function to transfer the user to a page in another Node, but within the same portal.
TransferNode can either start a new instance of the application and transfer to the new page, or close the old page and transfer to the new one in the same instance of PeopleTools.
Component scoped and Global scoped variables are not available if the new page is in a different node.
Entering null values ("") for the node opens the new component within the current node or portal.
If you want to transfer the end-user to another portal, use the TransferPortal function.
If you provide a valid search key for the new page in the optional fieldlist, the new page opens directly, using the values provided from fieldlist as search key values. If no key is provided, or if the key is invalid, the search dialog displays, allowing the end-user to search for a row.
Note. If Force Search Processing is specified in Application Designer for the component, the search dialog always displays, whether the keylist is provided or not.
If TransferNode is called in a RowInit PeopleCode program, the PeopleCode program is terminated. However, the component processor continues with its RowInit processing, calling RowInit on the other fields. The actual transfer won't happen until after that completes. You may want to place any TransferPage functions in the Activate event for the page, or later in the Component Processor event flow.
See Creating Component Definitions.
Restrictions on Use with a Component Interface
This function is ignored (has no effect) when used by a PeopleCode program that’s been called by a Component Interface.
Restrictions on Use with SearchInit Event
You can't use this function in a SearchInit PeopleCode program.
Considerations Using Exceptions and the TransferNode Function
Using the TransferNode function inside a try blockdoes not catch PeopleCode exceptions thrown in the new component. Starting a new component starts a brand new PeopleCode evaluation context. Catches are only caught for exceptions thrown within the current component.
In the following code example, the catch statement only catches exceptions thrown in the code prior to using the DoModal function, but not any exceptions that are thrown within the new component.
/* Set up transaction */ If %CompIntfcName = "" Then try &oTrans = &g_ERMS_TransactionCollection.GetTransactionByName(RB_EM_WRK.DESCR); &sSearchPage = &oTrans.SearchPage; &sSearchRecord = &oTrans.SearchRecord; &sSearchTitle = &oTrans.GetSearchPageTitle(); If Not All(&sSearchPage, &sSearchRecord, &sSearchTitle) Then Error (MsgGetText(17834, 8081, "Message Not Found")); End-If; &c_ERMS_SearchTransaction = &oTrans; /* Attempt to transfer to hidden search page with configurable filter */ &nModalReturn = DoModal(@("Page." | &sSearchPage), &sSearchTitle, - 1, - 1); catch Exception &e Error (MsgGetText(17834, 8082, "Message Not Found")); end-try;
Parameters
|
new_instance |
Set this parameter to True to start a new application instance, or to False to use the current window and replace the page already displayed. |
|
nodename |
Specify the name of the node that contains the content, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. |
|
menuname |
Specify the name of the menu containing the content, prefixed with the reserved word MENUNAME. You can also use a string, such as %Menu, for this value. |
|
marketname |
Specify the name of the market of the component, prefixed with the reserved word MARKET. You can also use a string, such as %Market, for this value. |
|
component_item_name |
Specify the component item name of the page to be displayed on top of the component when it displays. The component item name is specified in the component definition. If you specify a page, it must be prefixed with the keyword PAGE. You can also specify a null ("") for this parameter. |
|
action |
Specify a single-character code. Valid actions are:
You can also specify a null ("") for this parameter. |
|
keylist |
An optional list of field specifications used to select a unique row at level zero in the page you are transferring to, by matching keys in the page you are transferring from. It can also be an already instantiated record object. If a record object is specified, any field of that record object that is also a field of the search record for the destination component is added to keylist. The keys in the fieldlist must uniquely identify a row in the "to" page search record. If a unique row is not identified, of if Force Search Processing has been selected, the search dialog appears. If the keylist parameter is not supplied then the destination component's search key must be found as part of the source components level 0 record buffer. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if function completed successfully, False otherwise.
See Also
TransferPortal, TransferPage, Transfer.

 TransferPortal
TransferPortalSyntax
TransferPortal(new_instance, PORTAL.portalname, NODE.nodename, MENUNAME.menuname, MARKET.marketname, COMPONENT.componentname, PAGE.component_item_name, action [, keylist]);
where keylist is a list of field references in the form:
[recordname.]field1 [, [recordname.]field2]. . .
OR
&RecordObject1 [, &RecordObject2]. . .
Description
Use the TransferPortal function to transfer the user to a page in another Node in a different portal.
TransferPortal can either start a new instance of the application and transfer to the new page, or close the old page and transfer to the new one in the same instance of PeopleTools.
Component scoped and Global scoped variables are not available after this function.
If you want to transfer the end-user to another node within the same portal, use the TransferNode function.
If you provide a valid search key for the new page in the optional fieldlist, the new page opens directly, using the values provided from fieldlist as search key values. If no key is provided, or if the key is invalid, the search dialog displays, allowing the end-user to search for a row.
Note. If Force Search Processing is specified in Application Designer for the component, the search dialog always displays, whether the keylist is provided or not.
If TransferPortal is called in a RowInit PeopleCode program, the PeopleCode program is terminated. However, the component processor continues with its RowInit processing, calling RowInit on the other fields. The actual transfer won't happen until after that completes. You may want to place any TransferPortal functions in the Activate event for the page, or later in the Component Processor flow.
See Creating Component Definitions.
Restrictions on Use with a Component Interface
This function is ignored (has no effect) when used by a PeopleCode program that’s been called by a Component Interface.
Restrictions on Use with SearchInit Event
You can't use this function in a SearchInit PeopleCode program.
Restrictions on Use with Different Releases
You cannot use this function to transfer a user from a PeopleTools 8.42 portal to any base PeopleTools 8.1x portal that overwrites the expired cookie value when login occurs.
The TransferPortal function is currently supported to transfer users to pages in other nodes to base PeopleTools 8.18 portals, including all PeopleTools 8.18 versions and patches.
Considerations Using Exceptions and the TransferPortal Function
Using the TransferPortal function inside a try block does not catch PeopleCode exceptions thrown in the new component. Starting a new component starts a brand new PeopleCode evaluation context. Catches are only caught for exceptions thrown within the current component.
In the following code example, the catch statement only catches exceptions thrown in the code prior to using the DoModal function, but not any exceptions that are thrown within the new component.
/* Set up transaction */ If %CompIntfcName = "" Then try &oTrans = &g_ERMS_TransactionCollection.GetTransactionByName(RB_EM_WRK.DESCR); &sSearchPage = &oTrans.SearchPage; &sSearchRecord = &oTrans.SearchRecord; &sSearchTitle = &oTrans.GetSearchPageTitle(); If Not All(&sSearchPage, &sSearchRecord, &sSearchTitle) Then Error (MsgGetText(17834, 8081, "Message Not Found")); End-If; &c_ERMS_SearchTransaction = &oTrans; /* Attempt to transfer to hidden search page with configurable filter */ &nModalReturn = DoModal(@("Page." | &sSearchPage), &sSearchTitle, - 1, - 1); catch Exception &e Error (MsgGetText(17834, 8082, "Message Not Found")); end-try;
Parameters
|
new_instance |
Set this parameter to True to start a new application instance, or to False to use the current window and replace the page already displayed. |
|
PortalName |
Specify the name of the portal that you want to transfer to, prefixed with the reserved word Portal. |
|
nodename |
Specify the name of the node that contains the content, prefixed with the reserved word NODE. You can also use a string, such as %Node, for this value. |
|
menuname |
Specify the name of the menu containing the content, prefixed with the reserved word MENUNAME. You can also use a string, such as %Menu, for this value. |
|
marketname |
Specify the name of the market of the component, prefixed with the reserved word MARKET. You can also use a string, such as %Market, for this value. |
|
component_item_name |
Specify the component item name of the page to be displayed on top of the component when it displays. The component item name is specified in the component definition. If you specify a page, it must be prefixed with the keyword PAGE. You can also specify a null ("") for this parameter. |
|
action |
Specify a single-character code. Valid actions are:
You can also specify a null ("") for this parameter. |
|
keylist |
An optional list of field specifications used to select a unique row at level zero in the page you are transferring to, by matching keys in the page you are transferring from. It can also be an already instantiated record object. If a record object is specified, any field of that record object that is also a field of the search record for the destination component is added to keylist. The keys in the fieldlist must uniquely identify a row in the "to" page search record. If a unique row is not identified, of if Force Search Processing has been selected, the search dialog appears. If the keylist parameter is not supplied then the destination component's search key must be found as part of the source components level 0 record buffer. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if function completed successfully, False otherwise.
See Also
TransferNode, TransferPage, Transfer.

 TransferPanel
TransferPanel
Syntax
TransferPanel([PANEL.panel_name])
Description
Use the TransferPanel function to transfer control to the panel indicated by PANEL. panel_name_name within, or to the panel set with the SetNextPage function.
Note. The TransferPanel function is supported for compatibility with previous releases of PeopleTools. New applications should use the TransferPage function instead.
See Also

 TransferPage
TransferPageSyntax
TransferPage([PAGE.page_name_name])
Description
Use the TransferPage function to transfer control to the page indicated by PAGE. page__namename within, or to the page set with the SetNextPage function. The page that you transfer to must be in the current component or menu. To transfer to a page outside the current component or menu, or to start a separate instance of PeopleTools prior to transfer into, use the Transfer function.
See SetNextPage, Transfer.
Note. You can’t use TransferPage from a secondary page.
Any variable declared as a Component variable will still be defined after using a TransferPage function.
Considerations Using TransferPage
The following are important considerations when using the TransferPage function:
TransferPage always terminates the current PeopleCode program.
TransferPage is always processed after all events are completed.
Given these considerations, here are some scenarios for how TransferPage executes:
When called in RowInit: The current RowInit PeopleCode program is terminated, but RowInit processing continues. In addition, RowInit PeopleCode programs run for the rest of the fields in the row. Then TransferPage is processed.
When called in FieldEdit: The FieldEdit PeopleCode program is terminated. The FieldChange program for that field still runs. Then TransferPage is processed.
When called in SavePreChange: The SavePreChange program for that field is terminated. SavePreChange runs for the rest of the fields on that page. Then SavePostChange run for all the fields. Then TransferPage is processed.
When called in FieldChange in deferred mode: In deferred mode, changed fields are processed in order. The FieldChange program is terminated. Then any subsequent fields in the page order are processed with the normal FieldEdit-Field Change logic. Once that has finished, the TransferPage is processed.
When TransferPage is processed, any PeopleCode associated with the Activate event for the page being transferred to runs. This always occurs at the end, after all field processing.
If TransferPage is called multiple times during field processing, all the calls are processed at the end, in the same order the calls were made. The Activate event executes each time. The final active page is the one that was transferred to by the last call.
Restrictions on Use With a Component Interface
This function is ignored (has no effect) when used by a PeopleCode program that’s been called by a Component Interface.
Restrictions on Use With SearchInit Event
You can't use this function in a SearchInit PeopleCode program.
Parameters
|
page_name |
A String equal to the name of the page you are transferring to, as set in the page definition, prefixed with the reserved word Page. The page must be in the same component as the page you are transferring from. |
Returns
Optionally returns a Boolean value indicating whether the function executed successfully.
Example
The following examples both perform the same function, which is to transfer to the JOB_DATA_4 page:
TransferPage(PAGE.JOB_DATA_4);
or
SetNextPage(PAGE.JOB_DATA_4); TransferPage( );
See Also
DoModalComponent, SetNextPage, Transfer.

 Transform
TransformSyntax
Transform({XmlString | &XmlDoc}AE_Program_Name, Initial_Node_Name, Initial_Message__Name, Initial_Message_Version, Result_Node_Name, Result_Message_Name, Result_Message_Version)
Description
Use the Transform function to modify one transaction, as specified by the Initial parameters, to another transaction, specified by the Result parameters, using an Application Engine program. This is used with Integration Broker.
Generally using this function implies that you're transforming a message that you're not actually sending or receiving at the current time. By using this method, and specifying the two transactions, it's as if you're defining a relationship, without having to use the relationship component.
Considerations Using the Transform Functions
The Transform function uses an existing Application Engine program to do transformations. This enables you to break up the flow of Integration Broker and do transformations when you need to. If you wish to resuse your Application Engine programs, you can invoke them by using this function.
The TransformEx function does not use an Application Engine program to do a transformation. Instead, it does an Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformation (XSLT.) This enables you to dynamically do transformations outside of Integration Broker, such as, performing transformations on pagelets in a portal every time a page is accessed.
The TransformExCache function also does XSLT transformations without using an Application Engine program, outside of Integration Broker. Use TransformExCache when you have a large volume of similar transformations to be done. Caching technology is used with this function. You may see an increase in performance, as well as an increase in memory consumption, using this function.
Parameters
|
XmlString | &XmlDoc |
Specify an already populated XmlDoc object, an XML string, or other text that you want transformed. |
|
AE_Program_Name |
Specify the name of the Application Engine program that you want to use for the transformation. |
|
Initial_Node_Name |
Specify the name of the initial node as a string. |
|
Initial_Message_Name |
Specify the name of the initial message. |
|
Initial_Message_Version |
Specify the version of the initial message that you want to use. |
|
Result_Node_Name |
Specify the result, where you want the transformed message to go to. |
|
Result_Message_Name |
Specify the name of the result message, the one to use for the output. |
|
Result_Message_Version |
Specify the version of the result message to be used. |
Returns
An XmlDoc object containing the resulting XML from the transformation. Null is never returned. If you do not want to display an error to the user, place this function inside a try-catch statement.
See Also
TransformEx, TransformExCache.
Applying Filtering, Transformation and Translation

 TransformEx
TransformExSyntax
TransformEx(XmlString, XsltString)
Description
Use the TransformEx function to do an XSLT transformation of the specified XML string.
This function also strips off any encoding information located within the XML Declaration.
The input, output, and XSL string must all be well-formed XML. If the output is HTML, it is actually XHTML (which is well-formed XML.)
Considerations Using the Transform Functions
The Transform function uses an existing Application Engine program to do transformations. This enables you to break up the flow of Integration Broker and do transformations when you need to. If you wish to resuse your Application Engine programs, you can invoke them by using this function.
The TransformEx function does not use an Application Engine program to do a transformation. Instead, it does an Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformation (XSLT.) This enables you to dynamically do transformations outside of Integration Broker, such as, performing transformations on pagelets in a portal every time a page is accessed.
The TransformExCache function also does XSLT transformations without using an Application Engine program, outside of Integration Broker. Use TransformExCache when you have a large volume of similar transformations to be done. Caching technology is used with this function. You may see an increase in performance, as well as an increase in memory consumption, using this function.
Parameters
|
XmlString |
Specify the XML string that you want transformed. |
|
XsltString |
Specify the XSLT string you wish to use to transform the XML string. |
Returns
The output of the transformation as a string if successful, NULL otherwise.
Example
try &outStr = TransformEx(&inXML, &inXSLT); catch Exception &E MessageBox(0, "", 0, 0, "Caught exception: " | &E.ToString()); end-try;
See Also
Applying Filtering, Transformation and Translation

 TransformExCache
TransformExCache
Syntax
TransformExCache(&XmlDoc, FilePath, XsltKey)
Description
Use the TransformExCache function to do an Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformation (XSLT) transformation of the specified XmlDoc object.
The file specified by FilePath must be in well-formed XML.
Considerations Using the Transform Functions
The Transform function uses an existing Application Engine program to do transformations. This enables you to break up the flow of Integration Broker and do transformations when you need to. If you wish to resuse your Application Engine programs, you can invoke them by using this function.
The TransformEx function does not use an Application Engine program to do a transformation. Instead, it does an Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformation (XSLT.) This enables you to dynamically do transformations outside of Integration Broker, such as, performing transformations on pagelets in a portal every time a page is accessed.
The TransformExCache function also does XSLT transformations without using an Application Engine program, outside of Integration Broker. Use TransformExCache when you have a large volume of similar transformations to be done. Caching technology is used with this function. You may see an increase in performance, as well as an increase in memory consumption, using this function.
Parameters
|
&XmlDoc |
Specify an already instantiated and populated XmlDoc object that you want transformed. |
|
FilePath |
Specify an XSLT file. You must specify an absolute path to the file, including the file extension. |
|
XsltKey |
Specify a key to uniquely name the compiled and cached XSLT in the data buffers. This key is used both to create the item in memory as well as retrieve it. This parameter takes a string value, up to 30 characters. |
Returns
An XmlDoc object containing the resulting XML from the transformation. Null is never returned. If you do not want to display an error to the user, place this function inside a try-catch statement.
Example
Local XmlDoc &inXMLdoc = CreateXmlDoc(""); Local Boolean &ret = &inXMLdoc.ParseXmlFromURL("c:\temp\in.xml"); Local XmlDoc &outDoc = TransformExCache(&inXMLdoc, "c:\temp\in.xsl", "INBOUND");
See Also
Applying Filtering, Transformation and Translation

 TreeDetailInNode
TreeDetailInNodeSyntax
TreeDetailInNode(setID, tree, effdt, detail_value, node)
Description
Use the TreeDetailInNode function to determine whether a specific record field value is a descendant of a specified node in a specified tree.
Note. This function is not compatible with the PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture. However, this function is still available
for use with the PeopleSoft Tree Manager Windows client, available in the 8.1 product line.
An equivalent PeopleCode tree class method or built-in function for PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture does not exist,
however, you may achieve this same functionality using the tree classes.
Parameters
|
setID |
SetID for the appropriate business unit. This parameter is required. If there is no SetID, you can pass a NULL string ("", not a blank) and a blank will be used. |
|
tree |
The tree name that contains the detail_value. |
|
effdt |
Effective date to be used in the search. You must use a valid date. |
|
detail_value |
The recordname.fieldname containing the value you are looking for. |
|
node |
The "owning" tree node name. |
Returns
Returns a Boolean value, True if detail_value is a descendant of node in tree.
Example
This example sets the value of &APPR_RULE_SET to the value at the APPR_RULE_LN record and APPR_RULE_SET fieldname, on the tree ACCOUNT.
&APPR_RULE_SET = TreeDetailInNode("SALES", "ACCOUNT", %Date, APPR_RULE_LN.APPR_RULE_SET, "test");
See Also
Introduction to PeopleSoft Tree Manager

 TriggerBusinessEvent
TriggerBusinessEventSyntax
TriggerBusinessEvent(BUSPROCESS.bus_proc_name, BUSACTIVITY.activity_name, BUSEVENT.bus_event_name)
Description
Use the TriggerBusinessEvent funciton to trigger a business event and the workflow routings associated with that event. This function should only be used in Workflow PeopleCode. You can edit Workflow PeopleCode via the Event Definition dialog while you are defining a workflow event.
Parameters
|
bus_proc_name |
A string consisting of the name of the business process, as defined in the Business Process Designer, prefixed with the reserved word BUSPROCESS. |
|
activity_name |
A string consisting of the name of the business activity, as defined in the Business Process Designer, prefixed with the reserved word BUSACTIVITY. |
|
bus_event_name |
A string consisting of the name of the business event, as defined in the Business Process Designer, prefixed with the reserved word BUSEVENT. |
Returns
Returns a Boolean value: True if successful, false otherwise. The return value is not optional.
Note. You must check the return from TriggerBusinessEvent to see if you have an error. If you have an error, all of the updates up to that TriggerBusinessEvent process are rolled back. However, if you don’t halt execution, even if you have an error, all updates after the TriggerBusinessEvent process are committed. This could result in your database information being out of synch.
Example
The following example triggers the Deny Purchase Request event in the Manager Approval activity of the Purchase Requisition business process:
&SUCCESS = TriggerBusinessEvent(BUSPROCESS."Purchase Requisition", BUSACTIVITY."Manager Approval", BUSEVENT."Deny Purchase Request");
See Also
GetWLFieldValue, MarkWLItemWorked.

 Truncate
TruncateSyntax
Truncate(dec, digits)
Description
Use the Truncate function to truncate a decimal number dec to a specified precision.
Parameters
|
digits |
A Number value that sets the precision of the truncation (that is, the number of digits to leave on the right side of the decimal point). |
Returns
Returns a Number value equal to dec truncated to a digits precision.
Example
The example sets the value of &NUM to 9, 9.99, -9, then 0.
&NUM = Truncate(9.9999, 0); &NUM = Truncate(9.9999, 2); &NUM = Truncate(-9.9999, 0); &NUM = Truncate(0.001, 0);
See Also

 Try
TrySyntax
try
Protected StatementList
catch QualifiedID &Id
StatementList
end-try
Description
Use the Try statement as part of a Try-Catch statement to trap exceptions thrown either by the system or created using the CreateException function.
Parameters
|
Protected StatementList |
Specify the statements that are protected by the Try-Catch statement. |
|
catch QualifiedID &Id |
Specify the Catch statement at the end of the list of statements you want to protect. |
|
QualifiedID |
Specify what class of exception you are catching, that is, Exception or the name of a class extending it. |
|
&Id |
Specify a variable to be set with the caught exception. |
|
StatementList |
Specify the steps to be taken once the exception is caught. |
Returns
None.
Example
try &res = 15.3 / 7 * 22.1; catch Exception &c1 MessageBox(0, "", 0, 0, "Caught exception: " | &c1.ToString()); end-try;
See Also

 UnCheckMenuItem
UnCheckMenuItem
Syntax
UnCheckMenuItem(BARNAME.menubar_name, ITEMNAME.menuitem_name)
Description
Use the UnCheckMenuItem function to remove a check mark from the specified menu item.
Note. This function has been deprecated.

 Unencode
UnencodeSyntax
Unencode(URLString)
Description
Use the Unencode function to unencode URLString, converting all character codes of the form %xx where xx is a hex number, to the character represented by that number.
Parameters
|
URLString |
Specify the string you want unencoded. This parameter takes a string value. |
Returns
An unencoded URL string.
Example
For the following example, the URL is:
http://corp.office.com/human%20resources/benefits/401kchange_home.htm?FirstName=Gunter&LastName=D%c3%9crst
The encoded values are those beginning with the percentage sign (%). If you wanted to know the value in the Target Content’s URL for the parameter “LastName”, then the following PeopleCode would return the string “Dürst”:
&MENU = Unencode(%Request.GetParameter("LastName"));
This method works for any querystring in the Target Content’s URL.
If the link is constructed in a PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture page, and the value of a link field, you should not call EncodeURL to encode the entire URL, as the PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture does this for you. You must still unencode the parameter value when you retrieve it, however.
See Also
EncodeURL, EncodeURLForQueryString.

 Ungray
UngraySyntax
Ungray(scrollpath, target_row, [recordname.]fieldname)
where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ]] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can also use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Use the Ungray function to make a gray (non-editable) page field editable, if the field was grayed with a call to the Gray function.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the Enabled field property instead.
If the page field is made display-only in the Page Field Properties dialog, then Ungray has no effect.
The Gray, Ungray, Hide, and Unhide functions usually appear in RowInit programs that set up the initial display of data, and FieldChange programs that change field display based on changes the end-user makes to a field.
Generally, you want to put this function on the same scroll level as the field that is being changed in RowInit (which executes on every row) or FieldChange (which executes on the current row). This simplifies the function’s syntax to:
Ungray(fieldname)
A typical use of the more complex syntax is when looping through rows on a scroll on a lower level than the program.
Note. This function shouldn't be used in any event prior to RowInit.
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
Scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
target_row |
The row number of the target row. If this parameter is omitted, the function assumes the row on which the PeopleCode program is executing. |
|
[recordname .]fieldname |
The name of the field to ungray. The field can be on scroll level one, two, or three of the active page. The recordname prefix is required if the call to Ungray is in a record definition other than recordname. |
Returns
Optionally returns a Boolean value indicating whether the function executed successfully.
Example
The following example checks to see if a person’s emergency contact is the same as their home address and phone, then grays or ungrays the fields accordingly. In a typical case, this program would be in the FieldChange event.
If SAME_ADDRESS_EMPL = "Y" Then Gray(STREET1); Gray(STREET2); Gray(CITY); Gray(STATE); Gray(ZIP); Gray(COUNTRY); Gray(HOME_PHONE); STREET1 = PERSONAL_DATA.STREET1; STREET2 = PERSONAL_DATA.STREET2; CITY = PERSONAL_DATA.CITY; STATE = PERSONAL_DATA.STATE; ZIP = PERSONAL_DATA.ZIP; COUNTRY = PERSONAL_DATA.COUNTRY; HOME_PHONE = PERSONAL_DATA.HOME_PHONE; Else Ungray(STREET1); Ungray(STREET2); Ungray(CITY); Ungray(STATE); Ungray(ZIP); Ungray(COUNTRY); Ungray(HOME_PHONE); End-if;
See Also

 Unhide
UnhideSyntax
Unhide(scrollpath, target_row, [recordname.]fieldname)
where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ]] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Use the Unhide function to make a field visible that was previously hidden with Hide. If the field was hidden by setting its Invisible property in the Page Field Properties dialog box, then Unhide has no effect.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the Visible field property instead.
Generally, you want to put this function on the same scroll level as the field that is being changed in RowInit (which executes on every row) or FieldChange (which executes on the current row). This simplifies the function’s syntax to:
unhide(fieldname)
A typical use of the more complex syntax is when looping through rows on a scroll on a lower level than the program.
Note. This function shouldn't be used in any event prior to RowInit.
See Also
Hide.
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
target_row |
The row number of the target row. If this parameter is omitted, the function assumes the row on which the PeopleCode program is executing. |
|
[recordname .]fieldname |
The name of the field to unhide. The field can be on scroll level one, two, or three of the active page. The recordname prefix is required if the call to Unhide is in a record definition other than recordname. |
Returns
Optionally returns a Boolean value indicating whether the function executed successfully.
Example
The following example sets security for displaying a person’s password:
If (&DISPLAY) Then Unhide(EMPLOYEE.PASSWORD); Else Hide(EMPLOYEE.PASSWORD); End-if;
See Also

 UnhideRow
UnhideRowSyntax
UnhideRow(scrollpath, target_row)
Where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Use the UnhideRow function to programmatically unhide a row that has been hidden by HideRow. It unhides the specified row and any dependent rows at a lower scroll level.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the Visible row property instead.
UnhideRow works by putting the row that you unhide to the last non-hidden row in the list. When UnhideRow is used in a loop, you have to process rows from low to high to achieve the correct results.
Note. UnhideRow cannot be executed from the same scroll level where the insertion takes place, or from a lower scroll level. Place the PeopleCode in a higher scroll level record.
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
target_row |
An integer specifying which row in the scroll to unhide. |
Returns
Optionally returns a Boolean value indicating whether the function executed successfully.
Example
AE_ROW_COUNT = ActiveRowCount(RECORD.AE_STMT_TBL); for &ROW = ActiveRowCount(RECORD.AE_STMT_TBL) to 1 step - 1 UnhideRow(RECORD.AE_STMT_TBL, &ROW); UpdateValue(RECORD.AE_STMT_TBL, &ROW, AE_ROW_NUM, &ROW); end-for;
See Also

 UnhideScroll
UnhideScrollSyntax
UnhideScroll(Scrollpath)
Where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ] RECORD.target_recname
To prevent ambiguous references, you can use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Use the UnhideScroll function to programmatically unhide a scroll area that has been hidden with HideScroll. It unhides the specified scroll and any associated scrolls at a lower level.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the ShowAllRows rowset method instead.
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
Returns
Optionally returns a Boolean value indicating whether the function executed successfully.
Example
This example clears the contents of a level-one hidden scroll, then unhides it:
ScrollFlush(RECORD.ORDER_INQ_INV); UnhideScroll(RECORD.ORDER_INQ_INV);
The following example hides or unhides a level-three scroll:
If APPR_QTY_SW = "N" Then HideScroll(RECORD.APPR_RULE_LN, CurrentRowNumber(1), RECORD.APPR_RULE_DETL, CurrentRowNumber(2), RECORD.APPR_RULE_QTY); Else UnhideScroll(RECORD.APPR_RULE_LN, CurrentRowNumber(1), RECORD.APPR_RULE_DETL, CurrentRowNumber(2), RECORD.APPR_RULE_QTY); End-If;
See Also
HideScroll, RowScrollSelect, RowScrollSelectNew, ScrollSelect, ScrollSelectNew, SortScroll.

 UniformSeriesPV
UniformSeriesPVSyntax
UniformSeriesPV(int_rate,n_per)
Description
Use the UniformSeriesPV function to calculate the present value of a single monetary unit after a uniform series of payments at a specified interest rate.
Parameters
|
int_rate |
A Number specifying the interest rate on the basis of which to calculate the return value. |
|
n_per |
A Number specifying the number of payments in the uniform series. |
Returns
Returns a Number equal to the value of a single unit after n_per payments at an interest rate of int_rate.
Example
The example sets &NUM to 3.790786769408448256:
&NUM = UniformSeriesPV(10,5);
See Also

 UpdateSysVersion
UpdateSysVersionSyntax
UpdateSysVersion()
Description
Use the UpdateSysVersion function to coordinate system changes and changes to system objects maintained by pages, such as messages and Set Tables. This function is not normally used in standard applications and should only used in PeopleSoft-provided extensions of PeopleTools.
Returns
Returns the updated system version Number.
Example
The following example could be used to maintain the version number on MESSAGE_SET_TBL, which controls the refreshing of cache files for the message entries:
VERSION = UpdateSysVersion();

 UpdateValue
UpdateValueSyntax
UpdateValue(scrollpath, [recordname.]fieldname, target_row, value)
where scrollpath is:
[RECORD.level1_recname, level1_row, [RECORD.level2_recname, level2_row, ]]
To prevent ambiguous references, you can use SCROLL. scrollname, where scrollname is the same as the scroll level’s primary record name.
Description
Use the UpdateValue function to update the value of a specified field with the value provided. The value must be of a data type compatible with the field.
Note. This function remains for backward compatibility only. Use the Value field property instead.
See Also
Specifying Data with References Using Scroll Path Syntax and Dot Notation
Parameters
|
Scrollpath |
A construction that specifies a scroll level in the component buffer. |
|
target_row |
An integer specifying the row of the field to update. |
|
[recordname .]fieldname |
The name of the field that you want to update. The field can be on scroll level one, two, or three of the active page. The recordname prefix is required if the call to UpdateValue is in a record definition other than recordname. |
|
Value |
The new value to put into the target field. |
Returns
None.
Example
This example updates values in the level-one scroll:
For &I = 1 To &ROW_CNT UpdateValue(RECORD.ASGN_CMP_EFFDT, &I, ITEM_SELECTED, "Y"); End-For;
The next example loops through rows in the level-two scroll:
For &I = 1 To &CURRENT_L2 UpdateValue(RECORD.ASGN_CMP_EFFDT, &CURRENT_L1, RECORED.SOME_L2_RECORD, &I, TO_CUR, &HOME_CUR); End-For;
See Also

 UpdateXmlDoc
UpdateXmlDocSyntax
UpdateXmlDoc(&XmlDoc, PubID, PubNode, ChannelName, VersionName [, Message Name [, SubNode[, Segment]]])
Description
Use the UpdateXmlDoc function to update a message in the message queue with the specified message version.
If VersionName isn’t specified, the default message version is used. This method is commonly used in the OnRouteSend and OnRouteReceive PeopleCode events.
Note. This function can't be called from subscription PeopleCode.
Parameters
|
&XmlDoc |
Specify an already instantiated XmlDoc object. |
|
PubID |
Specify the PubID as a string. |
|
PubNode |
Specify the PubNode as a sting. |
|
ChannelName |
Specify the Channel name as a string. |
|
VersionName |
Specify the version name as a string. |
|
MessageName |
Specify the message name as a string. This is only used for Pub and Sub contracts. |
|
SubNode |
Specify the sub node as a string. This is only used for Pub contracts. |
|
Segment |
Specify an integer representing which segment you want to access. The default value is one, which means that if you do not specify a segment, the first segment is accessed. |
Returns
A Boolean value: True if function completed successfully, False otherwise.
See Also

 Upper
UpperSyntax
Upper(str)
Description
Use the Upper function to convert a text string to all uppercase. This function can be used to perform a case-insensitive string comparison. Upper does not change characters that are not letters or characters that do not have case sensitivity.
Parameters
|
str |
A String to convert to uppercase. |
Returns
Returns a String value equal to str converted to all uppercase.
Example
The following example converts the contents of two string variables to uppercase before determining if they are equal to simulate a case-insensitive comparison:
If Upper(&STR1) = Upper(&STR2) Then /* do something */ End-If;
See Also

 Value
ValueSyntax
Value(str)
Description
Use the Value function to convert a string representing a number to the number.
To convert a number using the user's local format for the number, use the ValueUser function.
Parameters
|
str |
A String value representing a number. |
Returns
Returns the Number value represented by str.
Example
The example sets &VAL1 to 5.25 and &VAL2 to 12500:
&VAL1 = Value("5.25"); &VAL2 = Value("12,500");
See Also

 ValueUser
ValueUserSyntax
ValueUser(str)
Description
Use the ValueUser function to convert a string representing a number to the number, using the locale-specific form for the current user for the number. For example, if your regional settings specify to use periods as the thousands separator, the number will use that form when displayed, instead of whatever form is specified for the database.
To convert a number without using the user's format for the number, use the Value function.
Parameters
|
str |
Specify the string value representing a number that you want converted to a number. |
Returns
Returns the number value represented by str.
Example
The example sets &VAL1 to 5.25 and &VAL2 to 12500:
&VAL1 = ValueUser("5.25"); &VAL2 = ValueUser("12,500");
See Also

 ViewAttachment
ViewAttachmentSyntax
ViewAttachment(URLSource, DirAndFileName, UserFile [, NewWindow[, PreserveCase]])
where URLSource can have one of the following forms:
URL.URLname
OR a string URL, such as
ftp://worker:[email protected]/
Note. You cannot specify a different port for an attachment when using an FTP server. You can only use the default port of 21.
Description
Use the ViewAttachment function to enable an end-user to view a file on a system. The file is actually downloaded into the directory indicated by the TMP environment variable.
The viewing file is temporary, and is store on web server's public location. The viewing file may have a different name than the name the end user just typed in.
Note. .exe and .bat files are launched instead of viewed.
Security Considerations
The FileType parameter used with AddAttachment is only a suggestion. Specifying it does not enforce specific file types. If you do not want specific file types (such as .exe or .bat) you must write PeopleCode to discern the name and file type of the attached file and delete it before viewing it.
When the end user views attachments using the ViewAttachment function, some browsers treat documents as HTML regardless of file extension, and thus execute embedded java script. You may want to write a PeopleCode program to only allow specific file extensions to be viewed.
Restrictions on Use in PeopleCode Events
ViewAttachment is a “think-time” function, which means that it shouldn’t be used in any of the following PeopleCode events:
SavePreChange.
SavePostChange.
Workflow.
RowSelect.
Any PeopleCode event that fires as a result of a ScrollSelect (or one of its relatives) function calls, or a Select (or one of its relatives) Rowset class method.
See Think-Time Functions.
File Name Considerations
When the file is transferred using AddAttachment or PutAttachment, the following characters are replaced with an underscore:
space
semicolon
plus sign
percent sign
ampersand
apostrophe
exclamation point
@ sign
pound sign
dollar sign
Parameters
|
URLSource |
A reference to a URL. This can be either a URL name, in the form URL.URLName, or a string. |
|
DirAndFileName |
A directory and filename. This is appended to the URLSource to make up the full URL of the file. Note. The URLSource requires "/" slashes. Because the DirAndFileName parameter is appended to the URL, it also requires only "/" slashes. "\" are NOT supported in anyway for either the URLSource the DirAndFileName parameter. |
|
UserFile |
The name of the file on the source system. |
|
NewWindow |
Specify if the browser should try to use a new window to display the attachment. This parameter takes a Boolean value. The default is True. |
|
PreserveCase |
Specify a Boolean value to indicate whether the case of the directory and file name specified with DirAndFileName are preserved or not; true, preserve the case, false otherwise. The default value is false. |
Returns
An integer value. You can check for either the integer or the constant:
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
0 |
%Attachment_Success |
File was attached successfully. |
|
1 |
%Attachment_Failed |
File was not successfully attached. |
|
2 |
%Attachment_Cancelled |
File attachment didn't complete because the operation was canceled by the user. |
|
3 |
%Attachment_FileTransferFailed |
File transfer didn't succeed. |
|
5 |
%Attachment_NoDiskSpaceWebServ |
No disk space on the web server. |
|
7 |
%Attachment_DestSystNotFound |
Cannot locate destination system for ftp. |
|
8 |
%Attachment_DestSystFailedLogin |
Unable to login to destination system for ftp. |
|
9 |
%Attachment_FileNotFound |
Cannot locate file. |
|
10 |
%Attachment_DeleteFailed |
Cannot delete file. |
Example
&retcode = ViewAttachment(URL.MYFTP, ATTACHSYSFILENAME, ATTACHUSERFILE); If (&retcode = %Attachment_Failed) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "ViewAttachment failed"); End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_Cancelled) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "ViewAttachment cancelled"); End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_FileTransferFailed) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "ViewAttachment failed: File Transfer did not succeed"); End-If; /* following error message only in PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture */ If (&retcode = %Attachment_NoDiskSpaceAppServ) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "ViewAttachment failed: No disk space on the app server"); End-If; /* following error message only in PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture */ If (&retcode = %Attachment_NoDiskSpaceWebServ) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "ViewAttachment failed: No disk space on the web server"); End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_FileExceedsMaxSize) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "ViewAttachment failed: File exceeds the max size"); End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_DestSystNotFound) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "ViewAttachment failed: Cannot locate destination system for ftp"); End-If; If (&retcode = %Attachment_DestSysFailedLogin) Then MessageBox(0, "File Attachment Status", 0, 0, "ViewAttachment failed: Unable to login into destination system for ftp"); End-If;
In the following example, using the file object, a file is written on the application server. Because the absolute path isn't specified, the file is written to PS_SERVDIR/files directory.
The function PutAttachment takes the file from PS_SERVDIR/files directory and puts it on the ftp server specified in URL.GRADEBOOK.
The ViewAttachment function downloads the file into the user's machine and opens it for viewing.
/* Data buffer */ Component Rowset &Level0, &Students_Hdr, &Student_Grade; Component Row &Level0_Row; /* standalone rowset - populate from LAM_CLASS_ACTV */ Component Rowset &Class_Activity; Component number &Class_Act_No; Local File &Export_File; Local string &Export_Line; DoSaveNow(); &File_Name = %OperatorId | "_" | String(CLASS_SCTN_SCTY.STRM) | "_" | String(CLASS_SCTN_SCTY.CLASS_NBR) | ".txt"; &Export_File = GetFile(&File_Name, "W"); If &Export_File.IsOpen Then &Export_Line = "Last,First,Emplid,"; For &i = 1 To &Class_Activity.ActiveRowCount &Export_Line = &Export_Line | &Class_Activity(&i).LAM_CLASS_ACTV.DESCRSHORT.Value | ","; End-For; &Export_File.WriteLine(&Export_Line); For &i = 1 To &Students_Hdr.ActiveRowCount &Export_Line = &Students_Hdr(&i).GetRecord(Record.PERSONAL_DTA_VW).GetField(Field.NAME).Value | ","; &Export_Line = &Export_Line | &Students_Hdr(&i).STDNT_GRADE_HDR.EMPLID.Value | ","; &Student_Grade = &Level0_Row.GetRowset(Scroll.STDNT_GRADE_HDR)(&i).GetRowset(Scroll.STDNT_GRADE_DTL); For &j = 1 To &Student_Grade.ActiveRowCount &Export_Line = &Export_Line | String(&Student_Grade(&j).STDNT_GRADE_DTL.STUDENT_GRADE.Value) | ","; End-For; &Export_File.WriteLine(&Export_Line); End-For; &Export_File.Close(); End-If; &Put_File_Name = "files/" | &File_Name; &ret = PutAttachment(URL.GRADEBOOK, &File_Name, &Put_File_Name, "PS_SERVDIR"); &ret = ViewAttachment(GetURL(URL.GRADEBOOK), &File_Name, &File_Name);
See Also
AddAttachment, DeleteAttachment, GetAttachment, PutAttachment.
Using File Attachments in Applications

 ViewContentURL
ViewContentURLSyntax
ViewContentURL(URL_str | URL.URL_ID)
Description
Use the ViewContentURL function to launch a new browser window and navigates to the location specified by URL_str or URL.URL_ID.
The content specified by the URL is not wrapped by the portal template. Use this function when you want to connect to third-party content. If you want to wrap the content in the portal template, use the ViewURL function.
This is a deferred execution command: the browser is launched after any executing PeopleCode has run to completion. This function automatically launches a new browser window.
Note. The ViewContentURL function does not work if being run on a Window 95 operating system and Internet Explorer version 3.02 or greater has not been installed.
Considerations Using javascript
The JavaScript window open method uses the backslash (\) as a quote for the next character. You must use double backslashes for the ViewContentURL function to work in a JavaScript. Note the four backslashes in the beginning of the following code example:
ViewContentURL("\\\\PT-NFS01\\PSUSERWS\\TEMP\\TVN\\81X-PATCHES.TXT");
Parameters
|
URL_str | URL. URL_ID |
Specify the location to where you want to navigate. You can specify either a URL string or a URL saved in the URL table, by specifying the reserved word URL followed by a dot and the URL Identifier. |
Returns
None.
Example
If &MyPage Then ViewURL(URL.MYPAGE); Else ViewContentURL("http://www.PeopleSoft.com"); End-If;
See Also

 ViewURL
ViewURLSyntax
ViewURL(URL_str | URL.URL_ID [, NewWindow])
Description
Use the ViewURL function to launch the default browser and navigate to the location specified by URL_str or URL.URL_ID. This is a deferred execution command: the browser is launched after any executing PeopleCode has run to completion. You can also specify whether the new page launches a new browser, or replaces the current page in the browser.
Note. This function does not issue any kind of warning to the user about losing data. Your application should verify that all data is saved before launching a new page.
The content specified by the URL is automatically wrapped by the portal template. If you do not want to wrap the content in the portal template, use the ViewContentURL function.
Note. The ViewURL function will not work if being run on a Window 95 operating system and Internet Explorer version 3.02 or greater has not been installed. Portal applications should use the RedirectURL Response class method instead of ViewURL.
See RedirectURL.
Parameters
|
URL_str | URL. URL_ID |
Specify the location to where you want to navigate. You can specify either a URL string, or, a URL saved in the URL table, by specifying the reserved word URL followed by a dot and the URL Identifier. |
|
NewWindow |
Specify whether the new page be opened in a new in the browser, or launch a new browser. This parameter takes a Boolean value: True to launch a new browser, False to replace existing page. The default value is False. |
Returns
None.
Example
If &MyPage Then ViewURL(URL.MYPAGE); Else ViewContentURL("http://www.PeopleSoft.com"); End-If;
See Also

 Warning
WarningSyntax
Warning str
Description
You typically use the Warning function in FieldEdit or SaveEdit PeopleCode to display a message alerting the end-user about a potentially incorrect data entry or change. It differs from the Error function in that it does not prevent the end-user from taking an action, and it does not stop processing in the PeopleCode program where it occurs.
Warning is also used in RowDelete and RowSelect PeopleCode, where its behavior is specialized. See the following sections Warnings in RowDelete and Warnings in RowSelect.
The text of the warning message (the str parameter), should always be stored in the Message Catalog and retrieved using the MsgGet or MsgGetText function. This makes it easier to translate the text, and it also enables you to include more detailed Explain text about the warning.
Warnings in FieldEdit and SaveEdit
The primary use of Warning is in FieldEdit and SaveEdit PeopleCode:
In FieldEdit, Warning displays a message and highlights the relevant field.
In SaveEdit, Warning displays a message, but does not highlight any field. You can move the cursor to a specific field using the SetCursorPos function.
See SetCursorPos.
Warnings in RowDelete
When the end-user attempts to delete a row of data, the system first prompts for confirmation. If the end-user confirms, the RowDelete event fires. A Warning in the RowDelete event displays a warning message with OK and Cancel buttons. If the end-user clicks OK, the row is deleted. If the end-user clicks Cancel, the row is not deleted.
Warnings in RowSelect
The behavior of Warning in RowSelect is totally anomalous and maintained for backward compatibility only. Use it to filter rows being added to a page scroll after the rows have been selected and brought to the component buffer. Warning causes the Component Processor to skip the current row (so that it is not added to the page scroll), then continue processing. No message is displayed.
Note. Do not use Warning in this fashion. Use the DiscardRow function for replacement instead.
See DiscardRow.
Warnings in Other Events
Do not use the Warning function in any of the remaining events, which include:
FieldDefault
FieldFormula
RowInit
FieldChange
RowInsert
SavePreChange
SavePostChange
Parameters
|
str |
A string containing the text of the warning message. This string should always be stored in the Message Catalog and retrieved using the MsgGet or MsgGetText function. This makes translation easier and also enables you to provide detailed Explain text about the warning. |
Returns
None.
Example
The following example shows a warning that alerts an end-user to a possible error, but allows the end-user to accept the change:
if All(RETURN_DT, BEGIN_DT) and 8 * (RETURN_DT - BEGIN_DT) < (DURATION_DAYS * 8 + DURATION_HOURS) then warning MsgGet(1000, 1, "Duration of absence exceeds standard hours for number of days absent."); end-if;
See Also
Error, MsgGet, MsgGetText, WinMessage.

 Weekday
WeekdaySyntax
Weekday(dt)
Description
Use the Weekday function to calculate the day of the week based on a date value.
Parameters
|
dt |
A Date value. Weekday determines the day of the week that dt falls on. |
Returns
Returns a Number value representing the day of the week. 1 is Sunday, 7 is Saturday.
Example
If &Date_HIRED equals October 30, 1996, a Monday, then the following statement sets &DAY_HIRED to 2:
&DAY_HIRED = Weekday(&Date_HIRED);
See Also
Date, Date3, DateValue, Day, Days360, Days365, Month, Year.

 While
WhileSyntax
While logical_expression statement_list End-while
Description
The While loop causes the statements of the statement_list to be repeated until logical_expression is false. Statements of any kind are allowed in the loop, including other loops. A Break statement inside the loop causes execution to continue with whatever follows the end of the loop. If the Break is in a nested loop, the Break does not apply to the outside loop.
Example
The following example counts from 0 to 10:
&COUNTER = 1; while &COUNTER <= 10 WinMessage(MsgGet(21000, 1, "Count is %1", &COUNTER)); &COUNTER = &COUNTER + 1; end-while;
See Also

 WinEscape
WinEscape
Syntax
WinEscape()
Description
Note. This function has been deprecated and is no longer supported.

 WinExec
WinExec
Syntax
WinExec(command_line, window_option [, synch_exec])
Description
Note. This function has been deprecated and is no longer supported.

 WinMessage
WinMessageSyntax
WinMessage(message [, style] [, title])
Description
Note. The WinMessage function is supported for compatibility with previous releases of PeopleTools. New applications should use MessageBox instead.
See MessageBox.
Use the WinMessage function to display a message in a message box.
Use the WinMessage for simple informational display, where the end-user reads the message, then clicks an OK button to dismiss the message box. WinMessage can also be used for branching based on end-user choice, in which case the message box contains two or more buttons (such as OK and Cancel or Yes, No, and Cancel). The value returned by the function tells you which button the end-user clicked, and your code can branch based on that value.
If WinMessage displays more than one button, it causes processing to stop while it waits for user response. This makes it a "user think-time" function, restricting its use in certain PeopleCode events.
The contents of the message displayed by WinMessage can be passed to the function as a string, but unless you are using the function for testing purposes you should always retrieve the message from the Message Catalog using the MsgGet or MsgGetText function. This has the advantage of making the messages much easier to localize and maintain.
Restrictions on Use in PeopleCode Events
The style parameter is optional in WinMessage. If style is omitted WinMessage displays OK and Cancel buttons, which causes the function to behave as a think-time function. To avoid unnecessary restrictions, you should always pass an appropriate value in the WinMessage style parameter.
If the style parameter specifies a single button (that is, the OK button), the function can be called in any PeopleCode event.
If the style parameter specifies more than one button, or if the style parameter is omitted, WinMessage returns a value based on user response and interrupts processing until the user has clicked one of the buttons. This makes it a "user think-time" function, subject to the same restrictions as other think-time functions which means that it cannot be used in any of the following PeopleCode events:
SavePreChange.
Workflow.
RowSelect.
SavePostChange.
Any PeopleCode event that fires as a result of a ScrollSelect (or one of its relatives) function calls, or a Select (or one of its relatives) Rowset class method.
See Think-Time Functions.
Restrictions on Use With a Component Interface
This function is ignored (has no effect) when used by a PeopleCode program that’s been called by a Component Interface.
Message Box Icons
In the PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture, you can’t change the icon of a message box. You can change the number and type of buttons, as well as the default button, but the message always displays with the warning icon (a triangle with an exclamation mark in it.)
Parameters
|
Message |
Text displayed in message box. Normally you want to use the MsgGet or MsgGetText function to retrieve the message from the Message Catalog. |
|
Title |
Title of message box. |
|
Style |
Either a numerical value or a constant specifying the contents and behavior of the dialog box. This parameter is calculated by cumulatively adding either a value or a constant from each of the following categories: |
|
Category |
Value |
Constant |
Meaning |
|
Buttons |
0 |
%MsgStyle_OK |
The message box contains one pushbutton: OK. |
|
1 |
%MsgStyle_OKCancel |
The message box contains two pushbuttons: OK and Cancel. |
|
|
2 |
%MsgStyle_AbortRetryIgnore |
The message box contains three pushbuttons: Abort, Retry, and Ignore. |
|
|
3 |
%MsgStyle_YesNoCancel |
The message box contains three pushbuttons: Yes, No, and Cancel. |
|
|
4 |
%MsgStyle_YesNo |
The message box contains two push buttons: Yes and No. |
|
|
5 |
%MsgStyle_RetryCancel |
The message box contains two push buttons: Retry and Cancel. |
Returns
If the style parameter is provided, WinMessage optionally returns a Number value. If the style parameter is omitted, WinMessage optionally returns a Boolean value: True if the OK button was clicked, otherwise it returns False.
The return value is zero if there is not enough memory to create the message box.
If the style parameter is provided, WinMessage returns one of the following Number values:
|
Value |
Constant |
Meaning |
|
-1 |
%MsgResult_Warning |
Warning was generated. |
|
1 |
%MsgResult_OK |
OK button was selected. |
|
2 |
%MsgResult_Cancel |
Cancel button was selected. |
|
3 |
%MsgResult_Abort |
Abort button was selected. |
|
4 |
%MsgResult_Retry |
Retry button was selected. |
|
5 |
%MsgResult_Ignore |
Ignore button was selected. |
|
6 |
%MsgResult_Yes |
Yes button was selected. |
|
7 |
%MsgResult_No |
No button was selected. |
Example
The following example displays a message dialog box with Yes and No buttons. The message is taken from the Message Catalog. The message displayed looks like this:
Message with Yes/No buttons
When the end-user clicks the Yes or No button, a result is passed back which the example tests and uses to control branching.
/* Displays Yes/No buttons in message box. */ &RESULT = WinMessage(MsgGetText(30000, 1, "Message not found."), 4, "Test Application"); if &RESULT = %MsgResult_Yes then /* Yes button was pressed -- do Yes button stuff */ else /* No button was pressed -- do No button stuff */ end-if;
See Also
Encrypt, MessageBox, MsgGet, MsgGetText, MsgGetExplainText.

 WriteToLog
WriteToLogSyntax
WriteToLog(AppFenceSetting, String)
Description
Use the WriteToLong function to write String to the PeopleTools log file if AppFenceSetting is less than or equal to the current application log fence (AppLogFence) setting in the application server configuration file (PSAPPSRV.CFG.)
Note. This is distinct from the PeopleTools LogFence capability which applies to PeopleTools level logging.
Parameters
|
AppFenceSetting |
Specify the level at which logging should occur, if AppFenceSetting is less than or equal to the current application log fence. You can use either a number or a constant value. The values are: |
|
Value |
Description |
|
%ApplicationLogFence_Error |
Allow all levels of errors to be written to the log. This is the lowest setting. |
|
%ApplicationLogFence_ Warning |
Allowing only warnings or higher to be written to the log. |
|
%ApplicationLogFence_ Level1 |
Allow only this level of errors or higher to be written to the log. |
|
%ApplicationLogFence_ Level2 |
Allow only this level of errors or higher to be written to the log. |
|
%ApplicationLogFence_ Level3 |
Allow only this level of errors to be written to the log. |
|
String |
Specify the message text to be written to the log file. |
Returns
None.
Example
WriteToLog(%ApplicationLogFence_Level2, "MYAPP" | &Somestring);
See Also

 Year
YearSyntax
Year(dt)
Description
Use the Year function to derive the year component of a Date value.
Parameters
|
dt |
A Date value from which to derive the year component. |
Returns
Returns a Number value between 1900 and 2078 equal to the year component in dt.
Example
The example sets &GRAD_YEAR to 1976:
&GRAD_DATE = DateValue("10/04/1976"); &GRAD_YEAR = Year(&GRAD_DATE);
See Also
Date, Date3, DateValue, Day, Days360, Days365, Month, Weekday.