 Understanding Draft Processing
Understanding Draft ProcessingThis chapter provides an overview of draft processing, the draft life cycle, and setup for draft processing; and discusses how to:
Review business events and subevents.
Define draft transaction types.
Define draft types.
Define where draft documents are stored.
Define draft collection methods.
Assign customers to draft groups.
Set up automatic numbering for draft processing.
Set up draft reference qualifiers.
Define Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) reason codes and EFT file layout codes.
Note. This chapter is required. You must complete the tasks discussed in this chapter to implement draft processing.
 Understanding Draft Processing
Understanding Draft ProcessingMany economies throughout the world use drafts as a payment method. The details vary country by country.
Vendor-initiated drafts, which are prepared by the vendor, are sometimes called bills of exchange. The vendor specifies the due date, whether the draft is to be discounted, and the remittance procedure (paper, EFT, or Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)). Typically, the vendor’s bank submits the draft to the customer's bank for processing.
Customer-initiated drafts, which are usually, but not always prepared by the customer, are sometimes called bills of order or promissory notes. The customer specifies the due date and when the customer is to remit payment. The drafts are sent preapproved to the vendor, who must either accept or refuse the draft. The customer decides whether or not the draft is to be discounted and the remittance procedure (paper, EFT, or EDI).
Both types of drafts involve an obligation on the part of the buyer to pay the seller a particular sum on a given date. The drafts are redeemable on or after their stated due date, and it is common for both types of drafts to be redeemed before their due date at a discounted amount.
 Understanding the Draft Life Cycle
Understanding the Draft Life CycleThis section discusses:
Draft life cycle overview.
Major events in the draft life cycle.
Additional draft events.

 Draft Life Cycle Overview
Draft Life Cycle Overview
Processing a draft normally occurs over an extended period of time. The events that occur during the draft life cycle are the same for both customer- and vendor-initiated drafts.
Each event in the draft life cycle generates accounting entries and changes the status of the draft. You initiate some of these events online and others occur automatically when you run the Receivable Update Application Engine process (ARUPDATE). PeopleSoft defines the draft processing rules for each business event that Receivables supports. You define how the system creates accounting entries for each event by draft type.
The path that a draft takes in the draft life cycle depends on if the draft is:
Drafts that are discounted with recourse and drafts that are discounted without recourse follow the same path but generate different accounting entries.
The following graphic shows the major events that occur in the draft life cycle:
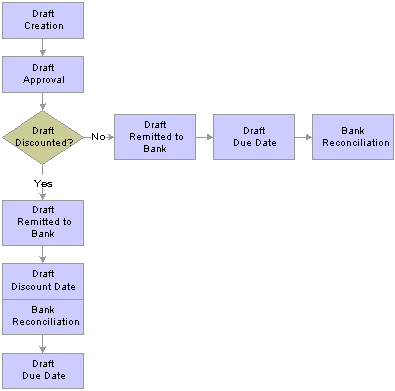
Draft life cycle
The system keeps an audit history of all events that occur for an individual draft and records the history in the Draft Activity table (PS_DRAFT_ACTIVITY). Some events, such as the draft approval event, generate a group ID when the event occurs. For other events, such as draft remittance, the Receivable Update process assigns a group ID. The Receivable Update process also updates the activity record with the posting date.

 Major Events in the Draft Life Cycle
Major Events in the Draft Life CycleThis section describes the major events in the draft life cycle:
Draft creation
Draft approval
Draft remittance
Draft discount date
Draft due date
Bank statement reconciliation
You create a draft using the Draft Request page or one of the two online entry pages (Draft Entry and Draft Mass Entry). The page that you use depends on whether you are creating a customer- or vendor-initiated draft. At this point in the draft life cycle, the draft enters the Receivables system. You can also load a kijitsu draft (from Japan) into the system electronically by using an EFT file. The status of a draft that you create is either Identified or Pending Acceptance.
After you apply items to the draft, you approve it using a draft worksheet or a draft approval worksheet. If the draft is preapproved, the system automatically approves the draft when you create it. The status of an approved draft is Accepted.
You send the draft to the bank to arrange for collection of the monies owed. You use the draft remittance worksheet to perform this task. The monies are collected at either the due date or the discount date, based on your specifications. If you specify that you want to collect the funds at the discount date, the bank normally charges a fee and interest. This effectively arranges for a short-term loan on the basis of the guaranteed future payment. The status of a remitted draft is Remitted.
When the draft reaches its discount date, the bank places the funds in your account. If you discount a draft, the Receivable Update process creates accounting entries on the discount date. If a draft is discounted with recourse, the system automatically creates the appropriate liability accounting entries to record your financial exposure. These entries are necessary because the bank reserves the right to take the money back from you if your customer (issuer) fails to pay.
The status of the draft becomes C (Complete) unless you discounted the draft with recourse. If you discount a draft with recourse, the draft status changes to M (Discounted) on the discount date or when you reconcile the draft on a bank statement. The draft status becomes Complete on the due date.
When a nondiscounted draft comes due (reaches its due date or maturity date), the vendor’s bank and the customer's bank process the exchange of funds. To accommodate this exchange, the Receivable Update process creates the accounting entries that are necessary to record the expected receipts. The bank statement records the actual funds when they are deposited in your bank account.
If you use cash clearing accounting and you have identified the bank account as a cash clearing account, the Receivable Update process transfers the amount from the cash clearing account to the cash account.
The status of the draft becomes Complete.
When you receive the bank statement, you have the option to use the bank reconciliation feature to mark the drafts as reconciled. You can do this manually, or you can reconcile it automatically using the automatic Bank Reconciliation Application Engine process (FSPRECON). The system records the funds received for each draft on the bank statement. The reconciliation module provides a manual way to match the amount of the draft received with the amount that was submitted to the bank.
When you reconcile a draft on a bank statement, the status of the draft remains Complete, but the Receivable Update process identifies the draft as reconciled by changing the RECON_PROCESSED field to Y. The Receivable Update process also generates the appropriate accounting entries to record the reconciliation.
You have the option to recognize the cash either when you reconcile the draft on a bank statement, or on the due date for nondiscounted drafts or the discount date for discounted drafts. Specify the method to use when you set up your draft types. This table shows how the draft cycle looks:
|
Type of Draft |
Draft Event |
|
Nondiscounted |
Remit ⇒ Due Date Or Remit ⇒ Bank Statement Reconciliation |
|
Discounted |
Remit ⇒ Discount Date ⇒ Due Date Or Remit ⇒ Bank Statement Reconciliation ⇒ Due Date |
See Also

 Additional Draft Events
Additional Draft Events
These additional events can occur in the draft life cycle at various points:
Dishonoring a draft.
Voiding a draft.
Cancelling a remittance.
You dishonor a draft at any point in the draft life cycle after you approve it. After you dishonor the draft, you decide what action to take on the draft. When you dishonor a draft, the system changes the draft status to D (dishonored). The system debits the dishonored draft receivable account and credits the appropriate account. The account that the system credits is based on the system function associated with the business event that occurred before you dishonored the draft.
You void a draft at any point in the draft life cycle after you approve the draft until you reconcile the draft on a bank statement. When you void a draft, the system reopens all the items associated with the draft. This process changes the draft status to E (Void).
You cancel a remittance after you remit a nondiscounted draft either before or after the due date but before you reconcile the draft on a bank statement. For discounted drafts, you must cancel the remittance before the discount date or after you dishonor it. Cancelling a remittance returns the draft to the state it was in after you approved and posted it. The system changes the draft’s status to A (Accepted). You can remit the draft again at a later date.
Accounting Entries for Draft Voids and Cancel Remittances
When you void a draft or cancel a remittance, the system looks at the last activity that occurred to determine what accounting entries to create. It creates accounting entries that net the activities that have occurred. For example, if you are voiding a non-discounted draft after the due date, the system credits Cash and debits Accounts Receivable to net the following entries:
|
Event |
Debit |
Credit |
|
Approve Draft |
Draft Receivable |
Accounts Receivable |
|
Remit to Bank |
Draft Cash Control |
Draft Receivable |
|
Draft Due Date |
Cash |
Draft Cash Control |
 Understanding Draft Setup
Understanding Draft SetupThis section discusses:
Draft setup overview
Draft business events
Draft types
Distribution codes
Bank account ChartFields
Bank fees
Draft Setup Overview
The setup for draft processing enables you to generate whatever accounting entries your organization requires at each step of the draft life cycle and to define different processing rules for each type of draft that you use. Draft processing uses the following options to determine how to process drafts:
System functions.
Draft business events.
Draft types.
Draft distribution codes.
Bank account ChartFields.
You generate different accounting entries for an event based on which path the draft follows. PeopleSoft provides you with the ability to define how the system generates accounting entries for each draft event for each type of draft that you use.
A draft business event is an action that can occur during draft processing that generates accounting entries and audit history information. Receivables delivers and supports the business events and defines the processing characteristics for the Receivable Update process for each one.
When you define draft types, you assign a system function to each event that occurs for the draft type and optionally define the draft distribution codes by business unit. This provides the flexibility to define the accounting entries that occur for each event, as necessary.
Draft types determine the processing characteristics for drafts. They also determine how to generate accounting entries for them. You use draft types to tailor draft processing and draft accounting entries to meet your processing requirements.
When you define your draft types, you specify the draft events for which you want to generate accounting entries. You also specify how to generate the accounting entries by assigning a system function to each of those events and optionally you assign separate draft distribution codes to each business unit for that draft type. In some cases, you may be able to select one of several system functions for a draft event based on your processing requirements. You also assign a system function that defines how to generate accounting entries when you dishonor a draft after the draft event.
Draft processing uses the distribution codes that you set up for these distribution types:
When you create a draft item by running the Create Drafts Application Engine process (AR_DRAFTS) or by applying items to a draft on the draft worksheet, the system assigns draft distribution codes for each distribution type to the draft item. It uses the following hierarchy to determine the correct distribution code:
Distribution code linked to the accounts receivable (AR) distribution code on the Distribution Code page for the original item.
Distribution code assigned to the draft type and business unit combination on the Draft Type Distribution Codes secondary page.
Distribution code assigned to the business unit on the Receivables Definition - Accounting Options 2 page.
When you run the Receivable Update process, it looks at the system function that you assigned to the event it is currently processing to determine which type of draft distribution code to use. The process uses the distribution code that is assigned to the draft item to create the accounting entries.
If the draft item does not have a draft distribution code for the event, the Receivable Update process marks the draft in error. To correct the error, you need to assign the appropriate draft distribution code to the business unit. You also assign one to the draft type and business unit combination, and (if necessary), to the AR distribution code for the original item. Then, you click the Update Distribution Codes button on the Correct Posting Errors, Draft - Group Action page to add the distribution code to the item. When you rerun the Receivable Update process, it creates the correct accounting entries.
See Setting Up Distribution Codes.
Several system functions use the ChartFields that you assign to your bank account on the External Accounts page. The types of cash control accounts that you set up depend on your country's accounting requirements. The following table lists the four cash accounts that you can assign to a bank account and their account types:
|
Account |
Account Type |
Description |
|
Cash |
Cash − AR |
Use to record cash when you receive it. |
|
Cash Control |
Control − AR |
Use for cash clearing to record cash prior to actually receiving the funds. Use when your organization uses only one account for all cash control activity. |
|
Draft Cash Control |
Draft − AR |
Use for cash clearing to record cash prior to actually receiving the funds. Use when your organization needs two cash control accounts. Use for nondiscounted drafts. |
|
Discount Draft Cash Control |
Discount − AR |
Use for cash clearing to record cash prior to actually receiving the funds. Use when your organization needs two cash control accounts. Use for discounted drafts. |
Each system function indicates which type of account to use to generate accounting entries. The Receivable Update process uses the cash account with the appropriate account type.
When you discount a draft, you normally have to pay a bank fee or interest on the money that you collect prior to the due date. PeopleSoft provides a system function (DM-90) for bank fees. You need to set up an entry type and automatic entry type for bank fees and assign them an entry reason for interest. When you remit a discounted draft, you specify the entry type that is used to generate the accounting entries for bank fees. When you run the Receivable Update process on the discount date, the process creates an item for the draft fees that has a zero amount and automatically closes the item. The process uses the entry type for bank fees to generate the appropriate accounting entries.
See Also
Defining Receivables Processing Options
Defining External Account Information
 Reviewing Business Events and Subevents
Reviewing Business Events and SubeventsTo review business events and subevents, use the Draft Business Events (DR_BUSINESS_EVENT) and Sub Events (DR_SUB_EVENT) components.
This section provides an overview of business events and discusses how to:
Review business events for drafts.
Review subevents for drafts.

 Understanding Business Events
Understanding Business EventsReceivables comes with predefined draft business events. Each draft business event has the processing characteristics already defined for the Receivable Update process, including those for dishonoring a draft after that event.
You initiate some events online, such as remitting a draft. The system automatically processes other events, such as due date processing, when you run the Receivable Update process. The process creates a group for each draft and posts the activity on the Draft Activity record.
The following table describes the delivered business events:
|
Draft Business Event |
Description |
|
A0 Draft Creation |
It creates the draft in the system. |
|
B0 Draft Approval |
The customer approves the draft by pre-existing arrangement (drafts are automatically approved when you create them) or by receiving a signed draft document. This event has subevents that you use to set up accounting entries for adjustments, write-offs, prepayments, or deductions on a draft worksheet. |
|
C1 Draft Remitted |
You send a nondiscounted draft to the bank for collection of the funds owed. Your bank collects the money at the due date. |
|
C2 Draft Remitted with Discount |
You send a discounted draft with recourse to the bank before the due date to obtain funds in advance of the customer actually paying the draft. The date that you require the funds is known as discount date. The bank charges a fee and interest. This is effectively arranging a short-term loan on the basis of a guaranteed future payment. |
|
D0 Cancel Remitted Draft |
You cancel a remitted draft. The status returns to Accepted. |
|
E2 Discounted Draft at Discount Date with Recourse |
A discounted draft with recourse reaches the discount date (the date that the bank should release money to your bank account). |
|
E3 Discounted Draft at Discount Date with no Recourse |
A discounted draft without recourse reaches the discount date (the date that the bank should release money to your bank account). |
|
F1 Draft at Due Date |
A nondiscounted draft reaches its due date (maturity date). This is the date you expect the bank to receive the money from the customer and to apply it to your bank account. |
|
F2 Discounted Draft at Due Date with Recourse |
A draft discounted with recourse reaches its due date (maturity date). |
|
F3 Discounted Draft at Due Date with no Recourse |
A draft discounted without recourse reaches its due date (maturity date). |
|
H1 Bank Statement Reconciliation |
The bank statement contains an entry that confirms a nondiscounted draft was paid. You have reconciled the bank statement. |
|
H2 Reconcile Discounted Draft with Recourse |
The bank statement contains an entry that the bank put money into your account for a discounted draft with recourse. You have reconciled the bank statement. |
|
H3 Reconcile Discounted Draft with no Recourse |
The bank statement contains an entry that a draft discounted without recourse was paid. You have reconciled the bank statement. |
|
10 Void Draft |
You mark a draft null and void. The system reopens the associated item to ensure that the outstanding debt is collected. |
We recommend that you do not change the system-defined draft business events or add new ones. To prevent users from changing business events, ensure that the page options for Draft Business Events and Draft Sub-Events are display-only for most users. If you must create a new event, ensure that you set it up properly.
For a new batch event (events that are system-generated), select the Batch Event check box and write the SQL that triggers the processing for the event. You must use the D alias type for DRAFT_CONTROL record and R alias type for POSTING_REQUEST record when you write the SQL. Review one of the existing events with SQL before you write your own.
If you are adding a new event that you will initiate from an online page, you must create a new page. The DRAFT_TYPE field in the FUNCLIB_ARINTFC record contains all the code that is necessary to perform online processing. View some examples to see how this code is implemented. PeopleSoft employs three different methods:
To see how PeopleSoft performs the processing for a single draft per page, look at the SavePreChange PeopleCode for DRAFT_WRK.APPROVE_BUTTON.
To see how PeopleSoft performs the processing for a set of drafts that need posting (multiple drafts per page), look at the SavePostChange PeopleCode for DR_REMIT_WRK.COMPLETE_BUTTON.
To see how PeopleSoft performs the processing of multiple drafts per page (line by line), look at the SavePreChange PeopleCode for DR_DISH_ITM_SBR.ITEM_SELECTED.
If you add a new system function for an on-account or prepayment item, you must update the PeopleCode for drafts to include the system function. You update the following:
FUNCLIB_AR (record)
RECNAME (field)
Field Change (event)
IsAdvancePayment (function)

 Pages Used to Review Business Events and Subevents
Pages Used to Review Business Events and Subevents
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
DR_BUSINESS_EVENT |
Setup Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Receivables, Drafts, Business Events, Business Events |
Review system-defined processing rules for draft business events. |
|
|
DR_SUB_EVENT |
Setup Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Receivables, Drafts, Sub-Events, Sub Events |
Review subevents that can occur for a draft event. You can display subevents only for draft events that require subevents, such as Draft Approval. |

 Reviewing Business Events for Drafts
Reviewing Business Events for Drafts
Access the Business Events page.
|
Specify System Function |
If selected, indicates that you must specify a system function for the event for each draft type to generate accounting entries. |
|
Post Action |
Select a value that indicates when the event occurs. Values are: Actual: For the actual business event. Dishonor: For drafts dishonored after the business event. Most business events have a set of actual rules and another set of dishonor rules. Use the scroll area to see both sets of rules. |
|
Use Sub-Events? |
If selected, indicates the event has a subevent. |
|
Include in Cancel Remittance |
If selected, indicates that the Receivable Update process reverses the accounting entries and status for the event when you cancel a remittance. |
|
SQL Object ID |
Enter the SQL object that ensures the draft is in the right condition for the event. |
Event Settings
The options in the Event Settings group box define the rules for the Receivable Update process when it posts the event.
Unpost Settings
The options in this group box define the rules for Receivable Update when it unposts the event.
|
Unpost Flag |
If selected, you can unpost the event. |
|
Draft Status |
Displays the status of a draft after the Receivable Update process runs for the unpost group. |
|
Disc Indic (discount indicator) and Recon (reconciliation) |
The Disc Indic and Recon check boxes for unposting work the same as they do for posting. |
See Also

 Reviewing Subevents for Drafts
Reviewing Subevents for Drafts
See Also
Defining Receivables Write-off and Discount Tolerances
 Defining Draft Transaction Types
Defining Draft Transaction TypesTo define draft transaction types, use the Draft Transaction Type component (DRAFT_TXN_TYPE).
If you plan to customize reports and want to use draft transaction types in the reports, you must define the types of transactions that drafts pay, such as assets or inventory.
This section lists the page used to set up draft transaction types.

 Page Used to Set Up Draft Transaction Types
Page Used to Set Up Draft Transaction Types
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
DRAFT_TXN_TYPE |
Setup Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Receivables, Drafts, Transaction Type, Draft Transaction Type |
Define the types of transactions that drafts pay, such as inventory or assets. |
 Defining Draft Types
Defining Draft TypesTo define draft types, use the Draft Type component (DRAFT_TYPE).
This section provides an overview of draft types and discusses how to:
Set up draft types.
Copy a draft type.
View accounting entry setup.
Assign distribution codes to a draft type.
Assign system functions to subevents.

 Understanding Draft Types
Understanding Draft TypesWhenever you create a draft, you must assign it to a draft type. Draft types determine the rules for processing drafts, such as the rules for creating and canceling drafts. Draft types also determine how accounting entries are generated.
Receivables delivers the following draft types:
|
Draft Type |
Description |
|
A vendor-initiated draft that is normally sent to the customer for approval. PeopleSoft provides five samples of bills of exchange. |
|
|
A customer-initiated draft that is sent preapproved to the vendor. PeopleSoft provides eight samples of promissory notes. |
You can use the sample draft types as defined. However, many countries have set requirements for the accounting entries that you must generate for draft processing. If you find a sample that almost meets your requirements, copy it and modify it to suit your needs.

 Pages Used to Define Draft Types
Pages Used to Define Draft Types
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
DRAFT_TYPE |
Setup Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Receivables, Drafts, Type, Draft Type |
Define the processing rules for drafts and the type of accounting entries for each draft event. |
|
|
DRAFT_TYPE_CPY_SEC |
Click the Copy Draft Type link on the Draft Type page. |
Create a new draft using an existing draft type as a template. |
|
|
DRAFT_TYPE_ACT_SEC |
Click the View Accounting link on the Draft Type page. |
View the accounts that the Receivable Update process debits and credits for each draft event when processing drafts for this draft type. |
|
|
DRAFT_TYPE_DST_SEC |
Click the Draft Distribution Codes link on the Draft Type page. |
Override the draft type distribution codes for specific business units. |
|
|
DRAFT_TYPE_AR_SEC |
Click the Sub-events link on the Draft Type page. |
Assign system functions to subevents for a draft event. You can also specify which system function to use when you dishonor a draft after the subevent. |

 Setting Up Draft Types
Setting Up Draft Types
Posting Details
Use the Posting Details grid to assign system functions to draft business events for two circumstances: when the actual event occurs and when you dishonor the draft. The system function that you assign to an event determines how the system creates accounting entries.
If you do not assign a system function to an event, the system does not generate accounting entries for the event for drafts using this draft type. For example, you may want to generate accounting entries to recognize cash after the Bank Statement Reconciliation event, instead of after the Draft at Due Date event. In that case, you would not assign a system function to the Draft at Due Date event.
If an event does not require a system function, it does not appear in the list. For example, the Receivable Update process does not require a system function for the Unpost event because it reverses the entries for the prior event.
Note. You must create an automatic entry type for each system function that you assign. The “Defining Receivables Processing Options” chapter contains a table that lists all system functions and describes the accounting entries that they generate.
See Understanding System Functions.
Example: Draft Types for French Accounting
The following table shows how to set up draft types that meet French accounting requirements:
|
Event |
Actual |
Dishonor |
|
B0 − Draft Approval |
DM-01 DM-02 DM-03 DM-04 DM-05 DM-06 DM-07 DM-08 DM-09 DM-10 |
DM-50 DM-50 DM-50 DM-50 DM-50 DM-50 N/A N/A N/A N/A |
|
C1 − Draft Remitted |
DM-20 |
DM-52 |
|
C2 − Draft Remitted with Discount |
DM-21 |
DM-53 |
|
E2 − Discounted Draft at Discount Date with Recourse |
DM-30 |
DM-57 |
|
E3 − Discounted Draft at Discount Date with no Recourse |
DM-31 |
DM-58 |
|
F1 − Draft at Due Date |
DM-40 |
DM-58 |
|
F2 − Discounted Draft at Due Date with Recourse |
DM-41 |
DM-58 |
|
F3 − Discounted Draft at Due Date with no Recourse |
DM-47 |
DM-58 |
|
H1 − Bank Statement Reconciliation |
N/A |
N/A |
|
H2 − Reconcile Discounted Draft with Recourse |
N/A |
N/A |
|
H3 − Reconcile Discounted Draft with no Recourse |
N/A |
N/A |
Example: Draft Types for German Accounting
The following table shows how to set up draft types that meet German accounting requirements:
|
Event |
Actual |
Dishonor |
|
B0 − Draft Approval |
DM-01 DM-02 DM-03 DM-04 DM-05 DM-06 DM-07 DM-08 DM-09 DM-10 |
DM-50 DM-50 DM-50 DM-50 DM-50 DM-50 N/A N/A N/A N/A |
|
C1− Draft Remitted |
DM-22 |
DM-54 |
|
C2 − Draft Remitted with Discount |
DM-22 |
DM-54 |
|
E2 − Discounted Draft at Discount Date with Recourse |
N/A |
N/A |
|
E3 − Discounted Draft at Discount Date with no Recourse |
N/A |
N/A |
|
F1 − Draft at Due Date |
N/A |
N/A |
|
F2 − Discounted Draft at Due Date with Recourse |
DM-43 |
DM-58 |
|
F3 − Discounted Draft at Due Date with no Recourse |
N/A |
N/A |
|
H1 − Bank Statement Reconciliation |
DM-42 |
DM-58 |
|
H2 − Reconcile Discounted Draft with Recourse |
DM-32 |
DM-57 |
|
H3 − Reconcile Discounted Draft with no Recourse |
DM-42 |
DM-58 |
Example: Draft Types for Spanish Accounting
The following table shows how to set up draft types that meet Spanish accounting requirements:
|
Event |
Actual |
Dishonor |
|
B0 − Draft Approval |
DM-01 DM-02 DM-03 DM-04 DM-05 DM-06 DM-07 DM-08 DM-09 DM-10 |
DM-50 DM-50 DM-50 DM-50 DM-50 DM-50 N/A N/A N/A N/A |
|
C1 − Draft Remitted |
DM-23 |
DM-55 |
|
C2 − Draft Remitted with Discount |
DM-24 |
DM-56 |
|
E2 − Discounted Draft at Discount Date with Recourse |
DM-33 |
DM-58 |
|
E3 − Discounted Draft at Discount Date with no Recourse |
N/A |
N/A |
|
F1 − Draft at Due Date |
DM-46 |
DM-58 |
|
F2 − Discounted Draft at Due Date with Recourse |
DM-41 |
DM-58 |
|
F3 − Discounted Draft at Due Date with no Recourse |
N/A |
N/A |
|
H1− Bank Statement Reconciliation |
DM-46 |
N/A |
|
H2 − Reconcile Discounted Draft with Recourse |
DM-33 |
DM-58 |
|
H3 − Reconcile Discounted Draft with no Recourse |
N/A |
N/A |
Example: Draft Types for Japanese Accounting
The following table shows how to set up draft types that meet Japanese accounting requirements:
|
Event |
Actual |
Dishonor |
|
B0 − Draft Approval |
DM-01 DM-02 DM-03 DM-04 DM-05 DM-06 DM-07 DM-08 DM-09 DM-10 |
DM-50 DM-50 DM-50 DM-50 DM-50 DM-50 N/A N/A N/A N/A |
|
C1 − Draft Remitted |
N/A |
DM-50 |
|
C2 − Draft Remitted with Discount |
N/A |
DM-50 |
|
E2 − Discounted Draft at Discount Date with Recourse |
DM-33 |
DM-58 |
|
E3 − Discounted Draft at Discount Date with no Recourse |
N/A |
N/A |
|
F1 − Draft at Due Date |
DM-44 |
DM-58 |
|
F2 − Discounted Draft at Due Date with Recourse |
DM-45 |
DM-58 |
|
F3 − Discounted Draft at Due Date with no Recourse |
N/A |
N/A |
|
H1 − Bank Statement Reconciliation |
DM-44 |
DM-58 |
|
H2 − Reconcile Discounted Draft with Recourse |
DM-33 |
DM-58 |
|
H3 − Reconcile Discounted Draft with no Recourse |
N/A |
N/A |

 Copying a Draft Type
Copying a Draft TypeAccess the Draft Type page for the draft type that you want to copy.
To copy a draft type:
Click Copy Draft Type to access the Draft Type Copy page.
Enter a setID and draft type code.
After you save the new draft type, modify it as needed.

 Viewing Accounting Entry Setup
Viewing Accounting Entry SetupAccess the View Accounting Entries page.
Review the Debit and Credit account fields for each draft event to make sure the accounting entries will be correct. If not, review your setup and make the necessary changes.

 Assigning Distribution Codes to a Draft Type
Assigning Distribution Codes to a Draft TypeAccess the Draft Type Distribution Codes page.
To override the default distribution code for a specific business unit for this draft type, enter a business unit. Then enter the distribution code to use for any of the following types of distribution types:
|
Draft AR |
Enter the receivable account for approved drafts. |
|
Remitted Draft |
Enter the receivable account for remitted drafts. |
|
Discount Recv (discount receivable) |
Enter the receivable account for discounted drafts. |
|
Discount Liab (discount liability) |
Enter the liability account for drafts discounted with recourse. |
|
Dishonored |
Enter the receivable account for dishonored drafts. |

 Assigning System Functions to Subevents
Assigning System Functions to SubeventsAccess the Draft Subevent System Function page.
Assign a system function to each Sub Event for which you want to create accounting entries. Enter the system function to use for the actual subevent in the Standard field.
Note. You enter the system function to use when you dishonor the draft after the subevent in the Dishonor field on the Draft Type page.
 Defining Where Draft Documents Are Stored
Defining Where Draft Documents Are StoredTo define where documents are stored, use the Draft Physical Location component (DRAFT_LOCATION).
You define each location where you store draft documents. You assign a draft location to a draft on the draft worksheet.
This section discusses how to define draft locations.

 Page Used to Define Where Draft Locations are Stored
Page Used to Define Where Draft Locations are Stored
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
DRAFT_LOCATION |
Setup Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Receivables, Drafts, Physical Location, Draft Physical Location |
Define where you store draft documents. |

 Defining Draft Locations
Defining Draft Locations
Access the Draft Physical Location page.
Enter the Location code and a description for each location.
 Defining Draft Collection Methods
Defining Draft Collection MethodsYou must define the collection information for the bank accounts that receive the EFT files that you send.
This section discusses how to define collection information.

 Page Used to Define Collection Methods
Page Used to Define Collection Methods
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
COLLECT_BANK |
Banking, Bank Accounts, External Accounts, Collection Methods |
Define collection information for the bank to which you send EFT files for drafts. |

 Defining Collection Information
Defining Collection Information
Access the Collection Methods page.
Select Draft in the Payment Method field. Then define the following additional information:
If your organization uses document sequencing, assign document types for draft processing.
Define the currency, minimum remittance amount, and the draft risk days.
If you use discount drafts, define the credit limit information for discounts.
Define the rules for determining the settlement date if the due date falls on a holiday.
Define the EFT file attributes.
See Also
 Assigning Customers to Draft Groups
Assigning Customers to Draft GroupsYou have the option of assigning customers to draft groups. When you create drafts, you can create them for all customers in a draft group at once.
This section discusses how to:
Create a draft group.
Assign a customer to a draft group.

 Pages Used to Assign Customers to Draft Groups
Pages Used to Assign Customers to Draft Groups
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
CUST_GROUP_TBL |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Customers, Customer Group Table, Customer Group Table |
Create draft groups for customers who share the same functionality. |
|
|
CUST_GROUP_INFO |
Customers, Customer Information, General Information, General Info Select 0070 - Customer Group in the General Info Links field on the General Info page for the customer. |
Assign individual customers to a draft customer group. |

 Creating a Draft Group
Creating a Draft Group
Access the Customer Group Table page.
Select Draft for the customer group type.
See Also
Establishing Customer Group Tables

 Assigning a Customer to a Draft Group
Assigning a Customer to a Draft Group
Access the General Information - Customer Group Info.
Select DRFT in the Group Type field and select the group in the Customer Group field.
 Setting Up Automatic Numbering for Draft Processing
Setting Up Automatic Numbering for Draft ProcessingYou must set up automatic numbering for draft IDs, draft approval IDs, draft remittance IDs, and IDs for the dishonor, void, and cancel remittance worksheets on the Automatic Numbering page.
The following table lists the number types that you must set up and the field name to select for each one:
|
Number Type |
Field |
|
Draft ID (DRFT) |
DRAFT_ID |
|
Draft Approval ID (DRAP) |
DR_APPROVE_ID |
|
Remittance ID (RMT) |
REMIT_ID |
|
Draft Worksheet ID (DISH) |
DR_DISHONOR_ID |
See Also
Setting Up Automatic Numbering
 Setting Up Draft Reference Qualifiers
Setting Up Draft Reference QualifiersTo set up draft reference qualifiers, use the Draft Reference Qualifier component (DR_FLD_REF_TBL).
Receivables delivers four draft reference qualifiers that you use to identify drafts when you build draft remittance worksheets: Draft ID, Draft Document Reference, Customer Bank, and Customer Group.
This section discusses how to set up reference qualifiers for remitting drafts.

 Page Used to Set Up Reference Qualifiers
Page Used to Set Up Reference Qualifiers
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
DR_FLD_REF_TABLE |
Setup Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Receivables, Drafts, Reference Qualifier, Draft Reference Qualifier |
Define new reference qualifiers for identifying drafts. |

 Setting Up Reference Qualifiers for Remitting Drafts
Setting Up Reference Qualifiers for Remitting Drafts
Access the Drafts Reference Qualifier page.
|
Record |
Enter the table that contains the data used to build draft remittance worksheets. |
|
Field Name 1 or Field 2 |
Enter values to reference a field in the table. Enter the name of the field on the table that you want to reference in the Fieldname field. Enter the object name of the record used to retrieve the field values in the Prompt Table field. |
Note. The Prompt table looks for fields that are in the DR_CONTROL_SBR and DR_CNTL_EVT_SBR records. It also looks for fields in any view that has the DR_CNTL[_]%VW profile. If you add new reference qualifiers for fields that are not contained in the DRAFT_CONTROL record, you must build a view that has the same profile as DR_CNTL[_]%VW. Look at the DR_CNTL_BNK_VW record for an example.
 Defining EFT Reason Codes and EFT File Layouts
Defining EFT Reason Codes and EFT File LayoutsTo set up EFT reason codes, use the EFT Reason Codes component (EFT_BANK_REASON).
This section provides an overview of EFT reason codes and discusses how to:
Add reason codes.
Select EFT file layouts.

 Understanding EFT Reason Codes
Understanding EFT Reason Codes
In some countries, the bank sends an EFT file after you submit your drafts to the bank confirming whether the payment was collected. The file contains a reason code for each payment record that indicates whether it was collected. If it is not collected the reason code indicates why it was not collected. You run the AR_DRAFT_BNK Application Engine process to process the bank EFT file and to update the status of the Draft Control record. When you run the Receivable Update process, it creates the appropriate accounting entries based on the change to the control record.

 Page Used to Define Reason Codes
Page Used to Define Reason Codes
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
EFT_BANK_REASON |
Setup Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, EFT, EFT Reason Codes, EFT Reason Codes |
Set up reason codes for draft processing. |

 Adding Reason Codes
Adding Reason CodesAccess the EFT Reason Codes page.
|
Reason Code |
Enter a user-defined reason code and description. |
|
Event |
Enter the appropriate draft business event, such as 10 (Void Draft) or F1 (Draft at Due Date) that the system should use to set the status for payment records returned with this reason. |
|
Post Action |
Indicate whether the system should use the actual or dishonored rules that you defined for the business event. Values are Actual or Dishonor. |
Set up the following reason codes for the RIBA files used in Italy. Other countries can use this as an example to set up their reason codes.
|
Reason Code |
Description |
Action |
|
30006 |
Incorrect due to technical problems |
Void draft |
|
30007 |
Incorrect bank details |
Cancel remittance |
|
30008 |
Payment stopped by issuer |
Void draft |
|
30009 |
Due date beyond SIA guidelines |
Void draft |
|
30010 |
Payment collected |
Apply cash |
|
42010 |
Insufficient funds |
Dishonor draft |

 Setting Up EFT File Layouts
Setting Up EFT File Layouts
The following is a list of EFT file layouts for draft processing:
|
Eft File Layout Code |
Description |
Country |
|
ETBDR |
Use for outbound transmissions. |
France |
|
RIBA |
Use for inbound and outbound transmissions. Receive information from the bank indicating the success of payments. |
Italy |
|
KIJ |
Use Kijitsu for inbound transmissions. |
Japan |
See Also