
 Understanding Data Preparation
Understanding Data Preparation
This chapter provides an overview of data preparation, lists prerequisites, and discusses how to:
Define ledger verification rules.
Define calendar mapping rules.
Define ChartField mapping rules.
Define currency mapping rules.
Define ledger preparation rules and groups.
Run ledger preparation.
Run currency adjustment.

 Understanding Data Preparation
Understanding Data Preparation
Once your source ledger data resides in the PeopleSoft Enterprise Performance Warehouse tables, you need to prepare the data before you can use it as input for any consolidation processes. Because the subsidiary ledgers may use different accounting calendars, account structures, and store amounts in different base currencies, they must be converted to a common structure prior to consolidations. This common structure is your consolidation ledger. To convert the subsidiary ledger data to the consolidation ledger, you define a series of mapping rules and run the data preparation process. As a result, the source ledger data is converted to the common structure, based on your mapping rules, and moved into the consolidation ledger. It is this consolidation ledger that is subsequently used as input for consolidation processes.
Note. If your source subsidiary ledger data is in the same format as the consolidation ledger, when you define its ledger preparation rule, you can indicate that no preparation is required.
Prerequisites
Before you can establish the mapping rules used for ledger preparation, you must define this supporting data in PeopleSoft Enterprise Performance Warehouse:
Calendars: detail and summary.
Currency rates, currency codes, currency quotation methods, market rate definitions, market rate index, market rate type, and market rates.
Warehouse business units for your subsidiary units and your common consolidation business unit.
Ledger templates, source ledgers, and consolidation ledgers.
Metadata and PeopleSoft Application Designer records for your subsidiary ledger records, source staging ledger records, mapping ledger records, and the consolidation ledger record.
Metadata for the trees used within consolidations.
See Setting Up EPM Foundation.
See Defining Your Organizational Structure.

 Ledger Preparation Processing Phases
Ledger Preparation Processing Phases
The ledger preparation processing phases are:
(Optional) Run the Ledger Verification Process prior to running the LeEdger Preparation process.
Maps the subsidiary source data, converts it to a common accounting calendar, and removes unnecessary keys to improve processing times.
Populates SLED.
Maps ledger accounts to a common account structure.
Populates MLED.
Converts monetary amounts to the consolidation ledger currency.
Updates MLED.
Moves data into the consolidation ledger.
Populates CLED.
These naming conventions identify the records used at each phase of ledger preparation processing; if customizing, replace XXX with a unique identifier of your choice for each record:
|
GC_SLED_XXX_TBL |
The name for the ledger record after the calendar map phase. This is the source stage ledger, or SLED. The delivered record for the source stage ledger, PS_LEDGER_F00 ledgers is GC_SLED_PGL_TBL. |
|
GC_MLED_XXX_TBL |
The name for the ledger record after mapping rules have been applied. This is the mapped ledger, or MLED. The delivered record for the mapping ledger is GC_MLED_MGT_TBL. |
|
GC_CLED_XXX_F00 |
The name for the resulting ledger record after ledger preparation is complete. This is the consolidation ledger, or CLED. The delivered record for the consolidation ledger is GC_CLED_MGT_F00. |
This diagram depicts the ledger preparation processing flow:
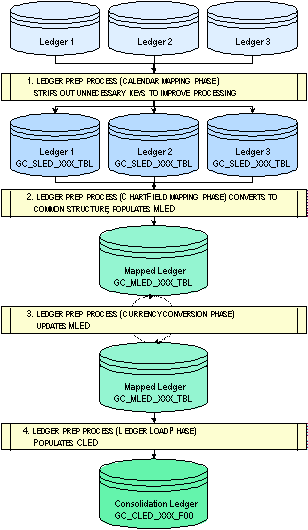
Ledger preparation process flow
The format of the consolidation ledger impacts ledger preparation processing:
If the consolidation ledger format is trial balance, the system processes both current period activity and year-to-date (YTD) activity (period end balances for balance sheet accounts and YTD activity for income statement accounts) from the source ledgers.
The system converts any YTD amounts to current period activity.
If the consolidation ledger format is financial statement, the source ledger data must also be in financial statement format.
No conversion occurs.
The consolidation ledger is balanced after currency conversion by using the balancing account type rule defined on the consolidation model.
See Also
Defining Balancing Account Type Rules

 Mapping to a Common Calendar
Mapping to a Common Calendar
Once the subsidiary ledgers are loaded into PeopleSoft Enterprise Performance Warehouse, you need to ensure that the fiscal year and accounting period for all of the ledgers is based on the same time frame (the same accounting calendar) before you can process consolidations. Because these ledgers may use a different accounting calendar than the calendar used for consolidations, the system can map the calendars for each ledger business unit to the consolidation calendar. You establish the calendar mapping rules by using the Calendar Map page, specifying the rules for mapping from one accounting calendar to the consolidation accounting calendar. You need to define calendar mapping rules for each unique accounting calendar used by the business units within your organization that you consolidate. However, if more than one subsidiary uses the same accounting calendar, you only need to define that particular calendar mapping once. You identify the specific calendar mapping rule that a ledger business unit uses when you define a ledger preparation rule.
Note. Specifically with trial-balanced-based ledgers, calendar mapping is mutually exclusive to supplying YTD amounts in the source ledger. That is, if you supply YTD amounts to the consolidation process and want the system to derive the period activity, then consolidations must assume that the YTD value is for the consolidation period. For example, the YTD balance in the source ledger for 2002 period 01 is for consolidation 2002 period 01. If calendar mapping is defined when the source ledger is identified to contain YTD amounts, you receive an error.

 Mapping to a Common Chart of Accounts (Data Mapper)
Mapping to a Common Chart of Accounts (Data Mapper)
Before consolidation can take place, you must map all of the subsidiary ledgers requiring consolidation to a common chart of accounts. Potentially, each subsidiary ledger could have its own set of ChartFields and chart of accounts. To consolidate all these ledgers, you must map each of them to a common ChartField structure and common chart of accounts. The target consolidation structure can be completely different from one or all source structures. Use the Enterprise Performance Warehouse Data Mapper component to define how your subsidiary ledgers map to a common ChartField structure and common chart of accounts. You identify the datamaps that define the source data and the target table, and the method by which to map the data in a data mapping rule. For Global Consolidations, the source data is a source staging ledger (SLED), and the target table is the corresponding mapping ledger (MLED).
These rules can be defined to:
Use any source staging ledger (SLED) as a source.
Use any mapping ledger (MLED) as a target.
Map to a target column by using the value from a source column, a fixed value, or a defined map.
Define maps with one or more source columns, mapped to one or more target columns.
Map source data with a value or a tree node.
Map to target columns with a value or a tree node.
The mapping can include as many fields as exist in the source and target. If you add new ChartFields to either the source or target records, you can extend the mapping rule to include these new fields. Data Mapper rules are effective-dated, enabling you to control when to use new fields.

 Converting to a Common Base Currency
Converting to a Common Base Currency
Because consolidation deals with multiple source ledgers as input into the process, one consideration is the issue of currency. The system cannot assume that all the subsidiary source ledgers are in the same currency as the consolidation currency, so there is a tool that can translate different currencies into a common consolidation reporting currency for the consolidation process. If you require more then one reporting currency, then you need to create additional scenarios for them.
Subsidiary ledgers are converted to a base consolidation currency prior to the consolidation process as part of ledger preparation processing. This occurs after the ledgers are converted to the common consolidation calendar and the common consolidation chart of accounts. The mapped ledger (MLED) stores ledger amounts in multiple currencies, so there is a way to audit and track the translated account balances; the original account balance and currency are preserved. The source ledger’s base currency amounts are converted to the consolidation currency using the defined rules and exchange rates. The rate type and exchange rates used are stored.
The new currency amount is computed by using this method:
The system obtains the number of decimal positions for the consolidation base currency from the Currency Code table (CURRENCY_CD_TBL).
This is used for rounding.
The Source Base Currency Amount is multiplied by the RATE_MULT amount from the Market Rate table (RT_RATE_TBL).
The result of the multiplication is divided by the RATE_DIV amount from the Market Rate table.
The result is rounded to the number of decimals defined for the currency in the Currency Code table.
Potentially, as a result of currency conversion, the ledger may be out of balance due to rounding or due to using different exchange rates for balance sheet accounts versus equity accounts. If so, the system generates the appropriate adjustment automatically. To balance the ledger, the system sums together all the account balances for a specific ledger business unit combination. If the result is not zero, than an adjustment is recorded to the account specified in the associated currency mapping rule.
Each ledger business unit is balanced independently of the other ledger business units that comprise the consolidation ledger. Each ledger business unit is adjusted separately as needed. The adjustment is recorded directly into the consolidation ledger with a source code of (02) Currency Conversion Adjustment or (2A) Currency Adjust - Manual Entry separate from any source ledger balance and journal activity.
This table lists required fields for currency conversion. The system uses these fields to generate an audit trail and to navigate to the source data:
|
Required Field Within the Mapped Ledger (GC_MLED_MGT_TBL) |
Description |
Populated By |
|
GC_SRC_TRAN_CURR |
The currency in which the source ledger transaction amount is recorded. |
Ledger Mapping |
|
GC_SRC_TRAN_AMT |
The source ledger transaction amount. |
Ledger Mapping |
|
GC_SRC_BASE_CURR |
The source ledger base currency. |
Ledger Mapping |
|
GC_SRC_BASE_AMT |
The transaction amount converted into the base currency. |
Ledger Mapping |
|
GC_CONSOL_BASECURR |
The consolidation ledger base currency. |
Currency Conversion |
|
GC_CONSOL_BASE_AMT |
The source ledger’s base currency amount converted to the consolidation base amount. |
Currency Conversion |
|
RT_TYPE |
The currency rate type. |
Currency Conversion |
|
RATE_MULT |
The currency exchange rate multiplier. |
Currency Conversion |
|
RATE_DIV |
The currency exchange rate divisor. |
Currency Conversion |
|
GC_CURR_RULE_ID |
The currency conversion rule ID. The audit utility uses this ID to navigate to the rule that was used to convert monetary amounts for this account. |
Currency Conversion |
Regardless of how many different transaction currencies the source ledger contains, the system moves only two currencies into the consolidation ledger once the ledger preparation process is complete:
The consolidation ledger’s base currency and its corresponding amount.
The source ledger's base currency and its corresponding amount.
This table lists the fields for currency conversion for the consolidation ledger:
|
Currency Field within the Consolidation Ledger (CLED) |
From MLED (For the row where currency code is equal to the source base) |
From MLED (For the base currency row if the source base not equal to consolidation base) |
|
CURRENCY_CD |
Source currency |
Consolidation currency |
|
BASE_CURRENCY |
Consolidation currency |
Consolidation currency |
|
POSTED_TOTAL_AMT |
Sum of source base PERIOD amount |
Sum of consolidation base amount (Source base PERIOD amount converted) |
|
POSTED_BASE_AMT |
Sum of consolidation base amount (Source base PERIOD amount converted) |
0 |
|
POSTED_TRAN_AMT |
Sum of source base PERIOD amount |
0 |
The system requires that the structure of all source ledgers follow these standards:
Debit and credit stored as +/-.
Specifically for trial balance format source ledgers, there should not be an equity account that stores YTD retained earnings.
Instead, the system derives YTD retained earnings on the balance sheet from the total of the revenue and expense accounts.
Period 0 (beginning balances) must be supplied for trial balance format source ledgers.
When ledger preparation is run for the common consolidation business unit for accounting period 1, period 0 (beginning balances) is also prepared and loaded into the consolidation ledger. The currency conversion and balancing of period 1 is done separately from period 0. For other accounting periods, only that specific accounting period is processed.
Currency Mapping Example
In this example, the subsidiary ledger contains multiple currencies—including entries for the consolidation currency—but the base currency of the source ledger is not the same as the consolidation currency. The consolidation currency is USD. The base currency of the source ledger is EUR. The fields within the source ledger, mapped ledger, and consolidation ledger appear in these tables.
This table depicts a trial balance based source ledger:
|
Business Unit |
Account |
Foreign Currency Code |
Foreign |
Base Currency Code |
Base Currency Amount |
|
SUB1 |
100002 |
CAD |
250.00 |
EUR |
202.50 |
|
SUB1 |
100002 |
EUR |
120.00 |
EUR |
120.00 |
|
SUB1 |
100002 |
USD |
80.00 |
EUR |
79.96 |
|
SUB1 |
100003 |
CAD |
-250.00 |
EUR |
-202.50 |
|
SUB1 |
100003 |
EUR |
-120.00 |
EUR |
-120.00 |
|
SUB1 |
100003 |
USD |
-80.00 |
EUR |
-79.96 |
First, ledger mapping takes place, and these fields are mapped:
The source Foreign Currency Amount field maps to Source Tran Amount.
The source Foreign Currency Code field maps to Source Tran Currency.
The source Base Currency Amount field maps to Source Base Amount.
The source Base Currency field maps to Source Currency.
Next, currency conversion converts the source base amount to the consolidation currency, and stores these details for each row in the mapped ledger:
Consolidation currency.
Consolidation base amount.
Rate type, rate multiplier, and rate divisor used to convert.
The source base amount is converted even when the Source Tran Currency field value is the same as the consolidation currency.
This table depicts the mapped ledger (MLED):
|
Source |
Source |
Source |
Source |
Cons |
Cons |
Market |
Rate |
Rate |
|
CAD |
250.00 |
EUR |
202.50 |
USD |
198.52 |
Average |
0.980332 |
1.000000 |
|
EUR |
120.00 |
EUR |
120.00 |
USD |
117.64 |
Average |
0.980332 |
1.000000 |
|
USD |
80.00 |
EUR |
79.96 |
USD |
78.39 |
Average |
0.980332 |
1.000000 |
|
CAD |
-250.00 |
EUR |
-202.50 |
USD |
-198.52 |
Average |
0.980332 |
1.000000 |
|
EUR |
-120.00 |
EUR |
-120.00 |
USD |
-117.64 |
Average |
0.980332 |
1.000000 |
|
USD |
-80.00 |
EUR |
-79.96 |
USD |
-78.39 |
Average |
0.980332 |
1.000000 |
During the consolidation ledger load phase, these actions occur:
An aggregation process creates the consolidation ledger. This process summarizes on these fields: ChartFields, source base currency, and consolidation currency.
The source ledger’s account balances are identified in the consolidation ledger with the addition of a unique source code.
The source ledger’s base currency is recorded as follows for each account or ChartField:
Currency Code contains the source ledger’s base currency code.
Base Currency contains the consolidation base currency code.
Posted Tran Amt is the sum of all Source Base Amount values.
Posted Base Amt is the sum of all Cons Base Amount values.
Posted Total Amt is the sum of all Source Base Amount values.
The consolidation base currency is recorded in a unique row for each account or ChartField, only if the consolidation base currency is different from the source ledger's base currency.
Currency Code and Base Currency both contain the consolidation base currency code.
Posted Tran Amt is zero, and Posted Base Amt is zero.
Posted Total Amt is the sum of all Cons Base Amount values.
This table depicts the consolidation ledger (CLED):
|
Scenario |
Source Code |
Account |
Cur Cd |
Base Cur |
Posted Tran Amt |
Posted Base Amt |
Posted Total Amt |
|
USCONS |
01 |
10002 |
EUR |
USD |
402.46 |
394.55 |
402.46 |
|
USCONS |
01 |
10002 |
USD |
USD |
0 |
0.00 |
394.55 |
|
USCONS |
01 |
10003 |
EUR |
USD |
-402.46 |
-394.55 |
-402.46 |
|
USCONS |
01 |
10003 |
USD |
USD |
0 |
0.00 |
-394.55 |

 Ledger Preparation Rules and Groups
Ledger Preparation Rules and Groups
After defining individual mapping rules, you establish ledger preparation rules to identify which mapping rules a ledger business unit uses to convert its data to the consolidation ledger. You can include one or more ledger business units in a single ledger preparation rule, depending on your requirements.
One or more ledger preparation rules are associated with a ledger preparation group. The group should encompass all the rules needed to describe the mapping for each ledger business unit in your consolidation. A single ledger preparation group is associated with the consolidation model.
You establish ledger preparation run groups to indicate which ledger business units should be processed at one time. You can define these groups in a way so that data that you expect to receive together can be grouped into one run group, since it is unlikely that all your ledger business unit data will be available for ledger preparation processing simultaneously. This can also help if you plan to process consolidations on a distributed basis; each run group could be managed by individuals, for example, who would be responsible for the ledger preparation process for their sets of data.
See Also
Rules, Rule Sets, and Rule Groups

 Defining Ledger Verification Rules
Defining Ledger Verification Rules
This section provides an overview of ledger verification rules and discusses how to establish ledger verification rules.

 Understanding Ledger Verification Rules
Understanding Ledger Verification Rules
After you load your ledgers and prior to running the ledger preparation process, you can verify the content of the ledger data for both manual data entry and ETL loaded source ledger data. You use the standard Enterprise Performance Warehouse Metadata tools to build checks and balance rules as well as the ledger verification component delivered with Global Consolidations. The Ledger Preparation application engine can resolve these rules, and create status log entries that you view with the Ledger Preparation Manager.
The ledger verification process can be invoked at the beginning of the Ledger Preparation Process. The ledger verification process validates the specified source business units based on user-defined rules for checks and balances and error handling. If an error occurs during the verification, (depending on what you specify for Verification Error Handling on the Ledger Preparation Run Group page), the Ledger Preparation Manager will either continue the ledger preparation process for the valid business units only, or abort the entire run. You can view the verification status results on the Ledger Preparation Manager page.
Global Consolidations delivers sample data for standard balance rules that you can access and modify to assist you with building your own ledger verification rules. You should adjust the verification rules according to your data and use those rules that make sense for your business practices. In addition to the user-defined rules, the verification process can optionally perform basic ChartField validation against the ChartField Edit on the Ledger Template.
Global Consolidations delivers the following sample metadata to support manual data entry:
TableMaps
DataMaps
Filters and Constraints
Job Total Metadata
Balance Rule Metadata
Global Consolidations delivers the following sample TableMap metadata to support manual data entry:
|
TableMaps |
Primary Table Name |
Description |
|
GCLEDMANL |
GC_LEDMANL_F00 |
Source Ledger records for user defined spreadsheet upload/manual entry ledger. |
|
GCSLEDMANL |
GC_SLED_MANL |
Prep Source Ledger - Manual Global Consolidations Preparation Source Ledger for source ledgers from user defined spreadsheet upload/manual entry ledgers. |
Global Consolidations delivers the following sample DataMap metadata to support manual data entry:
|
DataMaps |
Constraint Codes |
Constraint Description |
|
GCSLEDMANL |
GC_SLEDMANL_NONE |
Manual ledger no mapping |
|
GCLEDMPRVSLEDCNT |
Prior period SLED count |
|
|
GCRECNLEDMSRC |
Preparation manual source |
|
|
GCRECNMCALMAP |
Calendar map - manual |
|
|
GCLEDMANL |
GCLEDMASSET |
Source asset amount |
|
GCLEDMCREDIT |
Source credit amount |
|
|
GCLEDMCURACTIVITY |
Source current activity |
|
|
GCLEDMCURRETN |
Source current retained earnings |
|
|
GCLEDMDEBIT |
Source debit amount |
|
|
GCLEDMFUTPERIOD |
Reconciliation future activities |
|
|
GCLEDMLIABEQUITY |
Source liability plus equity |
|
|
GCLEDMPRVBAL |
Source prior balance |
|
|
GCLEDMPRVSRCCNT |
Prior period source count |
|
|
GCRECNMCALSRC |
Calendar source - manual |
Global Consolidations delivers the following sample Constraints and Filters to support manual data entry:
|
Constraint |
Description |
Filter Code |
|
GC_SLEDMANL_NONE |
Manual ledger no mapping |
None |
|
GCLEDMPRVSLEDCNT |
Prior period SLED count |
GCLEDMPRVSLEDCNT |
|
GCRECNLEDMSRC |
Preparation manual source |
GCRECNLEDMSRC |
|
GCRECNMCALMAP |
Calendar map - manual |
GCRECNMCALMAP |
|
GCLEDMASSET |
Source asset amount |
GCLEDMASSET |
|
GCLEDMCREDIT |
Source credit amount |
GCLEDMCREDIT |
|
GCLEDMCURACTIVITY |
Source current activity |
GCLEDMCURACTIVITY |
|
GCLEDMCURRETN |
Source current retained earnings |
GCLEDMCURRETN |
|
GCLEDMDEBIT |
Source debit amount |
GCLEDMDEBIT |
|
GCLEDMFUTPERIOD |
Reconciliation future activities |
GCLEDMFUTPERIOD |
|
GCLEDMLIABEQUITY |
Source liability plus equity |
GCLEDMLIABEQUITY |
|
GCLEDMPRVBAL |
Source prior balance |
GCLEDMPRVBAL |
|
GCLEDMPRVSRCCNT |
Prior period source count |
GCLEDMPRVSRCCNT |
|
GCRECNMCALSRC |
Calendar source - manual |
GCRECNMCALSRC |
Note. You will find the sample Constraints and Filters under the SHARE setID.
Global Consolidations delivers the following sample Job Total Metadata to support manual data entry:
|
Job ID |
Total ID |
Description |
Record Name |
Constraint Code |
|
GCRECNCAL |
TOT6 |
Calendar map - manual |
GC_SLED_MANL |
GCRECNMCALMAP |
|
GCRECNCLED |
TOT4 |
Preparation manual source |
GC_SLED_MANL |
GCRECNLEDMSRC |
|
GCVERFLEDM |
GC_PRVSLED |
Prior period SLED count |
GC_SLED_MANL |
GCLEDMPRVSLEDCNT |
|
GCRECNCAL |
TOT5 |
Calendar source - manual |
GC_LED_MANL_F00 |
GCRECNMCALSRC |
|
GCVERFLEDM |
GC_ASSETS |
Assets |
GC_LED_MANL_F00 |
GCLEDMASSET |
|
GCVERFLEDM |
GC_CREDIT |
Credit amount |
GC_LED_MANL_F00 |
GCLEDMCREDIT |
|
GCVERFLEDM |
GC_CURACT |
Current period activity |
GC_LED_MANL_F00 |
GCLEDMCURACTIVITY |
|
GCVERFLEDM |
GC_CURRETN |
Current period retained earnings |
GC_LED_MANL_F00 |
GCLEDMCURRETN |
|
GCVERFLEDM |
GC_DEBIT |
Debit amount |
GC_LED_MANL_F00 |
GCLEDMDEBIT |
|
GCVERFLEDM |
GC_FUTCNT |
Future periods count |
GC_LED_MANL_F00 |
GCLEDMFUTPERIOD |
|
GCVERFLEDM |
GC_LIABEQT |
Liabilities plus equity |
GC_LED_MANL_F00 |
GCLEDMLIABEQUITY |
|
GCVERFLEDM |
GC_PRVBAL |
Prior period balance |
GC_LED_MANL_F00 |
GCLEDMPRVBAL |
|
GCVERFLEDM |
GC_PRVCNT |
Prior period source count |
GC_LED_MANL_F00 |
GCLEDMPRVSRCCNT |
|
GCVERFMNL2 |
GC_CREDIT |
Credit |
GC_LED_MANL_F00 |
GCLEDMCREDIT |
|
GCVERFMNL2 |
GC_DEBIT |
Debit |
GC_LED_MANL_F00 |
GCLEDMDEBIT |
Note. You will find the sample Job Total Metadata under the SHARE setID.
Global Consolidations delivers the following sample Balance Rules Metadata to support manual data entry:
|
Balance Rules Metadata ID |
Description |
|
GCVERFLEDM |
GC_LEDMANL_F00 acceptance rule |
|
GCVERFMNL2 |
GC_LEDMANL minimum acceptance |
Note. You will find the sample Balance Rules Metadata under the SHARE setID.
Metadata Setup for Ledger Verification
The following example demonstrates how you can define a standard balance rule for the source manual ledger PS_GC_LEDMANL_F00 record.
You can use a balance rule to confirm that current end of period retained earnings equal prior end of period balance plus current period activity such as income and expenses plus dividends paid. This balance rule forms an equation that contains three terms. You can calculate each one of these terms using job total metadata.
Presuming that the record metadata, tablemap and datamap is setup and ready to go as delivered, let's start by setting up the filter constraints for the above scenario.
The following sample metadata setup will create the balance rule that uses the following accounting principle:
Current Period Retained Earnings = Prior Period Retained Earnings + Current Period Net Earnings
Where Net Earnings = (Revenues — Expenses + Dividend Payouts)
The filter for the first job total, for the left-hand side of the balance rule equation and specifies current end of period retained earnings, is set up as follows in the delivered filter metadata:
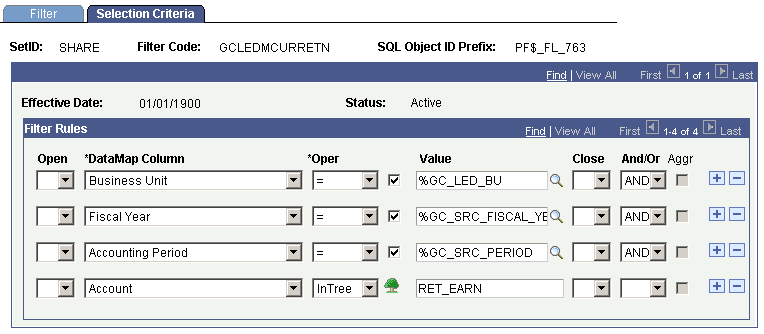
Filter Metadata Selection Criteria for Current End of Period Retained Earnings
You can use the sample filter metadata to establish the left-hand side of the balance rule criteria for calculating current end of period retained earnings. You need to establish your actual account value when setting this filter up.
The filter for the second job total, for the right-hand side of the balance rule equation and specifies prior end of period balance, is set up as follows in the delivered filter metadata:
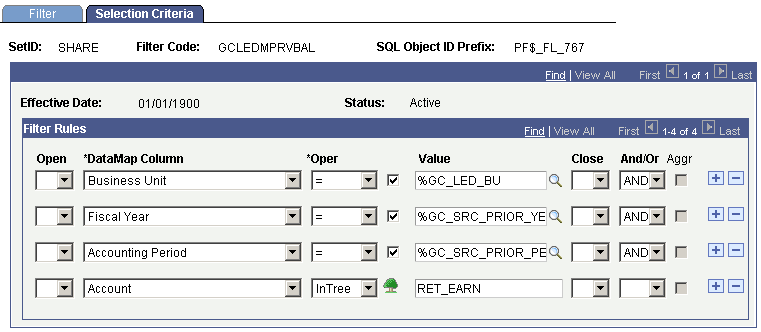
Filter Metadata Selection Criteria for Prior End of Period Retained Earnings
You can use the sample filter metadata to establish the right-hand side of the balance rule criteria for calculating prior end of period retained earnings. You need to establish your actual account value when setting this filter up.
The filter for the third job total, for the right-hand side of the balance rule equation and specifies current period revenue, is set up as follows in the delivered filter metadata:
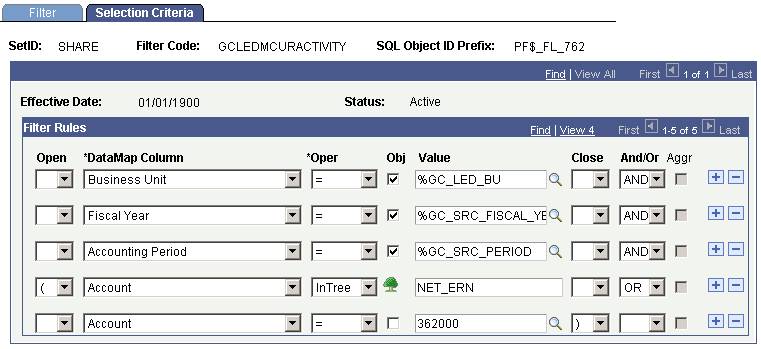
Filter Metadata Selection Criteria for Current Period Activity
You can use the sample filter metadata to establish the right-hand side of the balance rule criteria for calculating current end of period activity or net earnings. You need to establish your actual account value when setting this filter up.
With the three filters in place associate the filters with constraints as follows:
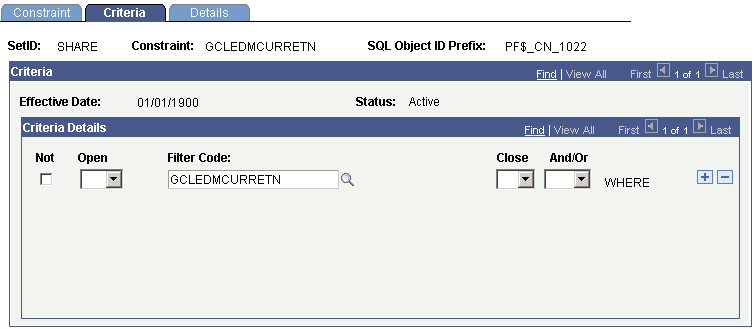
Constraint Criteria for Current Period Retained Earnings
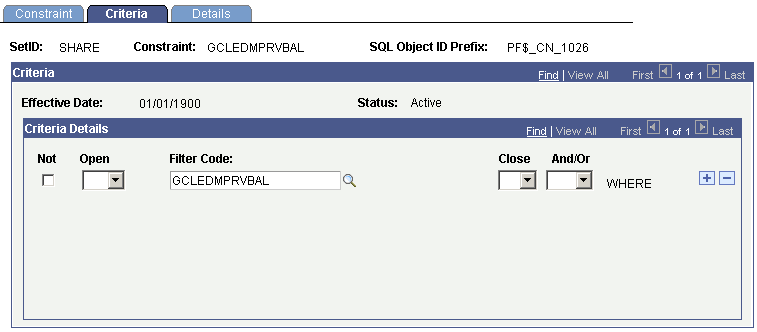
Constraint Criteria for Prior Period Retained Earnings
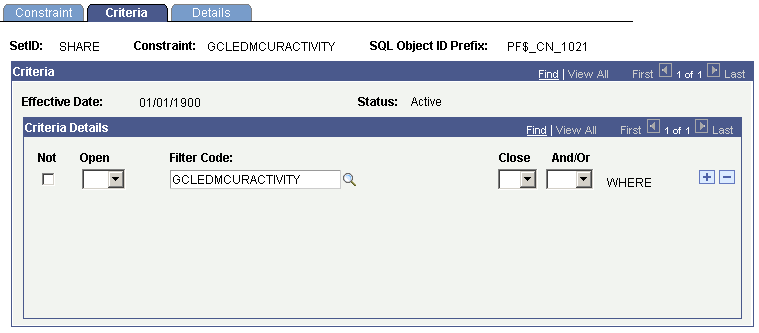
Constraint Criteria for Current Period Activity
With the filters and constraints in place, you can now setup the Job Total metadata as follows:
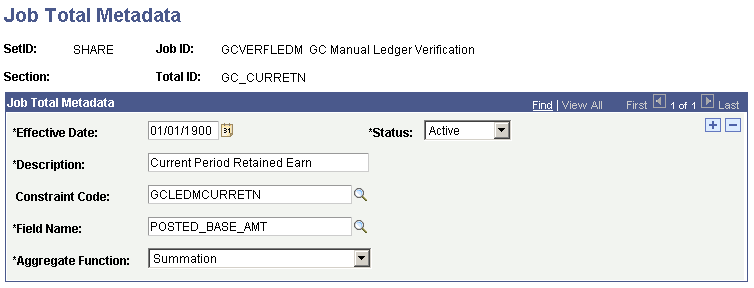
Job Total Metadata for Current Period Retained Earnings
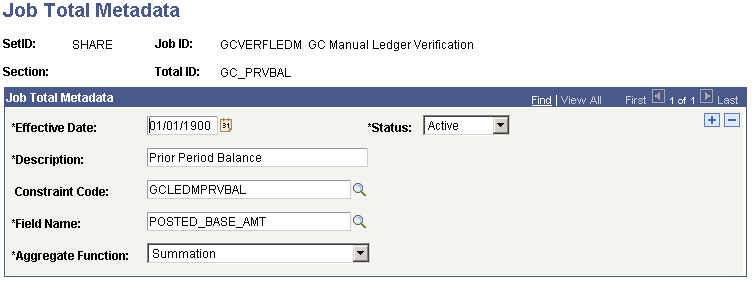
Job Total Metadata for Previous Period Retained Earnings
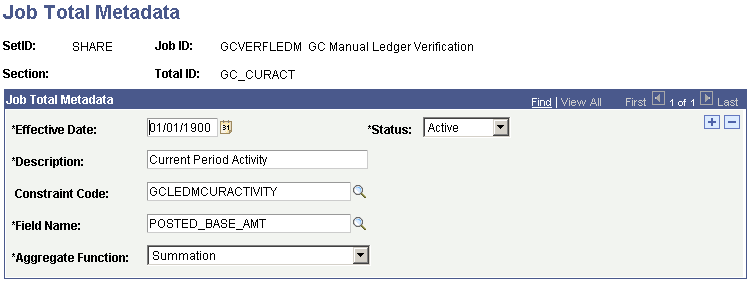
Job Total Metadata for Current Period Activity
Finally, set up the Balance Rules Metadata as follows:
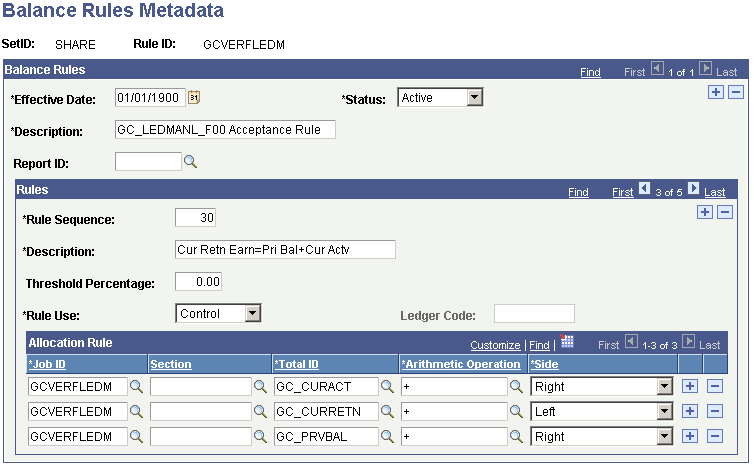
Balance Rules Metadata for Current Retained Earnings Ledger Verification Rule
This is one of several basic accounting principal rules delivered as sample EPM metadata that you can use or modify to suit your business practices. As you can see, the EPM metadata rules setup allows you to verify that the current period retained earnings is equal to the prior period retained earnings plus the current period activity or net earnings as a ledger verification rule.
Other balances rules that you can use to perform ledger verification are as follows:
Debits equal credits
Assets equal liabilities plus equity
Any other rules you can think of to verify your ledgers can be created with EPM metadata.

 Pages Used to Define Ledger Verification Rules
Pages Used to Define Ledger Verification Rules
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
GC_LEDVERF_RULE |
Global Consolidations, Define Consolidations, Ledger Preparation, Ledger Verification Rule |
Enables you to specify the period usage for ledger verification balance rules. |

 Establishing Ledger Verification Rules
Establishing Ledger Verification Rules
Access the Ledger Verification Rules page
|
Job ID |
Select the job total metadata Job ID you want to assign for the ledger verification rule |
|
ChartFields Validation |
Select to perform to perform ChartField (dimension) validation during the ledger verification rule process. |
Note. To perform ChartField validation, you must specify a TSE record for use on the Ledger Template Consolidation Variables setup page. The delivered TSE record for the manual data entry process is GC_TSE_MANL_FLD.
See Defining Spreadsheet/Manual Entry Ledger Templates.
See Defining Ledger Templates.
Period Usage
|
Current period only |
Select this option if you only want to apply the ledger verification rule on the current period. |
|
Current and other periods |
Select this option if you want to apply the ledger verification rule on the current period and to a specific number of future and prior periods. You can use the * wildcard value to select all periods. |

 Defining Calendar Mapping Rules
Defining Calendar Mapping Rules
This section discusses how to establish calendar mapping rules.

 Pages Used to Define Calendar Mapping Rules
Pages Used to Define Calendar Mapping Rules
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
GC_CALMAP_RULE |
Global Consolidations, Define Consolidations, Ledger Preparation, Calendar Map Rule, Calendar Map Rule |
Map a subsidiary ledger accounting calendar to the consolidation accounting calendar. |
|
|
Copy Calendar Map |
GC_CALMAP_COPY |
On the Calendar Map Rule page, click the Copy Map button. |
Copy a range of years on a calendar map to additional years. |
|
Calendar Map Rule - Notes |
GC_CALMAP_NOTES |
Global Consolidations, Define Consolidations, Ledger Preparation, Calendar Map Rule, Notes |
Enter details about a calendar map rule. |

 Establishing Calendar Mapping Rules
Establishing Calendar Mapping Rules
Access the Calendar Map Rule page.
If No Mapping Is Required
Select the Match Fiscal Year and Period check box if your subsidiary ledger's accounting calendar matches the common consolidation business unit's accounting calendar. No further information needs to be defined on this page when mapping is not required.
Identifying the Source and Target Calendars
|
Specify the subsidiary calendar to use as the source. |
|
|
To Calendar |
Specify the consolidation calender to which you are mapping the subsidiary calendar (the target). |
The selections within the Calendar Map grid are limited to values in your from and to calendars.
Completing the Calendar Map Grid
Insert rows as needed into the Calendar Map grid to define what each fiscal year and period in your source calendar maps to in your target calendar. The grid includes these fields:
|
From Year |
The source accounting year and period. |
|
To Year |
The corresponding fiscal year and period that the source calendar maps to in the target calendar. |
|
Begin Date |
Display-only information that shows the corresponding calendar dates for the accounting year and period. |
You can copy calendar map definitions from one or more fiscal years. This helps speed up data entry for this page, as it enables you to enter the map information once for a single year, then copy the information to additional years. Click Copy Map to activate the Copy Calendar Map page. Specify the year or years to copy from (which indicates the calendar data that you are copying) and the year or years to copy to (which indicates the year or years to which the data is copied), and then click OK.

 Defining ChartField Mapping Rules
Defining ChartField Mapping Rules
This section discusses how to:
Establish data mapper rule sets.
Establish data mapper value mappings.
Establish data mapper rule groups.
Note. Data Mapper moves only data that falls within the intersection of all the map rules.
See Also
Mapping to a Common Chart of Accounts (Data Mapper)

 Pages Used to Define ChartField Mapping Rules
Pages Used to Define ChartField Mapping Rules

 Establishing Data Mapper Rule Sets
Establishing Data Mapper Rule Sets
Access the Data Mapper Rule Set page.
Define the Source, Target, and Mapping Method
Select the source datamap, source constraint, and target datamap, to define your source and target data. For Global Consolidations, the source datamap should be based on your source subsidiary stage ledger records (SLEDs), and the target datamap should be based on your mapping ledger record (MLED).
The source constraint must be defined on the source datamap, and limits which data is used from the source—for example, base currency amounts only. It must be based on a source staging ledger record (SLED).
In the Rule Set Columns grid, for each target column listed, specify the map method. The rule set columns are determined by the target datamap. These are the columns to which your source data will be mapped.
The Map Method column specifies how to map the data from source to target. Each map method requires an additional parameter, as described.
|
Map Rule |
Select this option when you want to map specific values from a particular source column to specific values in the target. For example, you can map values associated with Account 201, Department HR in your source to Account 20001 in your target; in other words, with this method you can transform your data. The map rule ID identifies which columns to map, and the Data Mapper Value Mappings page associates the values to map with the map rule ID. You must use the Data Mapper Rule Set - Field Mapping Rule page to define the set of map rule IDs that you can use with this data mapper rule set. |
|
Use Source |
Select this option when you want to map values directly from a source column to the target. Select the source column that contains the data to use. The selections available within the source column are derived from the source datamap and source constraint. |
|
Use List |
Select to populate the target with a specified value. |
|
|
The system compiles the SQL from your completed map rule when you initially save the page. However, if you edit an existing rule, you need to click the compile (build) button to regenerate the SQL. |
Define the Field Mapping Rules
Access the Data Mapper Rule Set - Field Mapping Rule page.
This page establishes the map rule IDs that are used on the Data Mapper Rule Set page when you select the Map Rule mapping method. Insert and define as many field mapping rules as needed to use with your data mapper rule set. For each map rule, complete the fields within the Target Columns and Source Columns grids to identify which columns you want to map and whether to use a value or tree to specify which values to map. (You identify those values on the Data Mapper Value Mapping page.) Both source and target grids contains these fields:
|
Column |
Identify which source or target column contains the values to map. |
|
Value |
Select to enter specific values to map. |
|
Tree |
Select to use a tree node to specify the values when mapping. |
|
Wild Card |
Select to enter a wild card value to search for and specify for the mapping. |
|
Range |
Select to enter a range of values to specify for the mapping. |
These rules control which dimensions you can specify values for when mapping. If you select tree, then on the Data Mapper Value Mappings page, you can use tree nodes to specify the values. If you select value, then you select from a list of dimension or ChartField values. If you select range, then you select from a range of dimension or ChartField values. If you select wild card, then you select from a list of dimension or ChartField values based on your wild card designator. This is how the system determines which source values map to which target values.
Viewing the SQL
Access the SQL page to view the SQL statements that result from the rule.

 Establishing Data Mapper Value Mappings
Establishing Data Mapper Value Mappings
Access the Data Mapper Value Mappings page.
Within the Map Values group box, specify which source column values map to target column values.

 Establishing Data Mapper Rule Groups
Establishing Data Mapper Rule Groups
Access the Data Mapper Rule Group page.
In Rule Sets in Rule Group, insert rows as needed to add all the data mapper rule sets that comprise this rule group. The rules that you include must define all the data in your subsidiary ledgers that need to be mapped to a consolidation ledger, as only one rule group is processed during data preparation. Enter the use order and specify the rule set ID for each inserted row. The rules are used in ascending order based on the value that appears in the Use Order field. If the same source data is mapped with more than one rule set, only the first one encountered is used.

 Defining Currency Mapping Rules
Defining Currency Mapping Rules
This section discusses how to:
Establish currency rules
Establish currency groups
Note. The system does not support multiple base currencies for a consolidation ledger. To process consolidations in multiple base currencies, create additional scenarios for each base currency.
See Also
Converting to a Common Base Currency

 Pages Used to Define Currency Mapping Rules
Pages Used to Define Currency Mapping Rules
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
GC_CURR_RULE |
Global Consolidations, Define Consolidations, Ledger Preparation, Currency Conversion Rule, Currency Rule |
Define which exchange rate type to use to convert specified account balances to those of the consolidation base currency. |
|
|
Currency Rule - Notes |
GC_CURR_NOTES |
Global Consolidations, Define Consolidations, Ledger Preparation, Currency Conversion Rule, Notes |
Enter notes about the currency rule. |
|
GC_CURR_GRP_TBL |
Global Consolidations, Define Consolidations, Ledger Preparation, Currency Conversion Group, Currency Group |
Define the group of currency rules to use to convert account balances to the consolidation base currency and specify if you want to record adjustments to balance the ledger after conversion. |
|
|
GC_CURR_GRP_ADJ |
Global Consolidations, Define Consolidations, Ledger Preparation, Currency Conversion Group, Adjustment |
Specify the account used for posting any adjustments, if needed, to balance the ledger business unit after currency conversion. |
|
|
Currency Group - Notes |
GC_CURR_GRP_NOTES |
Global Consolidations, Define Consolidations, Ledger Preparation, Currency Conversion Group, Notes |
Enter notes about a currency group. |

 Establishing Currency Rules
Establishing Currency Rules
Access the Currency Rule page.
|
Ledger Template |
Select the ledger template structure. This must be the same template used for your consolidation ledger. This value controls which ChartFields are available. The ledger that you select must be defined on the Ledger Template page with the EPM Ledger Type field set to Consolidation Ledger. The ledger format option, which is established on the Ledger Template - Consolidation Variables page (either Trial Balance based or Financial Statement based) determines which fields are available for entry in the close rule process pages. The Ledger Template defines the data base records and the processing methods for your consolidation model. |
|
Consolidation Dimension |
Select the dimension by which you are consolidating. For example, Ledger Business Unit. |
Insert rows as needed into the Conversion Rule grid to define the exchange rate type used for a particular set of ChartField values (accounts) during currency conversion. For each row, complete these fields:
|
Use Order |
Enter a numeric value to control when this conversion rule is processed. The conversion rules are processed in ascending order based on this value. If the same ChartField value is included in multiple rules, only the first occurrence is used. |
|
ChartField Value Set |
Specify the group of specific ChartField values (accounts). |
|
Exchange Rate Type |
Specify the exchange rate to use for this group of ChartField values (accounts). |
|
Rate Type for Cash Flows |
Specify the cash flow rate type to use for this group of ChartField values (accounts). Rate Type for Cash Flows determines how the system translates cash flows. |
|
Create Translation Adjustment |
Select this option to create a currency translation adjustment for a given ChartField value set. The translation adjustment gets booked for the ChartField combination specified on Target for Translation Adjustment grid with the source code of '08’. This source code tracks currency translation adjustments related to currency rate changes for prior period adjustments. You specify a currency gain/loss account for booking the offset on the currency rule setup page. |
The rate type selections allow you to track flows for both cash flow reporting and footnote disclosures. For example, you might record fixed asset acquisitions at a current rate for footnote disclosure purposes and at an average rate for cash flow. Global Consolidations records the flow amount at both rates for reporting purposes.
Click the Edit/View ChartField Value Set link to review or modify the associated ChartField value set definition.
Specifying Targets for Translation Adjustments
|
Get ChartFields |
Click to add target ChartFields |
|
Field Name |
Select a target ChartField for translation adjustments. For example, Account. When selecting Account as the Field Name, your only option is to retain the account value. |
|
Option |
Select the option you want to use for target translation adjustments. This field controls whether or not you retain the detail from the source line in the generated translation adjustment. Select Retain to book the amount to the same ChartField value used in the source lines, or select Constant and enter a specific ChartField Value to book the amounts to, regardless of the source. The default is Retain. The Account ChartField uses only the Retain option. |

 Establishing Currency Groups
Establishing Currency Groups
Access the Currency Group page.
|
Ledger Template |
Select the ledger template structure. This must be the same template used for your consolidation ledger. This value controls which ChartFields are available. The ledger that you select must be defined on the Ledger Template page with the EPM Ledger Type field set to Consolidation Ledger. The ledger format option, which is established on the Ledger Template - Consolidation Variables page (either Trial Balance based or Financial Statement based) determines which fields are available for entry in the close rule process pages. The Ledger Template defines the data base records and the processing methods for your consolidation model. |
|
Generate Adjustment |
Select to require the system to balance each ledger business unit during currency conversion, generating an adjustment entry when needed. Note. There can be situations where the ledger business units do not balance after conversion due to multiple exchange rates in use by different ChartField values. |
|
Currency Rules |
Specify all the rules to include in this currency group, adding additional rows as needed. Include as many rules as needed to identify every ChartField value to convert, as only one currency group is used in a consolidation model. The rules are processed in ascending order based on the value that appears in Use Order. If the same ChartField value exists in more than one of the currency rules in the rule group, the first rule processed (based on the use order) determines how that ChartField converts; any subsequent rules that use that ChartField value are not used. |
|
Edit/View Conversion Rule |
Click to review or modify the associated currency conversion rule definition. |
Specifying Where to Record Adjustments
Access the Currency Group - Adjustment page.
If you select the Generate Adjustment option on the Currency Group page, use the fields on this page to indicate where to record any adjustments. Each business unit-ledger combination is balanced independently of the other business unit ledgers that are being consolidated, and each ledger business unit receives a separate adjustment as needed.
|
Conversion Gain |
Specify one or more ChartFields and their associated ChartField values to record any gains due to currency conversion. You must specify an account; insert additional rows to specify other ChartFields, such as department. |
|
Conversion Loss |
Specify one or more ChartField values to record any losses due to currency conversion. |

 Defining Ledger Preparation Rules and Groups
Defining Ledger Preparation Rules and Groups
This section provides an overview of ledger preparation rules and groups and discusses how to:
Establish ledger preparation rules
Establish ledger preparation groups

 Understanding Ledger Preparation Rules and Groups
Understanding Ledger Preparation Rules and Groups
Ledger preparation rules identify the specific calendar, currency, and ChartField mapping rules (data mapper rules) to use for your subsidiary ledger business units during ledger preparation processing. A ledger preparation group is made up of one or more ledger preparation rules. The ledger preparation process uses the ledger preparation group as input and ties the ledger preparation group to the consolidation model. The group must include rules for every ledger business unit within a consolidation.

 Pages Used to Define Ledger Preparation Rules and Groups
Pages Used to Define Ledger Preparation Rules and Groups
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
GC_MAP_SET_TBL |
Global Consolidations, Define Consolidations, Ledger Preparation, Ledger Preparation Rule, Preparation Rule |
Identify the specific calendar, currency, and ChartField (account) mapping rules (data mapper rule) to use for one or more ledger business units when running the ledger preparation process. |
|
|
Ledger Preparation Rule - Notes |
GC_MAP_SET_NOTES |
Global Consolidations, Define Consolidations, Ledger Preparation, Ledger Preparation Rule, Notes |
Enter notes about the ledger preparation rule. |
|
GC_MAP_SET_COPY |
Click Copy Rule on the Ledger Preparation Rule page. |
Create a new rule by copying the current rule. |
|
|
GC_MAP_GRP_TBL |
Global Consolidations, Define Consolidations, Ledger Preparation, Ledger Preparation Group, Preparation Group |
Define a group of ledger preparation rules to be processed. |
|
|
Ledger Preparation Group - Notes |
GC_MAP_GRP_NOTES |
Global Consolidations, Define Consolidations, Ledger Preparation, Ledger Preparation Group, Notes |
Enter notes about the ledger preparation group. |

 Establishing Ledger Preparation Rules
Establishing Ledger Preparation Rules
Access the Ledger Preparation Rule page.
|
Ledger Template |
Select the ledger template structure. This must be the same template used for your consolidation ledger. This value controls which ChartFields are available. The ledger that you select must be defined on the Ledger Template page with the EPM Ledger Type field set to Consolidation Ledger. The ledger format option, which is established on the Ledger Template - Consolidation Variables page (either Trial Balance based or Financial Statement based) determines which fields are available for entry in the close rule process pages. The Ledger Template defines the data base records and the processing methods for your consolidation model. |
Insert rows as needed within the Ledger Preparation Rule grid to add business units to this rule, and define the specific account mapping, calendar mapping, and currency conversion rules to use for each ledger business unit during ledger preparation. For each row, complete these fields:
|
Business Unit and Ledger ID |
Identify the ledger business unit and Ledger ID to which you are assigning mapping rules. |
|
Verification Rule |
Select the verification rule you want to use for the ledger preparation process. This identifies the rules for preparing the source ledger data for consolidations for a specific Business Unit and Ledger ID. Use the Ledger Verification Rule setup page to establish verification rules. |
|
Select if no currency conversion, calendar mapping, or ChartField mapping is required for this business unit's ledger data. For example, if the ledger data is already prepared when you receive it, or is already in the format of the consolidation ledger, select this option; you can leave the Data Mapper, Calendar Map, and Currency Group fields blank. Note. You cannot have multiple source ledgers for the same business unit and select No Preparation. The system does not aggregate the data when it populates the consolidation ledger. |
|
|
Calendar Map |
Select the calendar mapping rule to use for the ledger preparation process. |
|
Data Mapper |
Select the data mapper rule to use for the ledger preparation process. |
|
Currency Map |
Select this option if currency mapping is required. If you select this option, the system provides translations based on the currency group attached to the consolidation model. Note. If you select the No Preparation is Required option, you should leave this option off. |
You can select only mapping rules that use the same ledger template as the preparation rule.
Updating Multiple Rules
Expand and use the Update Rules group box to help you complete the Ledger Preparation Rule grid. Select the business unit tree name and a tree node that contains the business units for which you want to assign mapping rules. Then click Load Business Units to insert all the business units within that node that are not currently in the Ledger Preparation Rule grid. Similarly, you can populate one or more of the fields within Update Rules (Ledger ID, Calendar Map, Data Mapper, and Verification Rule ) or select No Preparation is Required, then click the Update Rules button to insert those field values into rows within Ledger Preparation Rule that do not currently contain any values for those fields.
To clear one or all rules, select the rule type from the Clear Rule drop-down list box, then click Update Rule.
To apply currency mapping to all of the business units in the Ledger Preparation Rule grid, select the Currency Mapping is Required check box and click Update Rules.
Copying Rules
To copy a rule, click the Copy Rule button. The Copy Rule page appears.
Specify the setID, effective date, new preparation rule ID, and description for the rule that you are creating by copying this rule, and then click OK.
Validating Rules
Click Validate Rule to have the system check that your ledger preparation rules are valid. This is especially important if you create a rule by copying another rule. If there is an issue with any rule, an error message appears indicating the specific problem. If you don't receive any errors, then your rules are okay.

 Establishing Ledger Preparation Groups
Establishing Ledger Preparation Groups
Access the Ledger Preparation Group page.
The ledger template must be the same template that is used for the consolidation ledger.
In the Ledger Preparation Rules grid, insert rows as needed to associate one or more preparation rules to this preparation group.
The preparation rules are processed in ascending order based on the value that appears in the Use Order field. If a ledger business unit is included in multiple rules, only the first rule encountered is used. In other words, only unique rules are used.

 Running Ledger Preparation
Running Ledger Preparation
This section discusses how to:
Define a ledger preparation run group.
Run ledger preparation.
Run currency adjustment.
See Also
Streamlining Processing with Jobstreams
PeopleSoft Performance Management Warehouse and Reporting

 Prerequisites
Prerequisites
Prior to running ledger preparation, complete these tasks:
Run the Consolidation Validation application engine.
This engine verifies that the ledger preparation mapping rules are set up correctly.
Define the consolidation model.

 Pages Used to Run Ledger Preparation
Pages Used to Run Ledger Preparation
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
Run Group |
GC_RUN_GROUP |
Global Consolidations, Define Consolidations, Common Definitions, Run Group |
Define a subset of ledger business units for which to process ledger preparation. |
|
Run Ledger Preparation |
GC_RUN_PREP |
Global Consolidations, Prepare Data for Consolidation, Run Ledger Preparation, Ledger Preparation |
Run ledger preparation. |
|
Run Currency Adjustment |
GC_RUN_FX_ADJ |
Global Consolidations, Prepare Data for Consolidation, Run Ledger Preparation, Currency Adjustment |
Run currency adjustment. |

 Defining a Ledger Preparation Run Group
Defining a Ledger Preparation Run Group
The Consolidation Models Defined grid displays the common consolidation business unit, and the business unit tree used by the consolidation model. This enables you to determine which trees you can use to specify the business units for this run group.
You can indicate which business units to include by either identifying a tree node or listing the specific business units.
To use a tree node to specify which business units to include, select the tree ID and tree node. Click the Tree button to view the tree, and select the node that contains the business units to include.
To list which business units to include, insert one or more rows within the Ledger Business Unit grid, and select the specific ledger business units.
Specifying Verification Error Handling
You can choose how to handle data processing for invalid entries while running the ledger group process. Select either Prevent all BU(s) to continue to stop all ledger group processing when ledger verification errors occur or Allow Valid Bu(s) to continue to allow the data with valid business unit to continue processing after ledger verification errors occurs.

 Running Ledger Preparation
Running Ledger Preparation
Access the Run Ledger Preparation page.
Specifying the Run Parameters
|
Business Unit, Scenario ID, Fiscal Year, and Accounting Period |
Specify the common consolidation business unit, scenario ID, fiscal year, and accounting period to process. The system derives the consolidation model and its associated rules from the information that you specify. |
|
Jobstream ID |
The default value is GC_PREPMGR. |
|
Run Group ID and Ledger Unit |
Specify either a run group ID to process or a single ledger unit (the business unit associated with the ledger). |
|
Data Source |
Select a data source for the ledger preparation process. The default is All sources. The other choices are ETL data only for processing only the ledger data that was brought into the warehouse through the ETL mapping process or Spreadsheet and manual source for processing only the ledger data brought into the warehouse through the spreadsheet upload or manual entry process. |
Select one or more of these options to indicate which preparation steps to process. There may be cases in which you want to run a specific step by itself (for example, to troubleshoot a particular problem with your data or a rule), or you want to run all the mapping steps, but wait until a later time to move the data to the consolidation ledger. You need to determine what is best for your particular implementation.
|
Perform Ledger Verification |
Select to process ledger verification (uses the ledger verification rules). The ledger verification process runs first, and then the ledger preparation process proceeds based on your error handling selection. |
|
Map Calendar |
Select to process calendar mapping (uses the calendar mapping rules). |
|
Map Fields |
Select to process ChartField mapping (uses the data mapper rules). |
|
Convert Currency |
Select to process currency conversion (uses the currency group rules). |
|
Load Consolidation Ledger |
Select to move data from the mapped ledger (MLED) to the consolidation ledger (CLED). |
The ledger preparation process uses the calendar mapping rules to determine which data to select from the individual ledgers. For example, assume that the run parameters specified are for 2002 period 4, and include BU1 and BU2. BU1's calendar mapping rule is defined to match the fiscal year and period (its calendar is the same as the consolidation calendar), so the system uses the data from BU1's ledger for 2002 period 04. BU2's calendar mapping does have rules. During processing, the system matches the to year and period of the BU2 calendar mapping rule to the run control date (2002/04) and, using the calendar mapping rule, determines the from year and period of BU2 to which that corresponds (perhaps 2002/01). Therefore, the system uses BU2 data from 2002/01 as input for ledger preparation processing.
Warning! If your source ledger data contains YTD balances, rather than balances by period, when processing ledger preparation, you must process each period in sequence, or the calculated period activity amounts will be incorrect.
Because many jobs may be spawned when you run ledger preparation, if you need to cancel processing, you should cancel spawned jobs first (the child jobs), then the parent job. If you are using the delivered jobstreams for processing, you can identify parent jobs by the process name PF_JOBSTREAM. The process name for ledger preparation spawned jobs is GC_PREP.
See Also
Viewing Ledger Preparation Status
Reconciliation for Consolidation Processes

 Running Currency Adjustment
Running Currency Adjustment
Access the Run Currency Adjustment page.
Specifying the Run Parameters
|
Business Unit, Scenario ID, Fiscal Year, and Accounting Period |
Specify the common consolidation business unit, scenario ID, fiscal year, and accounting period to process. The system derives the consolidation model and its associated rules from the information that you specify. |
|
Jobstream ID |
The default value is GC_FX_MGR. |
|
Run Group ID and Ledger Unit |
Specify either a run group ID to process or a single ledger unit (the business unit associated with the ledger). |