 Understanding Asset Management Business and Cash Generating Units
Understanding Asset Management Business and Cash Generating UnitsThis chapter provides an overview of asset management business and cash generating units and discusses how to:
Create asset management business units.
Create asset management cash generating units.
Note. This chapter is required. You must complete the tasks discussed in this chapter to implement Asset Management.
 Understanding Asset Management Business and Cash Generating Units
Understanding Asset Management Business and Cash Generating UnitsYou determine how to define business units in Asset Management to best facilitate asset management processing within your organization. You can set up an asset management business unit for each legal entity in your organization. You could, for example, have asset management activities processed by a central asset management department which will interface with and manage assets for each business unit. Alternatively, you could set up one business unit for each plant or branch office of your company, enabling these entities to manage their own assets independently while sending journals to a common general ledger business unit. You should establish your business units in the manner that best suits your organizational, structural, and reporting needs.
Tableset Sharing and PeopleSoft Trees
When you plan your business unit structure, you need to be familiar with TableSets, which are used in all PeopleSoft Enterprise Financials products. The accounting structure and processing rules for each PeopleSoft application are defined in a series of control tables. A TableSet is a group of rows across control tables, identified by the same setID, on which you define the accounting structure for each of your business units, aging rules, entry types and reasons, payment terms, credit and receivables personnel, and so forth. For a business unit to process transactions, it must have an associated TableSet.
A setID identifies each TableSet. You can have as many setIDs as you want. However, using numerous setIDs creates complex TableSet sharing. You must create at least one setID, even if you do not use TableSet sharing.
PeopleSoft provides a tool called Tree Manager to group business units together into a hierarchical structure. Tree Manager and your business unit structure provide a mechanism for defining reporting parameters. A business unit is the smallest structural unit that can be represented in Tree Manager.
PeopleSoft uses setID-driven trees. So that Asset Management trees will work properly, the setID assigned to record group FS_21 for each business unit must equal the business unit value. If the setID for FS_21 does not equal the business unit value, you cannot access your assets from the correct Asset Management tree.
When you use the Real Estate application, you will define a default tree for the business unit. The tree names available will depend on the trees you have defined. Plan your tree definitions with business unit definitions in mind.
Note. Each time you create a business unit, whether you copy the tableset sharing from another business unit or create a generic tableset sharing setup, the system automatically establishes the setID for record group FS_08 to equal the business unit that you are creating. You should not change this definition.
See Enterprise PeopleTools 8.46 PeopleBook, “PeopleSoft Application Designer”, Planning Records, Control Tables, and TableSets.
See Enterprise PeopleTools 8.46 PeopleBook, “PeopleSoft Tree Manager”, Introduction to PeopleSoft Tree Manager, Sharing Trees Across SetIDs.
Asset Management Business Unit Default Hierarchies and Options
A business unit is the highest level in the hierarchy and you must set default values for business units. All other entities fall beneath them in the hierarchy. Some of the attributes set at the business unit level may be set at lower levels in the hierarchy, such as the customer or item level, but are not required.
Default hierarchies exist throughout the system. Any time that a default hierarchy exists, you can:
Leave information blank at lower levels, because defaults are inherited from the next higher level.
Override information set at higher levels by entering different information at the lower levels.
Some business processes in Asset Management are based on your business unit definitions. These processes may require that you define field entries to be used by default or other options for transactions that are processed at the business unit level. These options include:
Asset Management processing options.
Besides asset management processing defaults, you should consider your requirements for value-added tax (VAT) processing, processing group assets and ChartField summarization, depreciation period end and closing processes, and asset book and accounting entry defaults.
(JPN) Asset Management numerical rounding options.
Define the rounding type for depreciation amounts.
Payables interface processing options.
Select voucher close transaction types.
Billing interface options.
Designate the defaulting business unit to run the Billing interface and define values for Billing business units, bill types, bill sources, and bill by identifiers.
Real Estate Management (space allocation) interface options.
Designate the defaulting tree name, statistics code and statistical accounts to be used when interfacing with Real Estate Management.
Maintenance Management interface options.
Designate the default options enabling retirements and transfer in or out of assets from work orders. Designate the default options for including or excluding subcomponents for transactions coming from MM.
If you are using General Ledger, you must also define at least one general ledger business unit to which you will generate journal entries from the asset management business unit. If General Ledger is already implemented, this step may have already been performed.
You can override most business unit defaults at a lower level when you enter asset information. Asset Management is delivered with a series of standard definition tables. Examine these tables to determine if the business unit that you’re setting up can share the same financial structure. If so, you can minimize the need to set up additional tables.
Value-added tax (VAT) defaults are controlled by VAT drivers at various levels of the hierarchy and the VAT defaults themselves are stored in a common set of defaulting tables. Depending on the driver, certain fields are available for setting and, lower in the hierarchy, overriding. There are two main components that control the VAT defaulting: the VAT Defaults Setup component and the Services VAT Treatment Setup component. Asset Management only handles goods for VAT setup. You can access these components from the common VAT menu (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definition, VAT and Intrastat, Value Added Tax) or from the applicable application pages. If you access these components from the VAT menu, the driver you select determines the fields that display. If you access either of these components from the application pages, the component you are accessing from determines the fields displayed. The VAT Defaults Setup and Services VAT Treatment Drivers Setup components and functionality are described in depth in the common VAT chapter in the PeopleSoft Enterprise Global Options and Reports 8.9 PeopleBook.
The values selected here become the default values for the business unit and can be overridden in the Asset Retirements component. If you leave these fields blank, you must enter this information in the Asset Retirements component each time VAT applies to the transaction.
Use the VAT Default page to specify VAT processing options. For countries that use VAT, Asset Management stores default information at the business unit, customer, customer location, and asset class levels to calculate VAT on asset retirements. VAT transaction types and VAT codes are set up in Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, VAT and Intrastat, Value Added Tax. You can select values for these and other control fields on this page.
See Working with VAT.
Cash generating units (CGUs) become important when you must perform impairment assessment and processing for an individual asset and the recoverable amount of that asset is in doubt. If an organization cannot determine recoverable value for an individual asset, it is required in some countries to identify the lowest aggregation of assets that generate largely independent cash flows. These aggregations of assets are known as cash generating units. A CGU is the smallest identifiable group of assets that generate cash inflows from continuing use and are largely independent of the cash inflows from other assets or groups of assets and should be defined consistently from period to period.
PeopleSoft supports the implementation of International Accounting Standards (IAS) 36 by providing for the definition of a Cash Generating Unit and enabling the association of CGUs with business units. This facilitates impairment processing within a defined business unit. You must define the business unit before it can be associated to a CGU definition.
See Adjusting for Asset Impairment.
 Creating Asset Management Business Units
Creating Asset Management Business UnitsTo set up business units, use the Business Unit Definition component (BU_DEFN).
This section describes how to set up Business Units.

 Prerequisites
Prerequisites
Before you set up business units, you must decide on your TableSet structure and set up setIDs.
See the documentation on planning records and TableSets in the Enterprise PeopleTools 8.46 PeopleBook, “PeopleSoft Application Designer”.

 Pages Used to Create Asset Management Business Units
Pages Used to Create Asset Management Business Units

 Creating Asset Management Business Units
Creating Asset Management Business UnitsAccess the AM Business Unit Definition page.
Note. When you create a business unit, Asset Management automatically defines tableset defaulting for the business unit so that it copies the tableset that you entered on this page. You can verify tableset sharing by using the PeopleTools Utilities TableSet Control Group pages.
See Enterprise PeopleTools 8.46 PeopleBook, “PeopleSoft Application Designer”, Planning Records, Control Tables, and TableSets, Sharing Tables.
|
Unit, Description, and Short Description |
Enter descriptive information to uniquely identify the business unit during set up. These fields are already populated when you select an existing business unit for update. |
Business Unit Definition
Define book to be used as the default book for general ledger entries for the business unit and all secondary books, including Corporate and Tax books (both state and federal).
|
Location |
Select a location for this business unit. Locations available are defined on the location page table. |
|
The last asset ID used displays here or the value is zero by default. To increment automatically from some other starting point, enter your starting point into the Last Asset ID Used field and click the Reset button. If there are no assets for this business unit, this will reset the last asset ID to zero. The Next value displays on the Asset Basic Add or Express Add pages when you use automatic numbering of asset ID. When the record is saved, the assigned asset ID displays and the value is incremented on this page. |
|
|
Default Book |
Select the book that is used by default when you enter assets. (This book is required for subsequent processing.) Note. PeopleSoft strongly recommends making the primary book in the ledger group in General Ledger the same as the default book in Asset Management in order to maximize synchronicity of transactions. |
|
Fed Book (federal book) |
Select the book to calculate the federal tax. |
|
AMT Book (alternative minimum tax book) |
Select the book to calculate the alternate minimum tax. |
|
ACE Book (adjusted current earnings book) |
Select the book to calculate the adjusted current earnings. |
|
CAP Book (capital acquisition planning book) |
Select the book used for capital acquisition planning (CAP). |
|
Lease Book |
Select the book where leased assets are primarily recorded. |
|
Suspense Account and Alt Acct (alternate account) |
Enter the translate account and alternate account here. If you have any transactions in a foreign currency within this business unit and want to enable the feature to translate currencies. If you do not have transactions outside of your local currency, you do not need to define these values. See Defining Journal Processing Options for a Business Unit. |
BU Set Up Options
|
Keep all books in synch |
Select this check box to keep all adjustments synchronized. Clearing this check box enables you to create adjusting entries to affect particular books while excluding others. If you select this option in conjunction with a business unit that is also enabled for impairment processing, you will have an option to create zero impairment costs for other books. This occurs when working in the Impairment Worksheet page or the batch run control page and you select the Copy To Other Booksthe check box. Warning! If you use this method to make adjusting entries, you must reselect the option before starting normal asset processing. Clearing or selecting this option does not enable retroactive adjustments. The function is applied from the point selected going forward until and unless you change it again. |
|
Default tag# from asset ID (default tag number from asset ID) |
Select this check box to use the same number for the tag as the assigned asset ID. |
|
Allow duplicate tag numbers |
Select this check box when you are processing physical inventory. This enables you to take physical inventory and process assets that may have the same tag number. |
|
Joint Venture Unit |
Select if this is a joint venture business unit. Note. You cannot perform interunit transfers on joint venture business units. |
|
Use JV Participant Bk Profile (use joint venture participant book profile) |
Select this option for participant level. Joint venture participant business units are governed by the book for the participant level business unit or by the book for the overall joint venture business unit. You can use this feature to maintain joint venture participant business units with separate profiles that enable different depreciation methods, conventions, calculation types, and so on, as required. |
|
Use Parent-Child Defaulting |
Select to enable automatic parent-child inheritance processing for this business unit. For example, when you create a child asset and you want it to inherit the tag or department number from the parent asset (as specified on the Profile Child Asset Inheritance page), select this check box. For more responsive performance of Express Add, Basic Add, and Transaction Loader processes, clear this check box. General parent-child asset processing is still enabled. |
|
Auto-Retire Fully Depr Assets (automatically retire fully depreciated assets) |
Select to enable automatic retirement of fully depreciated assets for this business unit. You must also enable the option at the book level. |
|
Use Add Conv for all TXNs |
Select this option to inherit the same convention used when you added an asset for any new transaction. |
InterUnit Transfer Defaults Options
Select the default asset information to be shared between the business units when you make interunit transfers. The information is derived from the Asset Information component.
|
Asset Acquisition Info |
Select to include information derived from the Asset Acquisition Detail (ASSET_ACQ_DETAIL) page and links (ASSET_ACQ_DET_AP, ASSET_ACQ_DET_VAT). |
|
Asset Attributes Info |
Select to include information derived from the Asset Location/Comments/Attributes (ASSET_IMAGE) page. |
|
Asset License/Register Info |
Select to include information derived from the Asset Custodian/License/Manufacturer page (ASSET_CUSTODIAN) and links (ASSET_LIC_ADDR_SEC). |
|
Asset Lease Info |
Select to include information derived from the Leased Assets component pages (ASSET_LEASE_01, ASSET_LEASE_02, ASSSET_LEASE_05, ASSSET_LEASE_03). |
|
Asset Non-Capitalized Cost |
Select to include information derived from the Asset Acquisition Detail (ASSET_ACQ_DETAIL) page and links (ASSET_ACQ_DET_AP, ASSET_ACQ_DET_VAT). |
|
Asset Maintenance Info |
Select to include information derived from the Track Service and Repairs component pages (ASSET_MAINT_01, ASSET_MAINT_01_S) and meter readings. |
|
Asset Comments |
Select to include information derived from the Asset Location/Comments/Attributes (ASSET_IMAGE) page. |
|
Asset Warranty Info |
Select to include information derived from the Asset Custodian/License/Manufacturer page (ASSET_CUSTODIAN) and links (ASSET_WARRANTY). |
|
Asset Insurance Info |
Select to include information derived from the Asset Custodian/License/Manufacturer page (ASSET_CUSTODIAN) and links (ASSET_INSURANCE). |
|
Asset Inspection Info |
Select to include information derived from the Asset Custodian/License/Manufacturer page (ASSET_CUSTODIAN) and links (ASSET_INSPECTION). |
|
Asset Component History |
Select to include asset component history (AM_AST_COMP_HIST) information. |
Open Transaction Processing Options
Open transactions are asset events such as depreciation and accounting entries that require processing. Asset Management assigns each open transaction a unique open transaction ID whenever a processing option is requested. For example, changing asset cost, adding or retiring assets, or changing asset depreciation attributes all create open transactions. Depreciation must be calculated, or recalculated, and allocated for each transaction before it is considered closed. An open transaction has a Pending status until it is processed.
|
Auto Increment Open Trans ID (automatically increment open transaction ID) |
If you want to process a large number of transactions as a group, you should clear the Auto Increment Open Trans ID check box. For example, you enter 300 new computers into Asset Management, and rather than process depreciation and distribution in 300 separate requests, you want to process all in a single request. To do so, establish an open transaction ID that identifies a single processing request for all 300 computers that you entered. In this case, you should clear the Auto Increment Open Trans ID check box. |
|
Open Trans ID (open transaction ID) |
The Open Trans ID field helps you keep track of open transaction processing status. You can enter a beginning open trans ID, or you can have Asset Management assign it. You can specify that Asset Management automatically increment the ID value each time a transaction is added to the open transaction table by selecting Auto Increment Open Trans ID. The next processing request that you enter is automatically assigned a number that is one greater than the last assigned value. Subsequent open transaction ID numbers will be incremented by one. |
See Also
Defining Your Operational Structure
Defining Financials and Supply Chain Management Common Definitions
Setting Installation Options for PeopleSoft Applications
Creating Asset Management Accounting Entries

 Defining Open Periods
Defining Open PeriodsAccess the Open Periods Update page.
The Update Open Periods page enables you to define which periods are open (periods in which transactions can be posted) for Asset Management. These can be defined in relation to, but not strictly governed by, the corresponding open period in General Ledger (GL).
See Also
Defining and Updating Open Periods and Adjustment Periods

 Defining VAT Defaults
Defining VAT DefaultsThis section provides an overview of VAT processing options and describes how to set up VAT processing defaults by business unit for Asset Management.
Understanding VAT Drivers, VAT Driver Keys, and the Defaulting Hierarchy for VAT Defaults
The following table lists the Asset Management-related VAT drivers and associated VAT driver keys in VAT default hierarchy sequence from most specific to least specific for the VAT Defaults component. The table also indicates which drivers control defaults for the Services VAT Treatment:
|
VAT Driver |
VAT Driver Keys |
Country |
State |
Applicable to Regular VAT Defaults |
Applicable to Services VAT Treatment Defaults |
|
ASSET_CLASS_TBL Asset Class |
Asset SetID Asset Class |
Optional |
Optional |
Yes |
No |
|
CUST_ADDR_SEQ Customer Location |
Customer SetID Customer ID Address Sequence Number |
Optional |
Optional |
Yes |
Yes |
|
CUSTOMER Customer |
Customer SetID Customer ID |
Optional |
Optional |
Yes |
Yes |
|
BUS_UNIT_TBL_AM AM Business Unit |
Business Unit |
Optional |
Optional |
Yes |
No |
|
VAT Entity Registration |
VAT Entity Country |
Not applicable |
Optional |
Yes |
No |
|
VAT Country |
Country |
Not applicable |
Optional |
Yes |
No |
Establishing the VAT Environment
For your system to track and process VAT, you must first set up basic information by defining VAT transaction types, VAT codes, and their associated VAT accounting templates, VAT countries, VAT entities, and VAT defaulting. Each piece builds upon the next so, for your basic setup, it’s important to implement each piece in the following order:
VAT transaction types.
VAT rates, VAT codes, and VAT accounting information.
VAT countries.
VAT entities.
VAT defaults.
In addition to the information you must set up, PeopleSoft delivers multiple account types for your VAT accounting and reporting with every application. You cannot add your own.
See Working with VAT.
Setting Up and Maintaining VAT Defaults
Access the VAT Defaults Setup page.
Specify the VAT driver and any VAT driver keys as applicable. You can insert rows for any or all of the VAT driver keys as well as the VAT country or state. You can also delete any existing rows.
|
Copy Values to New Rows |
If you are inserting a row for a VAT driver key, select this check box to copy all the VAT defaults from the previous row to the new row. Otherwise, all VAT default fields for the new row will be blank. |
VAT Defaults
|
VAT Reporting Country |
Select the VAT reporting country or countries for which you are defining VAT defaults. For service VAT treatment defaults, defaults are obtained for the supplier's location country. Asset Management does not use VAT for services, only goods. |
|
Defaulting State |
As applicable, enter the state for which you want to define defaulting values. (Optional depending on VAT Country) |
Copying VAT Defaults
Access the VAT Defaults Copy page by clicking the Copy Defaults From link.
|
Copy From Search Criteria |
Enter the criteria on which you want to search. When copying defaults for the Asset Management business unit driver, you can search by business unit, VAT reporting country, and defaulting state. |
|
Search |
Select to retrieve the results based on the criteria entered. The results display in the Copy From Results group box. |
|
Copy From Results |
In the Copy From Results group box, select the link for any of the results returned to view the details of the VAT setup from which to copy on the Copy VAT Defaults Setup page. Once you have viewed the details, you can select Copy to copy the VAT setup. The system returns you to the VAT Defaults Setup page with the copied fields. Or you can select the appropriate option for any of the results returned and select Copy to copy from the selected row. The system returns you to the VAT Defaults Setup page with the copied fields. |
Default Details
Enter the effective date and status.
The remaining fields on the page vary based on the combination of VAT driver and VAT driver keys. Depending on the combination of PeopleSoft products you are implementing and the VAT transactions conducted between your local country and other countries, you may require some variation in set up. The PeopleSoft Enterprise Global Options and Reports 8.9 PeopleBook documents these variations in working with VAT in greater detail.
You may define the following defaults for the Asset Management business unit:
See Establishing VAT Defaults.
VAT Control Defaults
|
VAT Applicable |
Select the appropriate VAT status. Values are: Exempt (not subject to VAT) Outside of Scope of VAT Taxable |
|
Goods Declaration Point |
Select when you want VAT transaction information for goods to be recognized for reporting purposes. Values are: At Invoice Time: VAT is recognized at time of invoice. At Payment Time: VAT is recognized at time of payment. Delivery: VAT is recognized at time of delivery. |
|
Calculation Type |
Select the type of calculation you want the system to use. Values are: Exclusive: VAT is calculated on top of the entered transaction amount, because it excludes any VAT. Inclusive: VAT is calculated from within the entered transaction amount, because it already includes the VAT. |
VAT Code Defaults
You use VAT codes to specify the rate at which VAT is calculated.
The VAT rate is frequently the key to reporting VAT because VAT amounts must often be reported separately by VAT rate on a VAT return. Therefore, the VAT code is part of the reporting definition.
|
Taxable Goods Sales |
Select the VAT code to be used for taxable sales within this VAT reporting country |
See Setting Up VAT Authorities and Tax Codes.
VAT Transaction Type Defaults
You use VAT transaction types to classify and categorize transactions at a more detailed level for both VAT reporting and accounting. These are specified for each transaction line when you enter a transaction.
You define the VAT transaction types you need for your VAT setup. PeopleSoft also delivers a set of VAT transaction types with your system as sample data.
|
Domestic Goods Sales |
Sale of goods within the same country. |
|
EU Goods Distance Sales (European Union goods distance sales) |
Sale of goods between European Union (EU) countries in which the supplier is registered in an EU country and the purchaser is not registered in an EU country. The VAT rate charged is the rate applicable in the supplier's country. |
|
EU Goods Sales (European Union goods sales) |
Sale of goods within the European Union. |
|
EU Sales, Simplification |
This treatment is used for the transaction between an intermediary and the purchaser in cases when there is a sale of goods between European Union (EU) countries involving three parties: the purchaser, an intermediary (bill-from) supplier, and the actual goods supplier. Each party is located in a different EU country and registered in his own country, and not in either of the other two countries. The only difference between this VAT treatment and that applied to normal EU sales is that the supplier is required to print a different message on the invoice referencing the statute that applies to triangulation, rather than the one that references the statute for normal EU sales. |
|
Exempt |
Not subject to VAT. |
|
Exonerated |
Subject to exoneration from VAT. |
|
Goods Exports |
Export sales of goods. |
|
Out of Scope |
Outside of the scope of VAT. |
|
Suspended |
Subject to suspension of VAT. |
See Defining VAT Transaction Types.

 (JPN) Defining Business Unit Information for Japan
(JPN) Defining Business Unit Information for JapanAccess the Business Unit Info for Japan page.
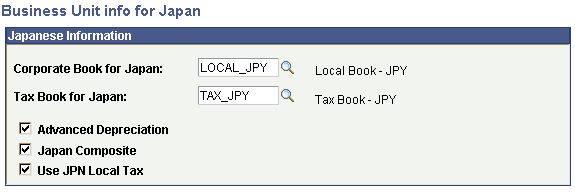
Business Unit Info for Japan page
|
Corporate Book for Japan |
Select the corporate book for Japan. |
|
Tax Book for Japan |
Select the tax book for Japan. Note. PeopleSoft recommends that you select the primary book in the ledger group in General Ledger to be the same as the default book in Asset Management. As tax books do not usually send accounting entries to General Ledger this maximizes synchronicity of transactions. |
|
Advanced Depreciation |
Select if advanced depreciation is used. |
|
Japan Composite |
Select if composite assets are used. |
|
Use JPN Local Tax |
Select if local tax reporting is enabled. |
Note. PeopleSoft strongly recommends making the primary book in the ledger group in General Ledger the same as the default book in Asset Management. This maximizes synchronicity of transactions.
See Also
(JPN) Using Asset Management Options to Meet Japanese Requirements

 Defining Business Unit Processing Options
Defining Business Unit Processing OptionsAccess the Business Unit/Book Definition page.
|
Book Name |
The Book Name field is used during asset and profile entry to designate book processing. At least one financial book for each business unit to record asset data in your general ledger is required. You may have other federal, state, and foreign tax or financial books as well. Transactions can be tracked in multiple currencies by designating the currency code within each transaction entry. |
|
Book Type |
Specify type of asset book processing. This feature acts as a filter for your tax and financial options when you define tax and depreciation information for asset transactions. For example, if you define your CORP book as a Corporate book, you will not be able to select any tax attributes for processing when you add an asset to this book. Select Corporate w/Tax Info if you maintain separate tax records for this business unit in the book. You can use this option to specify tax processing rules and track tax information for your assets. The Tax option enables you to maintain tax information for government reporting. The US AMT option enables you to maintain alternative minimum tax information for government reporting. This option enables you to separately track alternative minimum tax information. |
|
Book is Required |
Select Book is Required to ensure that this book will added for every asset in this business unit. |
Note. If you maintain multiple currencies you must define the exchange rate. Even if you use only one currency in Asset Management, you must still set up a one-to-one exchange rate and rate type to exchange that currency with itself. For example, to use U.S. dollars you must set up an exchange rate for U.S. dollars to U.S. dollars with an exchange rate of 1. To make changes, go to Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Market Rates page.
See Processing Multiple Currencies.
Book Options
|
Currency |
Displays the default currency for this business unit. |
|
Rate Type |
Select the currency exchange rate. Note. Even if you are using only one currency in Asset Management, you still need to set up a one-to-one exchange rate and rate type to exchange that currency with itself. For example, to use US Dollars you must set up an exchange rate for USD to USD with an exchange rate of 1. |
|
Calendar |
Select the accounting period calendar for this book and business units. General Ledger supports multiple calendars, so you can keep separate calendars for actual accounting activity, for budget and forecast activity, and for special reporting or transitional needs. For example, you can easily manage a conversion to different accounting periods or to a new fiscal year by maintaining two calendars. However, only one calendar can be active for a ledger group at a given time. A book must use the same calendar as the ledger. |
|
Capitalize Limit,Amount, and Limit Code |
Define these limits either by selecting Amount and entering a minimum, or by selecting Table Lim and selecting a Cost Limit Code. If you select Amount, you cannot add an asset with a cost that is less than the specified limit. If you select Table Lim, you may encounter an error or a warning, based on the actions that you set up in the Capitalization Limit table, when you try to add assets below the amounts in the table. |
|
Lease Cap Min (lease cap minimum) |
Define the lease cap as a minimum cost of the asset lease. (When you enter a leased asset with total cost below the lease cap, you will receive an error.) |
Accounting Entry Options
Your business unit accounting entry options enable you to associate an asset management business unit with a general ledger business unit and default ledger.
|
Create Accounting Entries |
Select this check box to make the accounting entry options available for selection. |
|
Retirements by Disposal Code |
Select the check box to enable retirement of assets based upon disposal code. A disposal code references a predefined disposal worksheet that includes asset rules such as asset ownership, eligible operators, and permitted transactions. The Transaction Code field on the Retirement page will be populated with the appropriate disposal code. See Initiating Asset Retirement Using the Disposal Worksheet. |
|
GL Business Unit |
The General Ledger business unit associated to this book displays here. |
|
Ledger Group, Budget Ledger Group, Ledger, and Budget Ledger |
A ledger is a set of posted balances that represents a set of books for a business unit. Ledger templates and detail ledgers can be added to the appropriate ledger group. A ledger group can have one primary ledger and zero to nine secondary ledgers. Each ledger within the ledger group shares a common physical structure based on the ledger template, as well as unique characteristics (such as its own base currency). The Ledger Group andBudget Ledger Group fields for Asset Management enable you to associate a ledger or ledger group to this business unit. In syncaccounting entries are a group of accounting entries for one transaction that the system distributes to different ledgers. In conjunction with the Keep all books in sync option, you define how a transaction is posted. If the Keep all books in sync option is selected, then one transaction will post to all ledgers in the group. If the Keep all books in sync option is clear, the system posts transactions only to those ledgers with transaction entries. One book will post to one ledger, but you can set up other books to point to the other ledgers in the group. If you will be generating budget accounting entries, specify the Budget Ledger Group and Budget Ledger to which you want to post them. If you leave ledger and budget ledger fields blank, the accounting entries will be made to the primary ledger. See Setting Up Ledgers. |
|
Book Code Distrib. Grp (book code distribution group) |
If the Book Code option is activated from the Installation Options page, this field will display. The book code is an Account attribute and a balancing ChartField. You can use book codes to simultaneously generate sets of entries to record related transactions according to multiple GAAPs for the same business unit in the same ledger. The book code distribution group defines a set of book codes to be used when distributing accounting entries for multiple GAAPs within one book. Using the book code distribution group restricts the duplication of accounting entries being passed to General Ledger. The book code distribution group value is defined on the Book Code Distribution Group page. Select from the available book code distribution groups defined for your organization. See Setting Installation Options for PeopleSoft Applications. See Creating Asset Management Business Units, Setting Up Accounting Entry and Financial Processing for Asset Management. |
|
Translate Gain/Loss |
If the ledger specified is a translate ledger, this check box appears. When you process accounting entries (AM_AMAEDIST), the gain or loss amount that is the result of a currency exchange transaction is converted from the primary book to the translate book. |
|
Account Entry Template ID |
Enter the account entry template ID; the default is DEFAULT. The accounting entry template ID provides the option to associate different books with different charts of accounts. To use derogatory depreciation for France, select the account entry template ID that corresponds. If you select the Derogatory depreciation template ID, you must also select the Derogatory Depreciation check box. |
|
(FRA) Derogatory Depreciation |
Select this check box to process derogatory depreciation with the derogatory account entry template ID. If this box is selected, you must use the appropriate account entry template ID associated with derogatory depreciation. You must also select the statutory book to which this book will be compared. This can be designated on the AM Business Unit Definition page as the federal book. See (FRA) Using Asset Management Options to Meet French Requirements. |
|
(FRA) Statutory Book |
Select the statutory book to which derogatory depreciation transactions stored in the book you are defining will be compared. When Derogatory Depreciation has been selected, you must also define statutory book. |

 Selecting Rounding Options
Selecting Rounding OptionsAccess the Round Options page.
|
Round Rule and Round Type |
Select the rounding rule and type that apply to this book. The rounding rules delivered with Asset Management are: Down NatRnd Up The rounding types delivered with Asset Management are: Currency: Generic |
|
Round Precision |
The number of places to the right or left of the decimal point to which the amount or number will be rounded. If you select Currency as the round type, the system automatically determines round precision from the currency code. |
|
Rounding Factor |
The number to which the amount will be rounded. For example, if you select Nat Rnd as the rounding rule and enter a rounding factor of 25, amounts will be rounded to the nearest multiple of 25; for example, an amount of 130 will be rounded to 125, and an amount of 140 will be rounded to 150. If you select Currency as the round type, the system will automatically determine the rounding factor from the currency code. |
|
Truncation Precision Flag |
The Truncation Precision Flag check box works with the round precision value. When you select it, amounts that contain many decimal places are truncated to one decimal place to the right of the rounding precision position before rounding is performed. If you clear it, the entire amount is rounded. This example illustrates truncation precision:
With the Truncation Precision Flag check box selected, the system truncates the fifth decimal place and rounds 10.0343. With the check box cleared, the system rounds the entire amount. Actual rounding results would depend on the selected rounding rule and round type. |

 Viewing the Depreciation Close List
Viewing the Depreciation Close List
Access the Depreciation Close List page.
View the years and periods for which depreciation has been closed. You cannot open or close periods from this page.
See Also

 Defining Business Unit/Book Feature Options
Defining Business Unit/Book Feature OptionsAccess the Business Unit/Book Feature page.
This page provides the book and impairment options available for the books that have been defined within this business unit definition. The Impairment Options group box displays only when Impairment Processing is selected on the Installation Options page.
See Setting Installation Options for PeopleSoft Applications.
Book Options
|
(DEU) Low Value Asset |
Select to enable low-value asset processing. In Germany, assets marked as low value should be depreciated in one year. Asset Management checks the capitalization limits against the amounts that are stored by code in the capitalization limit table. See (DEU) Using Asset Management Options to Meet German Requirements. |
|
Group Asset Processing |
Select to enable group asset processing. If checked, the Summary link displays on the Chartfield Summarization page. The system applies asset transactions at the group member level. |
|
Store Depr by Period (store depreciation by period) |
Select to store depreciation by period for the current fiscal year. Note. If you store depreciation entries by period, you increase the table size and decrease depreciation processing performance. For optimal depreciation processing performance and greater table efficiency, we recommend storing depreciation entries by fiscal year rather than by period. |
|
Child Inherits Parents Life |
Select to pass on the asset life of the parent asset to the child asset. |
|
Online Reporting |
Select to enable online reporting features. Note. You must run Load Depreciation Reporting process for at least one asset after this option is selected to be able to view online reporting for this business unit/book. |
|
(ARG, BRA, and MEX) Inflation Processing |
Select Inflation Processing if you want to enable the inflation processing feature. This optional feature is used for Argentina, Brazil, and Mexico to adjust assets for inflation associated with a particular inflation index appropriate for a country or currency. It provides for periodic inflation adjustment transactions (transaction type INF) that adjusts asset balances (cost, period depreciation, year-to-date depreciation, and accumulated depreciation) for inflation. The default is blank. (This field is available when you enable the corresponding installation options.) |
|
Calculation Type |
This option appears when you select the Inflation Processing check box. Select the calculation method for inflation processing. The available options are:
See Setting Installation Options for PeopleSoft Applications. |
|
Auto-Retire Fully Depr Assets (automatically retire fully depreciated assets) |
Select to enable the automatically retire fully depreciated assets feature. This field appears only if you select the Auto-Retire Full Depr Assets option on the Asset Management Business Unit Definition page. |
Impairment Options
|
Impairment Process |
Select this check box to enable impairment processing within this business unit book. |
|
Cost Type For Impairment Loss |
Select the default Cost Type for the impairment loss from the list of valid cost types. |
|
Impairment Reversal |
Select this check box to enable impairment reversal processing within this business unit book. |
|
Cost Type for Reval Reversal (cost type for revaluation reversal) |
Select the default Cost Type for the impairment revaluation reversal from the list of valid cost types. |

 Selecting Asset Management Interface Options
Selecting Asset Management Interface OptionsAccess the Interface Options page.
This page provides the options available for interfacing with Payables, Purchasing, Billing, Real Estate Management (space management allocation), and Maintenance Management applications.
AP/PO Interface Options
|
Map ChartField |
Select this check box to enable ChartField mapping for Payables and Purchasing asset processing. |
Voucher Close Transaction Type
When a new asset is created from a Payables voucher and sent to Asset Management, a new asset is created. If the payables voucher is then closed you have to post the voucher again. The default Voucher Close Transaction is Retirement.
Note. If a voucher is unposted, and the default voucher close transaction is Retirement , the load type will result in a negative ADD (Load type AAD).
|
Negative Addition |
Results in a negative addition (AAD) to the asset that was originally created by the voucher. |
|
No Transaction |
No transaction is generated for this event, and the process to remove it from Asset Management must be entered manually. You can remove the created transaction from open transactions if depreciation has not been run. If depreciation has been run, and the asset has been set up in the system and posted to GL, you must enter a retirement or negative addition transaction to remove it from the books. Acquisition detail will still be inserted for the closed voucher for audit purposes, but no cost rows or financial transaction will be generated. |
|
Retirement |
Creates a retirement transaction (RET) to retire the asset that was originally created by the voucher. If any depreciation has been taken during the interim period, it will be reversed and removed from the corporate books. Gain and loss will be calculated. This is the default if no other option is specified. |
Note. If either Negative Addition or Retirement are selected and both the first posting and the unposting of the voucher are processed in the same run of the AP/PO Interface (AMPS1000), no assets are created. The two transactions cancel each other out. The load status for both transactions is set toConsolidated.
See Sending Information to Asset Management.
See Retiring Assets.
Complete the appropriate definitions for processing billing transactions in the Billing Interface group box. The information entered here appears on the Create Bill tab of the Retirement page. The physical nature from Asset Management is Goods but can be changed in Billing.
|
Billing Interface Processing |
Select to establish processing between Asset Management and Billing. This activates integration between the two applications and enables the Create Bill option on the Asset Management Retirement page. Note. PeopleSoft Billing is the only billing interface that is supported by this feature. |
|
BI Unit |
Select the Billing default business unit. The available Billing business units are established during the Billing application implementation. You can override the BI Unitas needed. Only BI Unitcan be overridden on the retirement page for other Billing business units whose general ledger business unit matches the Asset Management business unit. |
|
Bill Source |
Select the billing source, such as Assets. Available options are established during the Billing application implementation. You cannot override Bill Source. |
|
Bill Type |
Select the Billing Bill Type, such as AM . Available options are established during the Billing application implementation. You cannot override Bill Type. |
|
Bill By Identifier |
Select the Billing Bill By Identifier such as Assets . Available options are established during the Billing application implementation. The Bill By Identifier will vary if the business unit is VAT enabled. You cannot overrideBill by Identifier. Note. If the Bill By Identifier should consider VAT transactions, PeopleSoft strongly recommends using the following fields: BUSINESS_UNIT_AM, BILL_SOURCE_ID, VAT_TREATMENT_GRP, COUNTRY_VAT_BILLFR, COUNTRY_VAT_BILLTO, COUNTRY_SHIP_FROM, COUNTRY_SHIP_TO, PHYSICAL_NATURE, SHIP_TO_CUST_ID, RATE_MULT, RATE_DIV, CUR_RT_SOURCE, SHIP_TO_ADDR_NUM. Otherwise: BUSINESS_UNIT_AM, BILL_SOURCE_ID, PHYSICAL_NATURE, RATE_MULT, RATE_DIV, CUR_RT_SOURCE. |
See Integrating with PeopleSoft Asset Management.
Space Management Allocation
Complete the appropriate definitions for processing Real Estate Management space allocation transactions in the Space Management Allocation group box. The information entered here creates the default tree name, statistics code, and statistical account for this business unit in the Real Estate Management space allocation application.
|
Tree Name |
Select the department tree to be associated with this space allocation. |
|
Statistics Code |
Select the statistics code value associated with this space allocation. |
|
Statistical Account |
Select the statistical account value associated with this space allocation. |
Work Order Management
When you integrate Asset Management with Maintenance Management, you can define work order transfer default options.
|
Retire Assets Components |
Select this check box to enable retirement processing for components from work orders. |
|
TRF Out Components for Reuse |
Select this check box to enable component transfers out for reuse from work orders. |
|
Transfer In Components |
Select this check box to enable component transfers in from work orders. |
|
Override Other Defaults |
Select this check box to allow default overrides from work order. This option is used for making the set up defined at BU level prevail over set up at other levels. |
 Creating Asset Management Cash Generating Units
Creating Asset Management Cash Generating UnitsUse the Cash Generating Unit Definition (AM_CGU_DEFN) component to define cash generating units.
This section provides an overview of cash generating units (CGUs) and describes how to create CGUs.

 Understanding Cash Generating Units
Understanding Cash Generating Units
A cash generating unit (CGU) is the smallest identifiable group of assets that generate cash inflows from continuing use and are largely independent of the cash inflows from other assets or groups of assets. A CGU is used to assist in determining the recoverable amount of an individual asset when performing impairment assessment and processing.
After you determine how many cash generating units you require, you must define them for Asset Management. You define them per business unit. Each business unit definition must already be established to associate the CGU to it.

 Prerequisites to Creating Cash Generating Units
Prerequisites to Creating Cash Generating Units
Before you can create a cash generating unit (CGU), you must select the impairment processing option when selecting installation options. This enables the Impairment Processing check boxes on the business unit pages.
See Setting Installation Options for PeopleSoft Applications.

 Page Used to Create Cash Generating Units
Page Used to Create Cash Generating Units
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
Cash Generating Unit Definition |
AM_CGU_DEFN |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain Management, Business Unit Related, Assets, CGU Definition, Cash Generating Unit Definition |
Define cash generating units to assign to individual assets. |

 Defining Cash Generating Units
Defining Cash Generating UnitsAccess the Cash Generating Unit Definition page.
To add a new CGU, select a business unit and enter an alphanumeric CGU code. The Cash Generating Unit Definition page appears.
|
Description |
Enter a description for this cash generating unit. |
|
Impair All Assets In This CGU |
When you select this check box, the system enables impairment processing for all assets that fall within this CGU regardless of the option to perform impairment processing at the asset level. |
Impairment Criteria
|
Field Name |
Select a field name from the list of available ChartField values. |
|
Select Detail Values |
If you select this option, you may then choose among all valid definitions for the ChartField selected. For example, if you select to define the CGU by operating unit, the valid values will be all defined operating units for this business unit. |
|
Range of Values |
If you select this option, you may then choose a range of valid definitions for the ChartField selected. For example, if you select to define the CGU by department, the valid range of values will be all defined departments for this business unit: you will define the from and to range of departments to be included. |
When you have completed your selections, save the CGU.
See Also
Adjusting for Asset Impairment