Defining General Ledger Business Units
To define General Ledger business units, use the General Ledger Definition component (BUS_UNIT_TBL_GL). Your business practices determine how to set up General Ledger business units and the journal processing options.
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
|
BUS_UNIT_TBL_GL1 |
Define a General Ledger business unit. |
|
|
BU_ID_NBRS_GL_SEC |
Enter the ID for the reporting entity for a business unit. |
|
|
BU_ADB_INCR_SEC |
Identify the ADB definition and period type combinations that the system runs regularly, and use the incremental method to calculate average balances. |
|
|
PMT_SEQ_NUM_SEC |
Identify the sequence type (mandate ID and reference number), beginning sequence number, maximum length and last auto-assigned number to apply to a mandate form. |
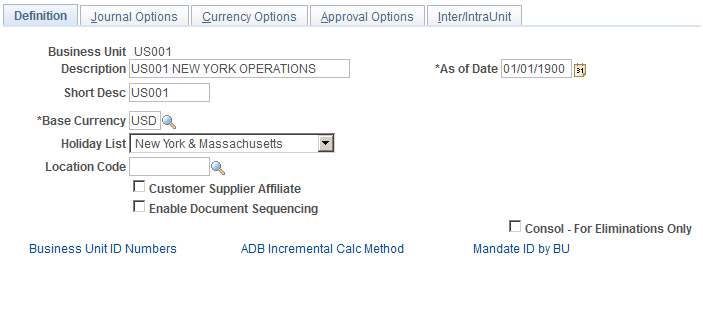
Use the General Ledger Definition - Definition page (BUS_UNIT_TBL_GL1) to define a General Ledger business unit.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the General Ledger Definition - Definition page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Base Currency |
Enter a code for the only primary currency for the General Ledger business unit. The base currency is sometimes referred to as the book currency. It is usually the local currency for the organization, although it can be different. |
As of Date |
Enter a date that is the benchmark for the system's current reporting period and calculations of year-to-date amounts. The as-of date is a report option on PS/nVision report requests. When you change the as-of date for a business unit, all reports using this option run relative to the as-of date that you specify here, so it is not necessary to change the report specifications. |
Default SetID |
Enter a SetID to determine the preliminary tableset sharing setup for the business unit. This field does not appear after the business unit is created. |
Create BU (create business unit) |
Click to create a new business unit. After you create the business unit, this button is not visible. |
Holiday List |
Select to identify holiday calendars for different countries or business units. Several General Ledger processes—including the Journal Post process, the Journal Entry process, and many others—use this calendar to determine working days and limit journal dates to working days only. |
Location Code |
Select a location code for the business unit. Financial Gateway uses this field to derive the address information for the business unit. |
Customer Supplier Affiliate |
Select to obtain the interunit ChartField value from the customer or supplier tables when you create a transaction for the business unit. |
Enable Document Sequencing |
Select to use document sequencing for business units that operate in a country requiring it. You can track journal entries by document sequence number, if desired. |
Consol - For Eliminations Only (consolidate - for eliminations only) |
To automate the elimination of intercompany transactions, select to set up this special type of General Ledger business unit as an eliminations entity for consolidations processing. |
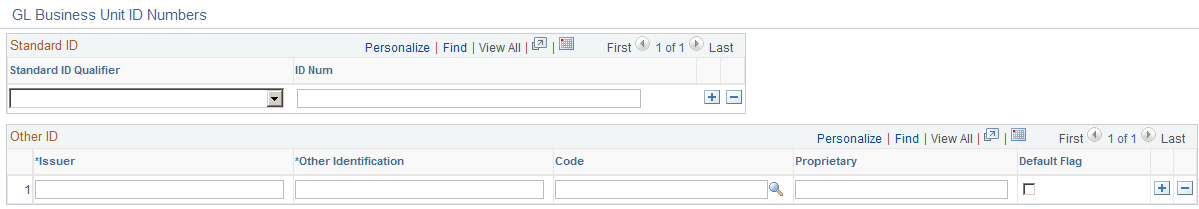
Use the Business Unit ID Numbers page (BU_ID_NBRS_GL_SEC) to enter the ID for the reporting entity for a business unit.
Navigation:
Click the Business Unit ID Numbers link on the General Ledger Definition - Definition page.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the GL Business Unit ID Numbers. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Standard ID Qualifier |
Select the qualifier for the type of reporting entity. Use BEI Identifier to populate the ISO and SEPA formats. |
ID Num (ID number) |
Enter the ID number for the reporting entity for the business unit. |
Other Identification |
Provide Other ID information for the business unit entity that will be used in ISO and SEPA formats. Other ID information consists of Issuer, Identification, and either an ISO Code List or a Proprietary Scheme Name under which the identification was issued. You must designate one issuer as the default that will be populated on the ISO and SEPA format. |
Use the Incremental Calculation Method page (BU_ADB_INCR_SEC) to identify the Average Daily Balance (ADB) definition and period type combinations that the system runs regularly, and use the incremental method to calculate average balances.
Navigation:
Click the ADB Incremental Calc Method (Average Daily Balance incremental calculation method) link on the General Ledger Definition - Definition page.
Note: Enabling the Average Daily Balance (ADB) feature in the middle of a fiscal year can lead to inaccurate ADB values.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Average Daily Balances |
Select an ADB definition from a list of definitions on the Average Daily Balance Definition - Definition page. Select only ADB definitions that you run regularly (for example, month-to-date averages). |
Period Type |
Select a period type to associate with the definition. Values are: Date to Date: Calculates ADBs from a beginning date to the run request date. Month to Date: Calculates ADBs from the first day of the month (which is the beginning date of the accounting period in which the run request date falls) to the run request date. To use this option, the detail ledger for the business unit must be tied to a detail calendar that uses monthly periods. Quarter to Date: Calculates ADBs from the first day of the quarter (the beginning date of the first accounting period in the quarter in which the run request date falls) to the run request date. To use this option, the detail ledger for the business unit must be tied to a detail calendar that uses monthly periods 1 through 12. Regular Date: Calculates average balances for the date range specified on the Average Daily Balance Process - Request page. Regular Period: Calculates ADBs for a specified period range in a specified fiscal year. The calculations use the beginning date of a From period to the ending date of a To period. Year to Date: Calculates ADBs from the first day of the year (which is the beginning date of accounting period 1) to the run request date. |
Use the Maintain Mandate Sequence Number page (PMT_SEQ_NUM_SEC) to identify the sequence type (mandate ID and reference number), beginning sequence number, maximum length and last auto-assigned number to apply to a mandate form.
Navigation:
Click the Mandate Sequence Number link on the General Ledger Definition - Definition page.
A mandate is an authorization and expression of consent given by the debtor to the creditor, which enables the creditor to initiate collections by debiting the specified debtor's bank account and enables the debtor's bank to comply with these instructions in accordance with the SEPA (Single European Payment Area ) Rulebook.
The mandate sequence number is an auto-assigned number on the Mandate Entry page. It is maintained by GL Business Unit. Mandate Reference Number is used to uniquely identify a mandate provided by a customer. You can print mandate forms where the reference number is auto-assigned.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Sequence Type |
Select the following sequence types for which to track the auto-assigned sequence numbers:
|
Beg Seq (beginning sequence) |
Enter the beginning number from which to increment the sequential counter for the sequence number. |
Max Length (maximum length) |
Enter the maximum length of the sequence number. |
Last Auto-Assigned Number |
Enter the number of the last sequence number that the system assigned. |