 Understanding the Fulfillment Engine
Understanding the Fulfillment EngineThis chapter provides overviews of the fulfillment engine and fulfillment engine processing groups and commit levels, and discusses how to:
Set up the fulfillment engine processing options.
Set up the picking location default structure.
Work with units of measure (UOM) on fulfillment transaction requests.
Process inbound application messages for the fulfillment engine.
Set up the templates for the fulfillment and shortage workbenches.
Use the fulfillment workbench.
Process fulfillment transaction requests from the staging tables.
Handle errors with the fulfillment engine.
 Understanding the Fulfillment Engine
Understanding the Fulfillment EngineThe fulfillment engine in PeopleSoft Inventory enables users to move orders from one fulfillment state to another fulfillment state with one easy user-defined process. The options for order fulfillment include:
Using run control pages.
All of the fulfillment processes, from the Reserve Materials process to the Shipping Requests process are designed to streamline the orders using the fulfillment engine.
Entering data on online pages.
The Fulfillment Workbench component and the Packing page enable you to enter requests to move stock orders and sales orders from one fulfillment status to another. Requests are placed in staging tables and then processed by the fulfillment engine using the Fulfillment Requests process.
Using external interfaces.
Messages from external systems can be processed through the PeopleSoft Integration Broker. These messages can request to move material stock orders and sales orders from one fulfillment status to another. These requests are placed in staging tables and then processed by the fulfillment engine using the Fulfillment Requests process
The fulfillment engine processes fulfillment transaction requests created by the online pages, external interfaces, and run control pages. These fulfillment requests identify the demand data (material stock orders and sales orders) to be moved from one fulfillment status to another. It is important to note that these fulfillment transaction requests are not orders but instructions to be applied to the Inventory demand tables. For example, you can enter a transaction request to move all orders to a shipped status with the carrier ID FEDEX and the scheduled ship date of today. The request is applied against the PeopleSoft Inventory demand tables by the fulfillment engine and the orders meeting the request criteria are moved to shipped status. The fulfillment transaction requests have this structure:
|
Level |
Description |
|
Header |
Contains fulfillment transaction request header information. |
|
Group |
Contains fulfillment transaction request group level information. One request can contain one or more groups. |
|
Detail |
Contains fulfillment transaction request detail level information within a group. |
|
LLS |
Contains picking location, lot ID, serial ID, and staged-date information, plus staged date information. |
The fulfillment engine is a PeopleSoft Application Engine program that uses a style of processing that works on groups of data as opposed to working on one row of data at a time. This technique maximizes performance when working with large quantities of data. Each fulfillment transaction request has one request header and at least one group record. When creating these group records, users have the added flexibility of defining exceptions and overrides to the group of demand lines. The main group selection information is defined at a group level on the fulfillment transaction request, while detail exceptions are defined at the detail level. The LLS level defines additional information about the request when exceptions have been defined at a detail level for a specific demand line.
|
Group Level |
Fulfillment requests consist of one or more groups. When creating the fulfillment request, you define the group. In its simplest form, the group level is an order and a detail level is a specific order line. However, flexibility exists to define a group as being just about any selection criteria used within the fulfillment system. Examples of a group include an order number, load ID, carrier ID, pick batch ID, or shipping container ID. It is important to note that when you define information at the group level, all demand lines meeting that selection criteria are processed. For example, if you want to ship all demand lines on a 1000 line order, then all you need to do is to create a group level containing that order number. If you want to exclude order lines or you want to process partial quantities on order lines, then you would add detail level entries to the fulfillment request only for those specific order lines in which you have exceptions. All other order lines are processed completely. Information overriding specific fields on the demand lines being processed can also be entered at the group level. For example, on a shipping request you may want to assign a specific pro-number. By entering this information at the group level, all demand lines processed within this group are assigned that pro-number. Note. Override information can be entered at the group level on fulfillment engine EIPs and the Fulfillment Workbench only. When using the run control requests process pages to initiate fulfillment requests, the override information applies to the full request. |
|
Detail Level |
The detail level enables you to further refine the group level selection by providing exceptions to demand lines within the group level definition. This level usually contains demand line level information; however, all group level selection criteria is available at the detail level. This flexibility enables you to define exceptions for individual demand lines or for groups of demand lines. The detail level can be used to:
Note. When entering exceptions referencing a specific demand line, the quantity and UOM provided at the detail level is used in place of the values that currently exist in the system for that demand line. The exception to this rule is when using the “exclude” option. Demand lines being excluded are always excluded completely, so the quantity and UOM fields are never used in this situation. Note. A detail level entry is referencing a specific demand line if one of four combinations of selection criteria is entered. The four combinations are the full demand key, pick batch ID and pick batch line number, external reference ID and external reference line number, and the TMS reference ID and TMS reference line number. Note. When the selection criteria is processing a group of demand lines, then the open order quantity on the demand lines in the demand tables is used when processing the demand lines. Fulfillment requests that define group information at the detail level are rejected if values are entered in the quantity and UOM fields. |
|
LLS |
The LLS entry is used to further identify instructions on how a transaction should be processed. Information such as bin locations, lot ID, serial ID, staged dates, and storage containers are carried at this level. Note. Transactions shipping from an unfulfilled or releasable state that reference items under lot, serial, or staged date control must provide LLS level information. |
Transaction Based Requests vs. Run Control Based Requests
The fulfillment engine can process run control based fulfillment requests or transaction based fulfillment requests. Each method has benefits in different procedural environments.
|
Transaction Based Run Requests |
When using transaction based fulfillment requests, each request is assigned a control ID that is tracked and controlled so that there is a history of the work being performed. If errors are found, the transaction request is rejected and users follow up by either reprocessing the transaction request after the error is fixed or by canceling the request. A series of staging tables and error handling pages are in place to manage this process. A fulfillment transaction request could be used when:
|
|
Run Control Based Run Requests |
When using run control based fulfillment requests, the transaction request record is created and passed on to PeopleSoft Process Scheduler. PeopleSoft Process Scheduler initiates the fulfillment engine and processes the data. If any errors are found, the appropriate error message is sent to the message log and can be viewed from the process monitor. When initiating the fulfillment engine from a run control request, you can enter only group level information. Only a single group can be processed at any one time. A run control fulfillment request could be used when:
|
Transaction Based Requests and the Staging Tables
This diagram illustrates how the fulfillment engine processes requests from online pages, external interfaces, and process pages:
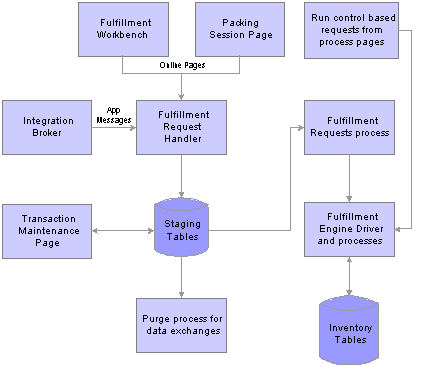
Processing fulfillment transaction requests using online pages, application messages, and run controls.
The Fulfillment Workbench and the Packing Sessions pages enable you to enter fulfillment transaction requests using online pages. The Fulfillment Workbench can move material stock orders and sales orders from an any fulfillment state to a downstream state. The Packing Sessions page can move an order from a confirmed state to a shipped state.
Messages from external systems can be processed through the PeopleSoft Integration Broker. These EIP application messages can request to move material stock orders and sales orders from one fulfillment state to another downstream fulfillment state. PeopleSoft delivers four asynchronous messages: Inventory_Reservation, Inventory_Pick_Confirm, Inventory_Front_End_Shipping, and Inventory_Shipping. These messages enable you to post a message to the Integration Broker and receive a response indicating that the message has been received.
Both the online pages and the external interfaces create fulfillment transaction requests. These requests identify the demand data (material stock orders and sales orders) to be moved from one fulfillment status to another. It is important to note that fulfillment transaction requests are not orders but instructions to be applied to the PeopleSoft Inventory demand tables. For example, you can enter a transaction request to move all orders to a shipped status with the carrier ID FEDEX and the scheduled ship date of today. The request is applied against the PeopleSoft Inventory demand tables by the fulfillment engine, and the orders meeting the request criteria are moved to shipped status.
Fulfillment Request Handler, a PeopleTools application class, takes the requests entered on the online pages or sent through the external interfaces, formats them, and populates the staging tables. For each request, the Fulfillment Request Handler assigns a unique ID, EIP_CTL_ID, based on the BCT setup transaction number defined on Data Collection page for the business unit or generates an unique ID using instructions from the external message. If the Auto Schedule Processing check box has been selected on the Setup Fulfillment - Fulfillment Engine page or the Fulfillment Workbench, then the Fulfillment Request Handler also schedules the Fulfillment Requests process to run immediately against the fulfillment transaction requests.
Note. The Auto Schedule feature is not available on the Packing Session page.
Requests are stored in staging tables. These staging tables hold the initial fulfillment transaction requests and any errors encountered when the request is processed by the fulfillment engine.
The Fulfillment Requests process page retrieves the requests from the staging tables and applies them to the PeopleSoft Inventory demand tables. If the requests are successfully processed against the PeopleSoft Inventory demand tables, then the requests are set to a status of complete. If the requests are not processed successfully, they are given an error status, and the appropriate error message is provided.
The Maintain Transactions component enables you to view and correct requests that contain errors. Once corrected, you can relaunch the Fulfillment Requests process. This is an optional step, you can choose to have the request errors canceled automatically, and then you could recreate another request.
The Purge process (IN_BCT_PURGE ) for data exchanges can also remove fulfillment transaction requests marked as complete or confirmed from the staging tables based on criteria that you define.
Staging Tables Used for the Fulfillment Engine
The staging tables are designed to be a temporary holding area for unprocessed requests and those in error. The staging tables are:
|
BCT_CTL |
Contains control information identifying request source and status. |
|
BCT_DTL |
Contains fulfillment request transaction header information. |
|
INV_FUL_GRP_EC |
Contains fulfillment request group level information. |
|
INV_FUL_DTL_EC |
Contains fulfillment request detail level information. This record could contain demand line level information or data to be excluded from the request (for example, at the group level you could have defined a carrier, and then at the detail level you could enter a specific order number to exclude). |
|
INV_FUL_LLS_EC |
Contains picking location, lot ID, and serial ID information. |
|
TSE_BCT_FLD |
Contains any errors encountered when processing the fulfillment transaction request. |
Each transaction written to the staging tables consists of the following hierarchy: a single BCT_CTL row, a single BCT_DTL row containing header level information, one or more INV_FUL_GRP_EC rows containing group level information, one or more INV_FUL_DTL_EC rows usually containing demand line information, and one or more INV_FUL_LLS_EC rows containing picking locations, lot IDs, and serial IDs.
Fulfillment requests are stored into the staging tables using these transaction codes:
|
Transaction Code |
Descriptions |
Used by |
|
0361 |
Reserve |
The Fulfillment Workbench and the Inventory_Reservation application message from external systems. |
|
0363 |
Picking Feedback |
The Fulfillment Workbench (action of Pick Confirm) and the Inventory_Pick_Confirm application message from external systems. |
|
0365 |
Front-end Ship |
The Fulfillment Workbench and the Inventory_Front_End_Shipping application message from external systems. |
|
0366 |
Ship |
The Fulfillment Workbench, Packing Session page, and Inventory_Shipping application message from external systems. |
Run Control Based Requests
All run control process pages in inventory order fulfillment initiate the fulfillment engine. For run control process pages, the fulfillment transaction requests are applied directly to the inventory demand tables; the staging tables are not used. Like all run controls, these processes can be scheduled to run one time or on a recurring basis. Any errors in the requests are placed in the Message Log for viewing. When initiating the fulfillment engine from a run control process page, only group level information can be provided. If detail information is required to include exceptions to the group level, then you must create a fulfillment transaction request using the Fulfillment Workbench or an fulfillment engine EIP.
Fulfillment Engine Error Handling
The fulfillment engine provides a number of alternatives for handling errors. This is necessary because many of the error conditions are not related to information entered on individual requests but are due to issues with demand lines that cannot be moved to the destination state defined in the fulfillment request. The fulfillment engine does identify errors; however, you'll need to correct these errors using pages in PeopleSoft Inventory.
Here are the components that you can use to view and, in most cases, correct errors found by the fulfillment engine:
Maintain Transactions
This component enables you to view and correct fulfillment transaction requests that contain errors. When a transaction is rejected due to errors, it is set to an error status. The transaction can then be viewed using the Maintain Transactions component. If the transaction has multiple group, detail, or loc/lot/serial segments, then only the segments in error and the parents of those segments are marked with an error status. Segments without errors or without children with errors remain in an open status. You can then search for only those segments in error to quickly find the error. Once corrected, you can relaunch the Fulfillment Requests process.
The Log Errors option on the Setup Fulfillment - Fulfillment Engine page provides an alternative for handling rejected transactions. When this option is set to Message Log, error messages are written to the message log and the transaction is canceled. This option would be used at sites that do not need to follow up on every transaction. As errors are found in the message log, fixes are made using online pages, such as the Shipping/Issues page, where the problem is not only resolved but also shipped complete at the same time. Because the transaction in the staging table has already been canceled, no additional follow up in the Maintain Transactions component is necessary.
Process Monitor Message Log
This component enables you to view messages that are inserted into the message log by the fulfillment engine. This page cannot be used to correct errors.
Correct Demand Errors
This component enables you to view and correct errors that occur when the fulfillment engine attempts to move unfulfilled orders to a releasable or shipped status.
Bar Code Transaction Errors Workflow
Select the worklist entry. When you do, the system transfers you to the Transaction Error page, where you can view and correct the errors in barcode transactions. This application engine workflow process checks for barcode transactions that have an error status and generates a worklist entry.
 Understanding Fulfillment Engine Processing Groups and Commit Levels
Understanding Fulfillment Engine Processing Groups and Commit Levels
Processing groups and commit levels are used by the fulfillment engine to improve throughput of work being processed. When the processing group and commit level features are not being used, the fulfillment engine processes all demand lines in a single grouping. When using processing groups and commit levels, work is broken up into more manageable portions that can be tuned for overall processing performance improvements in different environments.
The fulfillment engine has these three main sections that must be clarified in order to understand how to use the processing group and commit level features:
Selection processing
This section of the fulfillment engine uses the selection criteria on the fulfillment request to select a grouping of demand lines for processing. Selected demand lines are laid into temporary tables in preparation for the validation and update sections of the process. If a single processing group is being used, then all demand lines selected into the temporary tables are passed down to the validation and update routines and processing continues for all work in a single grouping. If multiple processing groups are being used, then the first processing group is identified and passed down to the validation and update routines. When the first processing group is completed, the next processing group is sent downstream for processing. By varying the size of the processing groups, chunks of work can be sent through the process that best fit individual operating environments.
All demand lines in the fulfillment request’s selection criteria are soft locked to prevent other processes from working with those demand lines. The term soft locked is used when a program updates the lock table with the demand line. Other processes recognize that the demand line is locked and will not attempt to do any processing on it until the process that set the soft lock is finished.
The fulfillment engine has an added feature that enables you to set the soft lock for only those items in the first processing group. By doing so, you free up the demand lines that are not being processed in the first processing group until it is absolutely necessary to lock other users out. This feature is set on the Setup Fulfillment - Fulfillment Engine page. This feature would be used in higher activity environments where fulfillment engine processes are being performed at the same time as other online and batch processing that may want access to these demand lines.
Note. The option to release soft locks is provided for times when you are working with multiple processing groups, when there is overhead necessary to determine the priority of demand lines being processed in the first processing group. When the soft locks are released, then this work has to be redone for each processing group. The need to establish processing groups and to hold or release the soft locks is dependent on processing variations at individual sites.
Validation processing
A series of validations are performed on demand lines before they are reserved or shipped. Wherever possible, the fulfillment engine performs these validations using set processing to take advantage of system performance features inherent in the database manager. The set of demand lines that the fulfillment engine works on is the processing group. The content of the processing group can be controlled using the different options available when defining processing groups either on the Setup Fulfillment - Fulfillment Engine Options page or by overriding these values when the fulfillment request is created.
Update processing
Update processing is performed on demand lines that have been validated and prepared in the fulfillment engine’s temporary tables. When performing update processing, different inventory system tables must be updated in sequence to prevent database contention issues. When working with the item balance tables, items are sequenced and updated in item ID order. If commit level controls are not being used, then all items are updated in a single commit level. This means that from the point in the process that the item is updated, it will be locked by the database manager. This prevents other users from updating that item until all processing is complete. Because many processes throughout the system use the item balance tables, single level commit processing can create database contention issues.
Database contention slows down processing and in some cases creates deadlocking situations that force the reprocessing of the transaction request. Commit levels can be established when using the fulfillment engine to reduce the amount of time that an item ID is locked. This can reduce contentious situations and improve overall performance. Carefully consider how commit levels are established, as overuse of commit processing can slow down overall processing. Actual options established for commit processing are dependent on volume and activity considerations in different processing environments.
When using processing groups and commit groups, these rules apply:
Use only request level processing groups on front-end shipping fulfillment requests.
Reservation fulfillment requests can use request, order, and line processing levels.
Shipping and front-end shipping fulfillment requests always use a single commit level for a processing group.
You would use the processing level of a request along with an entry in the processing count field to control the number of commits performed on a group of shipping or front-end shipping transactions.
Reservations fulfillment requests can use commit levels of request, order, line, or item.
The commit group is always equal to, or a subset of the processing group.
If the commit level is set at a level higher than the processing level, then the fulfillment engine adjusts the processing level to that of the commit level. For example, if the processing level is set at the line level but the commit level is set at the request level, then the fulfillment engine uses processing groups set at the request level using a processing count that's the same as that set up for the commit count.
When the pass through feature is used on reservations fulfillment requests, then the pass through level overrides the processing group and commit level, if either are set to a value less then the pass through level.
You can never break transaction-based fulfillment requests across multiple processing groups.
If a processing group reaches its maximum number of orders or demand lines before including all demand lines requested on a transaction-based fulfillment request, then the processing group expands to include all orders or demand lines requested in the selection criteria of the transaction.
You can break run control based fulfillment requests across multiple processing groups.
Fulfillment transaction requests in the staging tables are soft locked when they are first selected by the selection section of fulfillment engine processing.
Once the first processing group is determined, soft locks on those transactions not included in the first processing group are released if the Release Additional Locks option is set on the Setup Fulfillment - Fulfillment Engine page. By releasing these locks, the transactions can be picked up and processed by concurrent fulfillment engine processes.
 Setting Up the Fulfillment Engine Processing Options
Setting Up the Fulfillment Engine Processing Options
There are several processing options to be defined for the fulfillment engine. These options are defined in a default hierarchy. At each level, you can define processing options for the run control pages, the online pages, and the external interfaces. When the fulfillment engine needs to process transactions, it finds the necessary processing options by using the following default hierarchy:
Transaction level
The system looks to the run control page or online pages for overrides to the fulfillment engine default options. If overrides are not allowed or no entries are made, then the system looks to the business unit level.
Business unit level
The system looks to the Setup Fulfillment - Fulfillment Engine Options component defined for the PeopleSoft Inventory business unit. If a default is not defined at this level for a particular option, then the system looks to the set ID level.
Set ID level
The system looks to the Fulfillment Engine Options component defined by set ID. This is linked to one or more PeopleSoft Inventory business units on the TableSet Control - Record Group page using the record group, IN_17, Fulfillment Engine Options. If a default is not defined at this level for a particular option, then the system uses the system-defined options.
System level
If any of the processing options are not found, then the system-defined options are used.
The default options for the fulfillment engine are:
|
Auto Schedule Processing |
Select to immediately process the requests. The Fulfillment Requests process is launched when the requests are posted to the staging tables. This option is used when processing EIP messages and Fulfillment Workbench requests. |
|
Release Additional Locks |
Select to instruct the fulfillment engine to release any locks not identified by the first processing group of data determined at run time. If this option is cleared, then all fulfillment transaction requests and demand lines meeting those requests are soft locked until they are finished processing. When the locks are released using this option, both fulfillment transaction requests and demand lines that were not included in the initial processing group are released to be processed by concurrent fulfillment engine processes. |
|
Perform Validation |
Select to have the fulfillment engine validate data loaded into the demand table (IN_DEMAND) by external applications. |
|
Log Errors Option |
There are two options:
|
|
Allow Processing Overrides |
Select to enable the user to override the Processing Level, Processing Count, Commit Level, and Commit Count fields where provided on the Fulfillment Workbench, fulfillment process pages, and external messages. |
|
Processing Count |
Enter the number of lines that can be processed together by the fulfillment engine; in other words, define the size of the processing group. The processing count is used to tune an inventory environment that is running into database contention issues. A processing group should be defined to be smaller than the large fulfillment transaction requests of your environment. If the Processing Count field is blank or zero, then all the data identified by the transaction request is included in one processing group. A processing group breaks up the request into smaller chunks for processing, consequently reducing table locks and contention issues. For example, with a processing count of 500, the system processes rows in groups of 500. If the transaction request includes 1,050 rows of data, the system process the data in 3 processing groups, 2 groups of 500 rows, and 1 group of 50 rows at the end of the process. Note. If the fulfillment engine receives a commit count greater than the specified processing count and the processing level is the same as the commit level, then the processing count is set to the commit count. Also, if the pass through level field is greater than the value specified in the Processing Level field, then the processing group is expanded to include all data at the pass through level. |
|
Processing Level |
Determines how the system counts rows to reach the number entered in the Processing Count field. For example, with a processing count of 500 and a processing level of Order, the process would create a processing group per every 500 order numbers. You can create processing groups based on:
Note. When the Processing Count field is not blank or zero, the Processing Level must be greater than or equal to the Commit Level field. |
|
Commit Count |
Enter the number of lines that can be committed to the database together by the fulfillment engine; in other words, define the size of the commit group. The commit count is used to tune an inventory environment that is running into database contention issues. A commit group is a subset of the processing group; therefore, the Commit Count field should be the same as or smaller than the value in the Processing Count field. If the Commit Count field is blank or zero, then all the data rows identified in the processing group are committed to the database together. A commit group should break up the processing group into smaller chunks for committing to the database. For example, if you use a processing count of 500 and a commit count of 100, the system breaks up the transaction request of 1,050 data rows into 3 processing groups: 2 groups of 500 rows and 1 group of 50 rows. Each processing group is then broken up into commit groups of 100 rows each. The first 2 processing groups are divided into 5 commit groups each and the last processing group of 50 rows is 1 commit group. The system then commits the data to the database using 11 commit groups in total. Note. If the fulfillment engine receives a pass through level field that is greater than the value specified in the Commit Level field, then the commit group is expanded to include all data at the pass through level. |
|
Commit Level |
Determines how the system counts rows to reach the number entered in the Commit Count field. For example, with a commit count of 100 and a commit level of Item, the system issues a commit to the database for every 100 item IDs. You can issue commits based on:
Note. When the Commit Count field is not blank or zero, the commit level must be less than or equal to the processing level. |
|
Allow Pass-through Overrides |
Select to enable the user to override the pass through level on the Fulfillment Workbench, fulfillment process pages, and the fulfillment engine EIPs. |
|
Pass-through Level |
Provides the ability to pass good transactions through the system while holding up transactions that need additional review. On the request pages and on the transactions, the pass through level can have these values:
From a processing standpoint, the pass through level must be less than or equal to the processing level and commit level. If the fulfillment engine receives a pass through level greater than the specified commit level or processing level, the commit group or processing group is expanded to include all data at the pass through level. Note. The Reserve Materials process has restrictions based on lead times and item availability that determine whether demand lines are reserved. Demand lines that do not pass these restrictions are not considered errors for pass through purposes. |
|
Allow State Overrides |
Select to enable the user to override the from fulfillment status of the orders in the group. This applies to the Order Release Request process, Front-end Shipping Requests process, Shipping Requests process, and the fulfillment engine EIPs for front-end shipping and shipping. |
|
Allow Auto-Processing Override |
Select to enable the user to override the auto-processing option on process page, Fulfillment Workbench, or request transactions from an application message. |
|
Auto Processing Option |
Select the auto processing option to move your orders downstream to the desired state. Options include:
|
|
Auto Release User ID |
Enter any user IDs that has created a run control for the Order Release Request process page. |
|
Auto Release Run Control |
Select any run control for the Order Release Request process page defined by the user entered in the Auto Release User ID field to the left. This run control contains the parameters to be used when auto-processing orders from an unfulfilled state to another downstream state. The Auto-Processing Option field on the Order Release Request determines how far downstream the orders will be sent. |
|
Auto Process at Save |
Select this check box to launch the auto-processing option when the online page is saved. The online pages include Create/Update Stock Request component, Material Picking Feedback page, Express Issue page, and the Shipping/Issues page. |
|
Complete Flag |
Choose a Complete Flag option to automatically performing picking functionality on demand lines that have no previous picking activity reported against them. The LLS segment and the override location are applied prior to implementing the complete flag logic. Using the Complete Flag, the line can be moved to different sub-states within the Released state, or, with auto-processing, moved downstream to the shipped or depleted states. The complete flag is used for run control pages, fulfillment engine transaction requests, the Fulfillment Workbench, and the Inventory Picking EIP. The Complete Flag options are:
Note. For fulfillment engine transaction requests, the level (header, group or detail) where the Complete Flag is located determines what level to apply the complete flag logic. |
Fulfillment engine processing options can be set at different locations to default into the fulfillment transaction requests. This table displays where options can be set. Options set at the lower levels (that is, more specific to the request, such as on the run control page) override options set at the higher levels (such as at the set ID level).
|
Fulfillment Engine Options |
System Defined Options (1) |
Set ID Level (2) |
Unit Level (3) |
Transaction Level (4) |
|
Auto Schedule Processing |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Release Additional Locks |
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Perform Validation |
Yes |
|||
|
Log Errors Option |
Yes |
|||
|
Allow Processing Overrides |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Processing Count |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Processing Level |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Commit Count |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Commit Level |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Allow Pass through Overrides |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Pass through Level |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Allow State Overrides |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Allow Auto-Processing Override |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Auto Processing Option |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Auto Release User ID |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Auto Release Run Control |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Auto Process at Save |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
(1) System-defined options are used if no options are defined at the setID, business unit, or transaction level.
(2) SetID level options are defined on the Fulfillment Engine Options page.
(3) Business unit level options are defined on the Setup Fulfillment - Fulfillment Engine Options page.
(4) Transaction level options are defined on the Fulfillment Workbench, fulfillment engine EIPs, and the fulfillment process pages. Not all options are available on each transaction type.
The system-defined fulfillment engine processing options are set as follows:
|
Auto Schedule Processing |
The system-defined value is No. |
|
Release Additional Locks |
The system-defined value is No. |
|
Allow Processing Overrides |
The system-defined value is No. |
|
Processing Count |
The system-defined value is zero. |
|
Processing Level |
The system-defined value is Line. |
|
Commit Count |
The system-defined value is zero. |
|
Commit Level |
The system-defined value is Line. |
|
Allow Pass-through Overrides |
The system-defined value is No. |
|
Pass-through Level |
The system-defined value is Demand Line for reserve transactions and Request for shipping transactions. |
|
Allow State Overrides |
The system-defined value is No. The following states are set:
|
|
Allow Auto-Processing Override |
The system-defined value is No. |
|
Auto Processing Option |
The system-defined value is No Auto-Processing. |
|
Auto Process at Save |
The system-defined value is No. |

 Pages Used to Setup the Fulfillment Engine Processing Options
Pages Used to Setup the Fulfillment Engine Processing Options|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
INV_FUL_DFLT |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Inventory, Fulfillment Engine Options |
Define the fulfillment engine processing options for the set ID level. This is linked to one or more PeopleSoft Inventory business units on the TableSet Control - Record Group page using the record group, IN_17, Fulfillment Engine Options. |
|
|
TableSet Control - Record Group |
SET_CNTRL_TABLE1 |
PeopleTools, Utilities, Administration, Tableset Control, Record Group |
Select the SetID for the record group, IN_17, Fulfillment Engine Options to link the fulfillment engine processing options for the set ID level to the business unit (set control value). |
|
OF_SETUP1_INV |
Inventory, Fulfill Stock Orders, Fulfillment Rules, Setup Fulfillment, Fulfillment Engine |
Define fulfillment engine defaults at the business unit level. |
|
|
INV_FUL_DFLT_BU |
Select the Processing Options link on the Setup Fulfillment-Fulfillment Engine page. |
Define fulfillment engine processing options for the business unit level. |
See Also
Defining Fulfillment Engine Options

 Setting Up the Set ID Fulfillment Engine Options
Setting Up the Set ID Fulfillment Engine OptionsAccess the Fulfillment Engine Options page.
Processing Options
The columns on this page are defined at the beginning of this section.
This page defines default values to be used when the fulfillment engine processes fulfillment transaction requests.
|
Page/Process and Transaction |
Displays the type of interface that uses the processing options:
|
Passthrough Options
The columns on this page are defined at the beginning of this section.
From States
Select the From States tab.
The From State identifies the fulfillment status of the orders that users can select for processing by the fulfillment engine. For example, if the From State of Unfulfilled is selected, then users can select unfulfilled orders for processing.
|
Allow State Overrides |
Select to enable the user to select a different From State in the fulfillment transaction request. |
|
Select Unfulfilled,Select Releasable,Select Released, and Select Confirmed |
Select the from state (or starting fulfillment status) of the orders to be moved to another status by the fulfillment engine. |
Note. The From States for the Fulfillment Workbench page are defined in the template ID for the workbench, not on this page.
Auto Processing Options
The columns on this page are defined at the beginning of this section.
See Also
Defining Fulfillment Engine Options
 Setting Up the Picking Location Default Structure
Setting Up the Picking Location Default StructureThe fulfillment engine when shipping from an unfulfilled or releasable status does not use the directed picking algorithms defined in the Pick Plan Run Time Options group box of the Setup Item Fulfillment page or the business unit's Setup Fulfillment-Order Release page. To find the inventory stock to ship, the fulfillment engine derives the picking location by searching in this order:
A storage location specified on the transaction request at the various levels, header, group, detail, and LLS (location, lot, and serial) level.
If a level contains no picking location, then the system uses the default at the level above it. For example, if the header level contains a storage location and all other levels are blank, then the header's storage location is used for all demand lines shipped. The system searches in this order:
LLS level
Detail level
Group level
Header level
A default storage location specified by the Default Ship Location Option group box located on the Setup Item Fulfillment - Shipping Options page.
A default storage location specified by the Default Ship Location Option group box located on the business unit's Shipping Options page.
Note. The fulfillment engine must find the entire quantity to fulfill a demand line in one storage location; if not, the request line is set to error status. If negative inventory is enabled for the business unit, then the demand line can be fulfilled by driving the item balance in the storage location to a negative quantity. Also, if a default location is found but is on hold or suspended, then the request line is set to error status. In addition, if the item ID has never existed in designated storage location (that is, there is no row in the PHYSICAL_INV record), then the request is set to an error status regardless of the negative inventory feature.
See Also
Defining Fulfillment Engine Options
Defining Fulfillment Shipping Options at the Unit and Item Level
 Working with UOM on Fulfillment Transaction Requests
Working with UOM on Fulfillment Transaction RequestsThe fulfillment engine enables you to ship orders in one fulfillment request, skipping many steps in the multistep fulfillment process. In the process of completing the picking and shipping steps in the background, the fulfillment engine must choose the proper UOM for each task. The system must also convert between the different UOMs. The fulfillment engine works with these UOMs:
Entered UOM: The UOM that you entered on the transaction request.
Ordering UOM: The UOM entered on the material stock order or sales order line.
Stocking UOM: The UOM used to stock the item in the PeopleSoft Inventory business unit.
The system uses this UOM to pick stock when shipping from an unfulfilled or releasable status. If sufficient stock is not found for the stocking UOM at the designated storage location, then the transaction is set to error status unless the negative inventory feature is enabled. If shipping from a confirmed status, then the stocking UOM is used to reference a previously picked quantity when short shipping a demand line. In this case, if the quantity is not found in the stocking UOM, then the transaction is rejected.
Shipping UOM: The UOM used to ship stock.
Standard UOM: The base UOM established for the item ID on the Define Item - General: Common page.
When working with these different units of measure, the system uses the conversion rates entered on the Units of Measure page for the item.

 Creating a Transaction Request
Creating a Transaction Request
Here's how UOMs that are entered on the transaction request are handled:
|
Level on Request |
UOM Rules |
|
Group |
When working with group level information, the quantity and UOM fields are not entered on the transaction. In this case, the quantity and UOM on the demand lines within the group are converted to the stocking UOM for picking purposes. |
|
Detail |
You can enter any valid UOM for the item. The quantity associated with this UOM is converted to the stocking UOM for picking. If you leave the UOM field blank, then the system uses the standard UOM for the item. |
|
LLS |
You can enter any valid UOM for the item. The quantity associated with this UOM is converted to the stocking UOM for picking. If you leave the UOM field blank, then the system uses the standard UOM. |

 Picking with the Fulfillment Engine
Picking with the Fulfillment Engine
The unit of measure (UOM) used to pick the stock from a storage location is determined by taking the entered UOM and converting it to a stocking UOM based on the item's setting on the UOM Conversion Flag field in the Define Business Unit Item - Inventory: Shipping/Handling page. The options are:
Convert to Default Stock UOM: Converts the entered UOM on the transaction request to the default stocking UOM for the item.
Convert to Standard UOM: Converts the entered UOM on the transaction request to the item's standard UOM.
Use Entered UOM: Picks stock using the entered UOM on the transaction request.
There is one exception: the UOM Conversion Flag field is not used when dealing with fixed picking bins. When picking from fixed picking bins, the system always uses the default UOM established for the fixed picking bin.

 Shipping with the Fulfillment Engine
Shipping with the Fulfillment Engine
The shipping UOM is always the ordering UOM, unless the ordering UOM is not a valid shipping UOM. In this case, the shipping UOM is set to the standard UOM.
 Processing Inbound Application Messages for the Fulfillment Engine
Processing Inbound Application Messages for the Fulfillment EngineThird-party systems can send PeopleSoft fulfillment transaction requests to be processed by the fulfillment engine using three application messages:
Inventory_Reservation: Using transaction code 0361 (Reserve), this message creates a request to move material stock orders and sales orders from an unfulfilled state to a releasable state.
Inventory_Pick_Confirm: Using transaction code 0364 (Pick Confirm), this message creates a request to move material stock orders and sales orders from an unfulfilled or released state to a pick confirm state.
Inventory_Front_End_Shipping: Using transaction code 0365 (Front-end Ship), this message creates a request to move material stock orders and sales orders from an unfulfilled or releasable state to a shipped state.
Inventory_Shipping: Using transaction code 0366 (Ship), this message creates a request to move material stock orders and sales orders from an unfulfilled, releasable, or confirmed state to a shipped state.
The PeopleSoft Application Messaging functionality provides a method for communication between external systems and PeopleSoft Inventory using industry standard XML-formatted messages. These XML messages for fulfillment are automatically loaded into the PeopleSoft system by using subscription processes and the PeopleSoft Integration Broker. All four inbound messages are contained in the same message channel (Inventory_Fulfillment).
The third-party system posts a message to the PeopleSoft Integration Broker and receives a response indicating that the message has been received with guaranteed delivery to the requested node. For each active inbound asynchronous transaction defined in the system for the source node and message version, PeopleSoft Integration Broker generates a subscription contract and runs the appropriate Subscription PeopleCode. This subscription process passes the information to the Fulfillment Request Handler (an application class), which formats the inbound data within the staging tables.
The application messages have the same format as the fulfillment engine staging table:
|
Header |
Contains fulfillment request transaction header information. |
|
Group |
Contains fulfillment request group level information. |
|
Detail |
Contains fulfillment request detail level information. This record could contain demand line level information or data to be excluded from the request (for example, at the group level you could have defined a carrier and then at the detail level you could enter a specific order number to exclude). |
|
Loc/Lot/Ser (LLS) |
Contains picking location, lot ID, and serial ID information. This level applies only to the front-end shipping and shipping messages. |
You can view transactions from valid messages on the Transaction Maintenance page and access the detail pages that enable you to correct application-level errors. Invalid messages with system-level errors are rejected before entry on the staging tables. These messages can be viewed using the Integration Broker Monitor. System-level errors include these situations:
Invalid XML or message structure.
Transactions with an invalid PeopleSoft Inventory business unit.
Invalid data in date or numeric fields.

 Setting up the Fulfillment Engine EIPs
Setting up the Fulfillment Engine EIPsThere are four inbound application messages used by the fulfillment engine. The following setup is required to use the Fulfillment Engine EIPs:
Note. These setup instructions assume that the message environment has been set up in PeopleSoft Integration Broker.
Inventory Reservation EIP
To use the Inventory Reservation EIP:
Setup in PeopleTools:
Activate the INVENTORY_RESERVATION message.
Activate InventoryReservation subscription.
Set up an inbound asynchronous transaction defining the INVENTORY_RESERVATION message on each node that can send the message to your system.
Verify that the INVENTORY_FULFILLMENT message channel is in Run mode.
Setup in enterprise components: None.
Setup at the application level:
Set up the fulfillment engine processing options using the Setup Fulfillment - Fulfillment Engine Options component.
Inventory Pick Confirm EIP
To use the Inventory Pick Confirm EIP:
Setup in PeopleTools:
Activate the INVENTORY_PICK_CONFIRM message.
Activate InventoryPickConfirm subscription.
Set up an inbound asynchronous transaction defining the INVENTORY_PICK_CONFIRM message on each node that can send the message to your system.
Verify that the INVENTORY_FULFILLMENT message channel is in Run mode.
Setup in enterprise components: None.
Setup at the application level:
Set up the fulfillment engine processing options using the Setup Fulfillment - Fulfillment Engine Options component.
Inventory Front End Shipping EIP
To use the Inventory Reservation EIP:
Setup in PeopleTools:
Activate the INVENTORY_FRONT_END_SHIPPING message.
Activate the InventoryFrontEndShipping subscription.
Set up an inbound asynchronous transaction defining the INVENTORY_FRONT_END_SHIPPING message on each node that can send the message to your system.
Verify that the INVENTORY_FULFILLMENT message channel is in Run mode.
Setup in enterprise components: None.
Setup at the application level:
Set up the fulfillment engine processing options using the Setup Fulfillment - Fulfillment Engine Options component.
Inventory Shipping EIP
To use the Inventory Shipping EIP:
Setup in PeopleTools:
Activate the INVENTORY_SHIPPING message.
Activate InventoryShipping subscription.
Set up an inbound asynchronous transaction defining the INVENTORY_SHIPPING message on each node that can send the message to your system.
Verify that the INVENTORY_FULFILLMENT message channel is in Run mode.
Setup in enterprise components: None.
Setup at the application level:
Set up the fulfillment engine processing options using the Setup Fulfillment - Fulfillment Engine Options component.
These setup instructions assume that the message environment has been set up in PeopleSoft Integration Broker.
See Also
PeopleSoft Integration Broker PeopleBook
PeopleSoft Enterprise Integration PeopleBook
 Setting Up the Templates for the Fulfillment and Shortage Workbenches
Setting Up the Templates for the Fulfillment and Shortage WorkbenchesThe workbenches are online components that enable you to enter transaction requests to change orders. There are two workbenches:
The Fulfillment Workbench: Users can enter requests to move orders from one fulfillment state to another fulfillment state.
The Shortage Workbench: Users can enter requests to resolve stock shortages and other fulfillment issues.
Understanding the Workbench Template
To enter data into the Fulfillment or Shortage Workbenches, you must define one or more templates in the Template Maintenance component. A template ID is a collection of configuration options used to dynamically generate the selection criteria and other fields that appear to the user on the Workbenches. The fields are organized hierarchically, first by category and then by subcategory, so that multiple sets of fields can be defined for a page within the same template. Access can be granted to a template at the set ID level, at the business unit level, by user role, or by user ID. Set up different templates for different sets of users or business units; for example, an inventory supervisor would have greater access to view and edit more fields than a shipping clerk.
In order to add a template ID, you must identify the template code to be used. Template codes are system defined and cannot be altered. The system delivers two template codes: FULFIL_WRKBENCH and SHORT_WRKBENCH. The template code definition identifies the categories, subcategories, and fields that are valid to be added when creating a template, as well as the field types (that is, check boxes, edit boxes, and so on) and prompt tables.
When adding a template:
Be aware of dependencies between fields (for example, a user cannot add an order number without a source business unit).
Field dependencies are not enforced by the system in the Template Maintenance component.
Watch for duplicate field names and out of order sort sequence numbers; the system will not validate.
Remember that default value fields will not have prompt tables associated with them.
Remember that visibility, availability to edit, and default values for demand states are controlled by the template definition and that they are not derived from the fulfillment engine options at the set ID or business unit level.

 Pages Used to Setup Workbench Templates
Pages Used to Setup Workbench Templates
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
IN_TM_OPR_FLD |
Inventory, Fulfill Stock Orders, Fulfillment Rules, Template Maintenance, Definition |
Create or modify a template. Templates define what actions and fields appear to the user when using the Fulfillment Workbench or the Shortage Workbench. |
|
|
IN_TM_OPR_SEC |
Inventory, Fulfill Stock Orders, Fulfillment Rules, Template Maintenance, Permissions |
Identify the individuals who can access this template on the Fulfillment Workbench or the Shortage Workbench. Also, identify the individuals who will maintain this template. |
|
|
IN_TM_OPR_INQ |
Inventory, Fulfill Stock Orders, Fulfillment Rules, Template Permissions Inquiry |
Inquire on the existing templates defined for a set ID, inventory business unit, user role, or user ID. This page displays all templates meeting the search criteria and identifies if the template is active, who maintains the template, and who can access the template. |

 Creating a Template
Creating a TemplateAccess the Template Maintenance - Definition page.
|
Template Code |
Defines the template for the Fulfillment Workbench (FULFIL_WRKBENCH) or the Shortage Workbench (SHORT_WRKBENCH). When a template is first created, it is populated with all the categories, subcategories, and fields defined for the template code. |
|
Template ID |
Enter the unique identifier for this template. Different templates are defined for different user groups to limit users to the appropriate fields. In the Template Maintenance component, a user can access only those templates that the user is defined to maintain, by user ID or user role. |
|
Description |
Enter a description of the template ID. |
|
Create basic template |
Select to add a template directly without copying fields from another template. This field only appears if you are in add-mode. |
|
Copy Fields From, Template ID and Copy |
Select the Copy Fields From radio button to copy an existing template to this new template ID where you can alter it to match your needs. Enter the template ID to copy in the Template ID field. You can only access template of the same template code that your user ID or user role is defined to maintain in the Template Maintenance-Permissions page. Click the Copy button to initiate the copy. The field from the existing template are copied into the page. These fields only appear if you are in add-mode. |
|
Active |
Select to activate the template ID for use. |
Note. Use caution when changing an existing template. If you change the existing category or subcategory, all the information underneath it (subcategories and fields for subcategory) is removed and repopulated with the corresponding data from the template code.
Categories
|
Category |
Enter categories to:
Click the Insert Row button to add more than one category to the same template. |
|
Required |
Identifies whether the Category field is required or not. |
|
Default |
Select one category to be the default category. When a user enters the Fulfillment Workbench using this template ID, this category is the default value in the action field. When a user enters the Shortage Workbench using this template ID, this category is the default view in the View By field. |
Subcategories
|
Search By |
For the Shortage Workbench, the only value available in this field is SEARCH. For the Fulfillment Workbench, define the available options for each action in the Search By field. The subcategories determine how the user groups the demand data for processing. Click the Insert Row button to add more than one subcategory. There are two subcategories, or search by options, delivered with the template code FULFIL_WRKBENCH:
|
|
Required |
Identifies whether the value in the Search By field is required or not. |
|
Sort |
Select to sort the search criteria fields in the scroll area by sequence number. |
|
One Column |
Select to have the Workbench display the search criteria fields in one column. This is the default setting, |
|
Two Column |
Select to have the Workbench display the search criteria fields in two column. The system initially assigns every other field to the second column; however, you can change this for the individual field using the Display column in the Scroll Area group box. |
|
View Layout |
Select to view how the Workbench will display to the user based on your current settings and fields chosen. |
|
Insert Fields |
Select to insert additional fields into the template. The new field is added just below the currently selected field or, if no field name is currently selected, at the bottom of the scroll area. |
|
Delete Fields |
Select to delete the currently selected field name from the scroll area. This will remove the field from the Workbench. |
Scroll Area
Identify the search criteria fields that are valid to appear on the Fulfillment Workbench or the Shortage Workbench for this template ID, category, and subcategory combination. You can control how the fields appear using these options:
|
Seq Nbr (sort sequence number) |
Identify the order that appears on the Workbench. |
|
Required |
Select to define a field as required to display on the Workbench. The template code defines certain fields as required. You can chose to make additional fields required. For a required field, the Delete Fields button is disabled. |
|
Display |
Choose to display this field in the first or second column in the Workbench layout. |
|
Display Mode |
Define the conditions for this search criteria field. Options are:
|
|
Default From and Default To |
Use the Default From field to enter a default value to display on the Workbench. For fields defined to display as a check box, you can select to default the check box value to yes (selected) or no (unselected). If you want a range to display, use the Default From and Default To fields together. The range selects all values in the date range or alphanumeric sequence. The range option is valid only for specific fields based on the template code and cannot be used with check box type fields. |
Note. The fields available for selection are limited by the template code.
For drop down fields on the Workbench, the template has a link on the field name so that you can choose which options are available in the drop down. These fields include:
|
Demand Source |
Select the PeopleSoft application source of the orders that the user of the Fulfillment or Shortage Workbench can view and change. For example, a customer service representative might be limited to sales order from PeopleSoft Order Management. |
|
Select by Date |
Select the options to display in the Ship By Date field on the Fulfillment or Shortage Workbench. The options are; Schedule Date, Order Date, Ship Early Date, and Orders Placed Today. |
|
Select Lines |
For the Shortage Workbench, select the options available in the Select Lines field. This field enables the user to limit their search to demand lines that have been processed by reservations, not processed by reservations, or both. |
|
Reserve By Date |
For the Fulfillment Workbench with a reserve action, select the options to display in the Reserve By Date field. |
|
Use Lead Days |
For the Shortage Workbench, select the options to display in the Use Lead Days field. This option determines how the fulfillment lead days are used in the search criteria. |
|
Header Action |
For the demand summary view of the Shortage Workbench, select the actions that a user can perform using the Header Action field. |
|
Detail Action |
For the Shortage Workbench, select the actions that a user can perform using the Detail Action field. |
|
Line Action |
For the Shortage Workbench, select the actions that a user can perform using the Line Action field. |
|
Select Summary View |
For the demand summary view of the Shortage Workbench, choose the options available to the user in the Select Summary View field: order or item summary. |
Additional fields to note include:
|
Exclude |
Set the display and default options for this check box on the Fulfillment Workbench to enable the user to define the selection criteria as exclusion criteria. This check box appears only on the Fulfillment Workbench if Detail is selected in the Search By field. |
|
Select Unfulfilled, Select Releasable, and Select Confirmed |
Set the display and default options for these check boxes on the Fulfillment Workbench to enable the user to search for orders with these specific fulfillment states. The Shortage Workbench also uses the Select Fulfillment and Select Releasable options. |
|
BLANK |
Create a blank line on the Fulfillment or Shortage Workbench. All display and default options are disabled. |

 Granting Access to a Template
Granting Access to a TemplateAccess the Template Maintenance - Permissions page.
When defining a template, use the Template Maintenance - Permissions page to:
Identify which users maintain the template over time.
The ability change a template is granted to a user ID or a user role when the Maintain check box has been selected for that row. It is required that at least one user or user role be identified to maintain the template. The system automatically adds the user who created the template as a maintainer.
Identify the users who can use the template on the Fulfillment or Shortage Workbenches.
The ability to use a template on the Fulfillment or Shortage Workbenches can be granted to any of the following combinations:
Set ID
Business unit
User ID
User role name
Set ID and user ID
Set ID and user role name
Business unit and user ID
Business unit and user role name
 Using the Fulfillment Workbench
Using the Fulfillment WorkbenchThe Fulfillment Workbench is an online component that enables you to enter requests to move material stock orders and sales orders from one fulfillment state to another. Requests are placed in staging tables and then processed by the fulfillment engine using the Fulfillment Request process. Using the Fulfillment Workbench, you can skip the intermediate fulfillment steps and place an order directly in the state that you need. You can move orders from an:
Unfulfilled state to releasable state.
Unfulfilled state to shipped state.
Releasable state to shipped state.
Released state to shipped state.
Picked confirmed state to shipped state.
The Fulfillment Workbench also provides many other options, including the ability to:
Override picking material storage locations and shipping information.
Use template security to tailor what options and fields are available or not available for particular users or in particular environments.
Override processing defaults.
Search and process a group (group processing feature) while including or excluding certain orders or demand lines.
Submit a request with or without viewing the orders included for processing.
When viewing the orders in the processing queue, you can add or delete individual lines and even delete the queue and start over.
View orders packed in containers separately from unpacked orders.
Override the reserve or ship quantity at the demand line level.
Identify lot, serial, ship serial, and staged date information to be included or excluded in a shipment.
Understanding the Fulfillment Workbench
Users enter a request to alter the demand lines located in the PeopleSoft Inventory demand tables. The Fulfillment Workbench selects materials stock orders and sales orders to place on the request using the group processing feature. When the user clicks the Process button on the Fulfillment Workbench, one request is written to the staging tables. This request is picked up by the Fulfillment Request process and run against the PeopleSoft Inventory demand tables to process the demand lines specified by the request. One request can specify only one action and one business unit. The Fulfillment Workbench cannot be used to change data on an order or demand line; it leaves the data in its current fulfillment state.
When creating fulfillment transaction requests using the Fulfillment Workbench, the user has a choice of sending the transaction request to the staging tables directly from the group or detail selection pages or of building the transaction request in the fulfillment queue so that it can be checked and reviewed prior to sending it to the staging tables. The Process button is used from the group or detail selection pages to immediately send the fulfillment transaction request to the staging tables. The Add to Queue button is used to build the transaction request prior to releasing it to the staging tables.
The group and detail selection pages are used to quickly enter group level or detail information to a fulfillment transaction request when this information is already known. If a search is required to find this information or if exceptions must be entered, then the orders, demand lines, or location/lot/serial links can be used to assist in building the transaction request.

 Pages Used for the Fulfillment Workbench
Pages Used for the Fulfillment Workbench|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
IN_FW_SELECTION |
Inventory, Fulfill Stock Orders, Fulfillment Workbench |
Create a request to move material stock orders and sales orders from one fulfillment state to another. |
|
|
IN_FW_CART |
Select the Fulfillment Queue link on the Fulfill Workbench page, the Orders page, or the Demand Lines page. |
View the demand lines in the processing queue. These are the orders that will be processed by the Fulfillment Workbench request. You can add or delete individual lines and even delete the queue and start over. |
|
|
IN_FW_ORDERPOOL |
Select the Orders link on the Fulfill Workbench page, the Demand Lines page, or the Fulfillment Queue. |
View all of the material stock orders and sales orders matching the search criteria on the Fulfillment Workbench. Also include or exclude specific orders. |
|
|
Demand Lines |
IN_FW_DEMANDLINES |
Select the Demand Lines link on the Fulfill Workbench page, the Orders page, or the Fulfillment Queue. |
View the demand lines of the material stock orders and sales orders selected by the selection criteria on the Fulfillment Workbench or the order number chosen on the Orders page, depending on how the page was accessed. You can use this page to include or exclude specific demand lines. You can also change the quantity to be reserved or promised (if you are using an Action of Reserve) or shipped (if you are using an Action of Front End Ship or Ship). |
|
IN_FW_DEMANDLOC |
Select the Location / Lot / Serial link on the Demand Lines page. |
Review demand location information for a specific request detail row. When shipping from an unfulfilled or releasable state, you can enter the exact picking location, lot ID, stage date, serial ID, or ship serial ID. You can also exclude a specific picking location, lot ID, and serial ID when shipping from a confirmed state or change the pick or ship quantity and UOM. |
|
|
IN_FW_CART_LLS |
Select the Location / Lot / Serial link on the Location / Lot / Serial tab of the Fulfillment Queue page. |
Review demand location information for a specific request detail row. When shipping from an unfulfilled or releasable state, you can enter the exact picking location, lot ID, stage date, serial ID, or ship serial ID. You can also exclude a specific picking location, lot ID, and serial ID when shipping from a confirmed state or change the pick or ship quantity and UOM. |
|
|
IN_FW_SHP_DFT_1_SP |
Select the Group Picking/Shipping Default link or the Ship Defaults link on most pages of the Fulfillment Workbench component. |
Enter any picking and shipping override entries to be applied at the transaction request, group, detail, or LLS level. |
|
|
IN_FW_PROC_DFLT_SP |
Select the Process Default link on the Fulfill Workbench page. |
Change processing defaults for this request. |

 Using the Fulfillment Workbench Page
Using the Fulfillment Workbench PageAccess the Fulfillment Workbench page.
Note. The exact fields and field values available on this page are determined by the Template ID that you select.
|
Action |
Identify the type of request:
|
|
Search By |
Enter the level that you want to search for and process demand. The fields that appear on the Fulfillment Workbench component vary depending on the option that you select. Options are:
|
|
Group ID |
Enter a group identification code for the grouping of demand lines that you are creating on the transaction request. The group ID is assigned automatically using a sequential number starting with one. To create a new group, click the arrow button to the right of this field. |
Selection Criteria
Use the Selection Criteria group box to enter the search criteria to retrieve demand lines for processing. These search criteria fields include both group level fields (for example, load ID or pick batch ID) and order level fields (for example, order number). The actual search criteria fields that appear are determined by the value in the Template ID field, as well as the entries in the Action and Search By fields.
|
Exclude |
Select to define the search criteria as exclusion criteria. This check box appears only if Detail is selected in the Search By field. Selection criteria entered are used to exclude demand data from the group. For example, if you want to ship all demand lines on a pick batch except line number 55, then enter the pick batch ID at the group level and add the group segment to the fulfillment queue. Next, bring up the detail selection information by entering Detail in the Search By field and selecting the Exclude check box. Then enter the pick batch ID and line 55. Add the detail segment to the fulfillment queue. Then click the Fulfillment Queue link to review the transaction request. Write the request to the staging tables when you click the Process button. Note. If the Exclude check box is selected at the order or demand line level, then that order or demand line must exist in the selection criteria established at the group level. If it is not in the selection criteria, then the fulfillment engine rejects the transaction request. |
|
Select Unfulfilled |
Select this check box to include unfulfilled orders in the search results and request. |
|
Select Releasable |
Select this check box to include releasable orders in the search results and request. This check box appears only if you have selected an action of Front End Ship or Ship. |
|
Select Released |
Select this check box to include released orders in the search results and request. This check box appears only if you have selected the action of Ship. |
|
Select Confirmed |
Select this check box to include confirmed orders in the search results and request. This check box appears only if you have selected an action of Ship. |
The action of reserve only includes unfulfilled orders and the action of pick confirm only includes released orders.
|
Group Picking/Shipping Default |
Select to go to the Picking/Shipping Overrides page, where you can override the picking storage location and shipping parameters. The overrides entered through this link apply to all demand lines in the processing group. |
Other Options
|
Process |
Select to process all the demand lines matching the entered search criteria, without viewing any details. The entered search criteria (request) is written to the staging tables to be processed by the fulfillment engine using the Fulfillment Requests process. If you have selected the Auto Schedule Processing check box on the Processing Defaults page of this workbench or the Setup Fulfillment - Fulfillment Engine page, then the Fulfillment Requests process is launched when you click this button. Note. Because the Process button immediately adds the information to the staging tables, it is not available once you have added data to the fulfillment queue. Go to the fulfillment queue and click the Process button to write the transaction request to the staging tables. |
|
Add to Queue |
Select to add search criteria to the fulfillment queue to be processed later. You can view the search criteria on the Fulfillment Queue page. When an order or demand line is selected and added to the fulfillment queue using the Orders link or Demand Line link, then a group level entry is automatically created in the fulfillment queue if one was not previously added from the Fulfillment Workbench page. In this situation, the group level entry has no selection criteria. This is done to meet the fulfillment engine's requirement for all detail segments to belong to a group ID on the transaction request being processed. |
|
Clear |
Select to clear any search criteria fields that have been populated. |
|
Empty Queue |
Select to remove all demand lines from the request. |
|
Fulfillment Queue |
Select to go to the Fulfillment Queue page, where you can view and edit the details of the current search criteria added to this request. |
|
Orders |
Select to go to the Orders page, where you can view and select individual orders for processing. |
|
Demand Lines |
Select to go to the Demand Lines page, where you can view and select individual demand lines for processing. |
|
Ship Defaults |
Select to go to the Picking/Shipping Overrides page, where you can override the picking storage location and shipping parameters. The overrides entered through this link apply to all demand lines in the transaction request. |
|
Process Default |
Select to go to the Processing Defaults page, where you can alter the fulfillment engine processing options applied to this request. |

 Reviewing and Changing the Orders in a Request
Reviewing and Changing the Orders in a RequestAccess the Orders page.
The Unpacked Orders section displays all orders with unpacked quantities matching the search criteria entered on the Fulfillment Workbench page. These orders appear by business unit, demand source, source business unit, and order number. The Shipping Containers section displays orders matching the search criteria that have already been packed into a shipping container. These orders appear by business unit and container.
Orders that are partially packed or partially unpacked are shown in both the Unpacked Orders group box and the Shipping Containers group box. If the order is selected from the Unpacked Orders group box, then both the packed and unpacked demand lines on the order with full quantities are processed by the fulfillment engine. If the container is selected, then only the demand lines in the container and only the packed quantities in the container are processed.
|
Select All |
Click to select all the Select check boxes for each row. Any rows with clear Exclude check boxes are enabled. |
|
Select None |
Click to clear all the Select check boxes for each row. Any rows with selected Exclude check boxes are cleared and disabled. |
|
Exclude All |
Click to select all the Exclude check boxes for each row. Any rows with cleared Select check boxes are selected. |
|
Exclude None |
Click to clear all the Exclude check boxes for each row. |
|
Select |
Check to include this order in the request. |
|
Exclude |
Select to define the search criteria as exclusion criteria. This check box appears only if Detail is selected in the Search By field. Selection criteria entered are used to exclude demand data from the group. For example, if you want to ship all the orders in a pick batch ID except order number 55, then enter the pick batch ID at the group level and add the group segment to the fulfillment queue. Next, bring up the detail selection information by entering Detail in the Search By field and selecting the Exclude check box. Then enter the pick batch ID and order number 55. Add the detail segment to the fulfillment queue. Then use the Fulfillment Queue link to review the transaction request and write it to the staging tables when you click the Process button. Note. If the Exclude check box is selected at the order or demand line level, then that order or demand line must exist in the selection criteria established at the group level. If it is not in the selection criteria, then the fulfillment engine rejects the transaction request. |
|
Demand Lines |
Select to access the Demand Lines page, where you can view the demand lines associated with this order number. |
|
Ship Defaults |
Select to access the Picking/Shipping Overrides page where you can override the picking storage location and shipping parameters. The overrides entered through this link apply only to the order selected. |
|
Complete Flag |
Choose a Complete Flag option to automatically performing picking functionality on demand lines that have no previous picking activity reported against them. |
|
Add to Queue |
Select to add the order as a detailed-level segment in the fulfillment queue. You can view the demand lines on the Fulfillment Queue page. When an order is selected and added to the fulfillment queue, a group level entry is automatically created in the fulfillment queue if one was not previously added from the Fulfillment Workbench page. In this situation, the group level entry has no selection criteria. This is done to meet the fulfillment engine's requirement for all detail segments to belong to a group ID on the transaction request being processed. |
|
Workbench |
Select to go to the Fulfillment Workbench page. |
|
Fulfillment Queue |
Select to go to the Fulfillment Queue page, where you can view and edit the details of the current orders on this request. |

 Reviewing and Changing the Demand Lines in a Request
Reviewing and Changing the Demand Lines in a RequestAccess the Demand Lines page.
This page displays in fulfillment state and demand key sequence.
|
Select All |
Click to select all of the Select check boxes for each row. Any rows with disabled Exclude check boxes are enabled. |
|
Select None |
Click to clear all of the Select check boxes for each row. Any rows with Exclude selected are cleared and disabled. |
|
Exclude All |
Click to select all of the Exclude check boxes for each row. Any rows with Select check boxes cleared are selected. |
|
Exclude None |
Click to clear all the Exclude check boxes for each row. |
|
Select |
Select to include this demand line in the request. |
|
Exclude |
Select to exclude this demand line from the selection criteria entered at the group level. |
|
Qty (quantity) |
Enter an override quantity for this demand line. If you are using an action of Reserve on the Fulfillment Workbench page, then this value overrides the releasable quantity on the demand line. If you are using an action of Pick Confirm on the Fulfillment Workbench page, then this value overrides the released quantity on the demand line. If you are using an action of Front End Ship or Ship on the Fulfillment Workbench page, then this value overrides the shipped quantity on the demand line. |
|
UOM (unit of measure) |
Enter the UOM for the quantity field. The shipping UOM is used as the default for all actions but reserve, but you can override it with any valid UOM for the item. For the action of reserve, the ordering UOM is used as the default. |
|
Location / Lot / Serial |
Click this link to access the Fulfillment Queue Location / Lot / Serial page, where you can review and change information related to specific items picked and shipped for this detail row in the transaction request. |
|
Add to Queue |
Select to add the demand lines matching the search criteria to the fulfillment queue to be processed later. You can view the demand lines on the Fulfillment Queue page. When a demand line is selected and added to the fulfillment queue, a group level entry is automatically created in the fulfillment queue if one was not previously added from the Fulfillment Workbench page. In this situation, the group level entry has no selection criteria. This is done to meet the fulfillment engine's requirement for all detail segments to belong to a group ID on the transaction request being processed. |
|
Workbench |
Select to go to the Fulfillment Workbench page. |
|
Fulfillment Queue |
Select to go to the Fulfillment Queue page, where you can view and edit the details on this request. |
|
Orders |
Select to go to the Orders page, where you can view the orders in the current search criteria. |

 Reviewing and Changing LLS Details for Demand Lines
Reviewing and Changing LLS Details for Demand LinesAccess the Location / Lot / Serial page.
Review or change demand location information in this request detail row.
Lot / Serial
|
Serial ID |
Review or enter a serial ID for this request detail row or demand line. If the item is defined as a ship serial controlled item then enter the ship serial ID here. |
|
Qty |
Review or change the picking or shipping quantity for this request detail row. |
|
UOM (unit of measure) |
Review or change the picking or shipping UOM for this request detail row. |
Storage Location
|
Excluded |
Select to exclude a specific picking location, lot ID, or serial ID from this request detail row. This check box is available only when shipping from a confirmed state. |
|
Area, Lev 1, Lev 2, Lev 3, and Lev 4 |
Review or enter a specific picking location for this request detail row. |
Miscellaneous
|
Cntr ID and Staged Dt |
Review or enter an internal container ID or staged date for this demand line. |
|
Shipping Container ID |
Review or enter a shipping container ID for this demand line. |
|
Short Ship Opt |
Select an option for short shipping this demand line. Options are:
|

 Reviewing and Changing LLS Details in the Fulfillment Queue
Reviewing and Changing LLS Details in the Fulfillment Queue
Access the Fulfillment Queue Location / Lot / Serial page.
This page contains the same fields as the Location / Lot / Serial page above, but also includes the following additional fields:
|
Substitute Item ID |
Enter a substitute item ID if the original item is defined for substitutes. Item substitution is only allowed for the first LLS row. For subsequent rows of the same demand line, the substitute item is display-only. |
|
Seq Nbr |
Enter the sequence number. The sequence number is a unique identifier for rows with the LLS segment for each detail segment. |

 Applying Picking and Shipping Overrides
Applying Picking and Shipping Overrides
Access the Picking / Shipping Overrides page.
Enter picking and shipping overrides for demand lines processed on the Front End Shipping and Shipping Request transactions. When entering this page, the system displays any overrides previously entered for this request. This page can be accessed from several pages in the Fulfillment Workbench component. How you access the page determines the level that the picking and shipping overrides are applied. The overrides can be applied at the request, group, detail, of LLS levels, as follows:
|
Level Applied |
Navigation to Picking/Shipping Overrides Page |
|
Request Header Level: Applies to the entire transaction request. Overrides are applied unless another override exists at a lower level. |
|
|
Group Level: Applies to the group. One request can contain one or more groups. |
|
|
Detail Level: Applies to one detail level within a group. For example, one demand line in an order. |
Select the Ship Defaults link under the Miscellaneous tab on the Demand Lines page. |
|
LLS Level: Applies to one LLS within a detail. For example, as demand line might have multiple serial IDs. |
Select the Ship Defaults link under the Lot/Location/Serial tab on the Fulfillment Queue page. |
|
Freight Amount and Freight Calculate Flag |
These fields are only valid for sales orders from PeopleSoft Order Management. Enter the freight amount for this demand or select the Freight Calculation Flag check box to have the system calculate freight charges for the estimated shipments on the sales order. |
|
Tracking Number |
Enter a tracking number for this shipment. This field is only available if you have entered a Ship Cntr ID on this page. |
|
Storage Area |
Enter the material storage location to pick stock for shipment. This override is applied against all demand lines processed from an unfulfilled or releasable state that do not have picking locations identified at the Location/Lot/Serial segment of the transaction request. If a picking location is not entered on the request, then the fulfillment engine uses the picking location setup on the Setup Fulfillment component. |
|
Short Ship Opt |
Select an option for short shipping this demand line. Options are:
|

 Changing Processing Defaults
Changing Processing DefaultsAccess the Processing Defaults page.
Review or change any processing defaults for this request. Initially this page displays the current fulfillment engine options that are defined in the environment at the business unit level (in the Setup Fulfillment component) or at the set ID level (on the Fulfillment Engine Options page). The fields available on this page are determined by the selection of the Allow Processing Overrides check box in the fulfillment engine options.
|
Auto Schedule processing |
Select this check box to immediately process this request when you click the Process button on the Fulfillment Workbench page or the Fulfillment Queue page. Requests are placed in staging tables and then immediately processed by the fulfillment engine using the Fulfillment Requests process. |
|
Commit Count |
(For reserve requests) Enter the number of lines that can be committed to the database together by the fulfillment engine; in other words, define the size of the commit group. |
|
Pass-through Level |
An entry here enables error-free transactions to process through the system while holding back transactions that need additional review. This field is available only with a reservations transaction request. The options are:
|
|
Commit Level |
(For reserve requests) Select the level of commits based on the number of:
|
|
Auto Processing Option |
Select the auto processing option to move your orders downstream to the desired state. The options available depend on the action chosen on the Fulfill Workbench page. Options include:
|
|
Auto Release Run Control |
Select a run control for the Order Release Request process page. This run control contains the parameters to be used when auto-processing orders from an unfulfilled state to another downstream state. The Auto Processing Option field determines how far downstream the orders will be sent. |

 Reviewing Demand in a Request
Reviewing Demand in a RequestAccess the Fulfillment Queue page.
You can review the orders and demand lines that make up this request. You can also add, modify, or delete from the detail level and LLS level of this request.
Fulfillment Queue Group
The Fulfillment Queue group section displays the search criteria for each group defined in the fulfillment request transaction. The exact fields that appear are determined by the template definition and match the fields that appear in the Selection Criteria section of the Fulfillment Workbench page.
Fulfillment Queue Detail
The Fulfillment Queue Detail group box is used to review and edit detail level entries that have been created on a fulfillment transaction request.
|
Group Picking/Shipping Default |
Select this link to go to the Picking/Shipping Overrides page, where you can override the picking storage location and shipping parameters. The overrides entered through this link are applied at the group level. |
|
Exclude |
Under the Demand Key tab, select and enter information to identify demand that should be excluded from the request. |
|
Quantity (quantity) |
Under the Demand Key tab, enter an override quantity for this demand. If you are using an action of Reserve on the Fulfillment Workbench page, then this value overrides the releasable quantity on the demand line. If you are using an action of Pick Confirm on the Fulfillment Workbench page, then this value overrides the released quantity on the demand line. If you are using an action of Front End Ship or Ship on the Fulfillment Workbench page, then this value overrides the shipped quantity on the demand line. |
|
Unit of Measure |
Under the Demand Key tab, enter the UOM for the quantity field. The standard UOM is used as the default, but you can override it with any valid UOM for the item. |
|
Location / Lot / Serial |
Under the Lot/Location/Serial tab, select this link to access the Fulfillment Queue Location / Lot / Serial page, where you can review and change information related to specific items picked and shipped for this detail row in the transaction request. |
|
Ship Defaults |
Under the Lot/Location/Serial tab, select this link to go to the Picking/Shipping Overrides page, where you can override the picking storage location and shipping parameters. The overrides entered through this link apply to the detail level. |
|
Short Ship Opt |
Under the Lot/Location/Serial tab, select an option for short shipping this demand line. Options are:
|
Other Options
|
Process |
Select to process all the demand lines matching the entered search criteria. The entered search criteria (request) is written to the staging tables to be processed by the fulfillment engine using the Fulfillment Requests process. If you have selected automatic schedule processing on the Processing Defaults page or the Setup Fulfillment - Fulfillment Engine page, then the Fulfillment Requests process is launched when you click this button. |
|
Empty Queue |
Select to remove all demand lines from the request. |
|
Workbench |
Select to go to the Fulfillment Workbench page, where you can add additional selection criteria. |
|
Ship Defaults |
Select to go to the Picking/Shipping Overrides page, where you can override the picking storage location and shipping parameters. The overrides entered through this link apply to the entire transaction request. |
|
Orders |
Select to go to the Orders page, where you can view and select individual orders for processing. |
|
Demand Lines |
Select to go to the Demand Lines page, where you can view and select individual demand lines for processing. |
 Processing Fulfillment Transaction Requests from the Staging Tables
Processing Fulfillment Transaction Requests from the Staging TablesThe Fulfillment Requests process (IN_FUL_BCT ) retrieves the requests from the staging tables and applies them to the PeopleSoft Inventory demand tables. If the requests are successfully processed against the demand tables, then they are marked as complete in the staging tables. If the requests are not processed successfully, they are returned to the staging tables with an error status.

 Pages Used to Process Fulfillment Requests from the Staging Tables
Pages Used to Process Fulfillment Requests from the Staging Tables|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
BCT_INV_REQFUL |
SCM Integrations, Process Transactions, Inventory, Fulfillment Requests |
Process fulfillment transaction requests in the fulfillment staging tables against the material stock orders and sales orders located in the PeopleSoft Inventory demand tables. These requests can move an order from one fulfillment state to another downstream state, often skipping intermediate steps. |
|
|
INV_PROCESS_SEC |
Click the Processing Options link on the Fulfillment Requests page. |
Review or change the fulfillment engine processing options used by the Fulfillment Requests process. Initially this page displays the current fulfillment engine options that are defined in your environment at the business unit level (in the Setup Fulfillment component) or at the set ID level (on the Fulfillment Engine Options page). The fields available on this page are determined by the selection of the Allow Processing Overrides check box in the fulfillment engine options. |
|
|
INV_FUL_DFLT_BU |
Select the View Processing Defaults link on the Fulfillment Requests page. |
Review the fulfillment engine processing options defined in this run control for the Fulfillment Requests process. |

 Fulfillment Requests Process Page
Fulfillment Requests Process PageAccess the Fulfillment Requests page.
|
Unit and To Business Unit |
If this run control should process one PeopleSoft Inventory business unit, enter the unit in the Unit field. If you want to process a range of business units, enter the starting unit in theUnit field and the ending business unit in the To Business Unit field. The system processes all business units, for which the user has security privileges, sorted in alphanumerical order, that fall between the starting and ending unit. |
|
All Business Units |
Select to process all PeopleSoft Inventory business units in this run control. |
|
Transaction Code |
Enter the type of transaction to be processed. Leave this field blank to process all transaction types. Options are:
|
|
Re-process any Errors in Range |
Select to have the process pick up fulfillment transaction requests in the status of error, as well as requests with the status of new. |
|
Transaction Source and Source Reference |
Select to process all transaction requests coming from external systems (through application messages) and originating from a specific transaction source and source reference. These are free-form fields that can be populated by the source system. |
|
From EIP_CTL_ID and To EIP_CTL_ID |
Select to process one or more fulfillment transaction requests based on the EIP Control ID assigned. Each transaction request placed on the fulfillment staging tables is identified with a unique EIP Control ID. Enter a range in the From EIP_CTL_ID and To EIP_CTL_ID fields. For just one specific ID, use the From EIP_CTL_ID field only. |
|
Publishing Node and Publication ID |
Select to process all transaction requests coming from external systems (through application messages) and originating from a specific node with a given publication ID. |
|
Processing Options |
Select to access the Processing Controls page, where you can view and override, for the run control, some of the fulfillment engine processing options defined at the business unit or set ID level. |
|
View Process Defaults |
Select to access the Fulfillment Engine Options page, where you can view the fulfillment engine processing options defined at the business unit level. |
 Handling Errors with the Fulfillment Engine
Handling Errors with the Fulfillment EngineUse the Log Errors Option group box on the Setup Fulfillment - Fulfillment Engine page to define your approach to errors in processing fulfillment transaction requests in the staging table. The options are:
Transaction Error Log: Enables you to view and correct fulfillment transaction requests that contain errors using the Maintain Transactions page.
Once you correct the errors, you can relaunch the Fulfillment Requests process.
Message Log: Enables you to view error messages in the message log, as well as in the staging tables. This option is recommended for environments that do not want to follow up on every transaction because the fulfillment transaction requests in error are automatically canceled. Error can be viewed in the message log and fixed using online pages without having to make decisions about manually restarting or cancelling individual fulfillment transaction requests.

 Page Used to Handle Errors with the Fulfillment Engine
Page Used to Handle Errors with the Fulfillment Engine
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
BCT_CTL_UPD |
SCM Integrations, Transaction Error Handling, Maintain Transactions, Transaction Maintenance |
View all electronic transactions in the transaction log and access the detail pages that enable you to correct transaction errors. |