Establishing Actuarial Assumption Sets
To set up actuarial assumption sets, use the Actuarial Assumptions (ACTUARIAL_FACTORS) and Mortality Rates (MORTALITY_RATES) components.
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
|
PA_FACTORS_MORT |
Set up the mortality basis table to use and any adjustments you make. |
|
|
PA_FACTORS_INT |
Set up an interest rate assumption. |
|
|
PA_FACTORS_PAYMT |
Set up the payment timing assumptions. |
|
|
PA_MORT_RATES |
Set up the assumed death rates by age. |
Use the Mortality Basis page (PA_FACTORS_MORT) to set up the mortality basis table to use and any adjustments you make.
Mortality tables include assumptions about annuitants' life expectancies. You set up the mortality tables before you establish the assumption sets.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Mortality Basis page.
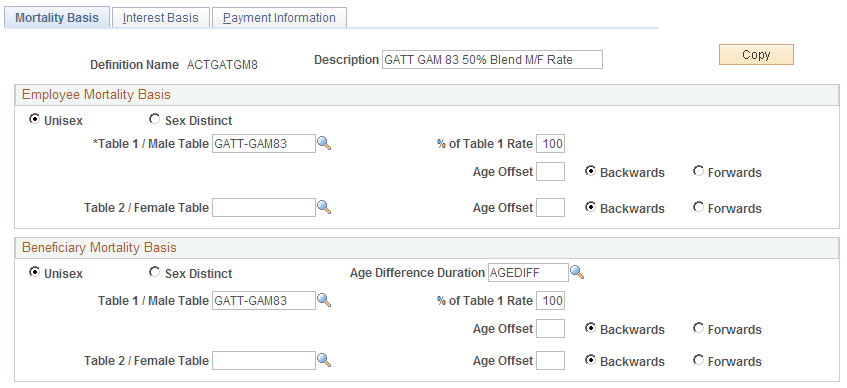
Employee Mortality Basis and Beneficiary Mortality Basis
An annuity provides an ongoing benefit for the life of a participant. Some payment forms also provide a continuing annuity for a beneficiary. Your actuarial assumption set must therefore have both an employee mortality basis and a beneficiary mortality basis. The parameter sets are identical, but they are applied to different individuals.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Unisex or Sex Distinct |
Select Sex Distinct to use one table, and select the table name in the Table 1 / Male Tablefield. Select Unisex to use a blend of male and female mortality tables. Then select the table names in the Table 1 / Male Table and Table 2 / Female Tablefields. In the % of Table 1 Rate field, enter a percentage that indicates the weight to assign to Table 1 in determining the final rate. For example, if you enter 75, the system computes the blended rate by adding 75 percent of the Table 1 rate and 25 percent of the Table 2 rate. Some tables—for example, the GAR94 and the GATT_GAM83 tables, which are supplied with the system—already include blended rates. Note: You only use sex distinct tables for reproducing historical calculations. It is currently illegal to use sex distinct mortality tables. |
Age Offset |
Select this option to use the mortality rate for an age which is a specified number of years older or younger than the actual age of the participant or beneficiary. Enter the number of years to adjust by, and select either Back or Forward to indicate whether the adjustment is to a younger or older age. |
Age Difference Duration |
This options appears only in the Beneficiary Mortality Basis group box. Enter a duration that measures the difference between the employee and beneficiary ages. This enables the system to more efficiently access the appropriate mortality information. Note: You do not need the actual employee and beneficiary ages at this point. You put those in the definitions of the functions that use actuarial assumptions. |
Use the Interest Basis page (PA_FACTORS_INT) to set up an interest rate assumption.
An actuarial assumption set must include an interest rate assumption. This enables the calculation to consider the potential gain or loss of interest resulting from an early or late benefit commencement.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Interest Basis page.
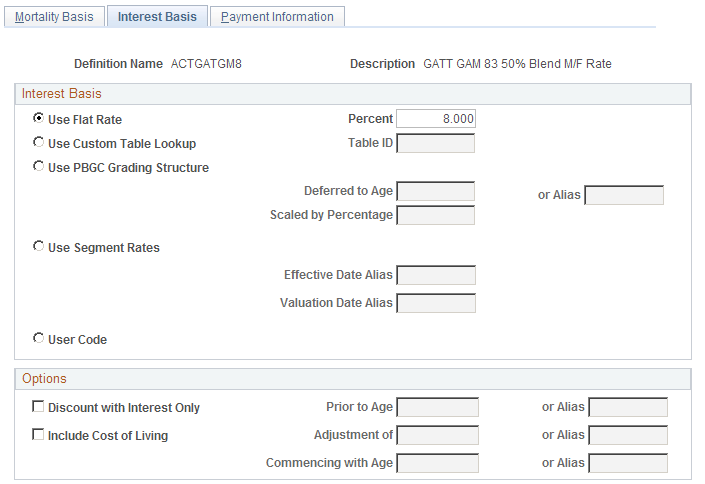
Interest Basis
Select one of the following options, and enter information in the associated field or fields.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Use Flat Rate of |
Select this option to use a specified interest rate, and enter the assumed interest rate in the adjacent % field. |
Use Custom Table Lookup |
Select this option to use a Table Lookup to get the interest rate from a standard rate table. In the Table ID field, enter the name of a table lookup alias to reference the table. Note: PeopleSoft delivers a rate table for 30-year treasury bond rates. If you use this table, you still need to set up a table lookup alias to reference it. |
Use PBGC Grading Structure (use Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation grading structure) |
Select this option to use the PBGC grading structure. This grading structure applies interest over a number of years, typically from the event date to the benefit deferral date if, for example, an employee terminates at age 40 but does not receive a benefit until age 65. The PBGC grading structure includes:
If you use PBGC grading, also enter information in these fields:
See PBGC Rates Page. |
Use Segment Rates |
Select this option to use the Segment Rate table. Segment rates are based on the yields on high quality corporate bonds as determined by the Internal Revenue Service. Different rates apply to different time periods; up to three different interest rates can be used depending on the duration of the liability. If you use segment rates, you can optionally enter information in these fields:
|
Options
Select one or more of the following options, and enter information in the associated field or fields.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Discount with Interest Only |
Select this option to disregard the mortality rates for employees under a certain age and instead use the interest assumptions. Specify the cutoff age in the Prior to Age field. |
Include Cost of Living |
Select this option if you want the assumption set to take into account an assumed cost of living adjustment (COLA). In the Adjustment of field, enter the adjustment percentage. In the Commencing with Age field, enter the age when you assume the adjustment is to occur. |
Use the Payment Information page (PA_FACTORS_PAYMT) to set up the payment timing assumptions.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Payment Information page.
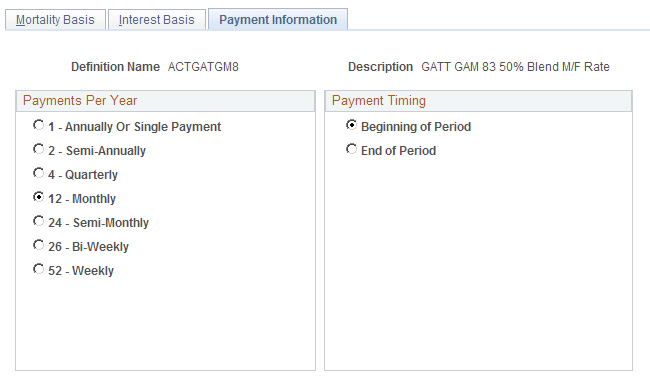
Payments Per Year
Select the assumed number of payments per year.
Note: Most pension plans make 12 monthly payments.
Payment Timing
Select either Beginning of Period or End of Period to indicate when the period payments occur.
Use the Mortality Rates page (PA_MORT_RATES) to set up the assumed death rates by age. These rates support the mortality assumptions in your actuarial assumption set.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Mortality rates page.
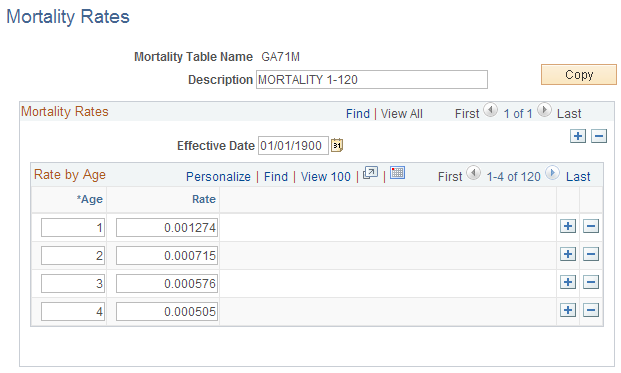
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Effective Date |
If the mortality rates for a particular mortality table change, create a new effective-dated row in the table definition. |
The following mortality tables are delivered:
PPAMORT: Mortality Table for the Pension Protection Act of 2006.
The IRS will provide a new updated Mortality table annually to account for the improved mortality. PeopleSoft Pension Administration will deliver this table annually to its customers.
GA71M: Male GAM71 table
GA71F: Female GAM71 table
GA83M: Male GAM83 table
GA83F: Female GAM83 table
GATT_GAM83: The blended table using 50 percent of the GAM83 male mortality rates and 50 percent of GAM83 female mortality rates published by the IRS. As a result of the General Agreements on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), this table is used when actuarially increasing or reducing 415 limits and for determining the present value of lump sum payments.
Note: GAR94, the 1994 Group Annuity Reserving Table, described below, has replaced the GATT_GAM83 table.
GAR94: The blended table using 50 percent of the male mortality rates and 50 percent of the female mortality rates from the 1994 Group Annuity Reserving Table projected to 2002. This table replaces the GATT_GAM83 table when actuarially increasing or reducing 415 limits and when determining the present value of lump sum payments as a result of IRS Revenue Ruling 2001-62.
UP1984: Unisex table.