
 Understanding Natural Language Processing
Understanding Natural Language ProcessingThis chapter provides an overview of natural language processing (NLP) and discusses how to:
Define knowledge base building blocks.
Setting Up system installation options and knowledge bases.
Maintain knowledge bases.
Monitor knowledge base.

 Understanding Natural Language Processing
Understanding Natural Language ProcessingThis section discusses:
NLP overview.
How does the NLP server work.
NLP usage in CRM.
System delivered knowledge bases.
Setting up NLP.

 NLP Overview
NLP OverviewNLP enables CRM applications to automate certain business tasks by running concept-based content analysis on information it receives and providing appropriate suggestions that can be used to drive business processes. For example, in a call center environment where agents handle a large amount of customer cases a day, you can eliminate manual agent tasks and increase agents' productivity by enabling the call center system to automatically suggest solutions for cases. You can use NLP to accomplish the solution suggestion piece of the process. At a high level, NLP is about categorizing contents—it analyzes information that comes in, suggests the most appropriate category for it and returns the result back to the calling application.
PeopleSoft CRM integrates with the Banter RME (Relationship Model Engine) Server through Integration Broker to build the natural language processing framework. This diagram illustrates the interaction between these two systems at a high level:
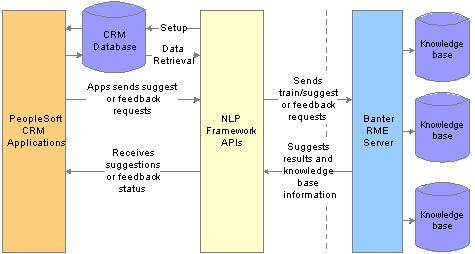
PeopleSoft CRM interacts with the Banter RME server
The CRM NLP Framework provides user interfaces that enable application administrators to easily set up knowledge bases to work with their applications without knowing the technical complexities of the integration. The NLP framework APIs provide an entry point for CRM application developers to integrate their applications with the third party NLP technology.
See Also
Supplemental Installation Instructions for PeopleSoft 8.9 Applications

 How Does the NLP Server Work
How Does the NLP Server WorkNLP performs concept-based content analysis, as opposed to traditional searching, which often requires some textual commonality between the source object (basis of the search, for example, case) and the target (result of the search, for example, solution). In other words, if a target object does not contain any of the source's keywords, the system never returns it as a search result even if it is the perfect match for the source. NLP takes a different content analysis approach: it extracts concepts from the source object, looks for categories within the system that have the most similar concepts, and suggest them (target objects). To better explain how NLP works from a CRM perspective, the example of case and solution is used in this chapter overview.
A case consists of numerous concepts. Its elements, such as case summary, product description, case notes, are all sources from where concepts can be derived. When a case is submitted to NLP for analysis, the NLP server uses the name value pairs (NVP) to identify which case field values to analyze and extracts concepts from them. In the knowledge base where these concepts are stored, it finds the categories (solutions) with the most matched concepts. It then uses the categories to represent these contents's intention or analysis result.
These contents and their categories indicate what kind of the contents this knowledge base is expected to handle. When the applications send these contents and their names, the NLP server uses natural processing technique and semantic analysis techniques to analyze these contents against the assigned knowledge base and also calculates the relevancy score for each content set that is stored in the knowledge base. It tries to return the categories that are most matched in the descending order of the relevancy score. The applications can also send feedbacks to the NLP server as an ongoing learning process. The feedback request consists of contents, content names and the category that these contents belong to. The NLP server uses these feedback to teach the knowledge base, which learns and becomes more efficient in providing suggestions over time.
Training, Feedback and Suggestion in Knowledge Base
Before a knowledge base goes into production, it has to be trained with a sufficient number of training data that are properly categorized. The data can come from different applications that uses NLP, such as PeopleSoft Support or PeopleSoft Email Response Management System (ERMS); or the data can come in a flat file format: .csv or .kb (the data file format that is specific to the NLP server).
The concept of training is very similar to that of feedback. Training is the initial learning process that the knowledge base undertakes, whereas feedback is the incremental learning that the knowledge base receives from the system over time. The goal of both processes is to teach the knowledge base more about their categories (discover concepts that can apply to categories) and be able to provide more accurate suggestion in the future. Below is an example of a feedback process that takes place in a support application:
An agent solves a case using a solution that is suggested by the NLP system and wants to send a feedback.
The NLP system receives the feedback about the case and solution. It extracts concepts from the case, and adds them to the list of concepts for that solution in the knowledge base.
The solution has learned about other kinds of cases (cases with the newly added concepts) that it can tackle.
With the training and feedback processes in place, the knowledge base matures over time. It has established numerous categories (in our case, solutions) and each category is associated with significant number of concepts that it applies to. When the NLP system receives a request to suggest a category, for example, suggest possible solutions to solve a case, these few things happen:
The NLP system extracts concepts from the case.
Then it scans the knowledge base for categories (solutions) that have matching concepts.
The NLP system sends the solutions back to the case as suggestions.

 NLP Usage In CRM
NLP Usage In CRMPeopleSoft CRM uses NLP in these areas primarily to:
Provide automated solution suggestions on cases, service orders, inbound emails and chat. Here's an example on cases.
The call center applications uses NLP to provide automated suggestion on solution to agents on cases. The system sends information about the case to NLP. NLP extracts concepts from the case, finds solutions that match those concepts and returns some of the most relevant solutions for the agent to try resolve the case.
Categorize cases and emails by content.
The returned categories can be used to drive business processes. Here's an example on Email Response Management System (ERMS):
ERMS uses NLP to analyze and categorize incoming emails. When the email process sends an email to the NLP system, it analyzes the email content, such as subject, sender email address, and body. Based on the amount of knowledge the system has acquired, it suggests categories that conclude the intention of the email (it's about a problem, it's complaint, spam mail, and so on). Suppose that NLP returns a category of problem for the email to ERMS with a high threshold value, which indicates the NLP is very confident that the email describes a problem, the email processor can perform actions based on any rule that is predefined for the problem category. In this case, the action can be routing the email to a specific group worklist that handles problems and sending automatic acknowledgment to the sender. If the returned category is spam, you may have a different action that the email processor performs, for example, delete the email from the database. ERMS uses NLP to automate the email handling process as much as possible, off-loading some of the manual tasks to the auto-response system so that agents can spend more time handling complex customer issues.

 System Delivered Knowledge Bases
System Delivered Knowledge BasesPeopleSoft CRM delivers a number of knowledge bases to support natural language processing in several areas:
|
Knowledge Base ID |
Knowledge Base Name |
Application that Uses It |
|
CASE |
Case Knowledge Base |
Call Center Support, used to suggest solutions for cases. |
|
CHAT_DEMO |
CHAT_DEMO |
Chat, used to suggest solutions before chat sessions begin. |
|
DEFECT |
Defect Knowledge Base |
Quality, used to suggest solutions for defects. |
|
ERMS_CATEGORY |
ERMS_CATEGORY |
ERMS, used to identify email category. |
|
ERMS_DOCUMENT |
ERMS_DOCUMENT |
ERMS, used to identify template packages for emails. |
|
ERMS_GRPWL |
ERMS Group Worklists |
ERMS, used to identify group worklists for emails. |
|
ERMS_MOOD |
ERMS_MOOD |
ERMS, used to identify email sender's mood. |
|
ERMS_PRIORITY |
ERMS_PRIORITY |
ERMS, used to identify email priority. |
|
ERMS_PRODGRP |
ERMS_PRODUCTGROUP |
ERMS, used to identify the product groups for emails. |
|
ERMS_PRODUCT |
ERMS_PRODUCT |
ERMS, used to identify the products for emails. |
|
ERMS_SOLUTION |
ERMS_SOLUTION |
ERMS, used to identify solutions for emails. |
|
ERMS_TYPE |
ERMS_TYPE |
ERMS, used to identify email type. |
|
KB_DEMO |
DemoKnowledgeBase |
Used for demonstration purposes. |
|
SO |
Service Order Knowledge Base |
FieldService, used to suggest solutions for service orders. |

 Setting Up NLP
Setting Up NLPIf you plan to enable natural language processing for an application, here are the high level steps for setting up the Banter RME server to work with the CRM system:
Install all required software on a Windows 2000 machine which the NLP system resides. They include: MS SQL Server with case-insensitive collation settings, Microsoft .Net Framework, Banter Server, Microsoft IIS server, and PeopleSoft web service software.
See Supplemental Installation Instructions for PeopleSoft 8.9 Applications
Create an integration broker node for the NLP server.
Define the NLP server.
See Defining NLP Servers, Specifying Knowledge Base Settings, Reviewing NLP Supported Languages, Registering Other Server Machines.
Verify that the NLP server is up and running.
If the server isn't running, you can review the server detail and ping, stop and start it as needed.
Define a knowledge base for the application that uses natural language processing, for example, case. Prior to that, define content fields that you need to reference in the knowledge base definition.
See Defining Content Fields for the Knowledge Base, Defining Knowledge Bases.
Create an application definition, for example, for case.
Define and analyze data that is used to train the knowledge base.
See Defining Training Data Sources, Analyzing Training Sources.
Build the knowledge base structure after you've created the definition, identified and analyzed the training data for it. The batch process performs a number of tasks:
See Setting Up Knowledge Bases.
Insert content fields to the knowledge base server dictionary if they don't already exist.
Create the knowledge base and build its structure that consists of business-sensitive categories.
Train the knowledge base using business runtime data.
Import knowledge base categories into the CRM system.
Configure the knowledge base.
Verify that the knowledge base structure is set up correctly and running.
Define feedback queue.
This is required if you want to enable the self-learning capability of the knowledge base.
Analyze the knowledge base.
This is optional. To analyze the built knowledge base, you have to prepare a set of data for analyzing purposes. The data used for analysis should be current to your implementation. It is highly recommended that you do not use old data or data that was used to build the knowledge base in the analysis.
Test the knowledge base and see if returns suggestions.

 Defining Knowledge Base Building Blocks
Defining Knowledge Base Building Blocks
This section discusses how to:
Define NLP servers.
Specify knowledge base settings.
Review NLP supported languages.
Register other server machines.
Define content fields for the knowledge base.
Define knowledge bases.
Set up application definition.
Review associated applications in the knowledge base.
Define training data sources.
Define feedback queues.
Define category sets.

 Pages Used to Define Knowledge Base Building Blocks
Pages Used to Define Knowledge Base Building Blocks
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
RBN_DFN_SERVER |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Define, Server, Server |
Define the NLP server. |
|
|
RBN_SRVRCNFG |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Define, Server, KB Settings |
Specify knowledge base settings on how often the feedback server saves processed feedbacks and how many composite knowledge bases are executed per process. |
|
|
RBN_SRVRLANG |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Define, Server, Languages |
Specify languages that the NLP server supports. |
|
|
RBN_SRVRMACHINE |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Define, Server, Machines |
Specify other server machines. |
|
|
RBN_MNG_CNTNT |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Define, Content Fields, Content Fields |
Define content fields that are referenced by knowledge bases. |
|
|
RBN_DFN_KB |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Define, Knowledge Base, Knowledge Base |
Define a knowledge base. |
|
|
RBN_DFN_APP |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Define, Application, Application Definition |
Set up application definition. |
|
|
RBN_DFN_KBAPP |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Define, Knowledge Base, Applications |
Review applications that are associated with the knowledge base. |
|
|
RBN_DFN_SAMPLEDATA |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Define, Training Source, Training Source |
Define data sources for the knowledge base training process. |
|
|
RBN_DFN_FDBKQUEUE |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Define, Feedback Queue, Feedback Queue |
Define queues for knowledge bases to collect entries for the feedback process. |
|
|
RBN_DFN_CATGSET |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Define, Category Set, Category Set |
Define categories in groups. You can manually create categories in the knowledge base without running the training data process. |

 Defining NLP Servers
Defining NLP Servers
|
Server Node |
Enter the integration broker node that is created for the NLP server. PeopleSoft delivers a predefined server node called NLP_DEFAULT. Use it as an example when you define your own server node. |
|
Server Usage |
Select whether this server definition is for production or development.
|
|
Authentication |
Specify whether server authentication is required. If yes, specify the user ID and password that are used. |
|
FTP Server URL |
Enter the URL identifier for the FTP server. It is the location where the transaction related data files are posted. Establish URLs on the URL Maintenance page. The administrator configures the web service configuration file to assign the FTP server folder location. Refer to PeopleSoft NLP web service configuration utility for more information. Note. It is highly recommended that the FTP server resides in the same machine where the NLP server is installed. |
Server Detail
|
Server Machine |
Displays the machine name of the NLP server. |
|
Database Server |
Displays the database server name of the NLP server database. |
|
Version and Database |
Displays the NLP server version and its database name. |
License Detail
|
Max. Machines |
Displays the maximum number of licensed machines. |
|
Expiration DateTime |
Displays the NLP server expiration date and time. |
|
Knowledge Bases |
Displays the maximum knowledge bases that you can create in each NLP server database. |
|
Accumulated Requests |
Displays the number of requests that the system receives so far. |
|
Requests per Year |
Displays the number of requests that the license allows per year. It returns errors after this number is reached. |
|
Span of Days |
Displays the number of days that the accumulated requests are distributed. |
|
Support system level APIs |
Indicates if the license supports the low-level API calls. |
|
Refresh |
Click tot call the NLP server to retrieve the its server definition and synchronize the current data on the page. Save the page if there is any data change. |
|
New License |
Click to access the Server Definition - Register New License page (RBN_NEWLICENSE_SEC) and renew license by entering the old and new license code. |

 Specifying Knowledge Base Settings
Specifying Knowledge Base Settings
|
Feedback Threshold |
Specify the number of feedback items that should be processed before the feedback information is saved to the database. The instance server then reloads the knowledge base and the feedback takes effect. The default value is 500. |
|
Time Threshold (minutes) |
Specify the time interval that the feedback server saves the feedback information to the database and wakes up the instance server to reload the knowledge base. The default value is 30 minutes. |
|
Knowledge Bases per Process |
Specify the number of composite knowledge bases that can execute in a process. The default value is 3. |

 Reviewing NLP Supported Languages
Reviewing NLP Supported Languages
Based on the license agreement, the Supported Languages column lists the languages that NLP supports. Map each language with a three-letter language code that is used in the PeopleSoft system.

 Registering Other Server Machines
Registering Other Server Machines
The NLP server allows multiple machines to be registered when these machines have the NLP server software installed and are connected to the same NLP server database. NLP uses this mapping table to translate the language code into the NLP language name before sending any request to the NLP server. Specify the network machine name in the Registered Machine Detail grid.

 Defining Content Fields for the Knowledge Base
Defining Content Fields for the Knowledge BaseAccess the Content Fields page.
Content Field Detail
Define content fields that knowledge bases reference in their definitions. A content field identifies the concept set that NLP uses to perform content analysis. When you associate a knowledge base to an application definition, you need to map each content field of the knowledge base to a page field of the application.
|
Content Field |
Enter the name of the content field. The system uses it to identify the contents for analysis. |
|
Content Type |
Specify the type of content. The NLP server processes contents in different ways. If the content type is one of the email types, it calls its text processor to process the content, such as removing signature from email body or removing the term Re from the email subject. There are four types of contents:
|

 Defining Knowledge Bases
Defining Knowledge BasesAccess the Knowledge Base page.
Knowledge Base Detail
|
Knowledge Base ID and Knowledge Base Name |
Enter a unique ID and name of the knowledge base. If you select single language as the knowledge base type, the system uses the knowledge base name to name these language-specific knowledge bases that are generated subsequently in this format: <knowledge base name>_<3-letter language code>. For example, Case Knowledge Base_KOR and Case Knowledge Base_FRA. If the knowledge base type selected is multiple languages, the knowledge base name is used as the related knowledge base name. |
Category Detail
|
Sequence and Field Name |
Enter the CRM field that is used to generate category and its order. The sequence and field name are used to determine the category value. For example, if there are two items in the Category Detail grid: the CASE_TYPE field in sequence 1 and SOLUTION_ID in sequence 2. In this case, the category value becomes CASE_TYPE:SOLUTION_ID. |
Content Field Detail
|
Content Field |
Enter the content fields for the knowledge base. A content field identifies the concept set that NLP uses to perform content analysis. When you associate a knowledge base to an application definition, you need to map each content field of the knowledge base to a page field of the application. For example, you map the Summary content field to the Case Summary application field. When the CRM system sends a case to NLP for suggestion on solutions, the associated knowledge base knows which concept set (the one related to the Summary content field) it should use to analyze the value entered in the Case Summary field of the case. Content fields are dictionary fields in the NLP server. Establish content fields on the Content Fields page. |
International Support Detail
|
Knowledge Base Type |
Select whether the knowledge base supports single language or multiple languages for each knowledge base. If you select multiple languages, the system adds a language rule layer in the knowledge base structure before you add any category to the knowledge base. |
|
Language |
Select the languages that the knowledge base supports if you select multiple languages as the type. The related knowledge base name for each selected language is the knowledge base name. If you select single language as the type, the related knowledge base name for each language is named in this format: <knowledge base name>_<three letter language code>, for example, case knowledge base_FRA. |

 Setting Up Application Definition
Setting Up Application DefinitionAccess the Application Definition page.
Application Detail
|
Application ID |
Enter the name of the application that takes advantage of the suggestion and categorization functionality that NLP offers. |
|
Status |
Select the status of the application definition. Options are active and inactive. Only active application definitions are used in NLP. |
|
Knowledge Base ID |
Enter the knowledge base that this application uses for suggestion and categorization. When you select a knowledge base, the system automatically populates the Content Fields grid and the Category field with the information that you defined for that knowledge base. |
|
Threshold (%) |
Enter the minimum score that the NLP server uses to compare with the calculated relevancy score for each category. The NLP server returns to the CRM system categories with scores that are equal to or higher than this threshold value. |
|
Maximum Return |
Specify the maximum number of suggested items should return to the CRM system. |
|
Description |
Enter descriptive text about the usage of the application definition. The text is displayed on the Applications page of the knowledge base record it is associated with. |
Content Field Mapping Detail
|
Relationship Record |
Enter the record that the application uses to submit suggest and feedback requests. This record should have the Category field and CRM application fields that can map to the knowledge base content fields specified in the Content Fields grid. The record can be a view or a work record. |
|
Content Field |
Displays the content fields that are defined for the selected knowledge base. |
|
CRM Application Field |
Enter the name of the CRM application field (available in the relationship record) that maps with the corresponding content field. The mapping indicates where the content data originates. |

 Reviewing Associated Applications in the Knowledge Base
Reviewing Associated Applications in the Knowledge Base
Application Reference Detail
This grid lists the application definitions in the system that are associated with the knowledge base. Click the View Detail button to access any given the application definition.

 Defining Training Data Sources
Defining Training Data SourcesAccess the Training Source page.
Your IT personnel uses this page to specify the data source for any associated application that the knowledge base can leverage for training purposes. Typically, this data comes from the CRM system. Specify a training source profile for each knowledge base.
Data Source Information
|
Application ID |
Enter the ID of the application definition where the data used for training originates. |
|
Data Source |
Specify the method that is used to retrieve data for the given application. There are four options:
There are several considerations for using the text file format. They are:
|

 Defining Feedback Queues
Defining Feedback QueuesAccess the Feedback Queue page.
When users provide feedback on suggestions returned from the NLP server, feedback entries are queued in the CRM system until they've reached a certain number (specified in the KB Settings page), which causes the daemon process to submit them to the NLP server for teaching purposes automatically. If the feedback process is not configured to be automatic, feedback submission becomes a manual process. Use this page to define the feedback queue for any given knowledge base.
|
Queue ID and Queue Name |
Displays the automatically assigned ID that uniquely identifies the queue, and the name you enter for the queue. |
|
Is feedback process Automated |
Select to automate the feedback process. A daemon process runs periodically to check if the total counts of feedback in the queue has reached the defined threshold. If yes, it takes care of the feedback automatically. By default the feedback process is automated. If you don't want the process to run automatically, clear this check box. You can access the Feedback Runner page to perform this process manually. |

 Defining Category Sets
Defining Category Sets
If you cannot get data to train the knowledge base and obtain categories, you can define categories manually and use them to build the knowledge base without sample data training.

 Setting Up System Installation Options and Knowledge Bases
Setting Up System Installation Options and Knowledge Bases
This section discusses how to:
Set up NLP system installation options.
Set up knowledge bases.

 Pages Used to Setting Up System Installation Options and Knowledge Bases
Pages Used to Setting Up System Installation Options and Knowledge Bases
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
RBN_DFN_SYSTEM |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Setup, System Installation, System Installation |
Set up NLP system installation options. |
|
|
RBN_SETUP_KB |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Setup, Knowledge Base, Setup Knowledge Base |
Specify configuration options for a knowledge base and set it up through a batch process. |

 Setting Up NLP System Installation Options
Setting Up NLP System Installation OptionsAccess the System Installation page.
This AE program triggers teaching processes based on the system installation setting (number of maximum parallel processes) and the number of current queue definitions. If the number of defined feedback queues is fewer than the maximum parallel processes specified on the system installation and the feedback process is automated for those queues, the daemon process triggers the same number of teaching processes as the feedback queue count.
The teaching process is triggered by the knowledge base daemon process. It is capable of processing multiple queues simultaneously as long as the feedback process for these queues is automated. The teaching process handles the feedback in the asynchronous mode.
The NLP feedback server does not process feedback requests immediately. Feedback entries for existing categories are in fact queued when they are submitted to the NLP server until next time the teaching process runs. When the teaching process runs, it checks for the status of feedback entries. If an entry has been processed, the system archives it in the feedback history table. Users can review the history of feedback that the knowledge base has adopted since it went into production.
For feedback entries with new categories, when the teaching process first runs, a “add new category” request is submitted to the NLP server if the number of feedback entries for any new category is greater than or equal to the minimum items per new category setting. Next time the teaching process runs, it checks for the “add new category” request status. If the request fails, the overall status is updated accordingly. If it succeeds, the new categories are updated to become existing categories. The process then counts the total number of feedback entries. If it's greater than the minimum feedbacks to submit setting, a “teaching knowledge base” request is then sent to the NLP server. When the teaching process runs at the third time, it checks for the “teaching knowledge base” request status. If the request is completed successfully, the processed feedback is archived in the feedback history.
NLP Server Vendor Setting
|
NLP Server Vendor |
Specify the NLP server vendor. PeopleSoft CRM uses the Banter Server. |
Feedback Process Settings
|
Feedback Process is Automated |
Select to execute the feedback process in a batch mode and run automatically as scheduled. If this check box is clear, the daemon process will not trigger any feedback process. You can run the feedback process manually. |
|
Minimum Items Per New Category |
Specify the minimum number of feedback items to receive before a new category can be added to the knowledge base. |
|
Maximum Parallel Processes |
Specify the maximum number of parallel teach processes that the system can execute simultaneously. This value applies when the feedback process is automated. |
|
Minimum Feedbacks To Submit |
Specify the minimum number of feedback items should be queued before they are sent to the NLP server for teaching purposes. |
|
Notification and Notification Email Address |
Select when an administrator receives notification about the status of the daemon process and teaching process. Options are always, only when the process fails, or only when the process is successful. Specify the email address to which the system sends the notification. |
KB analysis Settings
|
Analysis Data Chunk Size |
Specify the size of data that is submitted to the NLP server of analysis at a time. If the amount of data to send to the NLP server becomes too big, it takes longer time to transfer the data and can cause the connection with integration broker to time out. It does not become an issue if the data can be divided into manageable chunks. The default value is 100 rows of data. |
Server Object Lock Settings
|
Maximum Object Lock Retries |
Specify the maximum number of times that the knowledge base AE process can reschedule if the process is locked. Since the administration object cannot be accessed by more than one application, any access to the locked object generates system errors. The system uses the retry mechanism to avoid the multiple user object lock issues. |
|
Interval For Retry Attempt |
Specify the time period in seconds that the system reschedules each knowledge base AE process to avoid the server object lock. |
Environment Settings
|
Sample & KB Files URL |
Specify the URL identifier of the FTP server where the sample data and knowledge base files are stored. |
|
Temporary Files URL |
Specify the URL identifier of the FTP server where the temporary files are stored. |
|
Refresh Time (in Seconds) |
Enter the minimum interval for refreshing pages (for example, pages for running processes). Users can click the Refresh button on that page more frequently, but the refresh command will not be executed unless the specified interval has passed since the last refresh. This setting helps you avoid performance degradation when users press the Refresh button continuously. |

 Setting Up Knowledge Bases
Setting Up Knowledge BasesAccess the Setup Knowledge Base page.
|
Data Source Type |
Specify the source of the data that is used to build the knowledge base structure. First, specify from these types:
|
|
Run Mode |
Select the knowledge base deployment mode. Options are Composite, Distributed and Not in Use. When the knowledge base is running, it has three server objects that are available to calling applications. They are Instance Server Object, Configuration Server Object and Feedback Server Object. In the composite mode, the instance server object, feedback server object and configuration object execute in the same process. These objects share the same knowledge base data that is loaded in memory. Any processed feedback (that is, online learning) takes effect immediately. You can determine the number of composite knowledge bases can run in one process on the KB Settings page. In the distributed mode, each object runs in its individual process. Each object loads its own knowledge base data in memory. The processed feedbacks (online learning) does not take effect until the feedback entries are saved in the NLP database and each instance object has reloaded its knowledge base data into the memory. |
|
Lock Status |
Select whether the process is locked when in progress. When an instance is locked by an administrator, only that administrator can unlock it. |
|
Notification |
Select when the system sends a notification about the process. Options are always, when the process fails or when it is successful. |
|
Run Setup Process |
Click to schedule the setup job to run. |
|
Knowledge Base Process Monitor |
Click to access the Knowledge Base Process Monitor page (RBN_MONITOR_TXN) and review the schedule. |

 Maintaining Knowledge Bases
Maintaining Knowledge Bases
This section discusses utilities that are used to maintain knowledge bases after setup—operations related to categories, dictionary items, the feedback process, analysis on knowledge base, training sources and so on. It includes topics on how to:
Manage knowledge base configuration.
Manage categories.
Import categories.
Export knowledge bases.
Manage dictionary entries.
Analyze training sources.
Run manual feedback processes.
Analyze knowledge bases.
Test knowledge bases.
Create an integration broker node for the NLP server.
Note. When you run the knowledge base setup process, it performs some of the functions that can also be handled by utilities provided in the NLP framework. For example, the setup process import categories to the CRM system and insert content fields in the dictionary repository in the NLP server. If the setup process fails to finish any of these tasks for some reason, you can perform the tasks manually using the system provided utilities.

 Pages Used to Maintain Knowledge Bases
Pages Used to Maintain Knowledge Bases
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
RBN_CONFG_KB |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Utilities, KB Configurator, Knowledge Base Configurator |
Maintain the knowledge base configuration that is established by the knowledge base setup process. |
|
|
RBN_MANAGE_KBCATG |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Utilities, Category Manager, Category Manager |
Manage categories manually and enter threshold values for them if necessary. |
|
|
RBN_SYNCH_CATEGORY |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Utilities, Category Importer, Category Importer |
Import categories manually to the CRM database. |
|
|
RBN_EXPORT_KB |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Utilities, KB Exporter, Knowledge Base Exporter |
Export a knowledge base from the NLP server to the .kb file format that is stored in the FTP server for download. |
|
|
RBN_MNG_DICTIONARY |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Utilities, Dictionary Manager, Dictionary Manager |
Manage dictionary entries that are available on the NLP server. |
|
|
RBN_ANLAYZE_SAMPLE |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Utilities, Training Source Analyzer, Training Source Analyzer |
Analyze the training data and view the analysis report that gets generated. |
|
|
RBN_SBMT_FEEDBACK |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Utilities, Feedback Runner, Feedback Runner |
Run the feedback process manually. |
|
|
RBN_ANALYZE_KB |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Utilities, KB Analyzer, Knowledge Base Analyzer |
Analyze the knowledge base and view analysis reports it generates. |
|
|
RBN_KB_TESTER |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Utilities, KB Tester, Knowledge Base Tester |
Test the knowledge base. |
|
|
RBN_COPY_IBNODE |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Utilities, Server Node Creation, Create Server Node |
Define an integration broker node for the NLP server. |

 Managing Knowledge Base Configuration
Managing Knowledge Base ConfigurationAccess the Knowledge Base Configurator page.
Part of the knowledge base setup process is to configure the knowledge base using the run mode and machine name provided in the Setup Knowledge Base page. You can modify the configuration settings after the setup process using the Knowledge Base page.
|
Run Mode |
Specifies the run mode selected for the knowledge base: composite or distributed. |
|
Feedback Machine |
Specifies the name of the machine in which the knowledge base feedback server resides. This field appears if the run mode is distributed. |
Instance Servers
This applies only to the distributed mode.
|
Machine |
Select the name of the machine that runs the knowledge base instances. |
|
Minimum Instances and Maximum Instances |
Enter the minimum and maximum number of instances that must be created during runtime. The NLP server uses the load-balancing technique to distribute the request to different instance. |
|
Idle Time (minutes) |
Enter the sleep time of instance servers in minutes. |

 Managing Categories
Managing CategoriesAccess the Category Manager page.
The Category Detail grid lists the categories that have been added to the knowledge base as learning nodes. You can review the feedback statistics for each category and decide to remove obsolete categories.
|
Threshold (%) |
Enter a new threshold value for the category if necessary. If you want to set up applications that support auto-response or auto-routing, specify the threshold value for each category. The value is between 0.00 and 100. Changes on threshold values apply to the knowledge base on the NLP server immediately. The NLP server uses these values to determine the best matching suggestion to return for applications that support auto-routing and auto-response. |
|
Feedbacks |
Displays the total number of feedbacks from which the specified category has learnt. |

 Importing Categories
Importing CategoriesAccess the Category Importer page.
If the knowledge base setup process is unable to complete the knowledge base configuration due to object lock issue, you configure the knowledge base manually. In this case, you can run this process that imports categories to the CRM database from the knowledge base on the NLP server. Click the Run Import Process button to start the Category Import process. You can access the Knowledge Base Process Monitor (RBN_MONITOR_TXN) page to check the status of the process. Run this process if you wish to synchronize the CRM category repository with the one on the knowledge base as well.
After the import, you can manage categories from the CRM side through the category manager. If the knowledge base is monolingual, it imports categories to the CRM database under the root node. If the knowledge base is multilingual, it imports categories to the CRM database under language specific nodes.

 Exporting Knowledge Bases
Exporting Knowledge BasesAccess the Knowledge Base Exporter page.
You use this utility to export a knowledge base from the NLP server to a special knowledge base file format (with .kb extension). The system stores the .kb file in the FTP server that is specified when you set up the NLP server. Click the Run Export Process button to start the Knowledge Base Export process. You can access the Knowledge Base Process Monitor (RBN_MONITOR_TXN) page to check the status of the process.
Run this process if:
You want to make a copy of the knowledge base in a physical file.
You want to move the trained knowledge base from a test or development environment to a production environment. You can export the knowledge base to a .kb file and use it to train the knowledge base on the Setup Knowledge Base page.

 Managing Dictionary Entries
Managing Dictionary EntriesAccess the Dictionary Manager page.
Use this page to add, delete or load dictionary entries on the NLP server. add new dictionary entry from the PeopleSoft content field definition table or delete the dictionary entry from the NLP server directly.
|
Delete Selected Entries |
Click to remove selected dictionary entries from the NLP server. The deletion doesn't impact the content field repository in the CRM system. |
|
Add |
Click to access the Dictionary Manager - Select Content Fields page to add content fields (available in the CRM system) to be dictionary entries on the NLP server. |
|
Load Dictionary Entries |
Click to load dictionary entries from the NLP server. |

 Analyzing Training Sources
Analyzing Training SourcesAccess the Training Source Analyzer page.
One of the ways to set up the knowledge base is to use training data. The key factor of building a good knowledge base in the initial phase is having sufficient amount of data to train the knowledge base. As the knowledge base administrator, consider the right list of categories to include in the training data when you build and train a knowledge base. The list should be based on the current business environment and you may involve a business analyst to help you collect categories that make sense.
If you do not have the training data for your category list, you can create a .csv file for the category list. You use this file to build the knowledge base without going through the training process, which means that there's no need to run the training source analyzer.
If you have the training data for your category list, make sure that you have enough data for each category. For example, prepare 50 pieces of data for each category to train the knowledge base.
If your training data comes from a live production system, you may run the training source analyzer to analyze the data for each category. In this case you want to run the analyzer process even if you have the training data in a text file.

 Running Manual Feedback Processes
Running Manual Feedback ProcessesAccess the Feedback Runner page.
If the feedback process is not set to run automatically, you can perform the process manually by clicking the Run Feedback Process button. The NLP server uses feedback in the queue to teach the knowledge base immediately.
The batch process performs several tasks, which includes adding and training new categories, training existing categories with feedback entries, and archiving feedback into the feedback history. When the new categories and feedback are committed on the knowledge base, the knowledge base is then saved in the database. Note that if the knowledge base is run in the distributed mode, all its instance servers are notified to reload the knowledge base.

 Analyzing Knowledge Bases
Analyzing Knowledge BasesAccess the Knowledge Base Analyzer page.
Use the knowledge base analyzer to run analysis on the performance of the knowledge base. This process is useful especially during the initial training of the knowledge base, before the knowledge base goes live, or when you analyze the performance of a live knowledge base. The analysis helps you to:
Ensure that the configured knowledge base works fine.
Verify that the categories in the knowledge base work properly—whether some categories are under-performed or it needs new categories.
Identify performance issues as soon as possible.
Create performance reports.
Fine tune threshold values to work best for applications that support auto-routing and auto-response.
Training Source Detail
When selecting a training source to run the analysis, make sure that the data set mirrors your real business data as much as possible to produce meaningful analysis.
Click the Run Analysis Process button to start running the application engine process.
The knowledge base analysis process generates reports (in .csv file format) for you to measure the performance of the knowledge base based on the specified data set. They are:
Knowledge Base Overall Performance Report.
This report gives you the overall performance of the trained knowledge base. It is useful, for example, if you have an application that supports auto suggestion functionality (suggesting solutions automatically to handle incoming email). Based on the information provided in this report, you can adjust threshold values for categories and the number of returned suggestions so that the knowledge base is able to return highly accurate and reasonable number of suggestions for your application.
Category-based Cumulative Success Report.
This report measures the success rate of categories in different . For each category that is associated with the knowledge base, the report gives a percentage of how relevant the specified data set is to the category. In addition, the report displays the cumulative success rate (in percentage) for each category to be successfully identified as the first match, among the first two matches, first three matches and so on. For categories with low performance scores, it may be caused by:
Duplicated categories. Consider combining similar categories.
Insufficient training data for categories. Consider submitting more feedback entries to these categories if they are important to your business.
Precision & Recall Versus Threshold Report.
This report gives you the threshold, precision and recall values that are particularly useful for auto-responding and auto-routing applications. You want to provide highly accurate suggestions when the application automatically routes or responds, for example, incoming email, without human intervention. In this report, you can see for each category, what the precision rate and recall rate is for any given threshold value. For example, for a category with a cell value that reads:
30.67(50.00/100.00)
Where the threshold value is 30.67, the precision value is 50.00, and the recall value 100.00. That means to get a 50% accuracy rate for this category, the suggested category threshold value is 30.67%.

 Testing Knowledge Bases
Testing Knowledge BasesAccess the Knowledge Base Tester page.
Use this page to verify that the knowledge base you built is up and running. You can perform basic knowledge base performance test by entering content and searching for suggestions. Take advantage of the knowledge base analyzer if you wish to run analysis on the performance of the knowledge base.
Test Data Information
Specify the knowledge base on which you want to test. The page dynamically generates the Content Detail area with content fields based on the selected knowledge base. To test the knowledge base, enter content in this area, and specify the maximum suggestions to return and the threshold for the suggestions. Matching suggestions are listed in the Returned Suggestions grid.
|
Search Content |
Click to access the Knowledge Base Tester - Search Content page, where you can look for test content (to fill out the Content Detail area) from the CRM system or external CSV file. |
|
Suggest |
Click to call the NLP framework API to process the search request and return matching suggestions. |
|
Suggest For Auto Route |
Click to call the NLP framework API to process the search request and return matching suggestions. If you specify a positive threshold value on this page, the NLP server calls the suggestion method with this threshold value. If you don't specify a threshold value here, the NLP server calls the API with the threshold that is set up at the category level. You can change the threshold values for categories in the Category Manager page. |
|
Suggest For Auto Response |
Click to call the NLP framework API to process the search request with category-level threshold values. |
|
Identify Language |
Click to obtain the language code in which the content is written. |
|
Submit Feedback |
Click to send feedback to the knowledge base queue. Define feedback queues for the knowledge bases before submitting feedback to them. |

 Creating an Integration Broker Node for the NLP Server
Creating an Integration Broker Node for the NLP ServerAccess the Create Server Node page.
PeopleSoft CRM delivers an integration broker node, NLP_DEFAULT, to integrate with the NLP server. Use this page to define a new node for the NLP server based on this existing node. After saving the new node, the Go to New Node Definition link appears. You can click it to access the new node in Node Definitions component.
|
Server Node and Description |
Enter the name and short description for the new integration broker node. |
|
Integration Gateway ID |
Enter the CRM system web server gateway identifier; use the default value. |
|
Connector ID |
Enter the PeopleSoft connector identifier; always use HTTPTARGET. |
|
Web Service URL |
Enter the NLP web service HTTP link, which is based on the NLP web service installation in this format: http://<YourNLPWebServiceInstallationSite>/psftnlpservice.asmx |

 Monitoring Knowledge Bases
Monitoring Knowledge Bases
This section discusses how to:
Verify knowledge base setup.
View server status.
Monitor knowledge base processes.
Monitor feedback queues.
Review feedback history.
View server lock status.

 Pages Used to Monitoring Knowledge Bases
Pages Used to Monitoring Knowledge Bases
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
RBN_MONITOR_KB |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Monitor, Server, Knowledge Bases |
Verify the knowledge base setup. |
|
|
RBN_MONITOR_SERVER |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Monitor, Server, Servers |
View server running status. |
|
|
RBN_MONITOR_TXN |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Monitor, Process Monitor, Knowledge Base Process Monitor |
Monitor various knowledge base-related processes. |
|
|
RBN_FDBK_QUEUE |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Monitor, Feedback Queue, Feedback Queue Monitor |
Monitor feedback queues. |
|
|
RBN_FDBK_HISTORY |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Monitor, Feedback History, Feedback History |
Review information of past feedback processes. |
|
|
RBN_SERVER_LOCK |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Knowledge Base, Monitor, Server Lock Viewer, Server Lock Viewer |
View server lock statuses. |

 Verifying Knowledge Base Setup
Verifying Knowledge Base SetupAccess the Knowledge Bases page.
After the job to set up a knowledge base is run, you can access this page to make sure that the knowledge base is up and running.

 Viewing Server Status
Viewing Server Status
This page provides status information about NLP servers and machines that are registered in them.

 Monitoring Knowledge Base Processes
Monitoring Knowledge Base ProcessesAccess the Knowledge Base Process Monitor page.
Use this page to review the status of different types of batch processes that have run for knowledge bases in the system. Enter criteria to refine search results if necessary. Click the Details link to access the detail page for the corresponding process. It lists out steps in the process and provides status information and description for each of them. If the process is not completed for some reason, the page may help you identify the issue.

 Monitoring Feedback Queues
Monitoring Feedback QueuesAccess the Feedback Queue Monitor page.
You can review feedback status for each queue you set up in the specified knowledge base.
|
Feedback ID and Category |
Identifies the feedback item in the queue and the associated category value (suggested by the NLP server) on which the feedback was made. |
|
New |
Indicates if the category value is new or not. |
|
Task ID |
Displays the task identifier that is given by the NLP server. The feedback queuing process is asynchronous, which means that the NLP server doesn't process feedback immediately. It returns a task ID for each feedback, which you can use to further query the system and find out the progress of the submitted request. |
|
Task Status |
Displays the current status of the feedback. Values are:
Click the Detail button to see the category content for which the feedback was made. |

 Reviewing Feedback History
Reviewing Feedback HistoryAccess the Feedback History page.
Use this page to view a list of feedback entries that have been submitted since the knowledge base was in production.

 Viewing Server Lock Status
Viewing Server Lock StatusAccess the Server Lock Viewer page.
Use this page to monitor the server object lock status. There are two banter server objects that do not support multiple user access: Administration and Configuration.
|
Process Instance and Run Control ID |
Displays the number of the application engine process instance and the run control ID for the process that the specific locked server is running. |
|
Administration |
Displays as selected if the server is locked by an administration server object. |
|
Configuration |
Displays as selected if the server is locked by a configuration server object. |
|
Refresh |
Click to refresh the grid. The frequency is based on the NLP system installation refresh time setting. |