 Defining Items at the Business Unit Level
Defining Items at the Business Unit LevelBefore processing an inventory item in a PeopleSoft application, you must define the item within the system. Items are defined at the setID level first; then they are defined at the business unit level.
This chapter discusses how to:
Define items at the business unit level.
Assign serial numbers automatically.
 Defining Items at the Business Unit Level
Defining Items at the Business Unit LevelThis section discusses how to:
Define basic attributes for a business unit.
Define item cost profiles.
Define item usage attributes.
Define item export information.
Define customer ship to attributes for vendor managed inventory (VMI).
Define shipping and handling item attributes.
Associate an item with putaway and picking zones.
Define item replenishment attributes.
Define item weight and volume information.
Define item utilization types.
Define manufacturing information for an item.
Set up item replenishment defaults.
Specify planning information for an item.
Define generation of item supply information.
Define item forecast parameters.
Define planning order modifiers.
Define business unit attributes for configured items.

 Understanding how to Define Items by Business Unit
Understanding how to Define Items by Business Unit
To specify item attributes at the business unit level, use the Define Business Unit Item (ITEM_ATTRIBUTE_GBL) component. Inventory items are defined at the setID level and can be shared among all of the business units. However, some item information (such as rules for replenishment, planning, and physical accounting) may vary depending on which business unit the item is in. These are the types of item attributes to define at the business unit level.
Note. For non-inventory items, the only field values that you can override at the business unit level are Source Code (on the Define Business Unit Item - Manufacturing: General page), Explode Demand for Consumption, and Forecast Fulfillment Size (on the Define Business Unit Item - Planning: Forecast/Incremental page).

 Pages Used to Define Items for the Business Unit
Pages Used to Define Items for the Business Unit|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
Define Business Unit Item - General: Common |
GEN_ATTRIB_INV |
Items, Define Items and Attributes, Define Business Unit Item, General |
Define basic business unit item attributes such as the item's cost element and current purchase cost, at the business unit level. |
|
Define Business Unit Item - General: Costing |
CM_ITEM_METHOD |
Items, Define Items and Attributes, Define Business Unit Item, General Select the Costing link. |
Define item cost profiles of an item that is being added to a business unit in each of the books that the business unit uses. |
|
MATRL_USG_ATTRIB |
Items, Define Items and Attributes, Define Business Unit Item, General Select the Usage link. |
Define item usage attributes for an item at the business unit level. |
|
|
Define Business Unit Item - General: Export Information |
GEN_ATTRIB_EXP |
Items, Define Items and Attributes, Define Business Unit Item, General Select the Export Information link. |
Define item export information by specifying values that are used in export documentation that is generated for the business unit. |
|
VMI Item Ship To Customers |
IN_VMI_BU_ITEMS |
Items, Define Items and Attributes, Define Business Unit Item, General Select the VMI Item Ship To Customers link. |
Define customer ship to attributes for VMI items by selecting the ship to customers that are vendor managed by your organization for this item. |
|
Define Business Unit Item - Inventory: Shipping/Handling |
OVRD_ATTRIB_INV |
Items, Define Items and Attributes, Define Business Unit Item, Inventory |
Define item attributes for shipping and handling for the business unit. |
|
Item Zone Assignments |
ZONE_ATTRIB_INV |
Click the Assign Item to Zones link on the Define Business Unit Item - Inventory: Shipping/Handling page |
Associate an item with putaway and picking zones in the business unit. Zone assignment is optional; however, it enables much tighter control over the putaway and picking operations. |
|
Define Business Unit Item - Inventory: Replenishment |
REPLEN_ATTRIB_INV |
Items, Define Items and Attributes, Define Business Unit Item, Inventory Inventory, Replenish Inventory, Setup Item Replenishment |
Define item replenishment attributes for use in the automated replenishment routines of a particular business unit. |
|
Define Business Unit Item - Inventory: Weight/Volume |
WTVOL_ATTRIB_INV |
Items, Define Items and Attributes, Define Business Unit Item, Inventory |
Define item information for weight and volume at the business unit level. |
|
Define Business Unit Item - Inventory: Utilization Types |
COUNT_ATTRIB_INV |
Items, Define Items and Attributes, Define Business Unit Item, Inventory |
Define item types and groups for an item at the business unit level. |
|
Define Business Unit Item - Manufacturing: General |
MFG_ATTRIB |
Items, Define Items and Attributes, Define Business Unit Item, Manufacturing |
Define manufacturing information for an item by determining default production and bill of material (BOM) information if the installation includes PeopleSoft Manufacturing. |
|
Define Business Unit Item - Manufacturing: WIP Replenishment |
MFG_ATTRIB2 |
Items, Define Items and Attributes, Define Business Unit Item, Manufacturing |
Set up item replenishment defaults, if you use PeopleSoft Manufacturing. This is required for PeopleSoft Flow Production. Also, set up default values if you use replenishment as the component issue method and you don’t use PeopleSoft Flow Production. |
|
Define Business Unit Item - Planning: General |
PL_ATTRIB_INV |
Items, Define Items and Attributes, Define Business Unit Item, Planning |
Specify Planning information for an item. |
|
Define Business Unit Item - Planning: Fences/Lead Time |
PL_ATTRIB_INV2 |
Items, Define Items and Attributes, Define Business Unit Item, Planning |
Define how to generate item supply by determining the planning time, planning message parameters, safety stock and excess stock parameters, and other general information regarding how you generate supply for inventory items. |
|
Define Business Unit Item - Planning: Forecast |
PL_ATTRIB_INV3 |
Items, Define Items and Attributes, Define Business Unit Item, Planning |
Define forecast parameters by determining the parameters to control forecast consumption and incremental material supply and consumption. |
|
Define Business Unit Item - Planning: Order Modifiers |
PL_ATTRIB_INV4 |
Items, Define Items and Attributes, Define Business Unit Item, Planning |
Define order modifiers for planning by determining planned transfer, purchase, and order quantity default values for a manufactured item. PeopleSoft Supply Planning use these values when creating planning models. When planning transfers between business units, purchases from suppliers, or the production of items using PeopleSoft Manufacturing, consider defining modifiers to set up guidelines when creating planned supply in PeopleSoft Supply Planning. |
|
Define Business Unit Item - Configuration |
CONFIG_ATTR_PNL |
Items, Define Items and Attributes, Define Business Unit Item, Configuration |
Define business unit attributes for configured items if you use PeopleSoft Product Configurator. |
|
ITEM_ATTR_CHAR_PNL |
Items, Define Items and Attributes, Define Business Unit Item, Custom |
Define alphanumeric field values at the business unit level for item attributes that are unique to the enterprise. Values that you define for the setID on the Define Item - Custom: Character page appear by default on this page, but you can modify them for the business unit. |
|
|
ITEM_ATTR_NUMB_PNL |
Items, Define Items and Attributes, Define Business Unit Item, Custom |
Define numeric field values at the business unit level for item attributes that are unique to the enterprise. Values that you define for the set ID on the Define Item - Custom: Numeric page appear by default on this page, but you can modify them for the business unit. |
|
|
INV_BU_ITEM_LINKS |
Items, Define Items and Attributes, Business Unit Item Links |
Access all the pages that are related to the business process of defining an item for a business unit. |

 Defining Basic Business Unit Item Attributes
Defining Basic Business Unit Item AttributesAccess the Define Business Unit Item - General: Common page.
|
Current Status Date, Current Status, Future Status Date, and Future Status |
|
|
Cost Element |
Select the default material cost element for all receipts. The system requires this value for average-costed, actual-costed, and standard-costed items. You define cost elements on the Cost Elements page. |
|
Inventory Item |
Appears by default from item definition at the setID level and cannot be overridden. |
|
Standard Cost Group |
Select a cost group code to select a set of items to roll up or update. You can also compare cost versions and report inventory value by cost group code. Establish cost group codes on the Cost Groups page, which you access from the Set Up Financials/Supply Chain - Product Related - Cost Accounting - Standard Cost Groups menu item. |
|
Current Purchase Cost |
Enter a value for the system to use to determine the material cost of purchased items and the lower-level material cost of a manufactured item when the cost type that you are rolling uses current costs. This value is per the standard UOM. |
|
Avg Matl Cost (average material cost) |
This average material cost is automatically updated when a purchase receipt is put away. The current value is stored in the AVERAGE_COST_MAT field of the BU_ITEMS_INV record. This cost reflects the vendor's price of the item. This average cost calculation includes only the material portion of the purchase order cost; it does not include landed costs, voucher updates, or cost adjustments. |
|
Default Actual Cost |
Enter a value for actual-costed items that can be used by the Update Stock Quantity (INPOPOST ) process if the item can be included in an inventory count prior to an actual cost being generated from receipt of the item. The value in this field is used in these processes: INS5050 (Reconciliation Report). INS5200 (Slow Moving Inventory). INS9080 (Forecasting Download). INPBPROC (Confirmations). INPOPROC, INPOTEST (Stock Qty Update). INPQEOQC (Replenishment Parameters). INPVVALD (Inventory Adjustments). Note. You must enter a default actual cost if an average-costed book is defined for the business unit. |
|
Average Purchase Price |
The system updates this value whenever items are received and put away into an owned storage location or whenever the item is consigned. The only items that do not have this field updated are noncosted items or items for which all of the books are defined as standard costed. The average purchase price includes both the material and the landed cost of the item. This value is stored in the AVERAGE_COST field of the BU_ITEMS_INV record. |
|
Last Price Paid |
The system updates this value when stock is put away from purchase receipts. It includes only the material cost of the received item. |
|
Non-Owned Item |
When you are adding an item to a VMI business unit, the item must be an inventory item, and it must be owned and non-consigned. |
|
Consigned Purchase |
If the item is non-owned, indicate whether it is also consigned in this business unit. Although consigned items are physically stocked in the business unit, they are owned by the vendors and are therefore not counted as part of the business unit’s total stock owned. They are, however, eligible for all inventory transactions. Note. The item’s designation as non-owned or consigned appears by default from the Define Item - General: Common page, but you can override it. All transactions within PeopleSoft Inventory use the designation for the business unit rather than the designation that is assigned at the setID level. |
|
Vendor ID, Vendor Location |
If the item is consigned, you must indicate which vendor supplies the item by entering values. The item can be supplied to this business unit as a consigned item only by the vendor that you assign here. (Other vendors can supply the item as owned.) PeopleSoft Payables extracts this information for the creation of an invoice when the item is consumed. Note. Consignment vendors must be established on the Procurement Options page (available from the Vendor Information - Location page, which you access from the Vendor Setup/Maintenance menu) before they are available for selection here. |
See Also
Receiving and Putting Away Stock
Managing Consigned Purchases Inventory
Setting up the System for Consigned Purchases in Inventory Management

 Defining Item Cost Profiles
Defining Item Cost ProfilesAccess the Define Business Unit Item - General: Costing page.
|
Used in Mfg (used in manufacturing) |
Select if the item is used in PeopleSoft Manufacturing. |
|
Profile |
Scroll through all the books for this business unit to view or set the profile for the item in each of those books. The profile for each book appears by default from the cost profile group that you define on the Define Item - General: Common page. The item must have a profile for each book. If no cost profile group is associated with the item, or if a book is not associated with this cost profile group, the field is blank. Otherwise, an error message appears. You can change the profile for an item in a book if the book is not seeded for that item and if you select the Allow Overrides to Profile check box on the Group - Books page. Note. You cannot use this page to add or delete groups. To add, cancel, or delete books from a business unit, use the Define Inventory - Business Unit Books page. |
See Also

 Defining Item Usage Attributes
Defining Item Usage Attributes
Access the Define Business Unit Item - General: Usage page.
Use this page when tracking material usage for items that are issued from par locations.
|
Usage Tracking |
Select wether the item will be tracked for Billing or Costing purposes. |
|
Reconcile |
Select to indicate that this item should go through the reconciliation process. This option is available after you select Billing or Costing in the Usage Tracking field. |
See Also

 Defining Item Export Information
Defining Item Export InformationAccess the Define Business Unit Item - General: Export Information page.
|
Export License Nbr (export license number) |
The value is used in situations where the products that are shipped from the business unit are under a general classification of export license commonly known as the general destination license. This is the default export license that the system uses for products that do not specifically require export commodity control. |
|
ECCN (export commodity control number) |
Enter a value if the export control business needs require it. |
|
Origin Country |
Enter the country in which the item was originally manufactured. The system uses this value for Intrastat reporting purposes. The country is generally required for the Intrastat Arrivals Report; however, the PeopleSoft Intrastat Transaction Loader also provides the value in this field for arrival and dispatch transactions. You can enter a specific country code for the item. If you leave the field blank, the transaction loader uses the country code for the business unit that shipped the item as the default origin country for PeopleSoft Order Management and interunit shipment transactions. |
|
Region of Origin |
See Defining Purchasing Item Vendor Relationship Attributes and Priorities. |

 Defining Customer Ship To Attributes for VMI Items
Defining Customer Ship To Attributes for VMI Items
If the business unit is a VMI business unit, the VMI Ship To Customers link is displayed. Otherwise, the link is hidden. Only ship to customers that have material storage locations defined for the VMI business unit are displayed on this page.
|
Select |
Select the check box next to the customers that have storage locations defined for the VMI business unit to indicate that they will stock the item. |
See Also
Using Vendor Managed Inventory

 Defining Item Attributes for Shipping and Handling
Defining Item Attributes for Shipping and HandlingAccess the Define Business Unit Item - Inventory: Shipping/Handling page.
See Also

 Associating an Item with Putaway and Picking Zones
Associating an Item with Putaway and Picking ZonesAccess the Item Zone Assignments page.
|
Priority |
PeopleSoft Inventory uses zone priority levels to determine which storage locations to use when putting away or picking the item. For example, suppose that you assign an item to two putaway zones, specifying that the first priority zone is fast-moving goods and the second priority zone is bulk storage. During putaway, the system first tries to place the item into the fast moving goods zone; if not enough space is available in fast-moving goods, the system moves on to bulk storage. If you assign these same zones as picking zones, the picking plan directs pickers first to locations in the fast-moving goods zone, then to locations in the bulk storage zone. |
|
Zone Code |
The options include all zones that are defined for the business unit that are also identified as putaway or picking zones for at least one storage location. Note. Zone codes (defined on the Storage Zone Codes page, which you access from the Inventory menu) and storage location zone assignments (defined on the Zone Assignments page, which you access from the Maintain Storage Locations menu) must be established before they are available for selection. |
See Also
Establishing Putaway and Picking Zones
Setting Up Putaway Defaults and Rules

 Defining Item Replenishment Attributes
Defining Item Replenishment AttributesAccess the Define Business Unit Item - Inventory: Replenishment page.
See Also

 Defining Item Information for Weight and Volume
Defining Item Information for Weight and VolumeAccess the Define Business Unit Item - Inventory: Weight/Volume page.
|
Packing Code |
|
|
Packaging Code |
Establish packaging codes on the Item Packaging Codes Page, which you access from the Set Up Financials/Supply Chain - Product Related - Inventory menu, It can also be displayed in the Packing Session (PACK_EST_SHIP) component, which you access from the Fulfill Stock Orders - Shipping menu. |
|
Container Type |
Establish container types by using the Container Types (CNTR_TYPE_INV_1) component, which you access from the Maintain Containers menu. |
|
Stocking Weight and Stocking Volume |
Enter the measurements for the item, plus any external straps, containers, pallets, or packing material that you use to stock the item. Enter values based on the UOM. Note. If you change the stocking weight and volume, you must recalculate capacity for the storage locations where capacity is tracked. For each storage location where the item is stored, select the Calc capacity at save time option on the Volume/Weight Capacity Checking page. |
|
Shipping Weight and Shipping Volume |
Enter the stocking measurements, plus any packing material or container measurements that you need for shipment. Enter values based on the UOM. |
See Also
Checking Storage Location Capacity

 Defining Item Utilization Types
Defining Item Utilization TypesAccess the Define Business Unit Item - Inventory: Utilization Types page.
|
Utilization Group |
Select the utilization group to which this item belongs. Utilization groups are set up on the Items - Define Controls - Utilization Groups page. |
|
Utilization Type |
The Utilization Type Calculation (IN_UTIL_AE ) process assigns a type to an item. The system uses utilization types in conjunction with the due to count option for cycle counts. |
|
Last Cycle Count, Cyc Interval (days) (cycle interval days), and Next Cycle Count |
PeopleSoft Inventory considers the item's last cycle count date and cycle interval days, and then automatically calculates the next cycle count date when you launch the page. Note. If the business unit requires closure-calendar validation and processing for materials management activities as defined on the Closure Calendar page, and if the next cycle count date is on a defined closure date, then the system returns the first future valid date that is defined for the function. |
|
Last Physical Count |
The value from the Update Stock Quantity process. |
|
For Planning |
Select to indicate whether this is the default utilization group for inventory planning. This default is established on the Util Group Inv (Inventory Utilization Group) page, but can be overridden on this page. |
|
For Cycle Count |
Select to indicate whether this is the default utilization group for cycle counts. This default is established on the Util Group Inv page. |
See Also
Calculating Utilization Type Classifications

 Defining Manufacturing Information for an Item
Defining Manufacturing Information for an ItemAccess the Define Business Unit Item - Manufacturing: General page.
This diagram illustrates multiple outputs:
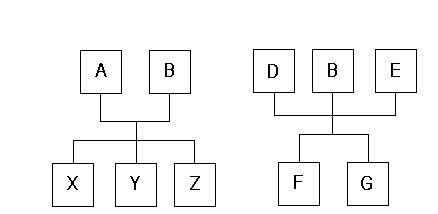
Example: Two processes with the same co-product
In the first structure, A is the primary item, B is the co-product, and X, Y, and Z are the components. In the second structure, D is the primary, B and E are the co-products, and F and G are the components. Because two ways of making the same product are available, you need to decide which structure to use when exploding to lower levels. Therefore, you need to signify a primary structure (Associated Primary BOM) that is associated with each item that may exist as a co-product but not as a primary. To do this, you can assign B’s associated primary BOM as either A or D. If B has its own BOM structure and you want to use that structure when exploding to lower levels, then you can leave B’s associated primary BOM as B.
With either option (using production option maintenance or using BOM/routing defaults), you can create specific BOM/routing combinations for PeopleSoft Supply Planning. By selecting a specific BOM code and a routing code, you can limit the number of BOM/routing combinations that are extracted by PeopleSoft Supply Planning. For example, by picking a specific BOM code and routing code, you eliminate all but this specific combination from consideration. At the other extreme, if you leave both fields blank, PeopleSoft Supply Planning extracts all possible combinations. Here is an outline of the production options that are created when you select various BOM code and routing code combinations:
|
BOM Code and Routing Code Settings |
Production Options Created |
|
Both BOM code and routing code are blank. |
The system creates a production option for every possible BOM/routing combination. |
|
A BOM code is selected but the routing code is blank. |
The system creates a production option for all routing codes with the specific BOM code selected. |
|
A routing code is selected and the BOM code is blank. |
The system creates production options for all BOMs with the specific routing code selected. |
|
Both a routing code and a BOM code are selected. |
The system creates one production option for the single specified BOM/routing combination. |
See Also
Assigning Associated Primary BOMs
Defining Your Business Unit Structure
Setting Up Manufacturing Business Unit Production Options

 Setting Up Item Replenishment Defaults
Setting Up Item Replenishment DefaultsAccess the Define Business Unit Item - Manufacturing: WIP Replenishment page.
When creating replenishment requests or Kanban cards, the system checks whether production replenishment location defaults exist first, then looks to the WIP replenishment defaults that you set up for replenishment guidelines.
|
Repl Point (replenishment point) and Iss Mult (issue multiple) |
Enter a value if you are using production replenishment as the component issue method. When the quantity that is on hand in the WIP location drops below the specified replenishment point, the system issues a workflow replenishment request indicating that additional material needs to be supplied, using the issue multiple that you specify here. If you use PeopleSoft Flow Production, the system uses the issue multiple for the Kanban quantity. If you do not have PeopleSoft Flow Production installed, the system uses only the Repl Point for items that have a WIP replenishment mode of Backflush-Controlled. |
|
Repl Max Qty (replenishment maximum quantity), WIP RPL Mode (WIP replenishment mode), andWIP RPL Type (WIP replenishment type) |
If you don’t use PeopleSoft Flow Production, the WIP fields are unavailable for entry. In this case, the system uses defaults for a WIP replenishment mode of Backflush Controlled and a replenishment method of Workflow. If you use PeopleSoft Flow Production, enter a replenishment maximum quantity to set the maximum amount of the item that you want stored at any WIP location using the item. It includes the item’s on-hand quantity and any open requests that are already made. The system issues a warning message if you perform a replenishment transaction that exceeds the replenishment maximum quantity. The replenishment maximum quantity is available for only those items that use the manual replenishment mode. PeopleSoft Flow Production uses the WIP RPL Mode to determine how to generate replenishment requests for this item. Options include: Backflush Controlled: You consume components from the WIP location while backflushing completions. When the quantity on hand falls below the replenishment point, the system automatically generates a replenishment request to bring the on-hand quantity back above the replenishment point. The replenishment request is a multiple of the issue multiple. For example, if the replenishment point is 60, the on-hand quantity is 30, and the issue multiple is 20, then the system generates a replenishment request for 40 to bring the on-hand WIP location quantity back above the replenishment point. Kanban Card: The replenishment process uses Kanban cards as a manual request for material. In this scenario, Kanban cards are either entered or imported into the system and then printed out. A Kanban card is attached to a box of components; as components are used on the production line, you place the Kanban cards in a Kanban holder. The Kanban cards are picked up periodically at the WIP location and taken to a Kanban sorting room or to the source location (such as inventory, feeder line, or vendor) on the card to get the components. Manual: You have a visual indicator that the WIP location needs replenishment, and you scan in the item ID and WIP location to generate a replenishment request for the specified issue multiple. This request includes the replenishment quantity and source location that is associated with that item and WIP location. This is largely used with electronic data collection. |
|
WIP RPL Source (WIP replenishment source) |
Determines where you send the PeopleSoft Flow Production replenishment request and what source supplies the WIP location. Options include: Feeder: A feeder line creates subassemblies that it feeds into the main production line. When you use a certain quantity of the subassemblies, you send a replenishment signal to start production on the feeder line. If you select this option, select the WIP production area that serves as a feeder line for this item. Inventory: Replenish the WIP location directly from an inventory location. Vendor: Use vendor replenishment to replenish the WIP location by directly receiving purchased components from a vendor. If you select this option, select the vendor ID and vendor location that directly replenish this item. You can override this prior to dispatch if necessary. |
|
WIP RPL Method (WIP replenishment method) |
Designate how the PeopleSoft Flow Production replenishment request is communicated. You must select Backflush or Manual as the WIP replenishment mode to use WIP replenishment methods. For vendor replenishment, a separate replenishment method is available and none of these options are used. The available WIP replenishment method options include: Workflow: The system generates a worklist entry that takes you to the Production Replenishment worklist and uses defaults for the item, quantity, and from/to WIP locations. You can override the values to complete the transfer. Pull Ticket: You create a one-time replenishment request through either a backflush or a manual scan and run the Pull Ticket print process to print the pull ticket. This is similar to a one-time Kanban card. You scan in the Kanban ID, and the system supplies the default item, Kanban quantity, source, and WIP location information. Pull List: A pull list is a list of Kanban requests that you use in a manner similar to the way you use a pick list. You scan in Kanban IDs to transfer quantities. You run the Pull List process on a scheduled basis, which picks up all new requests. As you do with pull tickets, you scan in the Kanban ID from the pull list to process each request. |
|
Source Location |
If you select Inventory as the WIP replenishment source, this field is available for entry. Select the source storage location that replenishes this item. The location field is not mandatory but, if entered, must be a valid location. The storage levels that appear depend on the storage structure that is established on the Inventory Options page, which you access from the Set Up Financials/Supply Chain - Business Unit Related - Inventory menu. |
See Also
Searching for Material Storage Locations

 Specifying Planning Information for an Item
Specifying Planning Information for an ItemAccess the Define Business Unit Item - Planning: General page.
|
Planner Cd (planner code) |
Planner codes are used to filter information in most pages and processes in PeopleSoft Supply Planning. Third-party forecasting applications also use planner codes. You set up planner codes by using the Planner Code page, which you access from the Set Up Financials/Supply Chain - Product Related - Planning menu. |
|
Planned By |
Select one of these methods: Distribution Planning: Select this method if you want to include the item in the distribution plan. The distribution plan typically displays the tasks that are quantities associated with the movement of the item throughout the distribution and manufacturing business units of the supply chain. Distribution-planned items are included in the PeopleSoft Supply Planning data model. You should select this option if the item is planned across multiple business units and is either a transfer or purchase item. A distribution-planned item is most likely a finished good or spare part that is used to fulfill customer demand at an inventory-only business unit. Master Planning: Select this method if you want to include the item in the master plan. The master plan provides a schedule of planned orders for the item at each manufacturing site. Typically, master-planned items are the top-level, finished-good manufactured items. Master-planned items can be included in either PeopleSoft Supply Planning models. You use the Manufacturing Business Unit Options page to specify which model (Supply Planning) includes the master plan. When the master plan is included in the PeopleSoft Supply Planning model, the system models production in a collapsed, aggregate view of all production capabilities for the item that is associated with the business unit. In addition, new planned orders and rescheduled messages for production can be returned from the planning server. When the master plan is included in the PeopleSoft Supply Planning model, the system models production based on the detailed bills and routings that are defined for the item in PeopleSoft Manufacturing. Material Planning: Select this method if you want to include the item in the material plan. The material plan schedules the raw materials and subassemblies that are required, supporting the production of finished goods. Material-planned items are included in the PeopleSoft Supply Planning model only. Not Planned: Select this method if you do not want to include the item in any of the PeopleSoft Supply Planning generated plans. |
|
Demand Planning Item |
Select to indicate that this item is available to be download from PeopleSoft Supply Chain Management tables into PeopleSoft Demand Planning. |
|
Inventory Policy Planning Item |
Select to indicate that this item is available to be downloaded from PeopleSoft Supply Chain Management tables into PeopleSoft Inventory Policy Planning. |
|
Use Ship To Locations |
Select this option if you want to model sourcing requirements for new planned purchase orders based on the ship to location information that is established for vendors within PeopleSoft Purchasing. By using the ship to location information, you can establish specific purchase–source definitions for a single inventory business unit. If you don’t select this option, the system bases the sourcing requirements for new planned orders on the item/vendor information. This information is used by the PeopleSoft Supply Planning solvers for modeling purposes. |
|
Spot Buy |
Select to indicate that this item is used by PeopleSoft Strategic Sourcing. This information is used by PeopleSoft Supply Planning solvers for modeling purposes. |

 Defining Generation of Item Supply Information
Defining Generation of Item Supply InformationAccess the Define Business Unit Item - Planning: Fences/Lead Time page.
This diagram illustrates time fences for new orders:
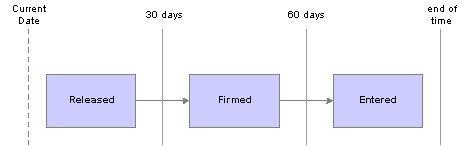
New order fence example
Suppose that you set a released order fence of 30 days and a firmed order fence of 60 days; then the system creates all new planned orders with start dates that are between the current date and 30 days in the future as Released. The system creates all planned orders with start dates that are between 31 and 60 days as Firmed, and all planned orders beyond 60 days as Entered.

 Defining Item Forecast Parameters
Defining Item Forecast ParametersAccess the Define Business Unit Item - Planning: Forecast page.

 Defining Order Modifiers for Planning
Defining Order Modifiers for PlanningAccess the Define Business Unit Item - Planning: Order Modifiers page.

 Defining Business Unit Attributes for Configured Items
Defining Business Unit Attributes for Configured ItemsAccess the Define Business Unit Item - Configuration page.
Rules Attributes - Components
|
Rule Based |
Indicates the component lists for production IDs that are based on component list rules that are carried out during production configuration. If a standard BOM exists for the item, the system doesn’t use it to create production; the system includes only components that are identified by component list rules with the production ID.
Note. When you select this option, create at least one component list rule for that item. |
|
Standard BOM |
Indicates the component lists for production IDs that are based on predefined standard BOMs. The system includes all components on the BOM on the component list for the production ID. The system might encounter a component list rule during the production configuration process. If the system interprets the condition for the rule as true, it includes the component list with the standard BOM. |
|
Reference BOM Item |
Enter an item whose BOM you want to use when the system produces this item. When you enter a value, the system ignores the current item's BOM. Use this field only for components that are based on a standard BOM. When the system uses components that are based on a standard BOM, it includes all components from the BOM for this item in the component list for the production ID. |
Additional Attributes
|
MFG Business Unit |
Enter business unit attributes; otherwise, the configuration process uses the setID values. The system uses business unit attributes to point to the business unit that produces the item and in distribution sites that don't produce the item. |
|
Ship Via |
Identifies the method of moving configured items between business units. This code identifies lead times to take into consideration for lower-level configured items that are manufactured in separate business units. |
|
Configuration Lead Time Hrs (configuration lead time in hours) |
Enter the average production time that is required for manufacturing the configured item. The production configuration process uses this lead time field to determine estimated start and due dates for production IDs. |
Rules Attributes - Operations
|
Rule Based |
Indicates to use operation lists for production IDs based on Operation List rules. Rules identify which routing operations to use from predefined routings. You do not need to use all operation sequences on the standard routing.
Note. Whether you use rule-based or standard routing, you must set up a routing. Rule-based routing enables the selection of steps to use. |
|
Standard Routing |
Indicates to use operations that generate operation lists based on standard predefined routings. The production ID's operation list includes all operation sequences on the standard routing. |
Processing Items with BOMs and Component Lists
PeopleSoft Product Configurator enables you to process a standard BOM and a component list rule when an item is in production.
To process an item with a BOM and a component list rule:
Create a standard BOM for the item on the BOM Maintenance page (Manufacturing, Maintaining Bills of Materials).
Select the Standard BOM option, and then include the reference BOM item on the Define Business Unit Item - Configuration page.
The reference BOM refers to BOMs that you create for the item in step 1. To review this BOM, select the item ID on the BOM Maintenance page.
Create a component list for the item on the Component List page, and then add the component list to the production model for the item on the Model page.
Materials from the standard BOM that you create in step 1 and from the component list that you create in step 3 are now associated with the item.
To verify that the setup is correct:
Create a configured direct order for the item on the Configuration Orders page.
Order the item by using the Order Entry Form page, and then configure the item on the Order Entry Form - Configuration page.
Run a production request for the item on the Production Request page.
Obtain the production ID for the item on the Direct Production page.
Enter the production ID that you obtain in step 4 and the business unit on the Component List Maintenance page, and then click the Search button.
A list of components for the item appears.
Verify that the list of components includes materials from the standard BOM and the component list rule.
See Also
 Assigning Serial Numbers Automatically
Assigning Serial Numbers AutomaticallyThis section discusses how to assign serial numbers automatically.

 Understanding how to Assign Serial Numbers Automatically
Understanding how to Assign Serial Numbers Automatically
To assign serial numbers automatically, use the Automatic Serial Numbers (AUTO_SERIAL_NUM_GBL) component. Use the AUTO_SERIAL_NUM_CI component interface to load data into the tables for this component
When you assign serial numbers to items on a regular basis, you can streamline the data-entry process by establishing default automatic-numbering rules. If the installation includes PeopleSoft Purchasing or PeopleSoft Manufacturing, you can use this default information to assign serial numbers for items that are received in inventory or for completed assemblies that are being moved to another production area.

 Page Used to Assign Serial Numbers Automatically
Page Used to Assign Serial Numbers Automatically|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
Automatic Serial Numbers |
AUTO_SERIAL_NUM |
Items, Define Items and Attributes, Automatic Serial Numbers |
Define criteria to automatically generate serial numbers. |

 Defining Criteria to Automatically Generate Serial Numbers
Defining Criteria to Automatically Generate Serial NumbersAccess the Automatic Serial Numbers page.
Note. If you don't define defaults by using this page, you can enter the information manually while receiving items or recording assembly completions.
|
Last Serial Number |
If you are generating shipping serial labels, the value in this field is updated by PeopleSoft Inventory. If you use PeopleSoft Manufacturing, the Completions process does not update this field. |
|
Zero Pad |
Select this option if you want to use zeros as placeholders for the serial number length that you define. |
See Also
Designing an Electronic Data Collection System