Viewing Event History
Access the Event History page (PeopleTools, Performance Monitor, History, Performance Event History).
Note: The search results of event history include history information that is collected by agents even if they are currently marked as inactive.
Before you can view historical performance data that is related to events, you need to specify search criteria. This section covers the search criteria for event history.
Click the Advanced Search link to expose all of the search criteria options.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
System ID |
Identifies each monitored system. PeopleSoft automatically generates this value incrementally. System definitions are created automatically when the first agent of a monitored system registers with the monitoring system. |
Database Name |
The name of the PeopleSoft application database running on the monitored system. The monitoring system automatically inserts this value when it recognizes and creates a monitored system. |
Event Definition Set |
Enter the event definition set to which the event definition belongs. Currently, only one definition set exists, and it is reserved for PeopleSoft development. |
Event ID |
Select a particular event that you want to monitor, such as event 300, Host Resource Status. |
Process ID |
Specify the process ID for which you want to locate event history. |
From/To Date/Time |
Specify the range of time during which you want to locate event history. The system searches the monitor date and time, not agent date and time. |
Domain Host/Port |
If you want to monitor events on a particular server, select the server name/IP address and port number on which the domain runs. |
Domain Name |
If you want to monitor events pertaining to a particular domain, select the application server, web server, or Process Scheduler domain for which you want to view event information. |
Agent ID |
Enter specific agent information if wanted. Identifies an agent within a domain. This is automatically generated by the monitor the first time an agent registers with it. |
Agent Type |
Specify the type of server process the agent is monitoring, such as PSAPPSRV, PSQRYSRV, PSQCKSRV, and so on. |
Filter Level |
To view only the information that is returned of a specific filter level, select the desired filter level. For example, if you want to view only Error alarms, select Error, and the system returns only event information of type Error. Each event definition has a filter level that is set to one of the following levels: error, warning, standard, verbose, or debug. Error and warning levels are associated with alarms, while standard, verbose, and debug levels are associated with informational performance data. The icon that is associated with each category of filter level (alarm or informational) appears in the grid, enabling you to recognize event information easily. |
Metric Chart |
The system creates a metric chart only when you have selected a single event in the search criteria. The metrics that appear in the charts vary depending on the event definition. |
Search |
The Search button performs a search based on the search criteria that is defined on the page. If you want to view the most current information, use theRefresh button after running the initial search. If you clickSearch repeatedly, the system returns the same results from the same time range for each search. |
Refresh |
Updates the value in the To Time field to equal the current time and performs a search. Enables you to view the most current results of a search. |
The Completed Events section contains the results of your event history search.
Note: If a "clone table" warning appears at the top of the page, the archive program is either currently running or has abnormally terminated. If this is the case, all new incoming information that is being sent to the monitoring system is currently being inserted into the clone tables. New performance data is not inserted into the current data tables until the archive program finishes successfully.
See Scheduling Performance Data Archiving.
Summary
The Summary tab displays the name of the event as well as the monitor date and time and agent date and time.
The maximum number of rows that are returned by the search is determined by the Search Row Limit on the Global Administration page.
See Setting Global System Options.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Event |
Displays the name of the event reported. Click the event name to view the Event Details page, which provides:
|
Monitor Date/Time |
The date and time that the monitoring system inserted the row of performance data into the monitoring database according to the database clock. |
Agent Date/Time |
The date and time according to the agent clock that the domain monitor used when it last sent performance data to the monitor. Note: The date and the time appearing on this page always applies to the system on which the agent runs. Keep this in mind if you are monitoring systems in other time zones. |
Identifiers
The Identifiers tab displays information to help further identify the event and a particular event's origin.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Event Set |
The event definition set to which the event definition belongs. |
Event ID |
The ID for a particular event definition, such as 300 for Host Resource Status. |
PID |
The operating system process ID of the process that generated the PMU. |
Agent ID |
The ID of the specific agent sending the event information. |
Domain Name |
The name of the domain in which the agent operates. |
Instance |
The system-generated identifier for a specific row of event information. |
Filter Level |
The filter level that is associated with an event definition. |
Description |
If applicable according to the event definition, a description appears to place the event in context. For example, with the Event 301 (Tuxedo "pq" Row) the description contains the name of the server process that is associated with a particular queue, such as PSAPPSRV, JSL, PSSAMSRV, and so on. The information corresponds to the Additional Data attribute that is part of the event definition. It stores data that exceeds the 128–character limitation of Metric 7. |
Metrics
The Metrics tab displays the metric values of the event definition for a specific reported event. Only metrics that are specified in an event definition contain values. For example, event 300 (Host Resource Status) does not assign values to metric 6 or 7; therefore, those metrics appear on the Metrics page as 0.0000.
Metric information appears in raw form.
See Metric Definitions.
Metric Charts
The system creates a metric chart only when you have selected a single event in the search criteria. The metrics that appear in the charts vary depending on the event definition.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Viewing an event metric chart. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
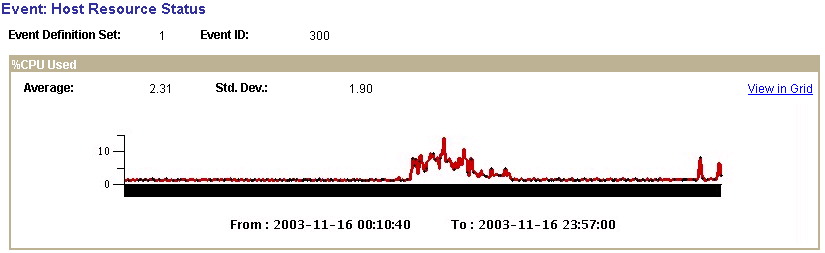
Note: %CPU Used is only one of the charts that appear in the metric charts for Host Resource Status.