 Using PeopleSoft MCF Broadcast
Using PeopleSoft MCF BroadcastThis chapter discusses how to:
Configure PeopleSoft MCF Broadcast.
Work with sample pages.
Use and demonstrate the JavaScript MultiChannel API (JSMCAPI).
Use PeopleCode built-in functions.
Use Universal Queue classes.
 Using PeopleSoft MCF Broadcast
Using PeopleSoft MCF BroadcastUse the broadcast function to broadcast a notification message. This function is typically used by a supervisor to send a notification message to specific recipients based on the parameters that are provided by the sender. Broadcast notifications can be sent system-wide, cluster-wide, queue-based, task-based, or activity-based.
System-wide broadcast notifications can be sent only using the PeopleCode API to all logical queues on the system. The same notification using JSMCAPI is sent to all the physical queues on the cluster.
Cluster-wide broadcast enables a user to broadcast to an entire audience that is logged on or subscribed to this broadcast topic on a particular cluster. A cluster broadcast can be configured to target a specific audience by specifying a particular queue, a channel, or an agent log state in the broadcast call.
A queue-based broadcast can send a notification to all agents on a particular queue. A channel-type broadcast is received by agents serving a particular channel. An agent working on multiple channels can receive broadcast that is meant for all those channels. An agent login state or activity-based broadcast allows a broadcast notification to be sent to all agents in a particular state.
The following diagram illustrates a cluster-wide broadcast:
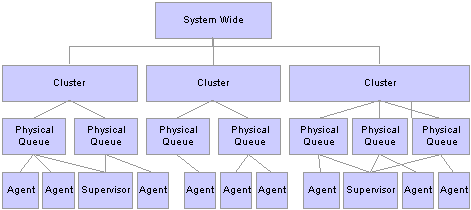
Cluster-wide broadcast
This section provides an overview of JSMCAPI broadcast and discusses how to:
Implement MCF broadcast.
Configure JSMCAPI Broadcast using MCF Supervisor console.
Configure PeopleCode broadcast.
View broadcast logs.

 Pages Used to Configure PeopleSoft MCF Broadcast
Pages Used to Configure PeopleSoft MCF Broadcast
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
JSMCAPI Broadcast |
MCF_BROADCAST |
PeopleTools, MultiChannel Framework, Universal Queue, Sample Pages, JSMCAPI Broadcast |
Configure JSMCAPI Broadcast using MCF Supervisor Console. |
|
PCodeBroadcast |
MCF_DEMO_BROADCAST |
PeopleTools, MultiChannel Framework, Universal Queue, Sample Pages, PCodeBroadcast |
Send a broadcast message using PeopleCode broadcast. |

 Understanding JSMCAPI Broadcast
Understanding JSMCAPI BroadcastA JSMCAPI console primarily operates on physical queues. Whenever an agent or a supervisor uses a JSMCAPI console, the agent chooses a physical queue and logs onto it. To broadcast a message, a console typically uses this physical queue as a parameter to determine the target cluster. JSMCAPI broadcast works on the following restrictions:
JSMCAPI broadcast function does not provide any routing logic because it operates within a limited set of physical queues that are assigned to the agent or supervisor.
The agent can choose any physical queue from the assigned queue list without logging onto any particular physical queue.
The supervisors or the users of JSMCAPI broadcast can use only the physical queues on their list to send a broadcast notification.
JSMCAPI works within the confine of a single cluster and does not have any knowledge or access to other clusters in the system.

 Implementing MCF Broadcast
Implementing MCF BroadcastTo enable you to implement broadcast, MultiChannel Framework provides a PeopleCode built-in function and a JSMCAPI interface for JSMCAPI users (agents and supervisors) to send broadcast notifications.
Note. The broadcast notifications are displayed only in the third-party sample pages.
Subscribing and Publishing Broadcast
The JSMCAPI broadcast function is a specialized publish call to the REN server. Both JSMCAPI and PeopleCode publish to physical-queue broadcast topic (such as /Broadcast/SALES1), and the subscribers always subscribe to broadcast topic for the physical queues to which they were assigned.
To subscribe, use the following function:
BroadcastSubscribe(cluster,queue,task,state,presence,method)
To publish, use the following function:
MCFBroadcast(cluster,queue,task,state,presence,message,securitylevel, importancelevel, senderid, NameValuePairString
To unsubscribe, use the following function:
void broadcastUnsubscribe(type)
where <type> determines the type of broadcast, system-wide, queue-wide, or agent-wide.
See Also

 Using JSMCAPI Broadcast with MCF Supervisor Console
Using JSMCAPI Broadcast with MCF Supervisor ConsoleAccess the JSMCAPI Broadcast page.
|
REN Server Cluster ID |
Select the REN server cluster on which to test the MCF Supervisor console. Note. The MCF Supervisor console is specific to the REN cluster Id selected. |
|
MCF Supervisor Console |
Click to initiate the supervisor console. Note. To demonstrate the MCF Supervisor console, you must have MCF servers, both queue and log servers, running and communicating with the specified REN server cluster. |
After you click MCF Supervisor console, a new browser window appears that displays the sample supervisor console.
Note. To enable the new browser window to appear, disable any pop-up blocking software for your browser.
MCF Supervisor Console
Access the MCF Supervisor console.
|
Cluster Name |
Displays the REN server cluster on which to test broadcast. |
|
Queue Name |
Enter the name of the queue that is in the specified cluster. Note. Enter the queue name only when you want to broadcast the message to a particular queue. |
|
Task |
Select the task. Values are email, chat, voice, generic, and none. |
|
State |
Select the state of the agent. Note. If the state of the agent is LoggedIn when the broadcast message is being sent by the supervisor, the agent receives the broadcast message using Agent console. |
|
Presence |
Select the presence. Note. If the agent is logged out, the presence should be inActive. The broadcast message is received only when the agent is currently logged in to the queue on which broadcast is sent. |
|
Message |
Enter the message that you want to broadcast. Note. To view the broadcast message that is sent by the supervisor, use the Agent console sample page. Select the same REN cluster that is used by the supervisor to broadcast, and the broadcast message is displayed on the Agent console. |
|
Security Level |
(Optional ) Enter the security level. |
|
Importance Level |
(Optional) Enter the importance level. |
|
Sender Id |
(Optional) Enter the sender ID. Use this option only when you want the sender ID to appear as something other than the ID that actually sent the message. |
|
Enter the name and value pairs to configure your data. Note. These name-value pairs are concatenated as a string. You can define any name-value parameters for your application and send them in the name-value pair string. The JSMCAPI passes the same as a string to the console. Your particular application needs to process that string accordingly. |
Note. For a system-wide or a cluster-wide broadcast, the broadcast message from the supervisor is sent to all agents, as well as
the supervisors who are logged in to the cluster that is specified by the supervisor. The system-wide broadcast is same as
cluster-wide broadcast because a JSMCAPI supervisor knows only the cluster it is operating on.
For a queue-wide broadcast, the broadcast message from the supervisor is sent to all agents who are currently logged in to
the queue that is used by the supervisor to broadcast the message. This assumes that the queue is in the same cluster as the
supervisor who is sending the broadcast message.
For agent-wide broadcast, the broadcast message will be sent to all agents who are currently logged to any queue in the same
cluster as the supervisor who is sending the message.
The following diagrams illustrate queue-wide and cluster-wide broadcast:
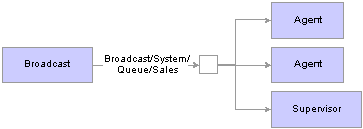
Queue-wide broadcast
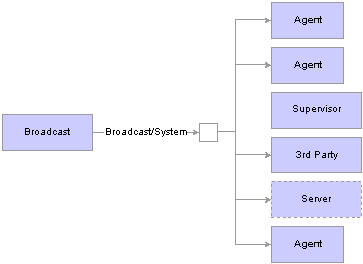
System-wide broadcast
The following table describes the combinations:
|
Type of Broadcast |
Cluster |
Queue |
Agent Login State |
Agent Activity State |
Broadcast Audience and Description |
|
JSMCAPI |
Not specified |
Not specified |
Not specified |
Not specified |
This is a cluster-wide broadcast. All agents on Cluster_1 will receive the broadcast. |
|
JSMCAPI |
Cluster_1 |
Not specified |
Not specified |
Not specified |
Same as the preceding. All agents on Cluster_1 will receive the broadcast. |
|
JSMCAPI |
Cluster_1 |
SALES |
Not specified |
Not specified |
All agents subscribing to SALES will receive the broadcast. This assumes that SALES is on Cluster_1. |
|
JSMCAPI |
Cluster_1 |
SALES |
Logged |
Not specified |
All agents who are logged (active and inactive) to sales will receive the broadcast. This assumes that SALES is on Cluster_1. |

 Using PeopleCode Broadcast
Using PeopleCode BroadcastAccess the PCodeBroadcast page.
|
MCF Cluster ID |
Select the target cluster receiving the broadcast message. |
|
Logical Queue ID |
Select the name of the target logical queue. |
|
Physical Queue ID |
Select the name of the target physical queue. |
|
TaskName |
Select the task. Select from email, chat, voice, generic or none. |
|
Agent State |
Select the state of the agent. Note. The agent receives the broadcast message only if the agent is logged in. |
|
Presence |
Select the presence. Note. If the agent is logged out, the presence should be inActive. All agents who are currently logged in receive the broadcast message. |
|
Message Set Number |
Select the message set number if you want to broadcast a message from the Message Catalog. |
|
Message Number |
Select the message number in the message set. |
|
Default Message |
Enter the default message. If no message is found in Message Catalog with the preceding message number, the text of the default message is used for the broadcast instead. |
|
Security Level |
(Optional) Enter the security level. |
|
Importance Level |
(Optional) Enter the importance level. |
|
Sender Id |
Enter the sender ID if you want the sender that is displayed with the notification to be an ID other than the one that sent the broadcast. |
|
Message |
Enter the message that you want to broadcast. Note. To view the broadcast message that is sent by the supervisor, use the Agent console sample page. Select the same REN cluster as used by the supervisor to broadcast, and the broadcast message is displayed on the Agent console. |
|
Enter the name and value pairs to configure your data. Note. These name-value pairs are concatenated as a string. You can define any name-value parameters for your application and send them in the name-value pair string. The JSMCAPI passes the same as a string to the console. Your particular application needs to process that string accordingly |
Note. For a system-wide PeopleCode Broadcast, the broadcast message from the supervisor is sent to all agents, as well as the supervisors
on all active REN clusters.
For a cluster-wide PeopleCode Broadcast, the broadcast message from the supervisor is sent to all agents, as well as the supervisors
on the specified REN clusters.
For a queue-wide broadcast, the broadcast message from the supervisor is sent to all agents who are currently logged in to
the queue that is specified by the queue ID in all clusters if the MCF cluster ID is not specified. If the cluster ID is specified,
all agents that are logged into the queue that is specified by the queue ID in the cluster that is specified by the cluster
ID receive the broadcast message.
For agent-wide broadcast, if both the cluster ID and queue ID are specified, the broadcast message is sent to all agents that
are currently logged into the queue that is specified by the queue ID. This assumes that the queue is in the cluster that
is specified by the cluster ID. However, if only the cluster ID is mentioned, all agents that are logged and active on any
queue on that cluster receive the broadcast message.
The following table describes the combinations:
|
Type of Broadcast |
Cluster |
Queue |
Agent Login State |
Agent Activity State |
Broadcast Audience and Description |
|
PeopleCode |
Not specified |
Not specified |
Not specified |
Not specified |
This is a true system-wide broadcast. All agents on all active REN clusters receive the broadcast. |
|
PeopleCode |
Cluster_1 |
Not specified |
Not specified |
Not specified |
All agents on Cluster_1 receive the broadcast. |
|
PeopleCode |
Cluster_1 |
SALES |
Not specified |
Not specified |
All agents subscribing to SALES receive the broadcast. This assumes that SALES is on Cluster_1. |
|
PeopleCode |
Not specified |
SALES |
Logged |
Not specified |
All agents that are logged (active and inactive) to SALES (all clusters with physical queues that are associated with SALES) receive the broadcast. |
|
PeopleCode |
Cluster_1 |
SALES |
Logged |
Active |
All agents that are logged into SALES and are in active state receive the broadcast. This assumes that SALES is on Cluster_1. |
|
PeopleCode |
Cluster_1 |
Not specified |
Logged |
Active |
All agents that are logged and active on any queue on Cluster_1 receive the broadcast. |
|
PeopleCode |
Cluster_1 |
Not specified |
Not specified |
Active |
All agents that are logged and active on any queue on Cluster_1 receive the broadcast. This is the same as the preceding because only agents that are logged in can be active. |
See Also

 Viewing Broadcast Logs
Viewing Broadcast Logs
To view broadcast log, use the Broadcast log page.
 Working with Sample Pages
Working with Sample PagesTo demonstrate MCF tools and functionality, use the MCF Sample Pages (MCF_DEMO_CMP) component.
This section discusses how to:
Use the Customer Chat sample page.
Use the URL wizard.
Use the Generic Event sample page.
Use the Generic Event window.
Use the Email sample page.
Use the Email window.

 Pages Used to Work with Sample Pages
Pages Used to Work with Sample Pages
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
Customer Chat |
MCF_DEMO_PG |
PeopleTools, MultiChannel Framework, Universal Queue, Sample Pages, Customer Chat |
View a customer chat session and built-in functions. |
|
Generic Event |
MCF_DEMO_NOTIFY_PG |
PeopleTools, MultiChannel Framework, Universal Queue, Sample Pages, Generic Event |
View a generic event notification and built-in functions. |
|
|
MCF_DEMOEM_NTFY_PG |
PeopleTools, MultiChannel Framework, Universal Queue, Sample Pages, Email |
View email retrieval, built-in functions, and application package classes. |

 Using the Customer Chat Sample Page
Using the Customer Chat Sample PageAccess the Customer Chat page.
Note. This page is available using both queue server and third-party routing server.
This page demonstrates the InitChat() built-in function, including required and optional parameters.
This page is not intended for production use. On a typical application page, the developer includes a Live Help or Customer Chat button that calls the InitChat() built-in function and passes required parameters, including the context of the chat request. The sample customer chat page demonstrates values that can be included in the InitChat() parameters. The user may not be prompted for any information.
To run a sample chat:
Access the MultiChannel Console.
Open the Customer Chat page.
Open the Queue ID drop-down list box and select the queue that you are logged on to.
The other fields are automatically populated with values that generate a sample chat session. You can change the values as long as valid required values are included.
The User URL is a required field that contains the application page URL to send to the agent chat browser.
The optional Wizard URL field represents a grab URL; the actual page that appears is determined by InitChat() parameters.
The text box displays error messages and additional information for using the sample page.
Click Customer Chat.
The customer chat window appears.
On the MultiChannel Console, click the flashing chat notification icon to accept the chat session.
The agent chat window appears.
You can enter text as both agent and customer to demonstrate chat functionality.

 Using the URL Wizard
Using the URL WizardClick Select from the agent chat window during a chat session to open the URL wizard:
Use the wizard to form a URL to send to the customer. The URL Wizard page is a template that demonstrates constructing a URL and sending it to a customer. The URL wizard can be used as is or as the basis for developing URL generation for your application.
|
URL Type |
Select the type of URL that is being accessed. Values are:
Fields that are not required by the selected URL type are not available. |
|
Show Relative URL |
Click to display the relative URL that is generated by the values that you have entered into the page's fields. |
|
URL |
Displays the generated relative URL. |
|
Push |
Click to send the generated relative URL to the customer's chat window. The Push button demonstrates functionality that must be included in an application-specific URL wizard. |
|
Push and Close |
Click to send the generated relative URL to the customer's chat window and close the URL wizard. The Push and Close button demonstrates functionality that must be included in an application-specific URL wizard. |

 Using the Generic Event Sample Page
Using the Generic Event Sample PageAccess the Generic Event page.
Note. This page is available using both queue server and third-party routing server.
This page demonstrates a generic persistent event using the EnQueue() and NotifyQ() built-in functions, including required and optional parameters.
This page is not intended for production use. On a typical application page, the developer includes an Enqueue or similar button that calls the EnQueue() built-in function and passes required parameters, including the context of the request. The sample customer chat page demonstrates values that can be included in the EnQueue() parameters. The user may not be prompted for any information.
To run a sample generic event:
Access the MultiChannel Console.
Open the Generic Event page.
Open the Queue ID drop-down list box, and select the queue that you are logged on to.
Open the Agent ID drop-down list box, and select the agent ID that you are logged on with.
Select Generic for the task type.
Click Notify.
On the MultiChannel Console, click the flashing event notification icon to accept the event.
The Generic Event window appears.

 Using the Generic Event Window
Using the Generic Event WindowThe format of the generic event window is determined by application developers. PeopleSoft supplies a sample generic event window to demonstrate the available functionality, including the DeQueue() built-in.
Configure the size and initial location of the generic event window on the Agent Window Configuration page:
|
Description |
Displays text from the generic event. |
|
To Queue ID |
Select a queue to which the generic event will be forwarded. |
|
Task ID |
Select the task ID of the generic event to forward. |
|
To Agent ID |
Select the agent ID to whom the generic event will be forwarded. |
|
Task Type |
Select the task type of the generic event to be forwarded. |
|
Forward |
Click to send the generic event to the selected agent or queue. This button demonstrates the functionality of the Forward() built-in function. |
|
Click to notify the real-time event notification (REN) server that you are done with this task. A message asks if you want to close the window. The Done button demonstrates the functionality of the DeQueue() built-in function. |
See Also

 Using the Email Sample Page
Using the Email Sample PageAccess the Email page.
Note. This page is available using both queue server and third-party routing server.
The email sample pages are intended for demonstration purposes and should not be used in production.
EnQueue() and NotifyQ() can also be called from PeopleSoft Application Engine batch programs.
See PeopleCode Built-in Functions.
Note. For you to fully demonstrate the functionality of the Email sample page, an email must be read and written to the email database using the GetMail - Server sample page.
To process a sample email:
Open the Queue ID drop-down list box and select the queue that you are logged on to.
Open the Agent ID drop-down list box and select the agent ID that you are logged on with.
Click Notify.
On the MultiChannel Console, click the flashing email notification icon to accept the email.
The email window appears.

 Using the Email Window
Using the Email WindowThe format of the email window is determined by application developers. PeopleSoft supplies a sample email event window to demonstrate available functionality.
Configure the size and initial location of the email event window on the agent's Window Configuration page.
The following example shows an email window:
|
To Queue ID |
To forward the email to another queue, select a queue ID from the drop-down list box and click Forward. |
|
To Agent ID |
To forward the email to another agent, select an agent ID from the drop-down list box and click Forward. |
|
Click to forward the email to the specified queue or agent. This button demonstrates the functionality of the Forward() built-in function. |
|
|
Click to quit the email and remove it from the queue. The Done button demonstrates the functionality of the DeQueue() built-in. |
Email Parts
If an email has been divided into parts stored in the email database, or has an attachment, they can be accessed here.
See Also
Demonstrating the Email Channel
 Using and Demonstrating JSMCAPI
Using and Demonstrating JSMCAPITo demonstrate MCF consoles and tools that use JSMCAPI, use the CTI Sample Pages (PT_CTI_DEMOOUTB) and MCF Sample Pages (MCF_DEMO_CMP) components.
This section provides an overview of JSMCAPI and discusses how to:
Use the CTI Sample Console page and Sample CTI Console.
Use the Agent Console page and Sample UQ Agent Console.
Use the Monitor Agents page and Sample Monitor - Agent States page.
Use the Monitor Queues page Sample Monitor - Queue Statistics page.

 Understanding JSMCAPI
Understanding JSMCAPIThe JSMCAPI enables custom configuration of MCF consoles (including the CTI console), MCF functionality on a PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture page, and queue and agent monitoring. For example, developers can create supervisor dashboards with which to monitor activity on their channels of interest, or developers can modify consoles according to their company's business requirements. The JSMCAPI builds on the REN JavaScript client. JSMCAPI uses standard JavaScript.
PeopleSoft provides sample pages demonstrating the functionality that is enabled by JSMCAPI. These pages are for demonstration purposes only, and should not be used in a production environment.
JSMCAPI is delivered with PeopleTools; you do not need a separate installation. The jsmcapi.js file is located in the <PS_HOME>\webserv\<domain>\applications\peoplesoft\PORTAL\ps\pMCF folder.
Understanding Reason Objects and Reason Codes
PeopleSoft MCF provides reason codes to explain any error or an event that has happened. The third party vendors uses the same reason codes as provided by PeopleSoft MCF to create reason objects that they send with the events. PSMCAPI internally parses the event, gets the reason code, and sends it to JSMCAPI with the event. The CTI sample console or third-party multichannel console looks up a mapper table that maintains the mapping of the reason codes to the Message Catalog entries and displays the reason code messages associated with the error or event that was sent by PSMCAPI.
To display the reason code messages, the sample console picks up all the reason codes and reason messages from the Message Catalogue. Whenever an error occurs, the JavaScript function will extract the reasoncode from the reason object in event and look for the reason message. Then, the JavaScript code prepares the reason message from the fields of reason object and displays the reason message in a new small window.
Reason codes can also be send with requests from JSMCAPI side. The JavaScript function will prompt for the reason codes and any extra data as part of reason.
The following table lists the reason codes and their corresponding reason messages:
|
Reason Code |
Description/Message Entry |
|
0 |
System or general error has occurred. |
|
1 |
See provider for details. |
|
2 |
Extension or agent is busy. |
|
3 |
No answer. |
|
4 |
Task is in transfer. |
|
5 |
Task is in conference. |
|
6 |
Task is abandoned. |
|
7 |
Searching for an agent. |
|
8 |
Incoming task. |
|
9 |
Task is assigned. |
|
10 |
Connection is established. |
|
11 |
User or Task data is updated. |
|
12 |
Request is completed successfully. |
|
13 |
State of the agent, group, or extension changed. |
|
14 |
New task is initiated. |
|
15 |
Conference is not successful. |
|
16 |
Transfer is not successful. |
|
17 |
Retrieve is not successful. |
|
18 |
Forward is not successful. |
|
19 |
Reject is not successful. |
|
20 |
Revoke is not Successful. |
|
21 |
Task is revoked. |
|
22 |
Task is withdrawn. |
|
23 |
Do Not Disturb is turned on. |
|
24 |
Do Not Disturb is turned off. |
|
25 |
Forwarding of calls is set. |
|
26 |
Forwarding of calls is canceled. |
|
27 |
Phone is on hook. |
|
28 |
Phone is off hook. |
|
29 |
New call is initiated. |
|
30 |
Call is put on hold. |
|
31 |
Call is parked. |
|
32 |
Call is cleared. |
|
33 |
Call is alternated between hold and active states. |
|
34 |
Call is taken off hold. |
|
35 |
Hold is not successful. |
|
36 |
Invalid session. |
|
37 |
Invalid State. |
|
38 |
Incorrect Data. |
|
39 |
Unsupported Feature. |
|
40 |
Configuration Error. |
|
41 |
Server is on. |
|
42 |
Server is off. |
|
43 |
Agent is Busy. |
|
44 |
Unexpected Error. |
The following table maps the reason codes to the entries in the Message Catalog:
|
Message Number MCFMSGNUM |
Message Set Number MCFMSGSETNUM |
Reason Code Number REASONCODENO |
|
2790 |
162 |
0 |
|
2791 |
162 |
1 |
|
2792 |
162 |
2 |
|
2793 |
162 |
3 |
|
2794 |
162 |
4 |
|
2795 |
162 |
5 |
|
2796 |
162 |
6 |
|
2797 |
162 |
7 |
|
2798 |
162 |
8 |
|
2799 |
162 |
9 |
|
2800 |
162 |
10 |
|
2801 |
162 |
11 |
|
2802 |
162 |
12 |
|
2803 |
162 |
13 |
|
2804 |
162 |
14 |
|
2805 |
162 |
15 |
|
2806 |
162 |
16 |
|
2807 |
162 |
17 |
|
2808 |
162 |
18 |
|
2809 |
162 |
19 |
|
2810 |
162 |
20 |
|
2811 |
162 |
21 |
|
2812 |
162 |
22 |
|
2813 |
162 |
23 |
|
2814 |
162 |
24 |
|
2815 |
162 |
25 |
|
2816 |
162 |
26 |
|
2817 |
162 |
27 |
|
2818 |
162 |
28 |
|
2819 |
162 |
29 |
|
2820 |
162 |
30 |
|
2821 |
162 |
31 |
|
2822 |
162 |
32 |
|
2823 |
162 |
33 |
|
2824 |
162 |
34 |
|
2825 |
162 |
35 |
|
2826 |
162 |
36 |
|
2827 |
162 |
37 |
|
2828 |
162 |
38 |
|
2829 |
162 |
39 |
|
2830 |
162 |
40 |
|
2831 |
162 |
41 |
|
2832 |
162 |
42 |
|
2833 |
162 |
43 |
|
2834 |
162 |
44 |
See Also
Pages Used to Use and Demonstrate JSMCAPI

 Common Elements Used in This Section
Common Elements Used in This Section
This section discusses common elements used on the CTI sample pages.
Common Elements Used in CTI Sample Pages
The following common elements are used in CTI sample pages.
|
Agent Id |
Select the CTI or MCF agent's agent ID. In the case of a CTI agent, the agent ID may be different from the agent's user ID. |
|
g/e/c (generic, email, chat) |
Represents three task types: generic, email, chat. |
|
|
Click to initiate the action that is selected in the associated drop-down list box. |
|
MCF Cluster ID |
Select the MCF cluster to be monitored or on which to test the sample console. |
|
Physical Queue |
Select the physical queue to be monitored. Each MCF logical queue can comprise one or more physical queues. Because each physical queue is associated with an MCF cluster, only physical queues can be monitored. |
|
State |
Displays a value indicating the state of the associated element. |
|
Statistics |
Display statistics that are generated by the CTI server. |
|
User Id |
Displays the CTI agent's PeopleSoft user ID. |

 Pages Used to Use and Demonstrate JSMCAPI
Pages Used to Use and Demonstrate JSMCAPI
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
Agent Console |
PT_SAMPLEAGNTCONSL |
PeopleTools, MultiChannel Framework, Universal Queue, Sample Pages, Agent Console |
View a sample MultiChannel Console that is generated using JSMCAPI. |
|
CTI Sample Console |
CTI_SAMPLECONSOLE |
PeopleTools, MultiChannel Framework, CTI Configuration, Sample Pages, CTI Sample Console |
View a sample CTI console that is generated using JSMCAPI. |
|
Monitor Agents |
PT_UQSAMPLECNSL |
PeopleTools, MultiChannel Framework, Universal Queue, Sample Pages, Monitor Agents |
View a sample agent statistics monitoring page. |
|
Monitor Queues |
PT_UQSAMPLECNSQ |
PeopleTools, MultiChannel Framework, Universal Queue, Sample Pages, Monitor Queues |
View a sample queue statistics monitoring page. |

 Using the CTI Sample Console
Using the CTI Sample ConsoleAccess the CTI Sample Console page.
|
REN Server Cluster ID |
Select the REN server cluster on which to test the sample console. |
|
CTI Sample Console |
Click to initiate the sample console. Note. To demonstrate the CTI sample console, you must have a CTI server running and communicating with the specified REN server cluster. |
After clicking CTI Sample Console, a new browser window appears that displays the sample console.
Note. To enable the new browser window to appear, disable any pop-up blocking software for your browser.
Open/Close Session
Access the Open/Close Session group box.
The Open/Close Session group box displays information about the session.
|
CTI Session Id |
This field displays a value identifying the session. If no session ID is displayed, check to ensure that the CTI server and REN server are both running. |
You can close an active session by clicking the Go button. You cannot make a selection from the drop-down list box.
Register User to Session
Access the Register User to Session group box.
Register a user to the session in the Register User to Session group box.
Because a CTI agent can have an agent ID different from the agent's user ID, both values are required. If the agent has a password, the password is also required.
|
Language |
Reserved for future use. The default language is English. |
You can register or unregister an agent by clicking the Go button. You cannot make a selection from the drop-down list box.
Register Group, Login User to Group, and User-Group States
Access the Register Group, Login User to Group, and User-Group States group box.
|
Group Id |
Enter the group ID to which the agent will be registered. To register the agent with the specified group, click the Go button. You cannot make a selection from the drop-down list box. |
|
Login |
Click the Go button to log in if Login appears in the drop-down list box. Click the Go button to log out if Logout appears in the drop-down list box. Note. The agent cannot receive calls until the agent is in the Ready state. Note. After you login to the group, a new pop-up window opens prompting for reason code data. If you register to an invalid group, the system displays an error message. |
|
Presence |
Enter a presence description to associate with the state that is selected in the drop-down list box. This presence value is different from any presence values that are predefined in the agent configuration. The agent cannot select from the pre-defined values. |
|
State |
Select an agent state. State options are:
Each state value has an associated state code that appears in the State field. To enable incoming calls, select Ready from the drop-down list box and click the Go button. |
|
Media Type |
Reserved for future use. The sample console supports only the telephone (voice) channel. However, JSMCAPI can support other channels. |
Register Extension to Session and Extension Operations
Access the Register Extension to Session, and Extension Operations group box.
|
Extension |
Enter a valid telephone extension number. |
|
Phone Number |
Enter a valid telephone number for use in subsequent operations, such as dial, forward, or do-not-disturb (DND). |
|
Select to mute a call. Note. This is enabled only when the agent is on a call. |
|
|
This flag is checked by the queue server for an agent handling a voice task. Note. If the flag is checked, the queue server will not assign new tasks to such an agent. The CTI Busy flag allows the application to implement a request which conveys the status of the agent to the queue server. Because the queue server stores the task list and the status in its temporary cache, a recovered or a rebooted queue server will not have the information of a agent's previous CTI status. The agent can send its CTI status to the queue server to indicate that it is busy with a CTI task. |
|
|
Select to forward incoming calls to the specified number. |
|
|
Select to put the selected extension in do-not-disturb status. |
|
|
Line 1 or Line 2 |
Displays a name or value for each line. On the sample console, the value will either be 1 or 2. |
|
Select to send DTMF digits on the line |
|
|
CallResult |
Select to set call result on the line |
|
ReScheduleTime |
Select to set reschedule time on the line |
|
Type |
Select to set reschedule type on the line. |
|
User Data |
Enter name-value pairs representing user data to be attached to a call. |
|
Call Data |
Enter any call data to be attached to the call. Call data includes:
|
Buddies
Access the Buddies group box.
Before an agent can chat with a buddy, the buddy must be registered in the Buddies group box.
Because a CTI agent can have an agent ID that is different from the agent's user ID, both values are required.
Note. If one agent is logged on the multichannel console and another agent is logged on the sample pages, the agents may see an incorrect buddy state for each other.
Error Messages/Information
Access the Error Messages/Information group box.
Any error messages associated with the process display in this section.
|
Clear |
Click the button to clear a displayed error message. |
Server State and Broadcasts
Access the Server State and Broadcasts group box.
|
CTI State |
Displays the status of the CTI server. |
|
REN State |
Displays the status of the REN server. |
|
Info (information) |
Displays the text of a broadcast message from the CTI server. |
Tracer
The tracer displays all requests between the CTI server and the console, which can be useful for debugging.

 Using the Agent Console Page
Using the Agent Console PageAccess the Agent Console page.
|
MCF Sample Console |
Click to initiate the sample console. Note. To demonstrate the MCF sample console, you must have an MCF cluster running and communicating with the specified REN server cluster. |
After you click MCF Sample Console, a new browser window appears that displays the sample console.
Note. To enable the new browser window to appear, disable any pop-up blocking software for your browser.
Open/Close Session
Access the Open/Close Session group box.
|
UQ Session Id |
The universal queue session ID. |
Register User to Session
Access the Register User to Session group box.
Register Group, Login User to Group, and User-Group States
Access the Register Group, Login User to Group, and User-Group States group box.
Note. The presence change happens only when you change from active to inactive or from inactive to active. When you log in, the default value is active and therefore no presence change occurs.
Address Operations
Access the Address Operations group box.
Buddies
Access the Buddies group box.
Note. If one agent is logged on the multichannel console and another agent is logged on the sample pages, the agents may see an incorrect buddy state for each other.
Note. The buddy states on this page are not automatically displayed. You must monitor an agent first using the Monitor Agents page before the buddy states are displayed.
See Using the Monitor Agents Page and Sample Monitor - Agent States Page.
|
|
Click to initiate an agent-to-agent chat session. |
Error Messages/Information
Access the Error Messages/Information group box.
Any error messages associated with the process display here.
|
Clear |
Click the button to clear a displayed error message. |
Server State and Broadcasts
Access the Server State and Broadcasts group box.
|
UQ State |
Displays the state of the queue server. |
|
REN State |
Displays the state of the REN server. |

 Using the Monitor Agents Page and Sample Monitor - Agent States Page
Using the Monitor Agents Page and Sample Monitor - Agent States PageAccess the Monitor Agents page.
Select the MCF cluster, physical queue on that cluster, and up to five agents on that queue to be monitored.
After you click Monitor Agent States, a new browser window appears.
Note. To enable the new browser window to appear, disable any pop-up blocking software for your browser.
Physical Queue
The ID of the physical queue that is being monitored appears in the first table.
Agent Statistics Table 1
The first agent statistics table displays information that is published by the JSMCAPI user.onStat1 event.
|
Time in Current State |
Displays the duration of the agent's current state. The value returned is timeInCurrentState. |
|
Time Since Login |
Denotes the duration since the agent logged in. The value returned is timeLogin. |
|
Num. Tasks Accepted: g/e/c (number of tasks accepted) |
Displays the number of tasks in each task type that the agent has accepted since login. The value returned is numTaskAccepted. |
|
Num. Tasks Unassigned: g/e/c (number of tasks unassigned) |
Displays the number of tasks in each task type that have been unassigned from the agent. Returned by numTasksUnassigned. |
|
Num. Tasks Done: g/e/c (number of tasks done) |
Displays the number of tasks in each task type that the agent has completed. Returned by numTasksDone. |
|
Most Recent Task: g/e/c |
Identifies the most recent task that was accepted since login for each task type. Returned by mostRecentTaskId. |
|
Most Recent Task Data: g/e/c |
Displays data on the most recent task that was accepted since login for each task type. Returned by mostRecentTaskInfo |
Agent Statistics Table 2
The second agent statistics table displays information that is published by the JSMCAPI user.onStat2 event.
|
Time Idle |
Displays the duration of time during which the agent has been idle. An agent is considered to be idle from the time the agent logs on until the agent accepts a task, and during the time between completing the last accepted task and accepting another task. The value returned is timeIdle. |
|
Time not Ready |
Displays the duration of time during which the queue could not assign tasks to the agent because the agent's maximum workload has been reached. The value returned is timeNotReady. |
|
Total Time Available |
Displays the total amount of time that the agent has been in an available status. The value returned is totalTimeAvailable. |
|
Total Time Unavailable |
Displays the total amount of time that the agent has been in an unavailable status. The value returned is totalTimeUnavailable. |

 Using the Monitor Queues Page and Sample Monitor - Queue Statistics Page
Using the Monitor Queues Page and Sample Monitor - Queue Statistics PageAccess the Monitor Queues Page.
Select the MCF cluster and up to five physical queues on that cluster to be monitored.
After you click Monitor Queue Statistics, a new browser window appears.
Note. To enable the new browser window to appear, disable any pop-up blocking software for your browser.
Queue Statistics 1
The first queue statistics table displays data that does not change frequently. The table displays information that is published by the JSMCAPI group.onStat1 event.
|
Queue |
Displays an identifier for this queue. The value returned is Queue_Id. |
|
Time Since Start |
The duration since this queue was started (application server domain start). The value returned is timeSinceStart. |
|
Num. Agents in Queue (number of agents in queue) |
The number of agents that are currently logged in to this queue. The value returned is numAgentsLoggedIn. |
|
Num. Agents Available (number of agents available) |
The number of agents that are currently logged in to this queue with an available status. The value returned is numAgentsAvail. |
|
Num. Tasks in Queue: g/e/c (number of tasks in queue) |
The number of tasks that are currently on this queue, by task type. The value returned is numTasksQueued. |
|
Num. Tasks Accepted: g/e/c (number of tasks accepted) |
The number of accepted tasks that are currently on this queue, by task type. The value returned is numTaskAccepted. |
|
Num. Tasks Done: g/e/c (number of tasks done) |
The number of tasks on this queue that have been completed, by task type. The value returned is numTaskDone. |
|
Num. Escalation: g/e/c (number of escalation) |
The number of escalated tasks on this queue, by task type. The value returned is numEscalation. |
|
Num. Overflow: g/e/c (number of overflow) |
The number of overflow tasks on this queue, by task type. The value returned is numOverflow. |
|
Task Total Time in System: g/e/c |
Displays the total duration of the most recently completed task in the system. The total time is the difference between the time that the task was enqueued and the time at which it was marked done. The value returned is taskTotalTimeInSystem. |
Queue Statistics 2
The second queue statistics table displays data that changes frequently. The table displays information that is published by the JSMCAPI group.onStat1 event.
|
Most Recent Task Enqueued: g/e/c |
Identifies the task that was most recently enqueued on this queue, by task type. The value returned is mostRecentTaskEnqueued. |
|
Most Recent Task Enqueued Data: g/e/c |
Displays data for the most recently enqueued task on this queue, by task type. The value returned is mostRecentTasksEnqueuedData. |
|
Most Recent Tasks Done: g/e/c |
Identifies the task that was most recently completed, by task type. The value returned is mostRecentTaskDone. |
|
Most Recent Task Done Data: g/e/c |
Displays data for the most recently completed tasks, by task type. The value returned is mostRecentTaskDoneData. |
Queue Statistics 3
The table displays information that is published by the JSMCAPI group.onStat2 event.
|
Oldest Task: g/e/c |
Identifies the oldest enqueued and accepted task on this queue, by task type. The value returned is oldestTask. |
|
Time Elapsed for Oldest Task: g/e/c |
Displays the duration that the oldest task on this queue has been enqueued, by task type. The value returned is timeElapsedOldestTask. |
|
Recent Task: g/e/c |
Identifies the most recent task that was enqueued and accepted on this queue, by task type. The value returned is recentTask. |
|
Time Elapsed for Recent Task: g/e/c |
Displays the duration that the most recent task on this queue has been enqueued, by task type. The value returned is timeElapsedRecentTask. |
|
Avg. Wait Time: g/e/c (average wait time) |
Displays the average time between a task being enqueued and being accepted, by task type. The value returned is averageWaitTime. |
|
Avg. Task Duration: g/e/c (average task duration) |
Displays the average duration before a task is completed. The value returned is averageTaskDuration. The average task duration is calculated by referencing a list of completed tasks. The size of that list is determined by the donelistsize parameter that is set on the Cluster Tuning page. |
 Using PeopleCode Built-in Functions with PeopleSoft MultiChannel Framework
Using PeopleCode Built-in Functions with PeopleSoft MultiChannel FrameworkPeopleSoft MultiChannel Framework uses several PeopleCode built-in functions. Application developers use these functions to communicate task requests and parameters to the queue server. For example, use InitChat code behind a button on an application page to initiate a chat session with an agent.
The built-in functions are:
Use DeQueue to notify the queue server that an enqueued task has been completed and to remove the task from the queue.
Use EnQueue to add a task to an active physical queue belonging to the specified logical queue.
Use Forward to transfer a task from one agent to another agent or another logical queue.
Use InitChat to place a customer chat request on a queue.
Use NotifyQ to notify the queue server of a task enqueued by EnQueue.
See PeopleCode Built-in Functions.
 Using Universal Queue Classes
Using Universal Queue ClassesThe universal queue classes provide the means by which applications can inspect objects that are processed by the queue server, such as tasks, agents, and queues. The classes also enable tasks to reenter the queue with their original task ID, as well as keep task times based on their original entry into the system.