Setting Up the Integration of External Data with PeopleSoft
Before you set up the integration of external data with PeopleSoft, you must decide whether SSL configuration for Logstash is required.
If you need to configure SSL for Logstash, see Configuring SSL for Logstash.
To set up the integration of external data with PeopleSoft, you must complete the following steps:
Create a search definition for external data.
Deploy an external data search definition to Elasticsearch.
Specify a data source for the external data search definition.
Build an index for the external data search definition.
To complete these steps, you may either use the External Data Source Setup navigation collection or the individual pages.
Use the External Definition page to create a new search definition for external data and to view a list of existing search definitions for external data. You could create a search definition for each functional area, for example, recruiting, job data, and so on.
Access the External Definition page by selecting , and from the left panel, choose External Data Search Defns and select the Add Definition or plus button.
Alternatively, you may select .
To create a new definition, select the Add Definition or plus button that displays the External Definition page.
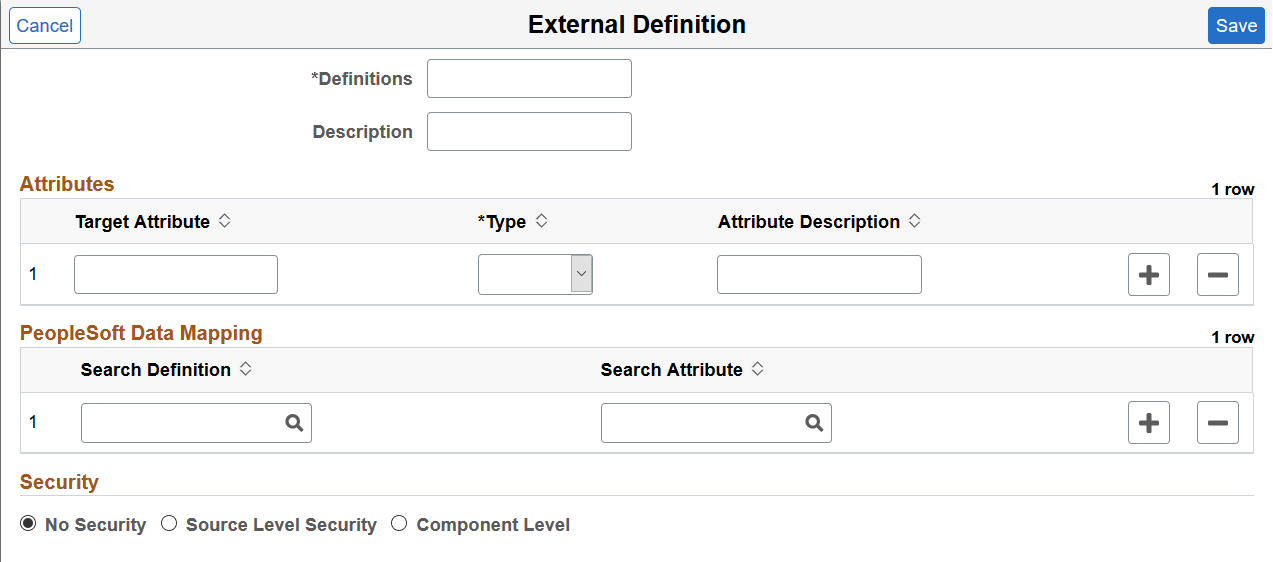
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the External Definition page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Definition |
Specify a name for the search definition. |
Description |
Enter a description. |
Attributes
You use the Attributes section to specify the attributes which are available in the external data and are functionally relevant in the external data index. Attributes are fields that form a part of each document in the Elasticsearch index of external data. You decide which attributes you want based on the functional information that you require in the index. These attributes can be obtained either from the external data or from PeopleSoft mapping to existing PeopleSoft fields.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Target Attribute |
Enter an attribute that is available in the external data that you want to include in the index. |
Type |
Choose a type for each attribute. The selected type is defined in Elasticsearch as part of the index mapping. |
Attribute Description |
Enter a description for an attribute. |
PeopleSoft Data Mapping
This section enables you to map some of the defined attributes with existing PeopleSoft fields. The purpose of PeopleSoft mapping is to provide fixed values per data source for each document indexed from a data source. The PeopleSoft mapping also helps to group all the documents for each data source with a specific attribute value stored in PeopleSoft.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Search Definition |
Choose a search definition that has the attribute that you want to map with the external data. |
Search Attribute |
Choose the attribute that you want to map. |
Security
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
No Security |
Select to define no security restriction for a search definition's data. Anyone with access to the application can view the data for a search definition set to No Security. That is, the data is public to all users. |
Source Level Security |
Select to allow or restrict access to the entire search definition as per the specified user or role. That is, only specified users and roles are able to view data for that search definition. Specify values for the following fields:
For more information on source level security, see Setting Source Level Security. |
Component Level |
Select to associate component level security with the external data search definition, that is, users who have access to a component can view the data of the external data search definition. Specify values for the following fields:
For more information on search criteria, refer to Mapping Components to Search Definitions. |
Use the Deploy External Search Defns page to deploy the external data search definition and create a placeholder in Elasticsearch.
Access the Deploy External Search Defns page by selecting , and from the left panel, choose Deploy External Search Defns.
Alternatively, you may select .
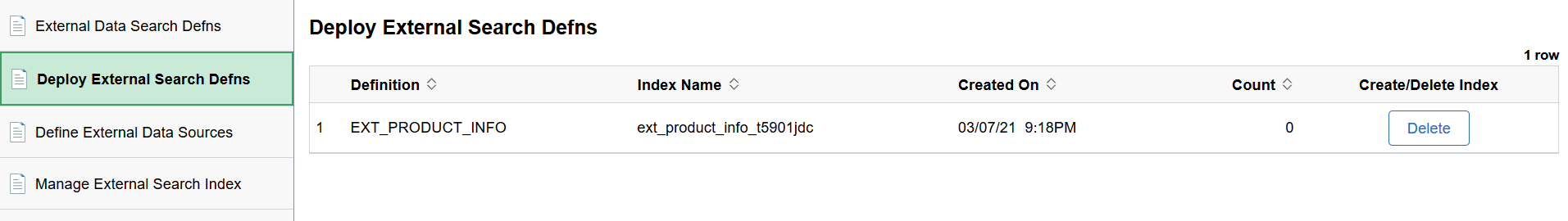
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Deploy External Search Defns page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Definition |
Displays a list of external data search definitions. |
Index Name |
When you click the Create button, the name of the Elasticsearch index for the specified external data search definition is generated. The naming convention is the name of the search definition with the database name appended to it. |
Created On |
Displays the day and time when the Elasticsearch index was created for the specified search definition. |
Count |
Displays the count of documents in an index. On the Deploy External Search Defns page, the count is zero because the index for the search definition is not built. After an index is built, the number of documents in an index is displayed. |
Create/Delete Index |
Select the Create button to create a placeholder for the index in Elasticsearch. Select the Delete button to delete the index. The delete action only removes the index placeholder from Elasticsearch; it does not delete the search definition. |
Use the Data Source Definition page to specify the actual source of data. In this context, a data source represents the actual source of external data from which the required data is retrieved and indexed.
Access the Data Source Definition page by selecting , and from the left panel, choose Define External Data Sources.
Alternatively, you may select .
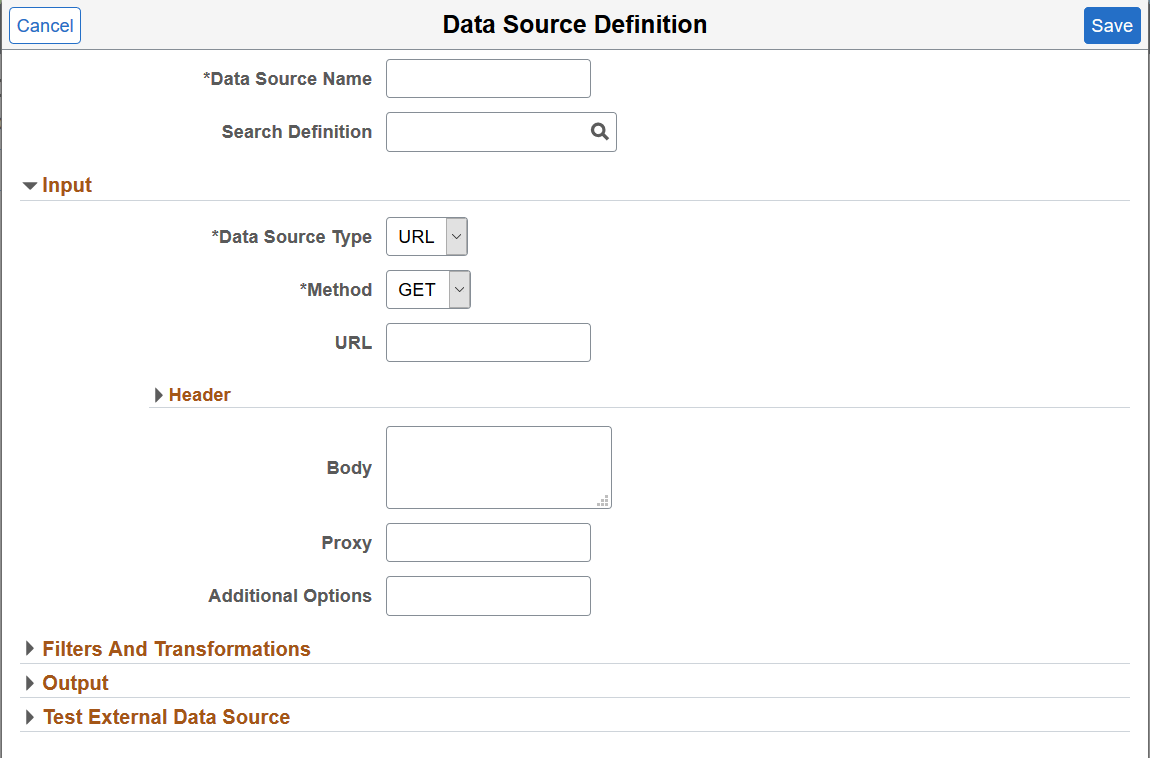
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Data Source Definition page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Data Source Name |
Specify a name for the data source. |
Search Definition |
Select an external data search definition to associate with the data source definition. If you’re creating a data source for intermediate processing, you do not associate a search definition with it. |
Input
In the Input and Header sections, the fields that appear are based on your selection of data source type.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Data Source Type |
Select a type for the data source. Valid options for type are:
|
File Type |
The File Type field appears when you select File as data source type. Note: CSV is the only supported file type. |
File Name |
The File Name field appears when you select File as data source type. All external CSV files should be placed in the psftappdata folder under <LOGSTASH_HOME>. Any generated files are also saved to this folder. Specify the absolute path of the CSV file. |
Method |
The Method field appears when you select URL as data source type. Choose the type of HTTP request that needs to be issued. Valid options for method are:
|
URL |
The URL field appears when you select URL as data source type. Specify the path of the external data. The path should not be absolute; it should be relative. Path should be relative to <LOGSTASH_HOME>/psftappdata. |
Header
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Body |
The Body field appears when you select URL as data source type. This field contains the JSON request for the POST and GET methods. |
Proxy |
Specify the proxy server details for REST API connection. |
Additional Options |
Specify any additional connection parameters. |
Filters and Transformations
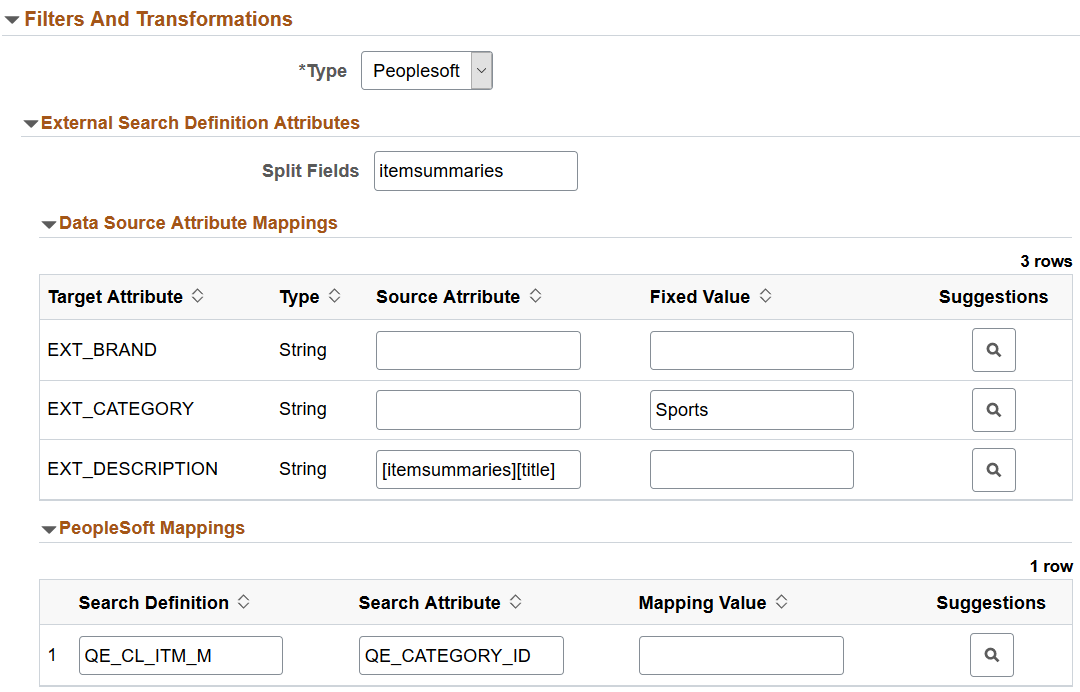
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Filters and Transformations section of Data Source page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
In the Filters and Transformations section, the fields that appear are based on your selection of type.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Type |
Specify the type of data transformation that you want to achieve.
|
External Attributes
The External Attributes section appears when you select External as the type.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Split Fields |
You need to specify split fields when you select URL as the data type. You indicate a field from the data source, which requires a split. When a request is made to the REST end point specified in the URL type, it returns a response containing JSON documents. These JSON documents can be nested or hierarchical in nature. If the data you require is under a parent node, then you need to use the split fields option to obtain the children under the parent node. For example, in a product data source, the information related to a product is under a parent node called itemSummaries. To obtain the information of sub-products (children) under the parent node for further mapping, you need to split the field. |
Allowlist |
Use this field to limit or filter the data from the data source that is passed to Elasticsearch. Enter comma separated values in this field. If you do not enter any values here, all data from the data source will be passed to Elasticsearch. |
External Search Definition Attributes
The External Search Definition Attributes section appears when you select PeopleSoft as the type.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Split Fields |
You need to specify split fields when you select URL as the data type. You indicate a field from the data source, which requires a split. When a request is made to the REST end point specified in the URL type, it returns a response containing JSON documents. These JSON documents can be nested or hierarchical in nature. If the data you require is under a parent node, then you need to use the split fields option to obtain the children under the parent node. For example, in a product data source, the information related to a product is under a parent node called itemSummaries. To obtain the information of sub-products (children) under the parent node for further mapping, you need to split the field. |
Data Source Attribute Mappings
In this section, you map the attributes of the external data search definition to the attributes of the data source. The attributes of the external data search definition associated with this data source are displayed enabling you to map these attributes to the attributes of the data source.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Target Attribute and Type |
Contains the attributes and its type from the external data search definition that you associated with the data source. These values cannot be edited here. |
Source Attribute |
As part of the mapping of the external data search definition with the attributes of data source, if you need to map any nested fields under a split attribute, the mapping can be done using the split field as described in the previous section. For example, to map the field, Title, under itemSummaries, you should enter it as [itemSummaries][title] in the Source field. |
Fixed Value |
The Fixed Value column enables you to specify a value that meets your requirements. For example, for the City source attribute, you want information only about San Francisco, so you should specify San Francisco in the Fixed Value column. |
Suggestions |
When you select the suggestions icon, it displays the attributes from the actual data source, which you can choose for the Source Attribute column. |
PeopleSoft Mappings
Use the PeopleSoft Mappings section to map a specific value from the data source to the PeopleSoft attribute. The mapping from the external data search definition, which you associated with this data source, is displayed here.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Search Definition |
The search definition defined in the PeopleSoft Mapping section of the external data search definition is displayed here. This field is read-only. |
Search Attribute |
The search attribute defined in the PeopleSoft Mapping section of the external data search definition is displayed here. This field is read-only. |
Mapping Value |
Map a specific value from the data source to the PeopleSoft attribute. For example, the EP_AP_VENDOR search definition contains the VENDOR_NAME_SHORT attribute. For this attribute for the vendor, XYZ, the value stored in PeopleSoft is XYZ01. You should enter this value, XYZ01, in the Mapping value column. This value is added to all the Elasticsearch documents which are indexed and obtained from the XYZ data source. |
Suggestions |
Displays the values from the selected search attribute, which you can choose for the Mapping Value column. |
If an external search definition, which is mapped to an external data source, is updated, then the updated data automatically reflects on this page.
Output
In the Output section, you specify where the data source output should be stored.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Output Type |
Select an output type based on your requirement.
If you select File, the following two fields —Codec and File— are displayed. |
Codec |
The Codec field corresponds to the codec setting of the Logstash file output plugin. The external data that is sent as input requires to be transformed in order to ensure that it has all the necessary attributes to be used in PeopleSoft. The following sample code shows the transformed data. Output gets transformed from: To: For more information on the codec setting, refer to Logstash Reference [7.10] in www.elastic.co. |
File |
Specifies the location of the file. |
Test External Data Source
This section enables you to check the REST end point request and response.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Request |
Specify a request to test the data source. |
Response |
Displays the REST end point response. |
Submit |
When you click Submit, the REST end point request is initiated. |
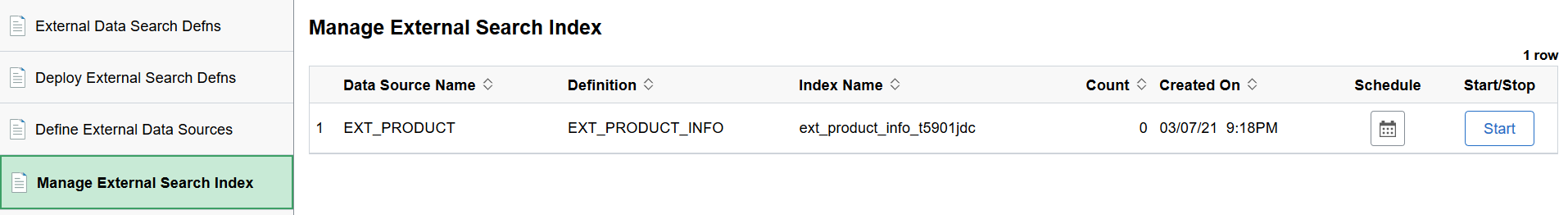
Use the Manage External Search Index page to control the indexing of data from the defined data sources using Logstash. The page lists the existing data sources and enables you to schedule the index build process or immediately start or stop the indexing process.
Access the Manage External Search Index page by selecting and from the left panel choose Manage External Search Index.
Alternatively, you may select .
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Manage External Search Index page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Data Source Name |
Specifies the data sources that you added on the Data Source page. |
Definition |
Specifies the external data search definition that you associated with a data source. |
Index Name |
Displays the Elasticsearch index name for the specified external data search definition. The index name is generated when you deploy the search definition.. |
Count |
Indicates the document count for each search definition. |
Created On |
Indicates the day and time when the index was built. |
Schedule |
Enables you to set up the time and frequency of the indexing process. The Schedule Definition page is described later in this topic. |
Start/Stop |
When you select Start, Logstash initiates the indexing process as per the schedule you’ve set. When you select Stop, Logstash aborts the indexing process. |
Scheduling the Indexing Process
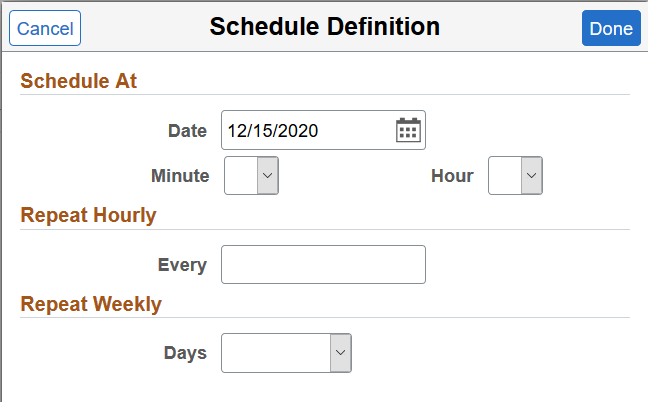
Use the Schedule Definition page to specify the time and frequency of the indexing process, which is performed by Logstash. The scheduling information is stored in the Logstash configuration file. After setting the time and frequency schedule, you must select the Start button (on the Schedule Definition page) that initiates the indexing process as per the schedule .
Access the Schedule Definition page by selecting the calendar icon on the Manage External Search Index page.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Schedule Definition page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Schedule At |
Specify the date and time when you want the index process to commence. The Schedule page provides you the flexibility to specify the exact minute to commence the indexing process. The time and frequency options are mutually exclusive. When you schedule the date and time for the indexing process, the other two frequency options are not considered and vice versa. |
Repeat Hourly |
Specify to repeat the indexing process by the number of hours, for example, you can set it to repeat every four hours. |
Repeat Weekly |
Specify to repeat the indexing process on a specific day of the week and the indexing process repeats every week on the specified day. |
Note: The default schedule for indexing is one minute. If you do not set the time or frequency, the system runs the indexing process after one minute from the time you press the Start button. It runs only once after one minute and does not repeat.
Note: After you’ve set the schedule and saved it, ensure that you select the Start button. The Start button initiates the indexing process as per the schedule.