 Understanding Tax Processing
Understanding Tax ProcessingThis chapter provides an overview of tax processing and discusses how to:
Define tax registration.
Set up payee overrides for tax calculation.
 Understanding Tax Processing
Understanding Tax ProcessingThis section discusses:
Delivered tax elements.
Tax calculation.

 Delivered Tax Elements
Delivered Tax ElementsGlobal Payroll for China delivers five tax deductions:
NORM TAX
DONATION
ANN BON TAX
SEVERANCE TX
INTERN TAX
These deductions along with the key supporting elements associated with them are discussed in the "Setting Up Deductions" chapter.
See Delivered Supporting Elements.

 Tax Calculation
Tax CalculationThis section discusses:
Overall tax calculation process.
Normal tax calculation.
Annual bonus tax calculation.
Severance tax calculation.
Intern tax.
Overall Tax Calculation Process
This diagram illustrates the flow of the overall tax calculation process:
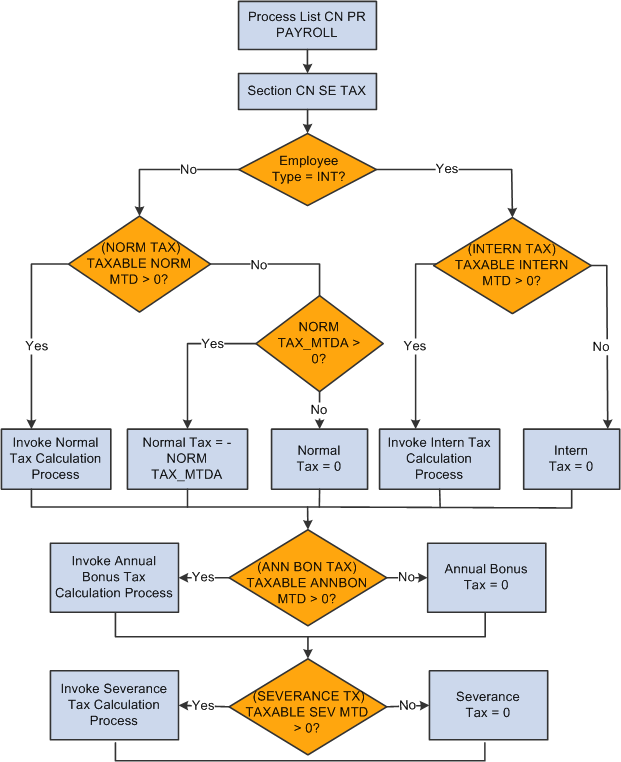
Overall tax calculation process
The tax section CN SE TAX calls each tax deduction sequentially to perform tax calculation: NORM TAX, ANN BON TAX, SEVERANCE TX, and INTERN TAX. It then calls a formula to insert tax values into the tax writable array CN WA TAX REPORT after each calculation.
This diagram illustrates the flow of normal tax calculation:
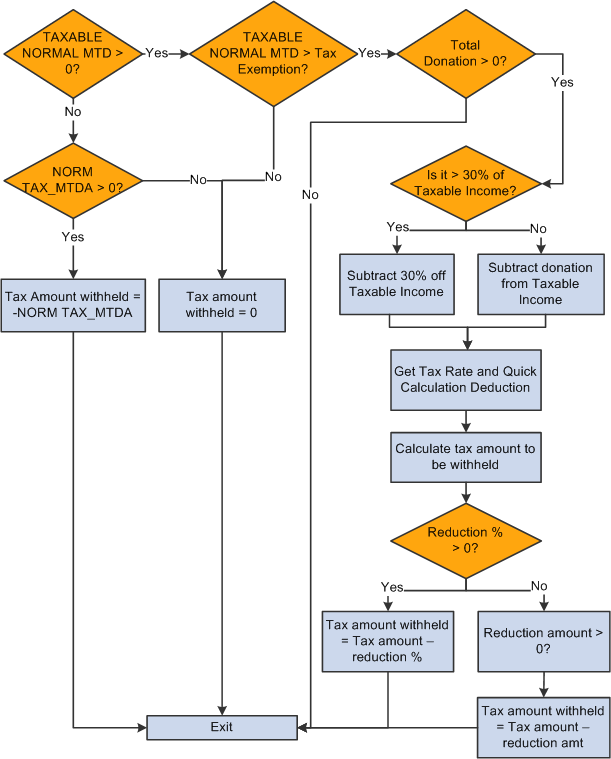
Normal tax calculation
The NORM TAX deduction invokes the formula CN FM CALC NORM TX, which derives normal tax from calculated normal salary. The formula references bracket CN BR TX EXEMPTION to load tax exemption according to the employee type CN VR EE TYPE. It calls formula CN FM DONATION to deduct the tax-exempt portion of donations from the taxable income if any donations exist. CN FM CALC NORM TX then calls formula CN FM CALC TAX to calculate tax.
The formula CN FM CALC NORM TX:
Deducts tax exemption CN BR TX EXEMPTION from taxable normal salary TAXABLE NORMAL MTD to get taxable income.
Calls CN FM DONATION to subtract the tax-exempt portion of donation from step 1 if any donations exist.
If the total donation is greater than 30% of the taxable income from step 1, the 30% of taxable income becomes the tax-exemption portion and the system deducts it from the amount derived in step 1 to obtain the final taxable income, CN VR TAX INCOME.
If the total donation is less than 30% of the taxable income from step 1, the entire donation is tax exempted and the system deducts it from the amount derived in step 1 to get the final taxable income, CN VR TAX INCOME.
Calls formula CN FM CALC TAX.
References the tax table CN BR TAX RATE to obtain the tax rate and quick calculation deduction to derive the withholding amount for the payee's normal salary for one pay period in the current financial year.
Subtracts the reduction from the tax amount if the payee is eligible for disability reduction. If a payee override exists, the assumption is that it overrides an amount; otherwise, the formula uses the percent value retrieved from the CN BR TX EXEMPTION bracket.
Therefore, if an override exists, the tax withheld equals the tax amount from step 3a minus the override amount. If the tax withheld is less than zero, the formula sets the tax to zero. If no override exists, the formula subtracts the reduction percent from the tax withheld from step 3a.
Deducts any normal tax already paid.
If TAXABLE NORMAL MTD is less than tax exemption and normal tax exists from earlier segments in the period, makes NORM TAX_MTDA negative to reverse calculated amount. Otherwise, sets NORM TAX_MTDA to 0.
This diagram illustrates the flow of annual bonus tax calculation:
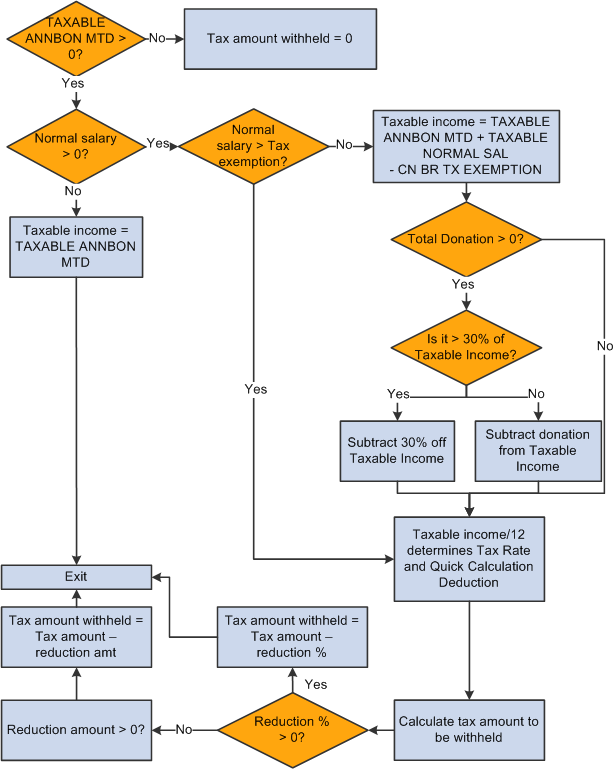
Annual bonus tax calculation
The ANN BONUS TAX deduction invokes the formula CN FM CALC SP TAX, which derives the annual bonus tax based on calculated annual bonus. If any unused tax exempted amount exists when the normal salary is lower than the tax exemption, the system subtracts it from taxable income. It calls formula CN FM DONATION to deduct the tax-exempt portion of donations from the taxable income if normal tax was not calculated because normal salary is lower than the tax-exempt amount. CN FM CALC SP TAX then calls formula CN FM CALC TAX to calculate tax.
The formula CN FM CALC SP TAX:
Calculates the taxable income by subtracting the unused portion of tax exemption if normal salary exists and no normal tax was calculated. In this case, taxable income = TAXABLE ANNBON MTD + TAXABLE NORMAL SAL – CN BR TX EXEMPTION. This taxable income is divided by 12 to find the tax rate and quick calculation deduction.
If normal salary is greater than the tax exemption, then taxable income equals the annual bonus amount. In this case, taxable income = TAXABLE ANNBON MTD. This taxable income is divided by 12 to find the tax rate and quick calculation deduction.
Calls formula CN FM CALC TAX.
References the tax table CN BR TAX RATE to obtain the tax rate and quick calculation deduction to derive the withholding amount for the payee's normal salary for one pay period in the current financial year.
Subtracts the reduction from the tax amount if the payee is eligible for disability reduction. If a payee override exists, the assumption is that it overrides an amount; otherwise, the formula uses the percent value retrieved from the CN BR TX EXEMPTION bracket.
Therefore, if an override exists, the tax withheld equals the tax amount from Step 3a minus the override amount. If the tax withheld is less than zero, the formula sets the tax to zero. If no override exists, the formula subtracts the reduction percent from the tax withheld from step 3a.
Subtracts any annual bonus tax already calculated in the month.
This diagram illustrates the flow of severance tax calculation:
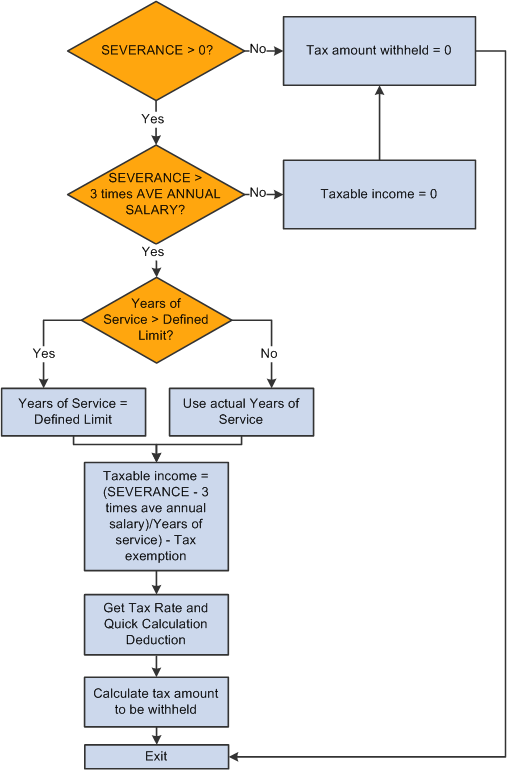
Severance tax calculation
The SEVERANCE TX deduction invokes the formula CN FM CALC SEV TAX, which derives severance tax from the calculated severance payment. CN FM CALC SEV TAX then calls formula CN FM CALC TAX to calculate tax.
The formula CN FM CALC SEV TAX:
Calculates taxable income.
If severance pay is below 3 times the city average annual salary, the system exempts it from tax. In this case, taxable income = 0.
If severance pay is 3 times higher than last year's city average annual salary, the system calculates tax based on the amount above 3 times the city average annual salary of last year by allocating the amount into the number of months equivalent to total years of service for the current employer. If years of service is more than the defined limit, the formula caps the value at that limit. In this case, taxable income = severance pay – 3 times city average annual salary ÷ years of service.
Note. PeopleSoft Enterprise Global Payroll for China delivers a years-of-service limit of 12. When determining years of service for a payee, the system rounds up to the nearest integer.
Calls formula CN FM CALC TAX.
References the tax table CN BR TAX RATE to obtain the tax rate and quick calculation deduction to derive the withholding amount for the payee's normal salary for one pay period in the current financial year.
Subtracts the reduction from the tax amount if the payee is eligible for disability reduction. If a payee override exists, the assumption is that it overrides an amount; otherwise, the formula uses the percent value retrieved from the CN BR TX EXEMPTION bracket.
Therefore, if an override exists, the tax withheld equals the tax amount from step 2a minus the override amount. If the tax withheld is less than zero, the formula sets the tax to zero. If no override exists, the formula subtracts the reduction percent from the tax withheld from step 2a.
Multiplies calculated tax by the years of service to calculate the final amount of tax withheld.
Subtracts any severance tax already calculated in the month.
Intern Tax
This diagram illustrates the flow of intern tax calculation:
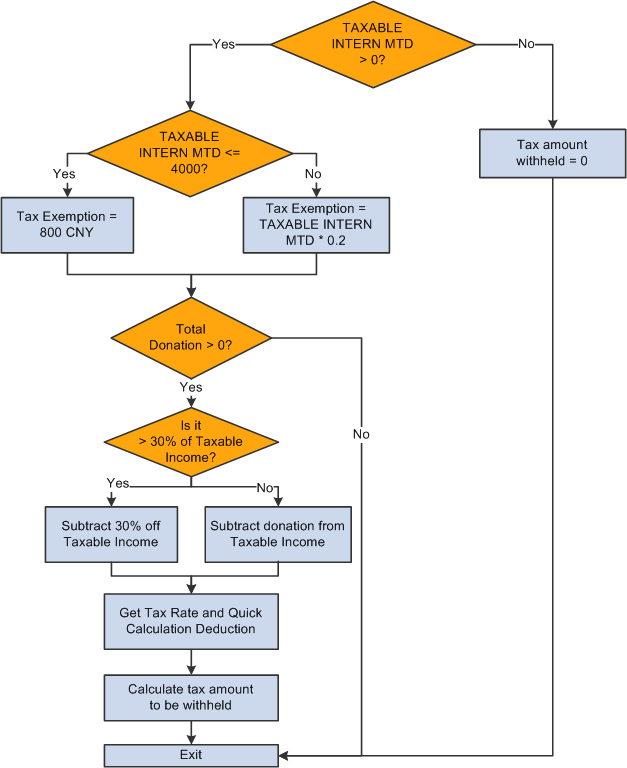
Intern tax calculation
The INTERN TAX deduction invokes formula CN FM CALC INTN TX, which calculates normal salary to derive intern tax. It then calls CN FM INTN TAX, which inserts the intern tax calculation values into the CN WA TAX REPORT writable array for tax reporting purposes.
The formula CN FM CALC INTN TX:
Calculates taxable income (CN VR TAX INCOME).
If TAXABLE INTERN MTD is less than or equal to 4,000 CNY, then CN VR TAX INCOME = TAXABLE NORMAL MTD – CN VR EXMPT AMT.
If TAXABLE INTERN MTD is greater than 4,000 CNY, then CN VR TAX INCOME = TAXABLE NORMAL MTD – (TAXABLE NORMAL MTD * CN VR EXMPT PCT).
Calls CN FM DONATION to subtract the tax-exempt portion of donation from step 1 if any donations exist.
If the total donation is greater than 30% of the taxable income from step 1, the 30% of taxable income becomes the tax-exemption portion and the system deducts it from the amount derived in step 1 to obtain the final taxable income, CN VR TAX INCOME.
If the total donation is less than 30% of the taxable income from step 1, the entire donation is tax exempted and the system deducts it from the amount derived in step 1 to get the final taxable income, CN VR TAX INCOME.
References the tax table CN BR TAX RT INTN to obtain the tax rate and quick calculation deduction to derive the withholding amount for the payee's intern salary for one pay period in the current financial year.
Calls the formula CN FM TX REDUCTION if the employee is disabled.
Deducts any intern tax already paid.
 Defining Tax Registration
Defining Tax Registration
This section discusses how to define tax registration for pay entities.

 Page Used to Define Tax Registration for Pay Entities
Page Used to Define Tax Registration for Pay Entities|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
GPCN_TAX_REG |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Framework, Organizational, Tax Registration CHN |
Define tax registration information for pay entities. |

 Defining Tax Registration for Pay Entities
Defining Tax Registration for Pay EntitiesAccess the Tax Registration CHN page (Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Framework, Organizational, Tax Registration CHN).
You must define tax registration details for each tax area within a pay entity.
 Setting Up Payee Overrides for Tax Calculation
Setting Up Payee Overrides for Tax Calculation
This section provides an overview of payee overrides for tax calculation and discusses how to add them.

 Payee Overrides for Tax Calculation
Payee Overrides for Tax CalculationGlobal Payroll for China delivers two tax-related variables that you can modify for payees using supporting element overrides:
CN VR EE TYPE (Employee Type)
CN VR TAX AREA (Tax Area)
Employee Type
The employee type, as defined by the CN VR EE TYPE variable, is used by the CN BR TX EXEMPTION and CN BR TX INTN EXEM brackets to determine a payee's tax exemption. Four values exist for the CN VR EE TYPE variable:
LOC indicates that the payee is local. This is the default value of the variable.
EXP indicates that the payee is an expatriate.
DIS indicates that the payee is disabled or has special needs and has been granted tax reduction by the government.
INT indicates that the payee is an intern.
You can change the value of the CN VR EE TYPE variable for a payee by creating a supporting element override (SOVR). In the absence of a SOVR, the system determines the value of CN VR EE TYPE based on the payee's Citizenship Status on the Citizenship/Passport page, Empl Class (employee class) on the Job Information page, and Disability Status on the Disability page.
|
Citizenship, Disability, and SOVR Combination |
Resulting CN VR EE TYPE Value |
|
Citizenship Status: Citizen Empl Class: Null Disability Status: No SOVR exists: No |
LOC |
|
Citizen Status: Expatriate Empl Class: Null Disability Status: No SOVR exists: No |
EXP |
|
Citizen Status: Not Indicated or Others Empl Class: Null Disability Status: No SOVR exists: No |
LOC |
|
Citizen Status: Citizen, Expatriate, Not Indicated, or Others Empl Class: CHN Intern Disability Status: No SOVR exists: No |
INT |
|
Citizen Status: Citizen, Expatriate, Not Indicated, or Others Empl Class: CHN Intern or Null Disability Class: Yes SOVR exists: No |
DIS |
|
Citizen Status: Citizen, Expatriate, Not Indicated, or Others Empl Class: CHN Intern or Null Disability Status: Yes or No SOVR exists: Yes |
SOVR value |
Tax Area
The tax area, as defined by variable CN VR TAX AREA, is associated with Location and Contribution Area in the CN BR CONT AREA bracket. This assumes that a payee based in a specific location also makes social contributions to this location and pays tax to this location's tax office. If the default tax area listed in the CN BR CONT AREA bracket does not apply to a payee, however, you can override the value of the CN VR TAX AREA variable by creating a supporting element override.

 Page Used to Set Up a Payee Override for Tax Calculation
Page Used to Set Up a Payee Override for Tax Calculation|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
Supporting Elements |
GP_PAYEE_SOVR |
Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Payee Data, Create Overrides, Supporting Elements, Supporting Elements |
Override the value of a tax-related variable for a payee. |

 Adding a Payee Override for Tax Calculation
Adding a Payee Override for Tax CalculationAccess the Supporting Elements page (Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Payee Data, Create Overrides, Supporting Elements, Supporting Elements).
See Also
PeopleSoft Enterprise Global Payroll 9.1 PeopleBook, "Setting Up Overrides," Defining Payee Overrides, Overriding Supporting Element Values for Payees
PeopleSoft Enterprise Human Resources 9.1 PeopleBook: Administer Workforce, "Managing Citizenship and Visa or Permit Information," Tracking Employee Passport and Citizenship Information
PeopleSoft Enterprise Human Resources 9.1 PeopleBook: Administer Workforce, "Tracking Disabilities," Entering Disability Information