Defining Asset Attributes
To define asset attributes, use the following components:
To set up asset classes, use the Asset Class (ASSET_CLASS) component.
To set up lease payment schedules, use the Payment Schedule (PYMNT_SCHED_TBL) component.
To set up joint venture allocations, use the Joint Venture Allocation (JV_BUS_ALLOC) component.
To set up agencies, use the Agencies (AGENCY_DEFN) component.
To set up area definitions, use the Area Definition (AM_AREA_TBL) component.
To set up asset types, use the Asset Type Options (AM_TYPE_OPT) component
To set up asset subtypes, use the Asset Subtype (AM_SUBTYPE) component.
To set up maintenance types, use the Maintenance Types (MAINT_TYPE_DEFN) component.
To set up location definitions, use the Location (AM_LOCATION) component.
To set up hazardous-material codes, use the Hazardous Codes (ASSET_FSC_DEFN) component.
To set up insurance types, use the Insurance Types (INSURANCE_TYPE) component.
To set up units of production, use the Units of Production (UOP_DEFN) component.
To set up user-defined asset attributes, use the Asset Attribute (AM_UD_ATTR) component.
To set up asset property subclasses, use the Asset Property Subclass (AM_PROP_SUBTYPE) component.
To set up asset meter types, use the Meter Types (AM_METER_TYPE) component.
To set up asset warranties, use the Warranty Type (AM_STD_WRTY) component.
To set up warranty templates, use the Warranty Template (AM_WRTY_TMPL) component.
To set up equipment parts list, use the Equipment Parts List (AM_PART_LIST_TMPL) component.
To set up criticality codes, use the Criticality Codes (AM_CRIT_LEVEL) component.
To access these components, select
Several procedures and options are available for establishing the core tables for PeopleSoft Asset Management. As previously noted, many of these tables are optional or conditional. Some are required before you can enter assets into the system; these tables are noted as such.
This topic discusses how to define Asset Attributes.
Note: You can also set up attribute groups.
See PeopleSoft Maintenance Management Integration with PeopleSoft Asset Management.
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
|
ASSET_CLASS_DEFN |
Maintain asset classes. Asset classes are set up at the tableset level. |
|
|
VAT Defaults Setup (value-added tax defaults setup) Page |
VAT_DEFAULTS_DTL |
Specify VAT defaults setup. |
|
LEASE_SCH_ID |
Add or modify payment schedules. When adding leased assets to your system, you must have at least one payment schedule defined. |
|
|
FERC_CD_DEFN |
Establish FERC (Federal Energy Regulatory Commission) codes for asset categories that are used in regulatory reporting. |
|
|
JV_BUS_ALLOC |
Define the percentage of asset ownership to allocate to each joint venture participant. Use this page to set up the Joint Venture Allocation table. |
|
|
MAINT_TYPE_DEFN |
Define maintenance types. |
|
|
UOP_DEFN |
Set up units of production definitions. |
|
|
Load UOP and Index Tables |
RUN_AMIF2000 |
Load units of production and index tables. |
|
AGENCY_DEFN |
Create agency codes. Keep track of the registration and licenses of an asset by using the information that is set up in Agency tables. |
|
|
AM_AREA_TBL |
Define an asset area within a location. |
|
|
AM_TYPE_OPT |
Define physical asset types to be applied to individual assets. Oracle delivers ten asset types: Hardware, Software, Equipment, Property, Fleet, Machinery, Furniture, Facility, Intangible, Other. |
|
|
AM_SUBTYPE |
Define asset subtypes as they relate to asset types. For example, if the asset type is Hardware, an asset subtype may be defined for a Laptop. |
|
|
AM_UD_ATTR |
Define any asset physical attribute to be associated with an asset. |
|
|
AM_PROP_SUBCLASS |
Define property asset subclasses as they relate to asset property classes: Site, Building, Floor, Area, Space. |
|
|
ASSET_FSC_DEFN |
Define hazardous-asset codes. The PeopleSoft system is delivered with the Federal Supply Class (FSC) codes, which are U.S. federal codes that identify predominant and significant hazardous materials. You may add other classifications. |
|
|
Location Definition |
AM_LOCATION_TBL |
Set up locations. |
|
Detail |
MAINT_CONTRACT_01 |
Define the detail terms for maintenance contracts by entering the effective, expiration, and contract dates, and the contract cost and supplier information. |
|
Coverage |
MAINT_CONTRACT_02 |
Define the maintenance contract coverage, including contact information. |
|
Insurance Types |
INSURANCE_TYPE |
Enter different types of insurance, such as liability for automobiles or property. |
|
Transaction Information |
UOP_DEFN_WRK |
Generate open transactions. Each time new detail is added to this table, you can generate open transactions for each asset associated with it. |
|
Work Order Options for Components Page |
AM_WOM_OPT_SUBTYPE |
Define Work Management work order options. |
|
AM_METER_TYPE1 |
Define meter types. |
|
|
Meter Type Comments |
AM_METER_TYPE2 |
Add comments that are relevant to meter type definition. |
|
AM_STD_WRTY |
Define standard warranties. |
|
|
AM_WRTY_TMPL |
Set up templates for warranty types to apply to asset types. |
|
|
AM_PART_LIST_TMPL |
Define equipment parts lists to be associated with asset classes, groups, categories, types and subtypes, or other asset definitions. |
|
|
AM_CRIT_LEVEL |
Establish levels of criticality. |
|
|
AM_END_LIFE_RSN |
Define end of life reasons for an asset. |
|
|
EFS_ID_DEFN |
Define an external funding source for assets. |
Use the Asset Class page (ASSET_CLASS_DEFN) to maintain asset classes.
Asset classes are set up at the tableset level.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Asset Classes page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
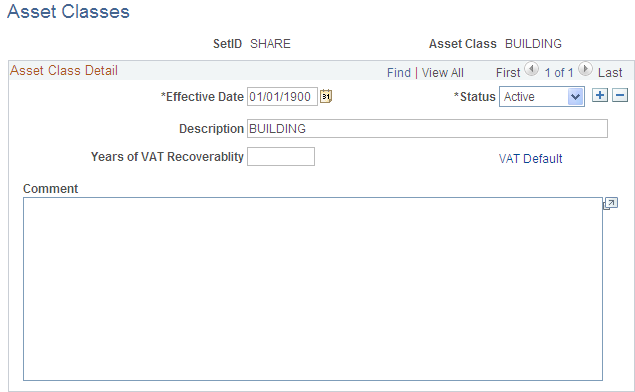
To add a new asset class, select the SetID and enter the name of the asset class. Complete the fields on the Asset Classes page as appropriate.
Use asset class to classify assets for reporting purposes. It can be used in combination with the category code to refine asset classification. For example, an executive desk is categorized as furniture and fixtures for the balance sheet. Within the broad category of furniture and fixtures, you can use an asset class code to specifically identify the asset as a desk.
For defining asset classes, Oracle provides the option to define value-added tax (VAT) processing defaults as well.
Defining Asset Class as VAT Driver
Asset class is also used as a VAT driver. Create classifications of assets based on the VAT treatment. For example, treatment of assets such as automobiles may be different from that of assets such as buildings or leases. In this way, the asset class can be used to determine the VAT treatment.
VAT defaults are also set up at the business unit level.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Years of VAT Recoverability |
Enter the number of years of VAT recoverability adjustment for the asset class. The number of years can be different from the useful life of the asset and is dictated by VAT legislation. For example, the number of years for recoverability for buildings is 20 and for all other asset classes is 5 years. |
Use the Payment Schedules page (LEASE_SCH_ID) to add or modify payment schedules.
When adding leased assets to your system, you must have at least one payment schedule defined.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Payment Schedule page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
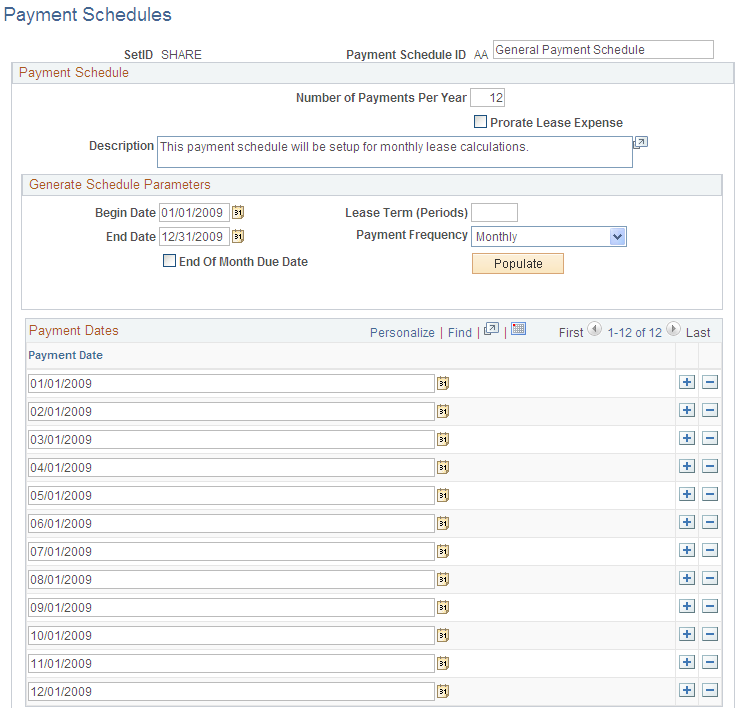
When working with leased assets, you must define payment schedules to be assigned to the leased assets.
You must have at least one payment schedule defined when working with leased assets. PeopleSoft Asset Management delivers four payment schedules in the SHARE tableset.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Prorate Lease Expense |
Select to prorate the accounting entries that are generated for lease payments by the depreciation close process on a monthly basis in accordance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). The payment schedule segregates the interest and principal for proper classification of accounting entries. |
End Of Month Due Date |
Select to always schedule the payment on the last day of the month, no matter what date is entered in the Begin Date field. |
Populate |
Click to enable PeopleSoft Asset Management to automatically enter the payment dates for the time period that you defined. Be sure to enter the number of payments per year to ensure that PeopleSoft Asset Management can determine the number of lease payments for the lease schedule. |
Use the FERC Code page (FERC_CD_DEFN) to establish FERC (Federal Energy Regulatory Commission) codes for asset categories that are used in regulatory reporting.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the FERC Code page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
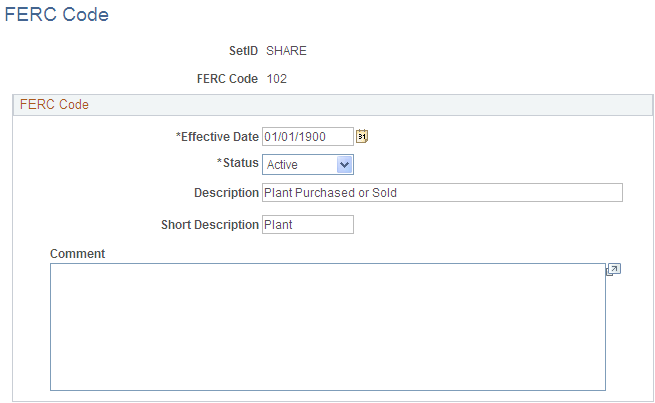
Add or update FERC codes in accordance with the U.S. Federal Energy Regulatory Commission. FERC codes are used to associate assets with the FERC Uniform System of Accounts for utilities. They are used for regulatory reporting and do not affect any calculations.
Use the Joint Venture Allocation page (JV_BUS_ALLOC) to define the percentage of asset ownership to allocate to each joint venture participant.
Use this page to set up the Joint Venture Allocation table.
Navigation:
Enter each participating business unit and its allocated percentage of equity in the shared assets. The sum of these percentages must equal 100 percent.
The joint venture allocation table affects only newly added assets. Changes made to the allocation table will not affect existing assets. To change ownership percentages of existing assets, you must run a mass change using the template that is supplied for this purpose. These joint venture mass change templates enable you to:
Add a joint venture business unit.
Remove a joint venture business unit.
Change joint venture ownership allocations.
When you have changed the assets, change the allocation table to reflect the new equity percentages.
Note: The joint venture allocation as defined in the allocation table need not match the actual ownership percentages. For example, if two companies enter a joint venture on a 60/40 basis, one of them can sell the joint venture asset on a 70/30 basis—effectively giving one party a discount while the other pays a premium. In this case, you would first enter the asset at the joint venture business unit level, then change the cost apportionment by using mass change.
Use the Maintenance Types page (MAINT_TYPE_DEFN) to define maintenance types.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Maintenance Types page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
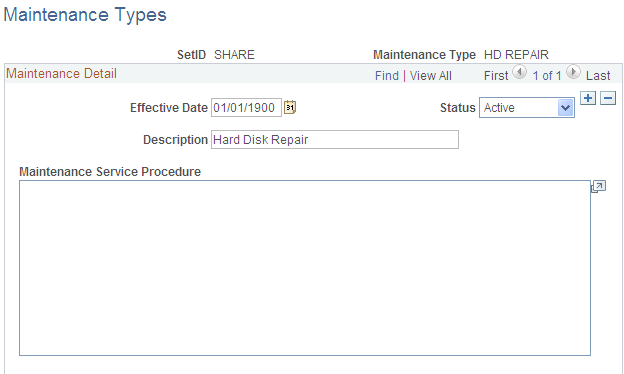
Maintenance types identify the type of maintenance and maintenance procedures to follow for a particular asset. For example, you might establish a Tune Up maintenance code that specifies routine maintenance for an automobile.
See Understanding Asset Maintenance, Repair, Warranties, and Insurance.
Use the Units of Production page (UOP_DEFN) to set up units of production definitions.
Navigation:
When you depreciate assets by using the units of production method, you must set up units of production definitions. This table defines the maximum units that an asset can produce and how many units have been posted for each period.
Adding and Adjusting Units of Production Detail Page
Access the Transaction Information page.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Transaction Date |
Reflects the date on which you made the changes. |
Accounting Date |
Reflects the date on which the entered changes will affect your general ledger. |
Both dates are used in recalculating depreciation. The difference between the transaction date and the accounting date determines whether production detail for this transaction will be posted as accumulated production.
The difference between the transaction date and the accounting date determines whether any prior period production needs to be posted. For example, consider a machine that was acquired and placed in service on March 15, 2008 but did not get entered in PeopleSoft Asset Management until August 1, 2008. All general ledger periods prior to August are closed. In this case, PeopleSoft Asset Management automatically posts any accumulated production to the general ledger in August.
Unlike accumulated depreciation, accumulated production is posted exactly the same as any other production detail. Nothing distinguishes it as accumulated production.
Accumulated production for a new units of production ID should be posted on a date that is before any assets associated with the units of production ID are added.
You will periodically update the information in your Index and Units of Production tables when you receive new information. You can load or update the Index and Units of Production tables automatically using the AMIF2000. This process takes data in a fixed length format ASCII file and loads it into the appropriate table.
Files to be loaded into the Index table should be in this format:
|
Field |
Length |
|---|---|
|
SETID |
5 |
|
INDEX_NAME |
20 |
|
EFFDT |
8 (MM/DD/YY) |
|
DESCR |
30 |
|
INDEX_DETAIL_NAME |
35 |
|
INDEX_AMOUNT |
15 |
Files to be loaded into the Units of Production table should be in this format:
|
Field |
Length |
|---|---|
|
SETID |
5 |
|
UOP_ID |
10 |
|
DESCR |
30 |
|
UOP_IN_SERVICE_DT |
8 (MM/DD/YY) |
|
UOP_MAX_UNITS |
12 |
|
UNIT_OF_MEASURE |
3 |
|
UOP_POSTING_DT |
8 (MM/DD/YY) |
|
UOP_UNITS |
12 |
To define asset physical definitions, use the following components:
Agencies (AGENCY_DEFN)
Area Definition (AM_AREA_TBL)
Asset Type Options (AM_TYPE_OPT).
Asset Subtype (AM_SUBTYPE).
Asset Attribute (AM_UD_ATTR).
Asset Property Subclass (AM_PROP_SUBTYPE).
Hazardous Codes (ASSET_FSC_DEFN)
Asset Meter Types (AM_METER_TYPE)
Location Definition (AM_LOCATION)
To access these components, select
Use the Agencies page (AGENCY_DEFN) to create agency codes.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Agencies Page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
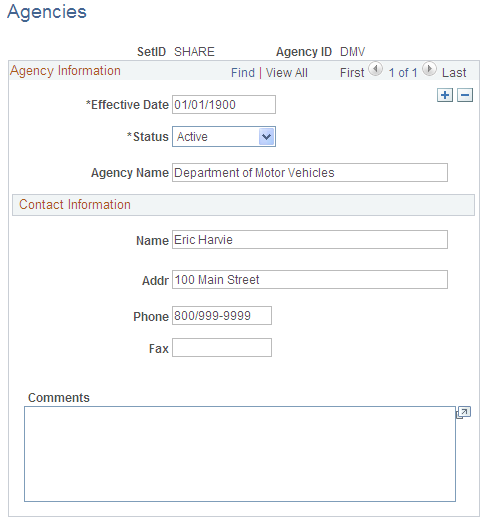
Keep track of the registration and licenses of an asset by using the information that is set up in Agency tables. Only agency IDs that are set up here can be entered on the Asset License/Registration page.
Use the Area Definition page (AM_AREA_TBL) to define an asset area within a location.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Area Definition Page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
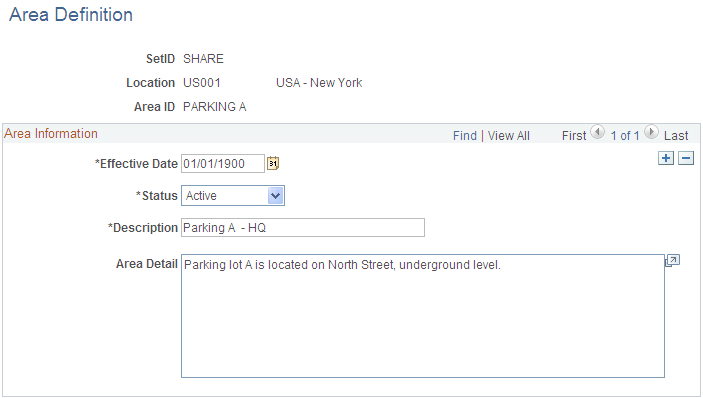
The Area Definition enables you to create a more granular level that further identifies the asset within a location. In PeopleSoft Asset Management, an asset can be physically located by region, location, and area.
Note: The system clears the area ID for an asset when you move that asset to a new location. You can then reassign new area IDs to the asset, as appropriate.
Use the Asset Type Options page (AM_TYPE_OPT) to define physical asset types to be applied to individual assets.
Oracle delivers ten asset types: Hardware, Software, Equipment, Property, Fleet, Machinery, Furniture, Facility, Intangible, Other.
You can assign the appropriate options that apply to each asset type for PeopleSoft Maintenance Management work orders and InterUnit Transfer Default values.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Asset Type Options Page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
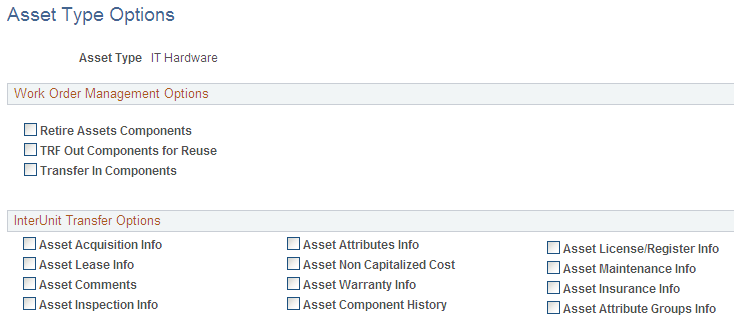
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Retire Assets Components |
Select to enable retirement processing for components from work orders. |
TRF Out Components for Reuse |
Select to enable component transfers out for reuse from work orders. |
Transfer In Components |
Select to enable component transfers in from work orders. |
Asset Attribute Groups Info |
Select to enable attribute group transfers in from work orders. |
Asset Acquisition Info |
Select to include information derived from the Asset Acquisition Detail (ASSET_ACQ_DETAIL) page and links (ASSET_ACQ_DET_AP, ASSET_ACQ_DET_VAT). |
Asset Attributes Info |
Select to include information derived from the Asset Location/Comments/Attributes (ASSET_IMAGE) page. |
Asset License/Register Info |
Select to include information derived from the Asset Custodian/License/Manufacturer (ASSET_CUSTODIAN) page and links (ASSET_LIC_ADDR_SEC). |
Asset Lease Info |
Select to include information derived from the Leased Assets component pages (ASSET_LEASE_01, ASSET_LEASE_02, ASSSET_LEASE_05, ASSSET_LEASE_03). |
Asset Non-Capitalized Cost |
Select to include information derived from the Asset Acquisition Detail (ASSET_ACQ_DETAIL) page and links (ASSET_ACQ_DET_AP, ASSET_ACQ_DET_VAT). |
Asset Maintenance Info |
Select to include information derived from the Track Service and Repairs component and Meter Reading component pages (ASSET_MAINT_01, ASSET_MAINT_01_S, AM_METER_READ). |
Asset Comments |
Select to include information derived from the Asset Location/Comments/Attributes (ASSET_IMAGE) page. |
Asset Warranty Info |
Select to include information derived from the Asset Custodian/License/Manufacturer page (ASSET_CUSTODIAN) and links (ASSET_WARRANTY). |
Asset Insurance Info |
Select to include information derived from the Asset Custodian/License/Manufacturer page (ASSET_CUSTODIAN) and links (ASSET_INSURANCE). |
Asset Inspection Info |
Select to include information derived from the Asset Custodian/License/Manufacturer page (ASSET_CUSTODIAN) and links (ASSET_INSPECTION). |
Use the Define Asset Subtype page (AM_SUBTYPE) to define asset subtypes as they relate to asset types.
For example, if the asset type is Hardware, an asset subtype may be defined for a Laptop.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Define Asset Subtype Page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
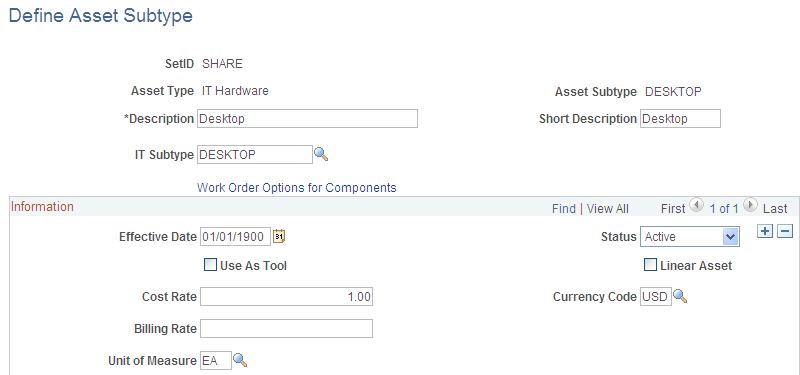
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
IT Subtype |
Map the Asset Subtype to an IT Subtype to create the association between the two fields for tracking IT assets within the asset repository for PeopleSoft IT Asset Management. Note: The IT Subtype field appears only when PeopleSoft IT Asset Management is installed. See Assets, Asset Types, and Asset Subtypes. See IT Subtypes. |
Use As Tool |
Check whether this subtype is used as a tool in support of another asset. When the asset specifies an asset subtype, the system applies the Use As Tool field value from the asset definition level. When defining an asset, you can associate it with a profile, such as Building or Automobile. If no profile is specified for the asset, the asset subtype value Use As Tool will apply when this subtype is selected for the asset. The following describes the system validation process: When working with assets in Add mode only, if no asset subtype is specified for the asset, the system checks the profile. From the profile definition, the system will populate the new asset with the asset type and asset subtype values. When the profile specifies an asset subtype, the system sets the Use As Tool field value to the same value of the asset subtype as defined in the associated profile. When the profile does not specify an asset subtype, no values are provided by default because the Use As Tool field value is blank on the profile and the newly added asset will follow suit. |
Linear Asset |
Identify this asset subtype as one that has coordinates for its start and end points, for example, a train track, a pipeline, or a roadway. You can override this option from the basic component when adding or updating assets. |
Cost Rate and Currency Code |
Enter the cost rate and currency to be used if a cost is applied for this asset subtype. |
Billing Rate |
Enter the billing rate to be used if the use of the asset subtype is to be billed. |
Unit of Measure |
Enter the units measured for cost and billing. |
Use the Define Asset Attribute page (AM_UD_ATTR) to define any asset physical attribute to be associated with an asset.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Define Asset Attribute Page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
Enter user-defined asset attributes to assign to assets. For example, you can create asset attributes to specify a quality, aspect, version, or other characteristic that can be applied to an asset. Asset attributes are optional.
Note: Asset attributes should not be confused with attribute groups. Asset attributes are used widely within PeopleSoft Asset Management to characterize assets regardless of the type of asset. Attribute groups are logical records that store the specific attributes that are of a particular interest for a certain type of asset. The attributes that are part of the attribute group are defined on the Fields Summary page within PeopleSoft Maintenance Management, Supplemental Data
Use the Define Property Subclass page (AM_PROP_SUBCLASS) to define property asset subclasses as they relate to asset property classes: Site, Building, Floor, Area, Space.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Define Property Subclass Page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
Define property subclass codes to apply to property asset classes: Site, Building, Floor, Area, Space. For example, you can define the corporate sites and further enter property subclasses for the buildings located on the site.
Use the Hazardous Codes page (ASSET_FSC_DEFN) to define hazardous-asset codes.
The PeopleSoft system is delivered with the Federal Supply Class (FSC) codes, which are U.S. federal codes that identify predominant and significant hazardous materials. You may add other classifications.
Navigation:
When you manage assets that can be classified as hazardous material, you must maintain the Hazardous Material codes table. U.S. Federal Supply Class codes are delivered with PeopleSoft Asset Management, and you can add codes to supplement the list. Hazardous assets can be reported using asset search functions, and storage locations can be managed with specific building, room, floor, and longitudinal and latitudinal information added to the location page that is associated with the asset.
Note: Hazardous material and waste is solid, liquid, or gaseous waste, or a combination of these wastes, that because of its quantity or concentration, or its physical, chemical, or infectious characteristics, may cause a significant increase in mortality or an increase in serious irreversible or incapacitating illness, or pose a substantial present or potential hazard to human health or the environment when improperly treated, stored, transported, disposed of, or otherwise managed (according to the United States Environmental Protection Agency).
Use the Meter Type Definition page (AM_METER_TYPE1) to define meter types.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Meter Type Definition page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
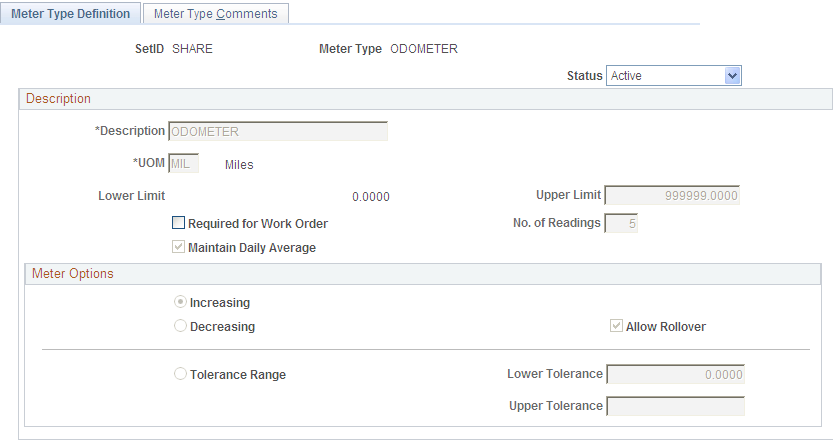
When you manage assets that use meters to track asset usage or that provide some other type of measurement associated with the asset, you need to define meter types.
Define meter types within SetIDs.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Status |
Set the meter status. Values are: Active: The meter is actively measuring. Inactive: The meter is not actively measuring but is available. |
Description
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Description |
(Required) Enter a meter description. |
UOM (units of measure) |
(Required) Enter the units by which the meter will measure, such as miles, kilometers, gallons, liters, square feet, and so on. Note: Many units of measure are provided with PeopleSoft software. You must define units of measure if the measurement is not common and not delivered with PeopleSoft software. |
Lower Limit and Upper Limit |
(Required) Enter the lowest and highest value that the meter can read. The lower limit is never greater or equal to the upper limit. The upper limit is never less than or equal to the lower limit. |
Required for Work Order |
Select to require this meter type in a work order before the status of the work order can be set to complete. This option is available only when PeopleSoft Maintenance Management is installed. |
Maintain Daily Average |
Select to maintain a daily average. The average is informational only for preventive maintenance schedules in PeopleSoft Maintenance Management. The option is not selected by default. |
No. of Readings (number of readings) |
Enter the number of readings to calculate the daily average. This is required when Maintain Daily Average is selected. |
Meter Options
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Increasing or Decreasing |
Select Increasing if the meter should increment along the useful life of the asset by the units of measure selected. Select Decreasing if the meter should decrement along the useful life of the asset by the unit of measure selected. The Increasing option is selected by default. |
Allow Rollover |
Select if the meter should reset to zero after reaching its defined maximum. It is selected by default. |
Tolerance Range |
Select to establish a tolerance range for a maintenance event. When this option is selected, the tolerance range fields become active. |
Lower Tolerance and Upper Tolerance |
Enter the tolerance range. For example, a piece of construction hydraulic equipment may use a pressure meter. If the meter falls below the lower tolerance or above the upper tolerance, you might initiate maintenance or replacement as needed. |
This section provides an overview of warranties and discusses how to:
Set up standard warranties.
Set up warranty templates.
Understanding Warranties
For the system to automatically assign one or more warranties to each newly acquired asset, standard equipment warranties and equipment warranty defaults must be defined. Each asset that is added to the repository is available to have the appropriate warranties automatically attached to it. You can update a warranty for an asset at any time after the addition of the asset to the asset repository, including changing the terms of the warranty, renewing or voiding the warranty associated with the asset, or making other notable changes in coverages or terms.
A warranty is established as a standard warranty that is applied to a single asset. Or a generic warranty that can be applied to multiple assets can be defined as a warranty template. This is useful when the same terms of a general warranty apply to many assets, such as multiple computer workstations or truck tires for a fleet of trucks. It is also useful when you are applying multiple standard warranties to assets. For example, an asset may be delivered with a manufacturer's warranty and an additional extended warranty that is purchased separately and provides different coverages.
Use the Standard Warranties page (AM_STD_WRTY) to define standard warranties.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Standard Warranties Page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
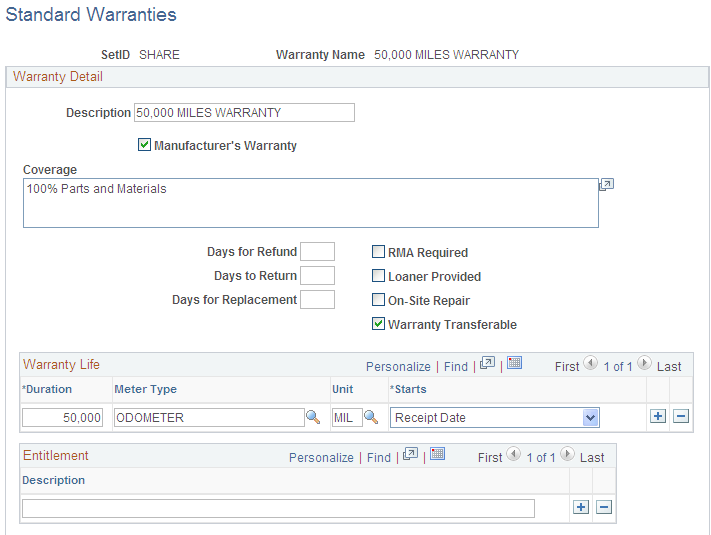
Enter the standard warranty information for an asset type, category, class, or other asset definition. Use the standard warranty to associate it with specific asset IDs.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Manufacturer's Warranty |
Select if the warranty is the original manufacturer's warranty. |
Coverage |
Enter a description of the warranty. |
Days for Refund |
Enter the number of days during which the asset is eligible for refund. |
Days to Return |
Enter the number of days during which the asset is eligible to be returned. |
Days for Replacement |
Enter the number of days during which the asset is eligible for replacement. |
RMA Required |
Select if an RMA (Return Material Authorization) is to be accompanied with the asset before it can be returned under warranty. |
Loaner Provided |
Select if the asset will be replaced with a similar loaned asset while under repair. |
On-Site Repair |
Select if the asset is eligible for repair at your place of business. |
Warranty Transferable |
Select if this warranty transfers when ownership of the asset transfers. |
Warranty Life |
Select the meters that can be associated with the asset to measure warranty life. For example, a vehicle usually has a warranted life based on miles which are measured by the vehicle odometer. |
Entitlement |
Enter a summary of what the warranty specifically entitles the owner to receive. |
Use the Warranty Templates page (AM_WRTY_TMPL) to set up templates for warranty types to apply to asset types.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Warranty Templates Page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
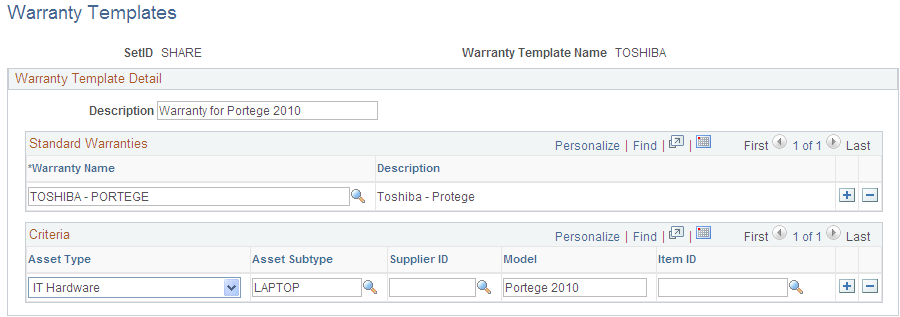
Define warranty templates that can be applied to multiple assets at one time, such as assets defined by asset type, category, class or other asset definition.
Select all standard warranties that apply to the individual asset category, class, type, and so on.
Use the Equipment Parts List page (AM_PART_LIST_TMPL) to define equipment parts lists to be associated with asset classes, groups, categories, types and subtypes, or other asset definitions.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Equipment Parts List page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
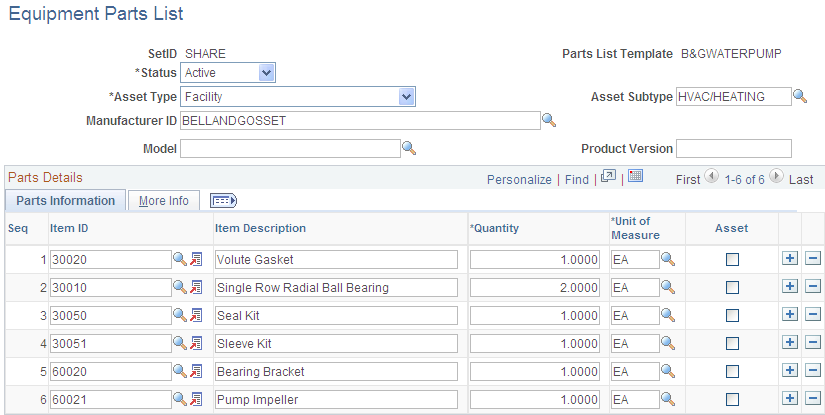
Asset equipment parts lists (EPL) are maintained by SetID. You can establish a parts list to correspond to asset classes, groups, categories, types, and subtypes, or to any asset definition. The EPL can then be associated with a specific asset ID.
Use the Criticality Codes page (AM_CRIT_LEVEL) to establish levels of criticality.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Criticality Codes page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
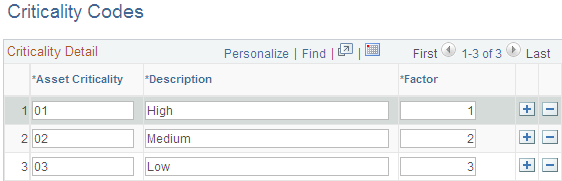
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Asset Criticality |
Enter a code that identifies the importance of this asset. |
Description |
Enter a description of the asset criticality code. For example, A1 is important, A2 is moderate, and A3 is low. |
Factor |
Enter a weighting factor that the system uses for sorting and prioritizing the criticality codes. |
Use the End of Life Reason Definition page (AM_END_LIFE_RSN) to define end of life reasons for an asset.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the End of Life Reason Definition page.
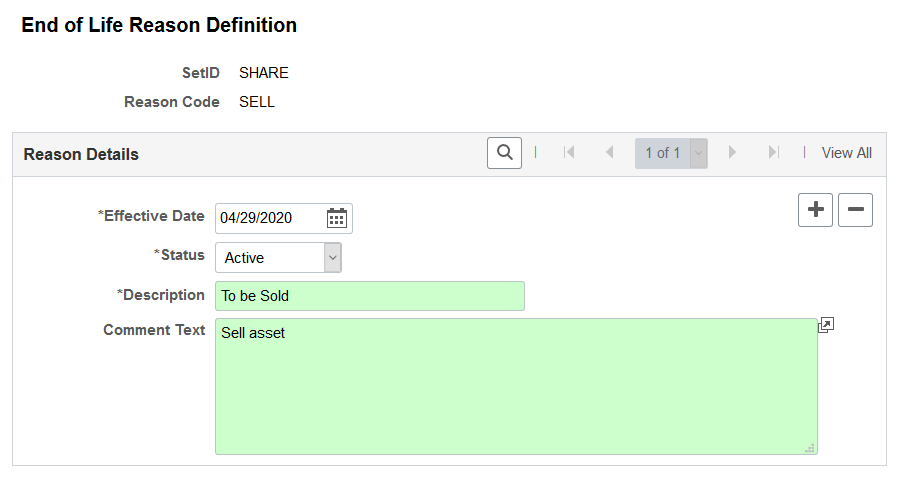
End of life reasons play a role in tracking the physical life of an asset, and are used on the Manufacture/License/Custodian Page and Define Asset Operational Information - Asset Information Page.
Use the External Funding Source (Setup) page (EFS_ID_DEFN) to define an external funding source for assets.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the External Funding Source (Setup) page.
You can associate the external funding source with an asset using theGeneral Information Page or Cost/Asset Information Page. In this way you can identify and closely monitor assets that must meet specific sponsor requirements and internal policies.