Establishing Retirement Types and Eligibility Conditions
To establish retirement types and eligibility conditions, use the Benefit Eligibility (BENEFIT_ELIG) component.
This topic provides an overview of retirement types and eligibility conditions and discusses how to establish these definitions.
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
|
PA_BENELIG_EZ |
Establish retirement types and eligibility criteria. |
Your plans most likely provide for several types of retirement benefits (for example, early, normal, and late retirement) and ancillary benefits (for example, death and disability). The criteria you define—typically age and service for retirement benefits—determine whether employees are eligible for particular benefits. You set up these criteria on the Benefit Eligibility - Benefit Eligibility page.
Use the Benefit Eligibility page (PA_BENELIG_EZ) to establish retirement types and eligibility criteria.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Benefit Eligibility page.
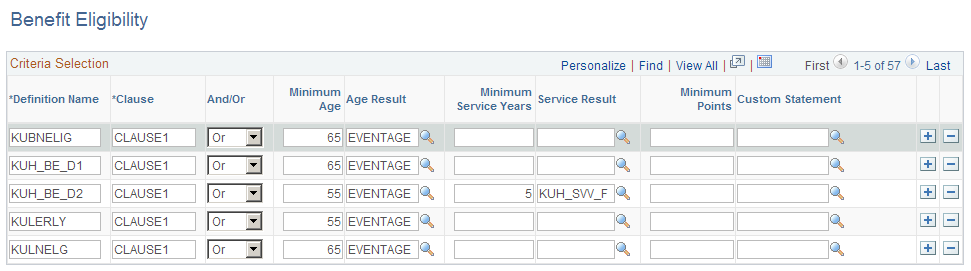
You'll see multiple definitions on this page. You can create additional definitions or add clauses to existing definitions. This is different from other functions, where you create additional definitions by accessing a component with the add action.
Note: If you want to see definitions in a particular order (for example, grouped by plan), create a naming standard so that the definitions appear on the page in alphabetical order.
Each definition consists of one or more eligibility clauses. To meet the eligibility requirements of a clause, an employee must meet all the criteria in that clause—that is, conditions within a row are connected with and. When a definition consists of multiple clauses, choose whether to connect the clauses with and or or logic.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Definition Name |
Name and identify definitions. Each row is a single clause in a definition. |
Clause |
When you create the first clause of a definition, enter a unique definition name. Enter the same definition name when you create additional clauses, and then distinguish the clauses by entering a unique value in the Clause field. PeopleSoft suggests numbering the clauses within a definition to easily see how many clauses there are. |
And/Or |
If a definition has multiple clauses, link clauses with and and or connectors. The system evaluates each clause independently and compares it to the cumulative result of all previous clauses. Therefore the order of the clauses is extremely important. |
Minimum Age (minimum age) |
Enter the minimum age. |
Age Result |
Enter the age result. The age result is the alias for an employee's age. It is a duration alias, typically for the employee's age at benefit commencement date. |
Minimum Service Years (minimum service) |
Specify the minimum service requirement. |
Service Result |
Specify the service (function) result that provides the employee service information. |
Minimum Points (minimum points) |
Specify the minimum points (age + service) requirement. |
Custom Statement |
Specify customized additional rules for eligibility requirements. |
Setting Other Eligibility Parameters
Benefit eligibility rules can contain a wide range of additional requirements. For example, eligibility rules for death benefits can check for the date of death field in the personal data record or look for a death action in an employee's job record. Furthermore, eligibility for a death benefit might depend on whether the employee was married at the time of death. The Custom Statement utility handles this type of logic.
A custom statement should
consist of a Boolean statement. An employee who meets the conditions
is deemed to meet the eligibility requirements. For example, if a
special early retirement is available to those in Union 81, you might
use a statement like this: If Union Code is equal
to 81. (As with all group custom statements, the then portion
is implied.)