(JPN) Using PeopleSoft Asset Management Options to Meet Japanese Requirements
This topic discusses how to use PeopleSoft Asset Management options to meet Japanese requirements.
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
|
Advanced Depreciation Page |
RUN_AMAD1000 |
Specify report request parameters to generate the advanced Depreciation Amount or Advanced Depreciation Reversal Schedule report. |
|
Owner Information Page |
OWNER_INFO_DEFN |
Enter owner information that is printed on the Depreciable Asset Tax Return (Tax Roll) report. |
|
Depreciation Rate-User Defined Page |
UD_DEPR_RATE_TBL |
Set up useful life and depreciation rate tables. |
|
Life and Rate Information Page |
MR_AM_LIFERATE |
Set up useful life and depreciation rate tables. |
|
AM_EXTENDED_DEPR |
Search for candidate assets according to desired parameters. Select to extend or not extend the depreciation period, remove from the list and enter the dates to resume depreciation. |
|
|
Return Information Page |
RETURN_INFO_DEFN1 |
Enter information that is required for the Depreciable Asset Tax Return (Tax Roll) report. |
|
Local Tax Return Page |
LTAX_ADD_INFO_SEC |
Enter local tax information when you acquire depreciable fixed assets. |
|
NBV - Assessment Calculation Page |
AMLTPROC_RQST |
Run an SQR process to load asset data and calculate the theoretical net book value and assessment value for each asset. (Theoretical NBV is not needed since 2009, but still available for historical reporting). |
|
Local Tax Information - Adjustment |
LTAX_ADJ_01 |
Change the theoretical net book value and assessment value. (Theoretical NBV is not needed since 2009, but still available for historical reporting). |
|
Local Tax Report Page |
RUN_LTAXPROCESS |
Run local tax reports for Japan. |
|
Local Tax Information |
LTAX_COST_01 |
Change the local tax office where the return is filed and the asset return type. |
|
Extended Depreciation Report |
RUN_AMED1000 |
Run the Extended Depreciation report to analyze the Tangible/Straight Line and Tangible/Declining Balance asset depreciation in compliance with Japanese tax law, as reformed. |
|
National Tax |
RUN_AMNT1000 |
Run a report of the depreciation calculation details to be reported to the Japanese Tax Office. The report includes all required information for the National Depreciable Asset Tax Return Beppyo 16(1), (2) in Japan. |
Many of the features for processing assets for Japan are dependent on the business unit information definitions established at the business unit level. You must establish these business unit definitions in order to complete processing for Japanese requirements.
Access the Business Unit Info for Japan page from the AM Business Unit Definition component Click the JPN Info link.
Note: To enable the JPN Info link, you must set up the overall options for user preferences in the Common Definitions component: Set the Localization Country value to JPN (Japan).
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Corporate Book for Japan |
Select the corporate book for Japan. |
Tax Book for Japan |
Select the tax book for Japan. |
Memorandum Amount and Currency |
Enter the memorandum amount at the end of the useful life of the asset as required by the Japanese tax regulation. This value can be updated, as the law requires. This value is used in conjunction with the following depreciation methods: J6 - Tangible Declining Balance, J7 - Tangible Straight Line, and Japan Extended Straight Line. The memorandum amount reflects the currency of the tax book for Japan as the default. For books that use one of the aforementioned depreciation methods in a currency other than JPY, the memorandum amount is translated to the respective book's currency. The memorandum value is established for each asset business unit. |
Advanced Depreciation |
Select if advanced depreciation is used. |
Japan Composite |
Select if composite assets are used. |
Use JPN Local Tax (use Japan local tax) |
Select if local tax reporting is enabled. |
See Business Unit info for Japan Page.
The following steps are recommended when implementing Japanese tax reform changes:
Establish the memorandum amount on the Business Unit Info for Japan page.
Verify that the proper and most current depreciation rates, guaranteed rates, and revised rates are represented on the Life and Rate information secondary page [MR_AM_LIFERATE].
Select the appropriate depreciation methods at the asset profile level or override them at the asset level.
Use the Extended Depreciation Worksheet to select the eligible assets for extended depreciation. As an alternative to the Extended Depreciation Worksheet, you can extend depreciation manually, asset by asset, from the Define Tax/Depr Book page.
Run the Transaction Loader process prior to calculating depreciation and closing. However, this step is not necessary if you have manually extended depreciation from the Define Tax/Depr Book page.
PeopleSoft Asset Management supports depreciation methods that are used in Japan for both fixed assets and leased assets.
Fixed Assets
This table shows depreciation methods, the calculations used by the methods, and the types of assets to which these methods are applied:
|
Asset Depreciation Method |
Asset Depreciation Method Translate Value |
Depreciation Calculation |
|---|---|---|
|
Changes 200/250 Declining Balance to Straight Line (Changes 200/250 DB to SL) |
J9 |
This depreciation method is used to convert the calculation method of assets using declining balance depreciations 200 (J8) and 250 (J6) to a straight line method. The calculation for this method is: (Beginning net book
value at method change) * straight line depreciation rate (based on
useful life, in years)
This method adapts the depreciation rate based on useful life (years). This method is determined by regulations instead of the rate based on useful life for salvage year. |
|
Changes Declining Balance to Straight Line 200 (Changes DB to SL 200) |
J8 |
For assets placed in service on or after April 1, 2012 the calculation is: If (beginning net book
value * declining balance depreciation rate of 200 percent) < (beginning
net book value * guaranteed rate per Japanese law) then, switch to
straight line method using the revised rate.
Note: Guarantee rates and revised rates are derived from the Life and Rate Information page for the Tangible/Declining Balance depreciation method. The final year's depreciation is the annual depreciation amount less the memorandum value (no salvage value). Understanding Depreciation Processing |
|
Changes Declining Balance to Straight Line 250 (Changes DB to SL 250) |
J6 |
For assets placed in service on or after April 1, 2007 and prior to April 1, 2012: If (beginning net book
value * declining balance depreciation rate of 250 percent) < (beginning
net book value * guaranteed rate per Japanese law) then, switch to
straight line method using the revised rate.
Note: Guarantee rates and revised rates are derived from the Life and Rate Information page for the Tangible/Declining Balance depreciation method. The final year's depreciation is the annual depreciation amount less the memorandum value (no salvage value). See Understanding Depreciation Processing |
|
Extended Straight Line (Extended/Strt Line) |
JE |
This depreciation method is used for fully depreciated assets under Tangible/Straight Line and Tangible/Declining Balance methods that are subject to an extended depreciation useful life of five years using a Straight Line depreciation method starting from the first period of the following fiscal year. The basis for this extended depreciation is the original 5 percent salvage value. There is no salvage value for the new round of depreciation but the memorandum value is taken from the business unit definition. |
|
Lease Depreciation |
J4 |
Declining balance depreciation
calculation result * 10/9.
|
|
Intangible/Straight Line (Intangible/Strt Line) |
J3 |
Acquisition cost * straight
line depreciation rate based on useful life (years)
|
|
Tangible/Declining Balance (Tangible/Declining Bal) |
J1 |
For assets placed in service prior to April 1, 2007: Beginning net book value
* declining balance depreciation rate based on useful life (years)
|
|
Tangible/Straight Line (Tangible/Strt Line) |
J2 |
For assets placed in service prior to April 1, 2007 the calculation used is: (Acquisition cost −
10% of acquisition cost) * straight line depreciation rate based on
useful life (years).
|
|
Changes Declining Balance to Straight Line (Changes DB to SL) |
J5 |
This depreciation method is used to convert the calculation method of assets using declining balance depreciation (J1) to a straight line method. This depreciation method adapts the depreciation rate based on useful life (years), and is determined by regulations instead of the rate based on useful life for salvage year. The calculation for this method is: (Beginning net book
value at method change – 10% of acquisition cost) * straight line
depreciation rate (based on useful life, in years)
|
|
Tangible/Straight Line Revenue (Tangible/Strt Line Rev) |
J7 |
For assets placed in service on or after April 1, 2007 the calculation used is: Cost basis * straight
line rate effective on or after April 1, 2007.
Note: The straight line rates are derived from the Life and Rate Information page for the Tangible/Straight Line Revenue (J7) depreciation method. The final year's depreciation is the annual depreciation amount less the memorandum value (no salvage value). See Understanding Depreciation Processing |
Depreciation Rate - User Defined – Life and Rate Information Page
PeopleSoft Asset Management supports useful life in years as specified for Japan. This is applied from the Rate-User Defined table (UD_DEPR_RATE_TBL, MR_AM_LIFERATE) in the Depreciation Rate-User Defined component. To apply the appropriate depreciation rates, use the delivered depreciation methods for Japan or add new ones as needed.
Use the Depreciation Rate-User Defined page (UD_DEPR_RATE_TBL) to set up useful life and depreciation rate tables.
Navigation:
Select a setID and a depreciation method code matching the depreciation method to be used. Enter the effective date, and click the Life and Rate Information button. The Life and Rate Information page displays.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Life and Rate Information page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
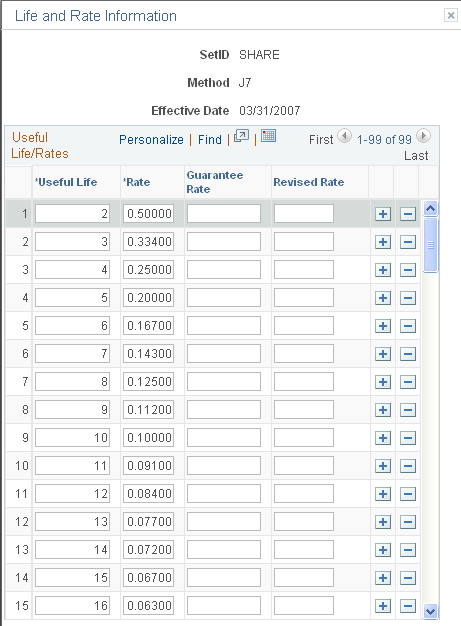
Enter the useful life and corresponding rates as determined by regulations issued from the Ministry of Finance. The Guarantee Rate and Revised Rate fields are only used in the Tangible/Declining Balance depreciation method.
Note: Useful Life rates also use the Residual Rate Definition.
Leased Assets
PeopleSoft Asset Management supports the Declining Balance Depreciation Method - Finance Lease (excluding transfer of ownership) 10/9 method, which is calculated in this way:
Use the Life and Rate Information page ( MR_AM_LIFERATE) to set up useful life and depreciation rate tables and to modify rates for the lease depreciation method.
Navigation:
Example Values
This table shows the values used in an example using the Declining Balance Depreciation Method - Finance Lease (excluding transfer of ownership) 10/9 method:
|
Acquisition Cost |
1,000,000 |
|
Useful Life |
5 years |
|
Depreciation Rate |
0.369 |
Calculation Results for Example Values
Using the values from the previous table and applying the Declining Balance Depreciation Method (J6) - Finance Lease (excluding transfer of ownership) 10/9 method, the results are:
|
Year |
Depreciation Amount by Declining Balance Method |
Depreciation Amount by 10/9 Method |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
369,000 |
410,000 |
|
2 |
232,839 |
258,710 |
|
3 |
146,921 |
163,245 |
|
4 |
92,707 |
103,007 |
|
5 |
58,588 |
65,038 |
|
Total |
900,000 |
1,000,000 |
Select the example depreciation methods on the Book-Tax page in the Asset Book Definition component, the Depreciation page in the Asset Profiles component, or the Depreciation Information page in the Asset ExpressAdd component.
Use the Extended Depreciation Worksheet page (AM_EXTENDED_DEPR) to search for candidate assets according to desired parameters.
Select to extend or not extend the depreciation period, remove from the list and enter the dates to resume depreciation.
Navigation:
The 2007 Japanese Tax Reform affects not only assets that are placed in service after March 31, 2007 but also increases the depreciation basis and expands the depreciation period for those fully depreciated assets that are using the Tangible/Straight Line and Tangible/Declining Balance depreciation methods. As a result, those depreciable assets acquired before April 1, 2007 are allowed, after having depreciated to the final depreciable limit, to depreciate the existing salvage value to the memorandum value of 1 JPY in five years using the Straight Line method.
Use the Extended Depreciation Worksheet to apply the extended depreciation calculation to assets after they have reached the depreciation limit under the Tangible/Straight Line and Tangible/Declining Balance depreciation methods. You can also identify assets that qualify for the extended depreciation using the Extended Depreciation Worksheet.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Extended Depreciation page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
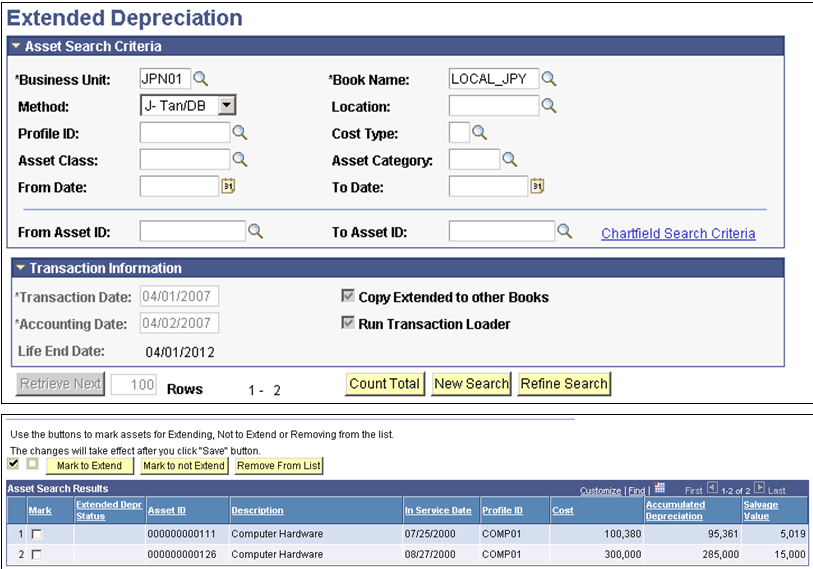
Enter the required fields Business Unit, Book Name, and Method to retrieve assets that are candidates for extended depreciation (those assets depreciated using the Tangible/Straight Line and Tangible/Declining Balance methods and are fully depreciated up to 95% of asset cost). You can also search by ChartField by clicking the ChartField Search Criteria link or use a date range to retrieve assets whose original transaction dates fall within the given period.
The Transaction Information section relates to the information needed to perform the extension of the asset useful life. It is applicable to the assets in the Results section. The Transaction Date should match the date that depreciation resumes for extended depreciation. The Life End Date field shows the calculated date in which the depreciation activity stops, including the additional period due to rounding down the remaining depreciation.
Note: It is important to run the Depreciation Reporting Table load process (AMDPREPT) as a prerequisite to retrieve fully depreciated assets from the Extended Depreciation page.
PeopleSoft Asset Management supports special depreciation (initial and accelerated) and increased depreciation used in Japan. This table shows the types of special depreciations and their associated accounting methods, depreciation calculations, and additional notes as appropriate:
|
Depreciation Method |
Type |
Accounting Method |
Depreciation Calculation |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Special |
Initial |
Expense |
Acquisition cost * special
depreciation rate
|
Book the initial special depreciation amount as the depreciation amount, and add it to the standard depreciation amount. |
|
Special |
Initial |
Reserve/Allowance |
Acquisition cost * special
depreciation rate
|
Do not add the initial special depreciation amount to the standard depreciation amount. |
|
Special |
Accelerated |
Expense |
Standard depreciation
amount * accelerated depreciation rate
|
Book the accelerated depreciation amount as the depreciation amount, and add it to the standard depreciation amount. |
|
Special |
Accelerated |
Reserve/Allowance |
Standard depreciation
amount * accelerated depreciation rate
|
Do not add the accelerated depreciation amount to the standard depreciation amount. |
|
Increased |
NA |
NA |
Standard depreciation
amount * increased depreciation rate
|
For the initial special depreciation and accelerated depreciation rate, specify the useful life in years and the depreciation rate on the Depreciation Terms Definition page.
For the increased depreciation rate, enter the specific rate on the Depreciation Details page.
See Understanding How PeopleSoft Asset Management Calculates Depreciation.
You can also use advanced depreciation for Japan. This table shows the accounting methods that you can use with advanced depreciation:
|
Accounting Method |
Action |
|---|---|
|
Expense |
Adds a cost line to the Corporate and Tax book for the advanced depreciation amount and enters a negative (–) cost as a compressed amount on the Asset/Cost Adjust Transfer page. |
|
Allowance |
Adds a cost line to the Corporate and Tax book for the advanced depreciation amount and enters a negative (–) cost as a compressed amount on the Asset Cost/Adjust Transfer page. You must select A (allowance) as the cost type. |
|
Reserve |
Adds a cost line to the Corporate and Tax book for the advanced depreciation amount and enters a negative (–) cost as a compressed amount on the Asset Cost Adjust/Transfer page. You must selectR (reserve) as the reserve method. |
Advanced Depreciation Reports
Use the Advanced Depreciation page (RUN_AMAD1000) to specify report request parameters to generate the advanced Depreciation Amount or Advanced Depreciation Reversal Schedule report.
Navigation:
When you adopt the advanced depreciation method by using the Allowance or Reserve method, you can verify the allowance or reserve amount for the compressed amount by using the Advanced Depreciation Amount of Advanced Depreciation Reversal Schedule report.
Composite depreciation, as practiced in Japan, is supported by calculating the useful life in years or by using the 5 percent retirement method.
Use the Run Mass Transactions page to process composite depreciation for Japan.
Navigation:
Note: To use the Composite Depreciation method for Japan, you must specify the Corporate and Tax book for Japan and select Japan Composite when you establish asset management business units.
You can add composite depreciable assets and individual assets by using the Asset Basic Information page. When you add composite depreciable assets, you must enter a profile ID, transaction date, and accounting date, and then click the Capitalize button on the Asset Acquisition Details page. When you add individual assets, you must enter the Reporting Lifein periods on the Asset Information page.
After adding composite depreciable assets and individual assets for composite assets, you must capitalize by using the Mass Transaction CC-JPN Capitalize Composite.
Calculating the Automatic Useful Life in Years for Composite Depreciable Assets
The total acquisition cost includes the acquisition cost of each composite member asset divided by its respective useful life, calculating the depreciation amount for each composite member asset.
The acquisition costs of each composite member asset are then summed, and the total is divided by the summed depreciation amounts for each composite member asset.
This table displays the depreciation values calculated to find the total depreciation for 20,000,000 of asset costs:
|
Assets |
Acquisition Cost (A) |
Useful Life (B) |
Depreciation Amount (A)/(B) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Asset1 |
1,000,000 |
4 years |
250,000 |
|
Asset2 |
3,000,000 |
5 years |
600,000 |
|
Asset3 |
4,000,000 |
4 years |
1,000,000 |
|
Asset4 |
7,000,000 |
10 years |
700,000 |
|
Asset5 |
5,000,000 |
8 years |
625,000 |
|
Totals |
20,000,000 |
NA |
3,175,000 |
The calculation of composite depreciation useful life is then:
Using the 5 Percent Retirement Method
When using this method, depreciable composite member assets are retired, and the book value is 5 percent of the acquisition cost of each member asset retired.
Composite member assets can be retired by using the mass transaction CR-JPN Composite Retirement.
Japanese accounting principles require that assets that are offered as collateral be treated according to financial reporting regulations under commercial law. Collateral assets are identified on the Cost/Asset Information page in the Asset ExpressAdd component as one of these types in compliance with Japanese reporting requirements:
Factory Foundation Mortgage.
Fixed Mortgage.
Mortgage.
Other.
Rounding options are applied to depreciation calculations and asset salvage values. You can select rounding options to be used for depreciation calculations on the Business Unit/Book Definition page in the Establish Business Units - Asset Management Definition component, and for salvage value calculations on the Depreciation page in the Asset Profiles component.
Select a rounding rule, which determines the type of rounding that is performed. Select the Currency rounding type.
Select the rounding precision, rounding factor, and truncation. Round precision is the number of places to the right or left of the decimal point to which the amount or number is rounded. Rounding factor is the number to which the amount is rounded.
Asset Management supports reporting requirements defined by Japanese local tax laws. The system provides these reports, including all required information for the local depreciable asset tax return:
Depreciable Asset Tax Return (Tax Roll or Depreciable Assets) report (AMLT1000).
Asset Detail (Increased Assets/All Assets) report (AMLT1100).
Asset Detail (Decreased Assets) report (AMLT1200).
Use the Owner Information page (Processing Local Tax ReportsOWNER_INFO_DEFN) to enter owner information that is printed on the Depreciable Asset Tax Return (Tax Roll) report.
Navigation:
Use the Return Information page (RETURN_INFO_DEFN1) to enter information that is required for the Depreciable Asset Tax Return (Tax Roll) report.
Navigation:
To set up local tax reporting:
Define the localization country as Japan.
This enables the business unit information link for Japan. The link appears in the Establish Business Units component. Use the User Preferences component, and set the overall preferences localization country to JPN.
Define business unit information for Japan.
This defines the corporate and tax default books for Japan, as well as enables advanced depreciation, composite asset functionality, and local tax usage. Specify the corporate and tax book that you use for Japan when you establish asset management business units, and select the Use JPN Local Tax check box.
Define owner information definition for Japanese assets.
This defines the information needed to process your local tax return.
Define local tax information in the Asset Information component.
Define the local tax return processing information.
To run the reports:
Process the theoretical net book value and assessment value calculation. (Theoretical NBV is not needed since 2009, but still available for historical reporting).
Process local tax reports.
Defining Local Tax Return Information
Use the Return Information page to define local tax return information.
Navigation:
.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Return Information Defn. - JPN page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
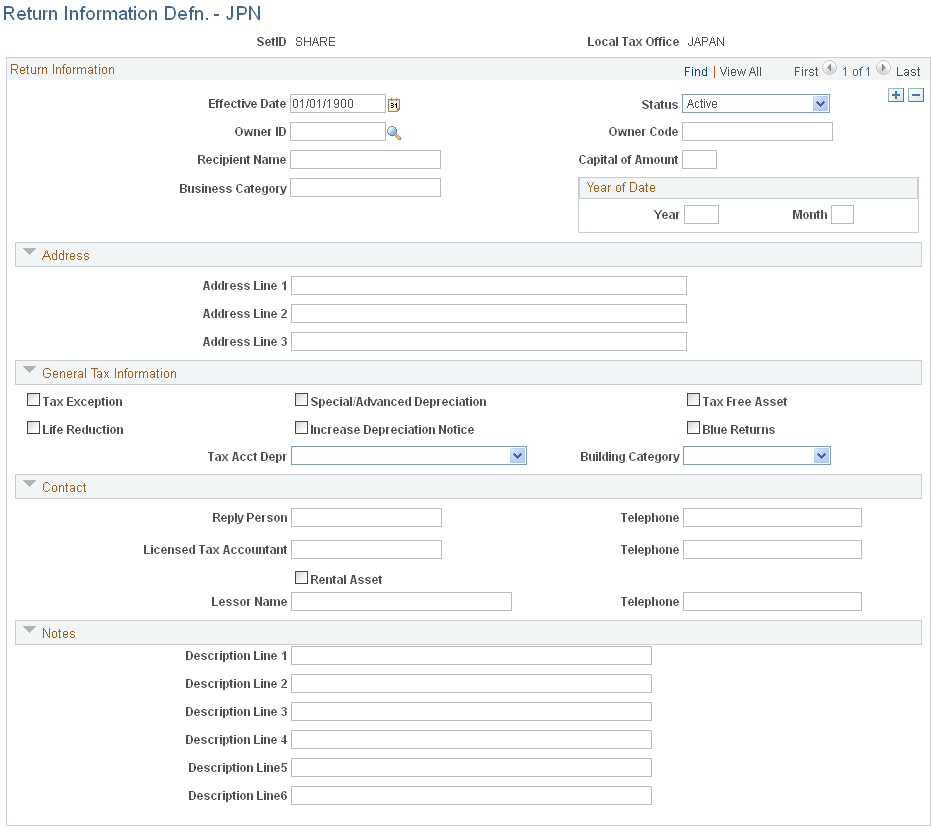
Select an owner ID. Enter an owner code, capital amount (in millions of yen), recipient name of the taxation office where the return is filed, business category, and the year and month that the company commenced business.
Enter address information for up to three branch offices within the same city, district, or town (place of tax payment).
Note: If a branch office is located at the same address that is defined on the Owner Information page, you can leave these fields blank.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Tax Exception |
Select if you have assets to apply to the special treatment of the taxation standard. |
Special/Advanced Depreciation |
Select if you have assets to be applied to special depreciation under the Special Taxation Measures Law, or to be applied to advanced depreciation under Articles 42 to 50 and Article 142 of the Corporation Tax Law, or from Article 42 to 44 and Article 165, or Article 58 of the Tax on Income Law. |
Tax Free Asset |
Select if you have assets without taxation. |
Life Reduction |
Select if you have assets that have been applied a shorter useful life approved by the Director or the District Tax Office under the Corporate Tax Law − Govt. Order 57-1 and Tax on Income − Govt. Order 130-1. |
Increase Depreciation Notice |
Select if you have assets that have been submitted on a detailed statement for increased depreciation to the tax office under the Corporation Tax Law − Govt. Order 60 and Tax on Income Law − Govt. Order 133. |
Blue Returns |
Select if you file a blue return under the Corporation Tax Law, Article 122. |
Tax Acct Depr (tax account depreciation) |
Select a depreciation method in tax accounting. |
Building Category |
Select the possession classification of the building for the business place. |
Reply Person |
Enter the name and telephone number of the accounting representative. |
Licensed Tax Accountant |
Enter the name and telephone number of the licensed tax accountant. |
Rental Asset |
Select if you have rental assets. |
Lessor Name and Telephone |
Enter the name and telephone number of the lessor. |
Use the Notes region to add any relevant descriptions, such as appendixes or remarks, or to identify any attachments.
Entering Asset Local Tax Return Information
Use the Local Tax Return page (LTAX_ADD_INFO_SEC) to enter local tax information when you acquire depreciable fixed assets.
Navigation:
or
Define the asset as New or Used, and select a local tax office.
Select one of these asset return type options:
Structure
Machinery
Ship
Airplane
Vehicle
Tool
Specify a numerator and denominator for the exception rate.
Specify a theoretical net book value and an assessment value for your information. (Theoretical NBV is not needed since 2009, but still available for historical reporting).
Note: The Theoretical Net Book Value and the Assessment Value fields are not required when you add a newly acquired asset in the current year, but you must enter the asset's assessment value reported in the previous year if you acquired assets in the previous year but added them to Asset Management for the first time.
Calculating Theoretical Net Book Value and Assessment Value
Use the NBV - Assessment Calculation page (AMLTPROC_RQST) to run an SQR process to load asset data and calculate the theoretical net book value and assessment value for each asset.
(Theoretical NBV is not needed since 2009, but still available for historical reporting).
Navigation:
Note: Enter the same local tax office code in both fields when you are reporting to a single tax office.
The results of this process populate the LTAX_INFO1_TBL.
Running Local Tax Reports
Select a range of local tax office codes to be declared for the theoretical net book value and assessment value.
Note: Enter the same local tax office code in both fields when you are reporting to a single tax office.
Use the Local Tax Report page (RUN_LTAXPROCESS) to run local tax reports for Japan.
Navigation:
Specify a return year.
Select one of the Request Local Tax Return options:
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
All |
Include all assets. |
Increase |
Include assets added and received by transfer in this fiscal year. |
Changing the Local Tax Office and Asset Return Type
Enter the transaction date on which to change the local tax office and asset return type. Enter the new local tax office code for filing the return.
Select one of these new asset return types:
Structure
Machinery
Ship
Airplane
Vehicle
Tool
Changing the Local Tax Office and Asset Return Type While Transferring Assets
When you transfer assets, the operation process varies according to the transfer scenario. This table displays the various operation processes:
|
Transfer Scenario |
Operation Process |
|---|---|
|
Asset is partially transferred to another local tax office, or the asset return type is changed, or both. |
Use InterUnit Transfer to change the local tax office, or the asset return type, or both. |
|
Asset is fully transferred to another department ID and the local tax office where the return is filed, and the asset return type has changed. |
Use Transfer to change the local tax office or asset return type. |
|
Asset is partially transferred to another department ID and the local tax office where the return is filed, and the asset return type has changed. |
Use InterUnit Transfer to change the local tax office and asset return type. |
Asset Management supports Japanese consumption tax on asset sales by using VAT functionality on the asset Retirement page. In addition to entering VAT information, you can enter customer information for asset sales.
See VAT Page.