 Understanding Excise Duty, Sales Tax, and Customs Duty Structure
Understanding Excise Duty, Sales Tax, and Customs Duty StructureThis chapter provides an overview of excise duty, sales tax, and customs duty structure, and discusses how to:
Set up the organizational structure.
Set up the common tax structure.
Set up items for tax processing.
Set up sales tax structure.
Set up excise duty structure.
Set up product kits for tax processing.
Set up customers for tax processing.
Set up vendors for tax processing.
Set up the customs duties foundation.
 Understanding Excise Duty, Sales Tax, and Customs Duty Structure
Understanding Excise Duty, Sales Tax, and Customs Duty StructureIndia’s excise duties, sales taxes, and customs duties are all similar in the way that they are set up and calculated. All three are tied closely to the location where business is conducted and have a tax determination structure that is influenced by common factors.
Excise duty, sales tax, and customs duty calculation methods are similar in that they can be calculated based on percentage, quantity, or ad hoc amount, and require the calculation of multiple taxes and tax lines for each tax type. The excise duty, sales tax, and customs duty structure is designed to be flexible enough to accommodate changes that may impact rate determination resulting from changes to excise, sales, and customs statutes and legislation.
There are various business rules for determining the basis on which taxes are calculated. Accordingly, you can define the elements that form the basis on which tax is calculated, and define the tax calculation scheme. You define how accounting entries are created for excise duties, sales taxes and customs duty, as well as how inventory values are updated with nonrecoverable taxes.
Note. The tax structure is geared toward handling excise, sales, service taxes, and customs duty. Luxury, entertainment, and other similar taxes are handled as service taxes. Other taxes, such as entry tax and Octroi, are handled by using the Miscellaneous Charges feature.

 Common Tax Structure Data Flow
Common Tax Structure Data FlowDefining data in the common tax structure populates tables that provide the hierarchical structure for excise duty, sales tax, and customs duty determination. The core of the common tax structure consists of the following elements:
Tax component codes.
Tax dependency codes.
Tax calculation codes.
Tax categories.
Data that is defined for each of these elements is used to build the Tax Determination table (EXS_TAX_DETERM). The following diagram illustrates the basic data flow within the common tax structure, resulting in tax determination data that provides tax calculation codes to transactions:
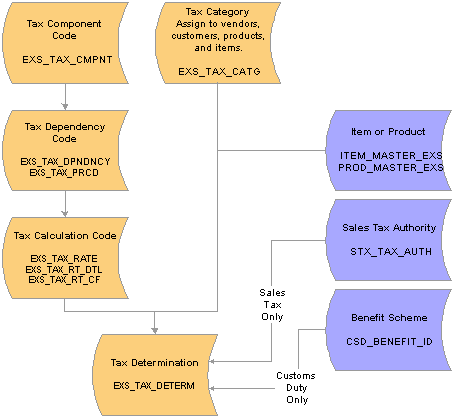
Tax Determination table

 Tax Calculation Code Default Hierarchy
Tax Calculation Code Default HierarchyBased on data that is stored in the Tax Determination table, the Tax Determination function (tax engine) selects default tax calculation codes for transactions by using one or a combination of parameters. It takes the transactions and lines that are in the Tax Determination table with common transaction types, tax authorities (for sales tax lines), and benefit schemes (for customs duty) and applies the following tax calculation code default hierarchies:
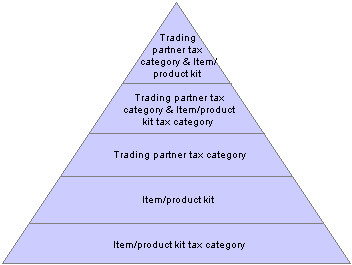
Tax calculation code default hierarchy for excise duty and sales tax
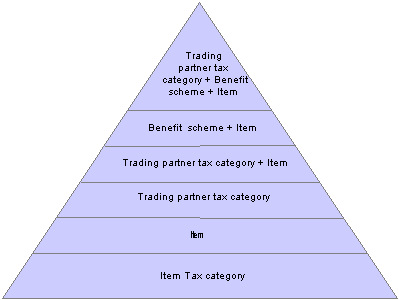
Tax calculation code default hierarchy for customs duty
Each level in these diagrams represent a factor in the hierarchy that can provide a tax calculation code default value. At the top of the triangle is the most specific level from which the Tax Determination function can derive a tax calculation code for excise duty, sales tax, and customs duty. At the base of the triangle is the least specific default level.
When determining the tax calculation code to use for a transaction, the tax routine first looks to the highest default level for a value. If it cannot find one there, it moves down the relevant levels in the triangle, searching for a defined value to use.
For example, if you have a purchase order for an excise-applicable item, the system looks at the transaction vendor and item and looks to the tax determination table to see if a tax calculation code is defined for the vendor’s tax category and item. If not, it looks to see if a tax calculation code is assigned to the vendor’s tax category and item’s tax category. It continues through the hierarchy until it finds a tax determination line that applies to the transaction.
If the Tax Determination function cannot find a tax determination line at the least-specific level, the tax calculation code derivation process is unsuccessful and no tax calculation code appears by default on the Tax page for the transaction.
See Also
Calling the Tax Determination Process
 Setting Up the Organizational Structure
Setting Up the Organizational StructureTo operate in India, an organization must register with various tax authorities and obtain permits that identify registration numbers. In India, excise duty, sales tax, and customs duty calculations are determined by the location of the business transaction, the vendor or customer category, exemptions that an organization, vendor, or customer obtains (identified by appropriate license numbers), and the tax rate.
You can define registration data at the organization setup level. You can define, for example, multiple tax locations for each organization and define for each tax location the excise registration's details, registers, document number ranges, and ChartFields. You can also associate multiple business units with a tax location and capture business unit tax applicability.
Note. Organizational structure setup for excise duty, sales tax, and customs duty is shared unless otherwise specified.
To set up the organizational structure, use the following components:
Organization Details (ORG_RGSTN_DTL).
BU Tax Applicability (ORG_BU_TAX_APPL).
Excise Number Series Document (ORG_DOC_NBR_SER).
Tax Location (ORG_TAX_LOC).
This section discusses how to:
Define organization details.
Define business unit tax applicability.
Define excise number series groups.
Define tax locations .
Define document number ranges.
Define the excise registration details.
Define the excise group details.
Define excise registers.
Define excise number ranges.
Define excise account type ChartFields.

 Pages Used to Set Up the Organizational Structure
Pages Used to Set Up the Organizational Structure|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
ORG_RGSTN_DTL |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Organization Details |
Define registration data at the organization level. |
|
|
ORG_BU_TAX_APPL |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, BU Tax Applicability. |
Assign a business unit to an organization and tax location code, and specify the business unit’s excise, sales tax and customs duty applicability. |
|
|
ORG_DOC_NBR_SER |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Excise Document Number Series |
Create excise number series groups for an excise transaction type. You can maintain number ranges for each excise transaction type for transactions beginning April 1 of each financial year at every tax location. You use this information during excise invoice creation to determine taxes and update excise registers. |
|
|
ORG_TAX_LOC |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Tax Location |
Specify the TAN registration numbers, as well as the default journal template, currency code, and rate type that is associated with a tax location. |
|
|
ORG_DOC_NBR_RNGE |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Tax Location, Document Number Range |
Define the effective date, number prefix, length, and ending sequence number for all combinations of excise document number series and excise transaction types that you set up on the Excise Number Series Document page. |
|
|
ORG_EXD_RGSTN |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Tax Location, Excise Registration |
Enter the excise registration details for the corresponding tax location. These details are used for reporting. |
|
|
ORG_EXD_GROUP |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Tax Location, Excise Group |
Enter capital goods information that is used to update registers and create accounting entries for excise duties. |
|
|
ORG_REGISTER |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Tax Location, Registers |
Define excise register details for excise register maintenance. |
|
|
ORG_EXD_CF_DET |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Tax Location, Chartfields |
The Register Update process creates the accounting entries to record excise duty from the shipping excise invoice, vendor excise invoice, and excise adjustments. For each type of CENVAT account, enter the ChartField combination that is to be used to create the accounting entries for the corresponding excise account type. The customs duty and service tax account types are also specified at the tax location level. |

 Defining Organization Details
Defining Organization DetailsAccess the Organization Details page.
|
PAN Number (permanent account number) |
Enter the number that is assigned by the income tax authority to identify the organization's tax returns. This number is usually a 10 digit alphanumeric code. PeopleSoft allows you to enter a 20 digit alphanumeric value. |
|
PAN Ward and PAN Circle |
Enter the location of the income tax offices to which the organization submits its taxes. Tax authorities assign these values. Wards and circles can change at the discretion of the income tax authority. |
|
Import Export Code |
Enter the code that is assigned to the organization by the Director General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) for identification purposes. The Import Export code must be used for all correspondence with customs authorities for import purchases. For example, this code is required on the Bill of Entry worksheet. |
|
BIN Number (business identifier number) |
Enter the business identification number that is assigned to the organization by the DGFT. The BIN must be used for all correspondence with the customs authorities for export purposes. For example, the BIN is required on the shipping documents that are sent to customs clearance. Note. PeopleSoft does not produce those Export Shipping Documents. |

 Defining Business Unit Tax Applicability
Defining Business Unit Tax ApplicabilityAccess the Business Unit Tax Applicability page.
|
Organization Code |
Select a valid organization code. You define organization codes on the Organization Details page. |
|
Tax Location Code |
Select a valid tax location code. You define tax location codes on the Tax Location page. |
|
Sales Tax (Sales) |
Select this option if sales tax is applicable during order-to-cash transactions for the corresponding business unit. |
|
Sales Tax (Purchase) |
Select this option if sales tax is applicable during procure-to-pay transactions for the corresponding business unit. |
|
Excise Duty (Sales) |
Select this option if excise duty is applicable during order-to-cash transactions for the corresponding business unit. If selected, then the business unit is India Tax enabled. |
|
Excise Duty (Purchase) |
Select this option if excise duty is applicable during procure-to-pay transactions for the corresponding business unit. If selected, then the business unit is India Tax enabled. |
|
Custom Duty Applicable |
Select this option if customs duty is applicable for the corresponding business unit. |
See Also
(IND) Processing Customs, Excise Duties, and Sales Tax for India

 Defining Excise Number Series Groups
Defining Excise Number Series GroupsAccess the Excise Document Number Series page.
|
Excise Transaction Type |
Select a valid transaction type. You can create multiple excise number series groups for each transaction type. Values are: Bill of Entry Deemed Export Deemed Export With Bond Domestic Receipt Domestic Sales Export with Bond Export without Bond Inter-Unit Sale InterUnit Receipt Manual Stock Transfer |
|
Overwrite Allowed |
Select this option if you want to provide your own excise number. |

 Defining Tax Locations
Defining Tax LocationsAccess the Tax Location - Tax Location Definition page.
|
Location |
Select a valid tax location. Every manufacturer of excisable goods is required to register the location with the Central Excise Department before commencing business. |
|
TAN Number |
Enter the code that is assigned to you by the tax authority that represents the location of the income tax office where you pay taxes |
|
TAN-Ward |
Enter the TAN ward number. For administrative convenience, income tax authorities divide the country into circles and wards. Depending on its location, each organization belongs to a certain ward and circle. |
|
TAN-Circle |
Enter the TAN circle number. For administrative convenience, income tax authorities divide the country into circles and wards. Depending on its location, each organization belongs to a certain ward and circle. |
|
CSD Tax Component (customs duty tax component) |
The tax component code that you enter here is of the type excise. It is used to allow for posting of the recoverable customs duty to the CENVAT registers. This applies only to internal vendor excise invoice tax details when the excise invoice type is set to BOE (bill of entry). |
|
Currency Code |
Select the default currency code to associate with this location. |
|
Rate Type |
Select the default rate type to associate with this location. |
|
Journal Template |
Select the journal template to associate with this location. |

 Defining Document Number Ranges
Defining Document Number RangesAccess the Tax Location - Document Number Range page.
|
Excise Document Number Series |
Select a valid excise document number series. You define the excise document number series on the Excise Document Number Series page. |
|
Start Date |
Select an effective start date. |
|
Max Length (maximum length) |
Specify the maximum length of the number of range. Due to physical limit of the excise invoice number, the maximum length cannot exceed 10. |
|
Nbr Prefix (number prefix) |
Define a three-digit alphanumeric number prefix. |
|
Last Number Used |
Define the last number that is used. |
Note. You cannot set up the same document number range in more than one excise number series group.

 Defining the Excise Registration Details
Defining the Excise Registration DetailsAccess the Tax Location - Excise Registration page.
|
Excise ECC Number (excise control code number) |
Enter the excise control code number, which is issued by tax authorities to registered dealers. |
|
Excise Range |
Enter the excise range for the organization. |
|
Excise Division |
Enter the excise division for the organization. |
|
Excise Collectorate |
Enter the excise collectorate for the organization. |
|
PLA Account Number (personal ledger account number) |
Enter the PLA account number. You maintain PLAs with excise authorities for making excise duty payments and adjustment of excise duty payables against dispatches. |
|
Notification Number |
Enter the notification number. |
|
Excise Registration Code |
Enter the excise registration code for the organization. |
|
Excise Zone |
Enter the excise zone for the organization. |
|
Excise Region |
Enter the excise region for the organization. |
|
Excise Circle |
Enter the excise circle for the organization. |
|
Service Tax Registration |
Enter the service tax registration number. |

 Defining the Excise Group Details
Defining the Excise Group DetailsAccess the Tax Location - Excise Group page.
|
Nature of Location |
Identify the type of inventory business unit. If you select Factory, the tax determination and tax calculation are based on the shipping ID quantity, inventory business unit, customer ID, and item ID. Note. This is currently the only available option. |
|
Cenvat % on Capital Goods |
Enter the percentage of excise duty on capital goods that should be applied to the CENVAT Capital Goods register for this year. The remaining excise duty is placed in the capital goods on hold account. Use the Excise Adjustment page to apply the on hold amount at the beginning of the next year. The excise duty is calculated on the vendor excise invoice for the receipt of capital goods. |
|
CENVAT Utilization |
Select when to run the CENVAT Utilization process. The CENVAT Utilization process selects pending excise invoices and updates the CENVAT value registers to clear excise duties. |
|
Subcontracting Overdue days |
Enter the number of days past due for a subcontractor to return subcontracted items. When the subcontractor exceeds this number of days, enter an excise adjustment to reverse the excise duty payable. In the period when the subcontractor delivers the item, create a second excise adjustment to increase the excise duty payable. This field is informational only. |
|
Depletion Check |
Select to require the Depletion process before a shipping excise invoice can be created for the shipping ID line. If Depletion Check is not selected, then the shipping excise invoice can be created before the Depletion process is run. |
|
Chapter wise validation |
Select to indicate that items of different chapters should not be shipped in a single excise invoice. This field is informational only. |

 Defining Excise Registers
Defining Excise RegistersAccess the Tax Location - Registers page.
|
Register |
Select a valid excise register account. Options are: DSA: Daily stock account. ICGH: CENVAT register - capital goods on hold. ICGQ: Quantity register - capital goods. ICGV: CENVAT register - capital goods. IRMQ: Quantity register - raw material. IRMV: CENVAT register - raw material. PLA: Personal ledger account. |
|
Item Product Flag |
Select Product to display product ID values in the Item/Product ID field. Select Item if you want to display item ID values in the Item/Product ID field. This field is available only when the register is daily stock account. |
|
Item/Product ID |
Depending on the Item Product Flag option, select a product ID or a valid item ID. Values for products and product kits are prompted from the PROD_MASTER_EXS table. Values for items are prompted from the ITEM_MASTER_EXS table. This field is available only when the register is daily stock account. |
|
Start Date |
Enter the effective date for this excise account. |
|
Status |
Indicate whether this excise register account is Active or Inactive as of the date that is defined in the Start Date field. |
|
Last Serial Number |
This is the last serial number of the concerned register. For the next entry into this register, the system updates the last serial number by one to create the last serial number. |

 Defining Excise Account Type ChartFields
Defining Excise Account Type ChartFieldsAccess the Tax Location - Chartfields page.
|
Excise Account Type |
Enter the account that is to be used to create accounting entries. Insert a new row for each account and identify the ChartField combination. The options are: CNCA: CENVAT clearing account. CNCG: CENVAT on capital goods. CNCI: CENVAT clearing imports ACD. CNHA: CENVAT utilization on hold account. CNHC: CENVAT hold on capital goods. CNHS: CENVAT hold on subcontracting. CNRM: CENVAT on raw materials. CSDN:Custom duty nonrecoverable. EXDC: Excise duty recovered from customer. EXDE: Excise duty expenses. PLAA: PLA account. SERV: Service tax. |
See Also
Recording Accounting Entries for Excise Duties and Customs Duties
 Setting Up the Common Tax Structure
Setting Up the Common Tax StructureTo set up the common tax structure, use the following components:
Tax Component (EXS_TAX_CMPNT)
Tax Dependency Code (EXS_TAX_DPNDNCY)
Tax Calculation Code (EXS_TAX_RATE)
Tax Category (EXS_TAX_CATG)
Tax Determination (EXS_TAX_DETERM)
This section discusses how to:
Define tax component codes.
Define tax dependency codes.
Define tax calculation codes.
Define tax categories.
Define tax determination parameters.
Note. Common tax structure setup for excise duty, sales tax, and customs duty is shared unless otherwise specified.

 Pages Used to Define the Common Tax Structure
Pages Used to Define the Common Tax Structure|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
EXS_TAX_CMPNT |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Tax Component |
Define a tax component code for each tax that is required. |
|
|
EXS_TAX_DPNDNCY |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Tax Dependency Code |
Define tax dependency codes that indicate the basis for calculating tax, as well as the precedence of taxes of the same tax type that must be included in the calculation. For example, if you want to calculate additional excise duty based on the assessable value plus the basic excise duty, you define this relationship on this page. |
|
|
EXS_TAX_RATE |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Tax Calculation Code |
Define tax calculation codes that group tax component codes of the same tax type along with tax rates and other attributes. |
|
|
EXS_TAX_CATG |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Tax Category |
Define tax categories for assignment to vendors, customers, product kits, and items for either excise duty, sales tax or customs duty tax determination. |
|
|
EXS_TAX_DETERM |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Tax Determination |
Assign a tax calculation code to one or more tax determination parameters. Available field values on the page are based on Tax Determination hierarchy. |

 Defining Tax Component Codes
Defining Tax Component CodesAccess the Tax Component page.
|
Tax Component Code |
The tax component code that you enter on the prompt page appears. You create tax component codes for each required tax. Use the Tax Calculation Code page to combine tax component codes of the same tax type. |
Tax Component Details
|
Tax Type |
Select a tax type with which to associate the tax component code. Defining this information filters tax component codes in the Tax Calculation Code table (EXS_TAX_RATE) to ensure that tax calculation code definitions contain only tax component code lines of the same tax type. Values are Excise, Sales Tax, or Custom. |
|
Register Column Sequence |
Select the column sequence in which this tax component code should appear in the register. Entering a field value is applicable only if the Tax Type field is set to Excise. Values are: Column 1 - 6: Select the register column in which you want the tax component code’s details to appear in the excise registers. You can specify placement in up to six columns, but use the sixth column for the Others component code. For example, if you have more than six tax component codes, you can combine multiple tax codes within column 6. In this case, column 6 in the excise registers contains the sum of the multiple tax code amounts. |
|
Calculation Scheme |
Assign a default calculation scheme to the tax component code. The value that you assign here appears by default on the Tax Calculation Code page, where you can override it. Values are: Amount: Ad hoc amount-based tax calculation. Percentage: Percentage-based tax calculation. This is the default value. Quantity: Quantity-based tax calculation. |
|
Miscellaneous Charge |
Assign a nonrecoverable value-added tax (VAT) miscellaneous charge code to the selected tax type code. The miscellaneous charge code value that you enter determines the cost element under which nonrecoverable excise duty, sales tax, and customs duty amounts are accounted for in PeopleSoft Inventory and Cost Management. Values are defined on the Misc Charge/Landed Cost Defn (miscellaneous charge/landed cost definition) page. PeopleSoft’s landed costing feature records the nonrecoverable portion of excise duty by using this charge code. When defining the miscellaneous charge code, enter the VAT Input Non-Recoverable type and select the Prorate and Landed Cost Component options. |

 Defining Tax Dependency Codes
Defining Tax Dependency CodesAccess the Tax Dependency Code page.
Note. Once you assign a tax dependency code to a tax calculation code, you cannot make further changes to the tax dependency code definition.
|
Tax Dependency Code |
The tax dependency code that you enter on the prompt page appears. Tax dependency codes indicate the basis for calculating tax, as well as the precedence of taxes of the same tax type that must be included. You assign tax dependency codes to tax calculation codes, enabling tax calculation codes to be calculated accordingly. |
|
Tax Type |
The tax type that you enter on the prompt page appears. |
|
Include Base |
Select to calculate tax with the base amount included. Leave this option clear if you want tax calculation to exclude the base amount. For example, leave this option cleared for a surcharge tax component that is calculated based on a preceding tax component rather than on a base amount. This option is selected by default. |
|
Include Freight |
Select to include freight as a part of the base value in tax calculation. This option is cleared by default. This setting is applicable only in the procure-to-pay process flow. In the order-to-cash process flow, freight cannot be assigned to sales order or bill lines. If required, freight must be provided on another sales order or bill line. If tax calculation on freight is required, this calculation can be performed in the same way that it is done for normal sales order or bill lines. |
|
Include Miscellaneous Charges |
Select to include miscellaneous charge expenses as a part of the base value for tax calculation. This option is cleared by default and is applicable only in the procure-to-pay process flow. |
Precedence Details
|
Tax Component Code |
If tax precedence is required, assign as many tax component codes as needed. Only tax component codes of the same tax type can be assigned to a tax dependency code.
Note. The system performs a validation to ensure that tax component codes that are assigned here are included in a tax calculation code definition. The tax component codes must be assigned to a tax calculation code definition so that appropriate tax rates can be derived. This validation is performed each time a tax calculation code is saved, updated, and saved. |

 Defining Tax Calculation Codes
Defining Tax Calculation CodesAccess the Tax Calculation Code page.
|
Tax Rate Code |
The tax rate code that you enter on the prompt page appears. Tax calculation codes group tax component codes of the same tax type along with tax rates and other attributes. Tax rate codes are used in the Tax Determination table to determine the tax rate that is applicable for a combination of various parameters, such as the trading partner (customer/vendor), tax category, item, item tax category, and so forth. |
|
Tax Type |
The tax type that you enter on the prompt page appears. A tax calculation code can have only one tax type. Values are: Excise: This is the default value. Also select for service taxes. When selected, the Service Tax Indicator and Use Assessable Value options become available for entry. Sales Tax: When selected, the Sales Tax Authority and Sales Tax Form Code fields become available for entry. The Chartfield Detail group box also becomes available for entry. Custom: When selected, the Customs Information group box becomes available. |
Sales Tax Details
The fields in the Sales Tax Details group box are relevant only to sales tax processing and are available for entry when the tax type field is set to Sales Tax.
|
Sales Tax Authority |
Select a tax authority. Values are defined on the Sales Tax Authority Code page. |
|
Sales Tax Form Code |
Select a form code if the tax rate code requires sales tax form tracking. Values are defined on the Form Code page. |
Excise Details
The fields in the Excise Details group box are relevant only to excise duty processing and are available for entry when the tax type field is set to Excise Duty. Selection of the Use Assessable Value and Service Tax Indicator options is mutually exclusive.
|
Use Assessable Value |
Select to indicate that excise duties should be calculated based on the sale price or the assessable value that is indicated at the item or product kit level. This option is cleared by default. For shipment of samples, often no sales value is applied to the order. However, excise duty is still payable on the assessable value of the items. |
|
Service Tax Indicator |
Select to indicate that the tax rate code is meant for calculation of service taxes. Subsequent processing is done accordingly. This option is cleared by default. |
Customs Information
The fields in the Customs Information group box are relevant only to customs duty processing and are available for entry when the tax type is custom. Select a vendor, location, and currency to define the third-party vendor to whom the customs duty is paid, such as a customs authority.
Tax Rate Details
Tax calculation codes must have at least one detail line. Create a detail line for each tax component code that is applicable to the tax calculation code.
Tax Components
|
Tax Rate Sequence |
Indicates the order in which tax component codes in the tax calculation code should be calculated. This line number is system generated. The system validates the relationship between a sequence number and the precedence that is defined in the Tax Dependency table for each of the tax dependency codes that are associated with the tax components of the tax calculation code. |
|
Tax Component Code |
Select a tax component code. Values are defined on the Tax Component page; however, only tax component codes that are associated with the selected Tax Type field value are available for selection. |
|
Tax Dependency Code |
Select a tax dependency code. Valid values are defined on the Tax Dependency Code page. |
|
Calculation Scheme |
Displays the default calculation scheme that is associated with the selected tax component code. You can override this value. Values are: Amount: Ad hoc amount-based tax calculation. Percentage: Percentage-based tax calculation. This is the default value. Quantity: Quantity-based tax calculation. |
|
Tax Rate Pct (tax rate percentage) |
If the Calculation Scheme field value is set to Percentage, enter a percentage that is to be applied against the taxable amount. |
|
Tax Amount |
If the Calculation Scheme field value is set to Quantity, enter an amount that is to be applied against the transaction quantity. The amount is applied in the Currency Code value that you enter, according to the transaction quantity in the Unit of Measure value that you enter.
Note. If the transaction unit of measure is different from the tax calculation code unit of measure, the system performs the conversion by using the PeopleSoft-delivered unit of measure conversion feature. If the Calculation Scheme field is set to Amount, enter the actual tax amount. Enter a Currency Code value. |
|
Currency |
If the Calculation Scheme field is set to Amount or Quantity, enter a currency code for the tax amount. Values are defined on the Currency Code page. |
|
Unit of Measure |
If the Calculation Scheme is set to Quantity, enter a unit of measure against which the tax amount is applied. Values are defined on the Units of Measure page.
Note. If the transaction unit of measure is different from the tax rate code unit of measure, the system performs the conversion by using the PeopleSoft-delivered unit of measure conversion feature. |
|
Recoverable Tax Pct (recoverable tax percentage) |
Enter the percentage of the excise tax that is recoverable. The system uses this value to split taxes into recoverable and nonrecoverable components. The nonrecoverable portion can be added to the value of the inventory item by using the landed cost feature of PeopleSoft. If the Tax Type field value is set to Excise, enter the CENVAT percentage that can be recovered. For example, enter 100 to indicate that the full amount of tax is eligible for CENVAT credit. If the Tax Type field value is set to Sales Tax, enter the setoff percentage for the tax rate code. For example, enter 60 to indicate that 60 percent of the tax amount is recoverable and eligible for set-off. The balance is added to the inventory cost or expensed depending on the treatment that is defined for the item. If the Tax Type field value is set to Custom, enter the CENVAT percentage that can be recovered. |
ChartField Details
Assign separate ChartField values to each available combination of sales tax authority and tax rate detail line in the ChartField Details group box. Default ChartField values populate from the sales tax authority that is selected on this page, but you can override them.
|
Tax Distribution Account Type |
Enter a ChartField account type. Values are: Setoff CF (setoff value ChartField): If selected, the ChartFields reflect the setoff ChartField values that are to be used to account for recoverable setoff amounts in the procure-to-pay process flow. Tax CF (tax value ChartField): This is the default value. If selected, the ChartFields reflect liability ChartFields that are to be used to account for sales tax in the order-to-cash process flow. |

 Defining Tax Categories
Defining Tax CategoriesAccess the Tax Category page.
Tax Category Details
|
Usage Type |
Select the tax category usage type. Values are: Vendor/Customer: Tax category for assignment to vendors and customers. This is the default value. Item: Tax category for assignment to items and product kits. |
See Also
Setting Up Product Kits for Tax Processing
Setting Up Items for Tax Processing
Setting Up Customers for Tax Processing
Setting Up Vendors for Tax Processing

 Defining Tax Determination Parameters
Defining Tax Determination ParametersAccess the Tax Determination page.
|
Tax Determination Option |
Select a tax determination option for which you want to define determining factors. The available field values represent levels in the tax determination hierarchy. When a particular level of the hierarchy is invoked on a transaction, the system looks at the parameters that you define on this page to determine the tax rate code that is to be used for the transaction. Values are: Item: Select to define factors for tax determination based on the transaction item or product. Item Category: Select to define factors for tax determination based on the transaction item or product tax category. Partner Category: Select to define factors for tax determination based on the transaction trading partner tax category. Partner Category + Item: Select to define factors for tax determination based on the transaction trading partner tax category and item. Partner Category + Product: Select to define factors for tax determination based on the transaction trading partner tax category and product kit. Partner Category + Item Category: Select to define factors for tax determination based on the transaction trading partner category and item tax category. Product Kit: Select to define factors for tax determination based on the transaction product kit. Benefit + Partner Category + Item: Select to define factors for customs duty tax determination based on the benefit ID, the transaction trading partner category and item. Benefit + Item: Select to define factors for customs duty tax determination based on the benefit ID and item |
Determination Parameters
|
Transaction Type |
Select a tax transaction type. Values are: DEB (direct export with bond). DEWB (direct export without bond). DIMP (direct import). Domestic (default value). LEB (local export with bond). LEWB (local export without bond). LIMP (local import). |
|
Tax Authority |
This field is relevant only to sales-tax processing and is available for entry when the Tax Type field is set to Sales Tax. Select a sales tax authority that is to be invoked for the tax determination combination. Values are defined on the Sales Tax Authority Code page. |
|
Partner Category |
Select a trading partner tax category that is to be invoked for the tax determination combination. Values are defined on the Tax Category page. |
|
Item Category |
Select an item tax category. Values are defined on the Tax Category page. |
|
Item/Prod (item/product) |
Displays the type of ID that you must enter in the Item Product ID field. The value that appears in this field is dependent on the Tax Determination Option field value that you select. Values are NA, Product, and Item. |
|
Item/Product ID |
Depending on the Item/Prod field value, select an item or product kit. Values for product kits are defined on the Product Tax Applicability page. Values for items are defined on the Item Defn Tax Applicability page. |
|
Tax Rate Code |
Select a tax rate code. Values are defined on the Tax Calculation Code page; however, only tax calculation codes that are associated with the selected Tax Type and STX Authority field values are available for selection. |
 Setting Up Items for Tax Processing
Setting Up Items for Tax ProcessingTo set up items for tax processing, use the Item Tax Applicability component (ITEM_MASTER_EXS) and the Item BU Tax Applicability component (ITEM_BU_EXS).
This section discusses how to:
Define item tax applicability.
Define business unit item tax applicability.
Note. Setting up items for tax processing for excise duty, sales tax and customs duty is shared unless otherwise specified.
See Also
Defining Purchasing Item Information

 Pages Used to Set Up Items for Tax Processing
Pages Used to Set Up Items for Tax Processing|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
ITEM_MASTER_EXS |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Item Tax Applicability |
Define excise duty, sales tax, and customs duty applicability details for items. |
|
|
ITEM_BU_EXS |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Item BU Tax Applicability |
Define business unit-level excise duty, sales tax, and customs duty applicability details for items. |

 Defining Item Tax Applicability
Defining Item Tax ApplicabilityAccess the Item Tax Applicability page.
Excise Duty Details
|
Excise Applicable |
Select if excise duties are applicable to the item. This option is cleared by default. |
|
Excise Tax Category |
Select a tax category for the item. Values are defined on the Tax Category page; however, only tax categories that are associated with the item usage type are available for selection. Defining tax categories for items helps group items with common attributes under a category that is to be used in the tax determination structure. |
|
Excise Units of Measure |
Select a unit of measure for the selected item for use in updating excise registers. Values are defined on the Units of Measure page.
Note. If necessary, the system makes appropriate conversions between tax calculation code, item, and transaction units of measure by using delivered unit of measure conversion functionality. |
|
Conversion Rate |
Enter the rate of conversion from the standard unit of measure to the excise unit of measure. This value is used by the Tax Calculation process in two scenarios:
|
|
Assessable Value |
Enter the assessable value of the item that is used to calculate duties based on a value that is other than the basic item price according to the orders when the tax calculation code has Use Assessable Value selected. The assessable value that is specified here is externally defined (for example, with the Excise Authority) and should not be confused with the calculated price of the orders that may vary by vendor or other pricing rules. |
|
Currency |
Enter the currency for the item. |
|
Rate Type |
Enter a rate type for the currency. |
|
Tax Item Type |
Select an appropriate tax classification for the item. The selection determines the registers that are updated during movement of incoming and outgoing excise goods. This field value determines amounts that are to be recovered for CENVAT credit. Options are Raw Material, Finished Goods, Capital Goods. |
|
Chapter ID |
Select a chapter ID to associate with the item. Valid values are defined on the Chapter ID Details page. Chapter IDs are printed on statutory excise documents and reports and can be useful in capturing register information. |
Sales Tax Details
|
Sales Tax Applicable |
Select if sales taxes are applicable to the item. This option is cleared by default. |
|
Sales Tax Category |
Select a tax category for the item. Valid values are defined on the Tax Category page; however, only tax categories that are associated with the item usage type are available for selection. Defining tax categories for items helps group items with common attributes under a category that is to be used in the tax determination structure. |
Custom Duty Details
|
Custom Duty Applicable |
Select if customs duty is applicable to the item. This option is cleared by default. |
|
Custom Tax Category |
Select a tax category for the item. Values are defined on the Tax Category page: however, only tax categories that are associated with the item usage type are available for selection. |

 Defining Business Unit Item Tax Applicability
Defining Business Unit Item Tax ApplicabilityAccess the Item Business Unit Tax Applicability page.
The Item Business Unit Tax Applicability page is identical to the Item Tax Applicability page. You define the excise duty, sales tax, and customs duty applicability details for items at the business unit level.
 Setting Up the Sales Tax Structure
Setting Up the Sales Tax StructureTo set up the sales tax structure, use the following components:
Form Name (STX_FORM_NAME)
Form Code (STX_FORM_CODE)
Registration Detail (STX_RGSTN_DTL)
Tax Authority (STX_TAX_AUTH)
This section discusses how to:
Define sales tax form names.
Define sales tax form codes.
Define sales tax registration details.
Define sales tax authority codes.
Note. Sales tax structure setup is applicable to sales tax only.

 Pages Used to Set Up Sales Tax
Pages Used to Set Up Sales Tax|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
STX_FORM_NAME |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Form Name |
Define sales tax declaration forms in the system. |
|
|
STX_FORM_CODE |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Form Code |
Define form codes, which are groupings of form names. Form codes are assigned to tax calculation codes. When a tax calculation code is associated with a transaction, the form code helps determine the applicable forms for the transaction for form tracking purposes. |
|
|
STX_RGSTN_DTL |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Registration Details |
Define sales tax registration number details for an organization. This number is used for printing invoices, reports, and so forth. |
|
|
STX_TAX_AUTH |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Tax Authority |
Define tax authorities for each type of sales tax, such as central sales tax and local sales tax. Associate ChartField combinations with each tax authority. These ChartField combinations appear by default on the Tax Calculation Code page and are used to create accounting entries for transactions with related tax authorities. |

 Defining Sales Tax Form Names
Defining Sales Tax Form NamesAccess the Form Name page.
Enter the sales tax declaration forms description and status.

 Defining Sales Tax Form Codes
Defining Sales Tax Form CodesAccess the Form Code page.
Form Code Details
|
Form Name |
Select a form name to include in the form code. Values are defined on the Form Name page. |
|
Form Direction |
Select the form direction. This indicates the direction in which the form name is moving between the seller and buyer. Values are Buyer to Seller and Seller to Buyer. |

 Defining Sales Tax Registration Details
Defining Sales Tax Registration DetailsAccess the Sales Tax Registration Details page.
|
Organization |
Organization with which the sales tax registration number is associated. Values are defined on the Organization Details page. |
|
Country |
Country in which the sales tax registration number is applicable. Values are defined on the Country - Country Description page. |
|
State |
State in which the sales tax registration number is applicable. Values are defined on the State page. |
|
Applicability Identifier |
Applicability identifier to indicate whether the sales tax registration number is local or central. Values are: Central Sales Tax: This is the default value. Local Sales Tax. |
|
Sales Tax Registration Number |
Enter the sales tax registration number. |

 Defining Sales Tax Authority Codes
Defining Sales Tax Authority CodesAccess the Sales Tax Authority page.
|
Sales Tax Authority |
The sales tax authority code that you enter on the prompt page appears. The sales tax authority is the entity to which the taxes have to be paid and reporting submitted. Tax authority codes are used in the Tax Calculation Code and Tax Determination tables. |
Tax Authority Details
|
IUT form code (interunit transfer form code) |
Select the form code that is applicable to interunit transfers to be used for form tracking. Some states require form tracking for interstate inventory interunit transfers. Values are defined on the Form Code page. |
ChartField Setup
The ChartField Setup group box enables you to assign ChartField combinations to tax authorities.
|
Tax Distribution Account Type |
Enter a ChartField account type. Values are: Setoff CF (setoff ChartField): If selected, the ChartFields reflect the setoff ChartField values that are to be used to account for recoverable setoff amounts in the procure-to-pay process flow. Tax CF (tax ChartField): This is the default value. If selected, the ChartFields reflect liability ChartField values that are to be used to account for sales tax in the order-to-cash process flow. |
 Setting Up the Excise Duty Structure
Setting Up the Excise Duty StructureTo set up the excise duty structure, use the Excise Chapter component (EXD_CHAPTER).
This section discusses how to define chapter ID codes.
Note. Excise duty structure setup is applicable to excise duty only.

 Page Used to Set Up Excise Duty
Page Used to Set Up Excise Duty|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
EXD_CHAPTER |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Excise Chapter |
Enter excise chapter IDs. Chapter ID codes are seven-digit alphanumeric codes that you associate with products and items. Chapter IDs are printed on statutory excise documents and reports and can be useful in capturing register information. Excise legislation requires that items and groups of items be tracked by chapter ID. |

 Defining Chapter ID Codes
Defining Chapter ID CodesAccess the Excise Chapter page.
|
Notification Number |
Enter the government-issued notification number that is associated with the chapter ID. |
 Setting Up Product Kits for Tax Processing
Setting Up Product Kits for Tax ProcessingTo set up product kits for tax processing, use the Product Tax Applicability component (PROD_MASTER_EXS).
This section discusses how to define tax details for product kits.
Note. Setting up product kits for tax processing is applicable to excise duty and sales tax only.
See Also
Defining Business Unit Tax Applicability

 Page Used to Set Up Product Kits for Tax Processing
Page Used to Set Up Product Kits for Tax Processing|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
PROD_MASTER_EXS |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Product Tax Applicability |
Define excise duty and sales tax applicability details for product kits. |

 Defining Product Tax Applicability
Defining Product Tax ApplicabilityAccess the Product Tax Applicability page.
Excise Duty Details
|
Excise Applicable |
Select if excise duties are applicable to the product kit. This option is cleared by default. |
|
Excise Tax Category |
Select a tax category for the product kit. Values are defined on the Tax Category page; however, only tax categories that are associated with the item usage type are available for selection. Defining tax categories for products helps group products with common attributes under a category that is to be used in the tax determination structure. |
|
Excise Units of Measure |
Select a unit of measure for the selected product for use in updating excise registers. Valid values are defined on the Units of Measure page. Note. If necessary, the system makes appropriate conversions between tax calculation code, item, and transaction units of measure by using delivered unit of measure conversion functionality. |
|
Conversion Rate |
Enter the rate of conversion from the standard unit of measure to the excise unit of measure. This value is used by the Tax Calculation process in two scenarios:
|
|
Assessable Value |
Enter the assessable value of the product, which is used when the tax basis amount of the tax calculation code is set to calculate duties based on the assessable value instead of the basic product price according to orders.
|
|
Currency |
Enter the currency for the product. |
|
Rate Type |
Enter a rate type for the currency. |
|
Tax Item Type |
Select an appropriate tax classification for the product kit. The selection determines which registers are updated during movement of incoming and outgoing excise goods. This field value determines the amounts to be recovered for CENVAT credit. Values are Raw Material, Finished Goods, Capital Goods. |
|
Chapter ID |
Select a chapter ID to associate with the product kit. Values are prompted from the EXD_CHAPTER_TBL table. Chapter IDs are printed on statutory excise documents and reports and can be useful in capturing register information. |
Sales Tax Details
|
Sales Tax Applicable |
Select if sales taxes are applicable to the product kit. This option is cleared by default. |
|
Sales Tax Category |
Select a tax category for the product kit. Values are defined on the Tax Category page; however, only tax categories that are associated with the item usage type are available for selection. Defining tax categories for a product helps group products with common attributes under a category that is to be used in the tax determination structure. |
 Setting Up Customers for Tax Processing
Setting Up Customers for Tax ProcessingTo set up customers for tax processing, use the Customer Tax Applicability component (CUST_ADDR_EXS).
This section discusses how to define tax details for customers.
Note. Setting up customers for tax processing is applicable to excise duty and sales tax only.

 Page Used to Set Up Customers for Tax Processing
Page Used to Set Up Customers for Tax Processing|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
CUST_ADDR_EXS |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Customer Tax Applicability, Customer Site Tax Applicability |
Define excise duty and sales tax applicability details for customers. |

 Defining Customer Tax Applicability
Defining Customer Tax ApplicabilityAccess the Customer Site Tax Applicability page.
|
Tax Transaction Type |
Select a tax transaction type. Values are: Direct Export With Bond. Direct Export Without Bond. Direct Import. Domestic: This is the default value. Local Export With Bond. Local Export Without Bond. Local Import. |
Excise Details
|
Excise Applicable |
Select if excise duties are applicable for the customer. This option is selected by default. |
|
Excise Tax Category |
Select an excise tax category for the customer. Values are defined on the Tax Category page. |
|
Excise ECC Number (excise control code number) |
Enter the excise control code number for the customer. |
|
Service Tax Registration |
Enter a service tax registration number for the customer. |
Sales Tax Details
|
Sales Tax Applicable |
Select if sales taxes are applicable for the customer. This option is selected by default. |
|
Sales Tax Category |
Select a sales tax category for the customer. Values are defined on the Tax Category page. |
|
CST Registration Number (central sales tax registration number) |
Enter a central sales tax registration number for the customer. |
|
LST Registration Number (local sales tax registration number) |
Enter a local sales tax registration number for the customer. |
 Setting Up Vendors for Tax Processing
Setting Up Vendors for Tax ProcessingTo set up vendors for tax processing, use the Vendor Tax Applicability component (VNDR_LOC_EXS).
This section discusses how to define tax details for vendors.
Note. Setting up vendors for tax processing is applicable to excise duty, sales tax, and customs duty.

 Page Used to Set Up Vendors for Tax Processing
Page Used to Set Up Vendors for Tax Processing|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
VNDR_LOC_EXS |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Vendor Tax Applicability, Vendor Location Tax Applicability |
Define excise duty, sales tax, and customs duty applicability details for vendors. |

 Defining Vendor Tax Applicability
Defining Vendor Tax ApplicabilityAccess the Vendor Location Tax Applicability page.
The Vendor Location Tax Applicability page is similar to the Customer Site Tax Applicability page for defining excise duty and sales tax applicability details. You define the customs duty details that are associated with the vendor on the Vendor Location Tax Applicability page.
Custom Duty Details
|
Custom Duty Applicable |
Select if customs duty is applicable for the vendor. |
|
Custom Tax Category |
Select a customs tax category for the vendor. Values are defined on the Tax Category page. |
See Also
Defining Customer Tax Applicability
 Setting Up the Customs Duties Foundation
Setting Up the Customs Duties FoundationTo set up the customs duties foundation, use the following components:
Organization Details (ORG_RGSTN_DTL)
Harmonized Tariff Code (HRMN_TARIFF_CD)
Item Definition (ITEM_DEFIN)
Automatic Numbering (AUTO_NUM_PNL)
Customs Benefit Scheme (CSD_BENEFIT_SCHEME)
Customs Item SION (CSD_ITEM_SION)
Accounting Entry Template (ACCOUNTINGENTRY)
Use the HRMN_TARIFF_CD_CI component interface to load data into the tables for the Harmonized Tariff Code component.
This section provides an overview of customs duties foundation and discusses how to:
Define benefit schemes for customs duties.
Define norms for standard inputs and outputs.
Define ChartField values for customs duty recoverable and nonrecoverable accounts.
Note. Customs duty foundation setup is applicable to customs duty only.

 Understanding Customs Duties Foundation
Understanding Customs Duties Foundation
The following customs duties information must be defined in PeopleSoft to be used on correspondence with customs authorities and other reporting requirements.
To define the customs duty structure:
Enter an import export code and the BIN (business identification number) on the Organization Details page.
For identification purposes, the Director General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) assigns the import export code and the BIN to the organization. The import export code is used for all correspondence with customs authorities for import purchases. For example, this code is required on the Bill of Entry worksheet. The BIN is used for all correspondence with the customs authorities for export purposes. For example, the BIN is required on the shipping documents that are sent to customs clearance.
Identify the harmonized tariff code for each item to be imported or exported.
The tariff codes are used on all documentation that is submitted to the customs authorities for import. Define the harmonized tariff codes that are to be used by the organization by using the Harmonized Tariff Code page. The Customs Tariff Act specifies the customs duty rates based on the tariff code classifications. Then for each item that is imported or exported, attach the identifying harmonized tariff code to the item by using the Item Definition - Inventory: Shipping/Handling page. Each item must be associated with a harmonized tariff code.
Define the identification number for the Bill of Entry worksheets.
In order to automatically number the Bill of Entry worksheets, define a numbering sequence by using the Auto Numbering page. For the Number Type field, use the Bill of Entry Number option and then enter a numbering sequence.
Define the benefit schemes for customs duties by using the Benefit Scheme page.
All items on an import purchase order and an export sales order need to be identified with a benefit scheme. This information appears by default in the Bill of Entry worksheet and other reports.
For export items that you produce by using imported items, use the Standard Input Output Norm page to identify the quantity of input items that are used.
The standard input output norms (SION) are used in reports and documents that are submitted to the customs authorities to justify the imported items that are consumed in the manufacture of exported items.

 Pages Used to Set Up the Customs Duty Structure
Pages Used to Set Up the Customs Duty Structure|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
ORG_RGSTN_DTL |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Organization Details |
Define registration data at the organization level, including import export code and BIN, for customs duty. |
|
|
HRMN_TARIFF_CD |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Shipping and Receiving, Harmonized Tariff Code |
Harmonized tariff codes are required on various documents that accompany shipments across international borders. Customs officials use these codes to determine duty on the commodities being shipped. The codes are preestablished for all commodities. |
|
|
INV_ITEMS_DEFIN5 |
Items, Define Items and Attributes, Define Item, Inventory Click the Shipping/Handling link. |
Select a tariff code to identify the harmonized tariff code for the item. |
|
|
AUTO_NUM_PNL |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Codes and Auto Numbering, Auto Numbering |
If you use automatic numbering, the system automatically assigns a number based on criteria that you define on the Automatic Numbering page. It then increases the number by one whenever you add a new transaction. In order to automatically number the bill of entry worksheets, define a numbering sequence by using the number type of bill of entry number. |
|
|
CSD_BENEFIT_SCHEME |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Customs Benefit Scheme, Benefit Scheme |
Define the benefit schemes for customs duties that can be used for imported and exported items. All items that are on an import purchase order and an export sales order need to be identified with a benefit scheme. This information appears by default on the Bill of Entry worksheet and other reports. |
|
|
CSD_ITEM_SION |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Custom Item SION |
Used to collect information to create reports for claiming customs duty exemptions and customs duty drawback benefits. For an export item, define the quantity of input items, including wastage, that are needed to produce this export item. |
|
|
ORG_EXD_CF_DET |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Excise and Sales Tax IND, Tax Location, Chartfields |
Define the accounting entries to record the customs duty recoverable and nonrecoverable amounts. |

 Defining Benefit Schemes for Customs Duties
Defining Benefit Schemes for Customs DutiesAccess the Benefit Scheme page.
Define the benefit schemes for customs duties that can be used for imported and exported items. Enter a benefit ID for all items on an import purchase order and on an export sales order. This information appears by default from the purchase order into the Bill of Entry worksheet and other reports.
|
Benefit ID |
Unique identification number for this benefit scheme. |
|
Benefit Type |
Identifies the type of duty benefit that is eligible for special treatment, such as: Concession: Imports are eligible for concessional rate of customs duty. Drawback: Imports are eligible for duty drawbacks in the form of refunds or credits from the government. Free: Imports are duty free. |
|
Begin Date |
Enter the date when this benefit scheme is available to be used against import purchase orders. |
|
End Date |
Enter the date when this benefit scheme is no longer available. |
|
Status |
The status of the benefit scheme. Select Active or Inactive. When the end date is in the past, the system automatically sets the status to Inactive. |

 Defining Norms for Standard Inputs and Outputs
Defining Norms for Standard Inputs and OutputsAccess the Standard Input Output Norm page.
The Standard Input Output Norm page collects information to create reports claiming customs duty exemptions and customs duty drawback benefits. Benefit schemes that specify an export obligation, require validation of the imported items that are used in the manufacture of the export items. This applies to items that are imported by using the Benefit Type of Drawback or Free on the Benefit Scheme page. To claim the benefits, the importer has to submit the proof of consumption of the imported inputs that are used to manufacture the exported output items. The customs authorities use the SION as the basis for determining the inputs that are considered for the benefit. SIONs are available from the customs authorities for the majority of export items. Each SION is identified with a unique SION number and SION date.
|
SION Number |
Enter the SION identification number that is given to you by customs authorities. |
|
SION Date |
Enter the SION date that is given to you by customs authorities. The current date is used as the default. |
|
Benefit ID |
Enter the benefit scheme that is associated with this item’s SION. |
|
Quantity (quantity) |
Enter the quantity of the export item that is produced in the manufacture process. |
Import Items
|
Item ID |
Enter the item ID of the imported item that is used in the manufacture of this export item. |
|
Quantity |
Enter the quantity for this import item that is consumed in the manufacturing process. |
|
UOM (unit of measure) |
Define the unit for measure for this input item’s Quantity field. |
|
Wastage % (wastage percentage) |
Enter the percentage of the input quantity that is lost during the manufacturing process. |
|
Ratio to Product |
The system calculates the percentage of the input item quantity that is part of the output product quantity. The system sets the input and output quantities to the same unit of measure by converting either the input or output quantities. Then, the system divides the input quantity by the output quantity and multiples the result by 100 to compute the percentage. |

 Defining Values for the Customs Duty Recoverable and Nonrecoverable Accounts
Defining Values for the Customs Duty Recoverable and Nonrecoverable AccountsAccess the Tax Location - Chartfields page.
Before you can create vouchers, you must ensure that all accounts are populated with valid values, including the customs duty recoverable and the customs duty nonrecoverable accounts.
Enter the ChartField values to record the CNCI and nonrecoverable CSDN accounting entries.
See Also
Setting Up the Organizational Structure