 Understanding OLAP
Understanding OLAP
This chapter discusses:
Online Analytical Processing (OLAP).
Cubes.
PeopleSoft Cube Manager.
How to use supported OLAP tools.
Cube design and components.
Note. The information presented here is not a substitute for your Oracle Essbase, Cognos PowerPlay, or other third-party technology documentation, but should help you integrate your PeopleSoft data with one or more of these tools.
See Also
 Understanding OLAP
Understanding OLAP
Most business software users are familiar with Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) applications, which are for used for creating and maintaining information about business operations . The transactions that are stored by these applications are the heart of any business software. At the database level, OLTP applications are designed to allow for speedy creation of data and to reduce redundant information. However, data structures of this design are not well suited to analysis.
The nature of OLTP databases poses a problem: how to analyze data in a database that is not designed for analysis. One solution is to use a product such as Oracle PeopleSoft nVision. Such products perform analysis on selected characteristics of the database. However, using a powerful tool, such as PeopleSoft nVision, on top of an OLTP database, takes time.
In contrast, OLAP applications are designed specifically for data analysis. The source of information for analysis is an OLTP database. To make the OLTP data available to analytical applications, data is extracted and transformed into a format that is easier to analyze. You can store the resulting OLAP database in several different formats, depending on the tools that you used to access the data.
Multidimensional OLAP (MOLAP) is a format that stores all of the data hierarchically. This type of database is mainly for small-to-medium data marts. MOLAP databases, such as Oracle Essbase, summarize and access data quickly. The only drawback of MOLAP systems is that as dimensional information, sizes, or numbers increase, the storage mechanism becomes less efficient.
Relational OLAP (ROLAP) is a format that stores the analytical data in relational tables. The main benefit of the ROLAP format is its ability to store vast amounts of data. However, ROLAP data storage is not as efficient in accessing aggregate information at higher levels of the hierarchy.
The structures of the data schema can be one of two types: snowflake or star schema. Snowflake schemas are designed to keep very little redundant data, whereas star schemas encourage duplicate data. This release of PeopleSoft Cube Manager supports only the star schema.
In a star schema, each dimension is represented in a single table. The fact data, data that is to be analyzed, is stored in a separate table. The fact table contains one column to represent each of the dimensions from which the data was created.
The following diagram illustrates a typical star schema:
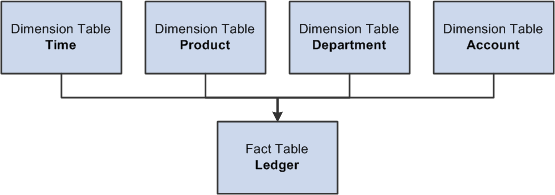
Star schema structure
See Understanding Cubes.
Hybrid OLAP (HOLAP) is the latest type of analytical structure. As the name implies, the data is stored in a hybrid format. The base fact data is stored in a set of relational tables, whereas the summary data is stored in a multidimensional format. This strategy is powerful, but can pose problems when you are combining data from the relational tables with the multidimensional summary data.
Generally speaking, multidimensional analysis is not a technology. Rather, it is a type of analysis that enables you to easily view data from many perspectives. These tools enable you to explore, interact with, and "slice and dice" complex data, guiding you to the multidimensional information that you can't easily discover with conventional reporting tools.
 Understanding PeopleSoft Cube Manager
Understanding PeopleSoft Cube ManagerThis section provides an overview of Cube Manager and discusses:
Cube Manager architecture.
PeopleSoft metadata.
PeopleSoft Process Scheduler integration.
Designing and building OLAP cubes.

 Cube Manager Overview
Cube Manager Overview
You can build an OLAP database out of PeopleSoft data without using PeopleSoft Cube Manager. In fact, customers have implemented custom OLAP solutions with previous PeopleSoft releases. However, PeopleSoft Cube Manager provides important benefits when connecting between your PeopleSoft application data and your OLAP platform.
PeopleSoft Cube Manager is a PeopleTool used to build OLAP databases or cubes. It provides a framework for modeling your OLAP cubes through its design tools: PeopleSoft Tree Managers and PeopleSoft Query. This framework supports the definition of all dimensions, attributes, measures, and cubes that you might want to build from PeopleSoft sources. You can share all of these definitions across cubes to ensure that OLAP results are consistent across your enterprise.
You can also use components designed in PeopleSoft Cube Manager across all target OLAP platforms supported by Oracle. PeopleSoft Cube Manager provides all these benefits while achieving a nearly platform-independent solution. You can apply the majority of a cube’s design attributes to Oracle Essbase, Cognos PowerPlay, or Generic Star Schema. PeopleSoft Cube Manager also enables you to leverage your existing PeopleSoft metadata to define the cube structure.

 Cube Manager Architecture
Cube Manager Architecture
The following diagram illustrates the cube building process:
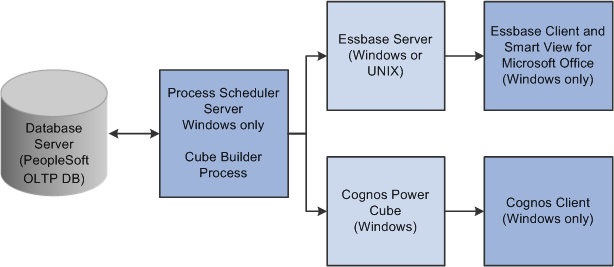
PeopleSoft Cube Manager: The big picture
The cube building process includes the following steps:
PeopleSoft Cube Manager extracts data from the PeopleSoft application (OLTP) database.
A third-party reporting tool directly analyzes the OLAP data store.

 PeopleSoft Metadata
PeopleSoft Metadata
Metadata is data that defines data. Metadata conveys information about how data is formatted, structured, and stored. In an OLAP cube, metadata defines dimensions, levels, members, member attributes, and interrelationships of the cube. PeopleSoft Cube Manager uses two types of PeopleSoft structures—trees and queries—to define cubes.
See Also

 PeopleSoft Process Scheduler Integration
PeopleSoft Process Scheduler Integration
Oracle PeopleSoft Process Scheduler includes a process type definition specifically for use with PeopleSoft Cube Manager. This process type is the Cube Manager process type, and you invoke it whenever you launch the process to create a cube from the standard run control page. During this process, depending on the OLAP tool that you specify, the data and metadata are translated into a format that is understood by Oracle Essbase, Cognos PowerPlay, or another ROLAP tool that can read a star schema.
See Also
Defining a Cube Build Process Using Process Scheduler Manager

 Designing and Building OLAP Cubes
Designing and Building OLAP Cubes
Identifying requirements is the most important part of any analytical application. An analytical application always produces results, regardless of whether those results are meaningful. Identifying requirements is essential to generating meaningful results.
Decide what aspects or processes of the business you want to capture. Examples can be sales activity, claims processing, or marketing return on investment. You might want to analyze several unrelated aspects of your business. Do not try to make one cube for all of the aspects. Instead, treat each set of related information as a single cube.
Next, identify the measures that you use to quantify those results, such as sales amounts in dollars or units. This information is almost always numeric. Then, identify the criteria with which you want to view the data and the granularity of the data. These criteria form the dimensions. The most common dimensions are time, accounts, geography, products, and department.
See the Oracle Essbase, Cognos PowerPlay, or other third-party technology documentation.
 Using Supported OLAP Tools
Using Supported OLAP Tools
Each PeopleSoft customer has unique reporting and analysis needs. To address these needs, Oracle provides support for various OLAP databases and tools, such as Oracle Essbase and Cognos PowerPlay.
If you have not selected an OLAP platform, the following descriptions should help you decide which platform best suits your needs.
This section discusses:
Oracle Essbase
Cognos PowerPlay

 Oracle Essbase
Oracle Essbase
Oracle Essbase is a robust, client/server-based product, and part of the Oracle Enterprise Performance Manager, the scope of which goes beyond individual users to the level of a data mart. However, because it supports metadata updates, Essbase enables you to keep a persistent data store, whereas you must re-create PowerCubes whenever any metadata changes.
Essbase includes the Smart View for Microsoft Office add-in that enables you to view OLAP cubes using Microsoft Excel and other Microsoft Office products—much like PS/nVision. Essbase is shipped separately from PeopleTools (separate licensing components are available for the integration and the end-user product).

 Cognos PowerPlay
Cognos PowerPlay
Cognos PowerPlay includes a product called Transformer, which builds the portable data cube. This cube is easy to attach as a file to email.
Cognos PowerPlay includes two components: a database engine component (the PowerCube) and an end-user component. This front-end component can be used not only for Cognos PowerPlay databases, but also for other OLAP databases, including Oracle Essbase.
Several new components exist in Cognos PowerPlay 7.x (Enterprise Server version) that work together to give you more functionality and to make Cognos PowerPlay cubes available to remote users. PeopleSoft Cube Manager has been modified to work with some of these new pieces, as described in this section.
See Supported Platforms on My Oracle Support for exact certified versions of third-party products such as Cognos PowerPlay.
This section discusses:
Enterprise Server.
PP Enterprise Server Administrator.
PPAdmtool.
PPApplications.
How PeopleSoft Cube Manager uses the EP Server.
Enterprise Server (EP Server) is a Microsoft Windows service that maintains cubes at a given location. Users from remote locations connect to this service and open the cubes in their choice of Cognos PowerPlay for Windows, Cognos PowerPlay for Excel, or Cognos PowerPlay for Web.
You can configure PeopleSoft Cube Manager to register cubes automatically with the EP Server. The EP Server needs a port number, server or machine name, user name, and password for registering a cube. However, PeopleSoft Cube Manager can add cubes only to the EP Server that is running locally, and only to the admin account. This means that users are required to specify only the port number and password for the admin account.
See Cognos PowerPlay Enterprise Server documentation.
Note. PeopleSoft Cube Manager and the EP Server must run on the same machine. When updating a cube, you should make sure that it is not being accessed by anyone prior to running PeopleSoft Cube Manager.
PP Enterprise Server Administrator
PP Enterprise Server Administrator is a Microsoft Windows application that can communicate with the EP Server, either locally or remotely, and can display the cubes that the EP Server is maintaining. Depending on the security privileges, you can add or remove cubes from the EP Server by using this application. You can also change passwords from this application.
PPAdmtool is a command-line program that can communicate with the EP Server. You can add or remove cubes from the EP Server by using this program. To carry out any commands using this program, you must specify the server or machine name, port number, and password.
The difference between the PP Enterprise Server Administrator and PPAdmtool is that PPAdmtool runs at the command prompt. The PP Enterprise Server Administrator is a Microsoft Windows application that you must start before viewing or manipulating the cubes. You can use PPAdmtool from the prompt to connect to, view, add, or remove cubes without performing the extra step of starting a program.
PPApplications are the actual Microsoft Windows applications (Cognos PowerPlay for Windows, Cognos PowerPlay for Excel, or Cognos PowerPlay for Web) that can open the cube .mdc files. These applications need either direct access to the .mdc file (locally or on the network) or access to the EP Server that is maintaining a particular cube.
How PeopleSoft Cube Manager Uses the EP Server
This example shows how PeopleSoft Cube Manager uses the new functionality of Cognos PowerPlay 7.x to manage a cube that exists on the EP Server.
Step 1:

PPAdmtool removes the .mdc file from the EP Server
Step 2:

PeopleSoft Cube Manager uses the transformer to create the .mdc file
Step 3:

PeopleSoft Cube Manager uses PPAdmtool to add the .mdc file to the EP Server
The Platform Options page (PeopleTools, Cube Builder, Cube Manager, Cube Instances, Platform Options) for Cognos PowerPlay has been modified to take the extra information needed to communicate with the EP Server.
See Also
Defining Cube Settings for Cognos PowerPlay
 Understanding Cube Design and Components
Understanding Cube Design and Components
Before using PeopleSoft Cube Manager, you should define the specific goals and results that you expect from online data analysis. After defining your goals, you should design the PeopleSoft trees and queries that are appropriate for creating both the structure and the data of the cube that you plan to build. These trees and queries supply data from your PeopleSoft application to any cubes that you create. After you establish your goals and create the necessary trees and queries upon which the resulting cube will be built, use PeopleSoft Cube Manager to begin designing a cube.
Many different kinds of components make up the cubes that you build with PeopleSoft Cube Manager: