
 Web Applications in PIA
Web Applications in PIAIn the current release, the PIA configuration of BEA WebLogic Server has been expanded to take advantage of WebLogic’s managed server architecture. This appendix provides overviews of web applications in PIA, WebLogic domain types, WebLogic domain directory structure and files, and PIA install and reinstall options, and discusses:
Administering a WebLogic server life cycle.
Tuning performance and monitoring resources.
Changing configuration settings.
Applying an example single-server configuration.
Applying an example multi-server configuration.
See Also

 Web Applications in PIA
Web Applications in PIAPIA is packaged as a J2EE Enterprise Archive and is comprised of five J2EE web applications, commonly referred to as webapps. The five webapps are as follows.
|
PORTAL |
PeopleSoft Portal |
|
PSIGW |
PeopleSoft Integration Broker |
|
PSOL |
PeopleSoft On-line Library |
|
PSEMHUB |
PeopleSoft Environment Management Framework |
|
PSINTERLINKS |
PeopleSoft Business Interlinks |
In addition to the PeopleSoft webapps, three more webapps are added when you install PIA on a WebLogic server machine. These three webapps are not added as part of the PeopleSoft Enterprise Archive, but instead are defined as individual webapps provided by BEA. These three webapps are as follows.
|
Reverse Proxy Server – Proxy to a single content server per URL. Each URL can provide unique content. |
|
|
Reverse Proxy Server – Proxy to multiple WebLogic servers. All content servers provide access to the same content for load balancing. |
|
|
BEA’s administrative console for WebLogic Server. |

 WebLogic Domain Types
WebLogic Domain TypesThis section provides an overview of Weblogic domain types and discusses:
Single-server domain.
Multi-server domain.
Distributed managed server.
Common default settings.
Single-server and multi-server/distributed server analogy.
Domain topology.

 Understanding WebLogic Domain Types
Understanding WebLogic Domain Types
During PIA setup, you can choose between two different WebLogic domain configurations: a single-server domain and a multi-server domain. In addition, a multi-server domain can be expanded across multiple machines using the distributed managed server option. Each of these domain configurations has a specific purpose but is fully customizable beyond that purpose.

 Single-Server Domain
Single-Server DomainThe single-server domain configuration consists of a single WebLogic server instance, with the WebLogic administration application and all of the web components of PeopleSoft Internet Architecture deployed to use it. This configuration is very similar in design to the WebLogic domain provided in previous PeopleTools releases.
This configuration is intended for single-user or very small scale, non-critical production environments. It can be used as a starting point for you to familiarize yourself with BEA WebLogic Server 8.1
In this configuration, the resources used to administer WebLogic Server and your PeopleSoft application are not isolated from one another, therefore leaving the applications vulnerable to possible resource starvation. The low resource requirements of this configuration make it ideal for small scale and non-production usage.
This configuration creates the following server:
|
PIA |
A server for WebLogic domain administration with PeopleSoft J2EE applications deployed. |
Single-Server Webapp Deployment
Some of the webapps deployed in a single-server domain configuration must be accessed using a modified URL:
http://server:port/webapp_name/...
The single-server domain configuration deploys webapps as follows:
|
Application |
Deployed to Server |
Webapp Name in URL |
|
PORTAL |
PIA |
(not needed) |
|
PSIGW |
PIA |
PSIGW |
|
PSOL |
PIA |
PSOL |
|
PSEMHUB |
PIA |
PSEMHUB |
|
PSINTERLINKS |
PIA |
PSINTERLINKS |
|
Console |
PIA |
console |
|
HttpProxyServlet |
Defined but not deployed. |
(not needed) |
|
HttpClusterServlet |
Defined but not deployed. |
(not needed) |
Single-Server Domain Specific Settings
To configure the single-server domain specific settings, launch the WebLogic Server Console.
In the console, navigate to Servers, PIA, Configuration, General to configure the PIA server. The default web application for the PIA server is PORTAL. The single-server domain specific default settings for the PIA server are as follows:
|
Setting |
Default Value |
|
IP address. |
* (all local IPs). |
|
HTTP Listen port. |
80 (set during PIA setup). |
|
SSL. |
Enabled with demonstration self-signed digital certificates. |
|
HTTPS Listen port. |
443 (set during PIA setup). |
Note. To configure SSL, you must also define SSL certificates.
See Implementing WebLogic SSL Keys and Certificates.

 Multi-Server Domain
Multi-Server DomainThe multi-server domain configuration consists of seven server definitions, a WebLogic cluster, and the web components of PIA split across multiple servers. This configuration takes advantage of WebLogic’s administration server and managed server architecture.
This configuration is intended for production environments.
A production application warrants process and resource pool isolation for greater stability and optionally tighter security controls, which this configuration provides. In this configuration, the resources used for WebLogic domain administration and monitoring are isolated from similar resources used to support the PIA application. A server process named WebLogicAdmin performs nothing but WebLogic administration, which includes domain administration and monitoring. Continuing that separation, the individual web applications of PIA might be, and usually are, isolated from each other. The PIA applications are targeted and deployed across a portion of the six remaining server definitions, all of which are classified as managed servers, which are delivered in the multi-server configuration.
This configuration creates the following servers:
|
WebLogicAdmin |
Administration server for WebLogic domain administration. |
|
PIA |
Server for the PeopleSoft Portal, integration gateway, and PeopleSoft Business Interlinks applications. |
|
PIA1 |
Server for the PeopleSoft Portal, integration gateway, and PeopleSoft Business Interlinks applications. |
|
PIA2 |
Server for the PeopleSoft Portal, integration gateway, and PeopleSoft Business Interlinks applications. |
|
PSOL |
Server for the PeopleSoft Online Library (PeopleBooks) application. |
|
PSEMHUB |
Server for the PeopleSoft Environment Management Framework application. |
|
RPS |
Server for WebLogic reverse proxy server applications. |
The multi-server domain configuration deploys webapps as follows:
Multi-Server Webapp Deployment
Some of the webapps deployed in a multi-server domain configuration must be accessed using a modified URL:
http://server:port/webapp_name/...
The multi-server domain configuration deploys webapps as follows:
|
Application |
Deployed to Server, Cluster (members) |
Webapp Name in URL |
|
PORTAL |
PIA, PeopleSoftCluster (PIA1, PIA2) |
(not needed) |
|
PSIGW |
PIA, PeopleSoftCluster (PIA1, PIA2) |
PSIGW |
|
PSOL |
PSOL |
PSOL |
|
PSEMHUB |
PSEMHUB |
PSEMHUB |
|
PSINTERLINKS |
PIA, PeopleSoftCluster (PIA1, PIA2) |
PSINTERLINKS |
|
Console |
WebLogicAdmin |
console |
|
HttpProxyServlet |
RPS |
(not needed) |
|
HttpClusterServlet |
Defined but not deployed. |
(not needed) |
Multi-Server Domain Specific Default Settings
To configure the multi-server domain specific settings, launch the WebLogic Server Console.
In the console, navigate to Servers, WebLogicAdmin, Configuration, General to configure the WebLogicAdmin server. The WebLogicAdmin server has no default web application. The domain specific default settings for the WebLogicAdmin server are as follows:
|
WebLogicAdmin Setting |
Default Value |
|
IP address |
* (all local IPs) |
|
HTTP Listen port |
9999 |
|
SSL |
Disabled |
In the console, navigate to Servers, PIA, Configuration, General to configure the PIA server. The default web application for the PIA server is PORTAL. The domain specific default settings for the PIA server are as follows:
|
PIA Setting |
Default Value |
|
IP address |
* (all local IPs) |
|
HTTP Listen port |
80 (set during PIA setup) |
|
SSL |
Enabled with demonstration self-signed digital certificates. |
|
HTTPS Listen port |
443 (set during PIA setup) |
In the console, navigate to Servers, PIA1, Configuration, General to configure the PIA1 server. The default web application for the PIA1 server is PORTAL. The domain specific default settings for the PIA1 server are as follows:
|
PIA1 Setting |
Default Value |
|
IP address |
Locally determined hostname. |
|
HTTP Listen port |
80 (set during PIA setup) |
|
SSL |
Enabled with demonstration self-signed digital certificates. |
|
HTTPS Listen port |
443 (set during PIA setup) |
In the console, navigate to Servers, PIA2, Configuration, General to configure the PIA2 server. The default web application for the PIA2 server is PORTAL. The domain specific default settings for the PIA2 server are as follows:
|
PIA2 Setting |
Default Value |
|
IP address |
127.0.0.1 |
|
HTTP Listen port |
80 (set during PIA setup) |
|
SSL |
Enabled with demonstration self-signed digital certificates. |
|
HTTPS Listen port |
443 (set during PIA setup) |
In the console, navigate to Servers, PSOL, Configuration, General to configure the PSOL server. The default web application for the PSOL server is PSOL. The domain specific default settings for the PSOL server are as follows:
|
PSOL Setting |
Default Value |
|
IP address |
* (all local IPs) |
|
HTTP Listen port |
6001 |
|
SSL |
Disabled |
In the console, navigate to Servers, PSEMHUB, Configuration, General to configure the PSEMHUB server. The default web application for the PSEMHUB server is PSEMHUB. The domain specific default settings for the PSEMHUB server are as follows:
|
PSEMHUB Setting |
Default Value |
|
IP address |
* (all local IPs) |
|
HTTP Listen port |
8001 |
|
SSL |
Disabled |
In the console, navigate to Servers, RPS, Configuration, General to configure the RPS server. The default web application for the RPS server is HttpProxyServlet. The domain specific default settings for the RPS server are as follows:
|
RPS Setting |
Default Value |
|
IP address |
* (all local IPs) |
|
HTTP Listen port |
8080 (set during PIA setup) |
|
SSL |
Enabled with demonstration self-signed digital certificates. |
|
HTTPS Listen port |
8443 (set during PIA setup) |
Note. To configure SSL, you must also define SSL certificates.
See Implementing WebLogic SSL Keys and Certificates.

 Distributed Managed Server
Distributed Managed ServerThe distributed managed server configuration, although listed alongside the single-server and multi-server domain types, is not a true domain type. It's an optional extension for an existing multi-server configuration that's used to extend a WebLogic domain configuration across multiple machines in a heterogeneous network. For example, on one machine you perform a PIA install and create a multi-server domain. On a second machine you again perform a PIA install but select to create a distributed managed server. You stop, start, and administer the distributed managed server on the second machine just as if it was a managed server local to the primary server’s machine.
As with the multi-server domain type, this configuration takes advantage of WebLogic’s managed server architecture.
Note. Only one managed server can be run per distributed managed server domain directory. If you intend to run multiple distributed managed servers on a single machine, perform the PIA install and create unique distributed managed server domain directories, one for each distributed managed server that you intend to run on that machine.
This configuration is intended for production environments that encompass multiple machines.
A distributed managed server configuration provides the same benefits as a multi-server configuration with the added benefit of hardware isolation. This option requires a multi-server installation to be performed to some other location, which will contain the configuration for this distributed managed server.
Distributed Managed Server Specific Defaults
The server configuration settings for a distributed managed server are maintained via that domain’s administration server and are stored locally on that administration server. Configuration settings are replicated to a managed server during its startup, but are only maintained as a read-only backup copy for that individual managed server in the event that the administration server isn't available the next time this particular managed server needs to be started.

 Common Default Settings
Common Default SettingsSingle-server and multi-server domain configurations have many settings in common.
Domain Defaults
Many of these common settings can be configured in the WebLogic Server Console, but some are configured in other environments. Default values are listed when available.
|
Setting |
Default Value |
Where To Configure |
|
SSL functionality |
Enabled with demonstration self-signed digital certificates. |
Console: Servers, server name, Configuration, Keystores & SSL. Command line: pskeymanager. |
|
Server logs |
Weblogic domain\logs\server name_*.log |
Console: Servers, server name, Logging, Server. |
|
HTTP access log |
Disabled |
Console: Servers, server name, Logging, HTTP. |
|
HTTP keep-Alive |
30 seconds |
Console: Servers, server name, Protocols, HTTP. |
|
HTTPS keep-Alive |
60 seconds |
Console: Servers, server name, Protocols, HTTP. |
|
Low JVM memory monitoring |
On |
Console: Servers, server name, Configuration, Tuning. |
|
Stuck thread seconds interval |
600 |
Console: Servers, server name, Configuration, Tuning. |
|
Domain administration port |
Disabled |
Console: Servers, server name, Configuration, General. |
|
PORTAL webapp HTTP session monitoring |
On (applies only to servers running PORTAL) |
Console: Deployments, Applications, peoplesoft, PORTAL, Monitoring. |
|
System administrator user ID |
system (set during PIA setup) |
Console: Security, Realms, myrealm, Users. |
|
System administrator password |
password (set during PIA setup) |
Console: Security, Realms, myrealm, Users. |
|
System operator user ID |
operator |
Console: Security, Realms, myrealm, Users. |
|
System operator password |
password |
Console: Security, Realms, myrealm, Users. |
|
System monitor user ID |
monitor |
Console: Security, Realms, myrealm, Users. |
|
System monitor password |
password |
Console: Security, Realms, myrealm, Users. |
Script and Environment Defaults
Modify these settings by editing a setEnv script or applying command line parameter overrides to WebLogic control scripts.
The following settings specify the names and structure of various directories on the web server machine.
|
Setting |
Default Value |
Description/Override |
|
PS_HOME |
(none) |
PeopleSoft home directory (set during PIA setup). |
|
BEA_HOME |
(none) |
BEA home directory (set during PIA setup). |
|
WL_HOME |
(none) |
WebLogic 8.1 home directory (set during PIA setup). |
|
DOMAIN_NAME |
peoplesoft |
Name of this WebLogic domain (set during PIA setup). |
|
JAVA_HOME |
(Depends on the OS platform.) |
Location of Java. Set during PIA setup or with a call to WebLogic's CommEnv script. |
Note. You configure Java VM options including JVM memory size using the JAVA_OPTIONS_OSplatform parameter, during PIA setup.
The following are miscellaneous settings.
|
Setting |
Default Value |
Description/Override |
|
HOSTNAME |
Local hostname |
Set during PIA setup. |
|
PRODUCTION_MODE |
TRUE |
Enable WebLogic production mode (set during PIA setup). |
|
DISCOVERY_MODE |
FALSE |
Disable auto detection of unregistered applications. Script: setEnv |
|
WLS_USER |
Operator |
Use to stop WebLogic with stop scripts and run it as a Windows NT service. |
|
WLS_PW |
Password |
Use to stop WebLogic with stop scripts and run it as a Windows NT service. |
|
ADMINSERVER_PROTOCOL |
HTTP |
Protocol used for managed server to connect to administration server (not used in single-server domain). |
|
ADMINSERVER_HOSTNAME |
Single-server: local hostname. Multi-server: local hostname. Distributed server: (none — set manually). |
Administration server’s hostname that managed servers attempt to connect to by default when started. Set during PIA setup (except distributed server). |
|
ADMINSERVER_PORT |
Single-server: HTTP port of PIA server. Multi-server: 9999. Distributed server: (none — set manually). |
Administration server’s Listen port that managed servers attempt to connect to by default when started. Set during PIA setup (except distributed server). |
|
ADMINSERVER_SERVERNAME |
Single-server: PIA. Multi-server: WebLogicAdmin. Distributed server: WebLogicAdmin. |
WebLogic server instance name of this domain's administration server, used for stopping and starting the server. |
|
WL_VERSION |
Detected major WebLogic version. |
|
|
WL_SERVICEPACK |
Detected minor WebLogic version. |
|
|
WL_PATCH |
Detected WebLogic patch version. |
|
|
BACKGROUND_PROCESS |
TRUE |
Run WebLogic server as a background process. On UNIX you can force foreground execution using the start script’s –foreground option. |
The following are debugging output settings.
|
Setting |
Default Value |
Description/Override |
|
SET CAPTURE_STDOUT_STDERR |
FALSE |
(Windows only) Capture standard output and standard error of a WebLogic server running as a foreground process. You can also set this with the start script’s –capture option. |
|
ENABLE_JDPA_DEBUG |
FALSE |
(PeopleSoft development only) Enable JDPA debug support. You can also set this with the start script’s –debug option. |
|
ENABLE_VERBOSE_GC |
FALSE |
Enable verbose output of Java’s garbage collector. You can also set this with the start script’s –verbose:gc option. |
|
ENABLE_VERBOSE_SSL |
FALSE |
Enable SSL debug support. Produces verbose SSL output. You can also set this with the start script’s –verbose:ssl option. |
|
ENABLE_VERBOSE_WL |
FALSE |
Enable verbose output for the core WebLogic server (not verbose output of PIA). You can also set this with the start script’s –verbose:wl option. |
The following are HTTP forward proxy support settings.
|
Setting |
Default Value |
Description/Override |
|
ENABLE_HTTP_PROXY |
FALSE |
Enable the use of the forward http proxy. |
|
HTTP_PROXY_HTTPHOST |
(none) |
IP address or hostname of the forward HTTP proxy server for HTTP requests. |
|
HTTP_PROXY_HTTPPORT |
(none) |
HTTP Port number of the forward HTTP proxy server for HTTP requests. |
|
HTTP_PROXY_HTTPSHOST |
(none) |
IP address or hostname of the forward HTTP proxy server for HTTPS requests. |
|
HTTP_PROXY_HTTPSPORT |
(none) |
HTTP Port number of the forward HTTP proxy server for HTTPS requests. |
|
HTTP_PROXY_NONPROXY_HOSTS |
localhost, local hostname, and domainname. |
Host names and domain names of content servers that will not be proxied. |

 Single-Server and Multi-Server/Distributed Server Analogy
Single-Server and Multi-Server/Distributed Server AnalogyIn a production environment it is highly recommended to use a multi-server or distributed server configuration. The multi-server selection provides an initial WebLogic domain configuration that consists of multiple server definitions: one administration server and multiple managed servers, each with a specific purpose. The distributed server option augments a multi-server configuration by expanding the domain configuration across multiple machines.
An analogy that can describe the differences between the single-server configuration and a multi-server or distributed server configuration uses the example of two common beverage distribution models: a single lemonade stand, and a large chain of coffee shops.
Single-Server Model — The Lemonade Stand
With a lemonade stand you have yourself, one table, one collection of resources and ingredients, and a single recipe. If any of these are ruined, your lemonade stand is out of business. Similarly, in a single-server configuration you have one server process, one machine, one collection of resources and program files, and a single domain configuration file. If any of those is ruined, your web server is out of business. Throughput can also be an issue for both a lemonade stand and a single-server configuration. For example, if the weather is warm and you receive a rush of thirsty customers, your throughput will reach a maximum at either the rate you accept new orders, ring up cashier transactions, or prepare drinks. If you accept orders and ring up transactions in half the time that you prepare drinks, adding a second bartender would double your throughput, but in this configuration you can't do that because it's only you. Likewise, the single-server configuration is constrained to provide server configuration and all web server based portions of PIA on a single process. The multi-server model enables you to overcome these limitations.
Multi-Server Model — The Coffee Shop Chain
Within the same analogy, a large chain of coffee shops has multiple employees, multiple cashier stations, multiple coffee prep stations, and recipes archived and known to multiple employees. Similarly, in a multi-server configuration you can have multiple machines, multiple collections of resources and program files, multiple web server processes, and a replicated domain configuration file. In this model, if any of those resources is ruined, work simply shifts to the next instance of that resource. In addition, throughput can be maintained. For example, if the coffee house received a rush of parched customers, additional cashiers and beverage engineers could be added to maintain throughput. Likewise, in the multi-server configuration, an increase in PeopleSoft Portal usage can easily be accommodated by configuring an additional WebLogic server instance to also serve the PeopleSoft Portal application. In this way, the multi-server model supports extendibility and resource independence.
The fundamental benefits of a multi-server configuration are:
Dedicated service providers.
Web servers can be dedicated to providing PeopleSoft Portal and are insolated from other portions of PIA such as PeopleSoft Integration Gateway or PeopleBooks.
Redundant service providers.
Multiple web servers can be used to serve different aspects of PIA, providing load balancing and failover support.
Distributed resources.
Multiple web server machines can be used, each capable of serving different or redundant aspects of PIA.
Centralized and replicated configuration.
Master domain configuration is centralized and distributed server information is replicated locally.

 Domain Topology
Domain TopologyA WebLogic domain can be as small and simple as the Single-server configuration or as broad and complex as the Multi-server configuration with distributed managed servers. In no way exhausting the possibilities, following are three sample layouts depicting each domain configuration.
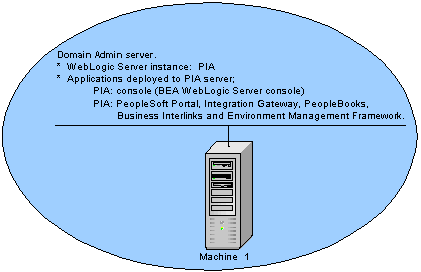
Single server — one machine
In a single-server configuration, the WebLogic domain’s administration console and the J2EE components of PIA are all provided on a single instance of WebLogic Server.
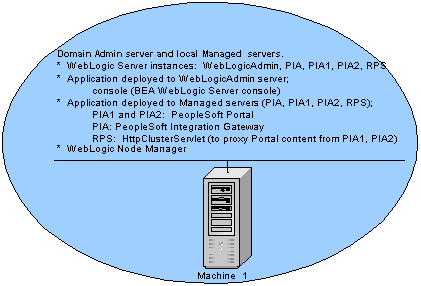
Multi-server — one machine
In a multi-server configuration, multiple instances of WebLogic server are used, each contributing a specific function. The WebLogic console is provided on the domain’s administration server, WebLogicAdmin, and the J2EE components of PIA are provided on individual or shared WebLogic managed servers.
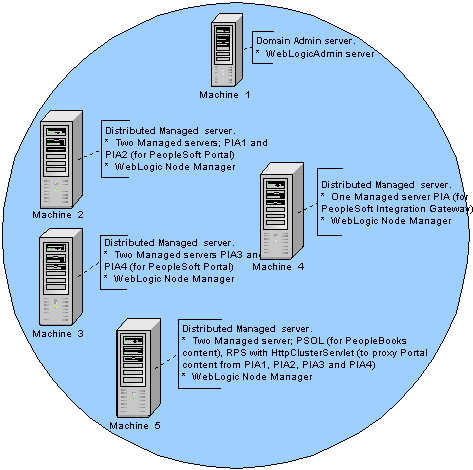
Multi-server with distributed managed servers — multiple machines
In a Multi-server configuration with distributed managed servers, multiple instances of WebLogic server are used, each providing a specific function. The WebLogic console is provided on the domain’s administration server, WebLogicAdmin, and the J2EE components of PIA are provided on individual or shared WebLogic managed servers. The only differentiating factor from the initial Multi serve configuration is that in this configuration two or more actual machines are used.

 WebLogic Domain Directory Structure and Files
WebLogic Domain Directory Structure and FilesThis section discusses:
WebLogic domain directory structure.
WebLogic domain file listing by type.
J2EE application files.

 WebLogic Domain Directory Structure
WebLogic Domain Directory Structure
File and directory layout of PIA on WebLogic 8.1 does differ from that on prior versions of WebLogic. At a high level, the first difference is that the WebLogic domains are installed within your PS_HOME directory structure, rather than into WebLogic’s directory structure as with prior versions of WebLogic Server.
The default home directories for PIA on different versions of WebLogic are as follows:
|
WebLogic Version |
PIA Home Directory |
|
WebLogic 5.1 |
weblogic_home\myserver\ |
|
WebLogic 6.1 |
bea_home\wlserver6.1\config\peopelsoft\ |
|
WebLogic 8.1 |
ps_home\webserv\peoplesoft\ |
This change was performed because managing the WebLogic configuration and PIA configuration similarly to the PeopleSoft application server and PeopleSoft Process Scheduler provided a clearer and more extendable architecture.
File and directory layout of PIA on WebLogic 8.1 differs from that of prior versions of PIA. The following illustration clarifies the directory structure layout of a PIA install on WebLogic Server 8.1.
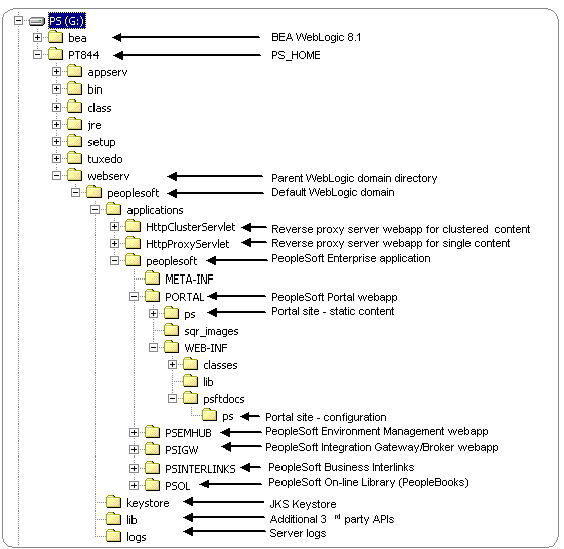
WebLogic domain directory structure

 WebLogic Domain File Listing by Type
WebLogic Domain File Listing by Type
Following are listings of all WebLogic domain files installed by the PIA setup, organized by file type. Where necessary, each table includes columns that indicate whether a given file is used in a single-server, multi-server, or distributed server configuration.
This listing does not include java classes or PIA configuration files. On UNIX an equivalent Bourne shell script is provided where a Windows script is listed.
The following table lists WebLogic server administration scripts.
|
Script |
Single-Server |
Multi-Server |
Distributed Server |
Description |
|
setEnv.cmd |
X |
X |
X |
Use this script to set required environment variables for the WebLogic server, for example: CLASSPATH, PATH, UNIX Library Path, and JVM options. |
|
startPIA.cmd |
X |
Use this script to start the WebLogic domain’s administration server (the PIA server) in a single-server configuration. On Windows this starts WebLogic as a foreground process. On UNIX this starts WebLogic as a background process. Run the script with –help for usage. |
||
|
startWebLogicAdmin. cmd |
X |
Use this script to start the WebLogic domain’s administration server (the WebLogicAdmin server) in a multi-server configuration. On Windows this starts WebLogic as a foreground process. On UNIX this starts WebLogic as a background process. Run the script with –help for usage. |
||
|
startManagedWebLogic.cmd |
X |
X |
Use this script to start a WebLogic managed server. All WebLogic servers in a WebLogic domain other than the administration server are WebLogic managed servers. Run the script with –help for usage. |
|
|
stopPIA.cmd |
X |
Use this script to stop the WebLogic PIA server. Run the script with –help for usage. |
||
|
stopWebLogic.cmd |
X |
X |
Use this script to stop WebLogic servers. Run the script with –help for usage. |
|
|
InstallNTservicePIA.cmd |
X |
(Windows only) Use this script to install the WebLogic PIA server as a Windows service. The service name is WebLogic_domain-PIA. Run the script with –help for usage. |
||
|
InstallNTservice.cmd |
X |
X |
(Windows only) Use this script to install a WebLogic server as a Windows service. The service name is WebLogic_domain-server_name. Run the script with –help for usage. |
|
|
uninstallNTServicePIA.cmd |
X |
(Windows only) Use this script to uninstall the WebLogic PIA server Windows service. Run the script with –help for usage. |
||
|
uninstallNTService.cmd |
X |
X |
(Windows only)Use this script to uninstall a WebLogic server Windows service. Run the script with –help for usage. |
|
|
pskeymanager.cmd |
X |
X |
X |
Use this script to manage the JKS keystore used by WebLogic Server, which is in WebLogic_domain\keystore\pskey. SSL certificates for WebLogic Server are stored in this keystore. PeopleSoft Integration Gateway can also share this keystore. Run the script with –help for usage. |
|
startWebLogicBuilder.cmd |
X |
X |
X |
Use this script to start WebLogic Builder, which is used to change local application deployment descriptors. |
|
createThreadDump.cmd |
X |
X |
X |
Use this script to create a JVM Thread dump. Run the script with –help for usage. |
The following table lists WebLogic server configuration files.
|
File |
Single-Server |
Multi-Server |
Distributed Server |
Description |
|
config.xml |
X |
X |
This file stores the WebLogic domain configuration, including information about server names, ports, IP addresses, webapps, and SSL. Edit these settings using the WebLogic administration console: http://webserver:port/console. |
|
|
msi-config.xml |
X |
X |
This is a version of config.xml that's copied for use with a distributed managed server configuration. It's automatically replicated from the original config.xml after a managed server successfully starts. |
|
|
boot.properties |
X |
X |
X |
THis file contains the WebLogic system ID and password used for administering the WebLogic domain. |
|
fileRealm.properties |
X |
X |
X |
This file is used by WebLogic's internal LDAP server for system administration. |
|
DefaultAuthenticatorInit.ldift |
X |
X |
X |
This file is used by WebLogic's internal LDAP server for system administration. |
|
DefaultRoleMapperInit.ldift |
X |
X |
X |
This file is used by WebLogic's internal LDAP server for system administration. |
|
SerializedSystemIni.dat |
X |
X |
X |
This file is used by WebLogic's internal LDAP server for system administration. |
The following table lists PeopleSoft J2EE application scripts, which are all used with PeopleSoft Integration Broker, and can be used with every WebLogic server configuration.
|
Script |
Description |
|
BatchProjectExecutor.bat |
Use this script for PeopleSoft Integration Broker batch EIP testing. |
|
HashKeyGenerator.bat |
Use this script to generate a hash key used for Integration Gateway playback. |
|
MessageExport.bat |
Use this PeopleSoft Integration Broker script for extracting transaction data from request and response data. |
|
PSCipher.bat |
Use this script for encrypting PeopleSoft Integration Broker passwords. |
|
StartSendMaster.bat |
This is a PeopleSoft Integration Broker test utility. |
The following table lists miscellaneous files, which can be used with every WebLogic server configuration.
|
File |
Description |
|
Businterlink.txt |
This file is used by PeopleSoft’s Business Interlinks servlet for loading PeopleSoft libraries when needed. |
|
piaInstallLog.xml |
This is the PIA install log. |
See Also
Enterprise PeopleTools 8.46 PeopleBook: PeopleSoft Integration Broker

 J2EE Application Files
J2EE Application FilesIn addition to WebLogic domain configuration files, application descriptors are installed with the PeopleSoft J2EE enterprise application. The following table lists these descriptor files. The path shown for each file is relative to PS_HOME\webserv\WebLogic_domain\applications\.
|
File |
Description |
|
peoplesoft\META-INF\MANIFEST.MF |
Use this script to set required environment variables for the WebLogic server, for example: CLASSPATH, PATH, UNIX Library Path, and JVM options. |
|
peoplesoft\META-INF\application.xml |
This file contains a list of the webapps that comprise the PeopleSoft J2EE enterprise application. |
|
peoplesoft\PORTAL\WEB-INF\web.xml |
This file is the web application descriptor for the PORTAL webapp. It lists all of the servlets deployed as part of that application. |
|
peoplesoft\PORTAL\WEB-INF\weblogic.xml |
This file is the PORTAL web application extension descriptor. It specifies, among other things, the HTTP session cookie name, optional cookie domain, and context path of this application. |
|
peoplesoft\PSIGW\WEB-INF\web.xml |
This file is the web application descriptor for the PeopleSoft Integration Gateway (PSIGW) webapp. It lists all of the servlets deployed as part of that application. |
|
peoplesoft\PSIGW\WEB-INF\weblogic.xml |
This file is the PSIGW web application extension descriptor. It specifies the context path of this application. |
|
peoplesoft\PSEMHUB\WEB-INF\web.xml |
This file is the web application descriptor for the PeopleSoft Environment Framework (PSEMHUB) webapp. It lists all of the servlets deployed as part of that application. |
|
peoplesoft\PSEMHUB\WEB-INF\weblogic.xml |
This file is the PSEMHUB web application extension descriptor. It specifies the context path of this application. |
|
peoplesoft\PSOL\WEB-INF\web.xml |
This file is the web application descriptor for the PeopleSoft Online Library (PSOL) webapp (PeopleBooks). It lists all of the servlets deployed as part of that application. |
|
peoplesoft\PSOL\WEB-INF\weblogic.xml |
This file is the PSOL web application extension descriptor. It specifies the context path of this application. |
|
peoplesoft\PSINTERLINKS\WEB-INF\web.xml |
This file is the web application descriptor for the PeopleSoft Business Interlinks (PSINTERLINKS) webapp. It lists all of the servlets deployed as part of that application. |
|
peoplesoft\PSINTERLINKS\WEB-INF\weblogic.xml |
This file is the PSINTERLINKS web application extension descriptor. It specifies the context path of this application. |
|
HttpProxtServlet\WEB-INF\web.xml |
This file is the web application descriptor for the BEA WebLogic Server Reverse Proxy Server (RPS) webapp that's used to proxy content from a single WebLogic server. It lists all of the servlets deployed as part of that application. |
|
HttpProxyServlet\WEB-INF\weblogic.xml |
This file is the single-server RPS web application extension descriptor. It specifies the context path of this application. |
|
HttpClusterServlet\WEB-INF\web.xml |
This file is the web application descriptor for the BEA WebLogic Server Reverse Proxy Server (RPS) webapp that's used to proxy content from a cluster of WebLogic servers. It lists all of the servlets deployed as part of that application. |
|
HttpClusterServlet\WEB-INF\weblogic.xml |
This file is the multi-server RPS web application extension descriptor. It specifies the context path of this application. |

 PIA Install and Reinstall Options
PIA Install and Reinstall OptionsThe PeopleSoft Internet Architecture (PIA) installer enables you to create a new WebLogic server domain or update a valid existing WebLogic domain. A valid domain is a domain built by the PIA installer in the PS_HOME directory that you specify.
Depending on which option you select, you're prompted for additional information relevant to that selection. When creating a new domain, you're prompted to select from three configuration types: Single-server, multi-server and distributed managed server. If you select to update an existing domain, you're prompted to indicate which domain you would like to update and what type of update you would like to perform, which are as follows:
Install additional PeopleSoft site.
This option is relevant only to the PeopleSoft PORTAL web application, and doesn't modify or revert any other configuration settings. Select this option to install only the necessary files for defining an additional PeopleSoft site onto an existing WebLogic configuration. The new site will be accessed using its name in the URL. A site named “CRM” would be accessed using a URL similar to http://mywebserver_machine/CRM. To reset or recreate an existing PeopleSoft site, simply enter that site’s name as the site to create. On your web server, a PeopleSoft site is comprised of the following directories within the PORTAL web application:
weblogic_domain\applications\peoplesoft\PORTAL\site\*
weblogic_domain\applications\peoplesoft\PORTAL\WEB-INF\psftdocs\site\*
See Enterprise PeopleTools 8.46 PeopleBook: Internet Technology.
Redeploy PeopleSoft Internet Architecture.
This selection affects all of the PIA web applications installed to the local WebLogic domain. Select this option to redeploy all of the class files and jar files that comprise web components of PIA. WebLogic Server configuration files, scripts and any existing PeopleSoft (PORTAL) sites are not overwritten, unless you specify an existing PeopleSoft site during this setup.
Re-create WebLogic domain and redeploy PeopleSoft Internet Architecture.
This option affects WebLogic Server configuration and all of the PIA web applications installed to the local WebLogic domain. Select this option to completely remove an existing WebLogic domain and create the newly specified PeopleSoft site.
Warning! The entire WebLogic and PIA configuration in the specified WebLogic domain is deleted when you select this option.
Deploy additional PeopleSoft application extensions.
This option is solely for use with PeopleSoft applications. PeopleSoft application extensions are provided with certain PeopleSoft applications, and this option enables you to deploy those extensions. Consult the installation documentation for your PeopleSoft application to see if this option is appropriate. PeopleTools does not use application extensions.

 Administering a WebLogic Server Life Cycle
Administering a WebLogic Server Life CycleThis section provides an overview of the WebLogic server life cycle and discusses how to:
Start and stop single-server processes.
Start and stop multi-server processes.
Start and stop a distributed managed server.
See Also

 Understanding the WebLogic Server Life Cycle
Understanding the WebLogic Server Life Cycle
You control a WebLogic server’s life cycle primarily using a collection of scripts provided in that server’s WebLogic domain directory. Each instance of a WebLogic server runs in an isolated Java Runtime Environment (JRE), regardless of whether you're testing with a single-server configuration or implementing a multi-server configuration for production. All scripts must be launched from the WebLogic domain directory; and provide usage syntax if run with –help.

 Starting and Stopping Single-Server Processes
Starting and Stopping Single-Server ProcessesIn a single-server configuration, there's only one server to administer: PIA. You can control the life cycle of the PIA server using scripts or in the WebLogic console.
Scripts
For all platforms:
|
startPIA |
Use this script to start the WebLogic server locally. |
|
stopPIA |
Use this script to connect to a locally running WebLogic server and issue a shutdown command through WebLogic APIs. |
For Windows only:
|
installNTservicePIA |
Use this script to register the PIA WebLogic server as a Windows service that runs as a background process. the service is named as WebLogicDomainName-PIA, for example: peoplesoft-PIA. |
|
uninstallNTservicePIA |
Use this script to deregister the PIA Windows service. |
WebLogic Console
A WebLogic server can also be shut down from its administration console. To shut down a WebLogic server in the WebLogic Server Console, sign in to the console at http://webserver/console and perform either of the following.
In the navigation tree on the left, expand your domain, then Servers, then right click the PIA server and select Start/Stop this server.
In the console, navigate to Servers, PIA, Control.
On the Start/Stop page, you can elect to perform either of the following two shutdown procedures:
|
Graceful shutdown of this server |
This option enables transactions in progress to complete before shutting down the server. To terminate all HTTP sessions immediately, you can first select Ignore Sessions During Shutdown. |
|
Force shutdown of this server |
Immediately terminate all HTTP sessions and transactions in progress, and shut down the server. |

 Starting and Stopping Multi-Server Processes
Starting and Stopping Multi-Server ProcessesIn a Multi-server configuration, as the title implies there are multiple servers to administer. Controlling the life cycle of these servers can be done via scripts, the WebLogic console and the WebLogic Node Manager.
Scripts
For all platforms:
|
startWebLogicAdmin |
Use this script to start the WebLogicAdmin server. |
|
startManagedWebLogic |
Use this script to start a WebLogic managed server. All of the servers defined in a multi-server domain, except the WebLogicAdmin server, are controlled as managed servers. For example, to start PIA1 as a managed server run startManagedWebLogic PIA1. |
|
stopWebLogic |
Use this script to connect to a locally running WebLogic server and issue a shutdown command using WebLogic APIs. A remote distributed managed server can be shut down using a local administration server. |
For Windows only:
|
installNTservice.cmd |
Use this script to register a WebLogic server as a Windows service that runs as a background process. The service is named as WebLogicDomainName-ServerName. For example, to define the PIA1 managed server as a Windows service, run installNTservice PIA1. To define the WebLogicAdmin server as a Windows service, simply run installNTservice. |
|
UninstallNTservice.cmd |
Use this script to deregister a WebLogic server that's defined as a Windows service. |
Following are some important managed server considerations for scripts:
For all platforms:
When starting a WebLogic managed server it will attempt to connect to its administration server. A managed server’s administration server is specified either as a command line parameter when starting the managed server, or using the three administration server environment variables in setEnv, specifically ADMINSERVER_PROTOCOL, ADMINSERVER_PORT, and ADMINSERVER_HOSTNAME. The first time a managed server starts, it must connect to its administration server. If on subsequent startups the administration server is not available, the managed server starts up in Managed Server Independence (MSI) mode by using its locally replicated msi-config.xml. A managed server running in MSI mode can't be administered from a console, so this situation should only be encountered when it is imperative that the managed server be started even though the administration server is not running. Once the administration server is back online, running managed servers that were not previously known by the administration server to be running may be rediscovered using WebLogic’s command line utility java weblogic.Admin DISCOVERMANAGEDSERVER, or you can just restart the managed server.
To use WebLogic’s java command line utility classes run setEnv to set up your environment, then run java weblogic.Admin for usage.
For Windows only:
When running a WebLogic managed server as a Windows service, the managed server’s administration server must be running. When installing a managed server as a Windows service, the managed server service can be configured to be dependent on its local administration server. To configure a managed server service to be dependent on its local admin server service use the –depends option of installNTservice.cmd when defining the Windows service for the managed server. In addition, when the administration server is also a Windows service, you must define it using the following command:
installNTservice.cmd –delay interval
Where intervalis a period in milliseconds, for example 6000. This allows the administration server sufficient time to start before the managed server starts.
WebLogic Server Console
A WebLogic server can also be shut down from its administration console. To shut down a WebLogic server in the WebLogic Server Console, sign in to the console of the WebLogicAdmin server (http://webserver:port/console) and perform either of the following:
In the navigation applet on the left, expand your domain, then Servers, then right click the PIA server and select Start/Stop this server.
In the console, navigate to Servers, PIA, Control.
On the Start/Stop page, you can elect to perform either of the following two shutdown procedures:
|
Graceful shutdown of this server |
This option enables transactions in progress to complete before shutting down the server. To terminate all HTTP sessions immediately, you can first select Ignore Sessions During Shutdown. |
|
Force shutdown of this server |
Immediately terminate all HTTP sessions and transactions in progress, and shut down the server. |
WebLogic Node Manager
The WebLogic Node Manager provides the ability to start a WebLogic managed server from the WebLogic Server Console. In addition, the console provides a way to automatically restart a failed server. As with all WebLogic servers, the WebLogic Node Manager runs isolated in its own JRE, and on Windows it can also run as a Windows service. The WebLogic Node Manager binds to a unique IP address and port at startup and accepts lifecycle commands from a WebLogic administration server.
Multiple WebLogic domains running on a singe machine can have its managed servers administered by a shared WebLogic Node Manager, as long as each WebLogic domain uses the same version of WebLogic.
The following table lists the WebLogic Node Manager files that are provided with WebLogic server, not the PIA install. These files are located in BEA_HOME\weblogic81\server\bin\, not your PeopleSoft created WebLogic domain directory.
|
File |
Description |
|
startNodeManager.cmd |
Use this script to start the WebLogic Node Manager as a foreground process. |
|
installNodeMgrSvc.cmd |
Use this script to define the WebLogic Node Manager as a Windows service that runs as a background process. The service is called BEA WebLogic Platform 8.1 NodeManager. |
|
uninstallNodeMgrSvc.cmd |
Use this script to uninstall the WebLogic Node Manager as a Windows service. |
|
nodemanager.properties |
This is the WebLogic Node Manager configuration file. |
Note. BEA_HOME\weblogic81\common\nodemanager\NodeManagerLogs\ is the default logs directory for WebLogic Node Manager.
To start a local WebLogic Managed server from the WebLogic Node Manager:
Start the WebLogic domain’s WebLogic administration server.
Start the Node Manager of that domain’s local BEA_HOME.
If you're attempting to start a distributed managed server, you must start the Node manager on that distributed machine, otherwise the administration server, Node Manager and managed server are all on one machine.
Sign on to the WebLogic Server Console by entering the following URL in a browser:
http://webserver:9999/console
Where webserver is the domain of the WebLogic server.
Traverse the following in the navigation tree on the left:
Expand your WebLogic domain (for example, peoplesoft).
Expand Servers.
Right click the server you would like to start and click ‘Start/Stop this server...’.
On the console home page, within “Domain Configuration” \ “Network Configuration” select Servers, click the server you want to start, then select the Control tab.
Click the “Start this server...” link to start that server.
If that text is not a hyperlink, either the WebLogic Node Manager is not running or the administration server was not able to communicate to the Node Manager.
A WebLogic Managed server started from the WebLogic Node Manager doesn't use Java options defined in setEnv, such as Java heap size. If you opt to use the WebLogic Node Manager, you should confirm or adjust the Java options in the WebLogic console of the administration server.
To adjust the Java options:
Expand your WebLogic domain (for example, peoplesoft).
Expand Servers.
Select the managed server that you would like to modify.
Select the first level Configuration tab
Select the second level Remote Start tab.
Update the Arguments field.
Click the Apply button.

 Starting and Stopping a Distributed Managed Server
Starting and Stopping a Distributed Managed ServerIn a multi-server configuration, a distributed managed server is simply a managed server that isn't started from the same physical location as its domain’s administration server. You can control the life cycle of these servers using scripts, the WebLogic Server Console and the WebLogic Node Manager.
See Starting and Stopping Multi-Server Processes.
In addition to the multi-server considerations, edit the following file:
BEA_HOME\weblogic81\common\nodemanager\nodemanager.hosts
Edit this file to include a list of IP addresses or host names of WebLogic administration servers from which the connection to the node manager will be accepted. In a typical configuration, there's only one such server

 Tuning Performance and Monitoring Resources
Tuning Performance and Monitoring ResourcesMonitoring the performance of a WebLogic instance is primarily performed at the WebLogic console. This section discusses how to:
Manage JVM heap size and execute thread usage.
Monitor HTTP session count for PeopleSoft portal.
See Also
Using WebLogic Server 8.1 Console to Monitor PeopleSoft Sessions

 Managing JVM Heap Size and Execute Thread Usage
Managing JVM Heap Size and Execute Thread UsageTwo of the main resource to monitor and tune with regards to WebLogic Server are the JVM memory heap size and the Execute thread count pool size. Monitoring and tuning both of these resources and more are describe below.
Monitoring JVM Heap and Execute Thread Usage
The JVM heap size is the amount of memory that a particular JRE (Java Runtime Environment) gives to the JVM (Java Virtual Machine) that it creates. The java.exe command on Windows, java on UNIX and beasvc.exe when running WebLogic as a Windows service is the JRE and the JVM exists within the JRE’s memory space. The two primary sources for monitoring the amount of memory that is in use within a JVM are the WebLogic console and the WebLogic logs.
To monitor the amount of the JVM heap size available and in use:
Sign on to the WebLogic Server Console by entering the following URL in a browser:
http://webserver:9999/console
Where webserver is the domain of the WebLogic server.
Traverse the following in the navigation tree on the left:
Expand your WebLogic domain (for example, peoplesoft).
Expand Servers.
Select the server you intend to monitor (for example, PIA).
Select the first level Monitoring tab.
Select the second level Performance tab.
|
Idle Threads |
Displays the number of execute threads available for work. Having an excessive number of idle threads, such as 200, will waste a small amount of JVM resources. Note. This value is static, so you must refresh the page to update it. Use the refresh icon at the top of the page. |
|
Oldest Pending Request |
Displays the date and time stamp of the oldest request in the queue. Note. This value is static, so you must refresh the page to update it. Use the refresh icon at the top of the page. |
|
Throughput |
Displays the number of requests over the displayed time frame that have been processed by an execute thread for the sampling time period. The top number on the left is the highest throughput, the bottom number on the left is the lowest throughput and the number on the right is the throughput for the current sample period. |
|
Queue Length |
Displays the number of requests over the displayed time frame that are queued up and waiting to be processed for the sampling time period. The top number on the left is the highest backlog, the bottom number on the left is the lowest backlog and the number on the right is the backlog for the current sample period. |
|
Memory Usage |
Displays the amount of JVM memory used in bytes over the displayed time frame. The top number on the left is the maximum memory available to the JVM (set using Java’s –Xmx setting) and the number on the right is the memory in use for the current sample period. |
If you need to adjust any of the Java options, most commonly the JVM heap size, you must manually edit that WebLogic domain’s local setEnv script. The two parameters, -Xms and -Xmx, control the JVM memory minimum and maximum heap size respectively.
Following are examples of the JVM heap size as specified in setEnv using the JAVA_OPTIONS_OSplatform environment variable. You only need to set the variables that correspond to the OS where the WebLogic server is running.
JAVA_OPTIONS_WIN32="-server -Xms32m -Xmx200m -XX:MaxPermSize=128m"
JAVA_OPTIONS_AIX="-Xms32m -Xmx200m"
JAVA_OPTIONS_HPUX="-server -Xms32m -Xmx200m -XX:MaxPermSize=128m"
JAVA_OPTIONS_LINUX="-Xms128m -Xmx256m"
JAVA_OPTIONS_TRU64="-Xms32m -Xmx200m"
JAVA_OPTIONS_SOLARIS="-server -Xms32m -Xmx200m -XX:MaxPermSize=128m"
Note. If you do adjust any of the Java options, most commonly the JVM heap size, you must restart WebLogic for these changes to
take effect.
If you're running WebLogic Server as a Windows service you must rerun the installNTservice script to propagate this change
into the Windows registry.
The WebLogic Node Manager does not use the Java options set in setEnv, but instead uses Java options set from the WebLogic console.
To modify the Java options for a WebLogic instance started via the WebLogic Node Manager:
Sign on to the WebLogic Server Console by entering the following URL in a browser:
http://webserver:9999/console
Where webserver is the domain of the WebLogic server.
Traverse the following in the navigation tree on the left:
Expand your WebLogic domain (for example, peoplesoft).
Expand Servers.
Select the server you intend to modify (for example, PIA).
Select the first level Configuration tab.
Select the second level Remote Start tab.
Update the Arguments field.
Click Apply.
Changing the Execute Thread Pool Size
To change the size of the Execute thread pool used by PeopleSoft applications for a particular WebLogic instance:
Sign on to the WebLogic Server Console by entering the following URL in a browser:
http://webserver:9999/console
Where webserver is the domain of the WebLogic server.
Traverse the following in the navigation tree on the left:
Expand your WebLogic domain (for example, peoplesoft).
Expand Servers.
Right-click the server you intend to modify (for example, PIA).
Select View Execute Queues.
Click the queue that your server is using, most likely weblogic.kernel.Default.
Adjust the queue size settings to fit your needs.
Click Apply.
See Also

 Monitoring HTTP Session Count for PeopleSoft Portal
Monitoring HTTP Session Count for PeopleSoft PortalIn addition to memory and thread usage, it's also possible to monitor the number of established HTTP sessions used in conjunction with the PeopleSoft PORTAL application. This number, although not necessarily directly related to current performance, is an indicator of the following performance factors:
JVM memory used to store HTTP session data.
Current number of logged on clients.
Peak number of logged on clients.
Idle time of logged on clients.
To monitor HTTP sessions:
Sign on to the WebLogic Server Console.
Traverse the following in the navigation tree on the left:
Expand peoplesoft.
Expand Deployments.
Expand Applications.
Expand peoplesoft.
Select PORTAL.
Select the Monitoring tab.
Select the Sessions tab.
Ensure that the Session Monitoring Enabled check box is selected, which enables it for the current WebLogic instance.
If the check box was previously cleared, restart WebLogic Server to apply the new setting.
Click the Refresh button at the top of the console page.
With HTTP session monitoring enabled, the information displayed will be users’ PeopleSoft ID, their workstation name or IP address, the PeopleSoft site they are logged onto and the time of their last request.
Note. Established HTTP sessions remain on the web server until users sign out of PeopleSoft or until the sessions time out. Simply closing the browser does not sign a PeopleSoft user out. You can control HTTP session time out settings from a site's web profile in the PeopleSoft database.
See Also

 Changing Configuration Settings
Changing Configuration Settings
This section provides an overview of the WebLogic server configuration files, and discusses how to:
Change the WebLogicAdmin server’s listen ports.
Change application and server deployment targets.

 Understanding the WebLogic Server Configuration Files
Understanding the WebLogic Server Configuration FilesWebLogic server configuration settings are stored in a collection of files, primarily the setEnv script, config.xml, and the web.xml and weblogic.xml for each webapp.
SetEnv contains statically and dynamically defined environment variables. It's called from all of the WebLogic administration scripts to assist in building the Java command line. You modify this file using a text editor.
Config.xml contains server runtime settings, such as the HTTP port. You modify this file using the WebLogic Server Console.
Web.xml and weblogic.xml, which are located in the WEB-INF directory of each webapp, are web application descriptors and contain settings relevant to their application.

 Changing the WebLogicAdmin Server’s Listen Ports
Changing the WebLogicAdmin Server’s Listen PortsIn the multi-server configuration, several parameters are set based on the environment detected and on delivered defaults. One such parameter is the HTTP port of the WebLogicAdmin server. By default the WebLogicAdmin server’s HTTP listen port is 9999.
To change this value:
Start the WebLogicAdmin server via the startWebLogicAdmin script
Sign on to the WebLogic Server Console by entering the following URL in a browser:
http://webserver:9999/console
Where webserver is the domain of the WebLogic server.
Navigate to Servers, WebLogicAdmin, Configuration, General.
Modify the value of the Listen Port field.
Click Apply.
Restart the WebLogic server.
Note. If you can't initially start the server due to a port conflict, you can manually edit the value of the ListenPort parameter in that domain’s config.xml file. Creating a backup of config.xml is recommended before manually changing this file.
After changing the ListenPort value in your domain’s config.xml, either directly or using the console, you must also update your setEnv script. Update the ADMINSERVER_PORT environment variable to reflect the new HTTP port. This setting is used by the stopWebLogic and startManagedWebLogic scripts as the default administration server HTTP port.

 Changing Application and Server Deployment Targets
Changing Application and Server Deployment TargetsWith WebLogic, J2EE applications are targeted to any combination of WebLogic servers and WebLogic clusters. A WebLogic cluster is a logical grouping of servers, generally all providing the same application, though that's not a requirement. To change the servers or clusters that an application is targeted and deployed to, sign on to the WebLogic Server Console and update the application's target assignments. You can view and modify application and server target assignments on the Deployments, Applications tabs, and on the Deployments tab for each server.
Following is an example of how to change the target assignments of the PeopleSoft Integration Gateway (PSIGW) web application so it’s the only application targeted to the PIA server, and is the sole application on that instance.
To change the target assignments of the PeopleSoft Integration Gateway web application:
Sign on to the WebLogic Server Console.
Traverse the following in the navigation tree on the left:
Expand peoplesoft.
Expand Deployments.
Expand Applications.
Expand peoplesoft.
Select PSIGW.
Select the Targets tab.
In the Clusters section, clear the peoplesoftCluster check box.
Click Apply.
In the navigation tree, select PORTAL.
Select the Targets tab.
In the Independent Servers grid, clear the check box for targeting the PORTAL webapp to this server.
Click Apply.
Repeat steps 7 to 10 for the PSEMHUB, PSINTERLINKS and PSOL web applications.
To deploy an application to a cluster, target the server to the cluster and target the application to the cluster.

 Applying an Example Single-Server Configuration
Applying an Example Single-Server ConfigurationThis section provides overviews of the basic machine configuration, PIA setup prompts, configuration file settings, and unprompted configuration file settings, and discusses how to start the weblogic server.

 Basic Machine Configuration
Basic Machine Configuration
This example single-server setup is performed on a machine with the following configuration:
Operating system: Windows
Hostname: DBROWN040403
PeopleSoft home directory: C:\PT845
BEA WebLogic Server home directory: C:\BEA

 PIA Setup Prompts
PIA Setup Prompts
Following are the PIA setup prompts and corresponding values appropriate to building the example single-server domain.
Note. The Prompt # column doesn't reflect actual step numbers during setup. The prompt numbers simply provide a reference for subsequent discussion of the configuration file settings.
|
Prompt # |
Prompted Field |
Value |
|
1 |
PeopleSoft CD install location (PS_HOME). |
C:\PT845 |
|
2 |
BEA WebLogic Server home directory. |
C:\BEA |
|
3 |
WebLogic domain admin ID. |
system |
|
4 |
WebLogic domain admin password. |
password |
|
5 |
WebLogic domain name. |
peoplesoft |
|
6 |
WebLogic domain type. |
Single Server |
|
7 |
Portal website name. |
ps |
|
8 |
Application Server hostname. |
DBROWN040403 |
|
9 |
Application Server JSL port. |
9845 |
|
10 |
HTTP Listen Port. |
80 |
|
11 |
HTTPS Listen Port. |
443 |
|
12 |
Authentication Token domain. |
.peoplesoft.com |
|
13 |
Web profile name. |
DEV |
|
14 |
Web profile user ID. |
PTWEBSERVER |
|
15 |
Web profile password. |
PTWEBSERVER |
|
16 |
Report Repository location. |
C:\psreports |

 Configuration File Settings
Configuration File Settings
As a result of the specified setup response values, several configuration files are updated. Following are the corresponding configuration file updates by prompt number.
|
Prompt # |
Configuration File |
Setting |
|
1 |
setEnv.cmd |
SET PS_HOME=C:/PT845 |
|
1 |
config.xml |
|
|
2 |
setEnv.cmd |
SET BEA_HOME=c:\bea SET WL_HOME=c:\bea\weblogic81 |
|
2 |
config.xml |
|
|
3 |
config.xml |
<ServerStart Username="system"... |
|
3 |
boot.properties |
(encrypted) |
|
4 |
boot.properties |
(encrypted) |
|
5 |
setEnv.cmd |
SET DOMAIN_NAME=peoplesoft |
|
5 |
config.xml |
<Domain Name="peoplesoft"... |
|
6 |
n/a (Domain configuration is based on this selection.) |
|
|
10 |
setEnv.cmd |
SET ADMINSERVER_PORT=80 |
|
10 |
config.xml |
<Server Name="PIA" ListenPort="80"... |
|
11 |
config.xml |
<Server Name="PIA" SSLListenPort="443"... |
|
12 |
..\applications\peoplesoft\PORTAL\WEB-INF\weblogic.xml |
|
Note. The prompts numbered 7, 8, 9, 13, 14, 15, and 16 don't directly affect the WebLogic configuration.

 Unprompted Configuration File Settings
Unprompted Configuration File Settings
In addition to the configuration file changes based on the setup response values, additional automatic configuration changes are performed based on the domain type you selected.
|
Configuration File |
Setting |
|
setEnv.cmd |
SET ADMINSERVER_HOSTNAME=DBROWN040403 SET ADMINSERVER_SERVERNAME=PIA |
|
config.xml |
<Server Name="PIA"… <SSL PrivateKeyAlias=" DBROWN040403"… |

 Starting the Weblogic Server
Starting the Weblogic Server
To start the WebLogic server created in this example, use the scripts created in the generated WebLogic domain directory of PS_HOME\webserv\peoplesoft\. To start this WebLogic server as a foreground process, run startPIA.cmd. A successful startup produces the following messages, which indicate that the server has started, that it has bound to all local IP addresses, and that it's listening on ports 80 and 443 for HTTP and HTTPS traffic respectively.
<Feb 27, 2004 11:23:41 AM PST> <Notice> <WebLogicServer> <BEA-000355> <Thread "ListenThread.Default" listening on port 80, ip address *.*> <Feb 27, 2004 11:23:41 AM PST> <Notice> <WebLogicServer> <BEA-000355> <Thread "SSLListenThread.Default" listening on port 443, ip address *.*> <Feb 27, 2004 11:23:41 AM PST> <Notice> <WebLogicServer> <BEA-000330> <Started WebLogic Admin Server "PIA" for domain "peoplesoft" running in Production Mode> <Feb 27, 2004 11:23:41 AM PST> <Notice> <WebLogicServer> <BEA-000360> <Server started in RUNNING mode>

 Applying an Example Multi-Server Configuration
Applying an Example Multi-Server ConfigurationThis section provides overviews of the basic machine configurations, PIA setup prompts for multi-server configuration, configuration file settings for multi-server configuration, unprompted multi-server configuration file settings, PIA setup prompts for distributed managed server configuration, configuration file settings for distributed managed server configuration, and unprompted distributed server configuration file settings, and discusses how to start the weblogic servers.

 Basic Machine Configurations
Basic Machine Configurations
An extended Multi-server configuration requires performing two PIA installs, once to create the Multi-Server configuration and a second time to create the Distributed Managed Server.
This Multi-Server installation was performed on a machine with the following configuration.
Operating system: Windows
Hostname: DBROWN040403
PeopleSoft home directory: C:\PT845
BEA WebLogic Server home directory: C:\BEA
This Distributed-Server installation was performed on a machine with the following configuration.
Operating system: RedHat Linux
Hostname: PT-LINUX01
PeopleSoft home directory: /apps/pt845
BEA WebLogic Server home directory: /apps/bea

 PIA Setup Prompts for Multi-Server Configuration
PIA Setup Prompts for Multi-Server Configuration
Following are the PIA setup prompts and corresponding values appropriate to building the example extended multi-server domain.
Note. The Prompt # column doesn't reflect actual step numbers during setup. The prompt numbers simply provide a reference for subsequent discussion of the configuration file settings.
|
Prompt # |
Prompted Field |
Value |
|
1 |
PeopleSoft CD install location (PS_HOME). |
C:\PT845 |
|
2 |
BEA WebLogic Server home directory. |
C:\BEA |
|
3 |
WebLogic domain admin ID. |
system |
|
4 |
WebLogic domain admin password. |
password |
|
5 |
WebLogic domain name. |
peoplesoft |
|
6 |
WebLogic domain type. |
Multi Server |
|
7 |
Portal website name. |
ps |
|
8 |
Application Server hostname. |
DBROWN040403 |
|
9 |
Application Server JSL port. |
9845 |
|
10 |
HTTP Listen Port. |
80 |
|
11 |
HTTPS Listen Port. |
443 |
|
12 |
Authentication Token domain. |
.peoplesoft.com |
|
13 |
Web profile name. |
DEV |
|
14 |
Web profile user ID. |
PTWEBSERVER |
|
15 |
Web profile password. |
PTWEBSERVER |
|
16 |
Report Repository location. |
C:\psreports |

 Configuration File Settings for Multi-Server Configuration
Configuration File Settings for Multi-Server Configuration
As a result of the specified setup response values, several configuration files are updated. Following are the corresponding configuration file updates by prompt number.
|
Prompt # |
Configuration File |
Setting |
|
1 |
setEnv.cmd |
SET PS_HOME=C:/PT845 |
|
1 |
config.xml Note. This setting occurs 6 times, once for each managed server. |
|
|
2 |
setEnv.cmd |
SET BEA_HOME=c:\bea SET WL_HOME=c:\bea\weblogic81 |
|
2 |
config.xml Note. This setting occurs 6 times, once for each managed server. |
|
|
3 |
config.xml Note. This setting occurs 6 times, once for each managed server. |
<ServerStart Username="system"... |
|
3 |
boot.properties |
(encrypted) |
|
4 |
boot.properties |
(encrypted) |
|
5 |
setEnv.cmd |
SET DOMAIN_NAME=peoplesoft |
|
5 |
config.xml |
|
|
6 |
n/a (Domain configuration is based on this selection.) |
|
|
10 |
setEnv.cmd |
SET ADMINSERVER_PORT=80 |
|
10 |
config.xml Note. This setting occurs 3 times, once each for the PIA, PIA1, and PIA2 managed servers. |
|
|
11 |
config.xml Note. This setting occurs 3 times, once each for the PIA, PIA1, and PIA2 managed servers. |
|
|
12 |
..\applications\peoplesoft\PORTAL\WEB-INF\weblogic.xml |
|
Note. The prompts numbered 7, 8, 9, 13, 14, 15, and 16 don't directly affect the WebLogic configuration.

 Unprompted Multi-Server Configuration File Settings
Unprompted Multi-Server Configuration File Settings
In addition to the configuration file changes based on the setup response values, additional automatic configuration changes are performed based on the domain type you selected.
|
Configuration File |
Setting |
|
setEnv.cmd |
SET ADMINSERVER_PORT=9999 SET ADMINSERVER_HOSTNAME=DBROWN040403 SET ADMINSERVER_SERVERNAME=WebLogicAdmin |
|
config.xml |
<Server Name="PIA"… <SSL PrivateKeyAlias=" DBROWN040403"… |

 PIA Setup Prompts for Distributed Managed Server Configuration
PIA Setup Prompts for Distributed Managed Server Configuration
Following are the PIA setup prompts and corresponding values appropriate to building the example extended multi-server domain.
Note. The Prompt # column doesn't reflect actual step numbers during setup. The prompt numbers simply provide a reference for subsequent discussion of the configuration file settings.
|
Prompt # |
Prompted Field |
Value |
|
1 |
PeopleSoft CD install location (PS_HOME). |
/apps/pt845 |
|
2 |
BEA WebLogic Server home directory. |
/apps/bea |
|
3 |
WebLogic domain admin ID. |
system |
|
4 |
WebLogic domain admin password. |
password |
|
5 |
WebLogic domain name. |
peoplesoft |
|
6 |
WebLogic domain type. |
Distributed Managed Server |
|
7 |
Portal website name. |
ps |
|
8 |
Application Server hostname. |
PT-LINUX01 |
|
9 |
Application Server JSL port. |
9845 |
|
10 |
HTTP Listen Port. |
80 |
|
11 |
HTTPS Listen Port. |
443 |
|
12 |
Authentication Token domain. |
.peoplesoft.com |
|
13 |
Web profile name. |
DEV |
|
14 |
Web profile user ID. |
PTWEBSERVER |
|
15 |
Web profile password. |
PTWEBSERVER |
|
16 |
Report Repository location. |
/apps/pt845/psreports |

 Configuration File Settings for Distributed Server Configuration
Configuration File Settings for Distributed Server Configuration
As a result of the specified setup response values, several configuration files are updated. Following are the corresponding configuration file updates by prompt number.
|
Prompt # |
Configuration File |
Setting |
|
1 |
setEnv.cmd |
SET PS_HOME=/apps/pt845 |
|
2 |
setEnv.cmd |
SET BEA_HOME=/apps/bea SET WL_HOME=/apps/bea/weblogic81 |
|
3 |
config.xml Note. This setting occurs 6 times, once for each managed server. |
<ServerStart Username="system"... |
|
3 |
boot.properties |
(encrypted) |
|
4 |
boot.properties |
(encrypted) |
|
5 |
setEnv.cmd |
SET DOMAIN_NAME=peoplesoft |
|
6 |
n/a (Domain configuration is based on this selection.) |
|
|
10 |
setEnv.cmd |
SET ADMINSERVER_PORT=80 |
|
10 |
config.xml Note. This value is set in the config.xml file of the administration server (where the multi-server configuration was set up). |
<Server ListenPort="80"... |
|
11 |
config.xml Note. This value is set in the config.xml file of the administration server (where the multi-server configuration was set up). |
<Server SSLListenPort="443"... |
|
12 |
../applications/peoplesoft/PORTAL/WEB-INF/weblogic.xml |
|
Note. The prompts numbered 7, 8, 9, 13, 14, 15, and 16 don't directly affect the WebLogic configuration.

 Unprompted Distributed Server Configuration File Settings
Unprompted Distributed Server Configuration File Settings
In addition to the configuration file changes based on the setup response values, additional automatic configuration changes are performed based on the domain type you selected.
|
Configuration File |
Setting |
|
setEnv.cmd |
SET ADMINSERVER_PORT= SET ADMINSERVER_HOSTNAME= SET ADMINSERVER_SERVERNAME=WebLogicAdmin |
|
config.xml |
<Server Name="PIA"… <SSL PrivateKeyAlias="PT_LNX01"... |

 Starting the WebLogic Servers
Starting the WebLogic Servers
To start the WebLogic Servers created in this example, use the scripts created in the generated WebLogic domain directory of PS_HOME\webserv\peoplesoft.
Starting the Domain Administration Server
To start the domain administration server, WebLogicAdmin, run the following command:
c:\pt845\webserv\peoplesoft\startWebLogicAdmin.cmd
A successful startup of this server produces the following messages, which indicate that the server has started, that it has bound to all local IP addresses, and that it's listening on port 9999 for HTTP traffic.
<Feb 27, 2004 11:23:41 AM PST> <Notice> <WebLogicServer> <BEA-000355> <Thread "ListenThread.Default" listening on port 9999, ip address *.*> <Feb 27, 2004 11:23:41 AM PST> <Notice> <WebLogicServer> <BEA-000330> <Started WebLogic Admin Server "WebLogicAdmin" for domain "peoplesoft" running in Production Mode> <Feb 27, 2004 11:23:41 AM PST> <Notice> <WebLogicServer> <BEA-000360> <Server started in RUNNING mode>
Starting the Local Managed Server
To start the local managed server (PIA) on DBROWN040403, the same machine where the WebLogicAdmin server is running, run the following command:
c:\pt845\webserv\peoplesoft\startManagedWebLogic.cmd PIA
A successful startup of this server produces the following messages, which indicate that the server has started, that it has bound to all local IP addresses, and that it's listening on ports 80 and 443 for HTTP and HTTPS traffic respectively.
<Feb 27, 2004 2:17:04 PM PST> <Notice> <WebLogicServer> <BEA-000355> <Thread "ListenThread.Default" listening on port 80, ip address *.*> <Feb 27, 2004 2:17:04 PM PST> <Notice> <WebLogicServer> <BEA-000355> <Thread "SSLListenThread.Default" listening on port 443, ip address *.*> <Feb 27, 2004 2:17:04 PM PST> <Notice> <WebLogicServer> <BEA-000330> <Started WebLogic Managed Server "PIA" for domain "peoplesoft" running in Production Mode> <Feb 27, 2004 2:17:04 PM PST> <Notice> <WebLogicServer> <BEA-000360> <Server started in RUNNING mode>
Starting a Remote Distributed Managed Server
Prior to starting a remote distributed managed server, which in this example is a WebLogic Reverse Proxy Server (RPS), you must modify the HttpProxyServlet web application’s web.xml file to specify the address of the back-end WebLogic instance from which content is proxied. The HttpProxyServlet webapp is the default webapp for the RPS server, and is used when proxing content from a single back-end WebLogic server.
To modify HttpProxyServlet’s web.xml you can use BEA’s graphical WebLogic Builder, or simply edit the HttpProxyServlet’s web.xml. To use WebLogic Builder, launch the startWebLogicBuilder script from within your WebLogic domain directory, and either specify applications/HttpProxyServlet as a command line parameter, or once in WebLogic Builder select File/Open and open the HttpProxyServlet application. To edit the web.xml file manually, the location of the file is weblogic_domain\applications\HttpProxyServlet\WEB-INF\web.xml.
The parameter values to adjust are the WebLogicHost and WebLogicPort init-params for the HttpProxyServlet servlet. Following the relevant part of a properly configured web.xml.
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN" "http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd"> <web-app> <display-name>HttpProxyServlet</display-name> <description>HttpProxyServlet</description> <servlet> <servlet-name>HttpProxyServlet</servlet-name> <display-name>HttpProxyServlet</display-name> <servlet-class>weblogic.servlet.proxy.HttpProxyServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>WebLogicHost</param-name> <param-value>DBROWN040403</param-value> <description>Hostname of WebLogic PIA/PORTAL server.</description> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>WebLogicPort</param-name> <param-value>80</param-value> <description>HTTP listen port of WebLogic PIA/PORTAL server.</description> </init-param> . . . . . .
To start the remote managed server (RPS) on PT-LINUX01, the machine where the distributed managed server setup was performed, run the following command:
/apps/pt845/webserv/peoplesoft/startManagedWebLogic.cmd RPS http://dbrown040403:9999
A successful startup of this server produces the following messages, which indicate that the managed server started and was able to connect to the administration server, that it has bound to all local IP addresses, and that it's listening on ports 80 and 443 for HTTP and HTTPS traffic, respectively.
<Feb 27, 2004 2:17:04 PM PST> <Notice> <WebLogicServer> <BEA-000355> <Thread "ListenThread.Default" listening on port 8080, ip address *.*> <Feb 27, 2004 2:17:04 PM PST> <Notice> <WebLogicServer> <BEA-000355> <Thread "SSLListenThread.Default" listening on port 8443, ip address *.*> <Feb 27, 2004 2:17:04 PM PST> <Notice> <WebLogicServer> <BEA-000330> <Started WebLogic Managed Server "RPS" for domain "peoplesoft" running in Production Mode> <Feb 27, 2004 2:17:04 PM PST> <Notice> <WebLogicServer> <BEA-000360> <Server started in RUNNING mode>
Note. During the PIA setup of the distributed managed server, nothing was specified to indicate which server would be run on PT-LINUX01. The managed server that's run as a distributed managed server is the server name specified as a command line parameter to running startWeblogic along with the URL of its administration server.