 Understanding Messaging Server Administration
Understanding Messaging Server AdministrationThis chapter provides an overview of messaging server administration and discusses how to:
Create and assign dedicated servers.
Edit messaging server queue lists.
Delete messaging servers.
Configure messaging servers.
Set the BEA Tuxedo queue size.
 Understanding Messaging Server Administration
Understanding Messaging Server AdministrationThis section discusses messaging servers, messaging server processes, and dedicated messaging servers.

 Messaging Servers
Messaging ServersThe PeopleSoft messaging infrastructure is the core system upon which PeopleSoft Integration Broker is built. Before using Integration Broker for asynchronous message processing, you must configure and start the messaging server.
Note. The messaging servers and messaging server processes are used for asynchronous integrations only. If you are performing only synchronous integrations, you need not configure a messaging server.
Activating Messaging Server Domains
Pub/sub server domains are delivered inactive, and you must active them for the pub/sub system to become available.
You can activate pub/sub server domains using the Integration Broker Quick Configuration page or on the Domain Status page in the Service Operations Monitor.
See Also
Using the Integration Broker Quick Configuration Page
Managing Pub/Sub Server Domains

 Messaging Servers in the DB2 UDB OS/390 and z/OS Environments
Messaging Servers in the DB2 UDB OS/390 and z/OS EnvironmentsFor DB2 UDB OS/390 and z/OS environments, PeopleSoft delivers messaging servers with persistent cursors off. Therefore, all SQL statements are compiled each time they are invoked.
To change the persistent cursors setting:
In PSADMIN locate the Values for config section — Publish&Subscribe.
Set the Persistent Cursors on DB2/OS390 option. The values are:
0: Persistent cursors off.
1: Persistent cursors on.

 Messaging Server Processes
Messaging Server ProcessesAlthough the server processes devoted to the messaging system are all part of the larger application server domain, they comprise a distinct set of processes that aren’t involved with the ordinary transactions associated with PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture connections.
Six processes of two types—dispatchers and handlers—are paired to produce the messaging servers that transmit asynchronous messages throughout the messaging system. A set of three messaging servers—a publication broker, a publication contractor, and a subscription contractor—is required by PeopleSoft Integration Broker. The following table lists the generic names for the processes:
|
Messaging Server |
Dispatcher Name |
Handler Name |
|
PSBRKDSP |
PSBRKHND |
|
|
PSPUBDSP |
PSPUBHND |
|
|
PSSUBDSP |
PSSUBHND |
To distinguish the messaging servers, the PeopleSoft Server Administration utility (PSADMIN) includes a separate menu for administering them—the Messaging Server Administration menu. You select this menu from the PeopleSoft Domain Administration menu, as shown in the following example:
PeopleSoft Domain Administration menu
From this menu, you can create new messaging servers, edit the queue list for existing messaging servers, and delete messaging servers that are no longer needed.
Note. Although you add new messaging servers using a separate menu, you configure the messaging server processes with PSADMIN as you would any other server process.
See Also

 Understanding Dedicated Messaging Servers
Understanding Dedicated Messaging ServersWhen you create a new application server domain, PSADMIN offers a set of messaging server processes that comprise the default messaging server set for that domain. The default messaging server set is sufficient for development, testing, or demonstrations.
You might use the default messaging server set as the only messaging server set; however, in most cases, it is insufficient. As the volume of published messages increases in a production system, it’s likely that a single messaging server set will become overloaded. To avoid potential overloads and performance degradation, create additional dedicated messaging servers to cope with an increase in message volume.
Note. Dedicated messaging servers are used only for asynchronous messaging.
When you create a new messaging server, you assign it to a particular queue using PSADMIN. If a given queue is the most active and creates performance bottlenecks, you can dedicate several messaging servers to that queue to cope with the message volume. A messaging server is capable of handling multiple message queues.
The following illustration depicts a dedicated messaging server set assigned to QUEUE_03:
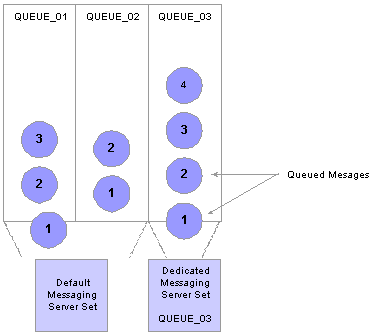
Dedicated messaging server set
In this scenario, the default messaging server set (_dflt process collection) continues to process the messages in the other message queues while the dedicated messaging server set processes only the messages within a specified queue. Unless you create and configure dedicated messaging servers, the default messaging server set handles all incoming messages. Remember that a messaging server set is a collection of six messaging server processes.
Note. Before you can assign messaging servers to message queues, you must first define the message queues using PeopleSoft Application Designer.
The process for adding a dedicated messaging server includes two parts:
Creating the new messaging server.
Use the Messaging Server Administration menu in PSADMIN. This is where you specify the type of server you’re adding, name the server, and assign it to specific message queues.
Configuring the new messaging server.
When you add a new messaging server of any type, the configuration files are updated to include parameters for the new server processes. Because a messaging server consists of two server processes, when you create a new one, you’ll see two additional configuration sections in the PSADMIN domain configuration menu. They appear identical to the _dflt messaging server processes, except they have the name that you gave them in place of the _dflt. For any new messaging server processes to take effect, you must first reconfigure the domain to include the new parameters.
Note. Typically, you add multiple messaging elements simultaneously, so you should create all the elements and then reconfigure the domain once.
 Considerations When Creating Dedicated Servers
Considerations When Creating Dedicated ServersWhen creating dedicated messaging servers, consider the following points:
There is no validation checking when you enter service operation queue names in PSADMIN. As a result, if service operation queue names are not spelled correctly and match those defined in the system, the dedicated server will not process any service operation. Instead the default server will process them.
Never split a service operation queue across domains. You don't want a situation where a service operation queue is assigned to domain A and the same service operation queue is also assigned to domain B, since both domains will try to do the same work. You want specific service operation queues for domain A and specific service operation queues for domain B.
Setting up a dedicated server consists of a creating a dedicated dispatcher and handler(s). Make sure that the number of handlers booted is sufficient to process the request volume.
If you create more than one dedicated server over different domains do not to include any service operation queues already specified for other dedicated servers of the same server type. For example, do not include service operation queue A in publication broker server X, as well as in publication broker server Y.
Verify that the BEA tuxedo queue size is large enough and correctly configured in PSADMIN.
If you choose to set up group domain failover for dedicated servers, ensure that:
Service operation queue sets within groups are identical.
Service operation queue sets between groups are unique.
When you create a messaging server, the following dispatcher parameters are populated with their default values. Verify those default settings you want to keep and those that you want to change.
Restart period.
Scan interval.
Dispatcher queue maximum queue size.
Memory queue refresh rate.
 Creating and Assigning Dedicated Servers
Creating and Assigning Dedicated ServersTypically, you create one server of each type to produce a complete messaging server set dedicated to one or more service operation queues.
Note. Although a messaging server set consists of one of each of the three server types, they do not all need to be dedicated servers. For example, for a given service operation queue, you can create only a dedicated publication contractor. If you haven’t assigned a dedicated publication broker or a dedicated subscription contractor to the service operation queue, the default publication broker and subscription contractor is used.
The following example shows the Message Server Administration menu:
To create a dedicated messaging server:
From the PeopleSoft Domain Administration menu, select the Messaging Server Administration menu.
From the Messaging Server Administration menu, select the Create a new messaging server.
From the submenu that appears, select the type of server to create.
You can create a publication broker, a publication contractor, or a subscription contractor.
Enter a name to identify the new messaging server.
The name is limited to six characters; for example, PT8MSG. The name that you enter is appended to each generic server process name; for example, PSBRKDSP_PT8MSG for the broker dispatcher and PSBRKHND_PT8MSG for the broker handler.
Note. The name that you enter must be unique for the messaging server type in the current domain.
Specify the service operation queue that is handled by the new messaging server.
You must specify a service operation queue, which must already be defined in the PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture.
Note. The service operation queue name that you enter must exactly match the name that appears in the PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture. No prompt or validation occurs between PSADMIN and PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture definitions.
Important! Don’t specify a given service operation queue for more than one messaging server of each type in the current domain. For example, you cannot have two subscription contractors assigned to the service operation queue. Nor can you have two dispatchers assigned to the service operation queue.
After several status messages, the Messaging Server Administration menu reappears, displaying a list of the existing dedicated messaging servers for the current domain.
 Editing Messaging Server Queue Lists
Editing Messaging Server Queue ListsAfter you create a publication broker, publication contractor, or subscription contractor, you may need to add more service operation queues to the server’s queue list, or you may want to decrease the number of service operation queues it services to improve performance. You use the commands shown in the following example:
To modify a queue list:
From the PeopleSoft Domain Administration menu, select Messaging Server Administration menu.
From the Messaging Server Administration menu, select Edit the queue list for a messaging server.
From the list of defined servers, select the messaging server for which you want to modify the queue list.
Specify a list of the message queues that will be handled by the selected server.
You must specify at least one message queue. Multiple queue names must be entered as a list separated by commas, with no spaces; for example, HRMS_01,HRMS_02,CRM_03.
Note. The new list of message queues that you enter replaces the current list of queues for the selected messaging server. The queues that you specify must already be defined in the PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture.
After several status messages, the Messaging Server Administration menu reappears, displaying the updated messaging server listing.
 Deleting Messaging Servers
Deleting Messaging ServersSometimes a previously created messaging server is no longer needed. Rather than allow the server to consume valuable system resources, you should remove it from the domain.
To delete a messaging server from a domain:
From the PeopleSoft Domain Administration menu, select Messaging Server Administration menu.
From the Messaging Server Administration menu, select Delete an existing messaging server.
From the list of defined servers, select the messaging server to delete.
After several status messages, the Messaging Server Administration menu reappears, displaying the remaining dedicated servers.
 Configuring Messaging Servers
Configuring Messaging ServersOnce you create dedicated messaging servers, you must configure their dispatcher and handler processes so that they boot when you start the application server. You configure these processes using PSADMIN, as you do other server processes that run on the application server. Before you configure additional messaging server processes, familiarize yourself with the other server processes that run on the application server.
See Using PSADMIN Menus.
Two types of server processes comprise each messaging server: a dispatcher and a handler. Each process type requires that you set a different set of parameters. Most of the parameters are similar to other server processes, such as PSAPPSRV, but some parameters are specific to messaging servers.
Note. The following sections also apply to the _dflt messaging server processes. Only one parameter is different for a dedicated messaging server process and its _dflt counterpart—the Queues parameter. That parameter enables you to add message queues to the queue list. The _dflt server processes cannot be associated with a specific message queue.

 Specifying Dispatcher Parameters
Specifying Dispatcher ParametersThere are three generic process types that are the basis for all dispatcher processes:
PSBRKDSP, which is the publication broker dispatcher.
PSPUBDSP, which is the publication contractor dispatcher.
PSSUBDSP, which is the subscription contractor dispatcher.
The following parameters apply to all three process types.

 Specifying Handler Parameters
Specifying Handler ParametersThere are three generic process types that are the basis for all handler processes:
PSBRKHND, which is the publication broker handler.
PSPUBHND, which is the publication contractor handler.
PSSUBHND, which is the subscription contractor handler.
The following parameters apply to all three process types.
 Setting the BEA Tuxedo Queue Size
Setting the BEA Tuxedo Queue SizeThe messaging system uses the Tuxedo queue size indicated in the application server domain section of PSADMIN to determine when the Tuxedo queue size has reached its maximum. The pub/sub system reads the actual queue size periodically, based on the Tuxedo Queue Status Check Count parameter. The system throttles itself so that it does not exceed this maximum, thereby preventing queue saturation and degraded performance.
Set the Tuxedo Queue Size parameter equal to that of the kernel parameter used by the machine running the pub/sub processes (msgsys:msgingo_msgmax).
To set the Tuxedo queue size for the messaging system:
In PSADMIN navigate to the Values for config section – PSAPPSRV part of the file. To do so:
Open PSADMIN.
Enter 1 for Application Server and press Enter.
Enter 1 for Administer a Domain and press Enter.
Choose a domain from the list and press Enter.
Choose 4 for Configure the Domain and press Enter.
Enter Y to shut down the domain.
Enter Y to change the configuration values.
Press Enter to scroll through the file and accept the current settings until you reach the following section:
Values for config section - PSAPPSRV
Enter Y and press Enter to change values in the section.
Navigate to the Tuxedeo Queue Size parameter. To do so, press Enter to scroll through the list and accept the current values. When you reach the Tuxedo Queue Size parameter enter a value.
A value of 0 (zero) disables Tuxedo queue threshold determination and usage.
Based on your environment, a value of -1 sets the queue size to the following default values:
Windows: 65535.
AIX: 4000000.
Solaris: 65535.
HP: 65535.
Press Enter to scroll through the remaining sections and accept the current settings.
PSADMIN will process the changes and then load the new configuration.
Boot the domain.
See Using the PSADMIN Utility, Using PSADMIN Menus.