Creating and Maintaining Global Policies and Constraints
To create global policies and constraints, use the Sourcing Constraints (CONSTRAINTS_COMP) component.
This topic discusses how to create and maintain global policies and constraints.
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
|
CONSTRAINT_PG |
Create and maintain constraints. |
|
|
CONSTRAINT_BU_SEC |
Assign constraints to business units. |
|
|
CONST_RULE_SEC |
Assign defaulting rules. |
Use the Constraint Setup page (CONSTRAINT_PG) to create and maintain constraints.
Navigation:
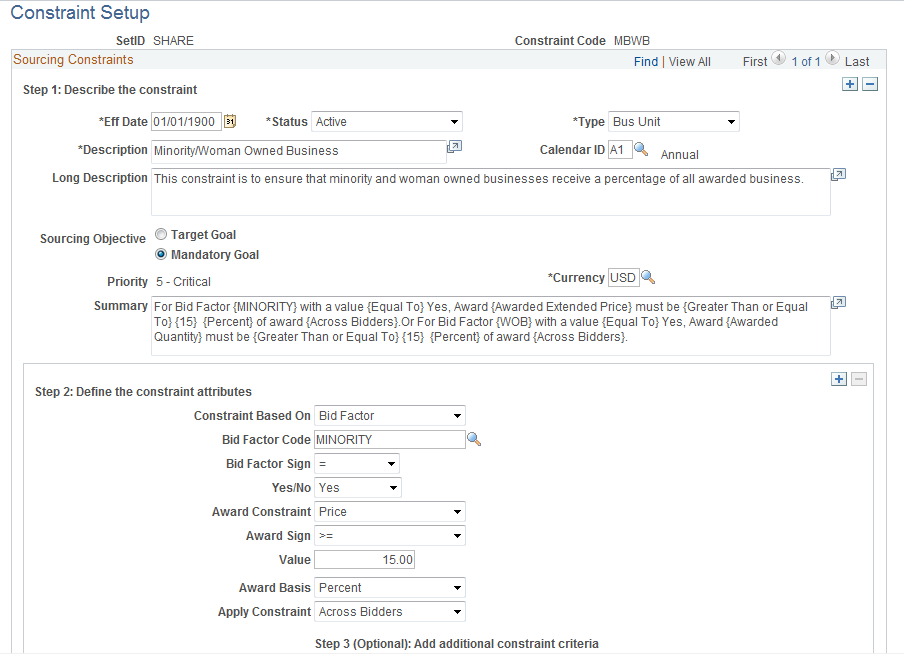
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Constraint Setup page (1 of 2). You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
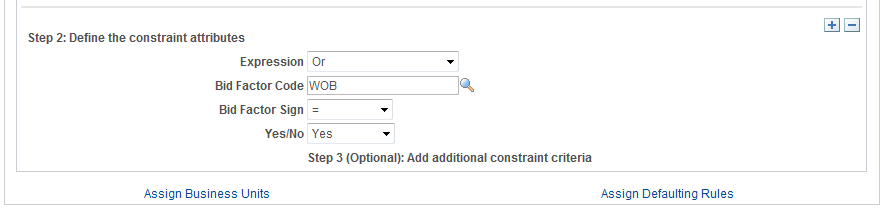
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Constraint Setup page (2 of 2). You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
Step 1: Describe the constraint.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Effective Date |
Indicate the date that the constraint is to be effective. |
Description |
Enter a short description for the constraint. This field is required. |
Calendar ID |
Select a calendar ID to use for global or business unit constraints. The calendar ID is used to calculate the progress to date for the selected constraint. This field is required for global and business unit constraints. For example, if your organization wants to ensure that 10 percent of business is awarded to minority and woman-owned businesses by the end of the year, you should select a calendar ID associated with an annual calendar. The total spend throughout the year is then compared to the spend awarded to minority and woman-owned businesses to calculate a progress to date that you can track throughout the year. |
Long Description |
(Optional) Enter a long description for the constraint. |
Currency Code |
Select a currency code for the constraint. |
Summary |
Displays a text description summarizing the constraint parameters. The summary field is automatically completed as you define the constraint attributes. |
Step 2: Define the constraint attributes.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Constraint Based On |
Select a value:
|
|
Click to add additional attributes to the constraint. You can add additional constraint criteria only for constraints that are based on bid factors. |
|
Value Selected in the Constraint Based On Field |
Fields that are Available in Step 2 |
|---|---|
|
Amount |
Award Sign Value Award Basis Apply Constraint (display only) |
|
Bid Factor |
Bid Factor Code Bid Factor Sign Award Constraint Award Sign Value Award Basis Apply Constraint |
|
Bidders |
Award Sign Value |
|
Quantity |
Award Sign Value Award Basis Apply Constraint (display only) |
(Optional) Step 3: Add additional constraint criteria.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
|
If the constraint is based on a bid factor, click to add additional constraint criteria to the constraint. For example, using the minority or woman-owned business constraint discussed earlier, if you have two different bid factors asking whether a bidder is a minority or woman-owned business, you would define the constraint as based on bid factor and first select the MINORITY bid factor. You could then add additional constraint criteria for the WOMANOWNED bid factor. |
Use the Assign Business Units page (CONSTRAINT_BU_SEC) to assign constraints to business units.
Navigation:
Click the Assign Business Units link on the Constraint Setup page.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Assign Business Units page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.

Select the business units that you want to associate with the constraint and click OK. You must associate at least one Sourcing business unit to business unit type constraints.
Use the Constraint Rules page (CONST_RULE_SEC) to assign defaulting rules.
Navigation:
Click the Assign Defaulting Rules link on the Constraint Setup page.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Constraint Rules page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
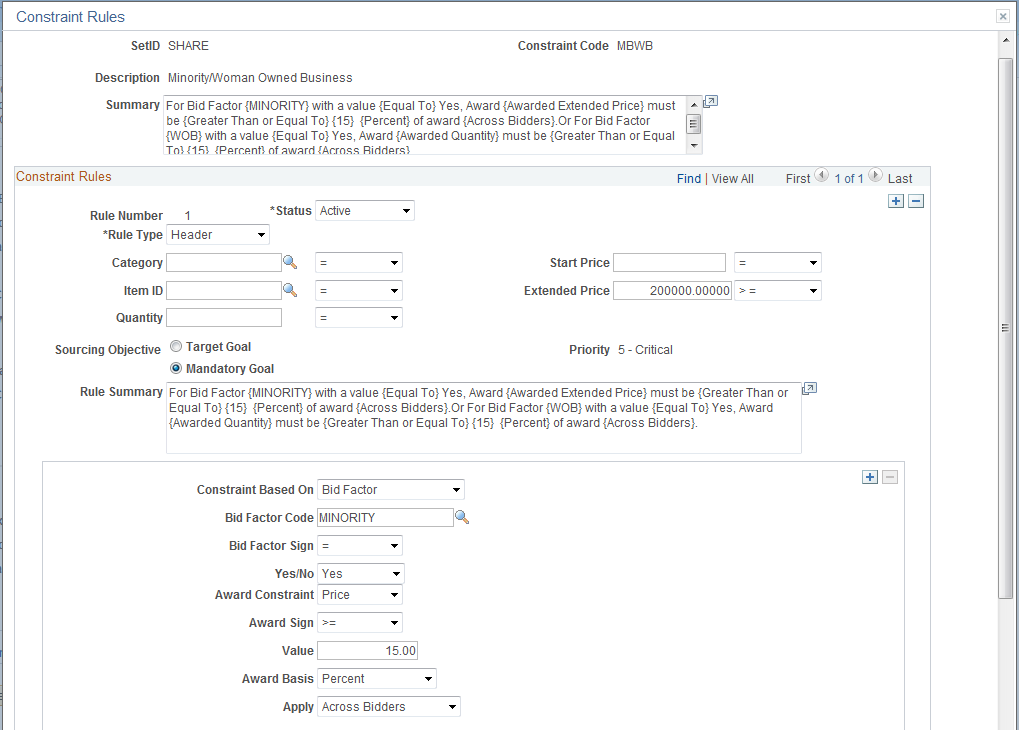
Constraint Rules
By defining defaulting rules and associating them to the constraint, the system automatically applies the defaulting rules to sourcing events. You can review the constraints associated with the event, and modify the constraints as needed based on the user preferences settings. Defaulting rules can be added at the event (header) level or at the line level.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Rule Type |
Select Header or Line to indicate whether to apply the constraint to the entire event (header) or per line. |
Category or Item ID |
(Optional) Select a value for these fields. |
Quantity |
(Optional) Enter as numerical value in this field. |
Start Price and Extended Price |
(Optional) Enter values in these fields. |
Copy Previous Rule Attribute |
If more than one rule is defined for the constraint, click this button to copy the previous rule's values into the new rule. |
Rule Summary |
Displays a system-defined summary of the constraint rule. |
|
Click to add constraints based on different criteria. See Step 2: Define the constraint attributes in Defining Constraints. |
 (Add Row icon)
(Add Row icon)
