Testing Raw Data
This section discusses how to:
Upload raw test data from a file.
Manually enter raw test data.
PeopleSoft enables you to upload raw document data from files and test it in the Document Tester.
The Document Tester features an Enter Input Data page (IB_LOGTESTER_SEC) that you use to upload raw test data from files. To access the page select and click the Enter Input Data button.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Enter Input Data page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
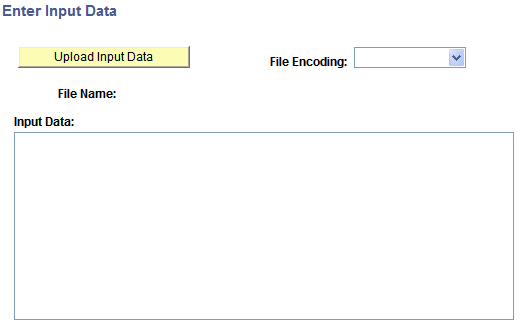
After you access Enter Input Data page you click the Upload Input Data button to specify the file to upload and test. You use the File Attachment page (IB_LOGTESTER_SEC) to upload the attachment:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the File Attachment page. Use the page to browse for and upload the raw data file to test.
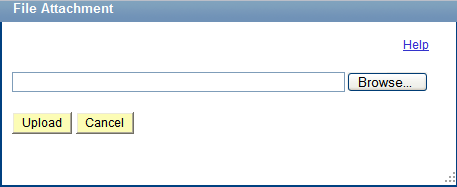
To upload raw test data from a file:
Access the Document Tester ()
Click the Provide Input Data button.
The Enter Data Input page appears.
From the File Encoding drop-down list, select the file encoding of the file you are uploading. The options are:
Non-encoded.
UTF-8.
UTF-16.
Click the Upload Input Data button. The File Attachment page appears.
Click the Browse button to navigate to and select the file to upload.
Click the Upload button.
The Enter Data Input page appears and the content of the raw data file appears in the Input Data section of the page.
Click the OK button to return to the Document Tester page where you generate and view the test results.
Generating and viewing test documents is described in the next section.
To manually enter data to test you use the Enter Data Input page described in the previous section.
To manually enter data to test:
Access the Document Tester (.
Click the Provide Input Data button.
The Enter Data Input page appears.
In the Input Data box enter the data to test.
Click the OK button to return to the Document Tester page where you generate and view the test results.
Generating and viewing test documents is described in the next section.