PeopleCode Built-in Functions and Language Constructs: M
The PeopleCode built-In functions and language constructs beginning with the letter M are listed in alphabetical order within this topic.
Syntax
MAddAttachment(URLDestination, DirAndFilePrefix, Prompts, &UserFileArray, &ActualSizeArray, &DetailedReturnCodeArrayName [, MaxSize [, PreserveCase[, UploadPageTitle[, AllowLargeChunks[, StopOnError]]]]])Description
Use the MAddAttachment function to upload one or more files from an end user specified location (local storage or cloud storage) to a specified storage location. The Prompts parameter specifies that maximum number of files that the end user can upload at one time. A user can select multiple files at once. Use the AddAttachment function to upload a single file.
Important! It is the responsibility of the calling PeopleCode program to store the returned file names for further use.
If a file exists at a particular place on a storage location and then another file with the same name is uploaded to that same place on that same storage location, the original file will be silently overwritten by the new file. If that is not the behavior you desire, it is recommended that you implement PeopleCode to guarantee the ultimate uniqueness of either the name of the file at its place on the storage location or the name of its place (the subdirectory) on the storage location.
You cannot use a relative path to specify the file that is to be uploaded; you must use a full path. If end users experience problems in uploading files, ensure that they browse to the file they wish to upload rather than attempting to manually enter the full path name of the file. This problem can manifest itself differently depending on the browser used. For example, with some browser versions, the PeopleSoft page appears to be in an infinite “Processing” state. Information is available on working with different browsers.
See PeopleTools Browser Compatibility Guide (Oracle Support Document 704492.1) on My Oracle Support for more information.
Additional information that is important to the use of MAddAttachment can be found in the PeopleTools: PeopleCode Developer's Guide:
PeopleTools supports multiple types of storage locations.
Certain characters are illegal in file names; other characters in file names are converted during file transfer.
Non-ASCII file names are supported by the PeopleCode file attachment functions.
The PeopleCode file attachment functions do not provide text file conversions when files are attached or viewed.
Because MAddAttachment is interactive, it is known as a “think-time” function, and is restricted from use in certain PeopleCode events.
See Restrictions on Invoking Functions in Certain PeopleCode Events.
You can restrict the file types that can be uploaded to or downloaded from your PeopleSoft system.
See Restricting the File Types That Can Be Uploaded or Downloaded.
You can restrict the file types that can be uploaded to or downloaded from your PeopleSoft system.
See Restricting the File Types That Can Be Uploaded or Downloaded.
Virus scanning can be performed on all files uploaded with the MAddAttachment function.
The HTML sanitizer can be enabled and configured to scan and sanitize specific HTML file types (specified by file extension) uploaded with the AddAttachment function.
You can use a file extension list to identify file types to accept or reject when using this function.
Parameters
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
URLDestination |
A reference to a URL. This can be either a URL identifier in the form URL.URL_ID, or a string. This is the storage location to which the files in this invocation of MAddAttachment are transferred. Note: When the URLDestination parameter is specified as a string value, forward slashes (/) are required. Backward slashes (\) are not supported for a string value. Note: Oracle recommends that
you do not use a URL of the form |
DirAndFilePrefix |
A directory and file name prefix. This is appended to the URLDestination to make up the full URL when the file is transferred to an FTP server or, when the file transferred to a database table, to make the file name unique. Note: If the destination location is an FTP server, then it is very important whether the value passed into a call of MAddAttachment for the DirAndFilePrefix parameter ends with a slash or not. If the value for the DirAndFilePrefix parameter ends with a slash, then it will be appended to the value of the URLDestination and used to indicate the relative (to the configured root directory of the FTP server) path name of the directory in which the uploaded file will be stored. If the value for the DirAndFilePrefix parameter does not end with a slash, then the portion of it prior to its rightmost slash will be appended to the value of the URLDestination and used to indicate the relative (to the configured root directory of the FTP server) path name of the directory in which the uploaded file will be stored, and the portion after the rightmost slash will be prefixed to the name of the file that will be created at the destination. Note: Because the DirAndFilePrefix parameter is appended to the URL, it also requires forward slashes (“/”). Backward slashes (“\”) are not supported for this parameter. |
Prompts |
Specifies the number of files that the end user will be prompted to upload as an integer. |
&UserFileArray |
Returns the names of the files on the source system as an array of strings. Note: You can specify this parameter as a zero-length array of string. The array will be populated by MAddAttachment with the actual file names. Note: The file name for each user-selected file cannot be greater than 64 characters. |
&ActualSizeArray |
Returns the file sizes in kilobytes for the uploaded files as an array of numbers. Note: You can specify this parameter as a zero-length array of number. The array will be populated by MAddAttachment with the actual file sizes. |
&DetailedReturnCodeArray |
Returns the return code for each individual file attachment operation as an array of numeric constants. Note: You can specify this parameter as a zero-length array of number. The array will be populated by MAddAttachment with the actual return codes. |
MaxSize |
Specify, in kilobytes, the maximum size of each file. If you specify 0, it indicates “no limit,” so any file size can be uploaded. The default value of this parameter is 0. Note: The system cannot check the size of the file selected by the end user until that file has been uploaded to the web server. |
PreserveCase |
Specify a Boolean value to indicate whether the case of the extension of the file to be uploaded is preserved or not at the storage location; True, preserve the case, False, convert the file name extension to all lowercase letters. The default value is False. Warning! If you use the PreserveCase parameter, it is important that you use it in a consistent manner with all the relevant file-processing functions or you may encounter unexpected file-not-found errors. Note: MAddAttachment provides no indication of a conversion in the file name it returns. |
UploadPageTitle |
Specify a string value to be displayed in the title bar of the file attachment dialog box (as its title). This string should be simple text and contain no HTML elements. If no value is specified, the default value is “File Attachment.” Note: In screen reader mode, the string value of the UploadPageTitle parameter is displayed in the body of the file attachment dialog box rather than as the title of the window. Note: The parameter does not automatically handle localization issues. The string passed into the function is the exact string embedded in the page. You and your application are responsible for any translation issues. |
AllowLargeChunks |
Specify a Boolean value to indicate whether to allow large chunks. If the value specified in the Maximum Attachment Chunk Size field on the PeopleTools Options page is larger than is allowed for retrieval, then the system breaks the file upload into the largest sized chunks allowed. If AllowLargeChunks is set to True, this behavior can be overridden so that it is possible for an end user to upload a file in chunks that are too large for the system to retrieve. If AllowLargeChunks is set to False, the system will use the largest size chunk that is allowed for retrieval, or the configured chunk size, whichever is smaller. Note: If the chunks are too big to be retrieved, then any file retrieval built-in function, such as GetAttachment, will fail. Note: The AllowLargeChunks parameter is only applicable when the storage location is a database record. It has no impact when the storage location is an FTP site or an HTTP repository, since attachments at those locations are never chunked. This is an optional parameter. The default value is False. |
StopOnError |
Specify a Boolean value to indicate whether to continue processing files when a system error is encountered. If StopOnError is set to False, processing continues with the next selected file. If StopOnError is set to True, MAddAttachment terminates on the first system error encountered (for example, %Attachment_Failed, %Attachment_FileTransferFailed, and so on). No attempt is made to upload any of the remaining files. For each of the remaining files, a return code of %Attachment_Unprocessed is returned as the detailed return code. This is an optional parameter. The default value is False. |
Returns
The MAddAttachment function returns one of the following summary return codes that you can check for either as an integer or as a constant value:
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
%Attachment_Success |
The upload was successful if and only if the upload was not cancelled, at least one non-empty file name was specified by the user, and all the files specified with non-empty names were successfully uploaded. |
|
1 |
%Attachment_Failed |
Either the user cancelled the upload, the user specified no files to upload, or at least one of the specified files did not successfully upload. |
In addition, the MAddAttachment function returns detailed return codes in the array specified by the &DetailedReturnCodeArray parameter. The array contains the number of elements specified by the Prompts parameter even if some files remain unprocessed or were not selected by the user. You can check for the detailed return codes either as integers or as constant values:
|
Numeric Value |
Constant Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
%Attachment_Success |
File was transferred successfully. |
|
1 |
%Attachment_Failed |
File transfer failed due to unspecified error. The following are some possible situations where %Attachment_Failed could be returned:
|
|
2 |
%Attachment_Cancelled |
File transfer didn't complete because the operation was canceled by the end user. |
|
3 |
%Attachment_FileTransferFailed |
File transfer failed due to unspecified error during FTP attempt. The following are some possible situations where %Attachment_FileTransferFailed could be returned:
|
|
6 |
%Attachment_FileExceedsMaxSize |
File exceeds maximum size, if specified. |
|
7 |
%Attachment_DestSystNotFound |
Cannot locate destination system for FTP. The following are some possible situations where %Attachment_DestSystNotFound could be returned:
|
|
8 |
%Attachment_DestSysFailedLogin |
Unable to login to destination system for FTP. The following are some possible situations where %Attachment_DestSysFailedLogin could be returned:
|
|
9 |
%Attachment_FileNotFound |
Cannot locate file. The following are some possible situations where %Attachment_FileNotFound could be returned:
|
|
11 |
%Attachment_NoFileName |
File transfer failed because no file name was specified. |
|
12 |
%Attachment_FileNameTooLong |
File transfer failed because name of selected file name is too long. Maximum is 64 characters. |
|
20 |
%Attachment_Unprocessed |
This file was not processed. The following are some possible situations where %Attachment_Unprocessed could be returned:
|
|
13 |
%Attachment_ViolationFound |
File violation detected by virus scan engine. |
|
14 |
%Attachment_VirusScanError |
Virus scan engine error. |
|
15 |
%Attachment_VirusConfigError |
Virus scan engine configuration error. |
|
16 |
%Attachment_VirusConnectError |
Virus scan engine connection error. |
|
21 |
%Attachment_Rejected |
File transfer failed because the file extension is not allowed. |
Example
&retcode = MAddAttachment(URL.MYFTP, ATTACHSYSFILENAME, 4, &MyFileArray, &MySzArray, &MyRtrnCodeArray, 0, False, "Upload Attachments", False, True);The following example demonstrates initialization of the arrays used to store the values returned by MAddAttachment:
&prompts = 2;
Local array of string &AttachUsrFiles;
&AttachUsrFiles = CreateArrayRept("", 0);
Local array of number &AttachSzs;
&AttachSzs = CreateArrayRept(0, 0);
Local array of number &AttachRtrnCds;
&AttachRtrnCds = CreateArrayRept(0, 0);
If Exact(Left(&URL_ID, 4), "URL.") Then
&sum_rt_cd = MAddAttachment(@(&URL_ID), ATTACHSYSFILENAME, &prompts, &AttachUsrFiles, &AttachSzs, &AttachRtrnCds);
Else
&sum_rt_cd = MAddAttachment(&URL_ID, ATTACHSYSFILENAME, &prompts, &AttachUsrFiles, &AttachSzs, &AttachRtrnCds);
End-If;
Syntax
MarkPrimaryEmailAddress(Type)Description
Use the MarkPrimaryEmailAddress function to specify which email address is the primary email address for the current user. You can only have one primary email address per user.
Parameters
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Type |
Specify the type that you want to change the email address to. This parameter takes a string value. The valid values are: |
|
Value |
Description |
|---|---|
|
BB |
Blackberry email address |
|
BUS |
Business email address |
|
HOME |
Home email address |
|
OTH |
Other email address |
|
WORK |
Work email address |
Returns
None.
Syntax
MarkWLItemWorked()Description
Use the MarkWLItemWorked function to mark the current Worklist entry as worked using this function. This function works only if you’ve invoked a page from the Worklist. This function should be called only in Workflow PeopleCode. You can use the %WLName system variable to check whether the page has been accessed using a Worklist.
Note: If the Worklist entry was created using a web service, and you do not need to send any additional information other than the Mark Worked reply message, you can use this function to mark the Worklist entry as worked. However, if you need to send additional data, you must use the WorklistEntry class SaveWithCustomData method to mark the Worklist entry as finished.
See SaveWithCustomData.
Parameters
None.
Returns
Returns a Boolean value indicating whether it executed successfully. The return value is not optional.
Example
This example, which would be in the WorkFlow event, checks to see whether a page check box MARK_WORKED_SW is selected, and if so, it marks the item in the worklist as complete:
If MARK_WORKED_SW = "Y" Then
If MarkWLItemWorked() Then
End-If;
End-If;Syntax
Max(param_list)Where param_list has the form
parameter1, parameter2 [, parameter3, . . . parameterN]Description
Use the Max function to determine the maximum value in the parameter list. The type of every item in the parameter list must be compatible with the first parameter in the list.
For example, if the first parameter is a string and the second parameter is a number with value 123.456, the second parameter is converted to the string "123.456" before the comparison is performed.
If all the values in the parameter list are alpha characters, "Z" is greater than "A" so Max("Z", "A") returns "Z".
Parameters
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
param_list |
Specify a list of items to be compared. All items in the parameter list must be of the same type. If a value isn't defined, the system assumes it's of the same type as the first parameter. |
Returns
The item in the list that has the maximum value.
Example
&RSULT = Max("A", "B", "C", "D", "E");Syntax
MCFBroadcast(ClusterID,QueueID, ChannelID, AgentState, AgentPresence, Message, MessageSetNumber, MessageNumber, DefaultMessage, SecurityLevel, ImportanceLevel, SenderId, NameValueString)Description
Use the MCFBroadcast function to broadcast a notification message. You can specify whether to send the message to agents, to a queue, or even system wide. This function is used with the MultiChannel Framework.
Parameters
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
ClusterID |
Specify the name of the cluster that you want to broadcast the message to, such as, RENCLSTR_001, as a string. |
QueueID |
Specify the name of the physical or logical queue that you want to broadcast the message to, such as, SALES, as a string. |
ChannelID |
Specify the name of the channel, or task, for the broadcast, such as Email, Chat, Voice or Generic, as a string. |
AgentState |
Specify the state of the agents you want to broadcast the message to, such as Available, as a string. |
AgentPresence |
Specify the presence of the agents you want to broadcast the message to, such as Active, as a string. |
Message |
Specify the text of the message you want to broadcast, as a string. |
MessageSetNumber |
Specify the message set number of a message from the message catalog if you want to broadcast a message from the message catalog. You must also specify values for the MessageNumber and DefaultMessageText parameters if you want to broadcast this type of message. Specify the message set number as a number. |
MessageNumber |
Specify the message number of a message from the message catalog if you want to broadcast a message from the message catalog. You must also specify values for the MessageSetNumber and DefaultMessageText parameters if you want to broadcast this type of message. Specify the message number as a number. |
DefaultMessageText |
Specify the text to be used if the specified message catalog message isn't found. Use the MessageSetNumber and MessageNumber parameters to specify the catalog message. Specify the default message text as a string. |
SecurityLevel |
Specify the security level for the broadcast message, as a string. |
ImportanceLevel |
Specify the importance level of the broadcast message, as a string. |
SenderID |
Specify the ID of the sender of the broadcast message, as a string. |
NameValueString |
Specify a string containing name-value pairs specific to your application. |
Returns
None.
Example
The following example would broadcast a message to a specific logical queue:
MCFBroadcast("", "SALES", "", "", "Best of Luck!", "", "", "Default Message", "PRIV1", "URGENT", "Admin", "EffDate, 2005-10-25:12:00:45");
Syntax
MessageBox(style, title, message_set, message_num, default_msg_txt[, paramlist])where paramlist is an arbitrary-length list of parameters of undetermined (Any) data type to be substituted in the resulting text string, in the form:
param1 [, param2]. . .Description
Use the MessageBox function to display a message box window. This function combines dialog-display ability with the text-selection functionality of MsgGet, MsgGetText, or MsgGetExplainText. The style parameter selects the buttons to be included. title determines the title of message.
Note: The title parameter is ignored for messages displayed in the PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture. The title of a message box displayed by the browser is always “Message”.
Also, style is ignored if the message has any severity other than Message.
The remaining parameters are used to retrieve and process a message selected from the Message Catalog.
MessageBox can be used for simple informational display, where the user reads the message, then clicks an OK button to dismiss the message box. Use MessageBox as a way of branching based on user choice, in which case the message box contains two or more buttons (such as OK and Cancel or Yes, No, and Cancel). The value returned by the function tells you which button the user clicked, and your code can branch based on that value.
In the MessageBox dialogs, both the Message Text and the Description, that is, more detailed information stored in the Message Catalog, are included.
If MessageBox displays buttons other than OK, it causes processing to stop while it waits for user response. This makes it a "user think-time" function, restricting its use to certain PeopleCode events.
See MsgGet, MsgGetText, MsgGetExplainTextThink-Time Functions.
Message Retrieval
MessageBox retrieves a message from the Message Catalog and substitutes the values of the parameters into the message and explanation.
You can access and update the Message Catalog by accessing You can enter message text in multiple languages. The message_set and message_num parameters specify the message to retrieve from the catalog. If the message is not found in the Message Catalog, the default message provided in default_msg_txt is used. Message sets 1 through 19,999 are reserved for use by PeopleSoft applications. Message sets 20,000 through 32,767 can be used by PeopleSoft users.
The optional paramlist is a comma-separated list of parameters; the number of parameters in the list is arbitrary. The parameters are referenced in the message text using the % character followed by an integer corresponding to the position of the parameter in the paramlist. For example, if the first and second parameters in paramlist were &FIELDNAME and &USERNAME, they would be inserted into the message string as %1 and %2. To include a literal percent sign in the string, use %%; %\ is used to indicate an end-of-string and terminates the string at that point. This is generally used to specify fixed-length strings with trailing blanks.
Message Severity
MessageBox specifies processing for error handling functions based on the message severity, which you can set in the Message Catalog. This enables you to change the severity of an error without changing the underlying PeopleCode, by setting the severity level for the message in the Message Catalog. The message severity settings and processing options are:
|
Severity |
Processing |
|---|---|
|
Message |
The message is displayed and processing continues. |
|
Warning |
The message is displayed and treated as a warning. |
|
Error |
The message is displayed and treated as an error. |
|
Cancel |
The message is displayed and forces a Cancel. |
In addition, in the PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture the Message Severity dictates how the message displays:
If the message has a severity of Warning, Error, or Cancel, the message is displayed in a pop-up dialog box with a single OK button regardless of the value of the style parameter.
If the message has a severity of Message and style is %MsgStyle_OK (0), the message displays in a pop-up dialog box with the single OK button.
If the message has a severity of Message and style is not %MsgStyle_OK (0), the message displays in a separate window.
Restrictions on Use in PeopleCode Events
If MessageBox displays any buttons other than OK, it returns a value based on the end user response and interrupts processing until the end user has clicked one of the buttons. This makes it a "user think-time" function, subject to the same restrictions as other think-time functions which means that it cannot be used in any of the following PeopleCode events:
SavePreChange.
Workflow.
RowSelect.
SavePostChange.
Any PeopleCode event that fires as a result of a ScrollSelect (or one of its relatives) function calls, or a Select (or one of its relatives) Rowset class method.
If the style parameter specifies a single button (that is, the OK button), the function can be called in any PeopleCode event.
Important! On the initial loading of a component (initial page Activate event), it is recommended that you allow the component to render correctly before you call any modality that requires user interaction (think-time functions).
If you call any modality that requires user interaction during the initial page Activate event, except if its a message box with only an OK button, the user interaction suspends the processing of the page load leading to undesired rendering. For example, the message box (with more than one button) loses its styling, and the rendering of the page and component is corrupted. If you use DoModalPopup or DoModalComponentPopup, you should note that it will render as a full page.
See Think-Time Functions.
Restrictions on Use With PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture
In the PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture, you can’t change the icon of a message box. You can change the number and type of buttons, and the default button, but the message always displays with the warning icon (a triangle with an exclamation mark in it.)
In addition, you can't change the message box title. The message box title is always 'Message'.
If the message has a severity of Warning and the MessageBox PeopleCode is in a SaveEdit event, the message is displayed in a new window with the OK and Cancel buttons.
Restrictions on Use With Application Engine
If you call MessageBox from a PeopleCode action in an Application Engine program, the syntax is the same. However, all GUI-related parameters like style and title are ignored. You should use 0 and "".
Note: If you have an existing MessageBox in code called from a page, it should work as is.
The actual message data is routed to PS_MESSAGE_LOG at runtime, and you can view it from the Process Monitor by drilling down to the process details.
Parameters
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
style |
Either a numerical value or a constant specifying the contents and behavior of the dialog box. This parameter is calculated by cumulatively adding either a value or a constant from each of the following list of categories: |
Note: In PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture style is ignored if the message has any severity other than Message. If the message has a severity of Warning and the MessageBox PeopleCode is in a SaveEdit event, the message is displayed in a new window with the OK and Cancel buttons.
|
Category |
Value |
Constant |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Buttons |
0 |
%MsgStyle_OK |
The message box contains one push button: OK. |
|
1 |
%MsgStyle_OKCancel |
The message box contains two push buttons: OK and Cancel. |
|
|
2 |
%MsgStyle_AbortRetryIgnore |
The message box contains three push buttons: Abort, Retry, and Ignore. |
|
|
3 |
%MsgStyle_YesNoCancel |
The message box contains three push buttons: Yes, No, and Cancel. |
|
|
4 |
%MsgStyle_YesNo |
The message box contains two push buttons: Yes and No. |
|
|
5 |
%MsgStyle_RetryCancel |
The message box contains two push buttons: Retry and Cancel. |
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
title |
Title of message box. If a null string is specified, then PeopleTools provides an appropriate value. |
Note: The title parameter is ignored for messages displayed in the PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture. The title of a message box displayed by the browser is always "Message".
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
message_set |
The message set number of the message to be displayed. When message set and number are provided, it overrides the specified text. A value less than one indicates that the message comes from the provided text and not the Message Catalog. |
message_num |
The message number of the message to be displayed. |
default_msg_txt |
Default text to be displayed in the message box. |
paramlist |
A comma-separated list of parameters; the number of parameters in the list is arbitrary. The parameters are referenced in the message text using the % character followed by an integer corresponding to the position of the parameter in the paramlist. |
Returns
Returns either a Number value or a constant. The return value is zero if there is not enough memory to create the message box. In other cases the following menu values are returned:
|
Value |
Constant |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|
|
-1 |
%MsgResult_Warning |
Warning was generated. |
|
1 |
%MsgResult_OK |
OK button was selected. |
|
2 |
%MsgResult_Cancel |
Cancel button was selected. |
|
3 |
%MsgResult_Abort |
Abort button was selected. |
|
4 |
%MsgResult_Retry |
Retry button was selected. |
|
5 |
%MsgResult_Ignore |
Ignore button was selected. |
|
6 |
%MsgResult_Yes |
Yes button was selected. |
|
7 |
%MsgResult_No |
No button was selected. |
Example
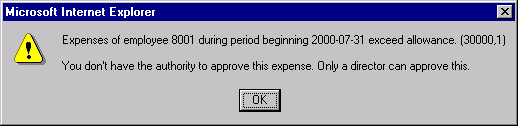
Suppose the following string literal is stored in the Message Catalog as the message text:
Expenses of employee %1 during period beginning %2 exceed allowance.The following is stored in the Explanation:
You do not have the authority to approve this expense. Only a director
can approve this. Here %1 is a placeholder for the employee ID and %2 a placeholder for the expense period date. The following MessageBox call provides bind variables corresponding to these placeholders at the end of its parameter list:
MessageBox(0, "", 30000, 1, "Message not found.", BUS_EXPENSE_PER.EMPLID, BUS_EXPENSE_PER.EXPENSE_PERIOD_DT);If the message severity is Error or Warning, the call would display a message box similar to this:
Suppose the following is stored in the Message Catalog as the message text:
File not found.The following is stored in the Explanation:
The file you specified wasn't found. Either select retry, and specify a new file, or cancel.Suppose this message had a Severity of message, and you used the %MsgStyle_RetryCancel, in the following code:
MessageBox(%MsgStyle_RetryCancel, "", 30000, 2, "Message not found.");This is how the message displays:

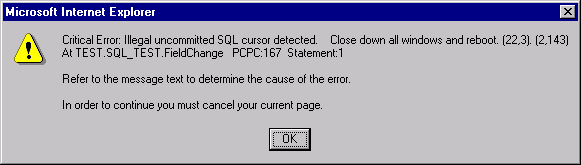
If the message severity is of type Cancel, a critical message is displayed similar to the following:
Syntax
Min(param_list)Where param_list has the form
parameter1, parameter2 [, parameter3, . . . parameterN]Description
Use the Min function to determine the minimum value in the parameter list. The type of every item in the parameter list must be compatible with the first parameter in the list.
For example, if the first parameter is a string and the second parameter is a number with value 123.456, the second parameter is converted to the string "123.456" before the comparison is performed.
If all the values in the parameter list are alpha characters, "a" is less than "m", so Min("a", "m") returns "a".
Parameters
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
param_list |
Specify a list of items to be compared. All items in the parameter list must be of the same type. If a value isn't defined, the system assumes it's of the same type as the first parameter. |
Returns
The item in the list that has the minimum value.
Example
&RES = Min(&A, Max(&B, &C, &D), "-20");Syntax
Minute(timevalue)Description
Use the Minute function to extract the minute component of a Time value.
Returns
Returns the minute part of timevalue as a Number data type.
Example
If &TIMEOUT contains "16:48:01" then the example sets &TIMEOUT_MINUTES to 48:
&TIMEOUT_MINUTES = Minute(&TIMEOUT);Syntax
Mod(x, divisor)Description
The Mod function is the modulus math function, which divides one number (x) by another (divisor) and returns the remainder.
Returns
Returns a Number equal to the remainder of the division of the number x by divisor.
Example
The example sets &NUM1 to 1 and &NUM2 to 0:
&NUM1 = Mod(10,3);
&NUM2 = Mod(10,2);Syntax
Month(datevalue)Description
Use the Month function to return the month of the year as an integer from 1 to 12 for the specified datevalue. The Month function accepts a date or DateTime value as a parameter.
Parameters
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
datevalue |
A date or DateTime value on the basis of which to determine the month. |
Returns
Returns a Number value from 1 to 12 specifying the month of the year.
Example
This example sets &HIRE_MONTH to 3:
&HIREDATE = DateTime6(1997, 3, 15, 10, 9, 20);
&HIRE_MONTH = Month(&HIRE_DATE);Syntax
MsgGet(message_set, message_num, default_msg_txt[, paramlist])where paramlist is an arbitrary-length list of parameters of undetermined (Any) data type to be substituted in the resulting text string, in the form:
param1 [, param2]. . .Description
Use the MsgGet function to retrieve the Message Text text of a message from the Message Catalog and substitutes in the values of the parameters into the message text
You can access and update messages on the Message Catalog page (select PeopleTools, Utilities, Administration, Message Catalog). You can enter message text in multiple languages. The Message Catalog also enables you to enter more detailed description text about the message. The message_set and message_num parameters specify the message to retrieve from the catalog. If the message is not found in the Message Catalog, the default message provided in default_msg_txt is used. Message sets 1 through 19,999 are reserved for use by PeopleSoft applications. Message sets 20,000 through 32,767 can be used by PeopleSoft users.
The optional paramlist is a comma-separated list of parameters; the number of parameters in the list is arbitrary. The parameters are referenced in the message text using the % character followed by an integer corresponding to the position of the parameter in the paramlist. For example, if the first and second parameters in paramlist were &Fieldname and &Username, they would be inserted into the message string as %1 and %2. To include a literal percent sign in the string, use %%; %\ is used to indicate an end-of-string and terminates the string at that point. This is generally used to specify fixed-length strings with trailing blanks.
MsgGet prefixes the message with "[Message Set# and Message Error#]", so it can be processed by a user not conversant in the translated language.
Example
&MsgText = MsgGet(30000, 2, "Message not found");Syntax
MsgGetExplainText(message_set, message_num, default_msg_txt[, paramlist])where paramlist is an arbitrary-length list of parameters of undetermined (Any) data type to be substituted in the resulting text string, in the form:
param1 [, param2]. . .Description
Use the MsgGetExplainText function to retrieve the Description text of a message from the Message Catalog and substitutes the values of the parameters in paramlist into the Description text. It returns the resulting message as a String data type.
You can access and update messages on Message Catalog page (select PeopleTools, Utilities, Administration, Message Catalog). You can enter messages in multiple languages.
Message sets 1 through 19,999 are reserved for use by PeopleSoft applications. Message sets 20,000 through 32,767 can be used by PeopleSoft users.
Unlike the MsgGet function, MsgGetExplainText returns the message without a message set and message number appended to the message.
Parameters
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
message_set |
Specify the message set to be retrieved from the catalog. This parameter takes a number value. |
message_num |
Specify the message number to be retrieved from the catalog. This parameter takes a number value. |
default_msg_txt |
Specify the text to be displayed if the message isn't found. This parameter takes a string value. |
paramlist |
Specify values to be substituted into the message explain text. The parameters listed in the optional paramlist are referenced in the message explain text using the % character followed by an integer referencing the position of the parameter in the function call. For example, if the first and second parameters in paramlist were &FIELDNAME and &USERNAME, they would be inserted into the message string as %1 and %2. To include a literal percent sign in the string, use %%; %\ is used to indicate an end-of-string and terminates the string at that point. This is generally used to specify fixed-length strings with trailing blanks. |
Example
Suppose the following Description text is stored in the Message Catalog:
A reference was made to a record.field (%1.%2) that is not defined within Application Designer. Check for typographical errors in the specification of the record.field or use Application Designer to add the new field or record.Here %1 is a placeholder for the record name and %2 a placeholder for the field name. If the record.field in error was MyRecord.Field5, the above would resolve as follows:
A reference was made to a record.field (MYRECORD.FIELD5) that is not defined within Application Designer. Check for typographical errors in the specification of the record.field or use Application Designer to add the new field or record.Syntax
MsgGetText(message_set, message_num, default_msg_txt[, paramlist])where paramlist is an arbitrary-length list of parameters of undetermined (Any) data type to be substituted in the resulting text string, in the form:
param1 [, param2]. . .Description
Use the MsgGetText function to retrieve the Message Text text of a message from the Message Catalog and substitutes the values of the parameters in paramlist into the message. It returns the resulting message as a String data type.
You can access and update messages on Message Catalog page (select PeopleTools, Utilities, Administration, Message Catalog). You can enter message text in multiple languages. The message_set and message_num parameters specify the message to retrieve from the catalog. If the message is not found in the Message Catalog, the default message provided in default_msg_txt is used. Message sets 1 through 19,999 are reserved for use by PeopleSoft applications. Message sets 20,000 through 32,767 can be used by PeopleSoft users.
The parameters listed in the optional paramlist are referenced in the message text using the % character followed by an integer referencing the position of the parameter in the function call. For example, if the first and second parameters in paramlist were &FIELDNAME and &USERNAME, they would be inserted into the message string as %1 and %2. To include a literal percent sign in the string, use %%; %\ is used to indicate an end-of-string and terminates the string at that point. This is generally used to specify fixed-length strings with trailing blanks.
Unlike the MsgGet function, MsgGetText returns the message without a message set and message number appended to the message.
Example
&MsgText = MsgGetText(30000, 2, "Message not found");