 Understanding the PeopleSoft XML Publisher and the XML Publisher Classes
Understanding the PeopleSoft XML Publisher and the XML Publisher ClassesThis chapter provides an overview of the PeopleSoft XML Publisher classes, and discusses the following topics:
XML Publisher terms
Life-cycles of the XML Publisher classes
XML Publisher classes hierarchies
Error handling
Data types of XML Publisher objects
Scope of XML Publisher objects
How to import XML Publisher classes
How to create XML Publisher objects
XML Publisher classes language reference
XML Publisher classes examples
See Also
Getting Started with XML Publisher
 Understanding the PeopleSoft XML Publisher and the XML Publisher Classes
Understanding the PeopleSoft XML Publisher and the XML Publisher ClassesThe PeopleSoft XML Publisher enables you to separate the data, layout, and translation layers of a report from each other. This can improve flexibility, as well as reduce maintenance. You need to create report definitions, define templates, and so on, using the XML publisher. The XML Publisher classes enable you to access the runtime portions of the XML publishing process programmatically, that is, after the templates and reports have been created.
The XML Publisher classes are divided into the following categories:
Report manager definition classes
Report manager search classes
XML generation classes
XML Publisher engine classes
Report Manager Definition Classes
You need to create a report definition for use by the XML Publisher and associates it with a data source using the XML Publisher. You also need to create templates and associate them with a report. Then at runtime, the definitional information is called by the page viewer or processing program to and fed to the XML Publisher core engine to produce the formatted output. You can specify the runtime parameters either using the XML Publisher or the XML Publisher report manager definition classes.
See Report Manager Definition Classes Constructors.
Report Manager Search Classes
After you've published a report, it is stored in the report repository. Using the report manager search classes, you can search for a report based on defined search keys, or even add additional search keys for searching.
See Report Manager Search Classes Constructors.
XML Generation Classes
Use the XML generation classes to generate XML sample data and XML schema for rowset and PeopleSoft query data.
See XML Generation Class Constructors.
XML Publisher Engine Classes
Use the XML Publisher engine classes to directly access the Oracle XML Publiser APIs, as well as to specify page numbers and watermarks on merged PDF reports.
See XML Publisher Engine Class Constructors.
 XML Publisher Terms
XML Publisher TermsThe following is a list of general XML publisher terms and their definitions.
|
EFT |
Electronic Funds Transfer, a format used by the banking industry. |
|
eText |
Electronic text, specifically, files in ASCII text format. |
|
FO |
Formatting objects, an XML markup language for document formatting. |
|
HTML |
Hyper Text Markup Language, a markup language designed for the creation of web pages. |
|
|
Portable Document Format, a file format developed by Adobe Systems for representing documents in an independent format. |
|
RTF |
Rich Text Format, a document file format used for cross-platform document interchange. |
|
XML |
Extendable Markup Language, a general purpose markup language for many types of data. |
|
SMS |
Short messaging service, a short alphanumeric (160 characters) that is generally sent to a mobile device, such as a mobile phone. |
 Life-Cycles of the XML Publisher Classes
Life-Cycles of the XML Publisher ClassesThe following is the general flow of the XML Publisher classes, how and when they're used in the publishing process.
For most reports, you do not need to use the XML Publisher engine classes. In addition, you may or may not use the report manager search classes after a report is published.
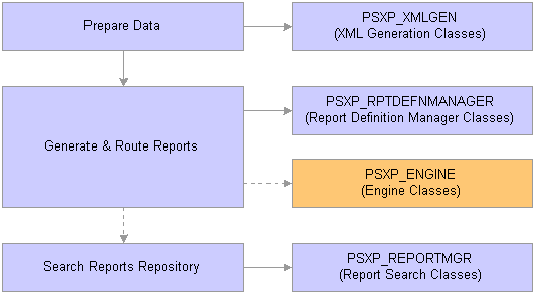
XML Publisher classes life-cycle flow
The following is a representation of how the different classes relate to each other.
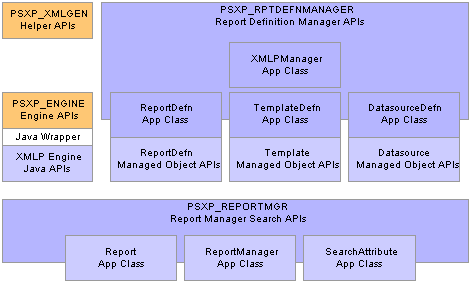
XML Publisher classes relationships
 XML Publisher Classes Hierarchies
XML Publisher Classes HierarchiesOnly the report manager definition and XML Publisher engine classes have a hierarchy. The other categories of classes do not have a hierarchy, that is, you can instantiate all the objects in that class from the top level object.

 Report Manager Definition Classes Hierarchy
Report Manager Definition Classes HierarchyThere are many different classes used with the report manager definition classes. The following flowchart shows the different classes, and how they are interrelated.
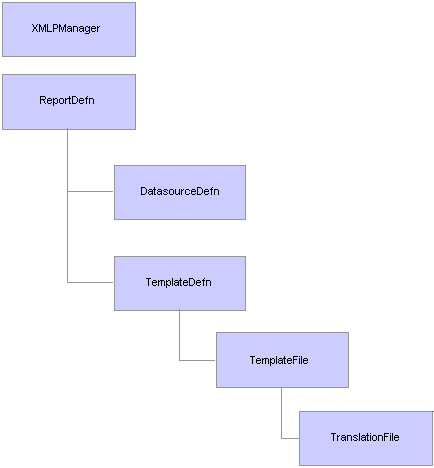
XML Publisher classes hierarchy

 XML Publisher Report Search Classes Structure
XML Publisher Report Search Classes Structure
The XML Publisher report search classes are composed of a few classes. All of the classes can be instantiated from a top level object. The following is the structure of the XML Publisher report search classes:

XML Publisher report search classes structure

 XML Publisher Generation Classes Structure
XML Publisher Generation Classes Structure
The XML Publisher generation classes are composed of a few classes. All of the classes can be instantiated from a top level object. The following is the structure of the XML Publisher generation classes:
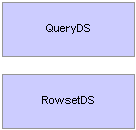
XML Publisher generation classes structure

 XML Publisher Engine Classes Hierarchy
XML Publisher Engine Classes HierarchyThe XML Publisher engine classes are composed of many different classes. Two classes, can't be instantiated from the top-level object, but instead, are instantiated from the PDFMerger class, the PageNumber and Watermark class. The following flowchart shows the different classes, and how they are interrelated.
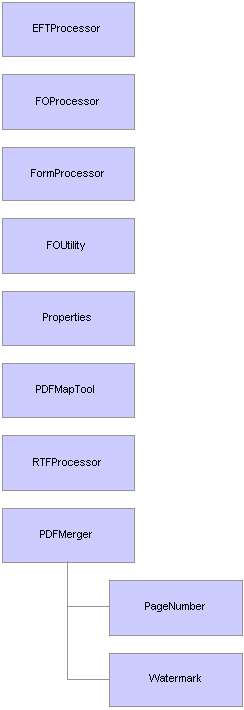
XML Publisher engine classes hierarchy
 Error Handling
Error HandlingThe different categories of classes handle errors differently.
The report manager definition and report manager search classes methods and properties should be wrapped in a try-catch statement to handle any errors.
The general classes generally return a populated object that can be checked for a null value to determine any errors.
The XML Publisher engine class methods generally contain an error parameter as part of their signature that you can check for any errors.
See Also
 Data Types of XML Publisher Objects
Data Types of XML Publisher ObjectsEvery XML Publisher class is its own data type, that is, report definitions are declared as data type ReportDefn, template definitions are declared as type TemplateDefn, and so on.
 Scope of XML Publisher Objects
Scope of XML Publisher ObjectsThese objects can only be instantiated from PeopleCode.
An XML Publisher object can be declared of type Local, Component or Global.
 How to Import the XML Publisher Classes
How to Import the XML Publisher ClassesThe XML Publisher classes are not built-in classes, like rowset, field, record, and so on. They are application classes. Before you can use these classes in your PeopleCode program, you must import them to your program.
An import statement names either all the classes in a package or one particular application class. For importing the XML Publisher classes, PeopleSoft recommends that you import all the classes in the application package.
|
Class Category |
Application Package Name |
|
Report manager definition classes |
PSXP_RPTDEFNMANAGER |
|
Report search manager classes |
PSXP_REPORTMGR |
|
XML generation classes |
PSXP_XMLGEN |
|
XML Publisher engine classes |
PSXP_ENGINE |
You should only import the classes that you need to for your application.
Your import statements should look like the following:
import PSXP_RPTDEFNMANAGER:*; import PSXP_REPORTMGR:*; import PSXP_XMLGEN:*; import PSXP_ENGINE:*;
Using the asterisks after the package name makes all the application classes directly contained in the named package available. Application classes contained in subpackages of the named package are not made available.
See Also
 How to Create XML Publisher Objects
How to Create XML Publisher ObjectsAfter you've imported the appropriate XML Publisher classes, you instantiate an object of one of those classes using the constructor for the class and the Create function.
The following example creates a new instance of a ReportDefn class, as the variable &rptDefn:
&rptDefn = Create ReportDefn(&rptDefnId);
 Search Operator Values
Search Operator ValuesMethods in the report manager definition and report search manager classes enable you to search for existing definitions. Many of the parameters for these methods should be specified in pairs, that is, a value specified with a search operator. All the search operator parameters use the same values.
The following lists the search operator values that can be used with the XML Publisher classes:
|
Value |
Description |
|
%PSXP_SrchBegins |
The name to search for begins with the specified value. |
|
%PSXP_SrchContains |
The name to search for contains the specified value. |
|
%PSXP_SrchEquals |
The name to search for equals the specified value. |
|
%PSXP_SrchNotEquals |
The name to search for does not equal the specified value. |
|
%PSXP_SrchLessThan |
The name to search for is less than the specified value. |
|
%PSXP_SrchLessEquals |
The name to search for is less than or equal to the specified value. |
|
%PSXP_SrchGreaterThan |
The name to search for is greater than the specified value. |
|
%PSXP_SrchGreaterEquals |
The name to search for is greater than or equal to the specified value. |
|
%PSXP_SrchBetween |
The name to search for is between two values. Separate the values by a comma. Do not use quotation marks. For example, ACCT1,ACCT9. |
|
%PSXP_SrchIn |
The name to search for is in the specified list. Separate the values with commas. Do not use quotation marks. For example, ACCT1, ACCT2, ACCT3. |
 Report Manager Definition Classes Constructors
Report Manager Definition Classes ConstructorsBefore you can use the report manager definition classes, you must import the application package that contains them, as follows:
import PSXP_RPTDEFNMANAGER:*;
You must use the constructor for each class to instantiate an instance of that class. The following are the constructors for the report manager definition classes, in alphabetical order.

 DataSourceDefn
DataSourceDefnSyntax
DataSourceDefn(DataSourceID, DataSourceType, Public)
Description
Use the DataSourceDefn constructor to instantiate a DataSourceDefn object. You must then use the Get method to initialize the object.
Parameters
|
DataSourceID |
Specify a unique name for the data source, as a string. |
|
DataSourceType |
Specify the type for the data source. Valid values are: |
|
Value |
Description |
|
QRY |
A PeopleSoft query. |
|
RST |
A PeopleSoft rowset. |
|
XMD |
An XmlDoc object. |
|
XML |
An XML file. |
|
Public |
If the data source type is a PeopleSoft query, specifying Public as true means that the data source is a public query. Specifying false for this parameter means the data source is a private query. For other data source types, you must specify true for this parameter. You receive an error if you specify false. |
Returns
A reference to a DataSourceDefn object.
See Also

 ReportDefn
ReportDefnSyntax
ReportDefn(ReportId)
Description
Use the ReportDefn constructor to instantiate a ReportDefn object. You must then use the Create or Get method to initialize the object.
Parameters
|
ReportId |
Specify a unique ID to be associated with the report definition. |
Returns
A reference to a ReportDefn object.
See Also

 TemplateDefn
TemplateDefnSyntax
TemplateDefn(TemplateID)
Description
Use the TemplateDefn constructor to instantiate a TemplateDefn object. You must then use the Get method to initialize the object.
You generally don't use the constructor to instantiate a TemplateDefn object. Instead, use the GetTemplateDefn method.
Parameters
|
TemplateId |
Specify a unique identifier for the template, as a string. |
Returns
A reference to a TemplateDefn object.
See Also
GetTemplate, GetDefaultTemplate.

 TemplateFile
TemplateFileSyntax
TemplateFile(&TemplateDefn, EffDate)
Description
Use the TemplateFile constructor to instantiate a TemplateFile object.
You generally don't use the constructor to instantiate a TemplateFile object. Instead, use the GetTemplateFile method.
Parameters
|
&TemplateDefn |
Specify an already instantiated and populated template definition object that is associated with the template file. |
|
EffDate |
Specify the effective date of the template file that you want to access. |
Returns
A reference to a TemplateFile object.
See Also
GetTemplateFile, GetActiveTemplateFile.

 TranslationFile
TranslationFileSyntax
TranslationFile(&TemplateDefn, EffectiveDate, LanguageCode)
Description
Use the TranslationFile constructor to instantiate a TranslationFile object.
You generally don't use the constructor to instantiate a TranslationFile object. Instead, use the GetTranslationFile method to access an existing translation file.
Parameters
|
&TemplateDefn |
Specify an already instantiated and populated template definition object, that is associated with the translation file. |
|
EffectiveDate |
Specify the effective date for the translation file, as a date. |
|
LanguageCode |
Specify the three-letter language code for the translation file, such as ENG, FRA, ESP and so on. |
Returns
A reference to a TranslationFile object.
See Also
 DataSourceDefn Class Methods
DataSourceDefn Class MethodsThe following are the DataSourceDefn class methods, in alphabetical order.

 Get
GetSyntax
Get()
Description
Use the Get method to initialize the object with the existing underlying data source definition.
Parameters
None.
Returns
None.

 GetData
GetDataSyntax
GetData(&PromptRecord)
Description
Use the GetData method to return the existing data file.
This method should only be used when the type of the data source is a PeopleSoft query.
If the query requires prompts, you must specify an already instantiated and populated record object that contains the values for the query prompts. Otherwise, specify a null value (" ").
Parameters
|
&PromptRecord |
Specify an already instantiated and populated record object that contains the prompts for the query if necessary, otherwise specify a null value. |
Returns
A string containing the path to the data.
See Also

 GetSampleData
GetSampleDataSyntax
GetSampleData()
Description
Use the GetSampleData method to return a path to the file containing the sample data.
The file is populated when the data source is first loaded into memory. The file is then created on the application server system. The path that is returned is an absolute path name.
Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A string containing the path name to the file containing the sample data.
See Also

 GetSchema
GetSchemaSyntax
GetSchema()
Description
Use the GetSchema method to return a path to the existing schema file. This method is only available for data source definitions that have PeopleSoft query defined as the type.
Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A string containing the path to the existing schema file.
See Also
 DataSourceDefn Class Properties
DataSourceDefn Class PropertiesThe following are the DataSourceDefn class properties, in alphabetical order.

 ActiveFlag
ActiveFlagDescription
This property returns the status of the data source definition. This property returns a boolean value: true if the data source definition is active, false otherwise.
This property is read-only.

 Description
DescriptionDescription
The Description property returns the description for the data source, as a string.
This property is read-only.

 IsPublic
IsPublicDescription
This property is only meaningful for data source definitions that are defined as PeopleSoft queries.
This property returns a boolean value: true if the data source is a public query, false if the data source is a private query.
For all other data source types, this property always returns a value of true.
This property is read-only.

 LastUpdatedBy
LastUpdatedByDescription
This property returns the user Id of the user who last updated the data source definition, as a string.
This property is read-only.

 LastUpdateDTTM
LastUpdateDTTMDescription
This property returns the date time of the last time the data source definition was updated, as a date time value.
This property is read-only.

 Name
NameDescription
This property specifies the name of the data source definition, as a string.
This property is read-only.

 ObjectOwnerID
ObjectOwnerIDDescription
This property returns the user Id of the user who currently owns the data source definition.
This property is read-only.

 RegisteredBy
RegisteredByDescription
This property returns the user Id of the user who originally registered the data source.
This property is read-only.

 RegisteredDTTM
RegisteredDTTMDescription
This property returns the date time of the time when the data source was originally registered, as a date time value.
This property is read-only.

 Type
TypeDescription
This property returns the type of the data source, as a string. Valid values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
QRY |
A PeopleSoft query. |
|
RST |
A PeopleSoft rowset. |
|
XMD |
An XmlDoc object. |
|
XML |
An XML file. |
This property is read-only.
 ReportDefn Class Methods
ReportDefn Class MethodsThe following are the ReportDefn class methods, in alphabetical order.

 DisplayOutput
DisplayOutputSyntax
DisplayOutput()
Description
Use the DisplayOutput method to display the report generated by the ProcessReport method in a separate browser window.
You must successfully call the ProcessReport method prior to calling this method.
This method displays a single report. Therefore, the report definition must not be set for bursting.
Parameters
None.
Returns
None.
See Also

 Get
GetSyntax
Get()
Description
Use the Get method to return a reference to the existing ReportDefn object.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A reference to the newly instantiated and populated ReportDefn object.

 GetActiveTemplatesByDistributionChannel
GetActiveTemplatesByDistributionChannelSyntax
GetActiveTemplatesByDistributionChannel(DistributionChannel, AsOfDate)
Description
Use the GetActiveTemplatesByDistributionChannel method to return an array of TemplateDefn objects for the specified distribution channel and as of date.
Parameters
|
DistributionChannel |
Specify the distribution channel name as a string. |
|
AsOfDate |
Specify the as of date for the template definitions that you want to access, as a date. |
Returns
An array of TemplateDefn objects.
See Also

 GetDatasource
GetDatasourceSyntax
GetDatasource()
Description
Use the GetDatasource method to return a reference to the data source definition object registered with the report definition.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A reference to a DatasourceDefn object.
See Also

 GetDefaultTemplate
GetDefaultTemplateSyntax
GetDefaultTemplate()
Description
Use the GetDefaultTemplate method to return a reference to the default template definition registered with the report definition.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A reference to a TemplateDefn object.
See Also

 GetOutDestFormatString
GetOutDestFormatStringSyntax
GetOutDestFormatString(OutDestFormat)
Description
Use the GetOutDestFormatString method to convert the output format returned from system variable %OutDestFormat to an XML Publisher output format string that can be passed to the output type parameter of the ProcessReport method. This method is useful when processing reports generated by application engine programs that are run process scheduler.
Parameters
|
OutDestFormat |
Specify the output destination format as a number. If you specify something other than a valid value, the method throws an exception. Valid values are: |
|
Value |
Description |
|
2 |
PDF format |
|
5 |
HTM format |
|
8 |
XLS format |
|
12 |
RTF format |
Returns
A string if successful. Valid values are:
HTM
XLS
RTF
See Also

 GetPSQueryPromptRecord
GetPSQueryPromptRecordSyntax
GetPSQueryPromptRecord()
Description
Use the GetPSQueryPromptRecord method to return the runtime prompts of a query as a record object. This method should only be used when the data source type associated with the report definition is a PeopleSoft query. This method returns a null when the data source type isn't a PeopleSoft Query.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A record object populated with the query prompts if the data source definition is a PeopleSoft query, null otherwise.
See Also

 GetTemplate
GetTemplateSyntax
GetTemplate(TemplateID)
Description
Use the GetTemplate method to access the specified template definition.
The template must have already been associated with the report definition.
Parameters
|
TemplateID |
Specify the name of the template that you want to access, as a string. |
Returns
A reference to a TemplateDefn object.
See Also

 GetTemplateList
GetTemplateListSyntax
GetTemplateList()
Description
Use the GetTemplateList method to return a list of templates registered with the report definition.
Parameters
None.
Returns
An array of TemplateDefn objects.
See Also

 PrintOutput
PrintOutputSyntax
PrintOutput(DestPrinter)
Description
Use the PrintOutput method to print the report definition object executing the method. The ProcessReport method must be called successfully before you use this method.
Parameters
|
DestPrinter |
Specify the printer you want to use for printing the report, as a string. |
Returns
None.

 ProcessEtextReport
ProcessEtextReportSyntax
ProcessEtextReport(TemplateID, LanguageCd, AsOfDate)
Description
Use the ProcessEtextReport when you want to process a report that has an etext template and the report output is expected to be a string read by PeopleCode instead of a file.
For any other type of report processing, use the ProcessReport method.
Note. ProcessEtextReport does not support following: bursting, dynamic template selection, and report definitions with template type other than etext.
Before you generate the report, if you are using a data source other than a PeopleSoft query, you must specify that data source using one of the set runtime data methods, such as SetRuntimeDataRowset or SetRuntimeDataXMLFile.
Parameters
|
TemplateId |
Specify the template to be used for processing this report, as a string. You can specify a null value for this parameter, that is, (""). When you specify a null value, the default template associated with the report definition is used. Note. The template must be an etext template. |
|
LanguageCD |
Specify the three-letter language code for the report definition, such as ENG, FRA, ESP and so on. This parameter controls both the translation and the language specific output details such as font selection and right-to-left page orientation for Arabic/Hebrew. You can specify a null value for this parameter, that is, (""). If you specify a null value, the current language of the session is used. |
|
AsOfDate |
Specify the as of date for the report, as a date. |
Returns
A string.
Example
/* XML Publisher sample report using XML Doc data source */ Local PSXP_RPTDEFNMANAGER:ReportDefn &oRptDefn; /* create report definition */ &oRptDefn = create PSXP_RPTDEFNMANAGER:ReportDefn("MYREPORT"); &oRptDefn.Get(); Local XmlDoc &inXMLDoc; Local string &strout; &inXMLDoc = CreateXmlDoc(""); &ret = &inXMLDoc.ParseXmlFromURL("D:\temp\etext\TestEft.xml"); /*attach XMLDoc Object to Report Definition;*/ &oRptDefn.SetRuntimeDataXMLDoc(&inXMLDoc); /* process etext report */ &strout = &oRptDefn.ProcessETextReport("", MYREPORT_AET.LANGUAGE_CD, %Date); WriteToLog(%ApplicationLogFence_Level1, "string output from processEtextReport API " | &strout);
See Also

 ProcessReport
ProcessReportSyntax
ProcessReport(TemplateId, LanguageCD, AsOfDate, OutputFormat)
Description
Use the ProcessReport method to generate a report and store the information.
Before you generate the report, if you are using a data source other than a PeopleSoft query, you must specify that data source using one of the set runtime data methods, such as SetRuntimeDataRowset or SetRuntimeDataXMLFile.
After you use the ProcessReport method, you can use the Publish method to post the report, the DisplayOutput method to display the report in a browser window, or the PrintOutput method to print the report.
Use the ProcessEtextReport instead when you want to process a report that has an etext template and the report output is expected to be a string read by PeopleCode instead of a file.
Parameters
|
TemplateId |
Specify the template to be used for processing this report, as a string. You can specify a null value for this parameter, that is, (""). When you specify a null value, the default template associated with the report definition is used. |
|
LanguageCD |
Specify the three-letter language code for the report definition, such as ENG, FRA, ESP and so on. This parameter controls both the translation and the language specific output details such as font selection and right-to-left page orientation for Arabic/Hebrew. You can specify a null value for this parameter, that is, (""). If you specify a null value, the current language of the session is used. |
|
AsOfDate |
Specify the as of date for the report, as a date. |
|
OutputFormat |
Specify the output format, as a string. See ReportDefn class: GetOutDestFormatString method. You can specify a null value for this parameter, that is, (""). When you specify a null value, the default output format associated with the report definition is used. |
Returns
None.
See Also
DisplayOutput, PrintOutput, SetPSQueryPromptRecord, SetRuntimeDataRowset, SetRuntimeDataXMLDoc, SetRuntimeDataXMLFile, SetRuntimeProperties.

 Publish
PublishSyntax
Publish(ServerName, ReportPath, FolderName, ProcessInstanceId)
Description
Use the Publish method to publish the current report definition
You must have successfully completed a call to the ProcessReport method before you can use this method, either directly or by using one of the XML Publisher XML Publisher engine classes.
Parameters
|
ServerName |
Specify the server to use for publishing the report, as a string. You can specify a null value for this parameter, that is, (""). |
|
ReportPath |
Specify an absolute path to the report, as a string. You can specify a null value for this parameter, that is, (""). This parameter should only be used for publishing reports that are not generated by directly using the ProcessReport method. Forward and backward slashes should be coded according to the operating system of the application server that contains the report. |
|
FolderName |
Specify the name of the report folder that the report should be posted to. You can specify a null value for this parameter, that is, (""). If you do not provide a value for this parameter, the default folder is used to post reports. |
|
ProcessInstanceId |
Specify the process instance of the calling process, such as the calling application engine program. If you specify a 0, a new process instance is generated to track the report posting process. |
Returns
None.
See Also

 SetPSQueryPromptRecord
SetPSQueryPromptRecordSyntax
SetPSQueryPromptRecord(&Record)
Description
Use the SetPSQueryPromptRecord method to specify an already instantiated record object that contains the prompt values for the query to be used to populate the report.
This method can only be used with reports that have a PeopleSoft query defined as the data source.
You must use this method before using the ProcessReport method.
Parameters
|
&Record |
Specify an already instantiated and populated record object that contains the values for the query to be used to populate the report. |
Returns
None.
See Also
ProcessReport, GetPSQueryPromptRecord.

 SetRuntimeDataRowset
SetRuntimeDataRowsetSyntax
SetRuntimeDataRowset(&Rowset)
Description
Use the SetRuntimeDataRowset method to specify an existing rowset object as the data source for the report.
Report definitions that use a data source other than a PeopleSoft query must set that data source before generating the report using the ProcessReport method.
Parameters
|
&Rowset |
Specify an already instantiated and populated rowset object to be used as the data source for the report. |
Returns
None.
See Also
GetDatasource, ProcessReport, SetRuntimeDataXMLDoc, SetRuntimeDataXMLFile.

 SetRuntimeDataXMLDoc
SetRuntimeDataXMLDocSyntax
SetRuntimeDataXMLDoc(&XmlDoc)
Description
Use the SetRuntimeDataXMLDoc method to specify an existing XmlDoc object as the data source for the report.
Report definitions that use a data source other than a PeopleSoft query must set that data source before generating the report using the ProcessReport method.
Parameters
|
&XmlDoc |
Specify an already instantiated and populated XmlDoc object to be used as the data source for the report. |
Returns
None.
See Also
GetDatasource, ProcessReport, SetRuntimeDataRowset, SetRuntimeDataXMLFile.

 SetRuntimeDataXMLFile
SetRuntimeDataXMLFileSyntax
SetRuntimeDataXMLFile(FilePath)
Description
Use the SetRuntimeDataXMLFile method to specify an existing file as the data source for the report.
Report definitions that use a data source other than a PeopleSoft query must set that data source before generating the report using the ProcessReport method.
Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server use a path with back slashes.
Parameters
|
FilePath |
Specify an absolute path to the file that you want to use. You must include the file name and file extension in the parameter. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server use a path with back slashes. |
Returns
None.
See Also
GetDatasource, ProcessReport, SetRuntimeDataRowset, SetRuntimeDataXMLDoc.

 SetRuntimeProperties
SetRuntimePropertiesSyntax
SetRuntimeProperties(&NameArray, &ValueArray)
Description
Use the SetRuntimeProperties method to set additional runtime values and properties required for generating this report.
Parameters
|
&NameArray |
Specify an already instantiated and populated array of string containing the names of the additional properties or variables that you need for this report. |
|
&ValueArray |
Specify an already instantiated and populated array of string containing the values of the additional properties or variables that you need for this report. The values should be in the same order as the names listed in &NameArray. |
Returns
None.
Example
The following example sets extra parameters for securing a document.
&asPropName = CreateArrayRept("", 0); &asPropValue = CreateArrayRept("", 0); &asPropName.Push("pdf-security"); &asPropValue.Push("true"); &asPropName.Push("pdf-open-password"); &asPropValue.Push("user1"); &asPropName.Push("pdf-permissions-password"); &asPropValue.Push("owner1"); &oRptDefn.SetRuntimeProperties(&asPropName, &asPropValue);
See Also
 ReportDefn Class Properties
ReportDefn Class PropertiesThe following are the ReportDefn class properties, in alphabetical order.

 AllowRecipientEntry
AllowRecipientEntryDescription
Use this property to specify whether the requester can add viewers to the process scheduler distribution page when running the report. This property takes a boolean value, true if requestor can add viewers, false otherwise.
This property is read-write.

 AllowViewerEntry
AllowViewerEntryDescription
Use the AllowViewerEntry property to specify whether the requestor can add email instructions to the process scheduler distribution page. This property takes a boolean value; true if the requestor can add the instructions, false otherwise.
This property is read-write.

 ArchiveAfter
ArchiveAfterDescription
Use this property to specify the number of days that the report is retained in the report repository.
This property is read-write.

 BurstFieldName
BurstFieldNameDescription
Use the BurstFieldName to specify the name of the field used for bursting the report when it is generated.
This property is required if you are going to burst a report. If this property has no value, the report will not be burst when it is generated.
If you are bursting a report, you also may also want to set the following properties:
SecurityFieldName
SecurityIDType
SecurityJoinTable
TemplateControlFieldName
UseBurstValueAsOutputValueName
This property is read-write.
Considerations Using Bursting with File Layouts
In order for bursting to work with a file layout, you must place the burst field at the highest repeating level in the file structure. You must also do the following:
Open the file in write mode.
Write the following code to the file:
&file.writeline("<?xml version='1.0'?>");
Close the file and open it again in append mode while processing the file layout. This ensures that:
The start tags (<start> </start>) are not inserted at the beginning and end of the file.
The first line in the file is "<?xml version='1.0'?>".
See Also
SecurityFieldName, SecurityIDType, SecurityJoinTable, UseBurstValueAsOutputFileName.

 CategoryId
CategoryIdDescription
Use the CategoryId property to specify the report category ID for the report definition.
This property is read-write.

 Description
DescriptionDescription
Use the Description property to specify a description for the report definition.
This property is read-write.

 DestinationPrinter
DestinationPrinterDescription
Use the DestinationPrinter property to specify a printer for the generated report.

 FolderName
FolderNameDescription
Use the FolderName property to specify a folder name for the generated report to be posted to.
This property is read-write.

 ID
IDDescription
Use the ID property to specify the ID for the report.
This property is read-write.

 IsReadOnly
IsReadOnlyDescription
This property returns a boolean value: true if the report definition is read-only to the current end user, false otherwise.
This property is read-only.

 LastUpdateDTTM
LastUpdateDTTMDescription
This property returns the last time that this report definition was updated, as a datetime.
This property is read-only.

 LastUpdateOprID
LastUpdateOprIDDescription
This property returns the last user Id of the user who updated this report definition.
This property is read-only.

 ObjectOwnerID
ObjectOwnerIDDescription
This property returns the user Id of the owner of the data source associated with the report definition.
This property is read-only.

 OutDestination
OutDestinationDescription
This property returns the output destination of the report definition, as a string.
This property is read-write.

 OutDestinationType
OutDestinationTypeDescription
This property returns the type of device specified for the output of the report definition, as a string.
This property is read-write.

 OutputEditable
OutputEditableDescription
This property specifies whether or not the internal Adobe flag of a PDF report output file has the setting turned on to allow editing.
Note. This property should only be specified when the template type is RTF or XSL, and when generating PDF output.
This property is read-write.

 RegisteredBy
RegisteredByDescription
This property returns the name of user who originally created the report definition, as a string.
This property is read-only.

 RegisteredDTTM
RegisteredDTTMDescription
This property returns the date time when the report definition was first created, as a date time value.
This property is read-only.

 SecurityFieldName
SecurityFieldNameDescription
Use this property to specify the field name from the Security Join Table that stores Viewer ID. This is used with bursting.
This property is read-write.
See Also
BurstFieldName, SecurityIDType, SecurityJoinTable.

 SecurityIDType
SecurityIDTypeDescription
Use this property to specify the type of ID that the Security Viewer ID is; either a user Id or a permission list. This is used with bursting. Valid values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
2 |
User Id |
|
3 |
Permission list role |
This property is read-write.
See Also
BurstFieldName, SecurityFieldName, SecurityJoinTable.

 SecurityJoinTable
SecurityJoinTableDescription
Use this property to specify the name of a record that stores either a user ID or permission list assigned to a data value found in the XML data for this report definition. This prompt list is filtered for records that meet this criteria. This is used for bursting reports.
This property is read-write.
See Also
BurstFieldName, SecurityFieldName, SecurityIDType.

 Status
StatusDescription
This property returns the status of the report definition. This property returns a string. Valid values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
A |
The report definition is active and can be run. |
|
I |
The report definition is inactive. It cannot be run and it isn't translatable. |
|
P |
The report definition is in progress. This is the default value. The report definition cannot be run, but it is translatable. |
This property is read-only.

 TemplateControlFieldName
TemplateControlFieldNameDescription
Use this property to specify the name of the template control field, as a string. This field is the schema tag value from first child level of the report definition.
This property is used with bursting.
This property is read-only.
See Also

 UseBurstValueAsOutputFileName
UseBurstValueAsOutputFileNameDescription
Use the UseBurstValueAsOutputFileName property to specify different names for all the files that result from bursting. This property takes a boolean value: true, the report output files are named BurstValue.Extention. False is the default value.
This property is read-write.
See Also
ReportDefn class: BurstFieldName property.
 TemplateDefn Class Methods
TemplateDefn Class MethodsThe following are the TemplateDefn class methods, in alphabetical order.

 Get
GetSyntax
Get()
Description
Use the Get method to populate the current TemplateDefn object with an existing template definition.
Parameters
None.
Returns
None.

 GetActiveTemplateFile
GetActiveTemplateFileSyntax
GetActiveTemplateFile(AsOfDate)
Description
Use the GetActiveTemplateFile method to return a reference to the active template file specified by the as of date. If you want to access inactive template files as well, use the GetTemplateFile method instead.
Parameters
|
AsOfDate |
Specify the as of date that you want to use for the active template file, as a date. |
Returns
A reference to a TemplateFile object.
See Also

 GetTemplateFile
GetTemplateFileSyntax
GetTemplateFile()
Description
Use the GetTemplateFile method to return a reference to the associated template file object.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A TemplateFile object.
See Also
GetActiveTemplatesByDistributionChannel, GetDefaultTemplate.

 GetTemplateFileList
GetTemplateFileListSyntax
GetTemplateFileList()
Description
Use the GetTemplateFileList method to return a list of all the template files associated with the template definition.
Parameters
None.
Returns
An array of TemplateFile objects.
See Also
 TemplateDefn Class Properties
TemplateDefn Class PropertiesThe following are the TemplateDefn properties, in alphabetical order.

 Description
DescriptionDescription
This property returns the description of the template definition, as a string.
This property is read-write.

 DistributionChannel
DistributionChannelDescription
This property returns the name of the distribution channel associated with the template definition, as a string. Valid values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
0 |
Web posting |
|
1 |
EFT format |
|
2 |
Printer |
|
3 |
|
|
4 |
Fax |
|
5 |
SMS |
This property is read-write.

 ID
ID
Description
This property returns the Id of the template definition, as a string.
This property is read-only.

 IsReadOnly
IsReadOnlyDescription
This property returns a boolean value; true if the template definition object is read-only to the current user, false otherwise.
This property is read-only.

 IsSubTemplate
IsSubTemplateDescription
This property returns a boolean value: true if the template definition is a sub-template, false otherwise.
This property is read-only.

 LanguageCode
LanguageCodeDescription
This property returns the language code associated with the template definition, as a string.
This property is read-only.

 LastUpdateDTTM
LastUpdateDTTMDescription
This property returns the date time of the last time the template definition was updated, as a date time value.
This property is read-only.

 LastUpdateOprID
LastUpdateOprIDDescription
This property returns the last user Id of the user who updated this template definition.
This property is read-only.

 ObjectOwnerID
ObjectOwnerIDDescription
This property returns the user Id of the owner of the data source associated with the template definition.
This property is read-only.

 RegisteredBy
RegisteredByDescription
This property returns the user Id of the user who originally registered the template definition.
This property is read-only.

 RegisteredDTTM
RegisteredDTTMDescription
This property returns the date time of the time when the template definition was originally registered, as a date time value.
This property is read-only.

 ReportCategoryID
ReportCategoryIDDescription
This property returns the report category Id associated with the template definition.
This property is applicable only if the template definition is a sub-template.
This property is read-only.

 Type
TypeDescription
This property returns the type of template definition, as a string. Valid values are:
ETX (Etext)
RTF
XLS
This property is read-only.
 TemplateFile Class Methods
TemplateFile Class MethodsThe following are the TemplateFile class methods, in alphabetical order.

 GetFile
GetFileSyntax
GetFile()
Description
Use the GetFile method to return a string that contains the absolute path to the file.
Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server use a path with back slashes.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A string.

 GetMapFile
GetMapFileSyntax
GetMapFile()
Description
Use the GetMapFile method to return the template map file. This method returns a string containing the absolute path to the file.
Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server use a path with back slashes.
Note. Only use this method when the template type is PDF. Map files are only used with PDF template processing.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A string containing the path name to the file.

 GetTranslationFile
GetTranslationFileSyntax
GetTranslationFile(LanguageCD)
Description
Use the GetTranslationFile method to return a reference to the specified translation file.
Parameters
|
LanguageCD |
Specify the three-letter language code for the report definition, such as ENG, FRA, ESP and so on. This parameter controls both the translation and the language specific output details such as font selection and right-to-left page orientation for Arabic/Hebrew. You can specify a null value for this parameter, that is, (""). If you specify a null value, the current language of the session is used. |
Returns
A reference to a TranslationFile object.
See Also

 GetTranslationFileList
GetTranslationFileListSyntax
GetTranslationFileList()
Description
Use the GetTranslationFileList method to return all the translation files associated with the template file.
Parameters
None.
Returns
An array of TranslationFile objects.
See Also
 TemplateFile Class Properties
TemplateFile Class PropertiesThe following describes the TemplateFile class properties, in alphabetical order.

 EffectiveDate
EffectiveDateDescription
This property returns the effective date associated with the template file, as a date value.
This property is read-only.

 FileName
FileNameDescription
This property returns the name of the template file. The file must already exist on the application server. If you want to create the file and then return a path to it, use the GetFile method instead.
This property is read-only.
See Also

 MapFileName
MapFileNameDescription
This property returns just the name of the map file associated with the template definition, as a string. This property is only used when the template type is PDF.
If you want to create the file and then return a path to it, use the GetMapFile method instead.
This property is read-only.
See Also

 Status
StatusDescription
This property returns the status of the template file. Valid values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
A |
The template file is active. |
|
I |
The template file is inactive. |
|
P |
The template file is in progress. This is the default value. |
This property is read-only.
 TranslationFile Class Method
TranslationFile Class MethodThe following is the TranslationFile class method.

 GetFile
GetFileSyntax
GetFile()
Description
Use the GetFile method to generate the file, as well as return a the path to the actual translation file.
Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server use a path with back slashes.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A string containing the absolute path to the file.
See Also
 TranslationFile Class Properties
TranslationFile Class PropertiesThe following are the TranslationFile class properties, in alphabetical order.

 Description
DescriptionDescription
This property returns the description of a translation file.
This property is read-only.

 FileName
FileNameDescription
This property specifies the file name of a translation file, as a string. This is just the file name, not the path to the file. This is the name that is displayed to the user.
This property is read-only.

 LanguageCode
LanguageCodeDescription
Use this property to specify the language code of the translation file. This is the translated language, not the base language.
This property is read-write.

 Status
StatusDescription
This property specifies the status of the translation file. Valid values are:
|
Value |
Description |
|
A |
The translation file is active. |
|
I |
The translation file is inactive. |
|
P |
The translation file is in process. This is the default value. |
This property is read-only.
 XMLPManager Class Methods
XMLPManager Class Methods
The following are the XMPLManager class methods, in alphabetical order.

 GetDatasourceDefnList
GetDatasourceDefnListSyntax
GetDatasourceDefnList(DataSourceId, DataSourceIdOp, DataSourceType, Owner, Descr, DescrOp, ObjectOwnerId, Active, CaseSensitive)
Description
Use the GetDatasourceDefnList method to return an array of DataSourceDefn objects.
Parameters
|
DataSourceId |
Specify a data source ID associated with a data source object that you want to access, as a string. |
|
DataSourceIdOp |
Specify the search operator to be used with the value specified in DataSourceIdOp, as a number. |
|
DataSourceType |
Specify the data source for a data source object that you want to access. Valid values are: |
|
Value |
Description |
|
QRY |
PeopleSoft query |
|
RST |
Rowset |
|
XMD |
XmlDoc object |
|
XML |
XML file |
|
Owner |
Specify whether to search based on owner. |
|
Value |
Description |
|
0 |
Do not search based on owner. |
|
1 |
Search public query based data source, and other data source types. |
|
2 |
Search private queries only. Note. If the data source type is not a PeopleSoft query, and the owner is 2 (private queries only,) result is always empty. |
|
Descr |
Specify the description of a data source that you'd like to access, as a string. |
|
DescrOp |
Specify the search operator to be used with the value specified in Descr, as a string. |
|
ObjectOwnerId |
Specify an object owner ID for a data source that you'd like to access, as a string. (Application owner?) |
|
Active |
Specify the status of the data source to be searched, whether active or inactive. Valid values are: |
|
Value |
Description |
|
I |
Search only inactive data sources. |
|
A |
Search only active data sources. |
|
CaseSensitive |
Specify whether the description specified by Descr is case sensitive. This parameter takes a Boolean value: True, the description is case sensitive, false otherwise. The default value is false. |
Returns
An array of DataSourceDefn objects.
See Also

 GetReportDefnList
GetReportDefnListSyntax
GetReportDefnList(ReportID, ReportIdOp, Descr, DescrOp , TemplateId, TemplateIdOp, TemplateDescr, TemplateDescrOp, DatasourceType, DataSourceId, DataSourceIdOp, DataSourceOwner, TemplateType, ReportCategoryId, ReportStatus, CaseSensitive)
Description
Use the GetReportDefnList method to return a list of all the report definitions in the system.
This method doesn't return any report definition based on a PeopleSoft query that the current user does not have access to, or any report that the current user doesn't have access to based on the report category.
Parameters
|
ReportID |
Specify the report ID of a report that you'd like to search for, as a string. |
|
ReportIDOp |
Specify the search operator to be used with the value specified in ReportID, as a string. |
|
Descr |
Specify the description of a report that you'd like to access, as a string. |
|
DescrOp |
Specify the search operator to be used with the value specified in Descr, as a string. |
|
TemplateId |
Specify the template ID associated with a report that you want to access, as a string. |
|
TemplateIdOp |
Specify the search operator to be used with the value specified in TemplateId, as a string. |
|
TemplateDescr |
Specify the description of the template associated with a report you want to access, as a string. |
|
TemplateDescrOp |
Specify the search operator to be used with the value specified in TemplateDescrOp, as a string. |
|
DataSourceType |
Specify the data source for a report that you want to access. Valid values are: |
|
Value |
Description |
|
QRY |
A PeopleSoft query. |
|
RST |
A PeopleSoft rowset. |
|
XMD |
An XmlDoc object. |
|
XML |
An XML file. |
|
DataSourceId |
Specify a data source ID associated with a report you want to access. |
|
DataSourceIdOp |
Specify the search operator to be used with the value specified in DataSourceId, as a string. |
|
DataSourceOwner |
Specify whether to search based on owner. |
|
Value |
Description |
|
0 |
Do not search based on owner |
|
1 |
Search public queries only. |
|
2 |
Search private queries only. If DataSourceType <> QRY and Owner = 2, result is always an empty array. |
|
TemplateType |
Specify a template type associated with a report that you want to access, as a string. Valid values are: |
|
Value |
Description |
|
RTF |
Specifies a template type of rich text format. |
|
|
Specifies a template type of published document format. |
|
HTM |
Specifies a template type hypertext markup language. |
|
ETX |
Specifies a template type of text. |
|
ReportCategoryId |
Specify a report category ID associated with a report that you want to access. |
|
ReportStatus |
Specify a report status associated with a report that you want to access. Valid values are:
|
|
CaseSensitive |
Specify whether the description specified by Descr or TemplateDescr is case sensitive. This parameter takes a Boolean value: True, the description is case sensitive, false otherwise. The default value is false. |
Returns
An array of ReportDefn objects.
See Also

 GetTemplateDefnList
GetTemplateDefnListSyntax
GetTemplateDefnList(TemplateId, TemplateIdOp, Descr, DescrOp, TemplateType, DistChannel, ReportCategoryId, IsSubtemplate, CaseSensitive)
Description
Use the GetTemplateDefnList method to return a list of template definition objects.
Parameters
|
TemplateId |
Specify the template ID associated with a template definition that you want to access, as a string. |
|
TemplateIdOp |
Specify the search operator to be used with the value specified in TemplateId, as a string. |
|
Descr |
Specify the description of a template definition that you'd like to access, as a string. |
|
DescrOp |
Specify the search operator to be used with the value specified in Descr, as a string. |
|
TemplateType |
Specify a template type associated with a template definition that you want to access, as a string. Valid values are: |
|
Value |
Description |
|
RTF |
Specifies a template type of rich text format. |
|
|
Specifies a template type of published document format. |
|
HTM |
Specifies a template type hypertext markup language. |
|
ETX |
Specifies a template type of text. |
|
DistChannel |
Specify the name of a distribution channel associated with a template definition, as a string. Valid values are: |
|
Value |
Description |
|
0 |
Web posting |
|
1 |
EFT format |
|
2 |
Printer |
|
3 |
|
|
4 |
Fax |
|
5 |
SMS |
|
ReportCategoryId |
Specify a report category ID associated with a template definition, as a string. |
|
IsSubTemplate |
Specify whether the template is a sub-template. This parameter takes a numeric value: |
|
Value |
Description |
|
0 |
The template is not a sub-template (false). |
|
1 |
The template is a sub-template (true). |
|
CaseSensitive |
Specify whether the description specified by Descr is case sensitive. This parameter takes a Boolean value: True, the description is case sensitive, false otherwise. The default value is false. |
Returns
An array of TemplateDefn objects.
See Also
 Report Manager Search Classes Constructors
Report Manager Search Classes ConstructorsBefore you can use the report manager search classes, you must import the application package that contains them, as follows:
import PSXP_REPORTMGR:*;
You must use the constructor for each class to instantiate an instance of that class. The following are the constructors for the report manager search classes, in alphabetical order.

 Report
ReportSyntax
Report(RptId, Prcsinstance, Contentid, Dbname, RptName, RptDescr, RptURL, RptCreateDttm, RptExpireDt, FldrName)
Description
Use the report constructor to instantiate and populate a report object with the data of an already published report.
Parameters
|
RptId |
Specify the report Id of the report you want to access, as a string. |
|
Prcsinstance |
Specify the process instance of the report you want to access, as a number. |
|
Contentid |
Specify the content Id number of the report you want to access, as a number. |
|
Dbname |
Specify the data base name, as a string. |
|
RptName |
Specify the name of the report you want to access, as a string. |
|
RptDescr |
Specify the description of the report you want to access, as a string. |
|
RptURL |
Specify the URL to the report details page, as a string. |
|
RptCreateDttm |
Specify the date and time of the report you want to access, as a date time value. |
|
RptExpireDt |
Specify the date when the report will be archived, and no longer considered active, as a date. |
|
FldName |
Specify the name of the folder the report was published to, as a string. You must specify an absolute path name, using forward and back slashes as required by the operating system of the application server or process scheduler. |
Returns
A reference to a report object.
See Also

 ReportManager
ReportManagerSyntax
ReportManager()
Description
Use the ReportManager constructor to instantiate an instance of the ReportManager class.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A ReportManager object.
See Also

 SearchAttribute
SearchAttributeSyntax
SearchAttribute(AttrName, AttrValue, CompareOperator)
Description
Use the SearchAttribute constructor to instantiate an instance of a SearchAttribute object.
Parameters
|
AttrName |
Specify the attribute name, as a string. |
|
AttrValue |
Specify the attribute value, as a string. |
|
CompareOperator |
Specify a comparison operator. |
Returns
A SearchAttribute object.
See Also
SearchAttribute Class Properties
 Report Class
Report ClassThe report class is one of the report manager search classes. Use the report class to access individual reports that have already been published to the report repository.
 Report Class Properties
Report Class PropertiesThe following are the report class properties, in alphabetical order.

 contentId
contentIdDescription
This property returns the content Id of the report, as a number.
This property is read-only.

 CreatedDateTime
CreatedDateTimeDescription
This property returns the date time when the report was created, as a date time.
This property is read-only.

 DatabaseName
DatabaseNameDescription
This property returns the data base name associated with the report, as a string.
This property is read-only.

 Description
DescriptionDescription
This property returns the description of the report definition, as a string.
This property is read-only.

 ExpireDate
ExpireDateDescription
This property returns the date when the report will be archived, as a date value.
This property is read-only.

 FileURL
FileURLDescription
This property returns a URL to the actual report file in the report repository.
Use the ReportURL property to access the report detail page instead.
This property is read-only.
See Also

 FolderName
FolderNameDescription
This property returns the full path name of the folder where the report is stored, as a string.
This property is read-only.

 ProcessInstanceID
ProcessInstanceIDDescription
This property returns the process instance Id associated with the report when it was posted, as a number.
This property is read-only.
See Also

 ReportInstanceID
ReportInstanceIDDescription
This property returns the report instance Id, that was populated when the report was run, as a number.
This property is read-only.
See Also

 ReportName
ReportNameDescription
This property returns the name of the report, as a string.
This property is read-only.

 ReportURL
ReportURLDescription
This property returns a URL as a string, that points to the report detail page.
Use the FileURL to access a URL to the actual file containing the report in the report repository.
This property is read-only.
See Also
 ReportManager Class
ReportManager ClassThe ReportManager class is one of the report manager search classes. Use the ReportManager class to access set the search criteria for reports that have already been published to the report repository.
 ReportManager Class Methods
ReportManager Class MethodsThe following are the ReportManager class methods, in alphabetical order.

 AddSearchFieldCriteria
AddSearchFieldCriteriaSyntax
AddSearchFieldCriteria(&SearchAttribute)
Description
Use the AddSearchFieldCriteria method to add an already instantiated and populated SearchAttribute object to the search.
Parameters
|
&SearchAttribute |
Specify an already instantiated and populated SearchAttribute object. |
Returns
A boolean, true if the criteria was added successfully, false otherwise.
Example
Local PSXP_REPORTMGR:SearchAttribute &oSearch; Local integer &compOpSrch; &CompOpSrch = oRptMgr.PSXP_SrchBegins; & oSearch = create PSXP_REPORTMGR:SearchAttribute (&sAttrname, &sAttrVal, &compOpSrch); &bResult = &oRptMgr.addSearchFieldCriteria(&oSearch);
See Also
SearchAttribute Class Properties

 GetReportList
GetReportListSyntax
GetReportList()
Description
Use the GetReportList method to return a list of the report definition objects that satisfy all the criteria you specified with the other methods associated with the ReportManager object.
Parameters
None.
Returns
An array of ReportDefn objects.
See Also

 SetBurstFieldCriteria
SetBurstFieldCriteriaSyntax
SetBurstFieldCriteria(BurstFld, BurstOp, BurstValue)
Description
Use the SetBurstFieldCriteria method to specify the burst criteria to be used with searching report definitions.
Parameters
|
BurstField |
Specify the name of the burst field used to generate the report, as a string. |
|
BusrtOp |
Specify the search operator to be used BurstField, as a string. |
|
BurstValue |
Specify the pattern string to be matched with burst field value using BurstOp. |
Returns
A boolean value, true if the method completes successfully, false otherwise.
See Also

 SetCaseSensitive
SetCaseSensitiveSyntax
SetCaseSensitive(IsCaseSensitive)
Description
Use the SetCaseSensitive method to specify the case sensitivity flag applicable to search field and bursting criteria for searching reports.
Parameters
|
IsCaseSensitive |
Specify a boolean value: true to make the search case sensitive, false to make it case insensitive. |
Returns
None.

 SetDateCriteria
SetDateCriteriaSyntax
SetDateCriteria(createdDate, createdLastVal, createdUnit)
Description
Use the SetDateCriteria method to specify the creation date criteria for searching reports.
Parameters
|
createdDate |
Specify a date used to search for reports generated on and after this date. You should specify a null value (" ") for this parameter if using createdLastVal and createdUnit. |
|
createdLastVal |
Specify a value to be used n conjunction with createdUnit, as a number. If you specify a value, it is used and any value given for createdDateis ignored. If you are not using this search criteria, you should specify a null value (" ") for this parameter. |
|
createdUnit |
Specify a value to be used for reports generated during last n number of periodic units. This value is used with createdLasVal. For example, if createdLastVal is set to 10, and createdUnit is set to 1, the reports generated in the last ten days are returned. Valid values are: |
|
Value |
Description |
|
1 |
Days |
|
2 |
Hours |
|
3 |
Minutes |
Returns
None.

 SetFolderCriteria
SetFolderCriteriaSyntax
SetFolderCriteria(FolderName)
Description
Use the SetFolderCriteria method to specify the folder criteria for searching reports.
Parameters
|
FolderName |
Specify the name of the folder the report is posted in, as a string. |
Returns
A boolean value, true if the search criteria is added successfully, false otherwise.

 SetProcessInstanceCriteria
SetProcessInstanceCriteriaSyntax
SetProcessInstanceCriteria(FromPID, ToPID)
Description
Use the SetProcessInstanceCriteria method to specify the process instance range criteria for searching reports.
Parameters
|
FromPID |
Specify a process instance Id to be used as the starting range from which to search, as a number. This value must be less than or equal to ToPID. You can specify a null value for this parameter, that is, (" "). |
|
ToPID |
Specify a process instance Id to be used as the ending range from which to search, as a number. This value must be greater than or equal to FromPID. You can specify a null value for this parameter, that is, (" "). |
Returns
A boolean value: true if the search criteria is added successfully, false otherwise.

 SetReportIDCriteria
SetReportIDCriteriaSyntax
SetReportIDCriteria(ReportId)
Description
Use the SetReportIDCriteria method to specify a report Id for searching reports.
Parameters
|
ReportId |
Specify a report Id to be used for searching for report definitions. |
Returns
A boolean value: true if the search criteria was set successfully, false otherwise.

 SetUserIdCriteria
SetUserIdCriteriaSyntax
SetUserIdCriteria(UserId)
Description
Use the SetUserIdCriteria method to specify a user Id to be used for searching reports intended to be accessed by that recipient.
Parameters
|
UserId |
Specify the user Id to be matched with the intended recipient of the report. |
Returns
A boolean: true if the search criteria is set successfully, false otherwise.
 SearchAttribute Class
SearchAttribute ClassThe SearchAttribute class is one of the report manager search classes. Use the SearchAttribute class to discovery name-value pairs for the search criteria for reports that have already been published to the report repository. In addition, you can also specify a comparison operator to be used with the name-value pairs.
 SearchAttribute Class Properties
SearchAttribute Class PropertiesThe following are the properties for the SearchAttribute class, in alphabetical order.

 attrName
attrNameDescription
This property returns the attribute name used with search.
This property is read-only.

 attrValue
attrValueDescription
This property returns the attribute value used with search???
This property is read-only.

 compareOp
compareOpDescription
This property returns the comparison operator used with search.
This property is read-only.
 XML Generation Class Constructors
XML Generation Class ConstructorsBefore you can use the XML generation classes, you must import the application package that contains them, as follows:
import PSXP_XMLGEN:*;
You must use the constructor for each class to instantiate an instance of that class. The following are the constructors for the report manager definition classes, in alphabetical order.

 QueryDS
QueryDSSyntax
QueryDS()
Description
Use the QueryDS constructor to instantiate a QueryDS object.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A reference to a QueryDS object.
See Also

 RowsetDS
RowsetDSSyntax
RowsetDS()
Description
Use the RowsetDS constructor to instantiate a RowsetDS object.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A reference to a RowsetDS object.
See Also
 QueryDS Class
QueryDS ClassUse the QueryDS class to generates query schema in XSD based on the query object passed in.
 QueryDS Class Methods
QueryDS Class MethodsThe following are the QueryDS class methods, in alphabetical order.

 GetXMLData
GetXMLDataSyntax
GetXMLData(&Query, &Rowset, XSDLocation)
Description
Use the GetXMLData method to create query data in XML format, based on the specified query and rowset objects.
Parameters
|
&Query |
Specify an already open query object to be used as the basis for the XML data. |
|
&Rowset |
Specify an already instantiated and populated rowset object to be used as the basis for the XML data. |
|
XSDLocation |
Specify the XSD location for the XML schema validation. You can also specify a null value for this parameter, that is, (" "). |
Returns
A string containing the generated XML data.
Example
Local PTXMLP_XMLGEN:QueryDS &oDS;&oDS = create PTXMLP_XMLGEN:QueryDS(); &oQuery = %Session.GetQuery(); &oQuery.Open(&sQueryName, False, False); &recPromptRec = &oQuery.PromptRecord; &bResult = Prompt(&sQueryName | " Prompts", "", &recPromptRec); &oRowSet = &oQuery.RunToRowset(&recPromptRec, 0); &sResult = &ds.getXMLData(&oQuery, &oRowSet, &strSchemaFile);
See Also

 GetXMLSampleData
GetXMLSampleDataSyntax
GetXMLSampleData(&Query, &Rowset, Rows, XSDLocation)
Description
Use the GetXMLSampleData method to create sample query data in XML from the query and rowset objects specified.
If you specify a populated rowset object, the method generates the XML from it. If you specify Null (" ") or if the rowset object is empty, the method generates random sample data.
Parameters
|
&Query |
Specify an already open query object to be used as the basis for the XML data. |
|
&Rowset |
Specify an already instantiated and populated rowset object to be used as the basis for the XML data. You can also specify a null value for this parameter, that is, (" "). |
|
Rows |
Specify the number of rows of XML data to be generated, as a number. |
|
XSDLocation |
Specify the XSD location for the XML schema validation. You can also specify a null value for this parameter, that is, (" "). |
Returns
A string containing the generated XML data.
Example
Local PTXMLP_XMLGEN:QueryDS &oDS; &oDS = create PTXMLP_XMLGEN:QueryDS(); &oQuery = %Session.GetQuery(); &oQuery.Open(&sQueryName, False, False); &sResult = &oDS.getXMLSampleData(&oQuery, "", &nNumRows, &sSchemaFile);
See Also

 GetXSDSchema
GetXSDSchemaSyntax
GetXSDSchema(&Query)
Description
Use the GetXSDSchema method to create a query schema in XSD format from the specified query object.
Parameters
|
&Query |
Specify an already open query object to be used as the basis for the XSD. |
Returns
A string containing the generated query schema in an XSD string.
 RowsetDS Class
RowsetDS ClassUse the RowsetDS class to generate XSD schema and XML data from a specified rowset object.
 RowsetDS Class Methods
RowsetDS Class MethodsThe following are the RowsetDS class methods, in alphabetical order.

 AddXMLData
AddXMLDataSyntax
AddXMLData(&ParentNode, &Rowset)
Description
Use the AddXMLData method to add the XML data of a rowset to the specified parent node. This method can be used to combine data of multiple rowsets in a single XML.
Parameters
|
&ParentNode |
Specify an already instantiated and populated XMLNode object. This is the parent node, where the XML data is to be added. Usually it is the DocumentElement of the combined XML. |
|
&Rowset |
Specify an already instantiated and populate rowset object containing the data to be added. |
Returns
None.
Example
Local XmlDoc &xmlDoc; Local XmlNode &xmlDocNode; Local PSXP_XMLGEN:RowSetDS &oDS; &oDS = create PSXP_XMLGEN:RowSetDS(); &xmlDoc = CreateXmlDoc("<?xml version='1.0'?><" | &sXmlDataName | " xmlns:xsi=" | """" | "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" | """" | "/>"); &xmlDocNode = &xmlDoc.DocumentElement; /* assume you have populated &rsResult1, &rsResult2 */ &dsRS.addXMLData(&xmlDocNode, &rsResult1); &dsRS.addXMLData(&xmlDocNode, &rsResult2); Return &xmlDoc.GenXmlString();

 AddXSDSchema
AddXSDSchemaSyntax
AddXSDSchema(&ParentNode, &Rowset)
Description
Use the AddXSDSchema method to add the XSD schema of a rowset to the specified parent node. This method can be used to combine schema of multiple rowsets in a single XSD.
Parameters
|
&ParentNode |
Specify an already instantiated and populated XMLNode object. This is the parent node, where the XSD data is to be added. Usually it is the DocumentElement of the combined XSD. |
|
&Rowset |
Specify an already instantiated and populate rowset object containing the data to be added. |
Returns
None.
Example
Local XmlDoc &xmlDoc; Local XmlNode &xmlDocNode; Local PSXP_XMLGEN:RowSetDS &oDS; &oDS = create PSXP_XMLGEN:RowSetDS(); &xmlDoc = CreateXmlDoc("<?xml version='1.0'?><xsd:schema xmlns:xsd=" | """" | "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" | """" | "/>"); &xmlDocNode = &xmlDoc.DocumentElement; /* assume you have populated &rsResult1, &rsResult2 */ &dsRS.addXSDSchema(&xmlDocNode, &rsResult1); &dsRS.addXSDSchema(&xmlDocNode, &rsResult2); Return &xmlDoc.GenXmlString();

 GetXMLData
GetXMLDataSyntax
GetXMLData(&Rowset, XSDLocation)
Description
Use the GetXMLData method to create query data in XML format, based on the specified rowset object.
Parameters
|
&Rowset |
Specify an already instantiated and populated rowset object to be used as the basis for the XML data. |
|
XSDLocation |
Specify the XSD location for the XML schema validation. |
Returns
A string containing the generated XML data.
See Also

 GetXSDSchema
GetXSDSchemaSyntax
GetXSDSchema(&Rowset)
Description
Use the GetXSDSchema method to create a schema in XSD format based on the specified rowset object.
Parameters
|
&Rowset |
Specify an already instantiated and populated rowset object to be used as the basis for the XSD. |
Returns
A string containing the generated query schema in an XSD string.
 XML Publisher Engine Class Constructors
XML Publisher Engine Class ConstructorsBefore you can use the XML Publisher engine classes, you must import the application package that contains them, as follows:
import PSXP_ENGINE:*;
You must use the constructor for each class to instantiate an instance of that class. The following are the constructors for the XML Publisher engine classes, in alphabetical order.

 EFTProcessor
EFTProcessorSyntax
EFTProcessor()
Description
Use the EFTProcessor constructor to instantiate an EFTProcessor object.
Parameters
None.
Returns
An EFTProcessor object.
See Also

 FOProcessor
FOProcessorSyntax
FOProcessor()
Description
Use the FOProcessor constructor to instantiate an FOProcessor object.
Parameters
None.
Returns
An FOProcessor object.
See Also

 FormProcessor
FormProcessorSyntax
FormProcessor()
Description
Use the FormProcessor constructor to instantiate an FormProcessor object.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A FormProcessor object.
See Also

 FOUtility
FOUtilitySyntax
FOUtility()
Description
Use the FOUtility constructor to instantiate a FOUtility object.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A FOUtility object.
See Also

 PageNumber
PageNumberSyntax
PageNumber()
Description
Use the PageNumber constructor to instantiate a PageNumber object.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A PageNumber object.
See Also

 PDFMapTool
PDFMapToolSyntax
PDFMapTool()
Description
Use the PDFMapTool constructor to instantiate a PDFMapTool object.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A reference to a PDFMapTool object.
See Also

 PDFMerger
PDFMergerSyntax
PDFMerger()
Description
Use the PDFMerger constructor to instantiate a PDFMerger object.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A reference to a PDFMerger object.
See Also

 Properties
PropertiesSyntax
Properties()
Description
Use the Properties constructor to instantiate a Properties object.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A Properties object.
See Also

 RTFProcessor
RTFProcessorSyntax
RTFProcessor()
Description
Use the RTFProcessor constructor to instantiate an RTFProcessor object.
Parameters
None.
Returns
An RTFProcessor object.
See Also

 Watermark
WatermarkSyntax
Watermark()
Description
Use the Watermark constructor to instantiate a Watermark object.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A Watermark object.
See Also
 EFTProcessor Class
EFTProcessor Class
Use the EFTProcessor class to access the Oracle EFTProcessor API.
 EFTProcessor Class Methods
EFTProcessor Class MethodsThe following are the EFTProcessor class methods, in alphabetical order.

 GenerateOutput
GenerateOutputSyntax
GenerateOutput(EFTFile, XMLDataFile, OutputFile, Error)
Description
Use the GenerateOutput method to create an output file from the specified EFT source file and XML data file.
Parameters
|
EFTFile |
Specify the full path name of the EFTFile to be used. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
XMLDataFile |
Specify the full path name of the XML data file to be used. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
OutputFile |
Specify the full path name of a text output file to be used to contain the output data. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
Error |
If any errors occur during processing, this parameter is populated with the text of the error message after processing. |
Returns
A boolean value: true if the method completes successfully, false otherwise.
Example
Local PSXP_ENGINE:EFTProcessor &oEFT; &oEFT = create PSXP_ENGINE:EFTProcessor(); &sErr = ""; &bResult = &oEFT.generateOutput(&sXSLFile, &XMLDatafile, &sOutputFile, &sErr);
See Also

 GenerateXSL
GenerateXSLSyntax
GenerateXSL(RTFTemplateFile, XSLOutputFile, Error)
Description
Use the GenerateXSL method to create an XSL file from the specified RTF template file. RTFTemplateName must actually be an EFT source file.
Parameters
|
RFTTemplateFile |
Specify the full path name of the EFT source file. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
XSLOutputFile |
Specify the full path name of a file to contain the XSL output. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
Error |
If any errors occur during processing, this parameter is populated with the text of the error message after processing. |
Returns
A boolean value: true if the method completed successfully, false otherwise. If false, the Error parameter is populated with the returned error message.
Example
Local PSXP_ENGINE:EFTProcessor &oEFT; &oEFT = create PSXP_ENGINE:EFTProcessor(); &sErr = ""; &bResult = &oEFT.generateXSL(&sEFTFile, &sXSLOutputFile, &sErr);
See Also
 EFTProcessor Class Properties
EFTProcessor Class Properties
The following are the EFTProcessor class properties, in alphabetical order.

 ConfFile
ConfFileDescription
Use the ConfFile property to specify a file that contains the configuration to be used for processing the document. This property enables you to accommodate different system configurations.
If you want to specify an already instantiated and populated Properties object that contains the configuration properties, use the ConfProp property instead.
This property is read-write.
See Also

 ConfProp
ConfPropDescription
Use the ConfProp property to specify an already instantiated and populated Properties object that contains the configuration to be used for processing the document. This property enables you to accommodate different system configurations.
If you want to specify a file that contains the configuration properties, use the ConfFile property instead.
This property is read-write.
See Also
 FOProcessor Class
FOProcessor Class
Use the FOProcessor class to access the Oracle FOProcessor API.
 FOProcessor Class Methods
FOProcessor Class MethodsThe following are the FOProcessor class methods, in alphabetical order.

 GenerateMergedOutput
GenerateMergedOutputSyntax
GenerateMergedOutput(&XSLTemplateFileArray, &XMLDataFileArray, &XliffFileArray, OutputFileName, OutputFormat, Error)
Description
Use the GenerateMergedOutput method to create formatted output from multiple XSL template files, XML data files and optionally, Xliff files.
The output is merged in the order of the files in the arrays, that is, the first part of the merged output comes from the first template with the first data file, as well as the first Xliff file (if appropriate), the second part from the second template and data file, and so on.
Parameters
|
&XSLTemplateFileArray |
Specify an already instantiated and populated array of string that contains the names of the XSL template files to be used. |
|
&XMLDataFileArray |
Specify an already instantiated and populated array of string that contains the names of the XML data files to be used. |
|
&XliffFileArray |
Specify an already instantiated and populated array of string that contains the names of the Xliff files to be used. If you do not want to use Xliff files, specify a null (" ") for this parameter. |
|
OutputFileName |
Specify the full path name of a file to be used for the merged output. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
OutputFormat |
Specify the format for the output. Valid values are: |
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
1 |
&FORMAT_RTF |
Specify RTF format. |
|
2 |
&FORMAT_PDF |
Specify PDF format. |
|
3 |
&FORMAT_HTML |
Specify HTML format |
|
4 |
&FORMAT_EXCEL |
Specify Excel format. |
|
Error |
If any errors occur during processing, this parameter is populated with the text of the error message after processing. |
Returns
A boolean value: true if the method completed successfully, false otherwise. If false, the Error parameter is populated with the returned error message.
See Also
GenerateMergedOutputFO, GenerateOutput.

 GenerateMergedOutputFO
GenerateMergedOutputFOSyntax
GenerateMergedOutputFO(&FOFIleArray, OutputFile, OutputFormat, Error)
Description
Use the GenerateMergedOutputFO method to create output from multiple formatted objects.
The output is merged in the order of the files in the arrays, that is, the first part of the merged output comes from the first template with the first data file, as well as the first Xliff file (if appropriate), the second part from the second template and data file, and so on.
Parameters
|
&FOFileArray |
Specify an already instantiated and populated array of string containing the file names of the formatted objects you want to use. |
|
OutputFile |
Specify the full path name of the file to contain the output from the method. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
OutputFormat |
Specify the format for the output. The valid values are: |
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
1 |
&FORMAT_RTF |
Specify RTF format. |
|
2 |
&FORMAT_PDF |
Specify PDF format. |
|
3 |
&FORMAT_HTML |
Specify HTML format |
|
4 |
&FORMAT_EXCEL |
Specify Excel format. |
|
Error |
If any errors occur during processing, this parameter is populated with the text of the error message after processing. |
Returns
A boolean value: true if the method completed successfully, false otherwise. If false, the Error parameter is populated with the returned error message.
See Also

 GenerateOutput
GenerateOutputSyntax
GenerateOutput(XSLTemplateFile, XMLDataFile, XLiffFile, OutputFile, OutputFormat, Error)
Description
Use the GenerateOutput method to create output from an XSL template file, an XML data file and, optionally, an Xliff file.
Parameters
|
XSLTemplateFile |
Specify the full path name of the XSL template file that you want to use for creating the output. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
XMLDataFile |
Specify the full path name of an XML file that contains the data you want to use for creating the output. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
XliffFile |
Specify the name of an Xliff file to be used. If you do not want to use an Xliff file, specify a null (“ ”) for this parameter. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
OutputFile |
Specify the full path name of a file to contain the output. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
OutputFormat |
Specify the format for the output. Valid values are: |
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
1 |
&FORMAT_RTF |
Specify RTF format. |
|
2 |
&FORMAT_PDF |
Specify PDF format. |
|
3 |
&FORMAT_HTML |
Specify HTML format |
|
4 |
&FORMAT_EXCEL |
Specify Excel format. |
|
Error |
If any errors occur during processing, this parameter is populated with the text of the error message after processing. |
Returns
A boolean value: true if the method completed successfully, false otherwise. If false, the Error parameter is populated with the returned error message.
See Also

 GenerateOutputFO
GenerateOutputFOSyntax
GenerateOutputFO(FOFileName, OutputFile, OutputFormat, Error)
Description
Use the GenerateOutputFO method to create output from formatted objects.
Parameters
|
FOFileName |
Specify the full path name of a file that contains the formatted object you want to use for output. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
OutputFile |
Specify the full path name of the file that you want to contain the output. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
OutputFormat |
Specify the format for the output. Valid values are: |
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|
1 |
&FORMAT_RTF |
Specify RTF format. |
|
2 |
&FORMAT_PDF |
Specify PDF format. |
|
3 |
&FORMAT_HTML |
Specify HTML format |
|
4 |
&FORMAT_EXCEL |
Specify Excel format. |
|
Error |
If any errors occur during processing, this parameter is populated with the text of the error message after processing. |
Returns
A boolean value: true if the method completed successfully, false otherwise. If false, the Error parameter is populated with the returned error message.
See Also
 FOProcessor Class Properties
FOProcessor Class Properties
The following are the FOProcessor class properties, in alphabetical order.

 ConfFile
ConfFileDescription
Use the ConfFile property to specify a file that contains the configuration to be used for processing the document. This property enables you to accommodate different system configurations.
If you want to specify an already instantiated and populated Properties object that contains the configuration properties, use the ConfProp property instead.
This property is read-write.
See Also

 ConfProp
ConfPropDescription
Use the ConfProp property to specify an already instantiated and populated Properties object that contains the configuration to be used for processing the document. This property enables you to accommodate different system configurations.
If you want to specify a file that contains the configuration properties, use the ConfFile property instead.
Example
Local PTXMLP_ENGINE:FOProcessor &oFO; Local PTXMLP_ENGINE:Properties &oProp; &oFO = create PTXMLP_ENGINE:FOProcessor(); &oProp = create PTXMLP_ENGINE:Properties(); &bResult = &oProp.setProperty("pdf-security", "true"); &bResult = &oProp.setProperty("pdf-permissions-password", "abc"); &bResult = &oProp.setProperty("pdf-encription-level", "0"); &oFO.ConfProp = &oProp;
See Also

 Locale
LocaleDescription
Use the Locale property to specify the locale for the processing. If no value is specified for this property, the default system locale will be used.
The locale is specified using a two character ISO language code and a two character ISO country code (LC-CC). When you don't need to reflect country specific formatting, the locale code is made up of just the language code.
This property is read-write.
 FormProcessor Class
FormProcessor Class
Use the FormProcessor class to access the Oracle FormProcessor API.
 FormProcessor Class Methods
FormProcessor Class MethodsThe following are the FormProcessor class methods, in alphabetical order.

 ExtractFieldNames
ExtractFieldNamesSyntax
ExtractFieldNames(PDFTemplateFileName, IncludeReservedNames, FieldNameArray, Error)
Description
Use the ExtractFieldNames method to extract the field names from the specified PDF template.
Parameters
|
PDFTemplateFileName |
Specify the full path name of the PDF template file that you want to extract the field names from. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
IncludeReservedNames |
Specify whether to include reserved names in the list of field names. This parameter takes a boolean value: true to include the reserved names, false otherwise. |
|
FieldNameArray |
Specify an already instantiated array of string to contain the names of the fields from the PDF template. The array doesn't have to be created with a length. |
|
Error |
If any errors occur during processing, this parameter is populated with the text of the error message after processing. |
Returns
A boolean value: true if the method completed successfully, false otherwise. If false, the Error parameter is populated with the returned error message.
See Also

 ExtractFieldValues
ExtractFieldValuesSyntax
ExtractFieldValues(PDFTemplateFileName, IncludeReservedNames, FieldValueArray, Error)
Description
Use the ExtractFieldValues method to extract the field values from the specified PDF template.
Parameters
|
PDFTemplateFileName |
Specify the full path name of the PDF template file that you want to extract the field values from. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
IncludeReservedNames |
Specify whether to include reserved names in the list of field values. This parameter takes a boolean value: true to include the reserved names, false otherwise. |
|
FieldValueArray |
Specify an already instantiated array of string to contain the values of the fields from the PDF template. The array doesn't have to be created with a length. |
|
Error |
If any errors occur during processing, this parameter is populated with the text of the error message after processing. |
Returns
A boolean value: true if the method completed successfully, false otherwise. If false, the Error parameter is populated with the returned error message.
See Also

 FillForm
FillFormSyntax
FillForm(PDFTemplateFile, XMLDataFile, PDFOutputFile, Error)
Description
Use the FillForm method to fill a PDF form by merging XML data into a PDF template.
Parameters
|
PDFTemplateFile |
Specify the full path name of the file that contains PDF template that you want to fill out. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
XMLDataFile |
Specify the full path name of the file that contains the XML data to be used for filling out the PDF template. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
PDFOutputFile |
Specify the full path name of the file where the output should be stored. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
Error |
If any errors occur during processing, this parameter is populated with the text of the error message after processing. |
Returns
A boolean value: true if the method completed successfully, false otherwise. If false, the Error parameter is populated with the returned error message.
 FormProcessor Class Properties
FormProcessor Class PropertiesThe following are the FOProcessor class properties, in alphabetical order.

 ConfFile
ConfFileDescription
Use the ConfFile property to specify a file that contains the configuration to be used for processing the document. This property enables you to accommodate different system configurations.
If you want to specify an already instantiated and populated Properties object that contains the configuration properties, use the ConfProp property instead.
This property is read-write.
See Also

 ConfProp
ConfPropDescription
Use the ConfProp property to specify an already instantiated and populated Properties object that contains the configuration to be used for processing the document. This property enables you to accommodate different system configurations.
If you want to specify a file that contains the configuration properties, use the ConfFile property instead.
This property is read-write.
Example
Local PTXMLP_ENGINE:FOProcessor &oFO; Local PTXMLP_ENGINE:Properties &oProp; &oFO = create PTXMLP_ENGINE:FOProcessor(); &oProp = create PTXMLP_ENGINE:Properties(); &bResult = &oProp.setProperty("pdf-security", "true"); &bResult = &oProp.setProperty("pdf-permissions-password", "abc"); &bResult = &oProp.setProperty("pdf-encription-level", "0"); &oFO.ConfProp = &oProp;
See Also

 Locale
LocaleDescription
Use the Locale property to specify the locale for the processing. If no value is specified for this property, the default system locale will be used.
The locale is specified using a two character ISO language code and a two character ISO country code (LC-CC). When you don't need to reflect country specific formatting, the locale code is made up of just the language code.
This property is read-write.
 FOUtility Class
FOUtility Class
Use the FOUtility class to access the Oracle FOUtility API.
 FOUtility Class Methods
FOUtility Class MethodsThe following are the FOUtility class methods, in alphabetical order.

 GenerateFO
GenerateFOSyntax
GenerateFO(XSLFile, XMLDataFile, OutputFOFile, Error)
Description
Use the GenerateFO method to generate a formatted object file from the specified XSL file and XML data.
Parameters
|
XSLFile |
Specify the full path name of a file that contains the XSL you want to use for the formatted objects. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
XMLDataFile |
Specify the full path name of an XML file that contains the data you want to use for the formatted objects. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
OutputFOFile |
Specify the full path name of a file to be used for the formatted object output. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
Error |
If any errors occur during processing, this parameter is populated with the text of the error message after processing. |
Returns
A boolean: true if the method completed successfully, false otherwise. If this method returns false, the Error parameter is populated with the text of the error message that occurred.

 MergeFOs
MergeFOsSyntax
MergeFOs(&FOFileArray, OutputFOFile, Error)
Description
Use the MergeFOs method to merge formatted objects into an output file.
Parameters
|
&FOFileArray |
Specify an already instantiated and populated array of formatted object file names. |
|
OutputFOFile |
Specify the full path name for the formatted object output file. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
Error |
If any errors occur during processing, this parameter is populated with the text of the error message after processing. |
Returns
A boolean: true if the method completed successfully, false otherwise. If this method returns false, the Error parameter is populated with the text of the error message that occurred.
Example
Local PTXMLP_ENGINE:FOUtility &oFOU; &oFOU = create PTXMLP_ENGINE:FOUtility(); &sErr = ""; &asFOFiles= CreateArray(&sFOFile1); &asFOFiles.Push(&sFOFile2); &bResult = &oFOU.mergeFOs(&asFOFiles, &sOutputFOFile, &sErr);
 FOUtility Class Property
FOUtility Class PropertyThe following is the FOUtility class property Prop.

 Prop
PropDescription
Use the Prop property to specify an already instantiated and populated Properties object that contains the configuration to be used for processing the document. This property enables you to accommodate different system configurations.
This property is read-write.
 PageNumber Class
PageNumber Class
Use the PageNumber class to set the page number for a merged PDF file. Objects in this class are used with the PDFMerger class property PageNumber.
 PageNumber Class Properties
PageNumber Class PropertiesThe following are the PageNumber class properties, in alphabetical order.

 BackgroundFile
BackgroundFileDescription
Use the BackgroundFile property to specify a file to be used for the page number, as a string.
You must specify an absolute file name.
This property is read-write.
Considerations Using the BackgroundFile Property
You should either use the BackgroundFile property, or you should use the other properties associated with this class, like position or font. You cannot use both.
The file you specify must be a PDF file. The page size of the background PDF must be the same as the target PDF document, otherwise the page numbering doesn't work properly. All page numbering starts on the first page of the target document.

 FontName
FontNameDescription
Use the FontName property to specify the name of the font to be used for the page number, as a string. Valid values are:
Courier
Courier-Bold
Courier-BoldOblique
Helvetica (this is the default value)
Helvetica-Bold
Helvetica-BoldOblique
Helvetica-Oblique
Symbol
Times-Bold
Time-BoldItalic
Time-Italic
Time-Roman
ZapfDingbats
If you specify an invalid font name, the default (Helvetica) is used.
This property is read-write.
See Also

 FontSize
FontSizeDescription
Use the FontSize property to specify the size of the page number, as a number.
The default value is 8.
This property is read-write.
See Also

 PositionX
PositionXDescription
Use the PositionX property to specify the X axis position of the text page number in the merged document.
This property is read-write.
See Also

 PositionY
PositionYDescription
Use the PositionY property to specify the Yaxis position of the text page number in the merged document.
This property is read-write.
See Also

 StartFromPageNum
StartFromPageNumDescription
Use the StartFromPageNum property to specify the page index from which you'd like to start the page numbering.
For example, if you have a PDF document which has two cover pages, and you want to start printing page numbers on the document from the third page, specify a three for this property.
This property is read-write.
See Also

 StartNum
StartNumDescription
Use the StartNum property to specify the page number to use as the first page number in the merged document. If you don't specify a starting number, the pages are numbered starting from 1.
This property is read-write.
See Also
 PDFMapTool Class
PDFMapTool Class
Use the PDFMapTool class to access the PeopleSoft map tool.
 PDFMapTool Class Methods
PDFMapTool Class Methods
The following are the PDFMapTool class methods, in alphabetical order.

 EnableMap
EnableMapSyntax
EnableMap(XSDFile, PDFTemplateFile, XMLInputFile, PDFOutputFile)
Description
Use the EnableMap method to create a map-enabled PDF file based on the specified PDF template file.
Parameters
|
XSDFile |
Specify the full path of the XSD (XML schema file) as a string. The file is used for field mapping between the PDF fields and the source data fields. You must specify the complete path to the file, using the appropriate back or forward slashes as required by the operating system of the application server. |
|
PDFTemplateFile |
Specify the full path of the PDF template file to be used, as a string. You must specify the complete path to the file, using the appropriate back or forward slashes as required by the operating system of the application server. |
|
XMLInputFile |
Specify the full path of the XML file containing sample data, as a string. The data is used for previewing. You can specify a null value for this parameter, that is, (""). You must specify the complete path to the file, using the appropriate back or forward slashes as required by the operating system of the application server. |
|
PDFOutputFile |
Specify the full path of the map-enabled PDF file to be generated by this method. You must specify the complete path to the file, using the appropriate back or forward slashes as required by the operating system of the application server. |
Returns
None.

 extractMap
extractMapSyntax
extractMap(PDFFile, OutMapFile)
Description
Use the extractMap method to extract a map file from a map-enabled PDF file.
Parameters
|
PDFFile |
Specify the full path of the file containing the map-enabled PDF that you want to extract the map from, as a string. You must specify the complete path to the file, using the appropriate back or forward slashes as required by the operating system of the application server. |
|
OutMapFile |
Specify the full path of the map file generated by this method. You must specify the complete path to the file, using the appropriate back or forward slashes as required by the operating system of the application server. |
Returns
None.

 processForm
processFormSyntax
processForm(PDFTemplateFile, XMLDataFile, MapFile, OutputPDFFile)
Description
Use the processForm method to generate a output from the PDF template and map-enabled file. This is not the same as ProcessReport, which performs full report generation.
Parameters
|
PDFTemplateFile |
Specify the full path of the PDF template file to be used in processing the form, as a string. You must specify the complete path to the file, using the appropriate back or forward slashes as required by the operating system of the application server. |
|
XMLDataFile |
Specify the full path of the XML data file to be used for generating the form, as a string. You must specify the complete path to the file, using the appropriate back or forward slashes as required by the operating system of the application server. |
|
MapFile |
Specify the full path of the map file to be used when generating the form, as a string. When a value isn't provided for this parameter, the field names in the PDF form and the tag names in XML document is used to fill the data. You can specify a null value for this parameter, that is, (""). You must specify the complete path to the file, using the appropriate back or forward slashes as required by the operating system of the application server. |
|
OutputPDFFile |
Specify the full path to the output PDF file generated by this method. You must specify the complete path to the file, using the appropriate back or forward slashes as required by the operating system of the application server. |
Returns
None.
 PDFMapTool Class Property
PDFMapTool Class Property
The following is a description of the PDFMapTool class property Locale.

 Locale
LocaleDescription
Use the Locale property to specify the locale for the processing. If no value is specified for this property, the default system locale will be used.
The locale is specified using a two character ISO language code and a two character ISO country code (LC-CC). When you don't need to reflect country specific formatting, the locale code is made up of just the language code.
This property is read-write.
 PDFMerger Class
PDFMerger Class
Use the PDFMerger class to access the Oracle PDFMerger API.
 PDFMerger Class Method
PDFMerger Class MethodThe following is the PDFMerger class method MergePDFs.

 MergePDFs
MergePDFsSyntax
MergePDFs(PDFFileArray, PDFOutputFile, Error)
Description
Use the MergePDFs method to merge the specified PDF files into a single output file.
The order of the files specified in the array are the order in which the files are merged.
Parameters
|
PDFFileArray |
Specify an already instantiated and populated array of string containing the names of the PDF files that you want to merge together. |
|
PDFOutputFile |
Specify the full path name of the file you want populated with the merged PDF file. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
Error |
If any errors occur during processing, this parameter is populated with the text of the error message after processing. |
Returns
A boolean: true if the method completed successfully, false otherwise. If this method returns false, the Error parameter is populated with the text of the error message that occurred.
Example
Local PTXMLP_ENGINE:PDFMerger &oMerger; &sErr = ""; &asNames = CreateArray(&sPdfFile1); &asNames.Push(&sPdfFile2); &bResult = &oMerger.mergePDFs(&asNames, &sOutputPdfFile, &sErr);
 PDFMerger Class Properties
PDFMerger Class PropertiesThe following are the PDFMerger class properties, in alphabetical order.

 ConfProp
ConfPropDescription
Use the ConfProp property to specify an already instantiated and populated Properties object that contains the configuration to be used for processing the document. This property enables you to accommodate different system configurations.
If you want to specify a file that contains the configuration properties, use the ConfFile property instead.

 Locale
LocaleDescription
Use the Locale property to specify the locale for the processing. If no value is specified for this property, the default system locale will be used.
The locale is specified using a two character ISO language code and a two character ISO country code (LC-CC). When you don't need to reflect country specific formatting, the locale code is made up of just the language code.
This property is read-write.

 PageNumber
PageNumberDescription
Use this property to specify an already instantiated and populated PageNumber object to be used with the merged document.
This property is read-write.
Example
Local PTXMLP_ENGINE:PDFMerger &oMerger; Local PTXMLP_ENGINE:PageNumber &oPageNumber; &oMerger = create PTXMLP_ENGINE:PDFMerger(); &oPageNumber = create PTXMLP_ENGINE:PageNumber(); &oPageNumber.FontName = "Symbol"; &oPageNumber.FontSize = 16; &oPageNumber.PositionX = 300; &oPageNumber.PositionY = 20; &oMerger.oPageNumber = &oPageNumber; &sErr = ""; &asNames = CreateArray(&sPdfFile1); &asNames.Push(&sPdfFile2); &bResult = &oMerger.mergePDFs(&asNames, &sOutputPdfFile, &sErr);
See Also

 Watermark
WatermarkDescription
Use this property to specify an already instantiated and populated Watermark object to be used with the merged object.
This property is read-write.
Example
Local PTXMLP_ENGINE:PDFMerger &oMerger; Local PTXMLP_ENGINE:Watermark &oWatermark; &oMerger = create PTXMLP_ENGINE:PDFMerger(); &oWatermark = create PTXMLP_ENGINE:Watermark(); &oWatermark.Text = "DEMO"; &oWatermark.TextStartPosX = 200; &oWatermark.TextStartPosY = 400; &oMerger.oWatermark = &oWatermark; &sErr = ""; &asNames = CreateArray(&sPdfFile1); &bResult = &oMerger.mergePDFs(&asNames, &sOutputPdfFile, &sErr);
See Also
 Properties Class
Properties Class
Use the Properties class to specify the properties for setting up the processor configuration. This class is used with the following classes:
EFTProcessor
FOProcessor
FormProcessor
FOUtility
PDFMerger
RTFProcessor
 Properties Class Methods
Properties Class MethodsThe following are the Properties class methods, in alphabetical order.

 GetProperty
GetPropertySyntax
GetProperty(Name, OutValue)
Description
Use the GetProperty method to return the value of the specified property.
Parameters
|
Name |
Specify the name of the property that you want to access the value. |
|
OutValue |
Specify a string to contain the value of the property you want to access. |
Returns
A boolean: true if the method completed successfully, false otherwise. If this method returns false, the Error parameter is populated with the text of the error message that occurred.
Example
Local PTXMLP_ENGINE:Properties &oProp; &oProp = create PTXMLP_ENGINE:Properties(); %sValue = ""; &bResult = &oProp.getProperty("pdf-security", %sValue);

 SetProperty
SetPropertySyntax
SetProperty(Name, Value)
Description
Use the SetProperty method to specify the value of the specified property.
Parameters
|
Name |
Specify the name of the property that you want to set. |
|
Value |
Specify the value of the property that you want to set. |
Returns
A boolean: true if the method completed successfully, false otherwise. If this method returns false, the Error parameter is populated with the text of the error message that occurred.
Example
Local PTXMLP_ENGINE:Properties &oProp; &oProp = create PTXMLP_ENGINE:Properties(); &bResult = &oProp.setProperty("pdf-security", "true");
 RTFProcessor Class
RTFProcessor Class
Use the RTFProcessor class to access the Oracle RTF processor API.
 RTFProcessor Class Methods
RTFProcessor Class MethodsThe following are the RTFProcessor methods, in alphabetical order.

 GenerateXSL
GenerateXSLSyntax
GenerateXSL(RTFTemplateFile, XSLOutputFile, Error)
Description
Use the GenerateXSL method to generate an XSL file from the specified RTF template.
Parameters
|
RTFTemplateFile |
Specify the full path name of an RTF template file, as a string. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
XSLOutputFile |
Specify the full path name of a file to contain the XSL output. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
Error |
If any errors occur during processing, this parameter is populated with the text of the error message after processing. |
Returns
A boolean: true if the method completed successfully, false otherwise. If this method returns false, the Error parameter is populated with the text of the error message that occurred.
Example
Local PTXMLP_ENGINE:RTFProcessor &oRTF; &oRTF = create PTXMLP_ENGINE:RTFProcessor(); &sErr = ""; &bResult = &oRTF.generateXSL(&sRTFFile, &sXSLFile, &sErr);
See Also

 GenerateXSLXliff
GenerateXSLXliffSyntax
GenerateXSLXliff(RTFTemplateName, XSLOutputFile, XliffOutputFile, Error)
Description
Use the GenerateXSLXliff method to generate the XSL file and the Xliff from the specified RTF template.
Parameters
|
RTFTemplateFile |
Specify the full path name of an RTF template file, as a string. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
XSLOutputFile |
Specify the full path name of a file to contain the XSL output. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
XliffOutputFile |
Specify the full path name of a file to contain the Xliff output. Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes. |
|
Error |
If any errors occur during processing, this parameter is populated with the text of the error message after processing. |
Returns
A boolean: true if the method completed successfully, false otherwise. If this method returns false, the Error parameter is populated with the text of the error message that occurred.
Example
Local PTXMLP_ENGINE:RTFProcessor &oRTF; &oRTF = create PTXMLP_ENGINE:RTFProcessor(); &sErr = ""; &bResult = &oRTF.generateXSLXliff(&sRTFFile, &sXSLFile, &sXliffFile, &sErr);
See Also
 RTFProcessor Class Properties
RTFProcessor Class PropertiesThe following are the RTFProcessor class properties, in alphabetical order.

 ConfFile
ConfFileDescription
Use the ConfFile property to specify a file that contains the configuration to be used for processing the document. This property enables you to accommodate different system configurations.
If you want to specify an already instantiated and populated Properties object that contains the configuration properties, use the ConfProp property instead.
This property is read-write.
See Also

 ConfProp
ConfPropDescription
Use the ConfProp property to specify an already instantiated and populated Properties object that contains the configuration to be used for processing the document. This property enables you to accommodate different system configurations.
If you want to specify a file that contains the configuration properties, use the ConfFile property instead.
See Also

 Locale
LocaleDescription
`
Use the Locale property to specify the locale for the processing. If no value is specified for this property, the default system locale will be used.
The locale is specified using a two character ISO language code and a two character ISO country code (LC-CC). When you don't need to reflect country specific formatting, the locale code is made up of just the language code.
This property is read-write.
 Watermark Class
Watermark Class
Use the watermark class to specify a watermark for a merged PDF file. Objects in this class are used with the PDFMerger class property Watermark.
You can generate a watermark either using text or an image. You can either use the text properties or the image properties. You cannot use both.
The following are the image watermark class properties:
ImageFile
ImageLowerLeftX
ImageLowerLeftY
ImageUpperRightX
ImageUpperRightY
The following are the text watermark class properties:
Text
TextAngle
TextFontName
TextFontSize
TextStartPosX
TextStartPosY
 Watermark Class Properties
Watermark Class PropertiesThe following are the properties for the Watermark class, in alphabetical order.

 ImageFile
ImageFileDescription
Use the ImageFile property to specify the full path name of an image file to be used for the watermark.
Forward or back slashes are used in the path according to the operating system of the application server or process scheduler server. That is, on Unix servers, the directory separator is a forward slash, while a Windows server returns a path with back slashes.
This property is read-write.

 ImageFileLowerLeftX
ImageFileLowerLeftXDescription
Use the ImageFileLowerLeftX property to specify the lower left, X-axis position for the watermark, as a number.
This property is read-write.

 ImageFileLowerLeftY
ImageFileLowerLeftYDescription
Use the ImageFileLowerLeftY property to specify the lower left, Y-axis position for the watermark, as a number.
This property is read-write.

 ImageFileUpperRightX
ImageFileUpperRightXDescription
Use the ImageFileUpperRightX property to specify the upper right, X-axis position for the watermark, as a number.
This property is read-write.

 ImageFileUpperRightY
ImageFileUpperRightYDescription
Use the ImageFileUpperRightY property to specify the upper right, Y-axis position for the watermark, as a number.
This property is read-write.

 PageIndex
PageIndexDescription
Use the PageIndex property to specify the page where the watermark begins. For example, you might not want a watermark to display on a cover page. The default value is 0, which sets the watermark on all pages (page index starts at 1.)
This property is read-write.

 Text
TextDescription
Use the Text property to specify the text for the watermark, as a string.
This property is read-write.

 TextAngle
TextAngleDescription
Use the TextAngle property to specify the angle of the watermark text across the page. You must specify a number between 1 and 360.
This property is read-write.

 TextFontName
TextFontNameDescription
Use the TextFontName property to specify the name of the font to be used for the text for the watermark.
This property is read-write.

 TextFontSize
TextFontSizeDescription
Use the TextFontSize property to specify the size of the text font. The default value is 8.
This property is read-write.

 TextStartPosX
TextStartPosXDescription
Use the TextStartPosX property to specify the starting position, X-axis location for the text to be used as the watermark.
This property is read-write.

 TextStartPosY
TextStartPosYDescription
Use the TextStartPosY property to specify the starting position, Y-axis location for the text to be used as the watermark.
This property is read-write.
 XML Publisher Classes Example
XML Publisher Classes ExampleThe following example lists a complete example of the code first, then goes through the program line by line.

 Generate and Publish a Report
Generate and Publish a ReportIn the following example, a report is created from an existing report definition. It is populated with an already instantiated and populated XmlDoc object, then published.
The following is the complete code sample: the steps explain each line.
import PSXP_RPTDEFNMANAGER:*; Local XMLDoc &xmlDoc; Local string &rptDefnId = "Financial"; Local string &LanguageCode = "ENG"; Local string &effdt = "2004-4-1"; Local string &outputfmt = "HTM"; Local String &reportPath = GetEnv("PS_SERVDIR") | "\files\reports"; Local String &folderName = "General"; Local string &serverName = "PSNT"; Local ReportDefn &rptDefn; &rptDefn = Create ReportDefn(&rptDefnId); &rptDefn.Get(); &rptDefn.SetRuntimeDataXMLDoc(&xmlDoc); &rptDefn.ProcessReport("", &languageCd, &effdt, &outputfmt); &rptDefn.Publish(&serverName, &reportPath, &folderName);
To generate and publish a report:
Import the appropriate application class.
Because this program generates and publishs a report, you need to import the report manager definition class.
import PSXP_RPTDEFNMANAGER:*;
Initialize variables.
The variable declaration strings not only specify values for the variables, but give them type and scope as well. This can be very useful when debugging.
Local XMLDoc &xmlDoc; Local string &rptDefnId = "Financial"; Local string &LanguageCode = %Language_User; Local string &effdt = "2004-4-1"; Local string &outputfmt = "HTM"; Local String &reportPath = GetEnv("PS_SERVDIR") | "\files\reports"; Local String &folderName = "General"; Local string &serverName = "PSNT"; Local ReportDefn &rptDefn;
Instantiate the report definition object and initialize it.
After you instantiate a report definition object, you must initialize it and populate it using the Get method.
&rptDefn = Create ReportDefn(&rptDefnId); &rptDefn.Get();
Specify the data for the report.
This report uses an XmlDoc for the data source, so you must specify the runtime data source for the report before you process it.
&rptDefn.SetRuntimeDataXMLDoc(&xmlDoc);
Process the report.
You must process the report, generate a version of it for the report repository, before you can distribute the report.
&rptDefn.ProcessReport("", &languageCd, &effdt, &outputfmt);
Publish the report.
After you've generated the report, you may want to publish it to another location.
&rptDefn.Publish(&serverName, &reportPath, &folderName);