 Understanding Payroll Data Processing for GLI or QSP
Understanding Payroll Data Processing for GLI or QSPThis chapter provides an overview of payroll data processing for general ledger interface (GLI) or QSP and discusses how to:
Link journal types to general ledger (GL) groupings.
Calculate accrued salary.
Calculate leave liability.
Report leave liability.
Calculate state payroll tax liability.
Run the GLI or QSP processes.
Remap ChartFields after initial calculation.
Note. The PeopleSoft system delivers a query that you can run to view the names of all delivered elements designed for Australia. Instructions for running the query are provided in the PeopleSoft Enterprise Global Payroll 9.0 PeopleBook.
See Also
Understanding How to View Delivered Elements
 Understanding Payroll Data Processing for GLI or QSP
Understanding Payroll Data Processing for GLI or QSPThe following diagram represents the processing of payroll data for the GLI or QSP. The two shaded boxes with borders show the added local functionality. The selected check boxes represent the options on the processing page. Note that the Leave Entitlement option adds data to the GP_GL_DATA table for inclusion in the output to either QSP or GLI:
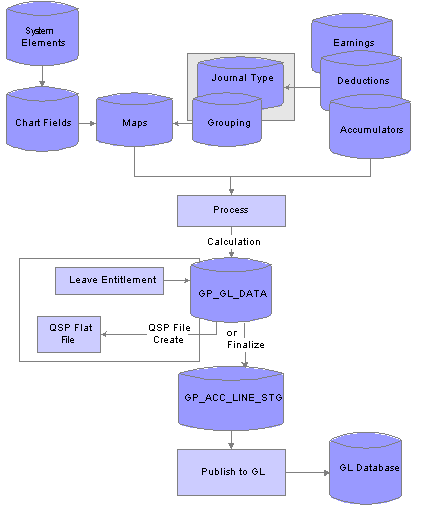
Processing of payroll data for GLI or QSP
 Linking Journal Types to GL Groupings
Linking Journal Types to GL GroupingsTo link journal types to GL groupings, use the Journal Type (GPAU_GLGRP_JOURNAL) component.
The Office for Government Online (OGO) QSP financials file requires payroll data reported by journal type.
You report payroll data to the GL by journal type by linking a journal type to a GL grouping.
A grouping comprises entry types of earnings, deductions, or segment accumulators. There are five delivered journal types: Accrual, Salary, Employee Entitlement, Statistical, and Terminated EE’s (employee’s) Entitlement.
Accrual and Statistical journal types are for QSP users only.
Note. The Leave Entitlements Application Engine process selects data for inclusion into the GPAU_LEAVE_LIAB record (from GP_GL_DATA) by the flags for journal types Employee Entitlement and Terminated EE's Entitlement. Therefore, any organization needing to resolve leave entitlement calculations within the Leave Entitlement phase of the GL Interface process needs to select a journal type for each GL grouping code associated with GL Liability earnings codes.
The following table shows an example setup. Columns 1 and 2 are from the core General Ledger Grouping page (select Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Integration, Element Groupings), and column 3 is from the Journal Type AUS page (select Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Integration, Journal Type AUS):
|
Grouping Code |
Element |
Journal Type |
|
Accrual |
GLI Accrual (segment accumulator) |
Accrual |
|
Earnings |
AUS GROSS (segment accumulator) |
Salary |
|
Entitlements |
LIAB ANN DAY, LIAB ANN HRS, LIAB LSL WKS (earnings) |
Employee Entitlement |
|
Termination |
LIAB TAL HRS, LIAB TAL DYS, LIAB TLS WKS (earnings) |
Terminated EE’s Entitlement |

 Understanding Accrued Salary Calculation
Understanding Accrued Salary CalculationIf the end date of the last pay period in a month is before the end of the financial month, you can send a percentage of total salary as the accrued costing for the “gap” between the two dates.
Accumulator GLI ACCRUAL has a single member AUS GROSS that contributes the variable GLI VR ACCRUAL PCT. The variable has a value of 0.00. You only want the accumulator’s value to be included in the GLI process in the last month, so on the pay calendar for the last period, you need to set the value of the variable as a calendar supporting element override. The value may vary according to the number of days in the gap.
The value sent to QSP is reversed by the financials system the following month and replaced by actual costings.
Note. Non-QSP users should give accrued salary journal type Entitlement.

 Understanding Leave Liability Calculation
Understanding Leave Liability CalculationThe amount of leave that an employee is owed needs to be costed as a liability in the GL. For leave liability reporting, we have set up earnings that store the monetary value of each employee’s leave entitlement. The earnings are not paid as earnings because they do not contribute to AUS GROSS.
Because the GLI and QSP flat file only requires the difference between the liability for the last pay period and the current pay period, this is what the Application Engine (AE) leave entitlement process calculates and passes to GP_GL_DATA.
If an employee has been terminated, the stored value of his or her processed liability has to be reversed out from the GL, because it is no longer a liability.
Reversing Leave Liability on Termination
Termination liability earnings LIAB TAL HRS, LIAB TAL DYS, LIAB TLS WKS, LIAB TLS FTM and LIAB TLS PTM all have a calculation rule of Amount, where the amount is the corresponding liability earnings:
|
Earnings |
Amount = Earnings (Calc Rule) |
|
LIAB TAL HRS |
LIAB ANN HRS (Entitlement balance × Hourly Rate) |
|
LIAB TAL DYS |
LIAB ANN DAY (Entitlement balance × Daily Rate) |
|
LIAB TLS WKS |
LIAB LSL WKS (Entitlement balance × Days to Weeks formula × Attrition Bracket) |
|
LIAB TLS FTM |
LIAB LSLFTM (Entitlement balance × Days to Month formula × Attrition Bracket) |
|
LIAB TLS PTM |
LIAB LSLPTM (Entitlement balance × Days to Month formula × Attrition Bracket) |
Each earnings element has generation control GLI GC TERM ENT attached, and the generation control’s condition is the HR status of Terminated. If an employee is terminated, his or her leave balance liability earnings value becomes the termination liability earnings value for reversal.

 Page Used to Link Journal Types to GL Groupings
Page Used to Link Journal Types to GL Groupings
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
GPAU_JOURNAL_TYPE |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Integration, Journal Type AUS, Journal Type |
Attach a journal type to each GL grouping. Select from Accrual, Employee Entitlement, Salary, Statistical, and Terminated EE’s Entitlement. |
 Understanding Leave Liability Reporting
Understanding Leave Liability ReportingThe data that the report process extracts for leave liability reporting can be transferred to the GL through the GLI and included in the QSP financials file.
The reports, the interface, and the QSP file depend on data that is created the same way as any other data that’s used for reports, the GLI, or the QSP file generation—by the use of Global Payroll rules.
Note. In this section, unless otherwise stated, the term reported means printed on a report, available for transfer to GLI, and available for inclusion in the QSP file.
Liability and absence history are calculated and reported to assist in the administration of employee absences and leave. They are used to identify trends in absence and for costing purposes.
Note. Absence history and its associated report are not part of the GLI functionality.
See Global Payroll for Australia: Additional Reports.
Liability is reported for annual leave accrued in hours, annual leave accrued in days, and long service leave accrued in weeks and months. The values are calculated as earnings: LIAB ANN HRS, LIAB ANN DAY, LIAB LSL WKS, LIAB LSLFTM and LIAB LSLPTM. These earnings do not contribute to accumulator AUS GROSS.
When you run the liability report, the parameters include the element category. Earnings LIAB ANN DAY and LIAB ANN HRS are category ANN and LIAB LSL WKS, LIAB LSLFTM and LIAB LSLPTM are category LSL. Entitlement ANN ENTHPH does not currently have a corresponding leave liability earnings created and therefore will not be included in the report. The category value is assigned as a variable LVE VR CATEGORY entered as a supporting element override for each earning.
This section discusses how the following leave liability events are calculated:
Annual leave liability for hourly accrual.
Annual leave liability for daily accrual.
Long service leave liability for weekly accrual.
Long service leave liability for monthly accrual.
Leave liability reversal when the cost center changes.
Note. The term pro rata refers to accrued leave that the payee may or may not be entitled to take. Pro rata becomes entitlement on an anniversary, usually of the payee’s hire date. Entitlement refers to leave that the payee is entitled to take and that may have once been pro rata leave. This PeopleBook makes this distinction because both entitlement and pro rata are referred to as entitlement in the system.

 Annual Leave Liability Calculation for Hourly Accrual
Annual Leave Liability Calculation for Hourly AccrualThe calculation rule for LIAB ANN HRS is Unit × Rate, where:
Unit = Accumulator ANN ENTHRS_BAL
Rate = System element HOURLY RT

 Annual Leave Liability Calculation for Daily Accrual
Annual Leave Liability Calculation for Daily AccrualThe calculation rule for LIAB ANN DAY is Unit × Rate, where:
Unit = Formula LVL FM ANN DYS VAL
Rate = System element DAILY RT
The formula LVL FM ANN DYS VAL adds the values of two accumulators, the day’s entitlement balance, and the day’s pro rata balance, ANN ENTDYS_BAL and ANN PRODYS_BAL.

 Long Service Leave Liability Calculation for Weekly Accrual
Long Service Leave Liability Calculation for Weekly AccrualThe calculation rule for earning LIAB LSL WKS is Unit × Rate × Percent, where:
Unit = Formula LVL FM LSL WKS VAL
Rate = Formula AUS FM DAYS TO WKS
Percent = Bracket LVL BR LIAB ATT
Formula LVL FM LSL WKS VAL calculates the units of leave that the payee has by adding the Long Service Leave entitlement balance (accumulator LSL ENTWKF_BAL) to the Long Service Leave pro rata balance (accumulator LSL PROWKF_BAL).
Formula AUS FM DAYS TO WKS—the earning’s rate—resolves to the payee’s pay per week by multiplying his or her FTE (from the Job record) by the variable AUS VR WKLY VAL (set to 5.00; that is, a week is five days) by the employee’s daily rate.
Bracket LVL BR LIAB ATT—the earning’s percentage—returns a value based upon the payee’s years of service and the attrition rates that apply. That is, for example, only 50 percent of payees who have five years of service will stay long enough to qualify for long-service leave.
This table lists the delivered values:
|
After Number of Years of Service |
Estimated Percentage of Payees Who Will Stay to Qualify for LSL |
|
5 |
50 |
|
8 |
75 |
|
10 |
100 |
The search key for the bracket is the formula LVL FM DUR IN YRS, which resolves the number of years the payee has served. The formula divides duration LSL DR DYS FR HIRE by the variable LVL VR DAY IN YEAR (set to 365.25) to convert the duration in days to a number of years.
The duration’s From date is LVE FM ACCR ST DT, which determines whether to use the payee’s hire date or rehire date in calculating the days of service (it uses rehire date if it is later than hire date). The duration’s To date is the period end date.
After determining the number of years of service, the bracket can return the value to use as the percentage in the earning’s calculation rule.
After the three earnings are calculated their values are available for reporting, passing to GL by the GLI, or including in the QSP file.

 Long Service Leave Liability Calculation for Monthly Accrual
Long Service Leave Liability Calculation for Monthly AccrualThe calculation rules for earnings LIAB LSLFTM and LIAB LSLPTM, the monthly full and part accruals, are Unit × Rate × Percent, where:
Unit = Formula LVL FM LSL MTHFTV and LVL FM LSL MTHPTV, respectively
Rate = Formula AUS FM DAYS TO MTH
Percent = Bracket LVL BR LIAB ATT
Formula LVL FM LSL MTHFTV calculates the units of leave that the payee has by adding the Long Service Leave entitlement balance (accumulator PSH LSLENTFT_BAL) to the Long Service Leave pro rata balance (accumulator PSH LSLPROFT_BAL) for the Full Time leave.
Formula LVL FM LSL MTHFTV and LVL FM LSL MTHPTV calculates the units of leave that the payee has by adding the Long Service Leave entitlement balance (accumulator PSH LSLENTPT_BAL) to the Long Service Leave pro rata balance (accumulator PSH LSLPROPT_BAL) for the Part Time leave.
Formula AUS FM DAYS TO MTH—the earning’s rate—resolves to the payee’s pay per month by multiplying his or her FTE (from the Job record) by the variable AUS VR MTHLY VAL (set to 30.00; that is, a month is thirty days) by the employee’s daily rate.
The attrition rates bracket is the same as that used in the LSL weekly accrual.
See Also
Long Service Leave Liability Calculation for Weekly Accrual
Global Payroll for Australia Reports

 Leave Liability Reversal When the Cost Centre Changes
Leave Liability Reversal When the Cost Centre ChangesThe Leave Entitlements process determines if there is a change of ChartField for each employee—where ChartFields represent cost centres such as department and pay group. When the program detects a change, it reverses the liability from the centre storing the processed liability and sends the full amount of the new (unprocessed) liability (not the difference) to the new cost centre.
 Calculating State Payroll Tax Liability
Calculating State Payroll Tax LiabilityTo set up calculation of state payroll tax liability, use the Sal Pkg Payroll Tax Rates AUS (GPAU_PYTX_RT_TBL) component.
Payroll tax liability is calculated and becomes earning PYRL TX PROV for mapping to the GL, as for any other earnings. Array GLI AR PYTX RT, with its processing formula GLI FM CHK STATE, determines an employee’s state and payroll tax rate. The rate is multiplied by the accumulator GLI SPT PROVISION, the members of which are the earnings and deductions liable for payroll tax.
Note. You need to ensure that all earnings and deductions liable for state payroll tax are in the GLI SPT PROVISION accumulator.
This is only a provision for GL reporting, not actual State Payroll Tax amounts.
This section lists the page used to calculate state payroll tax liability.
See Also
Setting Up and Viewing Salary Packaging Tax Options
Setting Up State Payroll Tax Reporting
Reporting State Payroll Tax Liabilities

 Page Used to Calculate State Payroll Tax Liability
Page Used to Calculate State Payroll Tax Liability
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
PKG_PYTX_RT_TBL |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Taxes, Sal Pkg Payroll Tax Rates AUS, State Payroll Tax or Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Compensation, Salary Packaging AUS, State Payroll Tax Rates, State Payroll Tax |
Maintain the tax rates state by state. The GLI needs the percentages to calculate the state payroll tax (SPT) provision. |
 Running the GLI or QSP Process
Running the GLI or QSP ProcessThis section provides an overview of GLI and QSP processes and discusses how to run the General Ledger process.

 Understanding GLI and QSP Processes
Understanding GLI and QSP ProcessesThe Calculate phase of GLI processing populates the GP_GL_DATA table. The Leave Entitlement process uses the Leave Entitlement Application Engine process (GPAU_LVE_ENT) to compare previous entitlement liability to current entitlement liability and load the difference into GP_GL_DATA. The GLI/QSP Application Engine process (GPAU_QSP_GLI) manages the payroll data and generates the QSP flat file.
You can also run The GL Mapping Application Engine process (GPAUS_GL_MAP) that updates ChartFields in GP_GL_DATA. The process selects and updates the necessary GP_GL_DATA records with specified ChartField overrides. When you run the GL Interface Finalize process, the data is summarized by using your selected (remapped) ChartFields for correct account mapping.
Note. You need to have already finalized your payroll to obtain up-to-date entitlement balances—upon which the liability calculation is based—for annual leave and long service leave.
After you have updated the GP_GL_DATA table, you can complete the standard core GLI process by running the Finalize process or you can generate the QSP file by running the QSP File Create process.

 Pages Used to Run the GLI or QSP Process
Pages Used to Run the GLI or QSP Process
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
GPAU_GL_PREPARE |
Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Time and Labor / GL Costs, Send Costs to GL AUS, Run General Ledger |
Initiate the processes for calculation of GL data, leave entitlement, QSP flat file creation, finalization of the GLI, and statistical data updating. |
|
|
GPAU_GL_INQUIRY |
Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Time and Labor / GL Costs, Review GL Costing Info AUS, Ledger Transaction |
View GL costing data. |

 Running the General Ledger Process
Running the General Ledger Process
Access the Run General Ledger page.
Note. The differences between this page and the page that you access by selecting Compensate Employees, Manage Payroll Process, Process are the three additional processing phases and options: Chart Field Remap, Leave Entitlement, and QSP File Create.
|
Chart Field Remap |
Select to enable the ChartField Remap Application Engine process (GPAUS_GL_MAP) when running the General Ledger process. This run control page enables you to run an Application Engine process that updates ChartFields in GP_GL_DATA. The program selects and updates the necessary GP_GL_DATA records with specified ChartField overrides. When you run the GL Interface Finalize process, the data is summarized by using your selected (remapped) ChartFields for correct account mapping. |
Running the ChartField Remapping Process
The ChartField remapping process:
Uses specified ChartField overrides and updates the GP_GL_DATA records.
Enables the GL Interface Finalize process to correctly summarize transactions by using your selected combination of ChartFields, grouping codes, and account values.
You run the new Application Engine process as part of the standard General Ledger Interface process in the following sequence:
Ensure that the GL Calculate phase is complete.
Run the new Application Engine process to perform department remapping.
You run the remap before the leave entitlement process. If you alter the remap, you must always rerun the calculate process. You can’t rerun the remap process until you have run the calculation process.
Ensure that the GL Leave Entitlement phase is complete.
Run the GL Finalize process.
Note. This process runs as a separate process and is not integrated into existing Application Engines. In this way, it does not affect the existing GLI.
The Journal Name field is used when you select QSP File Create. The journal name is a user-defined and entered value, which is included in the QSP file header.
The following table shows which processes apply:
|
Process or Phase |
PeopleSoft GL |
QSP GL |
|
Calculate |
Y (yes) |
Y |
|
Leave Entitlement |
Y |
Y |
|
QSP File Create |
N (no) |
Y |
|
Finalize |
Y |
N |
|
Update Statistics |
Y |
Y |
Note. The QSP File Create phase includes some of the GLI Finalize phase processing so that you do not have to finalize after creating the QSP flat file.
 Remapping ChartFields After Initial Calculation
Remapping ChartFields After Initial CalculationTo remap ChartFields, use the GL Chartfield Remapping AUS (GPAU_GL_MAP) component.
Global Payroll for Australia enables you to define ChartField remapping data used during the General Ledger (GL) interface process and post payroll costs to differing levels of ChartFields based on GL groupings codes or accounts. You set up GL ChartField parameters that enable you to remap default ChartFields after you run the initial Calculate process. For example, you might require that a higher level of ChartFields be attached to each of your account codes. Instead of using multiple departments for each account code, you may require one global ChartField level, which covers all departments.
This section discusses how to remap ChartFields.

 Page Used to Remap ChartFields After Initial Calculation
Page Used to Remap ChartFields After Initial Calculation
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
GPAU_GL_MAP |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Integration, GL Chartfield Remapping AUS, GL Chartfield Remap |
Set up GL ChartField parameters that enable you to remap ChartFields after you run the initial Calculate process. You can configure and maintain GL remapping data. Enables you to set up different levels of ChartFields based on GL groupings codes or accounts. |

 Remapping ChartFields
Remapping ChartFieldsAccess the GL Chartfield Remap page.
Chartfields
ChartFields represent attributes of a payee, such as department, company, or employee ID. When you send a payee's earnings, deductions, or accumulator amounts to General Ledger, you can also transmit the values that are associated with your specific combination of ChartFields for the payee.
|
Chartfields to be passed to GL |
A field appears for each ChartField that you set up on the Mapping page in Global Payroll. Use the specific ChartFields check boxes to prevent the system from sending particular ChartFields to the GL. During mapping, ChartFields can be used to cost to different account codes. You can then elect not to send the ChartFields to the GL and only send the values to the accounts. When integrating Global Payroll with General Ledger, you can remap ChartField values to a business unit's GL account numbers. To enter the new, remapped ChartField value, use the Transformed Values tab. |
Chartfield Transformations
The default ChartFields values appear in the fields on the ChartFields tab. To remap the default settings, select the new values on the Transformed Values tab.
Chartfields and Transformed Values
|
Account |
Displays the GL account number to which your ChartFields and grouping codes will map. |
|
Grouping Code |
Select the code to map to the GL account. This is the grouping code for the elements that are included in the GL transfer. A grouping comprises entry types of earnings, deductions, or segment accumulators. Elements must be in groups before they can be processed by General Ledger. Instead of entering earnings individually, you bundle them into one accumulator and create a grouping code for that accumulator. |
See Also
Integrating with PeopleSoft Enterprise General Ledger