Working with Custom Configuration Plug-ins
In addition to the plug-ins delivered by PeopleSoft, PeopleSoft allows you to create custom configuration plug-ins required for your specific environment.
A plug-in is an application class that corresponds to each configuration within a template. For example, to configure IB Gateway nodes, the application class (plug-in) PTIBConfigureGatewayNodes in the application package PTEM_CONFIG
Working with configuration plug-ins includes the following:
Creating a configuration plug-in.
Registering a configuration plug-in.
Adding a configuration plug-in to a template.
See Creating a Template.
Migrating a plug-in using ADS definition.
To create a configuration plug-in:
Use the PTEM_CONFIG application package to create a plug-in. If you need to use a custom package, ensure that the custom package starts with PTEM_CONFIG.
Write the plug-in class. The new plug-in class must extend from the base class — PTEM_CONFIG:EMConfigurationPlugin.
Override and implement the four base class methods:
getProperties - to provide plug-in properties and their details.
For example:
method getProperties /+ Returns Array of PTEM_CONFIG:PTEMVariableProperty +/ /+ Extends/implements PTEM_CONFIG:EMConfigurationPlugin.getProperties +/ Local array of PTEM_CONFIG:PTEMVariableProperty &propArray = Null; ---add the properties as shown below--------------- &variableProperty = create PTEM_CONFIG:PTEMVariableProperty("property_name", "datatype", True/False (is required?), True/False(is password?), "default value", Message set number of property description, message number, "default message", Null); &propArray.Push(&variableProperty); ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Return &propArray; end-method;Add the following base class methods:
validateVariables - to validate the plug-in property values.
configureEnvironment - to configure the environment with the provided values.
validateConfigurations - to validate whether the values are correctly configured.
dependant_plugins - to provide the names of dependent plug-ins.
For example:
method dependant_plugins /+ Returns Array of String +/ /+ Extends/implements PTEM_CONFIG:EMConfigurationPlugin.dependant_plugins +/ Local array of string &dependant_array; &dependant_array = CreateArray(""); -----add the plugins as comma seprated values, that this plugin depends on for its execution Return &dependant_array; end-method;getPluginHelpMessage - to provide a brief description of a plug-in.
For example:
method getPluginHelpMessage /+ Returns PTEM_CONFIG:PTEMHelpMessage +/ /+ Extends/implements PTEM_CONFIG:EMConfigurationPlugin.getPluginHelpMessage +/ Local PTEM_CONFIG:PTEMHelpMessage &tempMessage = Null; &tempMessage = create PTEM_CONFIG:PTEMHelpMessage(0, 0, "", Null); ---- "add the message set number, message number and default message of the help message" Return &tempMessage; end-method;isInternalPlugin - to differentiate between plug-ins that can be used internally by developers and externally by customers.
Valid values are:
False - specifies that the plug-in can be used by customers, and the plug-in can be added in a template in PIA.
True - implies that the plug-in can be used only through command line and will not be available in PIA.
For example:
method isInternalPlugin /+ Returns Boolean +/ /+ Extends/implements PTEM_CONFIG:EMConfigurationPlugin.isInternalPlugin +/ Return False; end-method;
Note: When you create a configuration plug-in an application package, the plug-in must be registered through the automated configuration management framework so that it can be included in a template for configuration through PIA. If a plug-in is not registered, it can be used only for execution through command line.
Use the Register Plugin page to register a configuration plug-in, which includes assigning a category for the plug-in.
Access the Register Plugin page using the following navigation path:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Register Plugin page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
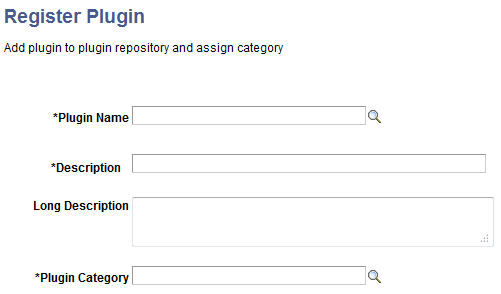
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Plugin Name |
Select the plug-in that you created. Note: If the isInternalPlugin method of a plug-in class is defined as false, the plug-in will be available in the Plugin Name list. |
Description |
Enter a description for the plug-in. |
Long Description |
Optionally, you may enter a long description for the plug-in. |
Plugin Category |
Select a category to which the plug-in will belong. Currently, the following categories are available:
|