
 Processing Retroactive Payments
Processing Retroactive PaymentsThis chapter discusses how to:
Process retroactive payments.
Enter additional paygroup information.
Enter additional calendar information.
Define triggers and segmentation events for Australia.
Identify proration rules for Australia.
Identify rounding rules for Australia.
Note. The PeopleSoft system delivers a query that you can run to view the names of all delivered elements designed for Australia. Instructions for running the query are provided in the PeopleSoft Enterprise Global Payroll 8.9 PeopleBook.
See Also
Viewing the Delivered Elements

 Processing Retroactive Payments
Processing Retroactive PaymentsThe default retro method and the on conflict retro method for Australia are both forwarding. You set this on the Country Setup page.
The core retro functionality suits all Australian requirements except the requirement to apply a different tax rate to retro payments that relate to periods more than 12 months before the date the forwarded retro payment is made.

 Determining Retro Pay Over 12 Months
Determining Retro Pay Over 12 MonthsTo meet this requirement, the PeopleSoft system provides the formula RTO FM SET OVRDSET, which uses the duration RTO DR MTH ARREARS to determine if a period of more than 12 months has elapsed between any of the periods being retroactively paid and the payment date of the retro. If any elapsed period is greater than 12 months, the system selects a new override set—also provided by the PeopleSoft system—to forward all the processed earnings to the single new earnings, RETRO12MTH, that the system taxes at the lower rate.
These are lump sum E payments, so RETRO12MTH earnings contributes to accumulator PD LUMP E as well as AUS GROSS, PAYROLL TAX PROV (Provision for Payroll Tax) and its own automatically assigned calendar and fiscal period, month, quarterly, and yearly accumulators.
The system provides one retro processing definition, AU RETRO (which is set to forwarding) and two override sets.
Note. If you add any earnings that can be retrospectively paid, you need to add them to both override sets and to the appropriate accumulators.

 Calculating the Months Exceeding 12 Months
Calculating the Months Exceeding 12 MonthsThe following diagram shows how the duration calculation result determines which override set to use. The system calculates the duration for each period, and when it exceeds 12 months, the second override set applies.
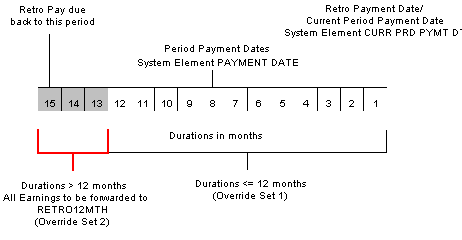
Application of override sets 1 and 2

 Processing Retro Over 12 Months
Processing Retro Over 12 MonthsHere are the processing steps:
Formula RTO FM SET OVRDSET—the formula specified on the Retro Process Overrides AU RETRO page—is called for each pay period identified for retro processing.
The formula uses duration RTO DR MTH ARREARS to calculate the months between the pay date of each pay period identified for retro processing (the duration From date—system element PAYMENT DATE) and the date the retro is to be paid (the duration To date—system element CURR PRD PYMT DT).
If the duration is 12 months or less, the formula returns 1, and the system uses override set 1 for forwarding retro; if the duration is greater than 12 months, the formula returns 2, and the system uses override set 2 for forwarding retro.
For each period that’s more than 12 months before the retro payment date, the system forwards all the retro earnings to the single earnings element RETRO12MTH.
The sum of the earnings forwarded to the single earnings RETRO12MTH represents a lump sum E payment, and the tax calculation uses the appropriate rate on the earnings.

 Entering Additional Paygroup Information
Entering Additional Paygroup InformationTo enter additional paygroup information, use the Pay Groups AUS (GPAU_PYGRP_DTL) component.
To accommodate local requirements, the Pay Groups AUS page enables you to specify payslip templates, salary packaging frequency, and leave paid in advance options.
This section discusses how to enter additional information.

 Page Used to Enter Additional Paygroup Information
Page Used to Enter Additional Paygroup Information
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
GPAU_PYGRP_EXT |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Framework, Organizational, Pay Groups AUS |
Specify payslip template, salary packaging frequency, and leave paid in advance options. |

 Entering Additional Information
Entering Additional Information
Access the Pay Groups AUS page.
Enter the name of the payslip template that the system uses for this paygroup.
Select the default pay frequency for the salary-packaged employees in the paygroup. An equivalent field exists in Human Resources in case an organization uses Human Resources but not Global Payroll. The pay frequency that you enter here appears by default as the pay frequency on the Salary Packing Pay Calendar Table page.
Select a regular run type. Within the general structure of Global Payroll calendars, periods and calendar groups, the system has to determine which calendar group an advance should be paid in.
When the system determine in which calendar group to include an advance, it takes into account the calendars each group contains to see when they are paid. However, a calendar group can contain many calendars, each with different periods and payment dates.
To determine the appropriate calendar group, the system typically uses the organization’s regular run type. You specify the regular run type on this additional paygroup page.
In the following diagram, the Advance calendar group for the advance type is Payment Prior to Absence Begin (PPAB). This refers to the payment date that is prior to the absence begin date—not the payment period that is prior to the absence begin date. For the prior payment period, you use the Period Prior to Absence option.
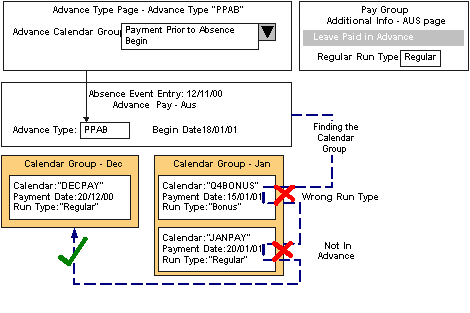
Determination of the calendar group in which to pay a leave advance payment

 Entering Additional Calendar Information
Entering Additional Calendar InformationTo set up additional calendar information, use the Calendar Groups AUS (GPAU_CAL_RUN) component.
To comply with local requirements, the Australian Information page enables you to mark a calendar group's calendars that can be advanced.

 Page Used to Enter Additional Calendar Information
Page Used to Enter Additional Calendar Information
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
GPAU_CAL_RUN_DTL |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Framework, Calendars, Calendar Groups AUS |
Mark a calendar group's calendars that can be advanced. The page displays the pay entities, paygroups, and calendars entered on the Calendar Group ID page. (You can add to them if necessary.) To enable the system to advance a calendar, select the Include in Advance check box. |
See Also

 Defining Triggers and Segmentation Events
Defining Triggers and Segmentation Events
These tables list triggers and segmentation events for Australia.

 Triggers
Triggers
The following table lists triggers for Australia:
|
Record (Table) Name |
Type |
Trigger Event ID |
|
ADDRESSES |
Iterative |
Not applicable (NA) |
|
COMPENSATION |
Iterative |
NA |
|
COMPENSATION |
Retro |
COMPENSATI |
|
CONTRACT_DATA |
Iterative |
NA |
|
EMPLOYMENT |
Iterative |
NA |
|
GPAU_ABSADV_SEG |
Segmentation |
AU_ABSADV |
|
GPAU_EE_TAX_DTL |
Iterative |
NA |
|
GPAU_GARN_DTLS |
Iterative |
NA |
|
GPAU_LSL_HISTRY |
Iterative |
NA |
|
GP_ABSEVT_SGPAU |
Iterative |
NA |
|
GP_ABS_EVENT |
Iterative |
NA |
|
GP_ABS_EVENT |
Retro |
GPABSEVENT |
|
GP_ABS_OVRD |
Iterative |
N/A |
|
GP_ABS_OVRD |
Retro |
GPABSOVRD |
|
GP_PI_MNL_DATA |
Iterative |
NA |
|
GP_PI_MNL_DATA |
Retro |
GPPIMNLDAT |
|
GP_PI_MNL_OSVR |
Iterative |
NA |
|
GP_PI_MNL_OSVR |
Retro |
GPPIMNLSOV |
|
GP_PYE_OVRD |
Iterative |
NA |
|
GP_PYE_OVRD |
Retro |
GPPYEOVRD |
|
GP_PYE_OVR_SOVR |
Iterative |
NA |
|
GP_PYE_OVR_SOVR |
Retro |
GPPYEOVRSO |
|
GP_PYE_SECT_DTL |
Iterative |
NA |
|
GP_PYE_SECT_DTL |
Retro |
GPPYESECTD |
|
GP_RTO_TRGR |
Iterative |
NA |
|
GP_RTO_TRGR_CTRY |
Iterative |
NA |
|
GP_SEG_TRGR |
Iterative |
NA |
|
JOB |
Iterative |
NA |
|
JOB |
Retro |
JOB |
|
JOB |
Segmentation |
NA |
|
JOB_JR |
Iterative |
NA |
|
PERSON |
Iterative |
NA |
|
PERS_DATA_EFFDT |
Iterative |
NA |
|
PERS_ORG_INST |
Iterative |
NA |
|
SCH_ASSIGN |
Iterative |
NA |
|
SCH_ASSIGN |
Retro |
SCHASSIGN |
|
SCH_MNG_SCH_TBL |
Iterative |
NA |
|
TL_PAYABLE_TIME |
Iterative |
NA |
|
WKF_CNT_TYPE |
Iterative |
NA |

 Segmentation Events
Segmentation Events
The following is a list of segmentation events for Australia.
|
Name |
Description |
Segment Type |
|
AU_ABSADV |
Pay Absence in Advance |
Period |
|
COMPRATE |
Comp Rate Segmentation |
Element (Slice) |
|
JOB |
Job Segmentation |
Period |

 Identifying Proration Rules
Identifying Proration RulesThe Australian extension includes two proration rules in addition to the fourteen rules supplied for all countries. The following table shows the key information about them:
|
Name |
Description |
Numerator |
Denominator |
|
AUS PO ANNL WRKDYS |
Percent of Annual - Workdays |
Count GP WORK DAY COUNT |
Formula AUS FM PRD WRKDAYS |
|
AUS PO ANNL CALDYS |
Percent of Annual - Cal Days |
Duration GP CAL DAYS SEG |
Formula AUS FM PRD CALDAYS |

 Identifying Rounding Rules
Identifying Rounding RulesThe Australian extension includes seven rounding rules in addition to the sixty rules supplied for all countries. The following table shows the key information about them. In the last column, R, U, or T indicates:
R: Round up if greater than or equal to the listed value; otherwise, round down.
U: Round up.
T: Truncate down.
|
Name |
Description |
Rounding (R) or Increment (I) |
Size |
R, U, or T |
|
AUS RR RND NR 3DEC |
Round Near 3 Decimals |
R |
03 |
R 5 |
|
AUS RR RND UP 3DEC |
Round Up to 3 Decimals |
R |
03 |
R 5 |
|
AUS RR RND DN 3DEC |
Round Down to 3 Decimals |
R |
03 |
R 5 or T |
|
AUS RR INC NR 0.05 |
Increment to Near 5 Cents |
I |
0.05 |
R 0.025 |
|
AUS RR INC UP 0.05 |
Increment Up to 5 Cents |
I |
0.05 |
R 0.025 or U |
|
AUS RR INC DN 0.05 |
Increment Down to 5 Cents |
I |
0.05 |
R 0.025 or T |
|
AUS RR RND UP 5DEC |
Round Up 5 Decimal Places |
R |
05 |
U |