 Understanding Journal Generator
Understanding Journal GeneratorThis chapter provides an overview of Journal Generator and discusses how to:
Set up for Journal Generator.
Generate journal entries.
 Understanding Journal Generator
Understanding Journal GeneratorThe Journal Generator process (FS_JGEN) creates journals from accounting entries from the following data sources:
Non-PeopleSoft systems.
PeopleSoft applications in the same database, such as Payables, Contracts, and Purchasing.
PeopleSoft applications from another database, such as PeopleSoft Enterprise Payroll and Student Financials.
Journal Generator does the following:
Transforms accounting entries into General Ledger journals.
Optionally edits and posts the journals created in Journal Generator.
Supports journals for multiple general ledger (GL) business units as well as multiple ledgers.
Supports debit and credit entries and negative correcting entries.
For non-PeopleSoft systems, the following examples are provided to interact with Journal Generator:
A generic accounting entry definition named GENERIC.
A journal generator template named GENERIC.
A generic accounting entry table (PS_JGEN_ACCT_ENTRY) used as an interface between external systems and Journal Generator.
It is not used by delivered PeopleSoft subsystems.
Use it or clone it to load transactions to be processed by Journal Generator. Create journal entries using these generic definitions, or use your own modified definitions.
See Also
Creating Journals from Accounting Entries Using Journal Generator

 Convert Accounting Entries to PeopleSoft Journals
Convert Accounting Entries to PeopleSoft JournalsThis diagram summarizes how PeopleSoft applications create journal entries:
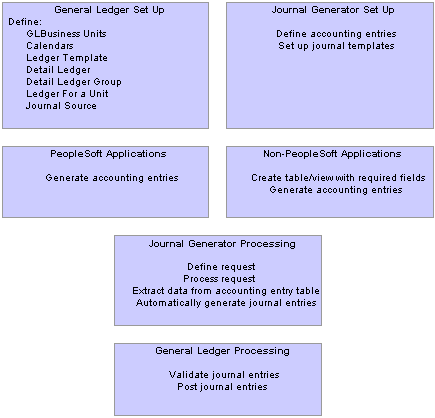
How PeopleSoft applications create journal entries
Accounting entries are created in other application systems, both PeopleSoft and non-PeopleSoft.
PeopleSoft entry event and interunit and intraunit processes also create accounting entries that can be processed by Journal Generator.
If you have installed Commitment Control, budget checking can be done with journal edit and validation.
The Journal Generator process transforms accounting entries into general ledger journals. Subsystem applications can create journals from the application business unit to different general ledger business units, as well as to different ledger groups and ledgers for a General Ledger business unit.
General Ledger validates journals according to the criteria that you set up in your general ledger system. It automatically validates a journal when you request a journal edit. The Journal Entry Errors page displays any errors that the system encountered; you can then access the appropriate Journal Entry page to correct the errors. After the system validates the journals with no error, you can request posting to your general ledger. You can initiate the Journal Edit and Budget Check (GL_JEDIT2) and Journal Post (GLPPPOST) processes from Journal Generator, or initiate them later in a separate process.
See Also

 Journal Generator Required Field Names
Journal Generator Required Field NamesThis table lists the fields that must be in the Accounting Entry table to run Journal Generator. Fields shown in upper case are exact field names that are required in the table. Mixed-case field names indicate that you can specify the field name on the Accounting Entry Definition page:
This table lists optional fields for the Journal Generator process. Uppercase fields are exact field names that are used in the Accounting Entry table. Mixed-case names indicate that you can specify the field name on the Accounting Entry Definition page:
|
Field Name |
Description |
|
Statistical Amount |
Statistical amount. |
|
Journal Ref (journal reference) |
Journal line reference used to track the source of the transaction. |
|
Journal Descr (journal description) |
Journal description used to describe a transaction. |
|
Open Item Key |
Open item key provides the link between related open item entries. |
|
ChartFields |
ChartFields that map directly to the General Ledger ChartFields. The Journal Generator process uses these ChartFields when it summarizes the accounting entries and creates journals. |
|
KK_AMOUNT_TYPE |
Commitment Control Amount Type provides commitment control accounting entries for budget checking in General Ledger on the journals created. |
|
DOC_TYPE |
Use document type for document sequencing. Use this field and the Document Type mapping feature on the journal generator template to group accounting entries according to the general ledger document type into different journals. |
|
DOC_SEQ_NBR |
Sequence number of the document. |
|
DOC_SEQ_DATE |
Date the document sequence number was assigned or validated. |
|
MOVEMENT_FLAG |
Defines the sign of the amount if you enabled the Separate Debit/Credit option. Otherwise Journal Generator ignores this flag. The values are: N: Natural sign of the monetary amount of the transaction. This is the default. For suspense balancing, base currency rounding adjustments, currency position, and interunit from and to lines, this field is always N. R: Reverse sign of the monetary amount of the transaction. If the Enable Separate Debit/Credit option is selected on the Ledgers For A Unit - Definition Page and you enabled separate debits and credits for your system, you can toggle this field to represent a reversing debit or credit amount. |
|
ADB_DATE |
If the Average Daily Balance Date field exists on the accounting entry table, Journal Generator uses it to populate the ADB date of the journal header. |
|
BOOK_CODE |
If the Book Code field exists in the accounting entry table and if Book Code has been activated on the Overall Installation Options page, Journal Generator groups accounting entries into different journals according to the Book Code. |

 Using Journal Generator with Commitment Control
Using Journal Generator with Commitment Control
Whether Journal Generator processing includes budget checking depends on the system source and the Skip Commitment Control in GL option in the accounting entry definition.
Accounting Entry Definition System Source with an Application Subsystem That Supports Commitment Control
General Ledger does not perform commitment control budget checking when journals are created with this type of definition because the entries are budget checked in the feeder, or subsystem.
The Budget Check option on the Journal Generator request page is not applicable for these entries.
Journal Generator processing occurs under these conditions:
If KK_AMOUNT_TYPE exists on the accounting entry table:
Journal Generator processes only those entries with a KK_AMOUNT_TYPE value of 1, indicating actuals.
If KK_AMOUNT_TYPE is not in the accounting entry table:
Journal Generator assumes that all entries are actuals, and processes them.
Accounting Entry Definition System Source Without an Application Subsystem That Supports Commitment Control
The Skip Commitment Control in GL option determines if General Ledger performs budget checking for journals created from this definition.
The Budget Check option on the Journal Generator request page specifies if Journal Edit includes budget checking as part of its edit process, which is called by Journal Generator after it creates journals. This is applicable only to journals generated from an accounting entry definition with Skip Commitment Control in GL cleared.
Journal Generator processing occurs under these conditions:
If KK_AMOUNT_TYPE exists on the accounting table:
Only those entries specified in the accounting entry definition are processed. If you specify Actualize, then Journal Generator processes only those entries with KK_AMOUNT_TYPE = 1 for actuals. If you leave the option blank (which means all entries), then Journal Generator processes all entries. Journal Generator creates a journal for each different KK_AMOUNT_TYPE value that it finds in the source table.
If KK_AMOUNT_TYPE is not in the accounting table:
Journal Generator assumes that all entries are actuals, and processes them all.
 Prerequisites
PrerequisitesBefore you begin:
Define the date range for extracting accounting entries on the Open Period page.
Review your record definitions for the ledger on the Ledger Template - Record Definitions page.
Journal Generator uses the following record names to create the journals:
Journal line record (JRNL_LN).
Journal generator temporary record (JGEN_WRK_TMP).
Journal header record (JRNL_HEADER).
JRNL_HDR_REC is a field on LED_TMPLT_TBL to specify the journal header record. The JRNL_HDR_REC field is not on the Ledger Template - Record Definitions page because General Ledger does not support a journal header record name other than JRNL_HEADER. However, Journal Generator can support a dynamic journal header record name. You can use the recommended SQL tools to update LED_TMPLT_TBL.JRNL_HDR_REC with another journal header record name for the specified ledger template.
Warning! If you install General Ledger, do not change the journal header record name. Otherwise, the journals that you create will not post to General Ledger.
On the Ledger Template - Field Definitions page, review the field definitions.
For third-party system transactions, Journal Generator summarizes debits together and credits together instead of summarizing them to the net amount if the following conditions are true:
Posted Total Debits and Posted Total Credits fields contain values.
You selected the Enable Separate Debit/Credit option for the ledger on the Ledgers For A Unit page.
Additionally, you can make adjustment entries for reversing debit and reversing credit in the accounting entries. Journal Generator summarizes these reversing entries separately.
On the Detail Ledger - Definition page, verify :
That the ledger template and the detail ledger are linked.
That multiple ledgers within the same journal belong to the same ledger group, as shown on the ledger group page.
When Journal Generator creates journals, it posts accounting entries based on the settings for the ledger group. It creates a distinct journal header for each ledger group.
That the Keep Ledgers in Sync field setting. The Keep Ledgers in Sync option determines if journal entries post to all ledgers in the ledger group or only to a single specified ledger.
The journals that the Journal Generator process creates depend on whether this option is selected or cleared and whether the Accounting Entry in Sync option in the journal generator template is selected.
Which journals Journal Generator creates depends on these settings:
The Keep Ledgers in Sync option, on the Detail Ledger Group - Definition page, decides if journal entries post to a single specified ledger (clear) or to all ledgers in the ledger group (selected).
The Accounting Entry in Sync option in the journal generator template, used for multibook, has many implications.
Whether you specified the ledger group and ledger for the accounting entry lines.
Review the Ledgers For a Unit pages.
On the Definitions page, verify the ledger groups for the business unit. The Journal Generator process generates journals for different ledger groups for the same general ledger business unit. If the ledger group field is blank in the Accounting Entry table, Journal Generator uses the default ledger group defined on the Ledgers For a Unit - Definitions page for the journals of this general ledger business unit.
On the Definitions page, verify the ledger definitions for the business unit.
On the Journal Edit Options page, verify the journal edit option definitions.
The journal balance option, journal edit errors option, journal amount errors option, and control total option determine the journal error processing.
On the Currency Options page, verify the currency option definitions.
The currency options determine the balancing, base currency adjustments, and rounding adjustments for the journals. The Foreign Currencies per Journal option determines if the Journal Generator process creates separate journals for each foreign currency. If you select Only One Foreign currency or No Foreign Currencies, the system creates one journal for each foreign currency.
On the Journal Post Options page, verify the journal post options.
On the Approval Options page, verify the approval options, which determine the approval rules for standard journals and budget journals.
On the Commitment Control Options page, verify the commitment control options.
See Also
 Setting Up for Journal Generator
Setting Up for Journal GeneratorTo set up the journal generator, use the Accounting Entry Definition component (JRNLGEN_DEFN), Journal Generator Template-Defaults component (JRNLGEN_APPL_ID) and the Journal Generator Template-Summarization component (JRNLGEN_APPL_ID).
This section provides an overview of Journal Generator setup and discusses how to:
Define accounting entries.
Define journal generator template defaults.
Define journal generator template summarization.

 Understanding Journal Generator Setup
Understanding Journal Generator Setup
The Journal Generator process creates general ledger journals for any application. The process uses the record and field names from the accounting entry definition to extract data from the Accounting Entry table and create journals.
It extracts data from any table in the database as long as the table contains the required fields listed in the Reviewing Journal Generator Required Field Names.
Your application may contain field names that are different from the required fields in the Accounting Entry table but have the same attributes. If this is the case, create a view in your system’s distribution line table and point the Journal Generator to it by specifying its name in the Accounting Entry Record field on the Accounting Entry Definition page.
If you changed or added fields and want to pass values associated with these fields to journals—that is, retain detail—you insert the new fields in five tables: Accounting Entry, Journal Generator Work (JGEN_WRK_TMP), Journal Generator Dynamic State Records (FS_JGEN_UPD_AET and FS_JGEN_PRV_AET), and Journal Line. The fields must have the identical field names and attributes in each table. Finally, in the journal generator template select Retain Detail.
Non-PeopleSoft systems can use the GENERIC accounting entry definition or create their own modified accounting entry definition.
See Also
Journal Generator Required Field Names

 Pages Used to Set Up for Journal Generator
Pages Used to Set Up for Journal Generator

 Defining Accounting Entries
Defining Accounting Entries
Access the Accounting Entry Definition page.
|
Accounting Definition |
Use this unique name on the Journal Generator Request page to tie your request to an accounting entry table and field definition. |
Accounting Entry
Field Names
Enter the field names to identify the columns in the Accounting Entry table that the Journal Generator uses to create the journal.
ChartField Mapping
Expand this grid to perform mapping.
|
Field Name |
Specify the accounting entry field names that map directly to the General Ledger ChartField names. |
|
ChartField |
Specify general ledger ChartField names. If you select the Summarize to All ChartField Level option on the Journal Generator Template - Summarization page, Journal Generator uses the listed ChartFields when it summarizes the accounting entries and creates journals. The ChartFields that are not listed have a blank value in the newly created journals. |
|
Summarize ChartFields |
Specifies the ChartFields that are summarized if the Summarize by Selected ChartFields on the Journal Generator Template - Summarization page is selected. The ChartFields that are not selected have a blank value in the newly created journals. |
Note. Journal Generator limits you to mapping a field once. For example, you cannot map Journal Ref and Open Item Key to the same field name. They must be mapped to different field names.
MultiBook Order By
Specify the field names for in-sync multibook accounting.
Within a ledger group, the accounting entries for one transaction that are distributed to different ledgers are referred to as in-sync accounting entries. These accounting entries have the same ChartFields, foreign currency, and foreign amounts. PeopleSoft applications that support multibook generate in-sync accounting entries to all ledgers within a ledger group.
If the Accounting Entry In Sync option is selected in the journal generator template, Journal Generator recognizes the in-sync accounting entries and marks them for the Journal Edit process to create any missing in-sync journals. When it generates the journal, Journal Generator uses the MultiBook Order By fields to determine how to group accounting entries for one transaction.
If the application subsystem supports multibook in sync, it sends in-sync entries, including those for the translation ledger, to the Journal Generator process. Journal Generator uses the MultiBook Order By fields to determine multibook entries for the same transaction.
|
Field Names |
If you create new accounting entries from third party systems, you can enter field names in the sort order required to group the new accounting entries. |
Warning! Do not change any of the values in these fields as delivered. The values are set for the delivered accounting entries and any changes can cause serious data problems.
See Also
Journal Generator Required Field Names

 Defining Journal Generator Template Defaults
Defining Journal Generator Template DefaultsAccess the Journal Generator Template - Defaults page.
The defaults and summarization options that you set up using the journal generator templates determine how journal generator summarizes accounting entries and creates journals. Typically, you set up Journal Generator templates for each application system source that distributes to the general ledger, as well as each type of transaction. For example, you can have a template for depreciation expense from Asset Management. For systems other than PeopleSoft systems, you can use the GENERIC journal generator template or create a modified journal generator template.
Journal Generator groups accounting entries together that share the same general ledger business unit, ledger group, book code (the field BOOK_CODE exists in the accounting entry table and Book Code has been activated on the Overall Installation Options page), journal template, journal date, general ledger document type, average daily balance date (the field ADB_DATE exists in the accounting entry table), and the commitment control amount type (field KK_AMOUNT_TYPE exists in the accounting entry table). Accounting entries with different foreign currencies might not be grouped in the same journal, depending on the currency balancing option for the:
Source.
Business unit ledger group.
General ledger business unit.
Options
If a PeopleSoft application that supports the multibook feature has generated in-sync accounting entries for this template, select the Accounting Entry In Sync check box. PeopleSoft applications that support multibook generate in sync accounting entries to most ledgers within a ledger group. The exception is that some products may not include the currency translation ledger. See the individual product documentation to determine if this feature is available for your product. If the Accounting Entry In Sync check box is selected, Journal Generator recognizes in-sync accounting entries and generates in-sync journals. The journals created by Journal Generator depend on the following:
For example, as this table shows the following accounting entries go into the same business unit journal for US003:
|
Application BU |
Voucher ID |
BU_GL |
Foreign Amount |
|
US001 |
VCHR1200 |
US003 |
300 |
|
US003 |
VCHR1202 |
US003 |
-300 |
Reversal Code
Select a Reversal Code option to specify when reversing entries are to be automatically generated. Reversal options become effective at the time this entry is posted.
|
Do Not Generate Reversal |
Journal Generator does not create the reversal entry, but it marks the journals with the reversal code. When the journals are posted later in a separate process, the system creates the reversal entry. |
|
Beginning of Next Period |
Creates a reversing entry dated the first business day of the next accounting period. It uses the business calendar that you assigned to the business unit on the General Ledger Definition - Definition page to determine the first business day. |
|
End of Next Period |
Creates a reversing entry dated the last business day of the next accounting period. It uses the business calendar that you assigned to the business unit on the General Ledger Definition - Definition page to determine the last business day. |
|
Next Day |
Creates a reversing entry dated the next business day. It uses the business calendar that you assigned to the business unit on the General Ledger Definition - Definition page to determine the next business day. |
|
Identifies the originating entity responsible for the journal entries, and also determines how the foreign currencies are grouped for each journal. |
|
|
Enter a unique journal ID mask to identify information such as the source or purpose of journal entries. Spaces are not allowed. A 10-character alphanumeric ID identifies PeopleSoft-system journals. The system automatically generates IDs based on the number or letter that you enter here. For example, if you enter AP, the system supplies the remaining eight characters based on the next available journal ID number. If you do not specify a journal ID mask, you can let the system automatically assign the journal IDs by accepting the default : NEXT. |
|
|
Journal Date |
Determines the journal date for the journals created and indirectly the number of journals created. From the Journal Date options, select the source of the header and line date for journals that use a business calendar. See Defining Business Calendars. Accounting Date on Transaction: Uses the accounting date on the accounting entries as the journal date. This selection may result in multiple journals. Begin Date - From Period: Uses the first open date of the From (year) Period set up on the Open Period page. Begin Date - To Period: Uses the beginning date of the open To (year) Period set up on the Open Period page. Current Date: Accepts the current system date when the process is run. End Date − From Period: Uses the ending date of the open From (year) Period set up on the Open Period page. End Date − To Period: Uses the last open date of the To (year) Period set up on the Open Period page. Period End − Accounting Date: Uses the period-end date that corresponds to the accounting date. This selection might result in multiple journals. Process Date: This refers to the Journal Process Date option specified on the General Ledger Business Unit Definition - Journal Options page. On that page, you can specify the process date defined for the business unit, or the current date. Specify Date: If you select this, the Date field is available for you to enter a specific date. |
|
Alt. Journal Date (alternate journal date) |
Determines the journal date for the journals created if the journal date determined from the journal date option is not within the open accounting period’s range. Select one of these values: Begin Date - From Period: Uses the first open date of the From (year) Period set up on the Open Period page. Begin Date - To Period: Uses the beginning date of the open To (year) Period set up on the Open Period page. End Date − From Period: Uses the ending date of the open From (year) Period set up on the Open Period page. End Date − To Period: Uses the last open date of the To (year) Period set up on the Open Period page. Retain Primary Journal Date: The system uses the date that you specify as the journal date in this journal generator template. |
|
Stay in Period |
Journal Generator derives the journal date according to the journal date options previously described. However, if you select the Stay in Period check box and the derived journal date is a not a working day, Journal Generator uses the next working day for the journal date. If the next working day is not in the same period, Journal Generator uses the day prior to the derived journal date for the journal date. If you clear the Stay in Period check box, Journal Generator changes journal dates that fall on nonworking days to the next working day, regardless of the accounting period. |
|
Descr (description) |
(Optional) Identifies information about the journal. It is useful for explaining any abnormalities in the journal. |
|
Reference |
Tracks the source of the transaction for the journal. |
|
The system uses the default GL document type to assign a document type on the journal header when you create journals through Journal Generator. Select a default GL document type. |
|
|
Currency Effective Date |
If you want to set the currency effective date on the journal header to be the average daily balance (ADB) date, select ADB Date in the template. Otherwise, the default is the journal date. If the ADB date does not exist on your accounting entry table, or if it is null, then the ADB date on the Journal Header will default to journal date. In this instance, selecting a currency effective date option does not make any difference because the currency effective date is always equal to the journal date. However, when the ADB date exists on your accounting table and it is not null, then Journal Generator can populate the ADB date from the accounting lines even if this date is different from the journal date. In addition to other existing groupings, Journal Generator also groups accounting lines into different journals by ADB date. |
If you use document sequencing, expand the Document Type Mapping grid to map application document types to general ledger document types. Document type mapping applies to all journals generated, whether they are summarized or retain detail.
If the application document type is not found on this mapping, it is assigned to the default GL document type. You can map multiple application document types to one GL document type, but you cannot map multiple general ledger document types to a single application document type. Each of the different GL document types results in a different journal.
Journal Line Fields
|
Line Descr (line description) |
Describes the transaction in more detail. Journal Generator uses the value entered here to populate the journal line description if one of the following is true:
|
|
Reference |
Refers each journal line back to a document, person, invoice, date, or any other information that helps to track the source of the transaction. Spaces are not allowed. Journal Generator uses the value entered here if one of the following is true:
|
See Also
Defining Sequencing Options for Accounting Entries

 Defining Journal Generator Template Summarization
Defining Journal Generator Template SummarizationAccess the Journal Generator Template - Summarization page.
Primary Summarization Option
These options identify how Journal Generator distributes account values from the application system source to General Ledger. In addition to the specified options, Journal Generator summarizes by entry event whenever that field exists on the accounting entry table and the summarization option is not Retain Detail.
|
How Specified Option |
Select to retain full details, or select a summarization level from the following values: Summarize to Account, AltAcct: Summarizes accounting entries at the account and alternate account level. All other ChartFields are blank. If alternate account is disabled at the ledger group level, it summarizes to account level only. Summarize to All ChartFields: Summarizes accounting entries to the level of all ChartFields that are listed on the Accounting Entry Definition page. Summarize by Selected CF’s: Summarizes accounting entries by ChartFields that have the Summarize ChartField check box selected on the Accounting Entry Definition page. Retain Detail: Distributes accounting entries in full detail. When this is selected, the Project ChartFields can be mapped on the Accounting Entry Definition page and Journal Generator populates the Project ChartFields in the journals that it creates. |
|
How Account Specified |
Your selection in the How Specified Option group box affects the accounts selected in this option. You can specify accounts or a tree to indicate the accounts that you want. It is recommended that you use trees whenever possible to reduce future maintenance should ChartField values change. Select an option for How Account Specified from the following values: All Account Values: Distributes all the accounting entries according to the how specified option. Selected Account Values: Distributes the selected account values according to the how specified option. Activates the Selected Values/Nodes and the Alternate Summarization Option fields. Selected Tree Nodes: Distributes the account values that are defined by the tree name, tree level, and selected nodes according to the how specified option. Activates the Selected Values/Nodes and Alternate Summarization Option fields, as well as the Tree Name and Level fields. Enter the name of the tree and the level to use for summarization. |
|
Tree Name |
Specify the name of the tree to use for summarization. |
|
Selected Values/Nodes |
Enter either accounts or tree nodes depending on the How Account Value Specified option. |
Alternate Summarization Option
The Alternate Summarization Option check boxes provide the same options as the Primary Summarization option for the accounts that are not selected in the Selected Values/Nodes field. Select the How Default Specified value. Choose to retain detail, or to summarize one of three ways.
|
How Default Specified |
Select one of these values: Summarize to Account, AltAcct: Summarizes accounting entries at the account and alternate account level if alternate account is selected for the ledger group. All other ChartFields are blank. Summarize to All ChartFields: Summarizes accounting entries at the full ChartField level defined in the ChartField mapping fields on the Accounting Entry Definition page. Summarize by Selected CF’s: Summarizes accounting entries by ChartFields that have the Summarize ChartField check box selected on the Accounting Entry Definition page. Retain Detail: Distributes accounting entries in full detail. |
 Generating Journal Entries
Generating Journal EntriesTo generate journal entries, use the Generate Journals Request (JRNLGEN_REQUEST).
Selecting journals for Journal Generator processing is the final step required to process accounting entries. In this step, Journal Generator extracts accounting entries from the accounting entry tables to generate the actual journal entries for editing and posting.
Each time that you run Journal Generator, it creates journals for all or one application business unit or units as well as all or one ledger group or groups, and all or one Journal Generator template or templates set up for those business units, depending on the options that you define on the Journal Generator Request page.
This section discusses how to:
Run Journal Generator processing.
Change journals created by Journal Generator.
Delete journals created by Journal Generator.

 Page Used to Generate Journal Entries
Page Used to Generate Journal Entries
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
JRNL_GEN_REQUEST |
General Ledger, Journals, Subsystem Journals, Generate Journals, Generate Journals Request |
Initiate Journal Generator processing. |

 Running Journal Generator Processing
Running Journal Generator ProcessingAccess the Generate Journals Request page.
Journal Processing Options Group Box
|
Edit |
Select this check box to run the Journal Edit process. No prerequisites are required. |
|
Budget Check |
Select this check box to run the Budget Check process. You must run the Journal Edit process before running this budget check. |
|
Post |
Select this check box to run the Post process. You must run edit and budget check before posting. |
Note. If you select none of these check boxes, no additional processes are run.
Process Request Parameters
|
Request Number |
To identify the process request, the system assigns this unique number to each run. You can create multiple requests. Use the scroll arrows to view requests already set up for the current user ID and run control ID. |
|
SetID |
This is required to extract the accounting entry definition for the request. |
|
Accounting Definition Name |
Identify which accounting entry definition the system should use when it creates the journal header and lines. |
|
Application Business Unit |
Journal Generator:
The application business unit can be other than the general ledger business unit. The prompt for this field depends on the system source of the accounting definition name. For example, if the system source of the accounting definition is JrnlGen-AP, Journal Generator uses the Payables business unit table. If the system source is JGen-Other, no prompt table is available. |
|
Ledger Group |
Journal Generator creates journal entries for the specified General Ledger ledger group. |
|
Template |
Journal Generator creates journal entries for the specified journal generator template. The setID of the prompt values is derived from the setID entered earlier on the page. |
|
From Date Option |
Select a value to further define which accounting entries Journal Generator extracts with this request. Journal Generator compares these dates to the accounting dates associated with each accounting entry. Select from the following values: Specify Date: Uses the date specified to identify the period. Current Date: Uses the date on which Journal Generator is run. Begin Date - From Period: Uses the beginning date of the from period in the ledger. Begin Date - To Period: Uses the beginning date of the to period in the ledger. No From Date: Uses all open dates of the ledger before the chosen to date. This means that the system processes all dates up to the date in the To Date field. Process Date: Date specified on the business unit journal process date option. It can be a specified date defined on the business unit, or it can be the current date. |
|
From Date |
Enter a to date if Specify Date is selected in the From Date Option field. |
|
To Date Option |
Select a value to further define which accounting entries Journal Generator extracts with this request. Journal Generator compares these dates to the accounting dates associated with each accounting entry. Select from the following values: Specify Date: Uses the date specified to identify the period. Current Date: Uses the date on which Journal Generator is run. End Date - From Period: Uses the ending date of the from period in the ledger. End Date - To Period: Uses the ending date of the to period in the ledger. Process Date: Date specified on the business unit journal process date option. It can be a specified date defined on the business unit, or it can be the current date. |
|
To Date |
Enter a to date if Specify Date is selected in the To Date Option field. |
Note. The application business unit and general ledger business unit that exist in the Accounting Entry table can differ. One business unit must be designated to derive the setIDs for the control records during the batch processing. The control records are ledger group and ledger definition tables, calendar tables, journal source table, and journal generator template table. The general ledger business unit is the business unit to derive the setIDs for these control records. In one particular request, whether all or one business unit is selected, Journal Generator might have multiple general ledger business units to process and cannot determine the associated setID at the point at which the request is defined. Therefore, the prompt setID that you see in the Ledger Group field and Journal Generator template may not necessarily be the same as the setIDs used by the batch programs.

 Changing Journals Created by Journal Generator
Changing Journals Created by Journal GeneratorWhen a journal comes from a subsystem, you can enable a specific user to change a journal that the Journal Generator process creates. On the Define User Preferences - General Ledger page, select this option, which allows a specific user to update the ChartField and amounts on the Journal Entry page for a journal that was created by the Journal Generator process. The ChartFields can be changed, even though the budget status is valid for the journal. Otherwise, all the fields are unavailable and the user can only edit and post the journal.
However, the business unit field is unavailable and cannot be changed on journal lines created from Journal Generator.
Warning! If you select Change Journal from Journal Generator and then change the ChartField values and re-edit the journal, you can
create inconsistencies between the subsystem data and the general ledger data. Also, for journals that are generated for a
subsystem that supported Commitment Control, the journal does not budget check again even though the ChartField values or
the amount are changed.
For example, if the ChartField entered in the subsystem is Account 5011, Fund 100, Dept ID 200, and you change the ChartField
to Account 5011, Fund 100, Dept ID 300, the accounting entry created in the subsystem is different from the one posted in
the ledger. If the transaction is impacting the budget for department 200 initially, after the modification, it still impacts
department 200 instead of 300 because it was budget checked in the feeder application, or subsystem.
The Journal Generator process always skips budget checking under the following circumstances:
When journals are generated by a subsystem that supports commitment control.
When you select the Skip Commitment Control in GL check box on the Accounting Entry Definition page.
The system does not budget check again an altered journal generated journal, whether or not you select Change Journal from Journal Generator on the Define User Preferences - General Ledger page.
For subsystems that do not support commitment control, including external source non-PeopleSoft applications, you can select Skip Commitment Control in GL on the accounting entry definition page. In this case, the journal-generated journals must be budget checked in General Ledger.
See Also
Defining General Ledger User Preferences

 Deleting Journals Created by Journal Generator
Deleting Journals Created by Journal Generator
The Journal Generator process gets rows from the Accounting Entry table when the value in the GL_DISTRIB_STATUS field is N. The process changes this value to D when it distributes the accounting entry to a general ledger journal. When a journal that was created from Journal Generator has an error, you can delete the journal on the journal entry page, and the system changes the value in the GL_DISTRIB_STATUS field in the Accounting Entry table to N. Then you can correct the error at the accounting entry level and rerun the Journal Generator process to create a new journal.